Frontiers in Preparations and Promising Applications of Mesoporous Polydopamine for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Polymerization Mechanisms of PDA
3. Mesoporous Polydopamine Preparation
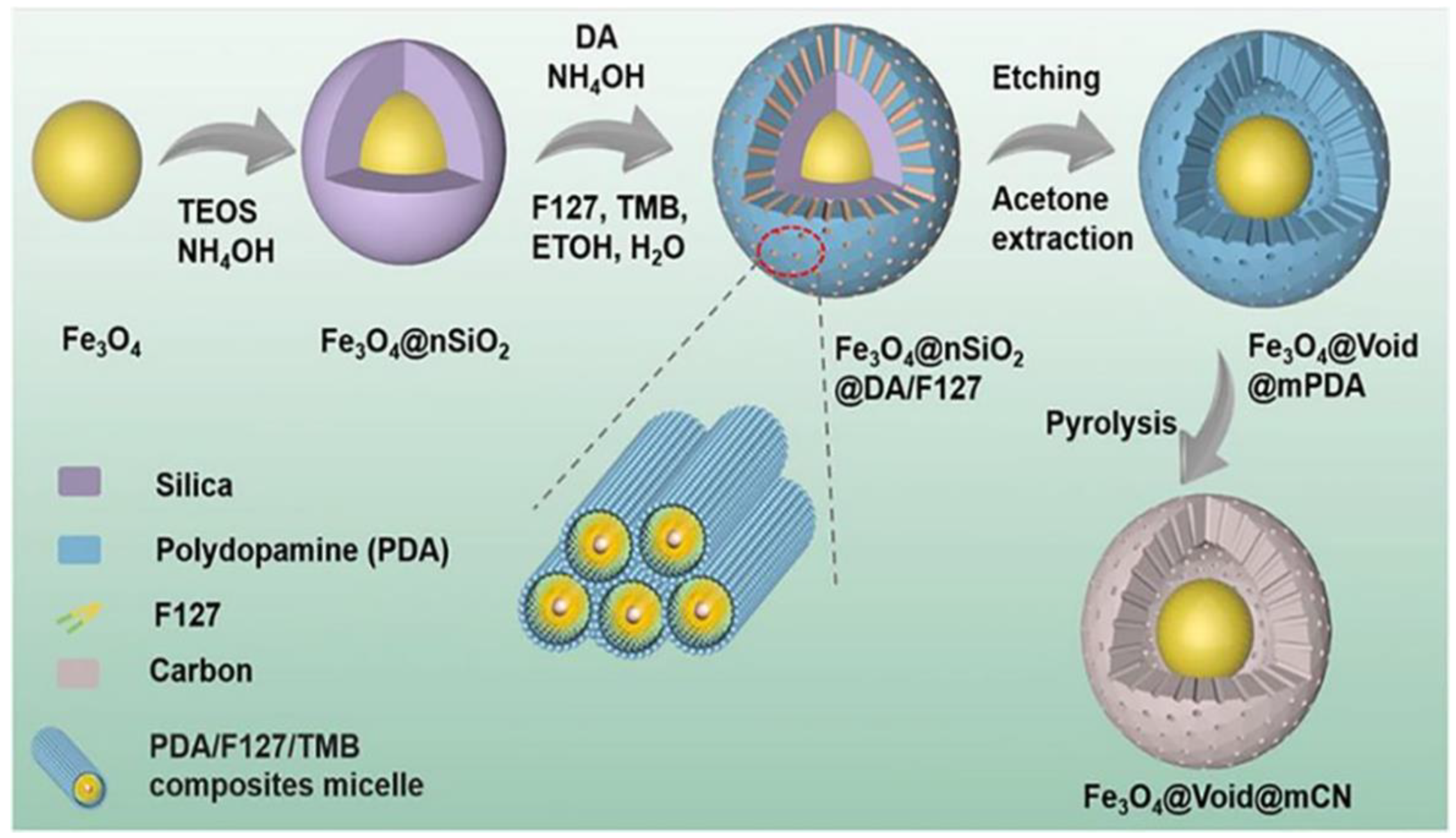
3.1. Hard Templating
3.2. Soft Templating
3.3. Preparation Conditions and Differences in Products
The Proportion of Pluronic F127 and TMB, and Usage of DA
4. Properties of MPDA
5. Application of MPDA in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy
5.1. Bioimaging
5.1.1. MRI
5.1.2. FLI
5.1.3. PAI
5.1.4. CT Imaging
5.2. Cancer Therapy
5.2.1. Photothermal Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
5.2.2. Photothermal Therapy Combined with Photodynamic Therapy
5.2.3. Photothermal Therapy Combined with Immunotherapy
5.2.4. Photothermal Therapy Combined with Chemotherapy
5.2.5. Chemotherapy Combined with Immunotherapy
5.2.6. Multi-Method Synergistic Treatment
6. Conclusions and Perspective
6.1. Significance of MPDA
6.2. Challenges
6.3. Perspective
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, K.; Jiao, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Han, S. All-In-One Biomimetic Nanoplatform Based on Hollow Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Synergistically Enhanced Radiotherapy of Colon Cancer. Small 2022, 18, e2107656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Lian, D.Z.; Ma, H.L.; Gao, N.S.; Zhao, L.M.; Luan, P.; Zeng, X.W. New advances in gated materials of mesoporous silica for drug controlled release. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3696–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Gu, X.; Wu, R.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, C.; Ling, J.; Liu, M.; et al. Silk-Inspired In Situ Hydrogel with Anti-Tumor Immunity Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy for Melanoma and Infected Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Shan, X.; Wang, X.; Ou, M.; Liu, Q.; Gao, N.; Chen, H.; Mei, L.; et al. Charge-reversal biodegradable MSNs for tumor synergetic chemo/photothermal and visualized therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.J.; Liu, H.X.; Xue, Y.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Fu, Y.; Xia, Z.H.; Pan, D.M.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, K.; Zhang, Z.Z.; et al. Reversing cold tumors to hot: An immunoadjuvant-functionalized metal-organic framework for multimodal imaging-guided synergistic photoimmunotherapy. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shan, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, N.; Zeng, W.; Zeng, X.; Mei, L. Applications of Surface Modification Technologies in Nanomedicine for Deep Tumor Penetration. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhang, D.; Peng, J.; Cheng, W.; Mei, L.; Chen, H.; et al. Charge-reversal nanomedicines as a smart bullet for deep tumor penetration. Smart Mater. Med. 2022, 3, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, M.; Ma, L. Current understandings and clinical translation of nanomedicines for breast cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 180, 114034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lin, C.; He, Y.; Tao, B.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Cai, K. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Nitric-Oxide-Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy and Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy for Biofilm Elimination. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3546–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zeng, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, W.; Mei, L.; Zhao, Y. Versatile Polydopamine Platforms: Synthesis and Promising Applications for Surface Modification and Advanced Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8537–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Na, Y.S.; Choi, S.; Song, I.T.; Kim, W.Y.; Lee, H. Non-Covalent Self-Assembly and Covalent Polymerization Co-Contribute to Polydopamine Formation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wang, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H. Progressive fuzzy cation-π assembly of biological catecholamines. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Tao, W.; Ouyang, X.-K.; Mei, L.; Zeng, X. Polyphenol-based hydrogels: Pyramid evolution from crosslinked structures to biomedical applications and the reverse design. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 17, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.J.; Han, Z.H.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.Y.; Peng, L.C.; Zhao, Y.B.; Sun, L. Construction of Double-Shelled Hollow Ag2S@Polydopamine Nanocomposites for Fluorescence-Guided, Dual Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery and Photothermal Therapy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Song, Y.H. Mesoporous carbons: Recent advances in synthesis and typical applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83239–83285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, M.; Toyoda, M.; Soneda, Y.; Tsujimura, S.; Morishita, T. Templated mesoporous carbons: Synthesis and applications. Carbon 2016, 107, 448–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, D.; Ma, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kang, Y.; Yue, Q. Multifunctional Yolk–Shell Structured Magnetic Mesoporous Polydopamine/Carbon Microspheres for Photothermal Therapy and Heterogenous Catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 23888–23895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Hung, C.T.; Wang, S.W.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhao, Z.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, D.Y. Versatile Nanoemulsion Assembly Approach to Synthesize Functional Mesoporous Carbon Nanospheres with Tunable Pore Sizes and Architectures. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 141, 7073–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Cai, K. Nanoscale Polydopamine (PDA) Meets π–π Interactions: An Interface-Directed Coassembly Approach for Mesoporous Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 12119–12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.P.; Gan, Y.; Zhu, P.D.; Li, S.S.; Lin, C.; Yu, S.L.; Zhao, S.; Shi, J.H.; Li, R.M.; Yuan, J.F. Hollow mesoporous polydopamine nanospheres: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 285602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Metal-Containing Polydopamine Nanomaterials: Catalysis, Energy, and Theranostics. Small 2020, 16, e1907042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, S.; Lu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Tan, F.; Li, J.; Li, N. Oxygen-supplementing mesoporous polydopamine nanosponges with WS2 QDs-embedded for CT/MSOT/MR imaging and thermoradiotherapy of hypoxic cancer. Biomaterials 2019, 220, 119405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, Y.; He, T.; Liu, G.; Lin, C.; Li, K.; Lu, L.; Cai, K. Lymph node-targeted immune-activation mediated by imiquimod-loaded mesoporous polydopamine based-nanocarriers. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Wang, Z.; Xia, D.; Zhu, J.; Huang, J.; Xing, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, K. Long-Lasting Reactive Oxygen Species Generation by Porous Redox Mediator-Potentiated Nanoreactor for Effective Tumor Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Hou, S.; Qian, H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, G.; Chen, Z.; Ping, Y.; et al. Mesoporous polydopamine with built-in plasmonic core: Traceable and NIR triggered delivery of functional proteins. Biomaterials 2020, 238, 119847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and Clearance of Silicon, Organosilica, Silsesquioxane, Silica Mixed Oxide, and Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Tade, M.O.; Dai, S.; Yamauchi, Y. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon spheres with extra-large pores through assembly of diblock copolymer micelles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Guo, R.; Sun, J.; Xie, R.; Yang, W. Multifunctional Mesoporous Polydopamine with Hydrophobic Paclitaxel for Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Chemo-Photothermal Synergistic Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8647–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, P.; Che, Z.; Zhang, L. A novel self-coated polydopamine nanoparticle for synergistic photothermal-chemotherapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Chen, M.; Song, J.; Xu, X.; Lu, C.; Du, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, M.; Fan, K.; et al. Sialic acid-engineered mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles loaded with SPIO and Fe(3+) as a novel theranostic agent for T1/T2 dual-mode MRI-guided combined chemo-photothermal treatment of hepatic cancer. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Ren, X.; Jiang, C.; Lu, L. Polydopamine-based coordination nanocomplex for T1/T2 dual mode magnetic resonance imaging-guided chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 77, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Huo, G.; Wu, A.; Zeng, L. Amplified Photoacoustic Signal and Enhanced Photothermal Conversion of Polydopamine-Coated Gold Nanobipyramids for Phototheranostics and Synergistic Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14866–14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, T.; Bai, S.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, T.; Peng, N.; Qiu, T.; Liu, Y. Multifunction in One Nanoparticle for Anticancer Therapy: Bowl-Shaped Au@PDA Yolk-Shell NPs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 27733–27742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Zuo, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X. H2O2 Self-Supplying and GSH-Depleting Nanoplatform for Chemodynamic Therapy Synergetic Photothermal/Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 43925–43936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y. Multi-responsive photothermal-chemotherapy with drug-loaded melanin-like nanoparticles for synergetic tumor ablation. Biomaterials 2016, 81, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; He, X.; Lei, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; You, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Facile preparation of doxorubicin-loaded upconversion@polydopamine nanoplatforms for simultaneous in vivo multimodality imaging and chemophotothermal synergistic therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.A.; Vo, V.G.; Shim, K.; Lee, S.W.; An, S.S.A. Multimodal Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers for Dual Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release and Excellent Photothermal Ablation of Cancer Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7667–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Shi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Guo, J.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; et al. Recent developments in mesoporous polydopamine-derived nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Fu, W.H.; Zhou, J.; Mei, L.Q.; Yang, J.M.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yin, W.Y. Mn2+-doped ZrO2@PDA nanocomposite for multimodal imaging-guided chemo-photothermal combination therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Yin, Q.; Lu, L. Multifunctional envelope-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Ding, F.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Pan, G.; Mei, L.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Ligand Clicking and Ion Coordination on 2D Black Phosphorus for Cancer Multimodal Imaging and Therapy. Small 2022, 18, 2201803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Liang, G.H.; Feng, B.X.; Wang, G.; Wu, N.; Deng, Y.H.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Alghamdi, A.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, J. Facile synthesis of metal-polyphenol-formaldehyde coordination polymer colloidal nanoparticles with sub-50 nm for T-1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, J.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X. MRI-guided liposomes for targeted tandem chemotherapy and therapeutic response prediction. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Chaudhary, R.K.; Gulyas, B. Nanoparticles in practice for molecular-imaging applications: An overview. Acta Biomater. 2016, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Dong, P.; Pi, L.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, H.; Liang, H.; Ma, D.; Chai, K.Y. Hydroxyl-PEG-Phosphonic Acid-Stabilized Superparamagnetic Manganese Oxide-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Synergistic Effects for Dual-Mode MR Imaging. Langmuir 2019, 35, 9474–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Wang, D.D.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, S.W.; Tang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.L.; Liu, L.D.; et al. Fe3O4@polydopamine Composite Theranostic Superparticles Employing Preassembled Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as the Core. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18389–18390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Jiang, M.N.; Xiong, L.W.; Yao, X.X.; Fan, M.J.; Chen, D.Y.; Jiang, Q.; Jin, Z.K.; He, Q.J. Novel photo-theranostic GdB6 nanoparticles for fluorescence imaging and NIR-photothermal therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3487–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zou, X.; Duan, W. Saddle-Point Excitons and Their Extraordinary Light Absorption in 2D β-Phase Group-IV Monochalcogenides. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qi, Y.X.; Jiang, X.Q.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Shi, G.; Zhang, M. Selective and Sensitive Monitoring of Cerebral Antioxidants Based on the Dye-Labeled DNA/Polydopamine Conjugates. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11647–11653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Feng, L.; Ji, Y.; Tao, L.; Li, S.; Wei, Y. Biocompatible polydopamine fluorescent organic nanoparticles: Facile preparation and cell imaging. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5581–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Liao, G.; Yu, C.; Xu, Z. Polydopamine-Based Tumor-Targeted Multifunctional Reagents for Computer Tomography/Fluorescence Dual-Mode Bioimaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. Porphyrin-based covalent organic framework nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging-guided photodynamic and photothermal combination cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2019, 223, 119459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Song, G.; Zhang, X.B.; Tan, W. NIR-II Driven Plasmon-Enhanced Catalysis for a Timely Supply of Oxygen to Overcome Hypoxia-Induced Radiotherapy Tolerance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15069–15075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Zhu, R.; Song, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Photoacoustic Imaging: Contrast Agents and Their Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1805875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Xia, Z.; Guo, S. Recent Advances on Black Phosphorus for Biomedicine and Biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liang, C.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Gao, N.; Tao, W.; Luo, L.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. TPGS-Functionalized Polydopamine-Modified Mesoporous Silica as Drug Nanocarriers for Enhanced Lung Cancer Chemotherapy against Multidrug Resistance. Small 2017, 13, 1700623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Yang, M.; Du, Z.; Feng, C.; Xing, C.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, F.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X.; et al. CX-5461-loaded nucleolus-targeting nanoplatform for cancer therapy through induction of pro-death autophagy. Acta Biomater. 2018, 79, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Xue, P. Polydopamine (PDA)-activated cobalt sulfide nanospheres responsive to tumor microenvironment (TME) for chemotherapeutic-enhanced photothermal therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.M.; Peng, W.; Liang, Z.G.; Zeng, X.W.; Wang, Q.X.; Gao, N.S. Charge-reversal nanomedicine based on black phosphorus for the development of A Novel photothermal therapy of oral cancer. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Lu, M.; Xia, X.H.; Huang, Y.Y. Recent advances in photothermal and RNA interfering synergistic therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chong, Y.; Pei, R. Dual-Stimuli-Responsive Multifunctional Gd2Hf2O7 Nanoparticles for MRI-Guided Combined Chemo-/Photothermal-/Radiotherapy of Resistant Tumors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35928–35939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Chi, B.; Han, Z.; He, Y.; Tian, F.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Controllable synthesis of rare earth (Gd(3+),Tm(3+)) doped Prussian blue for multimode imaging guided synergistic treatment. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 12327–12337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Xin, N.; Chen, S.; Sun, J.; Jin, R.; Nie, Y.; Fan, H. A Gd-doped polydopamine (PDA)-based theranostic nanoplatform as a strong MR/PA dual-modal imaging agent for PTT/PDT synergistic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.L.; Liu, T.; Zou, M.Z.; Yu, W.Y.; Li, C.X.; He, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.K.; Liu, M.D.; Li, Z.H.; Feng, J.; et al. Aggressive Man-Made Red Blood Cells for Hypoxia-Resistant Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1802006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Nie, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X.; Ma, H.; Zheng, Y.; et al. pH-Sensitive and Charge-Reversal Polymeric Nanoplatform Enhanced Photothermal/Photodynamic Synergistic Therapy for Breast Cancer. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 836468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, C.; Xing, B.; Yang, P.; Lin, J. Multifunctional UCNPs@PDA-ICG nanocomposites for upconversion imaging and combined photothermal/photodynamic therapy with enhanced antitumor efficacy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4884–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.Z.; Mei, L.; Zeng, X.W. Polymeric microneedle-mediated sustained release systems: Design strategies and promising applications for drug delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Q.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, H.; Kong, D.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L. Robust Nanovaccine Based on Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Effective Photothermal-Immunotherapy Against Melanoma. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yung, B.; Huang, P.; Chen, X. Nanotechnology for Multimodal Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13566–13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.; Lim, W.Q.; Phua, F.S.Z.; An, G.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Y. Reduction-sensitive fluorescence enhanced polymeric prodrug nanoparticles for combinational photothermal-chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 163, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Gong, H.; Gao, M.; Zhu, W.; Sun, X.; Feng, L.; Fu, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Polydopamine Nanoparticles as a Versatile Molecular Loading Platform to Enable Imaging-guided Cancer Combination Therapy. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Xue, P. PEGylated Polydopamine Nanoparticles Incorporated with Indocyanine Green and Doxorubicin for Magnetically Guided Multimodal Cancer Therapy Triggered by Near-Infrared Light. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2017, 1, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, F.; Ding, D.; Song, C.; Guo, C.; Liu, S. TiO2–x Based Nanoplatform for Bimodal Cancer Imaging and NIR-Triggered Chem/Photodynamic/Photothermal Combination Therapy. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9262–9274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, L.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Xue, B.; Zhang, L.; Liang, S.; et al. Tailoring morphologies of mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles to deliver high-loading radioiodine for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma imaging and therapy. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 15021–15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Guan, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Highly efficient cascading synergy of cancer photo-immunotherapy enabled by engineered graphene quantum dots/photosensitizer/CpG oligonucleotides hybrid nanotheranostics. Biomaterials 2019, 205, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Formulation | Drug | Cancer | Imaging | Therapy | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticles | Imiquimod | B16-F10 | PTT–Immunotherapy | [24] | |
| Nanoparticles | Paclitaxel | A549 | PA | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [29] |
| Nanoparticles | Docetaxel | 4T1 | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [30] | |
| Nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | HeLa | MRI | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [31] |
| Nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | HeLa | MRI | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [32] |
| Nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | 4T1 | PA | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [33] |
| Nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | HepG-2 | PA/CT | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [34] |
| Nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | K7M2-WT, U2OS | Chemo–photothermal/Chemodynamic therapy | [35] | |
| Nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | CT26 | MRI | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [36] |
| Nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | HeLa | MRI | Chemo–photothermal therapy | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Peng, J.; Zhang, J.; Pan, L.; Ouyang, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lian, D.; et al. Frontiers in Preparations and Promising Applications of Mesoporous Polydopamine for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010015
Ma H, Peng J, Zhang J, Pan L, Ouyang J, Li Z, Guo B, Wang Z, Xu Y, Lian D, et al. Frontiers in Preparations and Promising Applications of Mesoporous Polydopamine for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Hualin, Jingwen Peng, Jianing Zhang, Li Pan, Jiayi Ouyang, Zimu Li, Baochun Guo, Zhen Wang, Ying Xu, Daizheng Lian, and et al. 2023. "Frontiers in Preparations and Promising Applications of Mesoporous Polydopamine for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010015
APA StyleMa, H., Peng, J., Zhang, J., Pan, L., Ouyang, J., Li, Z., Guo, B., Wang, Z., Xu, Y., Lian, D., & Zeng, X. (2023). Frontiers in Preparations and Promising Applications of Mesoporous Polydopamine for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Pharmaceutics, 15(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010015






