PRID: Prediction Model Using RWR for Interactions between Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
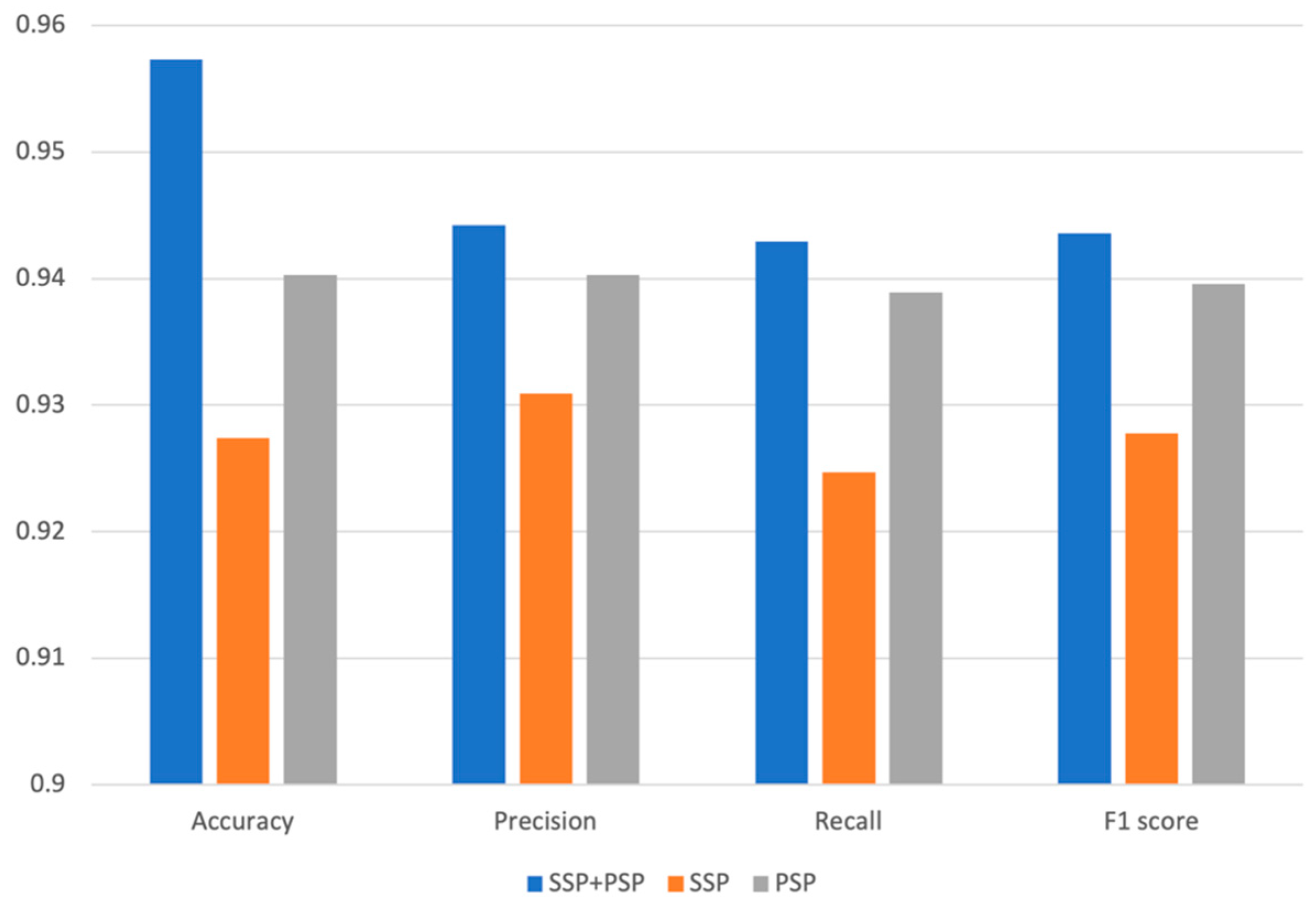
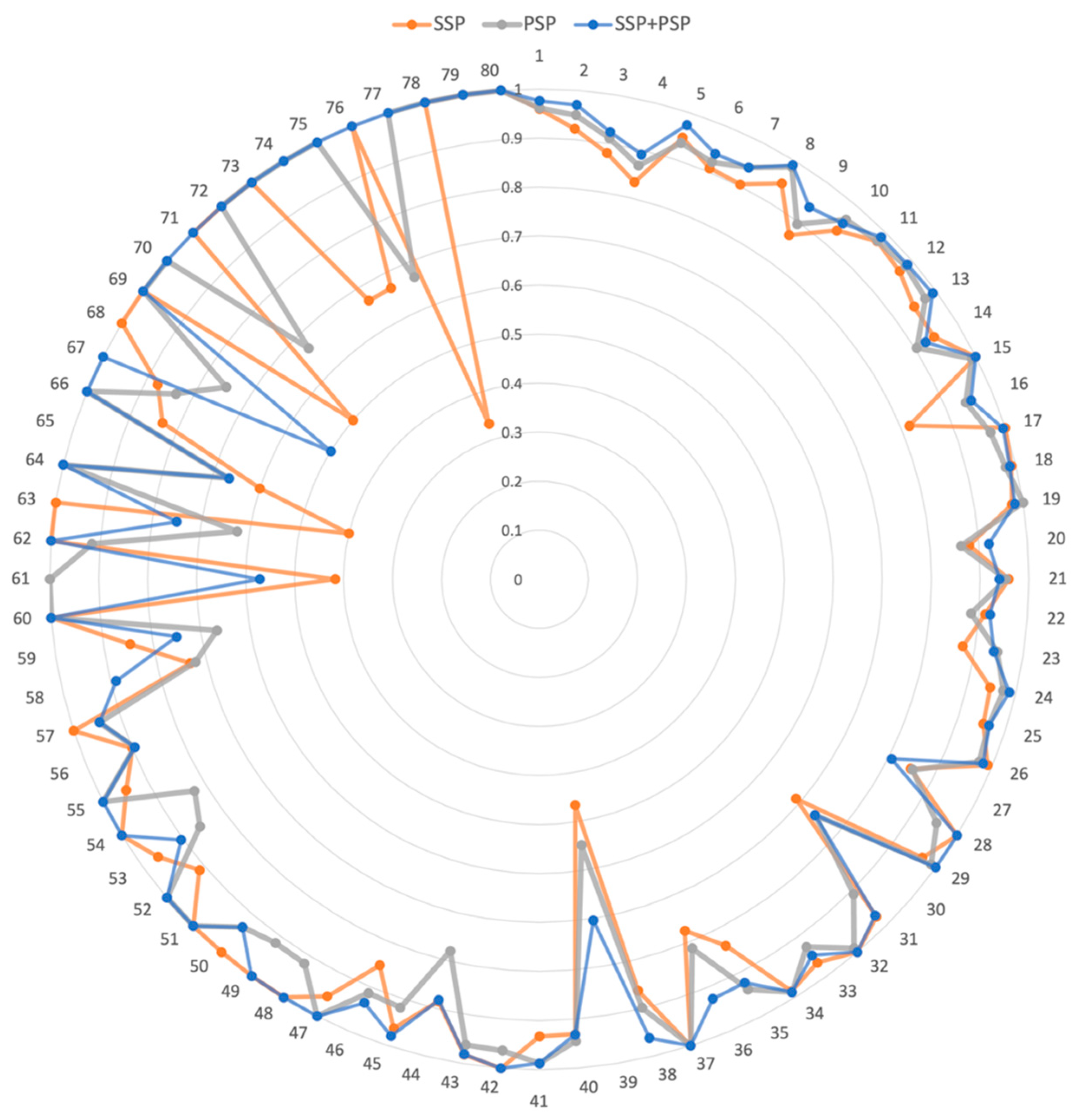
2.1. Performance of PRID Model
2.2. Clinical Validation for Predicted DDI
2.3. Validation for False Positive Data
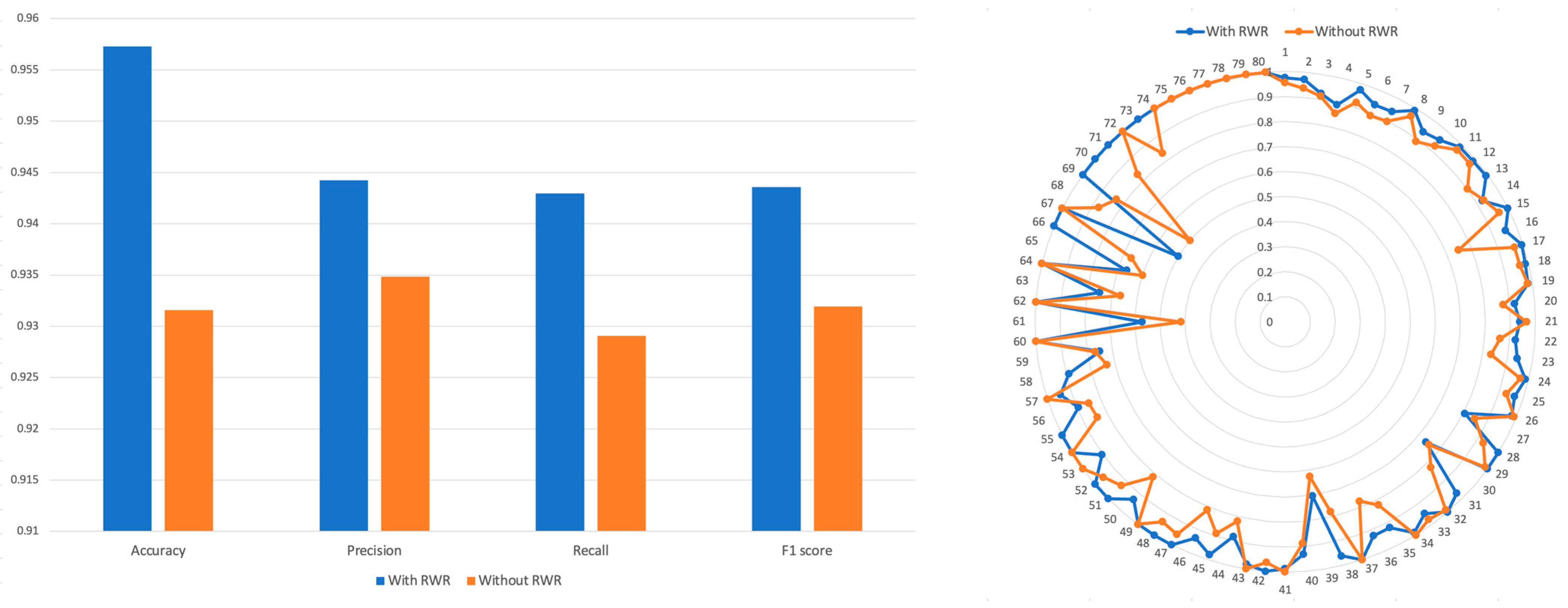
2.4. Comparison of RWR Methods and Non-RWR Methods
3. Discussion
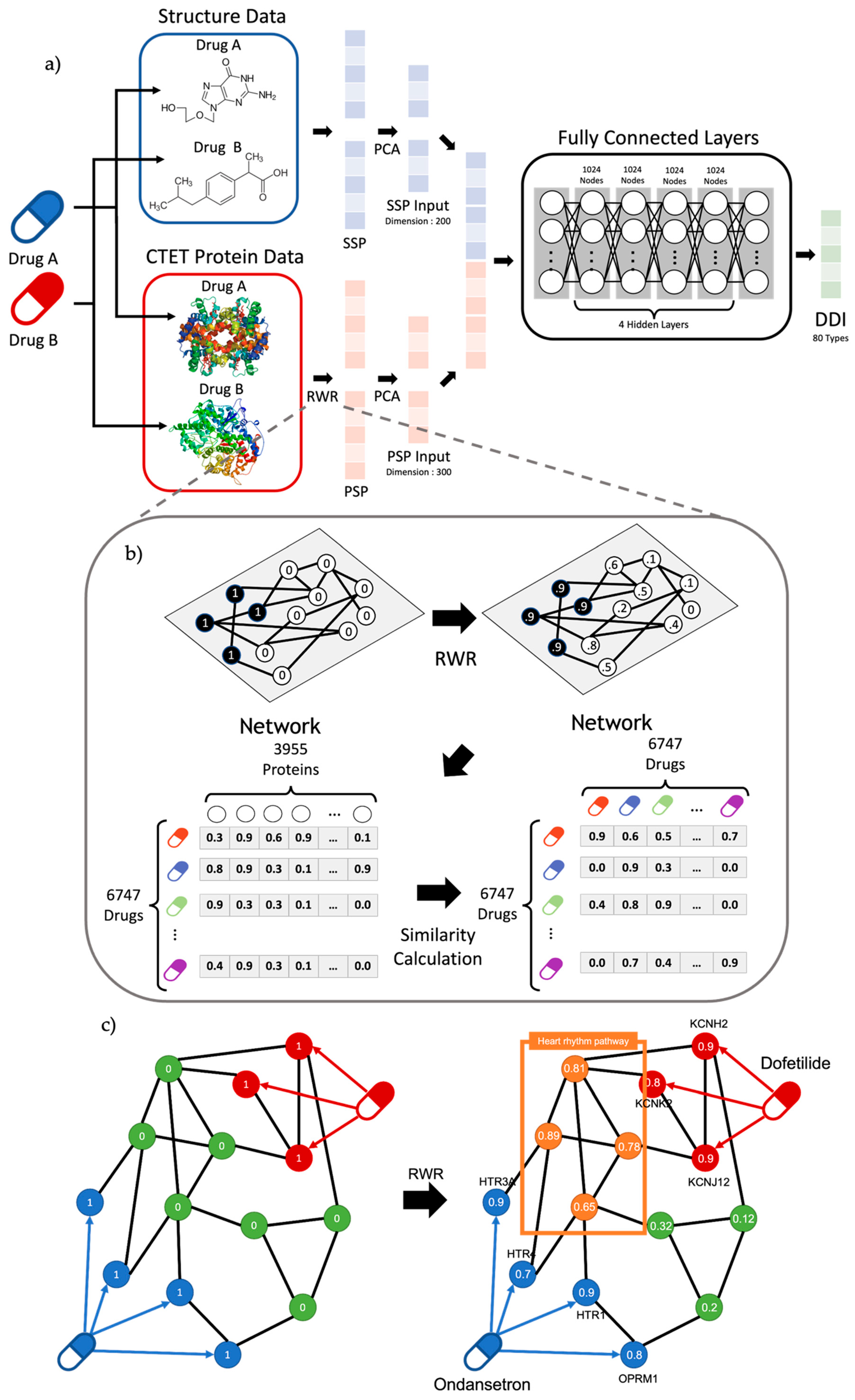
4. Methods
4.1. Drug–Drug Interaction Data
4.2. Protein–Protein Interaction Network
4.3. SSP (Structure Similarity Profile) of the Drug
4.4. PSP (Protein Similarity Profile) of the Drug and RWR
4.5. Deep Neural Network Structure for Prediction of DDIs
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cresswell, K.M.; Fernando, B.; McKinstry, B.; Sheikh, A. Adverse drug events in the elderly. Br. Med. Bull. 2007, 83, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, I.R.; Aronson, J.K. Adverse drug reactions: Definitions, diagnosis, and management. Lancet 2000, 356, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, C.M.; Dankoff, J.; Colacone, A.; Afilalo, M. Polypharmacy, adverse drug-related events, and potential adverse drug interactions in elderly patients presenting to an emergency department. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001, 38, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Cao, P.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F.; Ma, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J. A review of approaches for predicting drug–drug interactions based on machine learning. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 814858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W. A Comprehensive Review of Computational Methods for Drug-Drug Interaction Detection. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 19, 1968–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Chen, Y.; Min, Q.; Sun, Q.; Ye, K.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, S.; Sun, Z.; Liao, J. Similarity-based machine learning support vector machine predictor of drug-drug interactions with improved accuracies. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 44, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, S.; Harpaz, R.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Rabadan, R.; Friedman, C. Drug-drug interaction through molecular structure similarity analysis. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2012, 19, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Zhao, Z. Machine learning-based prediction of drug-drug interactions by integrating drug phenotypic, therapeutic, chemical, and genomic properties. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2014, 21, e278–e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.Y.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.Y. Deep learning improves prediction of drug-drug and drug-food interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4304–E4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Park, C.; Ahn, J. Novel deep learning model for more accurate prediction of drug-drug interaction effects. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Niu, C.; Green, C.D.; Yang, L.; Mei, H.; Han, J.D. Systematic prediction of pharmacodynamic drug-drug interactions through protein-protein-interaction network. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Kim, D.; Ha, S.; Lee, D. Predicting Pharmacodynamic Drug-Drug Interactions through Signaling Propagation Interference on Protein-Protein Interaction Networks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdousi, R.; Safdari, R.; Omidi, Y. Computational prediction of drug-drug interactions based on drugs functional similarities. J. Biomed. Inform. 2017, 70, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, S.; Hripcsak, G. The role of drug profiles as similarity metrics: Applications to repurposing, adverse effects detection and drug-drug interactions. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, S.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Lorberbaum, T.; Hripcsak, G.; Friedman, C.; Tatonetti, N.P. Similarity-based modeling in large-scale prediction of drug-drug interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitnik, M.; Agrawal, M.; Leskovec, J. Modeling polypharmacy side effects with graph convolutional networks. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i457–i466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtar, G.; Rokach, L.; Shapira, B. Detecting drug-drug interactions using artificial neural networks and classic graph similarity measures. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Hu, J.; Sorrentino, R. Label Propagation Prediction of Drug-Drug Interactions Based on Clinical Side Effects. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Yue, X. Manifold regularized matrix factorization for drug-drug interaction prediction. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 88, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S. A multimodal deep learning framework for predicting drug-drug interaction events. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4316–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrin, A.; Ferk, P.; Leskosek, B. Predicting potential drug-drug interactions on topological and semantic similarity features using statistical learning. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, C.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Ru, J.; Zheng, C.; Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; et al. Large-scale exploration and analysis of drug combinations. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Shukla, P.; Kumar Shukla, P.; Sharma, P.; Rawat, P.; Samar, J.; Moriwal, R.; Kaur, M. Efficient prediction of drug–drug interaction using deep learning models. IET Syst. Biol. 2020, 14, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdeolivas, A.; Tichit, L.; Navarro, C.; Perrin, S.; Odelin, G.; Levy, N.; Cau, P.; Remy, E.; Baudot, A. Random walk with restart on multiplex and heterogeneous biological networks. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, S.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Friedman, C. Detection of drug-drug interactions by modeling interaction profile fingerprints. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plumb, A.L. Drugs.com: Drug information online 2004. Ref. Rev. 2004, 18, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Van Jaarsveld, M.F.; Walubo, A.; Du Plessis, J.B. Interaction between valproic acid and acyclovir after intravenous and oral administration in a rabbit model. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 101, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drug A | Drug Name 1 | Drug B | Drug Name 2 | Interaction | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB00555 | Lamotrigine | DB00316 | Acetaminophen | 1 | 1 |
| DB00829 | Diazepam | DB00537 | Ciprofloxacin | 1 | 1 |
| DB00313 | Valproic acid | DB00787 | Acyclovir | 1 | 0.999995589 |
| DB01068 | Clonazepam | DB00501 | Cimetidine | 8 | 0.999974012 |
| DB01068 | Clonazepam | DB00338 | Omeprazole | 8 | 0.966016471 |
| DB00313 | Valproic acid | DB00199 | Erythromycin | 45 | 0.768196225 |
| DB01068 | Clonazepam | DB00951 | Isoniazid | 1 | 0.558177412 |
| DB00252 | Phenytoin | DB00364 | Sucralfate | 4 | 0.476196706 |
| Drug A | Drug A Name | Drug B | Drug B Name | Predict | Label | Prediction Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB00312 | Pentobarbital | DB01174 | Phenobarbital | 9 | 1 | The metabolism of Drug B can be increased when combined with Drug A. |
| DB00215 | Citalopram | DB06589 | Pazopanib | 2 | 3 | The metabolism of Drug B can be decreased when combined with Drug A. |
| DB00349 | Clobazam | DB00734 | Risperidone | 5 | 2 | Drug A may increase the hypotensive activities of Drug B. |
| DB08881 | Vemurafenib | DB00972 | Azelastine | 4 | 3 | The serum concentration of Drug B can be decreased when combined with Drug A. |
| DB00400 | Griseofulvin | DB00898 | Ethanol | 9 | 1 | The metabolism of Drug B can be increased when combined with Drug A. |
| DB01045 | Rifampicin | DB00199 | Erythromycin | 27 | 9 | The serum concentration of the active metabolites of Drug B can be increased when Drug B is used in combination with Drug A. |
| DB01174 | Phenobarbital | DB00541 | Vincristine | 9 | 4 | The metabolism of Drug B can be increased when combined with Drug A. |
| DB01026 | Ketoconazole | DB12001 | Abemaciclib | 2 | 3 | The metabolism of Drug B can be decreased when combined with Drug A. |
| DB00834 | Mifepristone | DB08903 | Bedaquiline | 7 | 3 | The risk or severity of QTc prolongation can be increased when Drug A is combined with Drug B. |
| DB01104 | Sertraline | DB01418 | Acenocoumarol | 10 | 2 | Drug A may increase the anticoagulant activities of Drug B. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, J.; Jung, H.; Ko, Y. PRID: Prediction Model Using RWR for Interactions between Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102469
Seo J, Jung H, Ko Y. PRID: Prediction Model Using RWR for Interactions between Drugs. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(10):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102469
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Jiwon, Hyein Jung, and Younhee Ko. 2023. "PRID: Prediction Model Using RWR for Interactions between Drugs" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 10: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102469
APA StyleSeo, J., Jung, H., & Ko, Y. (2023). PRID: Prediction Model Using RWR for Interactions between Drugs. Pharmaceutics, 15(10), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102469






