Characterization of a Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Formulation Loaded with Mitomycin C Lipidic Prodrug (MLP) and In Vitro Comparison with a Clinical-Stage Liposomal Formulation of MLP
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
2.2. Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Grafting to MSNPs-NH2
2.3. Prodrug MLP Loading
2.4. Formulation of Pegylated Liposomes with MLP
2.5. HPLC Analysis of MLP and MMC
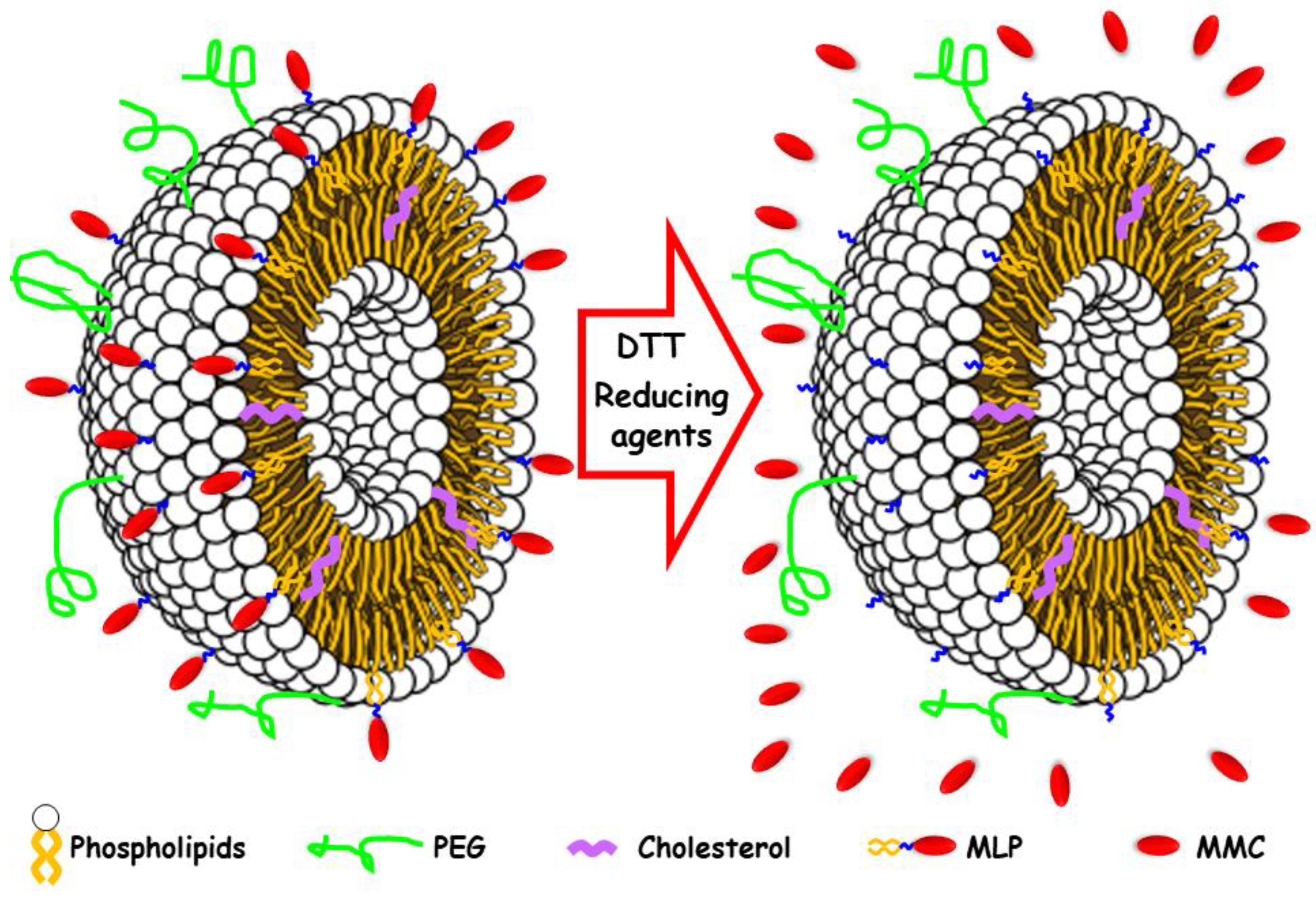
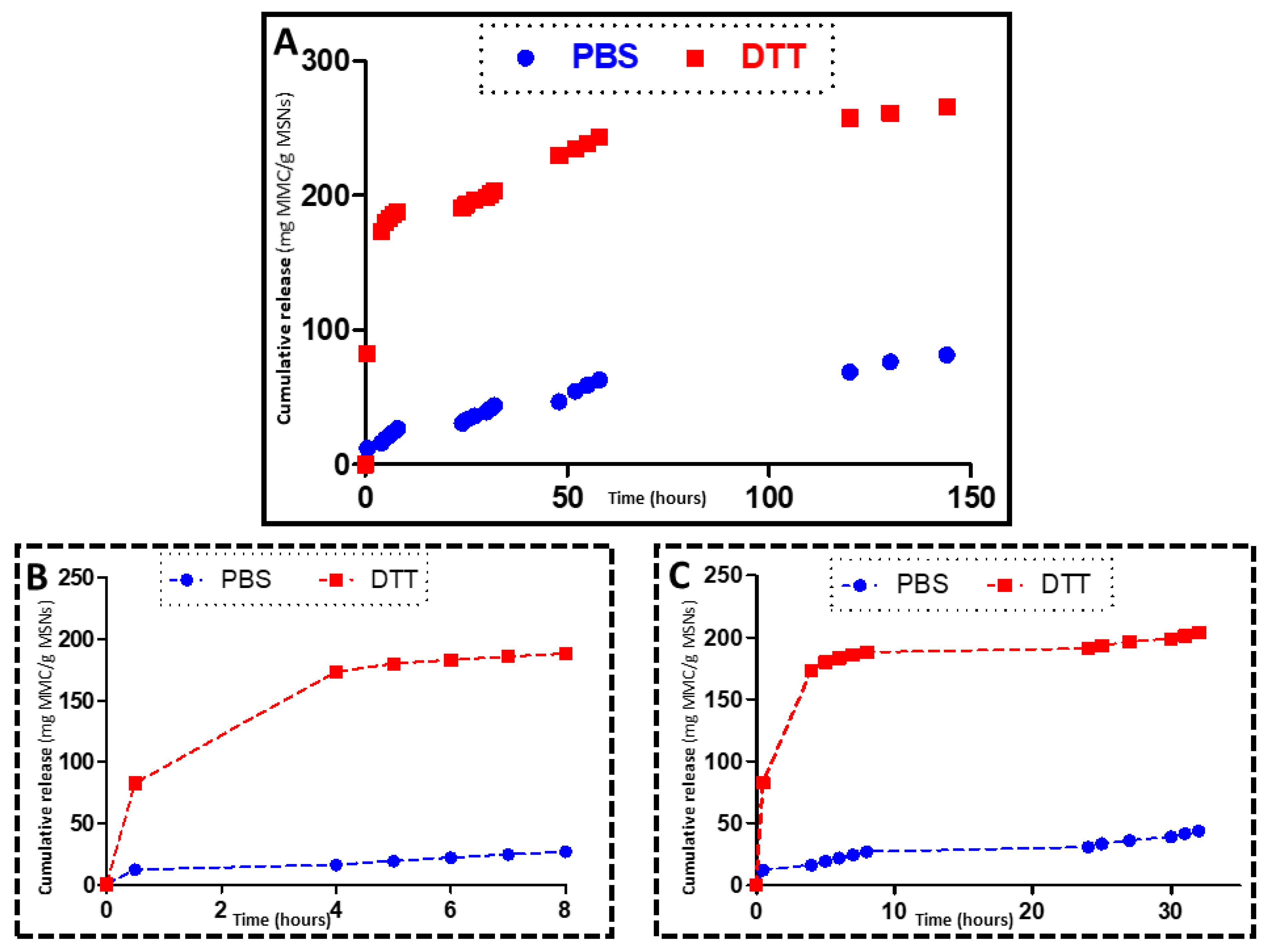
2.6. DTT Drug Release Test
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Experiments on Humar Cancer Cells with MLP-Loaded MSNPs
3. Results and Discussion
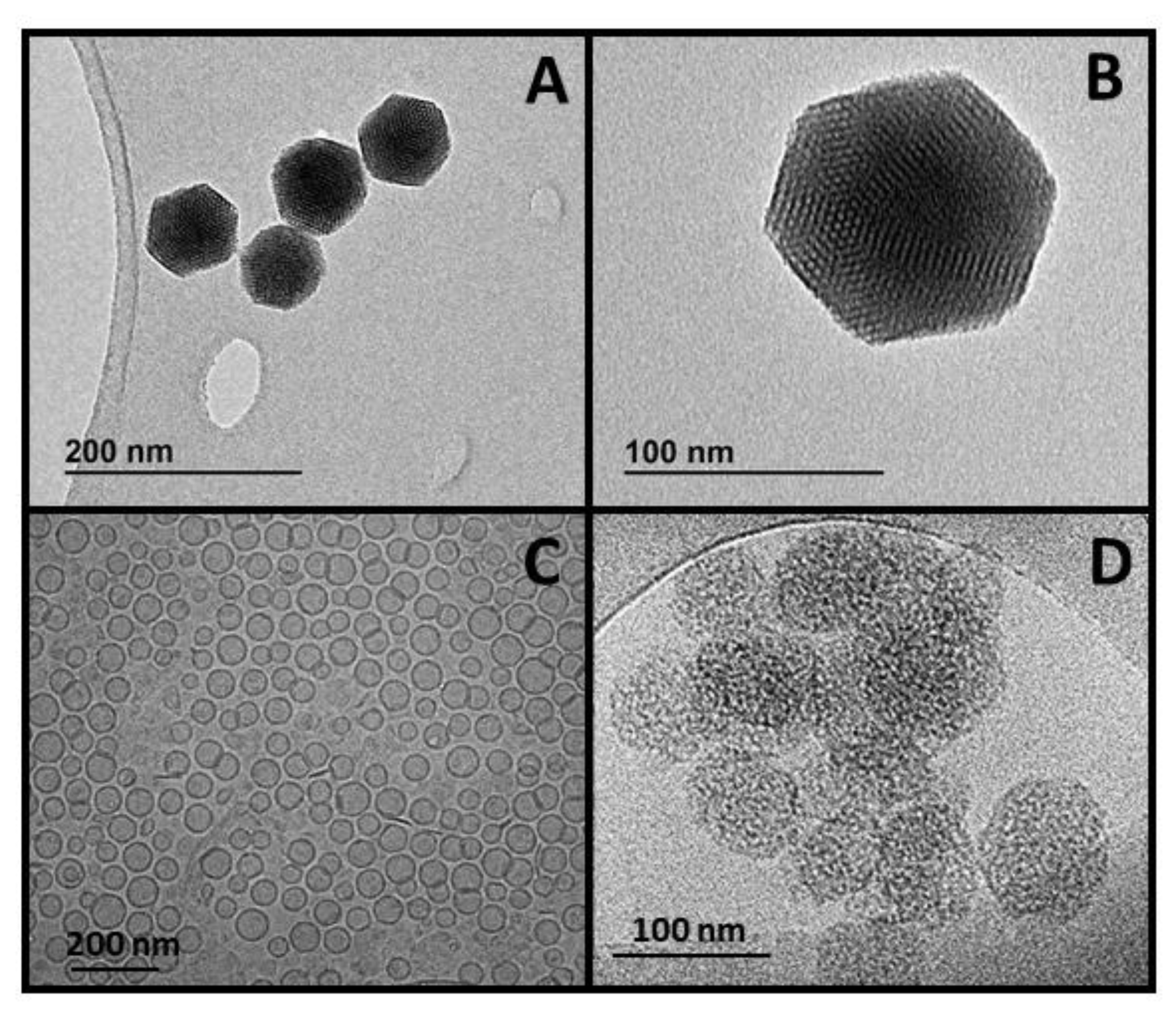
3.1. Nanoparticles Synthesis and Optimization
3.2. Prodrug Loading
3.3. In Vial Release
3.4. Cell Viability Experiments
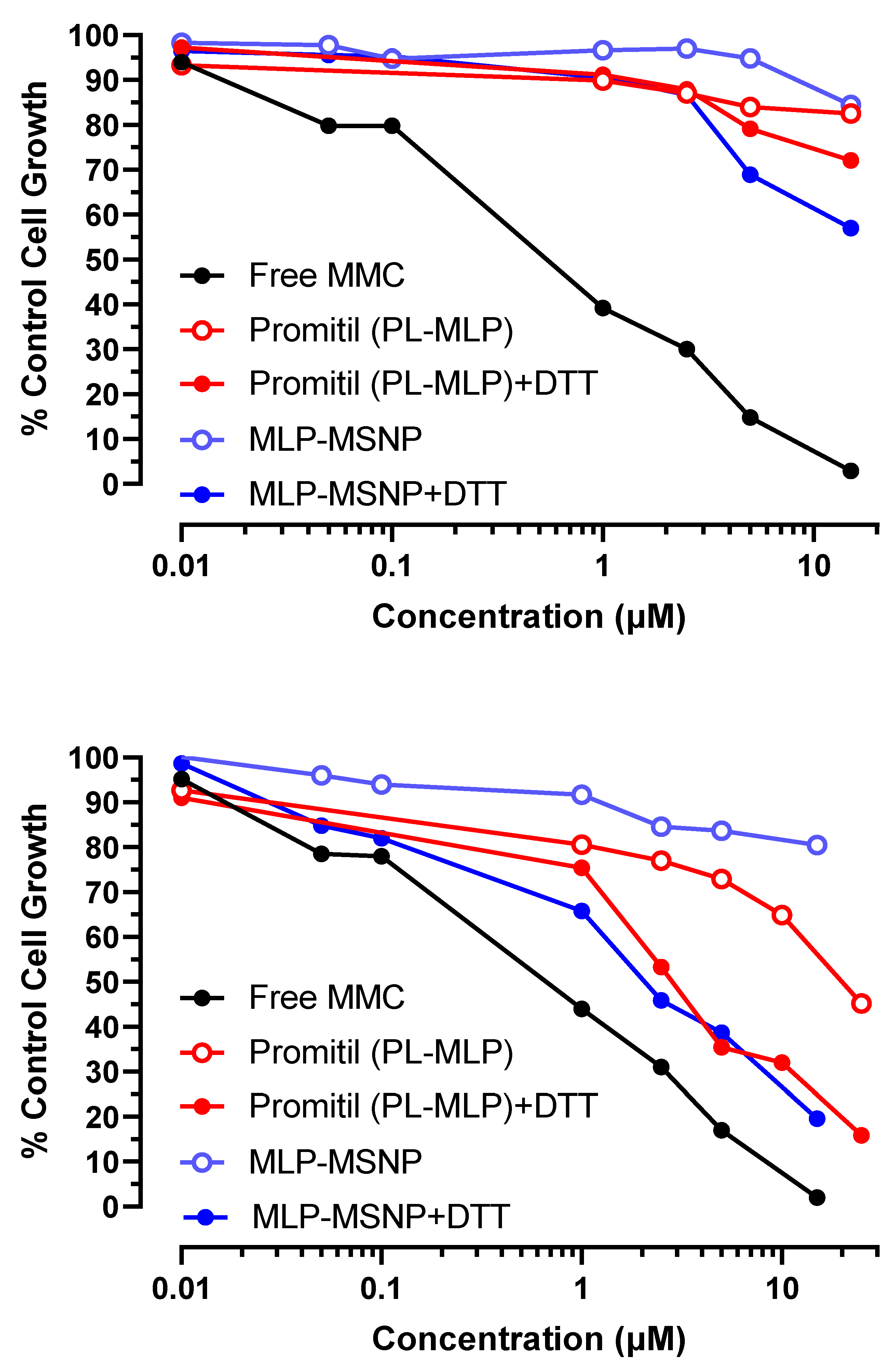
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Experiments
3.5.1. N87 Gastric Cancer Cells
3.5.2. KB Cervix Cancer Cells
3.5.3. Panc-1 Pancreatic Cancer Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, R.A.; Fawell, S.; Floc’h, N.; Flemington, V.; McKerrecher, D.; Smith, P.D. Challenges and Opportunities in Cancer Drug Resistance. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3297–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, P.D.; Gubler, D.A.; Judd, T.C.; Williams, R.M. Mitomycinoid Alkaloids: Mechanism of Action, Biosynthesis, Total Syntheses, and Synthetic Approaches. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 6816–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peer, D.; Margalit, R. Loading Mitomycin C inside Long Circulating Hyaluronan Targeted Nano-Liposomes Increases Its Antitumor Activity in Three Mice Tumor Models. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavaara, R.; Nordman, E. Renal Complications of Mitomycin C Therapy with Special Reference to the Total Dose. Cancer 1985, 55, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, A.A.; Tzemach, D.; Horowitz, A.T.; Shmeeda, H.; Yeh, J.; Zalipsky, S. Reduced Toxicity and Superior Therapeutic Activity of a Mitomycin C Lipid-Based Prodrug Incorporated in Pegylated Liposomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amitay, Y.; Shmeeda, H.; Patil, Y.; Gorin, J.; Tzemach, D.; Mak, L.; Ohana, P.; Gabizon, A. Pharmacologic Studies of a Prodrug of Mitomycin C in Pegylated Liposomes (Promitil®): High Stability in Plasma and Rapid Thiolytic Prodrug Activation in Tissues. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalipsky, S.; Saad, M.; Kiwan, R.; Ber, E.; Yu, N.; Minko, T. Antitumor Activity of New Liposomal Prodrug of Mitomycin C in Multidrug Resistant Solid Tumor: Insights of the Mechanism of Action. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Awwad, R.T.; Smart, D.D.K.; Spitz, D.R.; Gius, D. Thioredoxin Reductase as a Novel Molecular Target for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Lett. 2006, 236, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, A.; Amitay, Y.; Tzemach, D.; Gorin, J.; Shmeeda, H.; Zalipsky, S. Therapeutic Efficacy of a Lipid-Based Prodrug of Mitomycin C in Pegylated Liposomes: Studies with Human Gastro-Entero-Pancreatic Ectopic Tumor Models. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Grenader, T.; Ohana, P.; Amitay, Y.; Shmeeda, H.; La-Beck, N.M.; Tahover, E.; Berger, R.; Gabizon, A.A. Pegylated Liposomal Mitomycin C Prodrug Enhances Tolerance of Mitomycin C: A Phase 1 Study in Advanced Solid Tumor Patients. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Warner, S.B.; Wagner, K.T.; Caster, J.M.; Zhang, T.; Ohana, P.; Gabizon, A.A.; Wang, A.Z. Preclinical Evaluation of Promitil, a Radiation-Responsive Liposomal Formulation of Mitomycin C Prodrug, in Chemoradiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 96, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, A.; Shmeeda, H.; Tahover, E.; Kornev, G.; Patil, Y.; Amitay, Y.; Ohana, P.; Sapir, E.; Zalipsky, S. Development of Promitil®, a Lipidic Prodrug of Mitomycin c in PEGylated Liposomes: From Bench to Bedside. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®—The First FDA-Approved Nano-Drug: Lessons Learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Hennink, W.E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic Mesoporous Silica-Based Core/Shell Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9584–9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Smart Drug Delivery through DNA/Magnetic Nanoparticle Gates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, G.; Nairi, V.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Double Sequential Encrypted Targeting Sequence: A New Concept for Bone Cancer Treatment. Chem.—Eur. J. 2017, 23, 7174–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Manzano, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent Advances in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Antitumor Therapy: Our Contribution. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Complex Bone Diseases: Bone Cancer, Bone Infection and Osteoporosis. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Concanavalin A-Targeted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Infection Treatment. Acta Biomater. 2019, 96, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Nanoparticles to Knockdown Osteoporosis-Related Gene and Promote Osteogenic Marker Expression for Osteoporosis Treatment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Benito, M.; Mulero, F.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Osteoporosis Remission and New Bone Formation with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled Growth of Monodisperse Silica Spheres in the Micron Size Range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, P.P.; Jaroniec, M. Renaissance of Stöber Method for Synthesis of Colloidal Particles: New Developments and Opportunities. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 838–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfee, P.N.; Lin, Y.S.; Dunphy, D.R.; Muñiz, A.J.; Butler, K.S.; Humphrey, K.R.; Lokke, A.J.; Agola, J.O.; Chou, S.S.; Chen, I.M.; et al. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Supported Lipid Bilayers (Protocells) for Active Targeting and Delivery to Individual Leukemia Cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8325–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Abadeer, N.; Hurley, K.R.; Haynes, C.L. Ultrastable, Redispersible, Small, and Highly Organomodified Mesoporous Silica Nanotherapeutics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20444–20457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, G.; Biederbick, W.; Woschée, U.; Theisohn, M.; Klaus, W. Sensitive and Convenient High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Method for the Determination of Mitomycin C in Human Plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1997, 698, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, Y.; Amitay, Y.; Ohana, P.; Shmeeda, H.; Gabizon, A. Targeting of Pegylated Liposomal Mitomycin-C Prodrug to the Folate Receptor of Cancer Cells: Intracellular Activation and Enhanced Cytotoxicity. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Ibrahim, I.T. Carbodiimide Chemistry: Recent Advances. Chem. Rev. 1981, 81, 589–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a Strategy for Improving Nanoparticle-Based Drug and Gene Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nieto, A.; Colilla, M.; Balas, F.; Vallet-Regí, M. Surface Electrochemistry of Mesoporous Silicas as a Key Factor in the Design of Tailored Delivery Devices. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5038–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Manzano, M.; Cabañas, V.; Vallet-Regi, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Engineered for Ultrasound-Induced Uptake by Cancer Cells. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6402–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauda, V.; Argyo, C.; Bein, T. Impact of Different PEGylation Patterns on the Long-Term Bio-Stability of Colloidal Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8693–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bu, W.; Guo, L.; Chen, Y. The Effect of PEGylation of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on Nonspecific Binding of Serum Proteins and Cellular Responses. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR Effect for Macromolecular Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors: Improvement of Tumor Uptake, Lowering of Systemic Toxicity, and Distinct Tumor Imaging in Vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H. The 35th Anniversary of the Discovery of EPR Effect: A New Wave of Nanomedicines for Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery-Personal Remarks and Future Prospects. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Redox-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment: Recent Updates. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Colilla, M.; Nieto, A. Functionalization Degree of SBA-15 as Key Factor to Modulate Sodium Alendronate Dosage. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 116, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabanas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Ultrasound-Responsive Drug Carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AbouAitah, K.; Lojkowski, W. Delivery of Natural Agents by Means of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres as a Promising Anticancer Strategy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sample | % PEG:MSNPs (Precursor) | m PEG (mg) | m MSNPs (mg) | % PEG (Final Composition) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSNP-PEG10 | 10 | 1.5 | 15 | 1.91 |
| MSNP-PEG20 | 20 | 3 | 15 | 2.82 |
| MSNP-PEG30 | 30 | 4.5 | 15 | 2.97 |
| MSNP-PEG40 | 40 | 6 | 15 | 5.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manzano, M.; Gabizón, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Characterization of a Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Formulation Loaded with Mitomycin C Lipidic Prodrug (MLP) and In Vitro Comparison with a Clinical-Stage Liposomal Formulation of MLP. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071483
Manzano M, Gabizón A, Vallet-Regí M. Characterization of a Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Formulation Loaded with Mitomycin C Lipidic Prodrug (MLP) and In Vitro Comparison with a Clinical-Stage Liposomal Formulation of MLP. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(7):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071483
Chicago/Turabian StyleManzano, Miguel, Alberto Gabizón, and María Vallet-Regí. 2022. "Characterization of a Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Formulation Loaded with Mitomycin C Lipidic Prodrug (MLP) and In Vitro Comparison with a Clinical-Stage Liposomal Formulation of MLP" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 7: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071483
APA StyleManzano, M., Gabizón, A., & Vallet-Regí, M. (2022). Characterization of a Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Formulation Loaded with Mitomycin C Lipidic Prodrug (MLP) and In Vitro Comparison with a Clinical-Stage Liposomal Formulation of MLP. Pharmaceutics, 14(7), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071483







