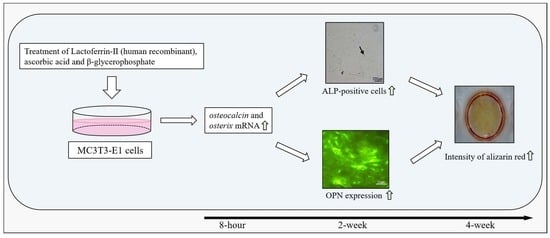
Human Recombinant Lactoferrin Promotes Differentiation and Calcification on MC3T3-E1 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
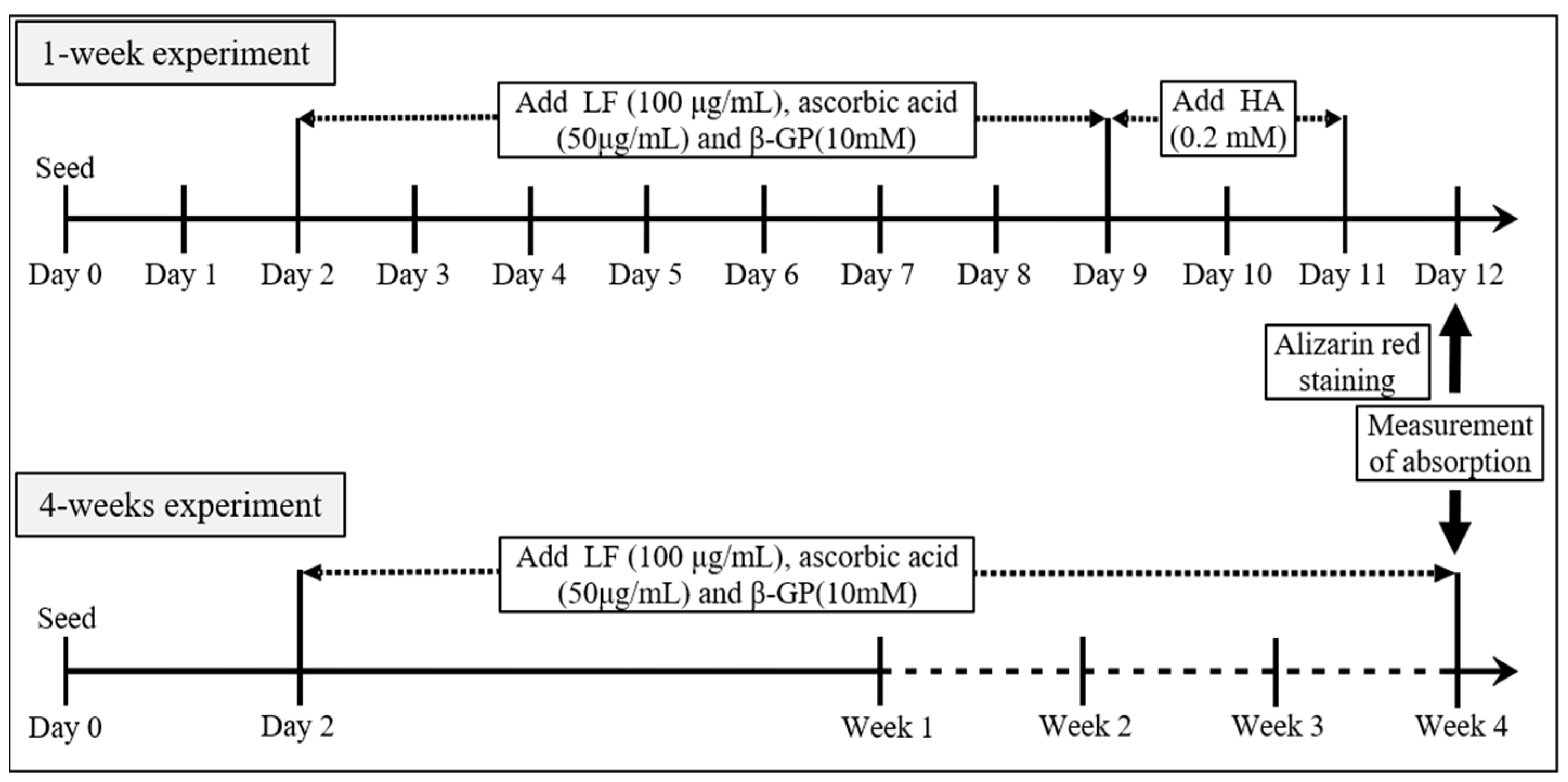
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Materials
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Calcification Assay
2.4. ALP Activity Assay
2.5. Immunocytochemical Staining
2.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of LF on Osteoblast Proliferation in Two Types of Media
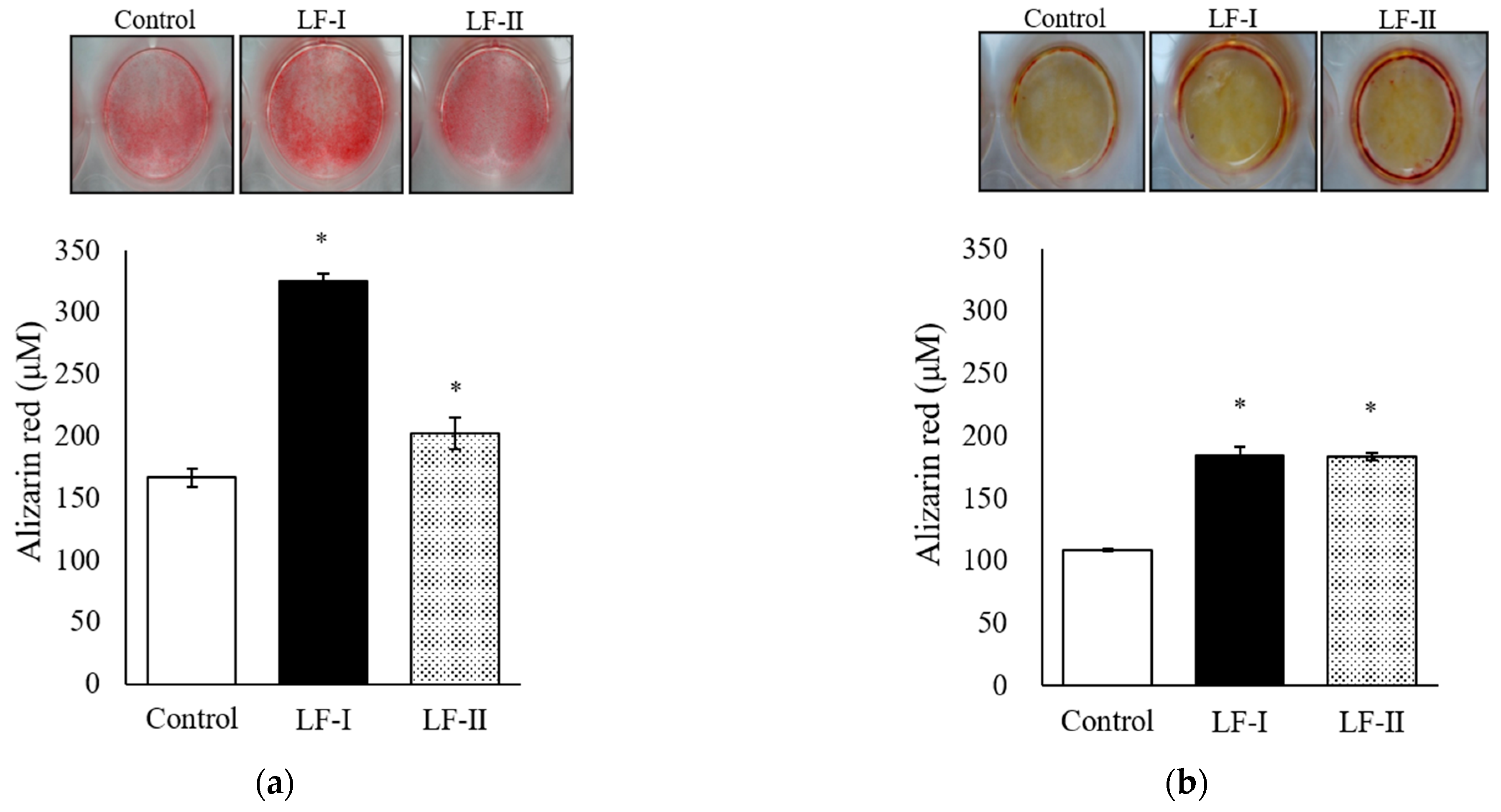
3.2. Evaluation of Calcification Using Alizarin Red Staining
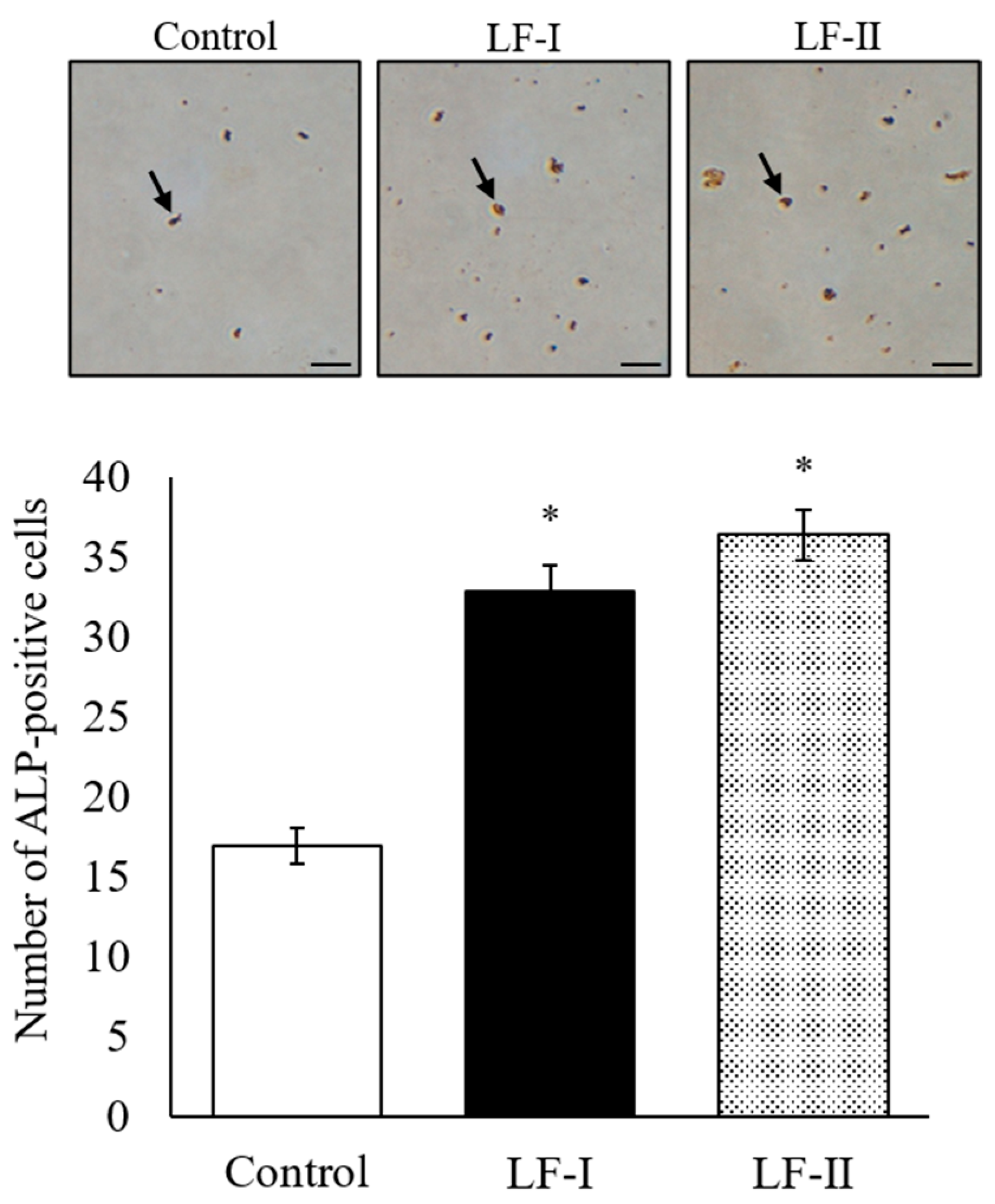
3.3. Number of ALP-Positive Cells
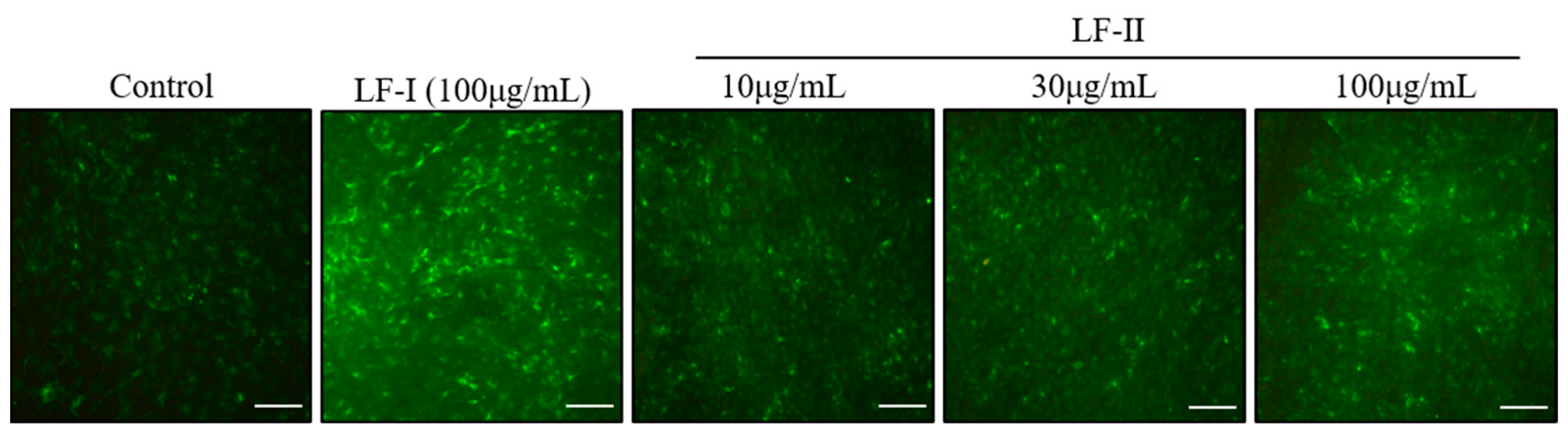
3.4. Immunocytochemical Staining of OPN Expression
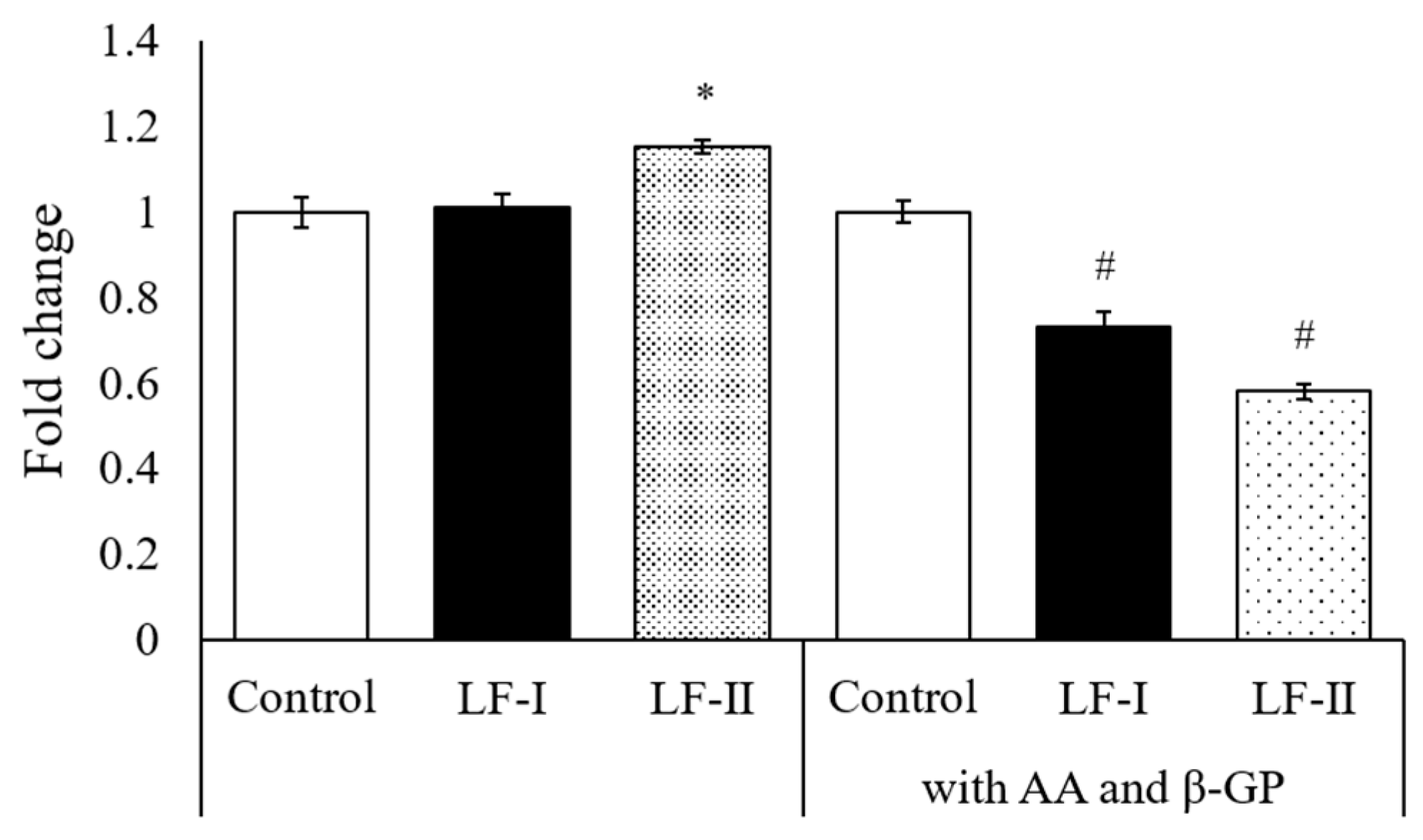
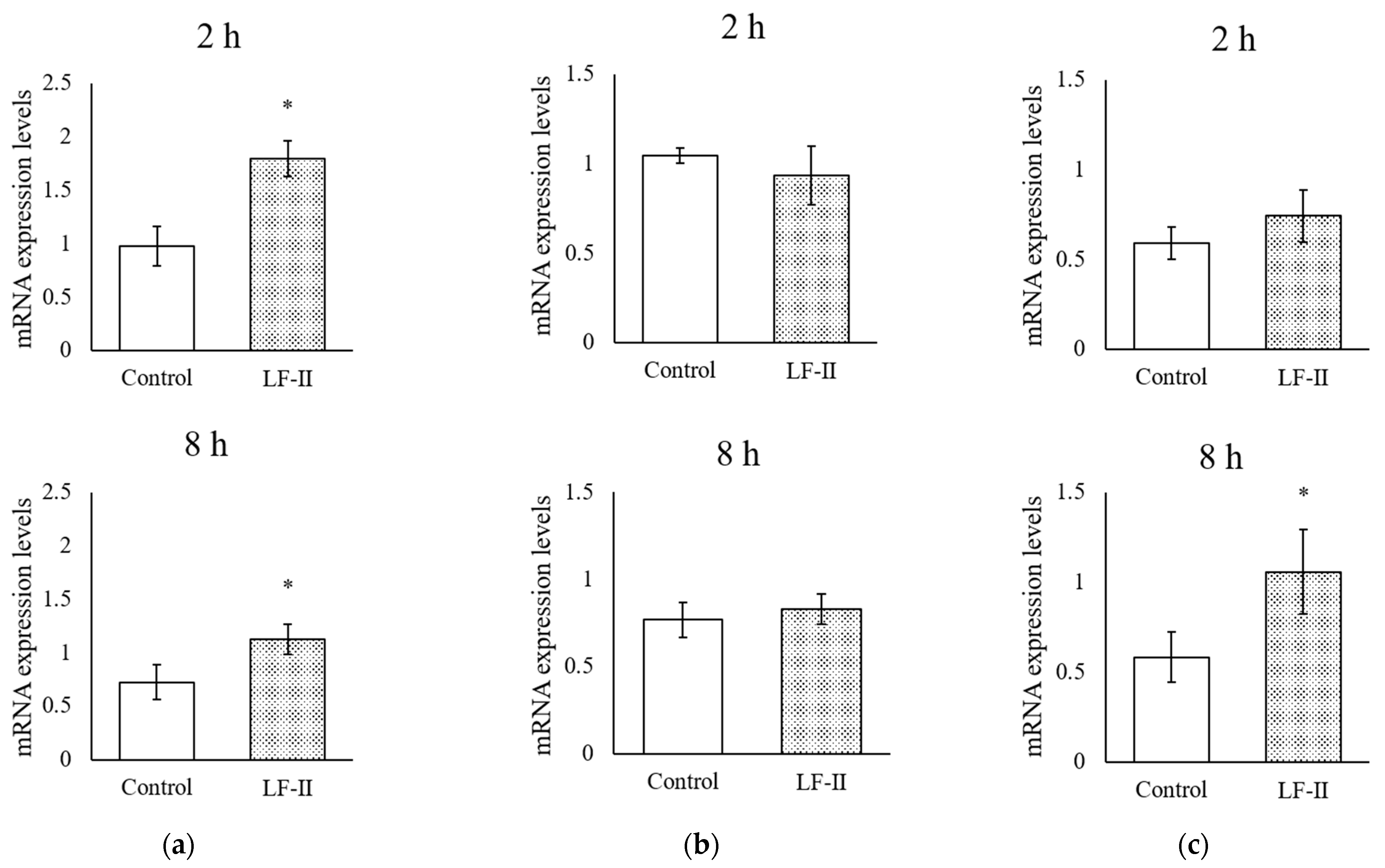
3.5. Osteocalcin, Runx2, and Osterix Expression with RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masson, P.L.; Heremans, J.F.; Schonne, E. Lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein in neutrophilic leukocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1969, 130, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhu, N.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, J. Lactoferrin protects against iron dysregulation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice. J. Neurochem. 2020, 152, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, D.C.; Nicolau, A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. The effect of bovine milk lactoferrin on human breast cancer cell lines. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.L.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qin, L.Q. Effects of lactoferrin on X-ray-induced intestinal injury in Balb/C mice. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 146, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, H.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yamauchi, K.; Abe, F. Lactoferrin and bifidobacteria. Biometals 2014, 27, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.; Cutone, A.; Lepanto, M.S.; Paesano, R.; Valenti, P. Lactoferrin: A Natural Glycoprotein Involved in Iron and Inflammatory Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toho, M.; Nagashima, D.; Komatsuzaki, H.; Furukawa, M.; Yamazoe, M.; Ohno, M.; Nitto, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Izumo, N. Lactoferrin-mediated Changes in Melanin and Moisture Levels in UV-A Exposed Mice. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2022, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumo, N.; Yukiko, I.; Kagaya, N.; Furukawa, M.; Iwasaki, R.; Sumino, A.; Hayamizu, K.; Nakano, M.; Hoshino, T.; Kurono, H.; et al. Lactoferrin Suppresses Decreased Locomotor Activities by Improving Dopamine and Serotonin Release in the Amygdala of Ovariectomized Rats. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.C.; Di Ceglie, I.; Arntz, O.J.; van den Berg, W.B.; van den Hoogen, F.H.; Ferreira, A.V.; van Lent, P.L.; van de Loo, F.A. Milk-Derived Nanoparticle Fraction Promotes the Formation of Small Osteoclasts But Reduces Bone Resorption. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Iemitsu, M.; Maeda, S.; Kitajima, A.; Nosaka, T.; Omi, N. Voluntary running exercise attenuates the progression of endothelial dysfunction and arterial calcification in ovariectomized rats. Acta Physiol. 2008, 193, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Guo, H. Lactoferrin Is a Potential Activator of the Vitamin D Receptor in Its Regulation of Osteogenic Activities in C57BL/6J Mice and MC3T3-E1 Cells. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Fan, F.; Chen, H.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Lu, W.; Du, M. A bovine lactoferrin-derived peptide induced osteogenesis via regulation of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3950–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, H.; Jing, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Ren, F. Lactoferrin stimulates osteoblast differentiation through PKA and p38 pathways independent of lactoferrin’s receptor LRP1. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, T.L.; Sondergaard, T.E.; Skorzynska, K.E.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Plesner, T.L.; Hauge, E.M.; Plesner, T.; Delaisse, J.M. A physical mechanism for coupling bone resorption and formation in adult human bone. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Gan, B.; Ding, Q.; Ren, F. Effect of glucose on the lactoferrin’s conformation and its effect on MC 3T3-E1 cell proliferation. Protein J. 2012, 31, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaeys, I.; Rusu, D.; Picard, S.; Pouliot, M.; Borgeat, P.; Poubelle, P.E. Osteoblast retraction induced by adherent neutrophils promotes osteoclast bone resorption: Implication for altered bone remodeling in chronic gout. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumo, N.; Kagaya, S.; Toho, M.; Furukawa, M.; Kabaya, Y.; Hirai, T.; Hayamizu, K.; Nakano, M.; Hoshino, T.; Watanabe, Y. Effects of lactoferrin on dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in mice. Glob. Drugs Ther. 2018, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Naot, D.; Grey, A.; Reid, I.R.; Cornish, J. Lactoferrin--a novel bone growth factor. Clin. Med. Res. 2005, 3, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, G.; Shapiro, I.M.; Golub, E.E. The phosphatidylinositol-glycolipid anchor on alkaline phosphatase facilitates mineralization initiation in vitro. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1995, 10, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, W.N.; Azari, F.; Sørensen, E.S.; Kaartinen, M.T.; McKee, M.D. Pyrophosphate inhibits mineralization of osteoblast cultures by binding to mineral, up-regulating osteopontin, and inhibiting alkaline phosphatase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15872–15883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liao, X.; Qin, X.; Shi, W.; Zhou, B. A novel chimeric peptide binds MC3T3-E1 cells to titanium and enhances their proliferation and differentiation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, T. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by Runx2. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 658, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cho, K.; Huang, Y.; Lyons, J.P.; Zhou, X.; Sinha, K.; McCrea, P.D.; de Crombrugghe, B. Inhibition of Wnt signaling by the osteoblast-specific transcription factor Osterix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6936–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Doll, B.; McNelis, T.; Hollinger, J.O. Osteoblast differentiation in vitro and in vivo promoted by Osterix. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 83, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Abbreviation | Source | Purity |
|---|---|---|
| LF-I | Bovine | >95% |
| LF-II | Human recombinant | >95% |
| Mouse | Universal Probe Library | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteocalcin | #32 | 5′-AGACTCCGGCGCTACCTT-3′ | 5′-CTCGTCACAAGCAGGGTTAAG-3′ |
| Runx2 | #34 | 5′-GCCCAGGCGTATTTCAGA-3′ | 5′-TGCCTGGCTCTTCTTACTGAG-3’ |
| Osterix | #106 | 5′-CTCCTGCAGGCAGTCCTC-3′ | 5′-GGGAAGGGTGGGTAGTCATT-3′ |
| β-actin | #64 | 5′-CTAAGGCCAACCGTGAAAAG-3′ | 5′-ACCAGAGGCATACAGGGACA-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagashima, D.; Ishibashi, Y.; Kawaguchi, S.; Furukawa, M.; Toho, M.; Ohno, M.; Nitto, T.; Izumo, N. Human Recombinant Lactoferrin Promotes Differentiation and Calcification on MC3T3-E1 Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010060
Nagashima D, Ishibashi Y, Kawaguchi S, Furukawa M, Toho M, Ohno M, Nitto T, Izumo N. Human Recombinant Lactoferrin Promotes Differentiation and Calcification on MC3T3-E1 Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagashima, Daichi, Yukiko Ishibashi, Sachiko Kawaguchi, Megumi Furukawa, Masahiro Toho, Megumi Ohno, Takeaki Nitto, and Nobuo Izumo. 2023. "Human Recombinant Lactoferrin Promotes Differentiation and Calcification on MC3T3-E1 Cells" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010060
APA StyleNagashima, D., Ishibashi, Y., Kawaguchi, S., Furukawa, M., Toho, M., Ohno, M., Nitto, T., & Izumo, N. (2023). Human Recombinant Lactoferrin Promotes Differentiation and Calcification on MC3T3-E1 Cells. Pharmaceutics, 15(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010060