Abstract
Wound healing is a significant healthcare problem that decreases the patient’s quality of life. Hence, several agents and approaches have been widely used to help accelerate wound healing. The challenge is to search for a topical delivery system that could supply long-acting effects, accurate doses, and rapid healing activity. Topical forms of simvastatin (SMV) are beneficial in wound care. This study aimed to develop a novel topical chitosan-based platform of SMV with folic acid (FA) for wound healing. Moreover, the synergistic effect of combinations was determined in an excisional wound model in rats. The prepared SMV-FA-loaded films (SMV-FAPFs) were examined for their physicochemical characterizations and morphology. Box-Behnken Design and response surface methodology were used to evaluate the tensile strength and release characteristics of the prepared SMV-FAPFs. Additionally, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD), and animal studies were also investigated. The developed SMV-FAPFs showed a contraction of up to 80% decrease in the wound size after ten days. The results of the quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis demonstrated a significant upregulation of dermal collagen type I (CoTI) expression and downregulation of the inflammatory JAK3 expression in wounds treated with SMV-FAPFs when compared to control samples and individual drug treatments. In summary, it can be concluded that the utilization of SMV-FAPFs holds great potential for facilitating efficient and expeditious wound healing, hence presenting a feasible substitute for conventional topical administration methods.
1. Introduction
Wound healing is a complex and dynamic process categorized into four distinct, sequential, and overlapping phases (hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and tissue remodeling) [1,2]. Vasoconstriction, thrombogenesis, angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, extracellular matrix (ECM) development, and remodeling are only a few dynamic processes during these stages [3]. Wound healing begins immediately after the injury happens and takes a variety of times to complete, depending on the severity of the injury [4]. As a result, several different medications and techniques have been widely employed to accelerate wound recovery [5]. As innovative wound-healing materials are needed, their creation becomes increasingly pressing [6]. In addition to lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, simvastatin (SMV) is a well-known cholesterol-reducing medicine (Figure 1A) that helps lower increased lipid levels [7]. Because of this, it reduces the likelihood of having a heart attack or stroke. However, SMV has different therapeutic actions besides its cholesterol-lowering effect [8,9]. One of these is its capacity to improve mice’s impaired wound healing by increasing VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) synthesis and release at the wound site, a vital step in producing new blood vessels [10,11]. SMV can improve epithelialization and restore the normal skin epidermal barrier by reducing the iso-prenylation of mevalonate and farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP downstream) targets. Decreased FPP levels can also promote keratinocyte migration in vitro, epithelialization, and wound closure in an ex vivo human culture wound healing model [12]. Wounds treated with folic acid (FA) showed markedly improved tissue regeneration (Figure 1B) due to enhanced re-epithelialization, neo-vessel formation, inflammatory cell migration, and collagen deposition [13].
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of (A) SMV, (B) FA, and (C) CHT.
The thin and flexible polymeric film, with or without a plasticizer, satisfies numerous criteria that make it an effective platform for drug release [14,15]. Polymeric films have been noticed to improve therapeutic efficacy by speeding up the initial action stage, decreasing dose frequency, and eliminating side effects [14]. Chitosan (CHT) is widely present in nature and has an antibacterial effect, heavy metal adsorption effect, antioxidation effect, and film formability [16,17,18]. They are using CHT (Figure 1C) as a polymer for manufacturing these films, which is a non-toxic, biodegradable, and biocompatible polymer [19,20]. So, CHT is considered a promising material in preparing various topical dosage forms to enhance wound healing [3,21].
An essential feature of materials used as wound dressings is their antimicrobial activity [22]. The interactions between negatively charged microbial cell membranes and positively charged CHT molecules may cause the microbial membrane to rupture, releasing proteinaceous and other intracellular constituents [23].
Considering exciting findings about the role of SMV, folic acid (FA), and CHT on wound healing, we report the novel combination of SMV and folate in CHT-based films to accelerate the healing process. Consequently, the primary goal of the current study is to formulate and characterize SMV-FAPFs for efficient wound healing. SMV-Folate loaded films were characterized for thickness, morphology, FT-IR, DSC, and XRD. An excisional wound model in rats was used to evaluate the SMV-FAPFs’ in vivo wound-healing capacity. Additionally, using the RT-PCR method, JAK3 in skin samples and the expression of CoTI have been investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Chitosan (MW∼100–300 kDa) was obtained from ACROS organics (Waltham, WA, USA). SMV was gifted by EVA pharmaceutical company and FA by El-Nile pharmaceutical company. Glycerol (≥99.5% Batch No. 360019) was procured from Lab Chem, and ethanol (CAS No. 64-17-5) was obtained from Fisher (Horsham, UK).
2.2. Animals and Ethical Approval
Twenty albino Rats were housed at room temperature and subjected to a light/dark cycle. Experiments were conducted per the internationally accepted Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The protocol was approved by the Faculty of Medicine Ethics Committee at Sohag University, Egypt (12/1/2022/3).
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Preparation of SMV-FA Polymeric Films
The solvent casting method prepared SMV-Folic acid Polymeric films (SMV-FAPFs). SMV, FA, and glycerol concentrations in all film formulations were kept constant. The solvent was prepared using a mixture of ethanol and water in different ratios (10%, 20%, and 30% v/v). SMV (100 mg) and folate (200 mg) were dissolved in 100 mL of previously prepared solutions over a stirring plate. Then, different amounts of CHT (0.5, 1, and 1.5 g) were added to the beaker with 0.1 mL of glacial acetic acid at 80 °C using a magnetic stirrer for two h, and 1 mL of glycerol was incorporated as a plasticizer. The polymer solution was sonicated for 30 min in a bath sonicator to remove bubbles in the polymeric solution, then allowed to cool to room temperature. This polymeric dispersion of the drug was poured into Teflon plates (41 cm2) and allowed to dry in an oven at 60 °C until a flexible film was formed. Dried films were carefully removed and checked for any imperfections or air bubbles. A funnel was placed inverted on the plate to prevent fast evaporation from the patches. Each film was cut into square batches (1 cm2) using a blade. The final formulations were stored in a resealable bag in a cool and dry place until use.
2.3.2. Experimental Design
A full factorial (32) experimental design was constructed using Stratigraphic Plus® 18 software, Stat point Tech., Inc., Warrenton, VA, USA [24,25]. Three levels of each independent variable were used to optimize the prepared SMV-FAPFs [26]. The selected levels of EtOH/W ratio in total dispersion (X1) were 10 (−1), 20 (0), and 30% (v/v) (+1), whereas the selected values for CHT concentration in the mixture (X2) were 0.5 (−1), 1 (0), and 1.5 (+1) % (w/v) (Table 1). Tensile strength (TS) (Y1), film expansion % (Y2), and cumulative percent released at 3 h (Y3) were selected as dependent (response) parameters [27].

Table 1.
Composition of different SMV-FAPFs.
2.3.3. Characterization of Prepared SMV-FAPFs
Films Expansion Profile (Expansion%)
The wound surface is simulated by a gelatin model [28], and SMV-FAPFs are placed on it. The disk-shaped films expand gradually in all directions. A clear gelatin solution was prepared by adding 4 g of gelatin powder to 100 mL of distilled water at 70 °C with constant stirring at 700 rpm. Then, 30 g of this 4% w/v gelatin solution was poured into a Petri dish and stored in the fridge overnight to form a gel. Next, each drug-loaded film was cut into a circular shape of a defined size (18 mm in diameter) and then placed on the gelatin gel (in the Petri dish). Film dressings are designed to expand after being applied to an injury and absorb wound exudate. The change in the diameter of the films was recorded after 24 h. The test was performed in duplicate for each formulation, and the mean value was used to calculate the expansion behavior using the following equation:
where E is the expansion ratio, Dt is the diameter of the film after expansion, and Do is the diameter of the film before expansion.
Tensile Strength
A universal testing device (Testometric M-500, Rochdale, Lancashire, UK) was used to measure tensile strength at the breakpoint using 3 samples cut from each film of 1.5 × 4 cm to fit into the equipment. Tensile strength was determined at 24 °C in the tension state. The instrument consisted of two tensile grips, the lower one fixed and the upper one movable. The insert formulations were positioned between two clamps. The upper arm pulled the polymeric films at a 1 mm/s rate until they broke. Tensile strength (mPa) was determined by using Exponent Lite version 6.1.4.0 (Stable Micro-System Ltd., Surrey, UK) [29].
In Vitro Release Study
The drug release studies from SMV-FAPFs were performed using the dissolution rate test apparatus (Hanson Research Co., Chatsworth, CA, USA). A patch of 1 cm2 was fixed to a circular glass slide with the help of cyanoacrylate adhesive. The pH was set to 7.4 to simulate the wound environment, and 500 mL of phosphate buffer solution and ethanol (9:1) were used as release media and deposited in a dissolving vessel. The study was conducted at 37 ± 1 °C, and paddle speed was kept at 50 rpm. Samples (5 mL) were collected for up to 6 h at suitable intervals. An aliquot of 1 mL was taken from each withdrawn sample and diluted with 1 mL of ethanol. UV-spectrophotometer measured the absorbance at λmax of 238. Then, a Kinetic study was carried out to identify the release model which explains the in vitro release pattern of the drug. The release data were fitted to the Korsmeyer- Peppas equation to clarify the mechanism of SMV release from the developed film formulations [30].
where Mt/M∞ is the fraction of drug released at time t, k is the kinetic constant, and n represents the release exponent. The value of the release exponent (n) determines the general release mechanism. The n value between 0.43 and 0.5 indicates the Fickian diffusion behavior, coupled diffusion, and polymer relaxation (non-Fickian diffusion) occurs if 0.5 < n < 1, erosion-mediated release (case II) takes place when n = 1 (zero-order kinetics, and super case II type of release, which is related to polymer relaxing and hydrogel expansion, takes place with n > 1 [31].
Thermal Analysis and Infrared Spectroscopy
Difference scanning calorimetry (DSC) tests were done on SMV, FA, CHT powder, and a physical mixture (1:1:1 w/w) on a calorimeter (DSC; PerkinElmer Thermal Analysis, Waltham, WA, USA). Three to five milligrams of a sample were sealed in a standard aluminum pan and heated over a temperature range of 25–350 °C. The thermograms were obtained at a constant heating rate of 10 °C/min in a 20 mL/min nitrogen flow rate. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) analysis was applied using a spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer Spectrum 100 FTIR Spectrometer). The FTIR spectra of the pure drug, FA, CHT, and drug-loaded films were recorded within 4000 to 550 cm−1.
X-ray Diffraction Studies
XRD has been widely used for the study of materials and thin films. XRD patterns of the pure drug, FA, polymer, physical mixture of ingredients, and SMV-loaded films are measured.
Microscopic Examination
Surface imaging of selected polymeric films was performed using a Scanning electron microscope. The morphology of films was determined by using a polarized microscope attached to a camera. The films were trimmed to approximately 3 cm2 and placed onto a glass slide covered with a slip.
Weight Variation
The patches were subjected to weight variation by individually weighing randomly selected patches by digital balance. Such determinations were carried out for each formulation.
Folding Endurance
The folding durability of polymeric films was evaluated by repeatedly folding the film strips at the same spot until the film ruptured. The polymeric films were cut into 5 cm2 squares. The value of folding endurance was determined by how many times the polymeric inserts could be folded at the same position without rupturing.
Film Thickness
The films’ thickness was measured using a digital caliper at three positions (one at the center, two near the edges). This test was performed three times for each film, and the average values were recorded.
Drug Content
UV-spectrophotometry was used to analyze the SMV-FAPFs for their SMV concentration. After 24 h of dissolving in 10 mL of the casting solvent, the applied film (area 1 cm2) was fully dissolved. After passing through a 0.45 µm filter, the solution was tested for its SMV concentration.
2.3.4. Efficient Formula Selection
The most efficient SMV-FAPFs were selected based on their highest tensile strength, percentage of expansion, and cumulative percentage of release after 3 h [32]. Based on the results, F3 (EtOH/W ratio of 10% and 1.5% w/v CHT) was chosen as the best and used for further in vivo inquiry.
2.3.5. In Vivo Study
Animal Experiments
The wound healing activities were tested in an excision wound model in rats [33,34,35,36]. Rats were housed at room temperature and subjected to a light/dark cycle. The protocols for the care and use of laboratory animals, which are universally recognized, were followed when conducting the experiments, and the protocol was approved by the Faculty of Pharmacy’s Ethics Committee (12/1/2022/3). A total of 20 albino rats were split into 4 groups of 5. The dorsal skin was shaved after intraperitoneal thiopental anesthesia, and a 1 cm2 circular incision was made using sterilized, sharp scissors [37,38,39]. Groups II, III, and IV received treatment twice daily with FA-loaded film, SMV-loaded film, and SMV-FAPFs 24 h after wound inoculation. Whereas the wounds of the non-treated control (group I) received blank, non-medicated films. A Canon D5200 camera (Canon, Tokyo, Japan) was used to take pictures of the wounds on days 1, 3, and 7 after the injury [6].
2.3.6. Histopathological Evaluation
Skin samples were dried, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 5 μm slices after being fixed in 10% formalin on day 7 [40,41,42]. To determine the general skin structure and histological alterations in the epidermis and dermis, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was performed [43,44,45].
2.3.7. CoTI and JAK3 RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR) Investigation for Skin Biopsies
RT-PCR was used to examine the expression of CoTI and JAK3 in skin biopsies from treated animals to determine the wound-healing-promoting effect of SMV-FAPFs [46]. RNA was extracted from skin biopsy samples using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) per the manufacturer’s instructions on day seven post-treatment when a 2.5 mm needle biopsy was obtained. The high-capacity cDNA synthesis kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) was then used to create cDNA. The 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR machine (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) performed RT-PCR. Expression levels of CoTI and JAK3 were evaluated using an evergreen based technique, and GAPDH was used as the endogenous control. Primers for the estimation of CoTI were: forward primer 5′-ATCAGCCCAAACCCCAAGGAGA-3′ and reverse primer 5′-CGCAGGAAGGTCAGCTGGATAG-3′, primers for the determination of JAK 3 were: JAK3 F 5′-CCTGGAGTGGCACGAGAATC-3′, JAK3 R 5′-TCCACAACCTCCCGCCTAT-3′ [46], while primers used for GAPDH estimation were: forward primer 5′-CCATTCTTCCACCTTTGATGCT-3′ and reverse primer 5′-TGTTGCTGTAGCCATATTCATTGT-3′ [47]. Denaturation was carried out for 10 min at 95 °C, after which a two-step cycling technique was used for 40 cycles: denaturation for 30 s at 95 °C, followed by annealing and extension for 30 s at 60 °C. RT-PCR results were analyzed using the comparative cycle threshold method (2−ΔΔCt method [48]) and represented a fold-change in expression compared to the untreated control group.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of SMV-FA Polymeric Film
Polymeric films were fabricated by the solvent casting method, in which the polymer is dissolved in one or more volatile solvents (organic or water) to get a homogeneous solution with a low viscosity. Nine formulations were prepared, and the composition of the investigated polymeric films is listed in Table 1. After solvent casting, the movie had smooth surfaces and was dry, thin, flexible, transparent, and free from bubbles. Tensile strength (Y1), film expansion % (Y2), and cumulative % released at 3 h (Y3) were selected as the response variables (Table 2).

Table 2.
Tensile strength, film expansion %, and cumulative % released at 3 h of SMV-FAPFs.
3.2. DSC Studies
SMV, CHT, and FA interactions were studied to explain the thermal characteristics of the drug and polymer used and, hence, predict any possible physicochemical interactions that might eventually affect the drug release rate from the polymeric film formulations. The thermal curves of SMV, FA, CHT, and their physical mixture (Ph.M) are shown in Figure 2. A typical thermal behavior was recorded for SMV; a sharp endothermic peak at 145.85 °C was due to SMV melting. At the same time, FA shows two endothermic peaks at 117.6 and 203.4. The DSC thermogram of CHT showed an endothermic peak between 74.58–76.25 °C, assigned to the loss of water associated with the hydrophilic groups of CHT, and an exothermic peak at 306.22 °C, representing the degradation of acetyl and deacetylated units, and glycoside bond cleavage of CHT. The thermogram of physical mixtures of the SMV with FA and CHT showed a decrease in the intensity of the endothermic peak of SMV, indicating the phase transition of SMV into the amorphous state.
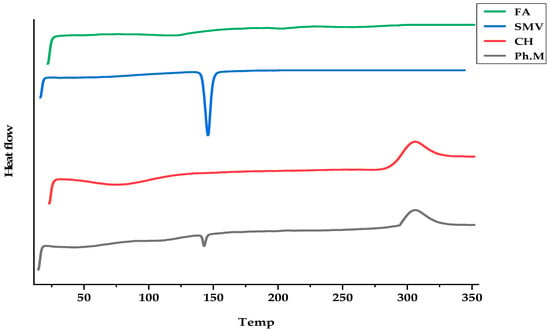
Figure 2.
DSC thermograms of FA, SMV, CHT, and physical mixtures.
3.3. FTIR Investigations
Figure 3 displays the FTIR spectra of powdered mixes of SMV, FA, CHT, and their pure forms. At 3546, 2952, 2870, and 1694 cm−1 (stretching vibrations of O–H, C–H, C–O and C=O groups), the FTIR spectra of SMV displays characteristic peaks. Spectra of unconstrained FA show the characteristic IR absorption peaks at 1603, 1690, and 1482 cm−1, which are attributed to the N–H bending vibration of the O=C–NH, the C=O amide stretching of the carboxyl group, and the absorption band of the phenyl ring. In the case of CHT alone, a prominent band at 3277–3369 cm−1 is indicative of NH and OH stretching as well as intramolecular hydrogen bonding. No significant changes in the characteristic band positions of SMV, FA, or the spectra for CHT were found, indicating no detectable physicochemical interactions between the SMV, FA, and CHT. A possible reaction occurred between the amino group of CHT and the carboxyl group of FA, forming an amide bond. Also, the hydroxyl stretching bands got much broader in the IR of the Ph.M, indicating the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the hydroxyl groups of SMV and CHT.
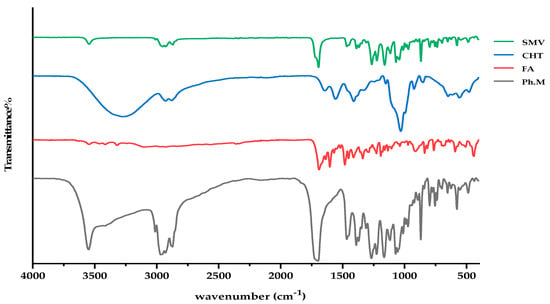
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of SMV, CHT, FA, and physical mixture.
3.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
XRD patterns of the pure SMV, FA, CHT, SMV loaded films, and physical mixture of SMV and other excipients are presented in Figure 4. From the XRD pattern in Figure 4, pure SMV, FA, and physical mixture exhibited crystalline patterns, whereas CHT alone showed no crystalline peaks, indicating the amorphous nature of this polymer. SMV exhibited several unique sharp peaks at 9.2°, 10.9°, 15.61°, 16.52°, 17.3°, 18.84°, 19.5°, and 22.6°, which resulted from its regular crystallization. Moreover, CHT Powder peaked at 13.1°, a typical broad peak at 20.5°, whereas the diffractogram of the polymeric film showed a broad peak at 12.4°.
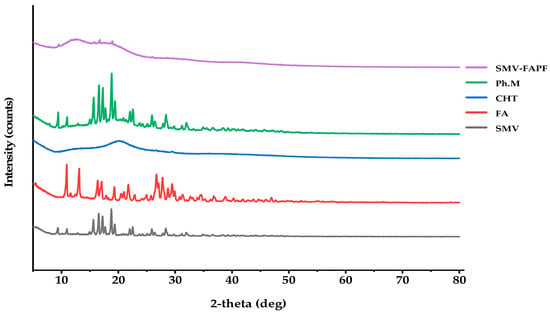
Figure 4.
XRD for SMV-FA loaded film, physical mixture, CHT, FA, and SMV.
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscope
Figure 5A–C show the microscopic surface morphology of three optimized film formulations (F1, F2, and F3) in a bright field. These films also demonstrated good compatibility within the film matrix, as observed by their uniform appearance, without any phase separation or noticeable cracks.
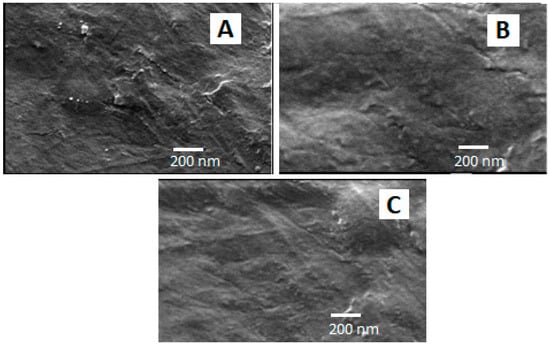
Figure 5.
SEM micrograph of three optimized SMV-FAPFs: F1 (A), F2 (B), and F3 (C).
3.6. Response Surface Methodology and Optimization of Formulation Factors
3.6.1. Tensile Strength
The tensile strengths of all SMV-FAPFs are represented in Figure 6. Tensile strength (TS) measures breakability parameters that determine the resistance to damage that can occur during production, handling by the patient, or placement by the clinician [6]. The TS measured in the range of 11–19 MPa. The results reported corresponded with Table 3’s folding endurance findings. Folding endurance is proportional to tensile strength. The main effects plot and response surface figure (Figure 7) showed that the SMV-FAPFs containing a lower ratio of EtOH/W have higher tensile strength than those containing higher ratios. The TS was found to be significantly affected by the ratio of EtOH/W in addition to the chitosan concentration. A high EtOH/W ratio in the polymer matrix may also produce regions of discontinuity, lowering the resistance of the matrix to fracture and leading to lower tensile strength and elastic modulus of the films. As the ratio of EtOH/W decreased, the ability of the formulated films to withstand stress increased. Also, increasing CHT concentration slightly enhanced the film’s resistance to breakage because the formation of macro-void structures became smaller and lesser, improving the film’s structure. The obtained results agreed with many studies showing that ethanol promotes the dehydration of polymer chains, increasing their intermolecular bonds and producing a stiffer material [49].
Figure 6.
Tensile strength of SMV-FAPFs (F1–F9).

Table 3.
Thickness, weight, drug content, surface pH, % moisture uptake, and mechanical (Tensile strength, expansion %, and folding endurance) characteristics for three selected SMV-FAPFs.
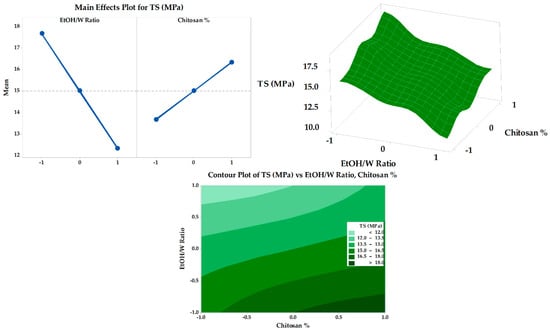
Figure 7.
Main effects, response surface plot, and contour plot of EtOH/Ratio and CHT% on TS.
3.6.2. Expansion Percentage
The obtained results of the fabricated SMV-FAPFs expansion percentage are presented in Table 2. The expansion percentage was between 30.88 ± 1.24 (F7) and 45.54 ± 1.67 (F3). The obtained result revealed a strong relationship between the EtOH/W ratio and concentration of CHT and the expansion % of the investigated SMV-FAPFs (Figure 8). A large percentage of expansion was obtained at a low EtOH/W ratio (10%). As the EtOH/W ratio increased (20% in F4, 5, and 6), the expansion percentage decreased and further decreased as the EtOH/W ratio increased to 30%. The results agree with previous studies, which explained that more hydrated films quickly absorbed more wound exudate and showed more expansion. Moreover, the concentration of CHT affected the expansion percentage. The results showed that the expansion percentage slightly increased as the CHT concentration increased. The most significant expansion percentage was recorded for F3, which has the lowest ratio of EtOH/W (10%) and the highest CHT concentration (1.5%). The expansion process included water uptake followed by the process of swelling of the polymer matrix. So, increasing CHT concentration resulted in a more significant expansion percentage, confirmed by experimental outcomes. The results showed that the expansion percentage slightly increased as the chitosan concentration increased.
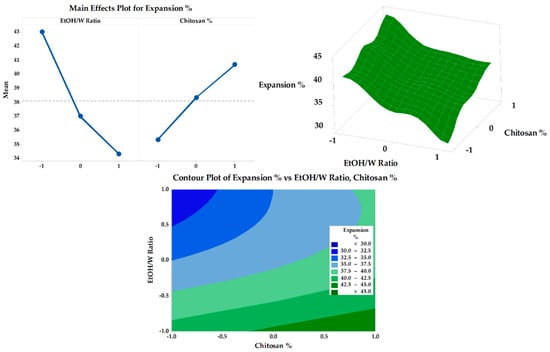
Figure 8.
Main effects, response surface plot, and contour plot of EtOH/W ratio and CHT% on expansion%.
3.6.3. In Vitro SMV-FAPFs Release
The diffusion rate often controls drug release from polymeric films through intact polymeric matrix or water-filled channels. Controlled drug release is due to the restricted mobility of tiny drug molecules distributed or dissolved in the dense macromolecular matrix films [50]. For SMV-FAPFs, the cumulative percentage of SMV released from the investigated formulations ranged from 46.44 ± 2.89 (F9) to 72.87 ± 2.32% (F1) after 3 h. Over 40% of SMV was released after 1 h (h) in F1, F2 and F3. In contrast, SMV cumulative % release after one h did not exceed 40% for other formulations. Other formulation did not exceed. The obtained results showed that the higher the EtOH/W ratio, the more complex the film was formed, and more time would be needed to get the film wet, resulting in a delayed SMV release. F1, prepared with a lower EtOH/W ratio, showed prompt drug release and a significantly higher value of cumulative percent release after 3 h as compared to other formulations. On the other hand, the concentration of CHT was inversely proportional to the cumulative percentage of SMV released. They were increasing the engagement of CHT results in delayed drug release due to the increment in crosslinking density [51]. Results showed that the longer the diffusion path and the more viscous the diffusion microenvironment, the slower the consequent release rate. So, when the EtOH/W ratio was constant, the formulations with low CHT concentration (F1, F4, and F7) showed enhanced SMV cumulative % released more than other formulations, as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10. Using Korsmeyer-peppas equation, the calculated diffusional exponents, n, from 3 formulations with different CHT concentration (F1, F2, and F3) were 0.53, 0.56 and 0.58, respectively. All values are between 0.5 and 1, indicating that the release mechanism for the tested topical film formulations was Coupled diffusion and polymer relaxation.
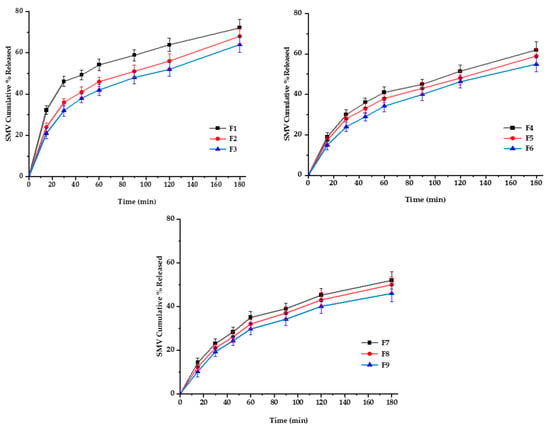
Figure 9.
In vitro release profiles of SMV-FAPFs (F1-F9) in phosphate buffer-ethanol solution (9:1), PH 7.4, at 37 ± 0.5 °C.
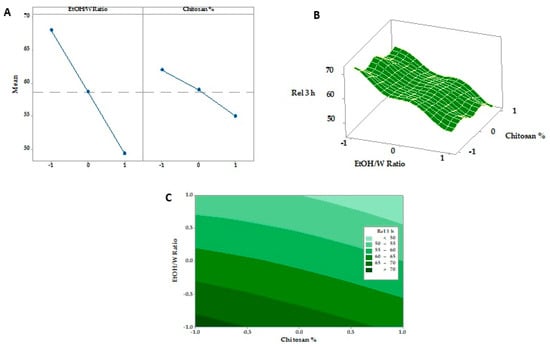
Figure 10.
Main effects (A), response surface plots (B), and contour plot (C) of EtOH/Ratio and CHT % on Rel 3 h.
3.7. Physical and Mechanical Characterization of the Prepared Films
The SMV-FAPFs were prepared by a simple and scalable method utilizing a mixture of water and ethanol as a solvent. The method of preparation, the amount of gel poured into the dish, and the flatness of the surface during drying all influence the thickness of the film. In this study, 20 g of gel was ideal for casting the film dressing in a plastic die with desirable properties. Films prepared from less than 20 g were so thin that they were difficult to remove from the plastic die since they were easily shredded. In contrast, thick films were unsuitable, needing more transparency and flexibility. Physical and mechanical characteristics of the optimum prepared formulae (F1, F2, and F3) according to Box-Behnken Design are shown in Table 3. Using plasticizers such as glycerin (GLY) was essential to stimulate better mechanical properties. GLY is a water-miscible liquid with a low molecular weight and a high propensity to diffuse and connect with polymer chains. The films become more malleable due to reduced stiffness and a spike in interchain distances [52]. As a result, a flexible, non-brittle, and conformable dressing for use on various wound sites has been developed. Simvastatin is a hydrophobic drug, so adding ethanol as a co-solvent enhances the solubility of the drug and gives a slight transparency to the films.
3.8. In Vivo Study
Rats treated with SMV-FA-loaded films exhibited improved skin appearance, accelerated wound closure, and regular hair growth compared to other groups that received the other treatments at 3-and 7-days post-wounding (Figure 11A). Additionally, this group exhibited the highest wound contraction percentage (Figure 11B), pointing to a marked reduction of the wound size with enhanced healing.
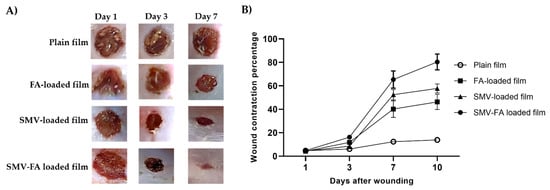
Figure 11.
The healing progression of wounds is treated with tested preparations. (A) Excision wounds of rats were treated with plain film, FA-loaded film, SMV-loaded film, and SMV-FA films and photographed at 1-, 3- and 7-days post-infection to follow up the healing process. (B) The effect of different formulations on the percentage of wound contraction was calculated at 1, 3,7, and 10 after wounding. The results are expressed as the means ± SD.
3.9. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR) Analysis of CoTI and JAK3 in Skin Biopsies
CoTI and JAk3 expression in the treated skin samples was assessed by RT-PCR analysis [6,53] to examine further the molecular pathways connected to SMV-FAPFs treatment, as shown in Figure 12. Generally, treated samples showed higher levels of CoTI and lowered JAK3 levels. It should be noted that skin samples treated with either SMV-film or FA-film alone had considerably lower CoTI expression than those treated with SMV-FAPFs. Samples treated with SMV-FAPFs had a mean fold change in collagen expression of 3.6 ± 0.3, while samples treated with SMV and FAPFs had fold changes of 2.6 ± 0.4 and 2.1 ± 0.5.
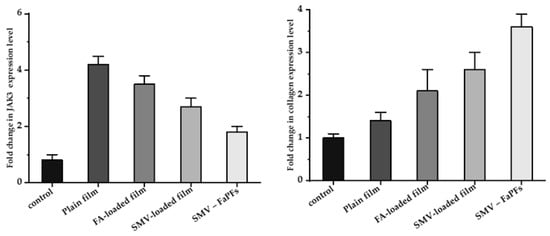
Figure 12.
Fold expression levels of JAK3 and CoTI in skin biopsies of treated rats.
Moreover, JAK3 expression after treatment with SMV-FAPFs was downregulated compared to samples treated with SMV or FA films alone. The average fold change for JAK3 expression was 1.8 ± 0.2 compared to 2.7 ± 0.3 and 3.5 ± 0.3 in SMV and FA-treated samples. Collagen synthesis is principally responsible for wound healing. The proliferative stage of the healing cycle is characterized by the growth of fibroblasts and the production of new collagen. The granulation layer contains collagen types I and III, with CoTI being the more prevalent protein there [54]. As a result, the assay of CoTI appears to be a valuable indicator of the wound-healing process [55]. Treatment with SMV-FAPFs was associated with a fourfold increase in CoTI expression, showing the preparation’s promising capacity for wound healing. Skin inflammation, linked to tissue damage, is primarily caused by the production of several immune modulators known as cytokines. Many substances mediate these cytokines’ signal transduction. One of the recently identified proteins, JAK3, is widely expressed in the epidermis and is essential for signaling many cytokine receptors, including IL-2R, IL-4R, IL-7R, and IL-9R [56]. Our results showed that the expression of JAK3 mRNA was significantly reduced following treatment with SMV-FAPFs, which coincided with the increase of CoTI. Reduced expression of JAK3 may be responsible for the reduced inflammation seen in SMV-FAPFs. Similarly, medicines that suppress JAK3 expression have shown promising benefits in reducing psoriasis cutaneous inflammation [57]. Data shows that these novel SMV-FAPFs have markedly promoted wound healing compared to SMV or FA alone.
3.10. Comparative Histological Investigation
Epidermis and dermis were both present in the analyzed rat skin. The epidermis consists of the four basal, spinous, granular, and cornified squamous keratinized epithelium layers. The dermo-epidermal junction (DED) is formed when epidermal invaginations and dermal papillae interdigitate. A highly vascular papillary layer surrounded a collagen, elastin, and connective tissue cell-rich reticular layer in the dermis [54]. In the untreated control group (A), the examined skin histopathological characteristics showed significant damage in the two layers of skin (epidermis and dermis) with loss of organization of structure. The treated skin with FA or SMV alone showed minimal or moderate improvements (B and C). Simvastatin, when applied topically, hastened the healing of wounds by promoting angiogenesis and lymphogenesis, and FA-treated wounds significantly accelerated tissue regeneration by promoting re-epithelialization, neo-vessel development, inflammatory cell migration, and collagen deposition. So, the combination of SMA and FA affected different stages of wound healing: inflammation, proliferation, and maturation, and resulted in more intact skin and less scar formation. Significant lesion healing and evident improvement in the skin layers (D) were observed in Group 4 receiving the combined treatment (Figure 13).
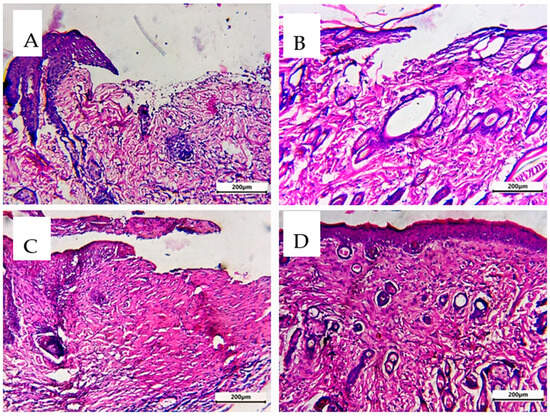
Figure 13.
Sections of the thin skin of all group rats were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. (A) Untreated control group, (B) FA-treated group, (C) SMV-treated group, and (D) SMV-FAPFs-treated group.
4. Conclusions
The solvent casting technique effectively produced SMV and FA-loaded chitosan dressings. The topical formulation in such dressings can significantly accelerate the rehabilitation process of infected wounds. The prepared sauces can be bent and molded to fit different wound sites, and they can be cut into varied sizes and shapes to provide different amounts of SMV. This in vivo wound reconstruction test on rats demonstrated conclusively that the combination of SMV and FA resulted in a more significant healing effect than that of SMV or FA alone. These combined films showed the highest expression of CoTI, four times more than the plain film, and the lowest expression of JAK3, which rapidly inhibited inflammation in treated wounds. Also, the histological analysis emphasized that the combination of SMV and CHT has a great healing power at different stages of the healing process. The curative effectiveness of SMV-FAPF dressings in managing the condition of chronic injuries will be the subject of additional studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.H., M.S.S. and M.M.A.E.; methodology, M.A.H., M.S.S., M.M.A.E., M.H.A., B.S.A., M.E.A., K.-T.L., A.K.H., A.B., A.H.H., H.A., M.A.E.-M. and A.A.A.-R.; software, M.M.A.E. and M.S.S.; validation, M.A.H., B.S.A. and M.E.A.; formal analysis, A.K.H. and A.B.; investigation, A.H.H., H.A., M.H.A., M.A.E.-M. and A.A.A.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.A.E., M.A.H. and K.-T.L.; writing—review and editing, M.M.A.E. and M.S.S.; supervision, M.A.H., M.S.S., M.M.A.E., B.S.A., M.E.A., K.-T.L., A.K.H., A.B., A.H.H., H.A., M.A.E.-M. and A.A.A.-R.; project administration, M.M.A.E., M.S.S. and A.B.; funding acquisition, M.M.A.E., K.-T.L., M.H.A., A.B. and B.S.A.; data curation, M.A.H. and M.M.A.E.; method validation, M.A.H., B.S.A. and M.E.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2023R73), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Ethical Committee of Sohag University, Faculty of Pharmacy; Sohag, Egypt (12/1/2022/3) approved the procedures.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2023R73), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sikareepaisan, P.; Ruktanonchai, U.; Supaphol, P. Preparation and characterization of asiaticoside-loaded alginate films and their potential for use as effectual wound dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoială, A.; Ilie, C.-I.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Synergic Effect of Honey with Other Natural Agents in Developing Efficient Wound Dressings. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ferjani, R.; Ahmad, M.; Dhiyaaldeen, S.M.; Harun, F.W.; Ibrahim, M.Y.; Adam, H.; Al-Obaidi, M.M.J.; Batran, R.A. In Vivo assessment of antioxidant and wound healing improvement of a new schiff base derived Co (ii) complex in rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niculescu, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M. An Up-to-Date Review of Biomaterials Application in Wound Management. Polymers 2022, 14, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.; Khan, N.R.; Razaque, G.; Shah, S.U.; Shahid, M.G.; Albarqi, H.A.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Alasiri, A.; Basit, H.M. Microwave-treated physically cross-linked sodium alginate and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose blend polymer film for open incision wound healing in diabetic animals—A Novel perspective for skin tissue regeneration application. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 418. [Google Scholar]
- Rezvanian, M.; Amin, M.C.I.M.; Ng, S.-F. Development and physicochemical characterization of alginate composite film loaded with simvastatin as a potential wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Say, K.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Fahmy, U.; Aldawsari, H.; Ahmed, O.A. Enhanced permeation parameters of optimized nanostructured simvastatin transdermal films: Ex vivo and In Vivo evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Techol. 2015, 20, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, A.; Mendes, M.; Cabral, C.; Mare, R.; Paolino, D.; Vitorino, C. Hybrid nanostructured films for topical administration of simvastatin as coadjuvant treatment of melanoma. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3396–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, J.; Zeki, A.A.; Mirzaei, N.; Tewary, S.; Rezaei Moghadam, A.; Glogowska, A.; Nagakannan, P.; Eftekharpour, E.; Wiechec, E.; Gordon, J.W.; et al. Mevalonate Cascade Inhibition by Simvastatin Induces the Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathway via Depletion of Isoprenoids in Tumor Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Álvarez, M.; López-Puente, V.; Rodríguez-Valencia, C.; Angelomé, P.C.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Serra, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; González, P. Osteogenic effects of simvastatin-loaded mesoporous titania thin films. Biomed. Mat. 2018, 13, 025017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohilla, A.; Rohilla, S.; Kumar, A.; Khan, M.U.; Deep, A. Pleiotropic effects of statins: A boulevard to cardioprotection. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S21–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, N.; Duman, R.; Tosun, M.; Akıcı, M.; Göksel, E.; Gökçe, B.; Alagöz, O. Topical folinic acid enhances wound healing in rat model. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.F.; Silva, C.; Coelho, J.F.J.; Simões, S. Oral films: Current status and future perspectives: I—Galenical development and quality attributes. J. Control. Release 2015, 206, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, A.-M.; Karaçelebi, Y.; Saatcioglu, E.; Altan, E.; Ulag, S.; Aydoğan, H.K.; Sahin, A.; Motelica, L.; Oprea, O.; Tihauan, B.-M. Electrically triggered drug delivery from novel electrospun poly (lactic acid)/graphene oxide/quercetin fibrous scaffolds for wound dressing applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Ma, R.; Lin, C.; Liu, Z.; Tang, T. Quaternized chitosan as an antimicrobial agent: Antimicrobial activity, mechanism of action and biomedical applications in orthopedics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1854–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, B.S.; Oprea, O.; Voicu, G.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Teodorescu, A.; Holban, A. Synthesis and characterization of a novel controlled release zinc oxide/gentamicin–chitosan composite with potential applications in wounds care. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Hong, S.-I.; Park, H.-M.; Ng, P.K. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-based nanocomposite films with antimicrobial activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5814–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Rasoul, A.; Ahmed, M.M. Chitosan polymer as a coat of calcium alginate microcapsules loaded by non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug. Bull. Pharm. Sci. Assiut 2010, 33, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M. Controlled release alginate-chitosan microspheres of tolmetin sodium prepared by internal gelation technique and characterized by response surface modeling. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 56, e18414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, M.; Morsi, R.E.; Kerch, G.; Elsabee, M.Z.; Kaya, M.; Labidi, J.; Khawar, K.M. Current advancements in chitosan-based film production for food technology; A review. Int. J. Bio. Macromol. 2019, 121, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Ifuku, S.; Osaki, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Minami, S. Preparation and biomedical applications of chitin and chitosan nanofibers. J. Biomed. Nanontechnol. 2014, 10, 2891–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddik, M.S.; Elsayed, M.M.; Abdel-Rheem, A.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Mosa, E.S.; Al-Hakkani, M.F.; Al-Shelkamy, S.A.; Khames, A.; Daha, M.A.; Abdel-Aleem, J.A. A Novel C@ Fe@ Cu Nanocomposite Loaded with Doxorubicin Tailored for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfeek, H.M.; Abdel-Aleem, J.A.; Ahmed, M.M. Development and optimization of itopride hydrochloride fast disintegrating tablets using factorial design and response surface methodology. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 6, 1661. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shenawy, A.A.; Elsayed, M.M.; Atwa, G.M.; Abourehab, M.A.; Mohamed, M.S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Mahmoud, R.A.; Sabry, S.A.; Anwar, W.; El-Sherbiny, M. Anti-Tumor Activity of Orally Administered Gefitinib-Loaded Nanosized Cubosomes against Colon Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M. Effect of different formulation variables on release characteristics of gastro-floating microspheres of ethyl cellulose/carbopol 934P encapsulating sorafenib. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 11, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.E.; Auffret, A.D.; Humphrey, M.J.; Eccleston, G.M. Lyophilised wafers as a drug delivery system for wound healing containing methylcellulose as a viscosity modifier. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 289, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkader, H.; Pierscionek, B.; Alany, R.G. Novel in situ gelling ocular films for the opioid growth factor-receptor antagonist-naltrexone hydrochloride: Fabrication, mechanical properties, mucoadhesion, tolerability and stability studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Rel. 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.M.; Aboelez, M.O.; Mohamed, M.S.; Mahmoud, R.A.; El-Shenawy, A.A.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A.; Santali, E.Y.; Alshehri, S.; Elsadek, M.E.M. Tailoring of rosuvastatin calcium and atenolol bilayer tablets for the management of hyperlipidemia associated with hypertension: A preclinical study. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, A.; Kant, V.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Chitosan-based copper nanocomposite accelerates healing in excision wound model in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 731, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shailajan, S.; Menon, S.; Pednekar, S.; Singh, A. Wound healing efficacy of Jatyadi Taila: In Vivo evaluation in rat using excision wound model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Verpoorte, R.; Suresh, B. Evaluation of In Vivo wound healing activity of Hypericum patulum (Family: Hypericaceae) leaf extract on different wound model in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 70, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, S.; Gautam, M.; Goel, S.; Purohit, V.; Sharma, H.; Goel, R. Evaluation of In Vivo wound healing activity of Bacopa monniera on different wound model in rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 972028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Hamzah, N.; Mohammed, A.; Sirajudeen, K.; Asari, M.; Hamzah, Z.; Shaik, I. Keladi candik (Alocasia longiloba Miq.) petiole extracts promote wound healing in a full thickness excision wound model in rats. Asian Pacif. J. Trop. Biomed. 2019, 9, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Adamskaya, N.; Dungel, P.; Mittermayr, R.; Hartinger, J.; Feichtinger, G.; Wassermann, K.; Redl, H.; van Griensven, M. Light therapy by blue LED improves wound healing in an excision model in rats. Injury 2011, 42, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanger, A.A.; Leo, M.D.; Gopal, A.; Kant, V.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Pro-healing effects of bilirubin in open excision wound model in rats. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürses, İ.; Özeren, M.; Serin, M.; Yücel, N.; Erkal, H.Ş. Histopathological evaluation of melatonin as a protective agent in heart injury induced by radiation in a rat model. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, N.; Hamar, P. Histopathological evaluation of contrast-induced acute kidney injury rodent models. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3763250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serin, M.; Gülbaş, H.; Gürses, İ.; Erkal, H.Ş.; Yücel, N. The histopathological evaluation of the effectiveness of melatonin as a protectant against acute lung injury induced by radiation therapy in a rat model. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2007, 83, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarabadi, M.; Iranshahi, M.; Amoueian, S.; Mehri, S.; Motamedshariaty, V.S.; Mohajeri, S.A. Neuroprotective and memory enhancing effects of auraptene in a rat model of vascular dementia: Experimental study and histopathological evaluation. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 623, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, P.; Hines, F.A.; Robl, M.G.; Dunkel, V.C. Histopathological evaluation of liver, pancreas, spleen, and heart from iron-overloaded sprague-dawley rats* 1, 2. Toxicol. Pathol. 1996, 24, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwin, N.; Bendele, A.; Glasson, S.; Carlson, C. The OARSI histopathology initiative–recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthitis Cartil. 2010, 18, S24–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemeier, K.; Olesen, J.; Haddad, F.; Langberg, H.; Kjaer, M.; Baldwin, K.; Schjerling, P. Expression of collagen and related growth factors in rat tendon and skeletal muscle in response to specific contraction types. J. Physiolog. 2007, 582, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Lou, J. Dynamic changes in the gene expression profile during rat oral carcinogenesis induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.F.; de Moraes, M.A.; Nogueira, G.M.; Rodas, A.C.; Higa, O.Z.; Beppu, M.M. Glycerin and ethanol as additives on silk fibroin films: Insoluble and malleable films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, L.A.; O’Donnell, P.B.; McGinity, J.W. Mechanical properties of polymeric films prepared from aqueous dispersions. In Aqueous Polymeric Coatings for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, F.; Browne, D.; Asuri, P. Role of Polymer Concentration and Crosslinking Density on Release Rates of Small Molecule Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, H.; Wertheim, D.; Pierscionek, B.; Alany, R.G. Curcumin In Situ Gelling Polymeric Insert with Enhanced Ocular Performance. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buabeid, M.; Arafa, E.-S.A.; Yaseen, H.S.; Umar, M.I.; Murtaza, G. Anti-inflammatory effect of simvastatin by impeding TNF-α and interleukin-1ß pathways: Antiangiogenic activity of simvastatin and simvastatin-loaded silver nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2022, 50, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, L. Current concepts in soft connective tissue wound healing. Br. J. Surg. 1983, 70, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukipuro, K.; Melkko, J.; Risteli, L.; Kairaluoma, M.; Risteli, J. Synthesis of type I collagen in healing wounds in humans. Ann. Surg. 1991, 213, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Signaling mechanisms through cytokine receptors that share signal transducing receptor components. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1995, 7, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves de Medeiros, A.K.; Speeckaert, R.; Desmet, E.; Van Gele, M.; De Schepper, S.; Lambert, J. JAK3 as an Emerging Target for Topical Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).