CCR7 Mediates Dendritic-Cell-Derived Exosome Migration and Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. MI Model Induction and Treatments
2.3. Cell Isolation and Culture
2.4. Lentivirus Production and Infection
2.5. Mimic MI Microenvironment
2.6. DEX Isolation and Characterization
2.7. Experimental Grouping
2.8. DEX Labeling and Fluorescence Imaging
2.9. Echocardiography
2.10. Histology
2.11. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.12. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
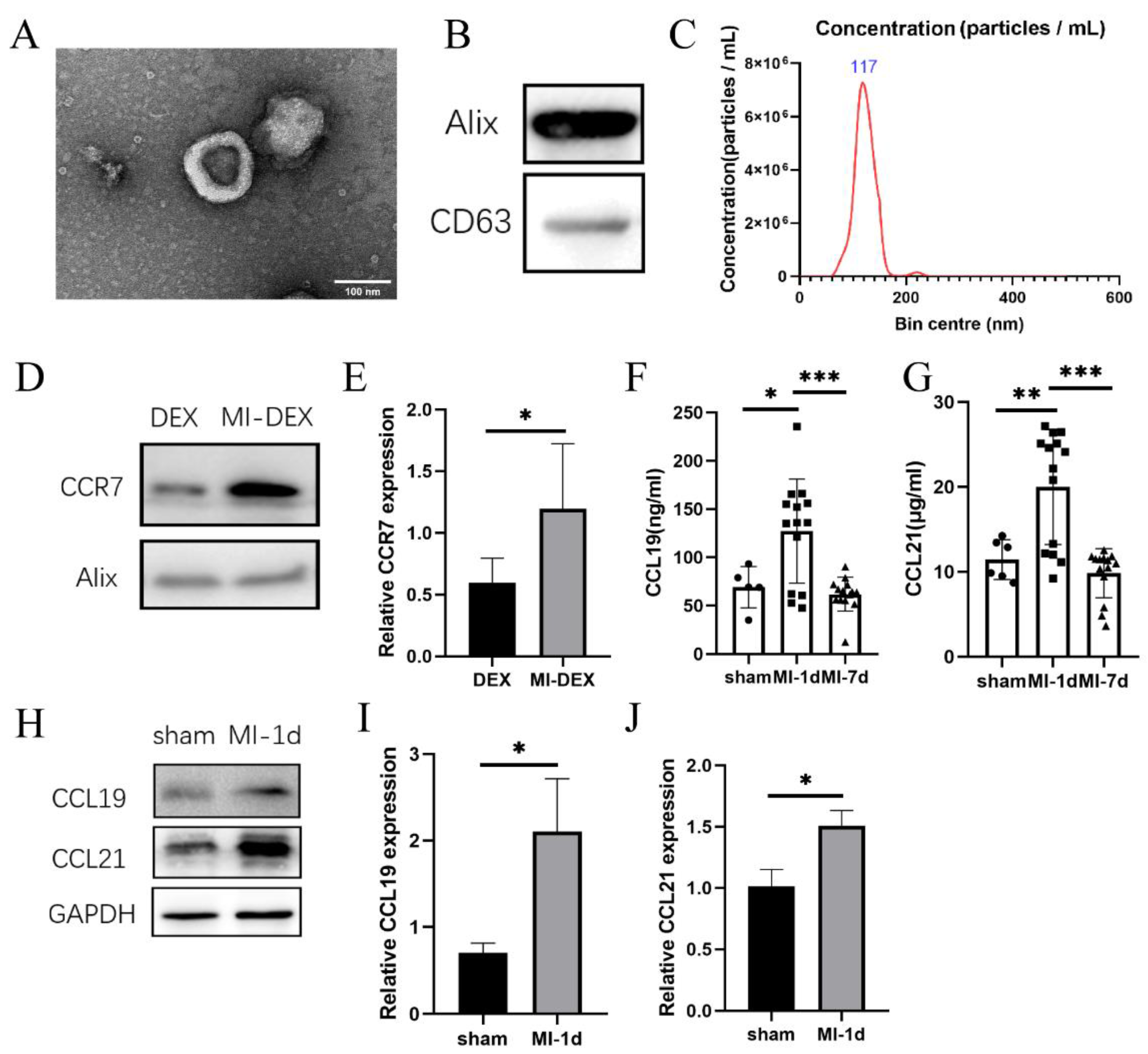
3.1. CCR7 Was Highly Expressed in MI-DEXs as well as Its Ligand CCL19/21 in MI-Mouse Spleen
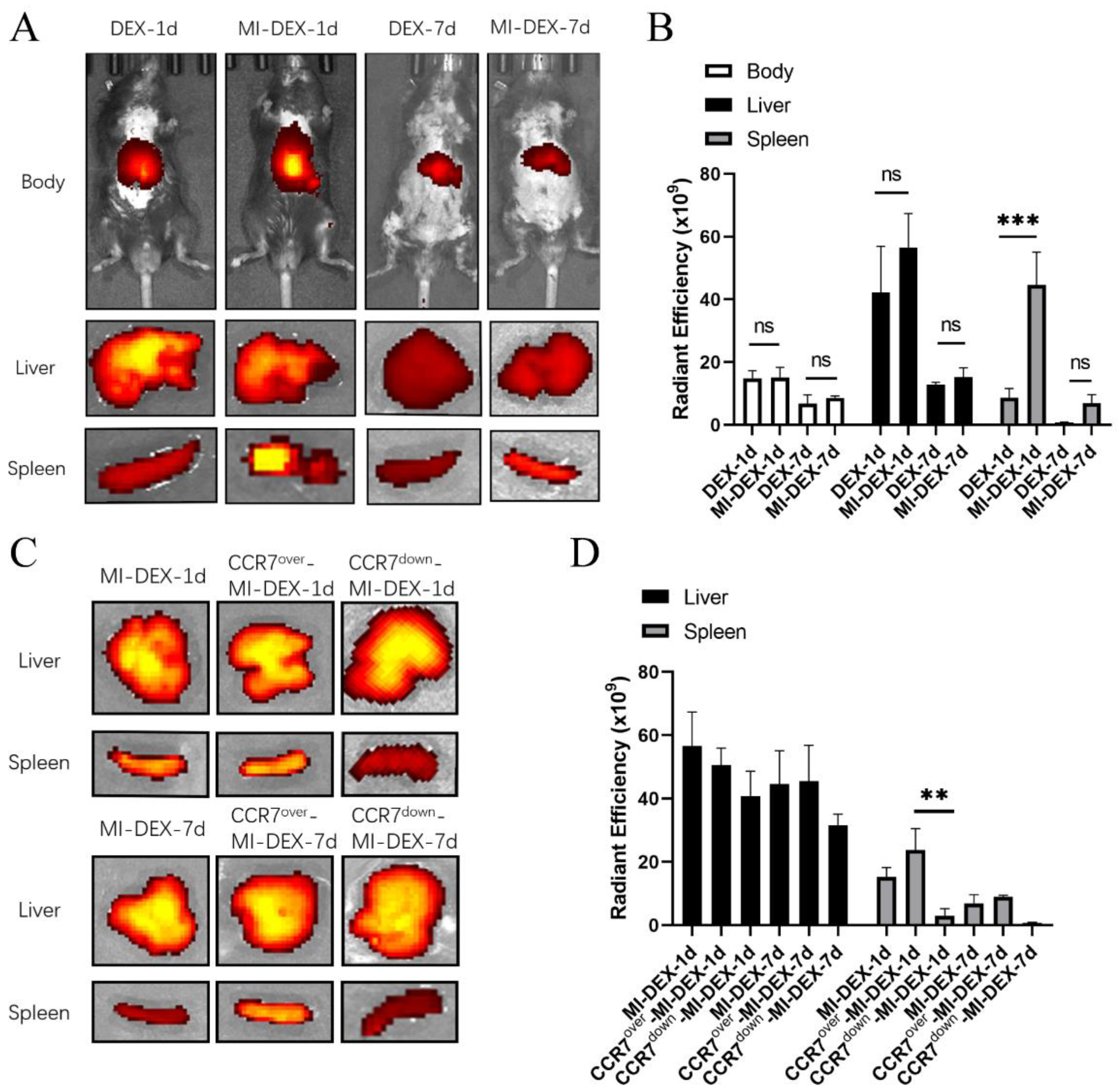
3.2. CCR7-Mediated MI-DEX Migration to the Spleen after MI
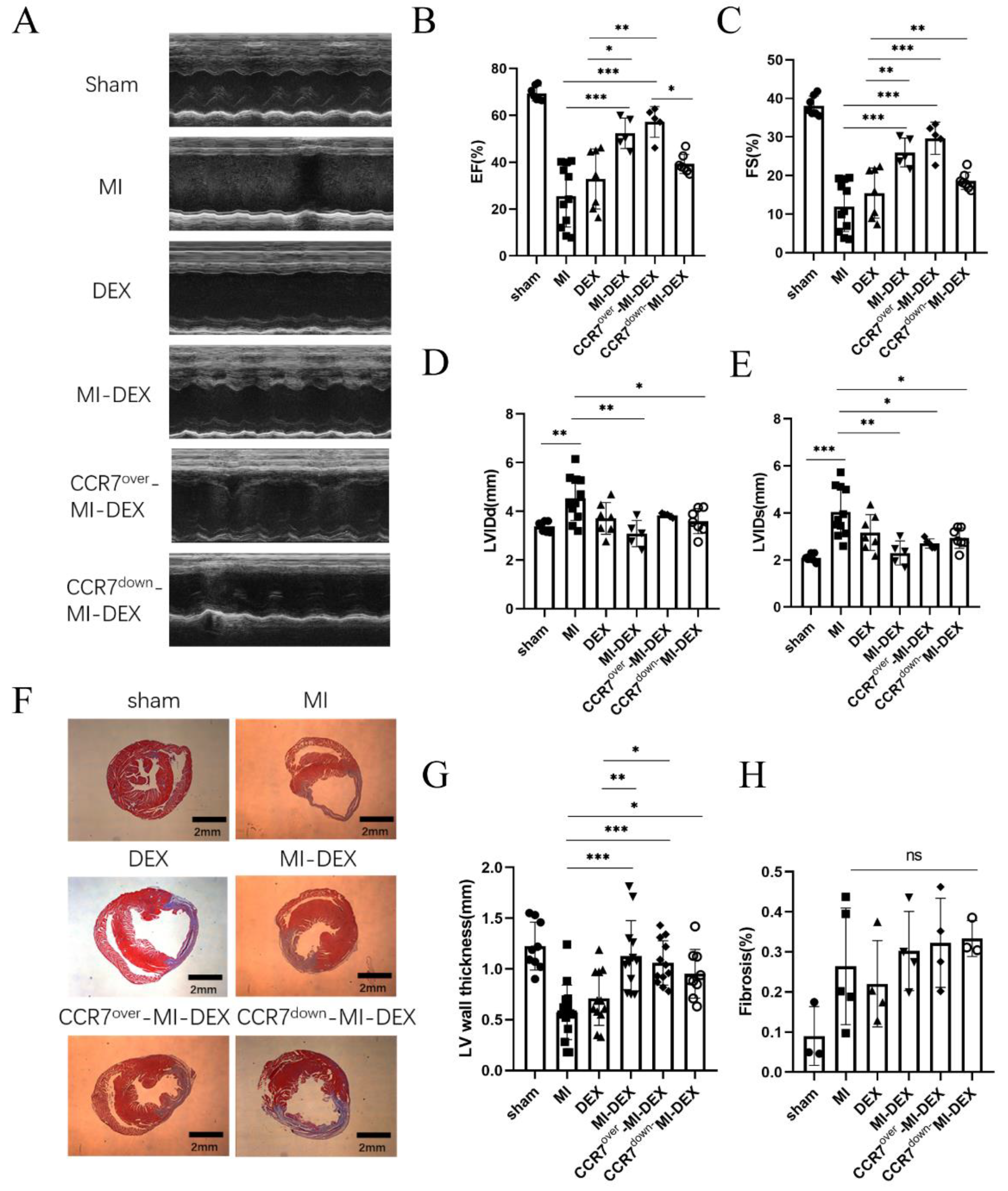
3.3. Enhancing the Migration Ability of MI-DEXs Can Improve Cardiac Function after MI
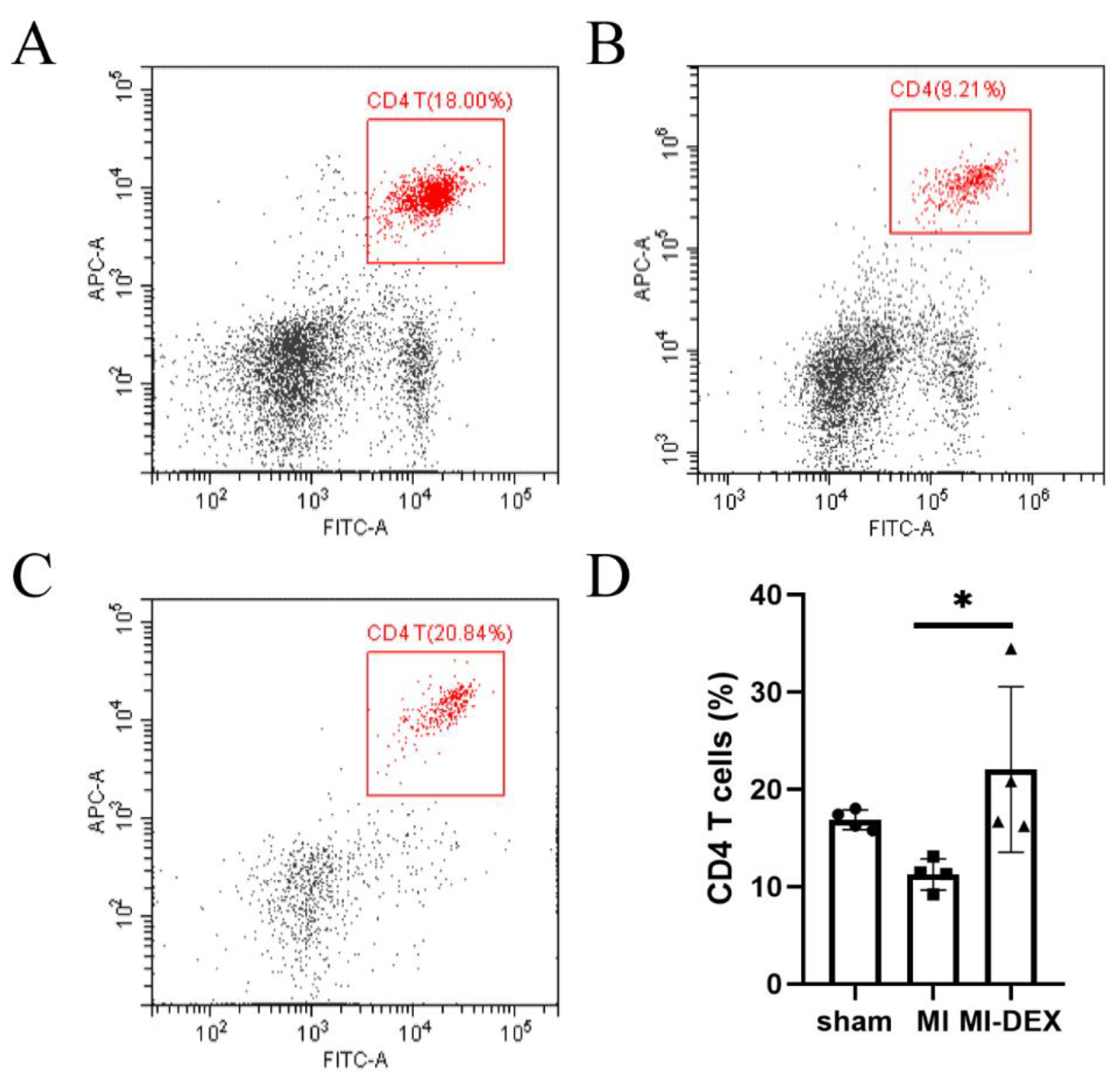
3.4. MI-DEXs’ Activation of CD4+ T Cells in the Spleen
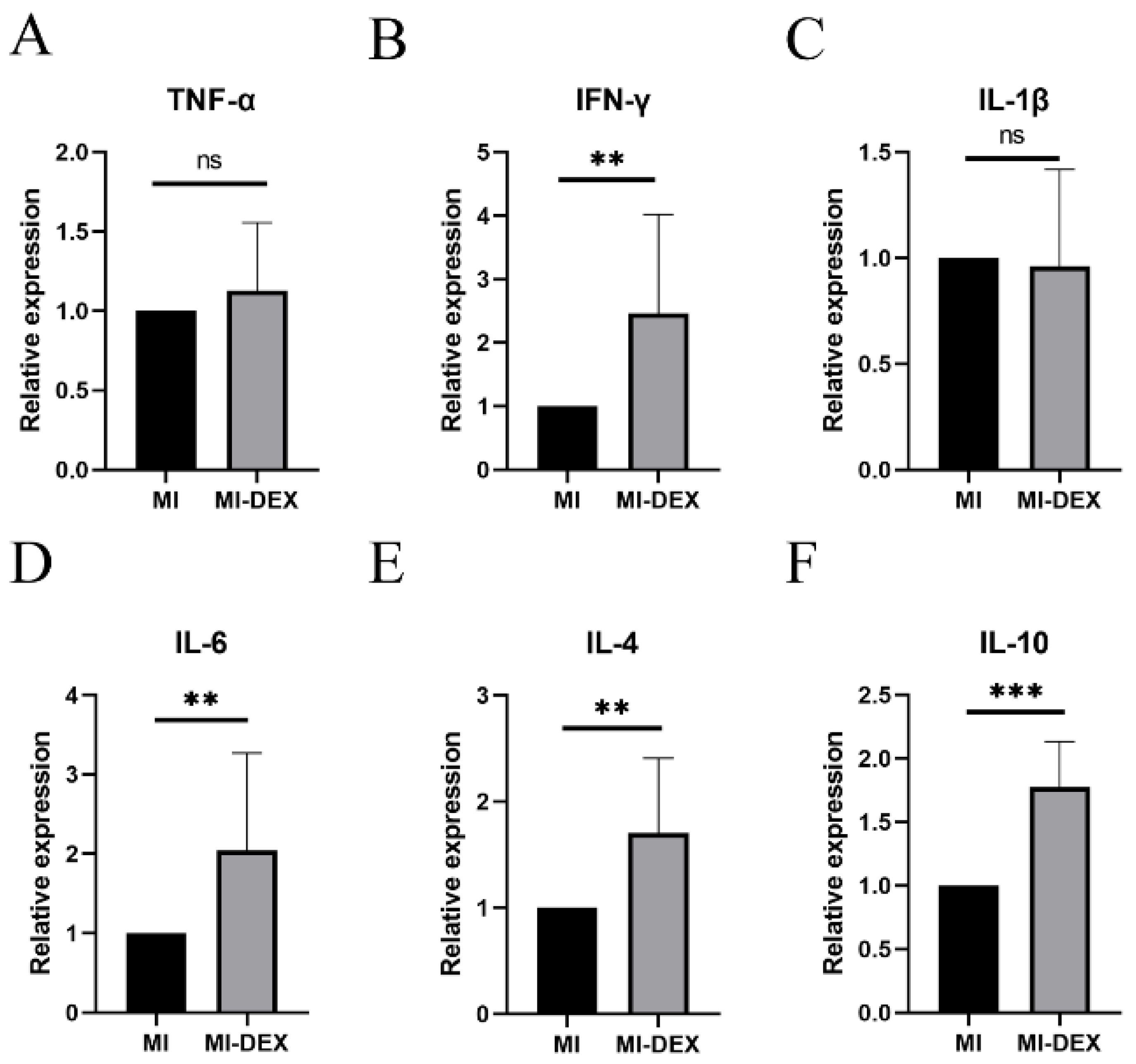
3.5. MI-DEXs Induce an Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Increase in Splenic CD4+ T Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergmark, B.; Mathenge, N.; Merlini, P.; Lawrence-Wright, M.; Giugliano, R. Acute coronary syndromes. Lancet 2022, 399, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Januzzi, J., Jr. Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, T.; Wang, P.; Ding, J.; Du, R.; Gao, J.; Li, A.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; He, Q. Global Research Trends on Ventricular Remodeling: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2012 to 2022. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, S.; Hundertmark, M.J.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Bengel, F.M.; Bauersachs, J. Left ventricular remodelling post-myocardial infarction: Pathophysiology, imaging, and novel therapies. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2549–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreadou, I.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Devaux, Y.; Frangogiannis, N.G.; Frantz, S.; Guzik, T.; Liehn, E.A.; Gomes, C.P.C.; Schulz, R.; Hausenloy, D.J. Immune cells as targets for cardioprotection: New players and novel therapeutic opportunities. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrief, T.; Davis, W.; Koyfman, A.; Long, B. Mechanical, inflammatory, and embolic complications of myocardial infarction: An emergency medicine review. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, W.M.; Liu, H.M. The Role of Immune Cells in Cardiac Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, W.; Yuan, J.; Wu, C.; Yao, K.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Zhu, J.; Zou, Y.; Ge, J. Exosomes derived from dendritic cells improve cardiac function via activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes after myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 91, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Q.; Gao, W.; Zhong, X.; Yao, K.; Yuan, J.; Liu, H. Hydrogel-load exosomes derived from dendritic cells improve cardiac function via Treg cells and the polarization of macrophages following myocardial infarction. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Li, Y.-Y.; Jin, J. A double-edged sword of immuno-microenvironment in cardiac homeostasis and injury repair. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, A.; Anzai, T.; Nagai, S.; Maekawa, Y.; Naito, K.; Kaneko, H.; Sugano, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Abe, H.; Mochizuki, S.; et al. Regulatory Role of Dendritic Cells in Postinfarction Healing and Left Ventricular Remodeling. Circulation 2012, 125, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, E.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, E.-H.; Park, H.E.; Jung, N.-C.; Kim, T.-H.; Koh, Y.-S.; Kim, E.; Seung, K.-B.; Park, C.; et al. Infarcted Myocardium-Primed Dendritic Cells Improve Remodeling and Cardiac Function After Myocardial Infarction by Modulating the Regulatory T Cell and Macrophage Polarization. Circulation 2017, 135, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieckmann, M.; Delgobo, M.; Gaal, C.; Büchner, L.; Steinau, P.; Reshef, D.; Gil Cruz, C.; Ter Horst, E.N.; Kircher, M.; Reiter, T.; et al. Myocardial infarction triggers cardioprotective antigen-specific T helper cell responses. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4922–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, A.; Pink, R.; Erdbrügger, U.; Siljander, P.; Dellar, E.; Pantazi, P.; Akbar, N.; Cooke, W.; Vatish, M.; Di-as-Neto, E.; et al. In sickness and in health: The functional role of extracellular vesicles in physiology and pathology in vivo: Part I: Health and Normal Physiology: Part I: Health and Normal Physiology. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Gao, W.; Yao, K.; Ge, J. Roles of Exosomes Derived From Immune Cells in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, J.L. The association of exosomes with lymph nodes. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 67, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjortø, G.M.; Larsen, O.; Steen, A.; Daugvilaite, V.; Berg, C.; Fares, S.; Hansen, M.; Ali, S.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Differential CCR7 Targeting in Dendritic Cells by Three Naturally Occurring CC-Chemokines. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Wang, J.; Weng, Q. New Insights of CCR7 Signaling in Dendritic Cell Migration and Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 841687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, U.; Beyersdorf, N.; Weirather, J.; Podolskaya, A.; Bauersachs, J.; Ertl, G.; Kerkau, T.; Frantz, S. Activation of CD4+ T Lymphocytes Improves Wound Healing and Survival After Experimental Myocardial Infarction in Mice. Circulation 2012, 125, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Ito, T.; Fields, L.; Shiraishi, M.; Ichihara, Y.; Sato, N.; Podaru, M.; Kainuma, S.; Tanaka, H.; Suzuki, K. IL-4 as a Repurposed Biological Drug for Myocardial Infarction through Augmentation of Reparative Cardiac Macrophages: Proof-of-Concept Data in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, K.; Endo, J.; Kataoka, M.; Katsumata, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Isobe, S.; Moriyama, H.; Goto, S.; Kitakata, H.; et al. IL (Interleukin)-10–STAT3–Galectin-3 Axis Is Essential for Osteopontin-Producing Reparative Macrophage Polarization After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2018, 138, 2021–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Frangogiannis, N. Anti-inflammatory therapies in myocardial infarction: Failures, hopes and challenges. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1377–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raemdonck, K.; Umar, S.; Palasiewicz, K.; Volkov, S.; Volin, M.V.; Arami, S.; Chang, H.J.; Zanotti, B.; Sweiss, N.; Shahrara, S. CCL21/CCR7 signaling in macrophages promotes joint inflammation and Th17-mediated osteoclast formation in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, L.; Moccetti, T.; Marbán, E.; Vassalli, G. Roles of exosomes in cardioprotection. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 38, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.-Y.; Gong, Z.-T.; Tang, R.-J.; Yang, Y.-J. The pivotal roles of exosomes derived from endogenous immune cells and exogenous stem cells in myocardial repair after acute myocardial infarction. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Su, C. Design strategies and application progress of therapeutic exosomes. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Yuan, J.; Zhong, X.; Yao, K.; Luo, R.; Liu, H. CCR7 Mediates Dendritic-Cell-Derived Exosome Migration and Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020461
Zhang Y, Gao W, Yuan J, Zhong X, Yao K, Luo R, Liu H. CCR7 Mediates Dendritic-Cell-Derived Exosome Migration and Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(2):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020461
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Youming, Wei Gao, Jie Yuan, Xin Zhong, Kang Yao, Rong Luo, and Haibo Liu. 2023. "CCR7 Mediates Dendritic-Cell-Derived Exosome Migration and Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 2: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020461
APA StyleZhang, Y., Gao, W., Yuan, J., Zhong, X., Yao, K., Luo, R., & Liu, H. (2023). CCR7 Mediates Dendritic-Cell-Derived Exosome Migration and Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020461





