The Influence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Duration of Sciatic Nerve Block with 1.3% Liposomal Bupivacaine and 0.25% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in a Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Assessment of Peripheral Neuropathy
2.3. Experimental Groups
2.4. Performance of Sciatic Nerve Block
2.5. Determination of Nerve Block Duration
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| AMDCC | Animal Models of Diabetic Complications Consortium |
| BH | Bupivacaine hydrochloride |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| LA | Local anesthetic |
| LB | Liposomal bupivacaine |
| MPE | Maximal possible effect |
| PN | Peripheral neuropathy |
| ROC | Receiver operating curves |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
References
- Petersmann, A.; Nauck, M.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Kerner, W.; Müller, U.A.; Landgraf, R.; Freckmann, G.; Heinemann, L. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2018, 126, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, A.D. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, S8–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, J.A. Etiology of Type 1 Diabetes. Immunity 2010, 32, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabravolski, S.A.; Orekhova, V.A.; Baig, M.S.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Starodubova, A.V.; Popkova, T.V.; Orekhov, A.N. The Role of Mitochondrial Mutations and Chronic Inflammation in Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, C.K.; Cvetko, E.; Umek, N. Skeletal Muscle Microvascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Shan, P.F. Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trend of Diabetes in 195 Countries and Territories: An Analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Lu, Y.; Hajifathalian, K.; Bentham, J.; di Cesare, M.; Danaei, G.; Bixby, H.; Cowan, M.J.; Ali, M.K.; Taddei, C.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Diabetes since 1980: A Pooled Analysis of 751 Population-Based Studies with 4.4 Million Participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Diabetes Mellitus and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-Based Study. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinero-Fort, M.Á.; San Andrés-Rebollo, F.J.; de Burgos-Lunar, C.; Abánades-Herranz, J.C.; Carrillo-De-Santa-Pau, E.; Chico-Moraleja, R.M.; Jiménez-García, R.; López-De-Andrés, A.; Gómez-Campelo, P. Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the MADIABETES Cohort Study: Association with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, Z.; Azmi, S.; Yadav, R.; Ferdousi, M.; Kumar, M.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Lim, J.; Malik, R.A.; Alam, U. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Pharmacotherapy. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 828–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhatariya, K.; Levy, N.; Kilvert, A.; Watson, B.; Cousins, D.; Flanagan, D.; Hilton, L.; Jairam, C.; Leyden, K.; Lipp, A.; et al. NHS Diabetes Guideline for the Perioperative Management of the Adult Patient with Diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2012, 29, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, K. Lower Extremity Regional Anesthesia with the Low Sciatic Nerve Block. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2008, 25, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocum, A.; Turkoz, A.; Bozdogan, N.; Caliskan, E.; Eker, E.H.; Arslan, G. Femoral and Sciatic Nerve Block with 0.25% Bupivacaine for Surgical Management of Diabetic Foot Syndrome: An Anesthetic Technique for High-Risk Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Clin. Anesth. 2010, 22, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Prasad, G.V.; Khanna, S.; Jaishree, S. Review of Adjuvants to Local Anesthetics in Peripheral Nerve Blocks: Current and Future Trends. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2020, 14, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirksey, M.A.; Haskins, S.C.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.S. Local Anesthetic Peripheral Nerve Block Adjuvants for Prolongation of Analgesia: A Systematic Qualitative Review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperer, M.; Gerner, P.; Memtsoudis, S.G. Additives to Local Anesthetics for Peripheral Nerve Blocks or Local Anesthesia: A Review of the Literature. Pain Manag. 2015, 5, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilfeld, B.M.; Malhotra, N.; Furnish, T.J.; Donohue, M.C.; Madison, S.J. Liposomal Bupivacaine as a Single-Injection Peripheral Nerve Block: A Dose-Response Study. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, C.M.; Woodruff, A.; Yang, R.; Kohane, D.S. Drug Delivery Systems for Prolonged Duration Local Anesthesia. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A.; Amin, P. A Recent Update on Drug Delivery Systems for Pain Management. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2021, 35, 175–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz-Montan, M.; Silva, A.L.R.; Cogo, K.; Bergamaschi, C.D.C.; Volpato, M.C.; Ranali, J.; de Paula, E.; Groppo, F.C. Liposome-Encapsulated Ropivacaine for Topical Anesthesia of Human Oral Mucosa. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 104, 1528–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereda, C.M.S.; Brunetto, G.B.; de Araújo, D.R.; de Paula, E. Liposomal Formulations of Prilocaine, Lidocaine and Mepivacaine Prolong Analgesic Duration. Can. J. Anesth. 2006, 53, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigham, N.C.; Ji, R.R.; Becker, M.L. Degradable Polymeric Vehicles for Postoperative Pain Management. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, O.; Kaye, A.D.; Kaye, A.; Belani, K.; Urman, R.D. Emerging Roles of Liposomal Bupivacaine in Anesthesia Practice. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyhre, H.; Söderberg, L.; Björkman, S.; Carlsson, C. Local Anesthetics in Lipid-Depot Formulations—Neurotoxicity in Relation to Duration of Effect in a Rat Model. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2006, 31, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, B.M.; Newton, P.; Ott, L.R.; Haan, D.; Brubaker, A.N.; Cole, P.I.; Ross, P.E.; Rebelatto, M.C.; Nelson, K.G. The Safety of EXPAREL® (Bupivacaine Liposome Injectable Suspension) Administered by Peripheral Nerve Block in Rabbits and Dogs. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 962101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlvin, J.B.; Padera, R.F.; Shankarappa, S.A.; Reznor, G.; Kwon, A.H.; Chiang, H.H.; Yang, J.; Kohane, D.S. Multivesicular Liposomal Bupivacaine at the Sciatic Nerve. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4557–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanovska, M.; Cvetko, E.; Hadzic, A.; Seliskar, A.; Plavec, T.; Mis, K.; Vuckovic Hasanbegovic, I.; Stopar Pintaric, T. Neurotoxicity of Perineural vs Intraneural-Extrafascicular Injection of Liposomal Bupivacaine in the Porcine Model of Sciatic Nerve Block. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.J.; Vermeulen, K.; Langerman, L.; Zakowski, M.; Turndorf, H. Prolonged analgesia with liposomal bupivacaine in a mouse model. Reg. Anesth. 1994, 19, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grant, G.J.; Barenholz, Y.; Piskoun, B.; Bansinath, M.; Turndorf, H.; Bolotin, E.M. DRV Liposomal Bupivacaine: Preparation, Characterization, and in vivo Evaluation in Mice. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, L.; Umek, N.; Horvat, S.; Hadžić, A.; Kuroda, M.; Pintarič, T.S.; Mrak, V.; Cvetko, E. Neurotoxicity of Bupivacaine and Liposome Bupivacaine after Sciatic Nerve Block in Healthy and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lirk, P.; Flatz, M.; Haller, I.; Hausott, B.; Blumenthal, S.; Stevens, M.F.; Suzuki, S.; Klimaschewski, L.; Gerner, P. In Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats, Subclinical Diabetic Neuropathy Increases in vivo Lidocaine Block Duration but Not in Vitro Neurotoxicity. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2012, 37, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroin, J.S.; Buvanendran, A.; Williams, D.K.; Wagenaar, B.; Moric, M.; Tuman, K.J.; Kerns, J.M. Local Anesthetic Sciatic Nerve Block and Nerve Fiber Damage in Diabetic Rats. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2010, 35, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroin, J.S.; Buvanendran, A.; Tuman, K.J.; Kerns, J.M. Effect of Acute versus Continuous Glycemic Control on Duration of Local Anesthetic Sciatic Nerve Block in Diabetic Rats. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2012, 37, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council (U.S.). Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; Institute for Laboratory Animal Research (U.S.) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Research Council: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- du Sert, N.P.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLOS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.K.; Huan, Y. Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Models in Mice and Rats. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2008, 5, 5.47.1–5.47.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Ding, Y.; Yan, N.; Nie, Y.; Li, M.; Tong, L. Trehalose Prevents Sciatic Nerve Damage to and Apoptosis of Schwann Cells of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic C57BL/6J Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvazava, I.G.; Rogovaya, O.S.; Borisov, M.A.; Vorotelyak, E.A.; Vasiliev, A.V. Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Rodent Experimental Models. Acta Nat. 2018, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Kratz, K.M.; Karnes, J.L.; Litchy, W.J.; Klein, R.; Pach, J.M.; Wilson, D.M.; O’Brien, P.C.; Melton, L.J. The Prevalence by Staged Severity of Various Types of Diabetic Neuropathy, Retinopathy, and Nephropathy in a Population-Based Cohort: The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 1993, 43, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Giannini, C. Pathologic Alterations in the Diabetic Neuropathies of Humans: A Review. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1996, 55, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trojaborg, W. The Electrophysiologic Profile of Diabetic Neuropathy. Semin. Neurol. 1996, 16, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiswenger, K.K.; Calcutt, N.A.; Mizisin, A.P. Dissociation of Thermal Hypoalgesia and Epidermal Denervation in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 442, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’brien, P.D.; Sakowski, S.A.; Feldman, E.L. Mouse Models of Diabetic Neuropathy. ILAR J. 2014, 54, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.W.; Yaksh, T.L. Assessment of Acute Thermal Nociception in Laboratory Animals. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 99, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, K.; Elkassabany, N.M.; Liu, J. Dexamethasone as Adjuvant to Bupivacaine Prolongs the Duration of Thermal Antinociception and Prevents Bupivacaine-Induced Rebound Hyperalgesia via Regional Mechanism in a Mouse Sciatic Nerve Block Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.J.; Vermeulen, K.; Zakowski, M.I.; Sutin, K.M.; Ramanathan, S.; Langerman, L.; Weissmann, T.E.; Turndorf, H. A Rat Sciatic Nerve Model for Independent Assessment of Sensory and Motor Block Induced by Local Anesthetics. Anesth. Analg. 1992, 75, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.; Erickson, S.; Wojtalewicz, S.; Simpson, A.; Metcalf, C.; Sant, H.; Shea, J.; Gale, B.; Agarwal, J. Entrapping Bupivacaine-Loaded Emulsions in a Crosslinked-Hydrogel Increases Anesthetic Effect and Duration in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Block Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-Y.; Li, S.-D.; Sun, P. Kinetic and Dynamic Studies of Liposomal Bupivacaine and Bupivacaine Solution after Subcutaneous Injection in Rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumaker, R.C. PKCALC: A BASIC Interactive Computer Program for Statistical and Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Data. Drug Metab. Rev. 1986, 17, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramabadran, K.; Bansinath, M.; Turndorf, H.; Puig, M.M. Tail Immersion Test for the Evaluation of a Nociceptive Reaction in Mice. Methodological Considerations. J. Pharmacol. Methods 1989, 21, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The Meaning and Use of the Area under a Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zel, J.; Hadzic, A.; Cvetko, E.; Seliskar, A.; Damjanovska, M.; Kuroda, M.M.; Sega Jazbec, S.; Stopar Pintaric, T. Neurological and Histological Outcomes after Subarachnoid Injection of a Liposomal Bupivacaine Suspension in Pigs: A Pilot Study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.M.; Ashmawi, H.A.; Costa, L.S.; Posso, I.P.; Slullitel, A. Percutaneous Sciatic Nerve Block with Tramadol Induces Analgesia and Motor Blockade in Two Animal Pain Models. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. Pesqui. Med. Biol. 2012, 45, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.J.; Piskoun, B.; Bansinath, M. Analgesic Duration and Kinetics of Liposomal Bupivacaine after Subcutaneous Injection in Mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2003, 30, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araujo, D.R.; Cereda, C.M.S.; Brunetto, G.B.; Pinto, L.M.A.; Santana, M.H.A.; de Paula, E. Encapsulation of Mepivacaine Prolongs the Analgesia Provided by Sciatic Nerve Blockade in Mice. Can. J. Anaesth. J. Can. D’anesthesie 2004, 51, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, S.Y.; Zhang, Q.G.; Xu, R.; Lei, H.Y. Bupivacaine Induces Apoptosis via Mitochondria and P38 MAPK Dependent Pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 657, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Abrahams, M.S.; Hurn, P.D.; Grafe, M.R.; Kirsch, J.R. Local Anesthetic Schwann Cell Toxicity Is Time and Concentration Dependent. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2011, 36, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlinde, M.; Hollmann, M.W.; Stevens, M.F.; Hermanns, H.; Werdehausen, R.; Lirk, P. Local Anesthetic-Induced Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byram, S.C.; Bialek, S.E.; Husak, V.A.; Balcarcel, D.; Park, J.; Dang, J.; Foecking, E.M. Distinct Neurotoxic Effects of Select Local Anesthetics on Facial Nerve Injury and Recovery. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2020, 38, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.H.; Baik, J.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Han, S.H. Neurotoxic Effects of Local Anesthetics on Developing Motor Neurons in a Rat Model. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, E.M.; Kaye, A.J.; Eng, M.R.; Emelife, P.I.; Motejunas, M.W.; Bonneval, L.A.; Terracciano, J.A.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D. Regional Nerve Blocks-Best Practice Strategies for Reduction in Complications and Comprehensive Review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2019, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeriswyl, M.; Taffé, P.; Kirkham, K.R.; Bathory, I.; Rancati, V.; Crevoisier, X.; Cherix, S.; Albrecht, E. Comparison of Peripheral Nerve Blockade Characteristics between Non-Diabetic Patients and Patients Suffering from Diabetic Neuropathy: A Prospective Cohort Study. Anaesthesia 2018, 73, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ten Hoope, W.; Hollmann, M.W.; de Bruin, K.; Verberne, H.J.; Verkerk, A.O.; Tan, H.L.; Verhamme, C.; Horn, J.; Rigaud, M.; Picardi, S.; et al. Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics of Lidocaine in a Rodent Model of Diabetic Neuropathy. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lirk, P.; Verhamme, C.; Boeckh, R.; Stevens, M.F.; ten Hoope, W.; Gerner, P.; Blumenthal, S.; de Girolami, U.; van Schaik, I.N.; Hollmann, M.W.; et al. Effects of Early and Late Diabetic Neuropathy on Sciatic Nerve Block Duration and Neurotoxicity in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, B.W.; Schwartz, S.; Stubbs, H.A.; Block, J.E. Glycemic Characteristics in Continuously Monitored Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Normative Values. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Wiley, J.W. Early Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Is Associated with Differential Changes in the Expression and Function of Vanilloid Receptor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zherebitskaya, E.; Schapansky, J.; Akude, E.; Smith, D.R.; van der Ploeg, R.; Solovyova, N.; Verkhratsky, A.; Fernyhough, P. Sensory Neurons Derived from Diabetic Rats Have Diminished Internal Ca2+ Stores Linked to Impaired Re-Uptake by the Endoplasmic Reticulum. ASN Neuro 2012, 4, e00072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivalt, C.G.; Fineman, M.; Deacon, C.F.; Carr, R.D.; Calcutt, N.A. GLP-1 Signals via ERK in Peripheral Nerve and Prevents Nerve Dysfunction in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salviz, E.A.; Onbasi, S.; Ozonur, A.; Orhan-Sungur, M.; Berkoz, O.; Tugrul, K.M. Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Axillary Brachial Plexus Block Properties in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2017, 42, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvillon, P.; Reubrecht, V.; Zoric, L.; Lemoine, L.; Belin, M.; Ducombs, O.; Birenbaum, A.; Riou, B.; Langeron, O. Comparison of Subgluteal Sciatic Nerve Block Duration in Type 2 Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 110, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perkins, B.A.; Dholasania, A.; Buchanan, R.A.; Bril, V. Short-Term Metabolic Change Is Associated with Improvement in Measures of Diabetic Neuropathy: A 1-Year Placebo Cohort Analysis. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertoz, N.; Deniz, M.N.; Ayanoglu, H.O. Relationship between Glycosylated Hemoglobin Level and Sciatic Nerve Block Performance in Diabetic Patients. Foot Ankle Int. 2013, 34, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.W.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of Glycaemia with Macrovascular and Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective Observational Study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Onel, E.; Singla, N.; Kramer, W.G.; Hadzic, A. Pharmacokinetic Profile of Liposome Bupivacaine Injection Following a Single Administration at the Surgical Site. Clin. Drug Investig. 2013, 33, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberón, J.R.; Duncan, S.F.; Sternbergh, W.C. Treatment of Digital Ischemia with Liposomal Bupivacaine. Case Rep. Anesthesiol. 2014, 2014, 853243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soberón, J.R.; Truxillo, T.M.; Gethers, C.C.; Smith, T.A.; Davis, W.E. Axillary Block-Induced Chemical Sympathectomy in the Setting of Digital Ischemia. Ochsner J. 2016, 16, 450. [Google Scholar]
- Vital, P.; Larrieta, E.; Hiriart, M. Sexual Dimorphism in Insulin Sensitivity and Susceptibility to Develop Diabetes in Rats. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 190, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidmark, A.S.; Nawroth, P.P.; Fleming, T. STZ Causes Depletion of Immune Cells in Sciatic Nerve and Dorsal Root Ganglion in Experimental Diabetes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 306, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsidag, S.; Morali, S.; Sargin, M.; Salman, S.; Karsidag, K.; Us, O. The Electrophysiological Findings of Subclinical Neuropathy in Patients with Recently Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2005, 67, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dvorakova, L.S.; Vetter, I. Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabeeb, D.; Najafi, M.; Hasanzadeh, G.; Hadian, M.R.; Musa, A.E.; Shirazi, A. Electrophysiological Measurements of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, S.; Kumar, J.; Turan, A. New Peripheral Nerve Blocks and Local Anesthetics. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2021, 27, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
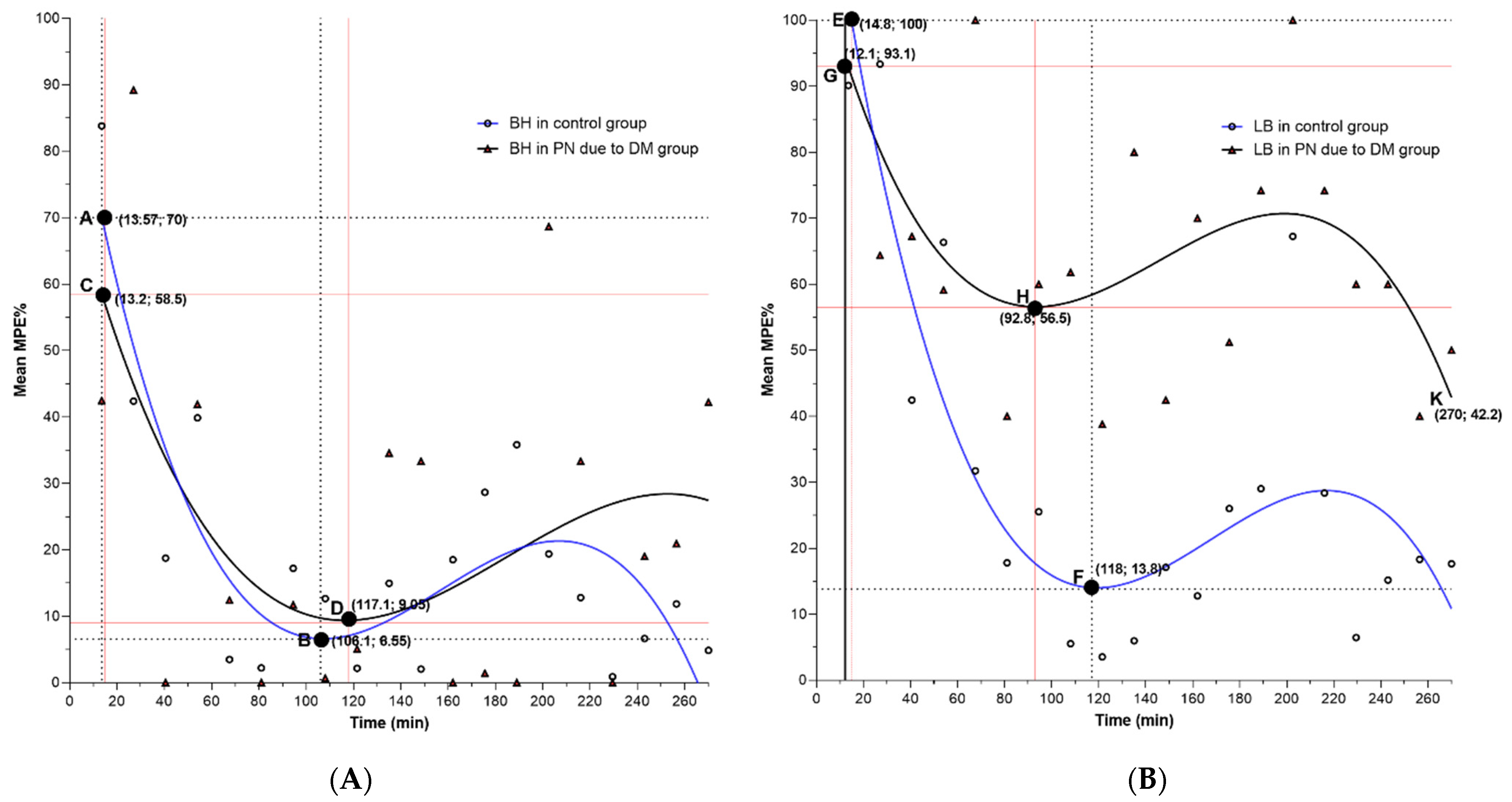
| Variable | Total | Control | Induction with STZ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BH | LB | Total | BH | LB | Total | ||
| Sensory design N (%) | 24 (100) | 6 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | 12 (100) | 6 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | 12 (100) |
| Mean (SD) blood glucose before STZ (mmol/L) | 7.27 (0.8) | 6.15 (0.9) | 7.35 (0.5) | 6.8 (1.0) Ⴕ | 7.4 (1.4) | 7.4 (1.0) | 7.4 (1.2) Ⴕ |
| Mean (SD) weight before STZ (g) | 23.8 (1.7) | 23.8 (2.1) | 24.4 (1.5) | 24.1 (1.7) Ⴕ | 23.3 (1.7) | 23.7 (1.6) | 23.5 (1.7) Ⴕ |
| Mean (SD) blood glucose after STZ * (mmol/L) | n.a. | 8.0 (0.6) | 7.3 (1.2) | 7.6 (0.9) ‡ | 25.3 (5.9) | 23.9 (5.2) | 24.6 (5.4) ‡ |
| Mean (SD) weight after STZ (g) | n.a. | 29.0 (2.2) | 28.3 (2.3) | 28.5 (2.2) ‡ | 21.1 (1.6) | 21.5 (3.3) | 21.3 (2.4) ‡ |
| Plantar test (s) | n.a. | 6.1 (2.7) | 6.7 (1.8) | 6.4 (2.8) ‡ | 13.0 (3.3) | 10.8 (3.4) | 11.9 (3.4) ‡ |
| Tail flick test (s) | n.a. | 1.9 (0.4) | 1.9 (0.4) | 1.9 (0.4) † | 2.0 (0.2) | 2.2 (0.6) | 2.2 (0.4) † |
| Model sample N (%) | 24 (100) | 6 (50) | 6 (50) | 12 (100) | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | 8 (100) |
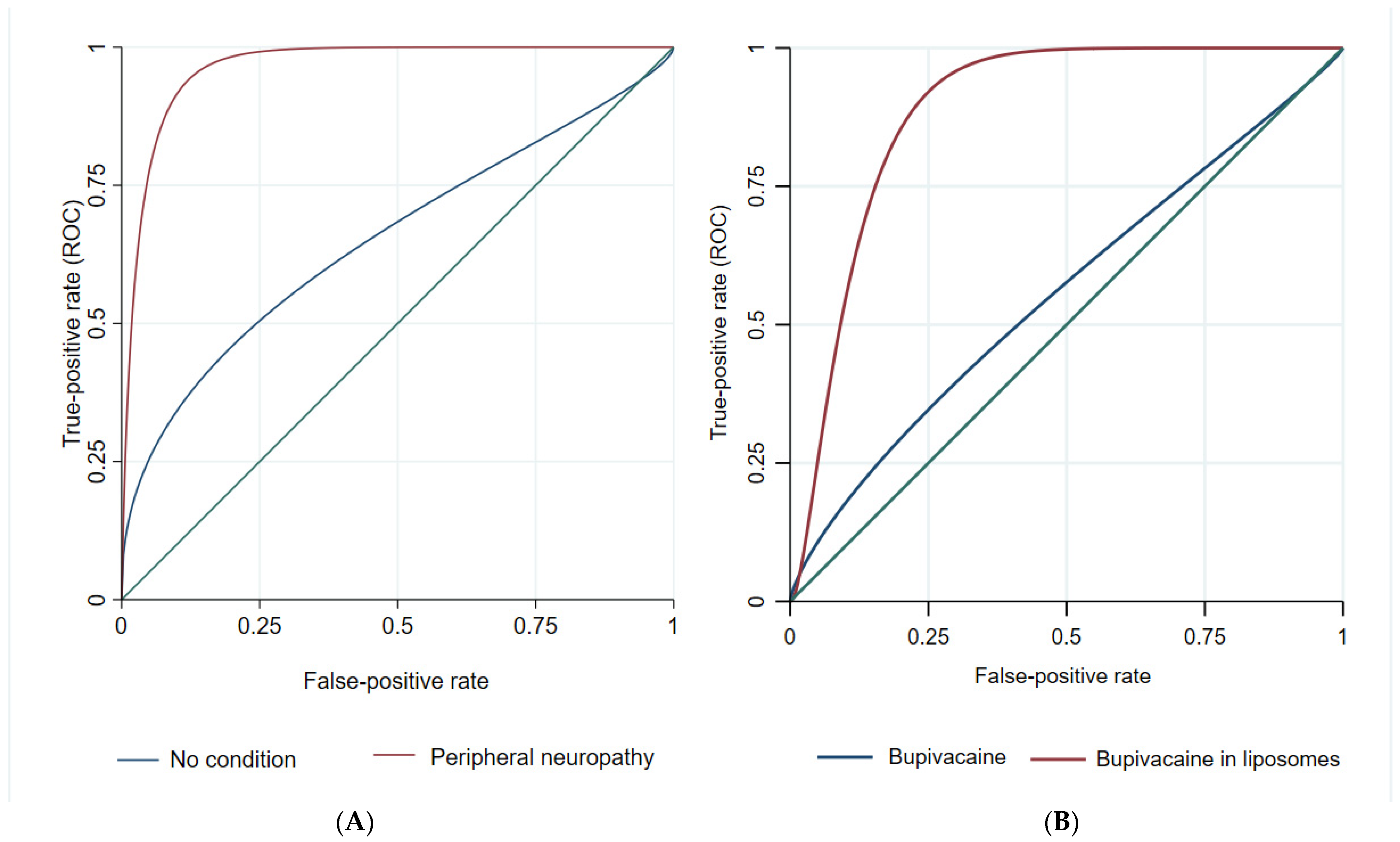
| Model | Obs. | ROC Area | Std. Err. | 95% Conf. Interval | χ2 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | ||||||||
| Model 1 | BH | 20 | 0.56 | 0.137 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 5.3 | 0.022 |
| Model 2 | LB | 20 | 0.88 | 0.010 | 0.69 | 1.00 | ||
| Condition | ||||||||
| Model 1 | No condition | 20 | 0.68 | 0.128 | 0.43 | 0.93 | 5.1 | 0.023 |
| Model 2 | PN due to DM | 20 | 0.92 | 0.068 | 0.78 | 1.00 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markova, L.; Cvetko, E.; Ugwoke, C.K.; Horvat, S.; Umek, N.; Stopar Pintarič, T. The Influence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Duration of Sciatic Nerve Block with 1.3% Liposomal Bupivacaine and 0.25% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in a Mouse Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091824
Markova L, Cvetko E, Ugwoke CK, Horvat S, Umek N, Stopar Pintarič T. The Influence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Duration of Sciatic Nerve Block with 1.3% Liposomal Bupivacaine and 0.25% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in a Mouse Model. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091824
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkova, Liljana, Erika Cvetko, Chiedozie Kenneth Ugwoke, Simon Horvat, Nejc Umek, and Tatjana Stopar Pintarič. 2022. "The Influence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Duration of Sciatic Nerve Block with 1.3% Liposomal Bupivacaine and 0.25% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in a Mouse Model" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091824
APA StyleMarkova, L., Cvetko, E., Ugwoke, C. K., Horvat, S., Umek, N., & Stopar Pintarič, T. (2022). The Influence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Duration of Sciatic Nerve Block with 1.3% Liposomal Bupivacaine and 0.25% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in a Mouse Model. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091824






