Nucleoside Analog 2′,3′-Isopropylidene-5-Iodouridine as Novel Efficient Inhibitor of HIV-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry
2.1.1. Reagents and Technical Equipment
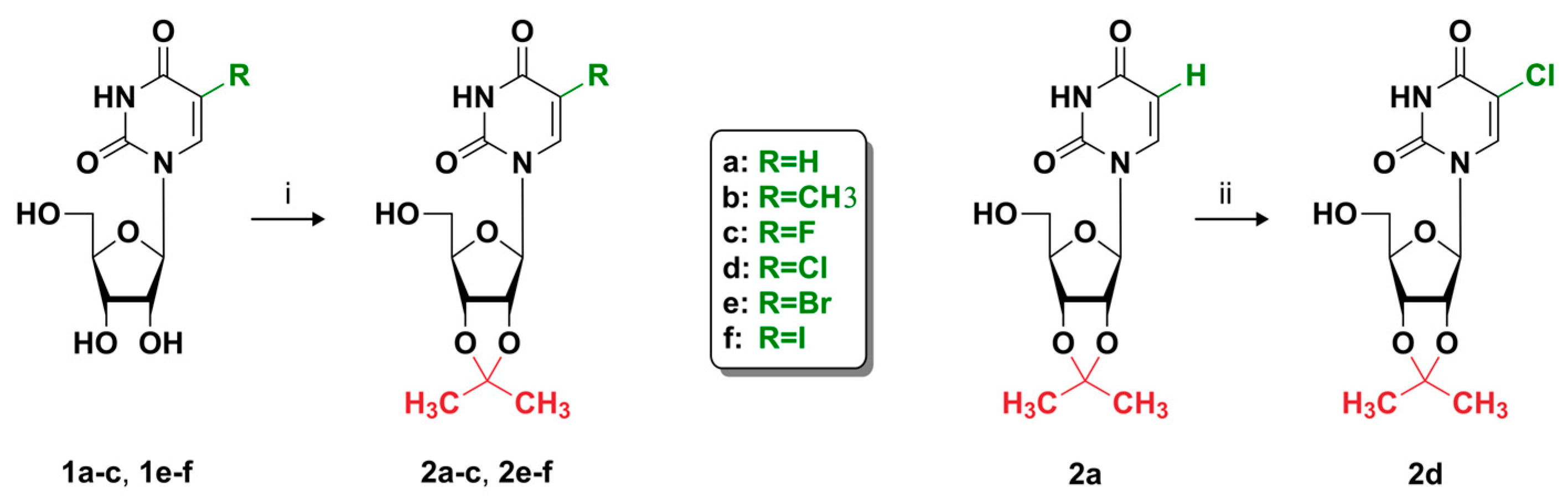
2.1.2. General Procedure for Preparation of 5-Substituted 2′,3′-O-Isopropylideneuridine Derivatives
2.2. Biology
2.2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2.2. Pseudotyped Lentiviral Vector Particles Production
2.2.3. Cell Viability Analysis
2.2.4. Analysis of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle
2.2.5. Antiviral Activity Analysis
2.2.6. Drug Combination Analysis
2.3. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
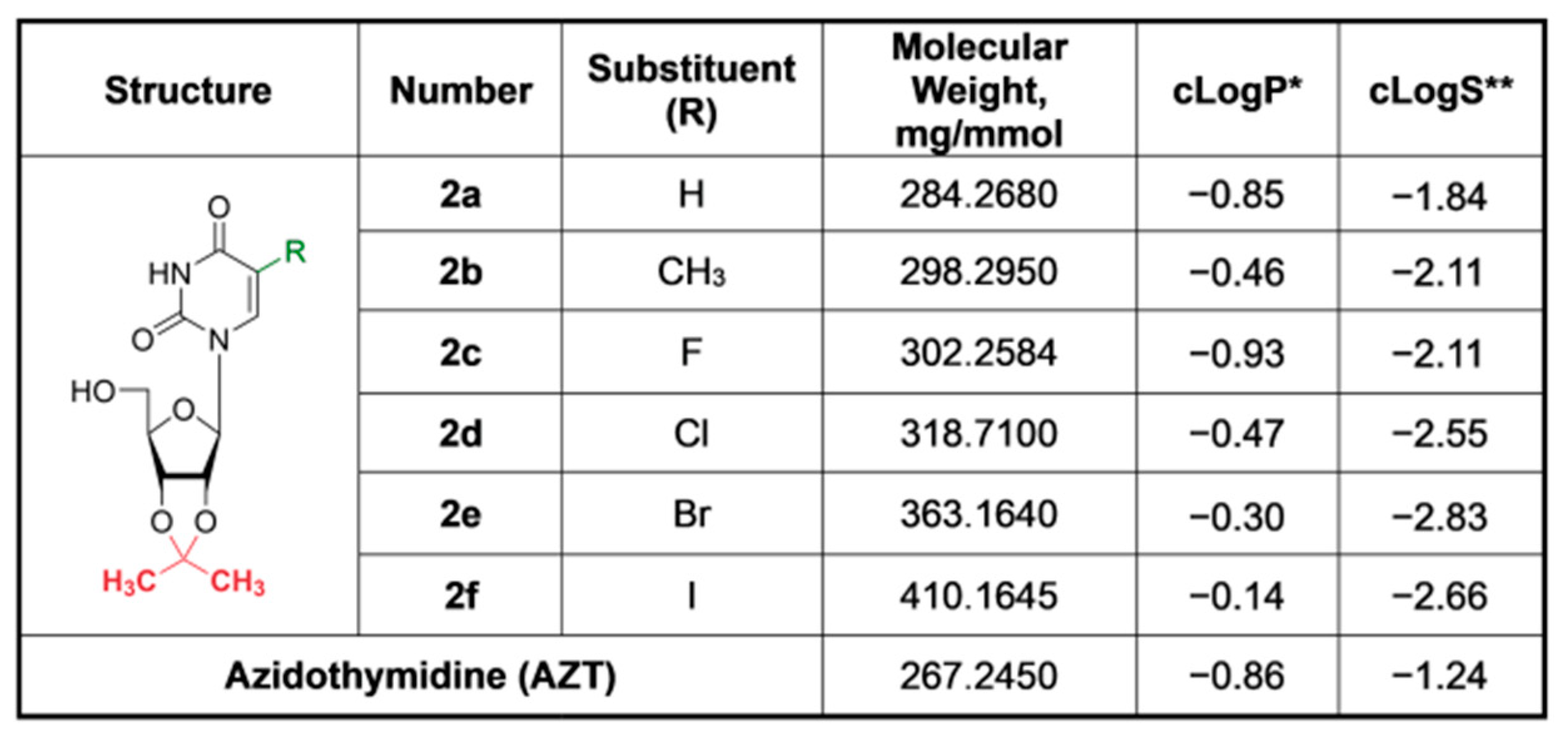
3.1. Synthesis and Characteristics of Compounds
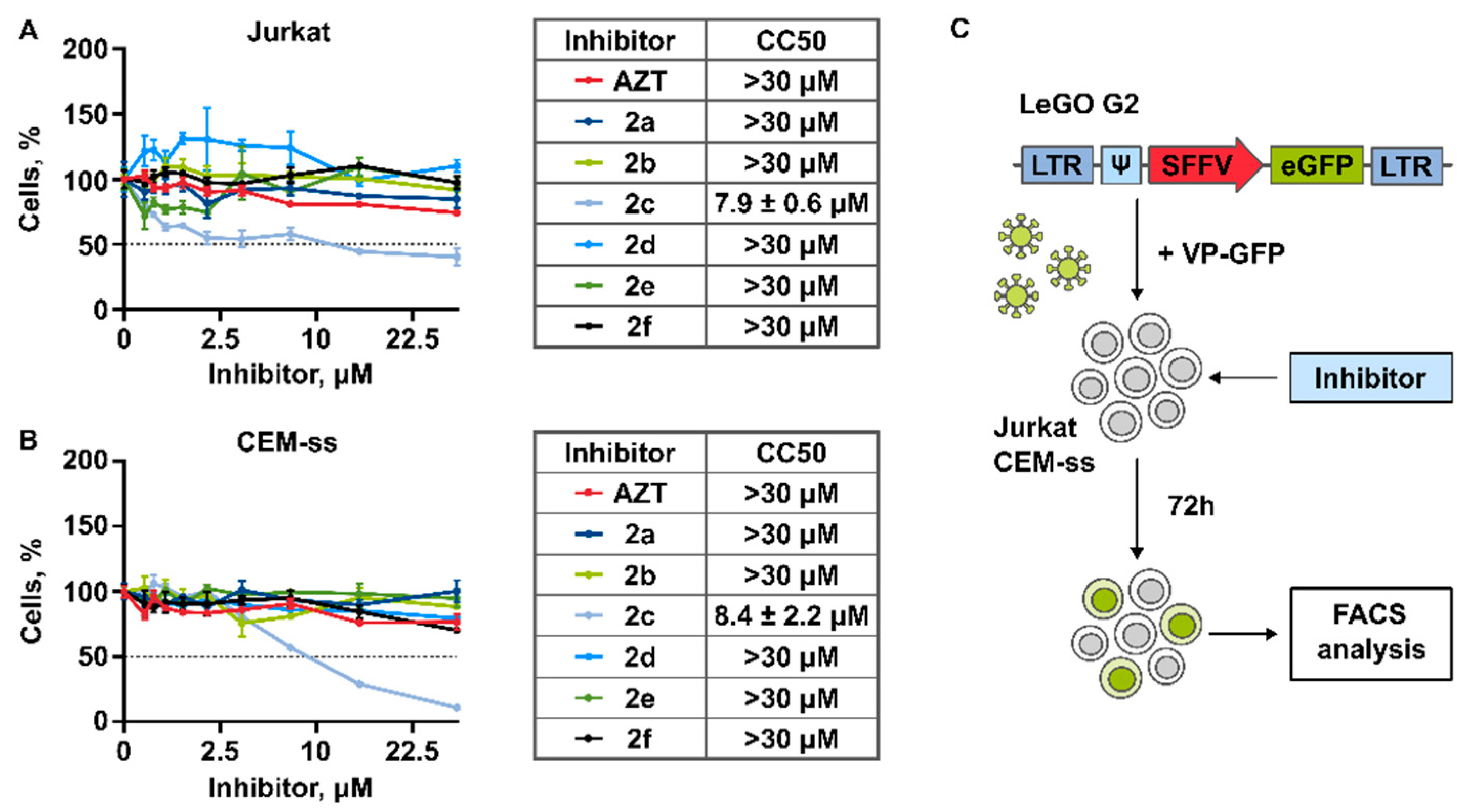
3.2. Cytotoxicity of Compounds
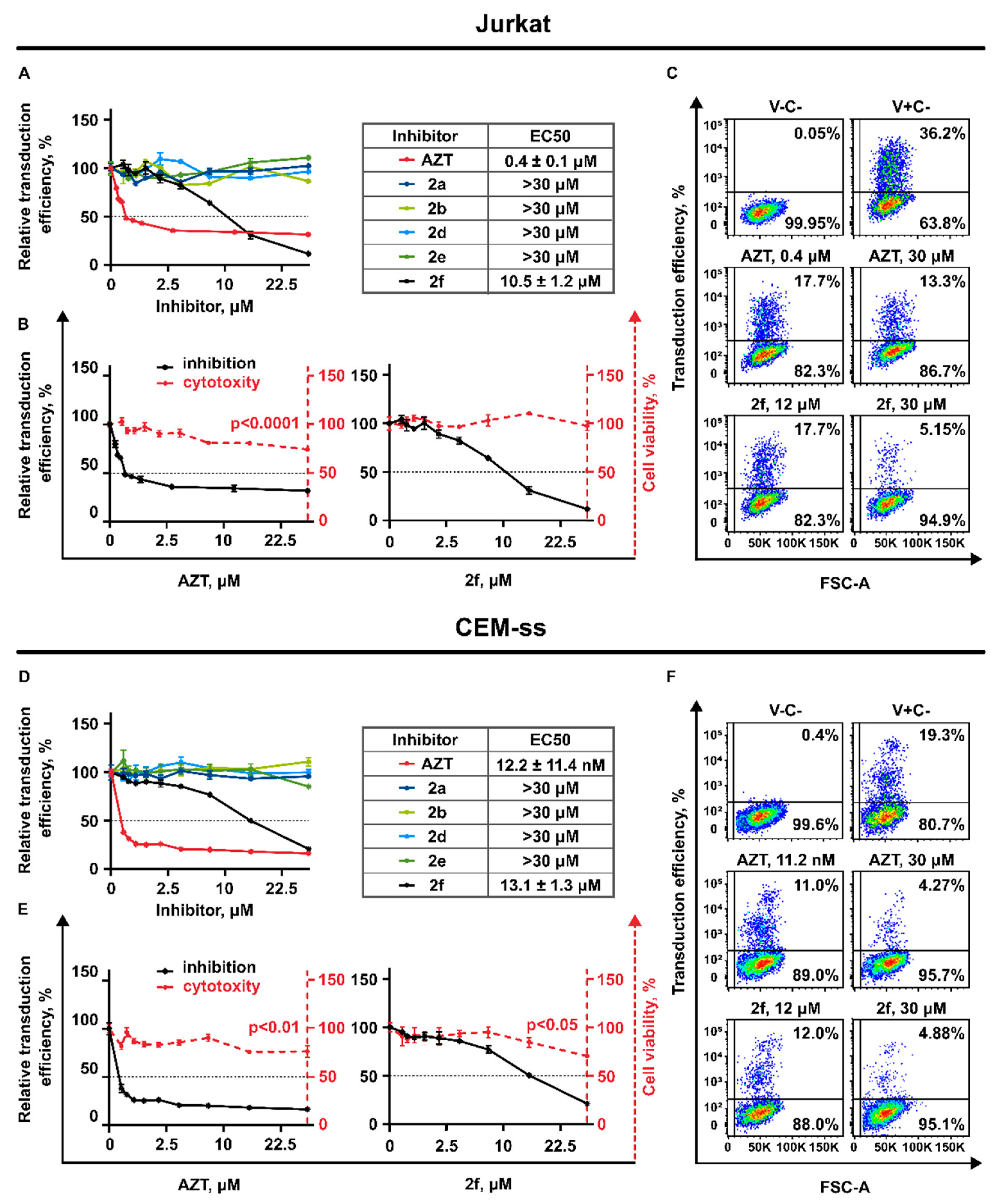
3.3. Antiviral Activity
3.3.1. Generation of Lentiviral Particles Pseudotyped with VSV-G Envelope Protein
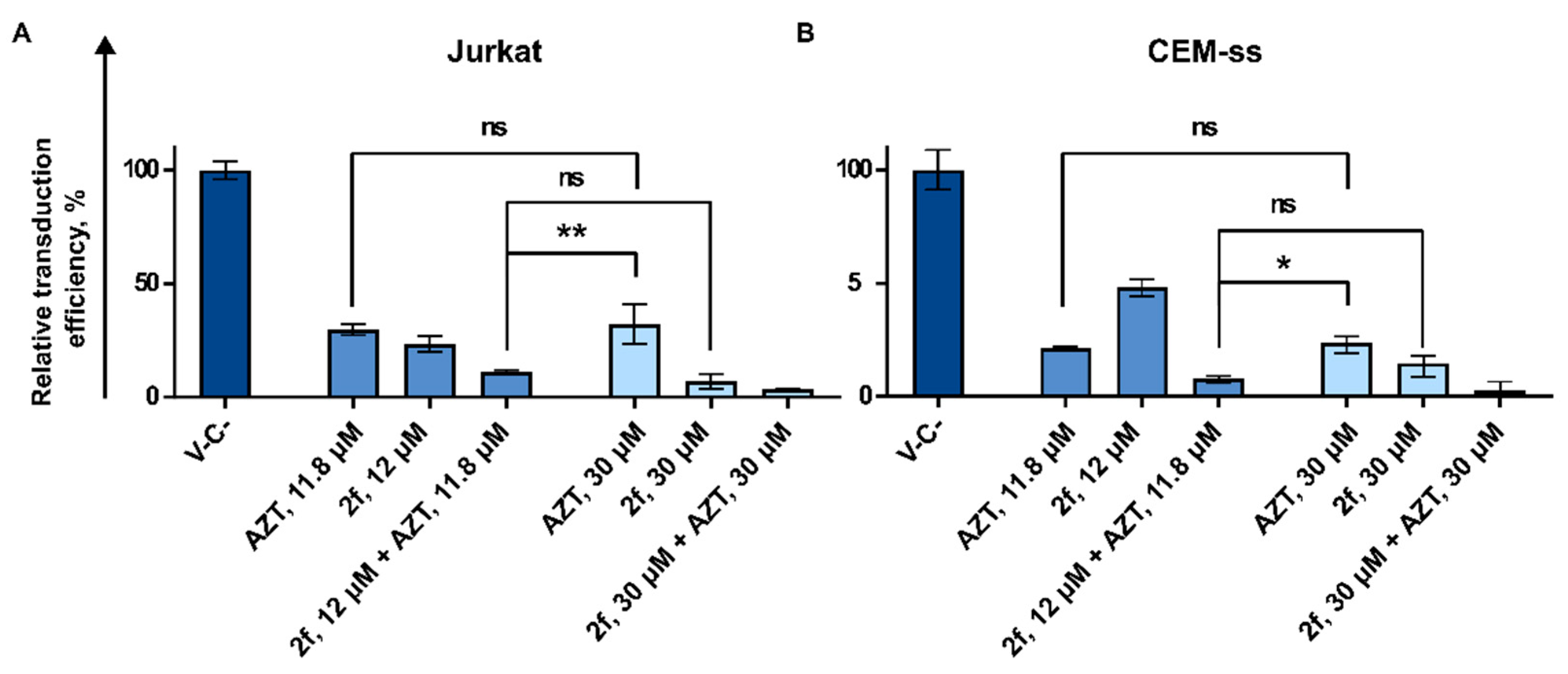
3.3.2. AZT and 2f Do Not Act Synergistically but Cause Pronounced Suppression of Lentiviral Transduction When Used in Combination at the High Non-Toxic Concentrations
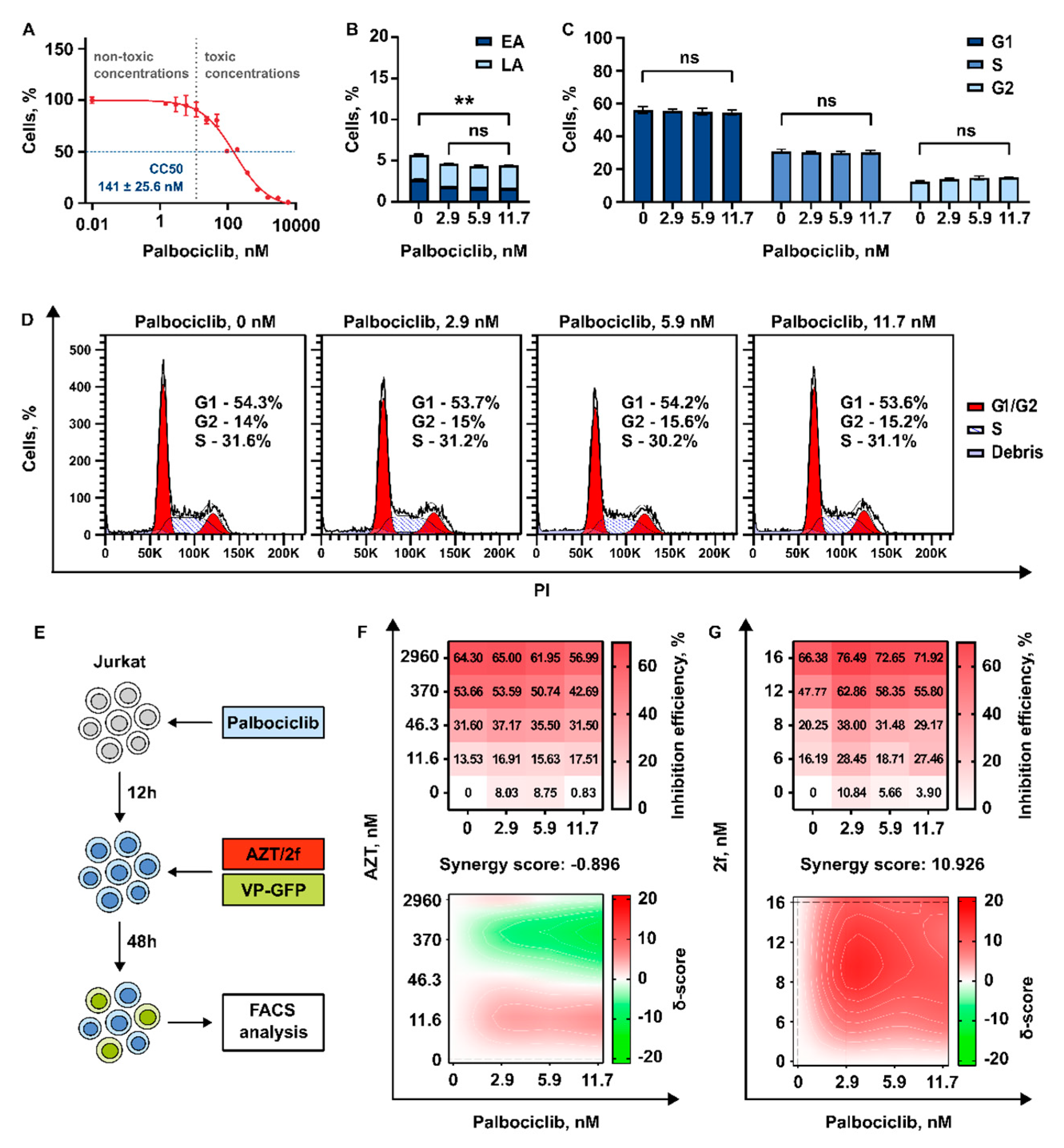
3.3.3. 2′,3′-Isopropylidene-5-Iodouridine in Combination with Palbociclib Acts Synergistically to Reduce Transduction Efficiency of HIV-1 Based Replication Deficient Virus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weichseldorfer, M.; Reitz, M.; Latinovic, O.S. Past Hiv-1 Medications and the Current Status of Combined Antiretroviral Therapy Options for Hiv-1 Patients. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holec, A.D.; Mandal, S.; Prathipati, P.K.; Destache, C.J. Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors: A Thorough Review, Present Status and Future Perspective as HIV Therapeutics. Curr. HIV Res. 2017, 15, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, P.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Liu, X. Anti-HIV Drug Discovery and Development: Current Innovations and Future Trends. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2849–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, E.K.; Adan, A.A.; Mureithi, H.; Muriuki, J.; Lwembe, R.M. A Review of Current Strategies Towards the Elimination of Latent HIV-1 and Subsequent HIV-1 Cure. Curr. HIV Res. 2020, 19, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpa, D.A.; Chomont, N. HIV Persistence in the Setting of Antiretroviral Therapy: When, Where and How Does HIV Hide? J. Virus Erad. 2015, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadol, E.; Lust, K.; Boesecke, C.; Schwarze-Zander, C.; Mohr, R.; Wasmuth, J.C.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Trebicka, J. Exposure to Previous CART Is Associated with Significant Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnani, H.; Agrawal, N.; Khatri, A.; Vialet, J.; Zhang, M.; Cervia, J. Impact of Antiretroviral Therapy on Kidney Disease in HIV Infected Individuals—A Qualitative Systematic Review. J. Int. Assoc. Provid. AIDS Care 2022, 21, e0191118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Gangwani, M.R.; Chaudhari, N.S.; Glazyrin, A.; Bhat, H.K.; Kumar, A. Neurotoxicity in the Post-HAART Era: Caution for the Antiretroviral Therapeutics. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 30, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Su, G.S.; Huang, J.P.; Wu, J.Y.; Su, H.Z.; Huang, W.H.; Ni, Z.Y. yan Incidence and Types of HIV-1 Drug Resistance Mutation among Patients Failing First-Line Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 139, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungkanuparph, S.; Oyomopito, R.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Sirisanthana, T.; Li, P.C.K.; Kantipong, P.; Lee, C.K.C.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Messerschmidt, L.; Law, M.G.; et al. HIV-1 Drug Resistance Mutations among Antiretroviral-Naïve HIV-1-Infected Patients in Asia: Results from the TREAT Asia Studies to Evaluate Resistance-Monitoring Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Frutos-Beltrán, E.; Kang, D.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Menéndez-Arias, L.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P. Medicinal Chemistry Strategies for Discovering Antivirals Effective against Drug-Resistant Viruses. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4514–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirivolu, V.R.; Vernekar, S.K.; Ilina, T.; Myshakina, N.S.; Parnjak, M.A.; Wang, Z. Clicking 3′-azidothymidine into novel potent inhibitors of human immunodificiency virus. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8765–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernekar, S.K.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, J.; Kankanala, J.; Li, H.; Geraghty, R.J.; Wang, Z. 5’-Silylated 3’-1,2,3-triazolyl Thymidine Analogues as Inhibitors of West Nile Virus and Dengue Virus. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4016–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhana, N.; Ormrod, D.; Perry, C.M.; Figgitt, D.P. Zidovudine: A Review of Its Use in the Management of Vertically-Acquired Pediatric HIV Infection. Pediatr. Drugs 2002, 4, 515–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.M.; Nickel, G.; Crawford, M.; Kyeyune, F.; Venner, C.; Nankya, I.; Nabulime, E.; Ndashimye, E.; Poon, A.F.Y.; Salata, R.A.; et al. Sensitive Detection of HIV-1 Resistance to Zidovudine and Impact on Treatment Outcomes in Low- to Middle-Income Countries. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenchenko, A.A.; Drenichev, M.S.; Il’icheva, I.A.; Mikhailov, S.N. Antiviral and Antimicrobial Nucleoside Derivatives: Structural Features and Mechanisms of Action. Mol. Biol. 2021, 55, 786–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, L.M.; Kohn, B.D.; Kohn, P. Preparation of Nucleosides via Isopropylidene Sugar Derivatives. 3. Synthesis of 9-Beta-D-Gulofuranosyladenine and 9-Alpha-L-Lyxofuranosyladenine. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 1780–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.F.; Holman, M.J.; Kramer, M.J.; Trown, P.W. Fluorinated Pyrimidine Nucleosides. 3. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of a Series of 5′-Deoxy-5-Fluoropyrimidine Nucleosides. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Vankar, Y.D. Selective Deprotection of Terminal Isopropylidene Acetals and Trityl Ethers Using HClO4 Supported on Silica Gel. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onobun, E.; Crich, D. Synthesis of 3-Deoxy-d-Manno-Oct-2-Ulosonic Acid (KDO) and Pseudaminic Acid C-Glycosides. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 16035–16042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, M.; Gauthier, C. 3-Deoxy-d-Manno-Oct-2-Ulosonic Acid (Kdo) Derivatives in Antibacterial Drug Discovery. In Carbohydrates in Drug Discovery and Development; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 155–212. ISBN 9780128166758. [Google Scholar]
- Prokofjeva, M.M.; Orlova, N.N.; Gornostaeva, A.S.; Shulgin, A.A.; Nikitenko, N.A.; Senchenko, V.N.; Lebedev, T.D.; Spirin, P.V.; Riecken, K.; Fehse, B.; et al. Universal Modular System for in Vitro Screening of Potential Inhibitors of HIV-1 Replication. Mol. Biol. 2014, 48, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokofjeva, M.M.; Riecken, K.; Spirin, P.V.; Yanvarév, D.V.; Düsedau, A.; Ellinger, B.; Fehse, B.; Stocking, C.; Prassolov, V.S. A New System for Parallel Drug Screening against Multiple-Resistant HIV Mutants Based on Lentiviral Self-Inactivating (SIN) Vectors and Multi-Colour Analyses. AIDS Res. Ther. 2013, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanov, O.A.; Prokof’eva, M.M.; Stocking, K.; Varlamov, V.P.; Levov, A.N.; Vikhoreva, G.A.; Spirin, P.V.; Mikhailov, S.N.; Prassolov, V.S. Replication-Competent Gamma-Retrovirus Mo-MuLV Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein as Efficient Tool for Screening of Inhibitors of Retroviruses That Use Heparan Sulfate as Primary Cell Receptor. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.; Anastyuk, S.; Kravchenko, A.; Helbert, W.; Glazunov, V.; Shulgin, A.; Spirin, P.; Prassolov, V. New Insights into the Structure of Kappa/Beta-Carrageenan: A Novel Potential Inhibitor of Hiv-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, P.; Yu, B.; Ouyang, L. Drug Repurposing: An Effective Strategy to Accelerate Contemporary Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, J.; Mohan, M.; Byrareddy, S.N. Drug Repurposing Approaches to Combating Viral Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, T. Strategy, Progress, and Challenges of Drug Repurposing for Efficient Antiviral Discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 660710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, A.P.; Cummins, N.W.; Badley, A.D. The Role of the BCL-2 Family of Proteins in HIV-1 Pathogenesis and Persistence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Q.; Zhao, M.; Kong, W.-H.; Tang, L.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Wang, X.; Qiu, H.-Y.; Zhou, D.-J.; Wang, X.; et al. Combination Antiretroviral Therapy (CART) Restores HIV-1 Infection-Mediated Impairment of JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22524–22533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, M.D.; Song, C.; Hancock, S.C.; Pereira Ribeiro, S.; Kulpa, D.A.; Gavegnano, C. Repurposing BCL-2 and Jak 1/2 Inhibitors: Cure and Treatment of HIV-1 and Other Viral Infections. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1033672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, A.; Le, N.; Gartenhaus, R.B.; Sausville, E.; Medina-Moreno, S.; Zapata, J.C.; Davis, C.; Gallo, R.C.; Redfield, R.R. Targeting of MTOR Catalytic Site Inhibits Multiple Steps of the HIV-1 Lifecycle and Suppresses HIV-1 Viremia in Humanized Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9412–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbay, B.; Shmakova, A.; Vassetzky, Y.; Dokudovskaya, S. Modulation of MTORC1 Signaling Pathway by HIV-1. Cells 2020, 9, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, P.; Bradel-Tretheway, B.; Monteiro-Filho, C.M.R.; Planelles, V.; Maggirwar, S.B.; Dewhurst, S.; Kim, B. Akt Inhibitors as an HIV-1 Infected Macrophage-Specific Anti-Viral Therapy. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, G.R.; Bruckman, R.S.; Herns, S.D.; Joshi, S.; Durden, D.L.; Spector, S.A. Induction of Autophagy by PI3K/MTOR and PI3K/MTOR/BRD4 Inhibitors Suppresses HIV-1 Replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 5808–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, E.; Badia, R.; Torres-Torronteras, J.; Ruiz, A.; Permanyer, M.; Riveira-Muñoz, E.; Clotet, B.; Marti, R.; Ballana, E.; Esté, J.A. Palbociclib, a Selective Inhibitor of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase4/6, Blocks HIV-1 Reverse Transcription through the Control of Sterile α Motif and HD Domain-Containing Protein-1 (SAMHD1) Activity. AIDS 2014, 28, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.Y.; Cara, A.; Gallo, R.C.; Lori, F. Low Levels of Deoxynucleotides in Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes: A Strategy to Inhibit Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8925–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Gelais, C.; de Silva, S.; Amie, S.M.; Coleman, C.M.; Hoy, H.; Hollenbaugh, J.A.; Kim, B.; Wu, L. SAMHD1 Restricts HIV-1 Infection in Dendritic Cells (DCs) by DNTP Depletion, but Its Expression in DCs and Primary CD4+ T-Lymphocytes Cannot Be Upregulated by Interferons. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokofjeva, M.M.; Imbs, T.I.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Spirin, P.V.; Horn, S.; Fehse, B.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Prassolov, V.S. Fucoidans as Potential Inhibitors of HIV-1. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3000–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirin, P.; Shyrokova, E.; Vedernikova, V.; Lebedev, T.; Prassolov, V. Emetine in Combination with Chloroquine Induces Oncolytic Potential of HIV-1-Based Lentiviral Particles. Cells 2022, 11, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levene, P.A.; Tipson, R.S. The Partial Synthesis of Ribose Nucleotides: I. Uridine 5-Phosphoric Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1934, 106, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.E.; Todd, S.A.; Rich, A. A Synthesis Of Ribothymidine-5′-Pyrophosphate And Its Conversion To Polyribothymidylic Acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1958, 44, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.A.; Matsuda, A.; Halat, M.J.; Hollenberg, D.H.; Nisselbaum, J.S.; Fox, J.J. Nucleosides. 114. 5′-0-Glucuronides of 5-Fluorouridine and 5-Fluorocytidine. Masked Precursors of Anticancer Nucleosides. J. Med. Chem. 1981, 24, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, T. Studies on Coenzyme Analogs. III. Syntheses of 5-Substituted Uridine 5′-Phosphates. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1960, 8, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, B.A.; Falco, E.A.; Fox, J.J. Nucleosides. LVIII. Transformations of Pyrimidine Nucleosides in Alkaline Media. 3. Conversion of 5-Halouridines into Imidazoline and Barbituric Acid Nucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 1969, 34, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenner, G.W.; Todd, A.R.; Weymouth, F.J. Nucleotides. Part XVII. * N-Chloroamides as Reagents for the Chlorination of Diesters of Phosphorous Acid. A New Synthesis of Uridine-5′ Pyrophosphate. J. Chem. Soc. 1952, 705, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Gao, N.; Meng, L.; Gai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Yu, B.; et al. A Novel HIV-1 Inhibitor That Blocks Viral Replication and Rescues APOBEC3s by Interrupting Vif/CBFβ Interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14592–14605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hain, A.; Krämer, M.; Linka, R.M.; Nakhaei-Rad, S.; Ahmadian, M.R.; Häussinger, D.; Borkhardt, A.; Münk, C. IL-2 Inducible Kinase ITK Is Critical for HIV-1 Infection of Jurkat T-Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crater, J.M.; Nixon, D.F.; Furler O’Brien, R.L. HIV-1 Replication and Latency Are Balanced by MTOR-Driven Cell Metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1068436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Thomaschewski, M.; Warlich, M.; Volz, T.; Cornils, K.; Niebuhr, B.; Täger, M.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Pollok, J.-M.; Stocking, C.; et al. RGB Marking Facilitates Multicolor Clonal Cell Tracking. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Mock, U.; Petrowitz, B.; Bartsch, U.; Fehse, B. Lentiviral Gene Ontology (LeGO) Vectors Equipped with Novel Drug-Selectable Fluorescent Proteins: New Building Blocks for Cell Marking and Multi-Gene Analysis. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Bartsch, U.; Stocking, C.; Fehse, B. A Multicolor Panel of Novel Lentiviral “Gene Ontology” (LeGO) Vectors for Functional Gene Analysis. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, K.; Thomaschewski, M.; Benten, D.; Fehse, B. RGB Marking with Lentiviral Vectors for Multicolor Clonal Cell Tracking. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braal, C.L.; Jongbloed, E.M.; Wilting, S.M.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Jager, A. Inhibiting CDK4/6 in Breast Cancer with Palbociclib, Ribociclib, and Abemaciclib: Similarities and Differences. Drugs 2021, 81, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oslovsky, V.E.; Drenichev, M.S.; Sun, L.; Kurochkin, N.N.; Kunetsky, V.E.; Mirabelli, C.; Neyts, J.; Leyssen, P.; Mikhailov, S.N. Fluorination of Naturally Occurring N6-Benzyladenosine Remarkably Increased Its Antiviral Activity and Selectivity. Molecules 2017, 22, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sánchez-Roselló, M.; Aceña, J.L.; del Pozo, C.; Sorochinsky, A.E.; Fustero, S.; Soloshonok, V.A.; Liu, H. Fluorine in Pharmaceutical Industry: Fluorine-Containing Drugs Introduced to the Market in the Last Decade (2001–2011). Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 2432–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.; Faeh, C.; Diederich, F. Fluorine in Pharmaceuticals: Looking beyond Intuition. Science 2007, 317, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-H. ABC Transporters as Multidrug Resistance Mechanisms and the Development of Chemosensitizers for Their Reversal. Cancer Cell Int. 2005, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellví, M.; Felip, E.; Ezeonwumelu, I.J.; Badia, R.; Garcia-Vidal, E.; Pujantell, M.; Gutiérrez-Chamorro, L.; Teruel, I.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Clotet, B.; et al. Pharmacological Modulation of SAMHD1 Activity by CDK4/6 Inhibitors Improves Anticancer Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glumakova, K.; Ivanov, G.; Vedernikova, V.; Shyrokova, L.; Lebedev, T.; Stomakhin, A.; Zenchenko, A.; Oslovsky, V.; Drenichev, M.; Prassolov, V.; et al. Nucleoside Analog 2′,3′-Isopropylidene-5-Iodouridine as Novel Efficient Inhibitor of HIV-1. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102389
Glumakova K, Ivanov G, Vedernikova V, Shyrokova L, Lebedev T, Stomakhin A, Zenchenko A, Oslovsky V, Drenichev M, Prassolov V, et al. Nucleoside Analog 2′,3′-Isopropylidene-5-Iodouridine as Novel Efficient Inhibitor of HIV-1. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(10):2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102389
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlumakova, Ksenia, Georgy Ivanov, Valeria Vedernikova, Lena Shyrokova, Timofey Lebedev, Andrei Stomakhin, Anastasia Zenchenko, Vladimir Oslovsky, Mikhail Drenichev, Vladimir Prassolov, and et al. 2023. "Nucleoside Analog 2′,3′-Isopropylidene-5-Iodouridine as Novel Efficient Inhibitor of HIV-1" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 10: 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102389
APA StyleGlumakova, K., Ivanov, G., Vedernikova, V., Shyrokova, L., Lebedev, T., Stomakhin, A., Zenchenko, A., Oslovsky, V., Drenichev, M., Prassolov, V., & Spirin, P. (2023). Nucleoside Analog 2′,3′-Isopropylidene-5-Iodouridine as Novel Efficient Inhibitor of HIV-1. Pharmaceutics, 15(10), 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102389





