Sugar-Triggered Burst Drug Releasing Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA) Microneedles and Its Fabrication Based on Solvent-Casting Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
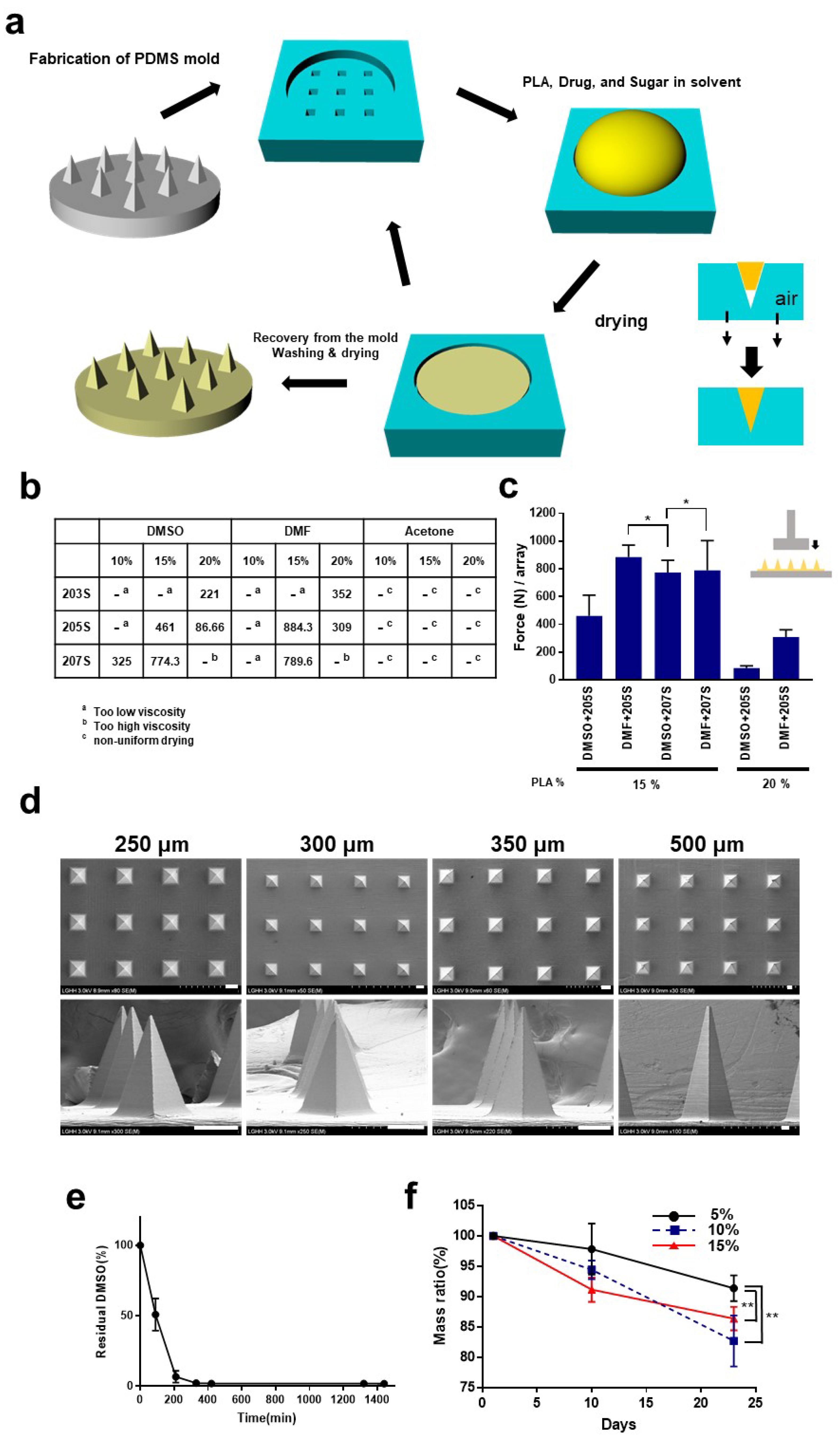
2.1. Fabrication of Microneedles
2.2. Characterization of the Microneedles
2.3. Skin Penetration Test
2.4. Transdermal Delivery In Vitro Using Franz-Type Diffusion Cells
3. Results and Discussion
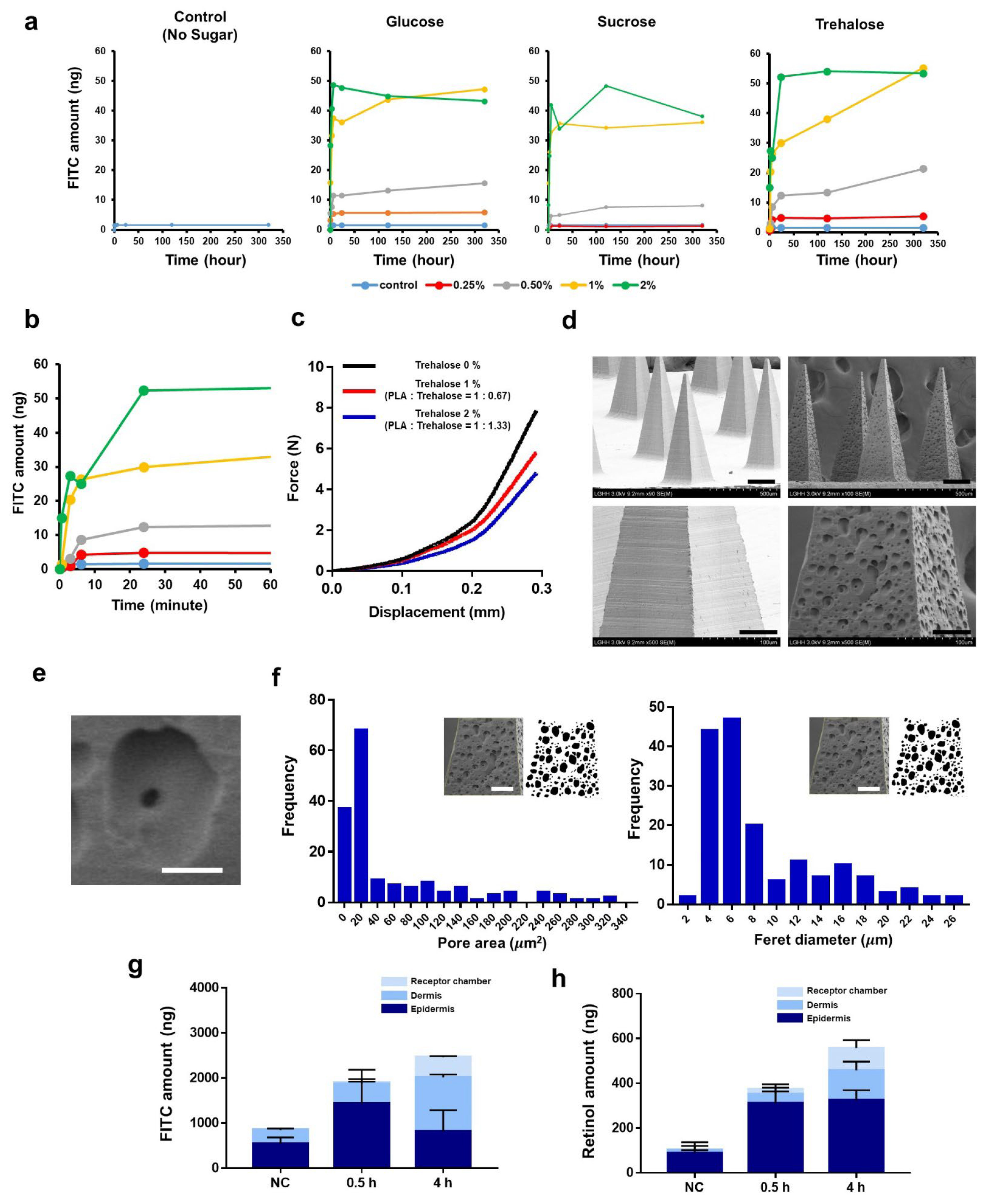
3.1. Fabrication of the Microneedles
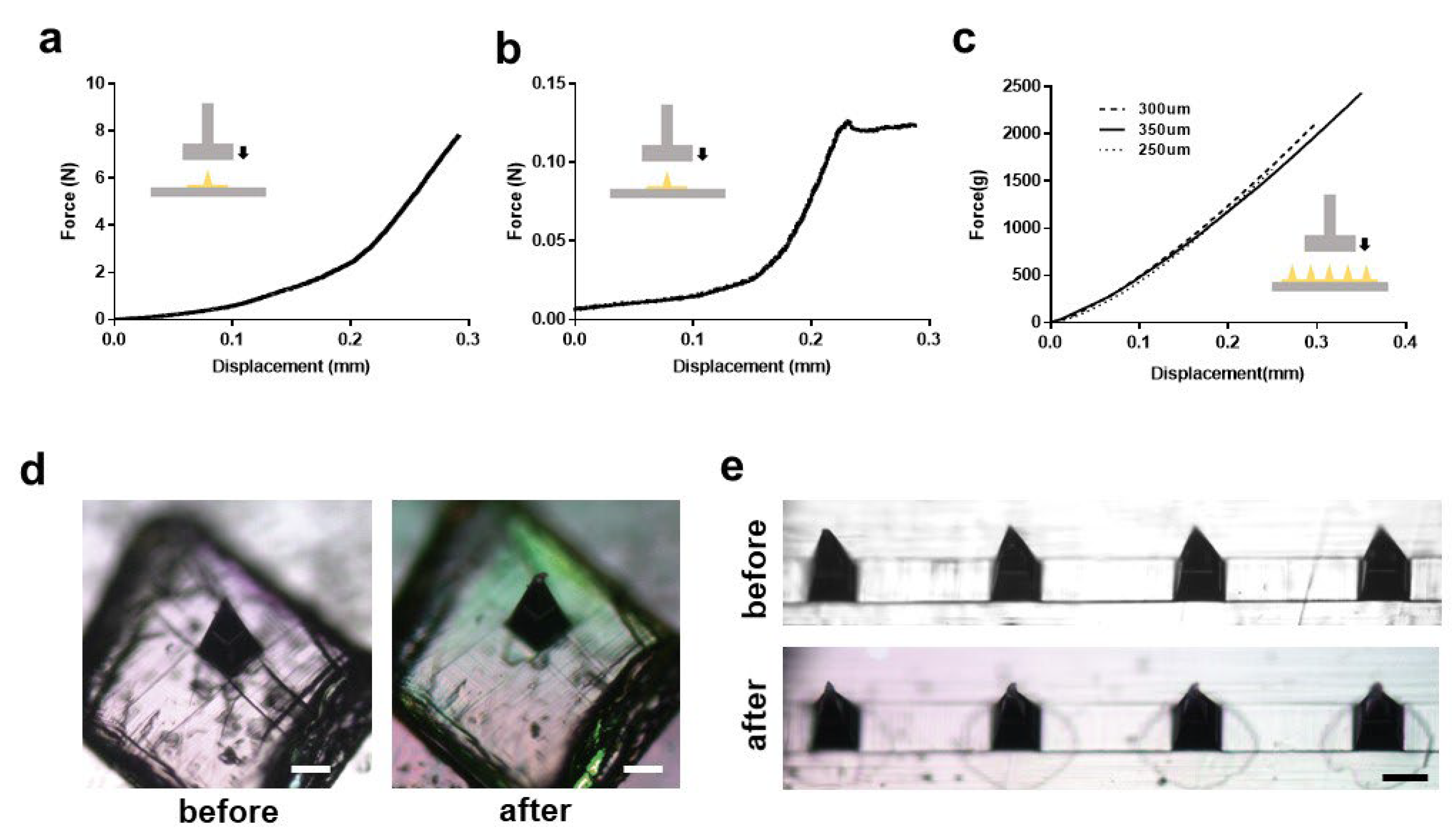
3.2. Mechanical Characteristics of the Microneedles
3.3. Applications to Micro-Needling and Other Combined-Platforms
3.4. Burst-Based Drug Release by Sugar-Containing PLA Microneedle Fabricated via Solvent Casting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Tian, R.; Xu, C.; Yung, B.C.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Ni, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J. Microneedle-array patches loaded with dual mineralized protein/peptide particles for type 2 diabetes therapy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivamani, R.K.; Liepmann, D.; Maibach, H.I. Microneedles and transdermal applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y. The current status of clinical research involving microneedles: A systematic review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, F.K.; Andar, A.; Desai, S. A Comprehensive Review of Microneedles: Types, Materials, Processes, Characterizations and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Dave, K.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Microneedles in the clinic. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, R.; Singh, M.; Nguyen, H.X.; Jonnalagadda, S. A review of recent advances in microneedle technology for transdermal drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmeyer, M.D.; Anderson, L.L.; Wang, A.R. Silicone migration and granuloma formation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2009, 8, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Castañeda, P.; Escobar-Chávez, J.J.; Rodríguez-Cruz, I.M.; Melgoza, L.M.; Martinez-Hernandez, J. Microneedles as enhancer of drug absorption through the skin and applications in medicine and cosmetology. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 21, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Biodegradable polymer microneedles: Fabrication, mechanics and transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, B.; Gullotti, D.; Mangraviti, A.; Utsuki, T.; Brem, H. Polylactic acid (PLA) controlled delivery carriers for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, D.; Kaduri, M.; Poley, M.; Adir, O.; Krinsky, N.; Shainsky-Roitman, J.; Schroeder, A. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and excretion of polylactic acid (PLA) in medical implants and theranostic systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Sun, K.; Sun, Z.; Lv, Z.; Xu, J. Nitric oxide nanomotor driving exosomes-loaded microneedles for achilles tendinopathy healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13339–13350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, K.; Gavitt, T.D.; Farrell, N.J.; Curry, E.J.; Mara, A.B.; Patel, A.; Brown, L.; Kilpatrick, S.; Piotrowska, R.; Mishra, N. Transdermal microneedles for the programmable burst release of multiple vaccine payloads. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, Y. Exploring Trehalose on the release of levonorgestrel from implantable PLGA microneedles. Polymers 2020, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Terry, R.N.; Tang, J.; Feng, M.R.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rapidly separable microneedle patch for the sustained release of a contraceptive. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäder, K. RESOMER®—Biodegradeable Polymers for Sutures, Medical Devices, Drug Delivery Systems and Tissue Engineering. Polym. Adv. Archit. 2011, 6, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.E.; Jun, S.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Kang, N.-G. A Semi-Dissolving Microneedle Patch Incorporating TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery. Polymers 2020, 12, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Shive, M.S. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.S.; Chung, W.K. Curved microneedle array-based sEMG electrode for robust long-term measurements and high selectivity. Sensors 2015, 15, 16265–16280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D.V.; Wang, P.M.; Davis, S.P.; Park, J.-H.; Canatella, P.J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13755–13760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent compatibility of poly (dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, J.N.; Guo, X.D. In vitro and in vivo assessment of polymer microneedles for controlled transdermal drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, B. Medical use of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Rev. Clin. Basic Pharmacol. 1985, 5, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Scailteur, V.; Lauwerys, R. Dimethylformamide (DMF) hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 1987, 43, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmert, S.C.; Carey, C.D.; Falo, G.D.; Sethi, S.K.; Erdos, G.; Korkmaz, E.; Falo, L.D., Jr. Dissolving undercut microneedle arrays for multicomponent cutaneous vaccination. J. Control. Release 2020, 317, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Chen, G. Purification and characterization of poly (L-lactic acid)-degrading enzymes from Amycolatopsis orientalis ssp. orientalis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 282, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Hiyama, M.; Kabe, T.; Kimura, S.; Iwata, T. Enzymatic self-biodegradation of poly (l-lactic acid) films by embedded heat-treated and immobilized proteinase K. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ye, R.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Gao, J.; Ren, L.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L. Touch-actuated microneedle array patch for closed-loop transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M.-C.; McKenna, P.E.; Quinn, H.L.; Courtenay, A.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and Development of Liquid Drug Reservoirs for Microneedle Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drug Molecules. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Kim, M.; Yang, H.; Lee, K.; Jung, H. Droplet-born air blowing: Novel dissolving microneedle fabrication. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, T.; Akizuki, S.; Horiuchi, H.; Yasukawa, Y. Foreign body gonitis caused by a broken poly-L-lactic acid screw. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 1998, 14, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, J.-H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Yadav, S. Microneedling: Advances and widening horizons. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaut, L.; Hoeksema, H.; Pirayesh, A.; Stillaert, F.; Monstrey, S. Microneedling: Where do we stand now? A systematic review of the literature. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2018, 71, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, L.; Marquardt, Y.; Amann, P.; Heise, R.; Huth, L.; Wagner-Schiffler, S.; Huth, S.; Baron, J.-M. Comprehensive molecular characterization of microneedling therapy in a human three-dimensional skin model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, J.M.; Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M. The roles of vitamin C in skin health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, P.K. Topical vitamin C: A useful agent for treating photoaging and other dermatologic conditions. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Maibach, H.I. Effects of skin occlusion on percutaneous absorption: An overview. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2001, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.H.; Nielsen, F.; Sørensen, J.A.; Nielsen, J.B. Dermal penetration of fentanyl: Inter-and intraindividual variations. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 93, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraeye, T.; Bahrami, F.; Ding, L.; Malini, R.I.; Terrier, A.; Rossi, R.M. Predicting transdermal fentanyl delivery using mechanistic simulations for tailored therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 585393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.; Zhang, X.; Chuah, Y.J.; Wu, Y.; Kang, Y. Flexible PEGDA-based microneedle patches with detachable PVP–CD arrowheads for transdermal drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75204–75209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, D.; Siepmann, F.; Elkharraz, K.; Krenzlin, S.; Siepmann, J. How porosity and size affect the drug release mechanisms from PLGA-based microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 314, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Soto, F.; Wang, C.; Rueda, R.; Shukla, S.; Silva-Lopez, C.; Kupor, D.; McBride, D.A.; Pokorski, J.K.; Nourhani, A. Built-in active microneedle patch with enhanced autonomous drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, C.; Cassel, S.; Blanzat, M. Vesicular systems for dermal and transdermal drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadale, R.S.; Londhe, V.Y. A systematic review of carbohydrate-based microneedles: Current status and future prospects. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2021, 32, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlister, E.; Kearney, M.-C.; Martin, E.L.; Donnelly, R.F. From the laboratory to the end-user: A primary packaging study for microneedle patches containing amoxicillin sodium. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 2169–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.; Song, J.E.; Jun, S.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Kang, N.-G. Sugar-Triggered Burst Drug Releasing Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA) Microneedles and Its Fabrication Based on Solvent-Casting Approach. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091758
Kang S, Song JE, Jun S-H, Park S-G, Kang N-G. Sugar-Triggered Burst Drug Releasing Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA) Microneedles and Its Fabrication Based on Solvent-Casting Approach. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091758
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Seongsu, Ji Eun Song, Seung-Hyun Jun, Sun-Gyoo Park, and Nae-Gyu Kang. 2022. "Sugar-Triggered Burst Drug Releasing Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA) Microneedles and Its Fabrication Based on Solvent-Casting Approach" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091758
APA StyleKang, S., Song, J. E., Jun, S.-H., Park, S.-G., & Kang, N.-G. (2022). Sugar-Triggered Burst Drug Releasing Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA) Microneedles and Its Fabrication Based on Solvent-Casting Approach. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091758





