Critical Analysis and Quality Assessment of Nanomedicines and Nanocarriers in Clinical Trials: Three Years of Activity at the Clinical Trials Office
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Type of Nanomedicines
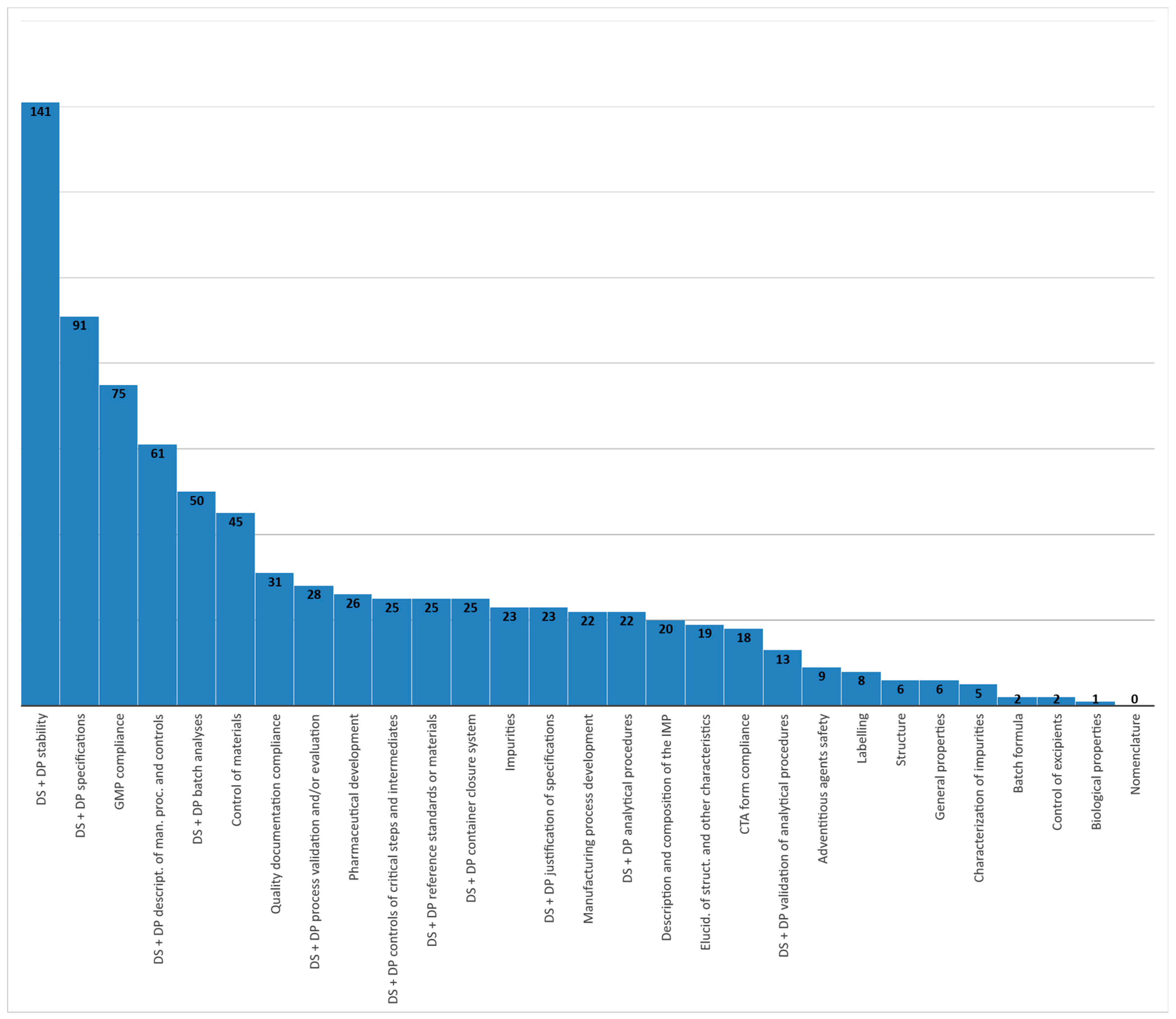
3.2. Quality Issues
3.2.1. Stability
3.2.2. Specifications
3.2.3. GMP Compliance
3.2.4. Description of the Manufacturing Process and Process Controls
3.2.5. Batch Analyses
3.2.6. Control of Materials
3.2.7. Quality Documentation Compliance
3.2.8. Process Validation and/or Evaluation
3.2.9. Pharmaceutical Development
3.2.10. Controls of Critical Steps and Intermediates
3.2.11. Reference Standards or Materials
3.2.12. Container Closure System
3.2.13. Impurities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Code | Description | Nanomedicine-Related Term | Analytical Method Confirming Nanoscale Dimension | Pharmaceutical Form | Study Phase | Therapeutic Area | Active Substance of Chemical Origin | Active Substance of Biological/Biotechnological Origin | Gene Therapy Medicinal Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N23 | RNA–peptide | Polymer | Yes | Solution for injection | I | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| complex | therapeutic | ||||||||
| N24 | Recombinant type 5 adenovirus vector | Nanocarrier | Yes | Concentrate for solution for infusion ev | III | Cancer | No | No | Yes |
| N25 | Pegylated protein | Polymer | No | Solution for injection | I/II | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| therapeutic | |||||||||
| N17 | Pegylated peptide | Polymer | No | Solution for infusion | III | Blood and lymphatic | Yes | No | No |
| therapeutic | diseases | ||||||||
| N26 | Recombinant | Nanocarrier | No | Solution for infusion ev | III | Blood and lymphatic | No | No | Yes |
| adeno-associated virus | diseases | ||||||||
| vector serotype 5 | |||||||||
| N27 | Monoclonal antibody conjugated to a fluorochrome through a linker | Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) | No | Concentrate for solution for injection | III | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| N28 | Monoclonal antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic agent through a linker | Antibody– | No | Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion | III | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| drug | |||||||||
| conjugate | |||||||||
| (ADC) | |||||||||
| N29 | Recombinant protein attached to an albumin binding moiety | Nanocarrier | No | Solution for injection | III | Hormonal diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N30 | Recombinant adenovirus serotype 155 viral vector | Nanocarrier | No | Suspension for injection | I | Respiratory tract diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N17 | Pegylated peptide | Polymer | No | Solution for injection | III | Eye diseases | Yes | No | No |
| therapeutic | |||||||||
| N17 | Pegylated peptide | Polymer | No | Solution for injection | III | Eye diseases | Yes | No | No |
| therapeutic | |||||||||
| N7 | Pegylated enzyme | Polymer | No | Concentrate for solution for infusion | III | Body processes—genetic phenomena | No | Yes | No |
| therapeutic | |||||||||
| N31 | Recombinant adeno-associated viral vector | Nanocarrier | Yes | Concentrate for solution for infusion | I/II | Congenital, hereditary, and neonatal diseases and abnormalities | No | No | Yes |
| N32 | Liposomal adjuvant | Liposome | Yes | Powder for solution for injection | II | Respiratory tract diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N33 | Beads coated with the active ingredient | Nanocarrier | No | Soft capsule | II | Immune system diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N34 | Pegylated recombinant protein | Polymer | No | Powder for solution for injection | II | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| therapeutic | |||||||||
| N35 | Recombinant adeno virus vector serotype 26 | Nanocarrier | Yes | Solution for injection | III | Virus diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N36 | Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector serotype 2 | Nanocarrier | No | Solution for injection | I/II | Blood and lymphatic diseases | No | No | Yes |
| N37 | Pegylated peptide | Polymer | No | Solution for injection | II | Hormonal diseases | Yes | No | No |
| therapeutic | |||||||||
| N38 | Pegylated enzyme | Polymer | No | Concentrate for solution for infusion ev | III | Congenital, hereditary, and neonatal diseases and abnormalities | No | Yes | No |
| Therapeutic | |||||||||
| N39 | Liposome-based adjuvant | Liposome | Yes | Powder for solution for injection | II | Virus diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N28 | Monoclonal antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic agent through a linker | Antibody– | No | Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion | III | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| drug | |||||||||
| conjugate | |||||||||
| (ADC) | |||||||||
| N28 | Monoclonal antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic agent through a linker | Antibody– | No | Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion | III | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| drug | |||||||||
| conjugate | |||||||||
| (ADC) |
| Code | Description | Nanomedicine-Related Term | Analytical Method Confirming Nanoscale Dimension | Pharmaceutical Form | Study Phase | Therapeutic Area | Active Substance of Chemical Origin | Active Substance of Biological/Biotechnological Origin | Gene Therapy Medicinal Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N40 | Monoclonal antibody | Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) | No | Powder for solution for injection | II | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| conjugated to a | |||||||||
| cytotoxic agent through | |||||||||
| a linker | |||||||||
| N41 | Plasmid vector | Nanocarrier | No | Solution for injection | II | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| N42 | Antibody conjugated with a biopolymer | Polymer therapeutic | No | Solution for injection | II | Eye diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N43 | Adeno-associated virus serotype 9 vector | Nanocarrier | No | Concentrate for solution for infusion ev | III | Nervous system diseases | No | No | Yes |
| N44 | Monoclonal antibody | Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) | Yes | Concentrate for solution for infusion | III | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| conjugated to a | |||||||||
| cytotoxic agent through | |||||||||
| a linker | |||||||||
| N45 | Monoclonal antibody | Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) | No | Powder for solution for infusion | I | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| conjugated to a | |||||||||
| cytotoxic agent through | |||||||||
| a linker | |||||||||
| N46 | Monoclonal antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic agent through a linker | Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) | No | Concentrate for solution for infusion | III | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| N7 | Pegylated enzyme | Polymer | No | Concentrate for solution for infusion | III | Body processes—genetic phenomena | No | Yes | No |
| therapeutic | |||||||||
| N47 | Pegylated oligonucleotide | Polymer therapeutic | No | Solution for injection | III | Eye diseases | Yes | No | No |
| N48 | Adenoviral vector | Nanocarrier | No | Suspension for injection | I | Virus diseases | Yes | Yes | No |
| N34 | Pegylated recombinant protein | Polymer therapeutic | No | Powder for solution for injection | III | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| N49 | Trivalent nanobody | Nanobody | No | Solution for infusion ev | II | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| N50 | Pegylated monoclonal antibody | Polymer therapeutic | No | Powder for solution for infusion ev | III | Immune system processes | No | Yes | No |
| N51 | Liposomal formulation | Liposome | Yes | Powder for nebulization solution | II | Virus diseases | Yes | No | No |
| N52 | Monoclonal antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic agent through a linker | Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) | No | Powder for solution for infusion ev | II | Cancer | No | Yes | No |
| N53 | Liposome suspension | Liposome | No | Inhalation suspension | III | Respiratory tract diseases | Yes | No | No |
| N54 | Adenoviral vector | Nanocarrier | Yes | Solution for injection | III | Respiratory tract diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N42 | Antibody conjugated with a biopolymer | Polymer therapeutic | No | Solution for injection | III | Eye diseases | No | Yes | No |
| N53 | Liposome suspension | Liposome | No | Inhalation suspension | III | Respiratory tract diseases | Yes | No | No |
| Classification Label of Quality Issues | Totals Per Classification | |
|---|---|---|
| CTA Form Compliance | 18 | |
| Quality documentation compliance (IMPD, S-IMPD, SmPC, CE mark) | 31 | |
| GMP compliance: information about all manufacturers involved (drug substance, drug product) and evidence of GMP (manufacturing licenses/GMP certificates, QP declarations, CEPs provided) | 75 | |
| Drug Substance (DS) | ||
| General information | Nomenclature | 0 |
| Structure | 6 | |
| General properties | 6 | |
| Biological properties | 1 | |
| Manufacture | Description of manufacturing process and process controls | 42 |
| Control of materials | 45 | |
| Control of critical steps and intermediates | 15 | |
| Process validation and/or evaluation | 6 | |
| Manufacturing process development | 22 | |
| Characterization | Elucidation of structure and other characteristics | 19 |
| Impurities | 23 | |
| Control of drug substance | Specifications | 44 |
| Analytical procedures | 13 | |
| Validation of analytical procedures | 9 | |
| Batch analyses | 33 | |
| Justification of specification(s) | 12 | |
| Reference standards or materials | 20 | |
| Container closure system | 9 | |
| Stability | 57 | |
| Drug Product (DP) | ||
| Description and composition of the investigational medicinal product | 20 | |
| Pharmaceutical development | 26 | |
| Manufacture | Batch formula | 2 |
| Description of manufacturing process and process controls | 19 | |
| Controls of critical steps and intermediates | 10 | |
| Process validation and/or evaluation | 22 | |
| Control of excipients | 2 | |
| Control of drug product | Specifications | 47 |
| Analytical procedures | 9 | |
| Validation of analytical procedures | 4 | |
| Batch analyses | 17 | |
| Characterization of impurities | 5 | |
| Justification of specification(s) | 11 | |
| Reference standards or materials | 5 | |
| Container closure system | 16 | |
| Stability | 84 | |
| Labeling | 8 | |
| Adventitious agents’ safety | 9 | |
| TOTAL | 822 | |
References
- Samrot, A.V.; Sean, T.C.; Kudaiyappan, T.; Bisyarah, U.; Mirarmandi, A.; Faradjeva, E.; Abubakar, A.; Ali, H.H.; Angalene, J.L.A.; Kumar, S.S. Production, characterization and application of nanocarriers made of polysaccharides, proteins, bio-polyesters and other biopolymers: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 3088–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminu, N.; Bello, I.; Umar, N.M.; Tanko, N.; Aminu, A.; Audu, M.M. The influence of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems in drug therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longo, J.P.F.; Muehlmann, L.A.; Calderón, M.; Stockmann, C.; Azevedo, R.B. Editorial: Nanomedicine in Cancer Targeting and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, M.; Lambe, U.P.; Brar, B.; Shah, I.; Manimegalaj, J.; Ranjan, K.; Rao, R.; Kumar, S.; Mahant, S.; Khurana, S.K.; et al. Nanotherapeutics: An insight into healthcare and multi-dimensional applications in medical sector of the modern world. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 97, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. Progress in Nanomedicine: Approved and Investigational Nanodrugs. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 742–755. [Google Scholar]
- Farjadian, F.; Ghasemi, A.; Gohari, O.; Roointan, A.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Nanopharmaceuticals and nanomedicines currently on the market: Challenges and opportunities. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa-Nguanmoo, N.; Namdee, K.; Khongkow, M.; Ruktanonchai, U.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.-J. Review: Development of SARS-CoV-2 immuno-enhanced COVID-19 vaccines with nano-platform. Nano Res. 2021, 15, 2196–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, J.P.F.; Muehlmann, L.A. How has nanomedical innovation contributed to the COVID-19 vaccine development? Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Brayden, D.J. Addressing the challenges to increase the efficiency of translating nanomedicine formulations to patients. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, M.; Caputo, F.; Metcalfe, S.; Tosi, G.; Spring, K.; Åslund, A.K.; Pottier, A.; Schiffelers, R.; Ceccaldi, A.; Schmid, R. Delivering the power of nanomedicine to patients today. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Đorđević, S.; Gonzalez, M.M.; Conejos-Sánchez, I.; Carreira, B.; Pozzi, S.; Acúrcio, R.C.; Satchi-Fainaro, R.; Florindo, H.F.; Vicent, M.J. Current hurdles to the translation of nanomedicines from bench to the clinic. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 500–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halwani, A.A. Development of Pharmaceutical Nanomedicines: From the Bench to the Market. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, B.; Gupta, R.; Gulati, M.; Singh, S.K.; Khursheed, R.; Gupta, M. The Why, Where, Who, How, and What of the vesicular delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 271, 101985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. EudraLex—Volume 10—Clinical Trials Guidelines. 2010. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/eudralex/vol-10_en (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Directive 2001/20/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 April 2001 on the Approximation of the Laws, Regulations and Administrative Provisions of the Member States Relating to the Implementation of Good Clinical Practice in the Conduct of Clinical Trials on Medicinal Products for Human Use. Available online: https://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2001:121:0034:0044:en:PDF (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- European Commission. Annex 13 to Volume 4, EU Guidelines to Good Manufacturing Practice, Medicinal Products for Human and Veterinary Use. 2010. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/default/files/files/eudralex/vol-4/2009_06_annex13.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Regulation (EU) No 536/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 April 2014 on Clinical Trials on Medicinal Products for Human Use, and Repealing Directive 2001/20/EC. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/default/files/files/eudralex/vol-1/reg_2014_536/reg_2014_536_en.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Italian Minister of Health Decree Dated 21 December 2007. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/atto/serie_generale/caricaDettaglioAtto/originario?atto.dataPubblicazioneGazzetta=2008-03-03&atto.codiceRedazionale=08A01360&elenco30giorni=false (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- AIFA. Osservatorio Nazionale Sperimentazione Clinica. 2022. Available online: https://www.aifa.gov.it/osservatorio-nazionale-sperimentazione-clinica (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Quirós Pesudo, L.; Balahur, A.; Gottardo, S.; Rasmussen, K.; Wagner, G.; Joanny, G.; Bremer-Hoffmann, S. Mapping Nano-medicine Terminology in the Regulatory Landscape; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018; ISBN 978-92-79-89872-3. [Google Scholar]
- AIFA. Rapporto Sulla Sperimentazione Clinica dei Medicinali in Italia. 2022. Available online: https://www.aifa.gov.it/rapporto-sulla-sperimentazione-clinica-dei-medicinali-in-italia (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Dri, D.A.; Marianecci, C.; Carafa, M.; Gaucci, E.; Gramaglia, D. Surfactants, Nanomedicines and Nanocarriers: A Critical Evaluation on Clinical Trials. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Annex 1: Clinical trial Application Form Request for Authorisation of a Clinical Trial on a Medicinal Product for Human Use to the Competent Authorities and for Opinion of the Ethics Committees in the Community. Revision 4 November 2009; Updated on 22 November 2019. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/system/files/2019-11/application-form_en_0.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Van Kan-Davelaar, H.E.; Van Hest, J.C.M.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M.; Koay, M.S.T. Using viruses as nanomedicines. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 171, 4001–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.H.; Han, H.-K. Nanomedicines: Current status and future perspectives in aspect of drug delivery and pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 48, 43–60, Correction in J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Titov, A.; Zmievskaya, E.; Ganeeva, I.; Valiullina, A.; Petukhov, A.; Rakhmatullina, A.; Miftakhova, R.; Fainshtein, M.; Rizvanov, A.; Bulatov, E. Adoptive Immunotherapy beyond CAR T-Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP)-Guideline on the Requirements for the Chemical and Pharmaceutical Quality Documentation Concerning Investigational Medicinal Products in Clinical Trials. 27 January 2022. EMA/CHMP/QWP/545525/2017 Rev. 2. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-requirements-chemical-pharmaceutical-quality-documentation-concerning-investigational_en-1.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP)-Guideline on the Requirements for Quality Documentation Concerning Biological Investigational Medicinal Products in Clinical Trials. 27 January 2022. EMA/CHMP/BWP/534898/2008 Rev. 2. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-requirements-quality-documentation-concerning-biological-investigational-medicinal_en-2.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- EudraCT. Available online: https://eudract.ema.europa.eu (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- AIFA. Aggiornamento dei Modelli Delle Lettere di Ttrasmissione e Della Documentazione da Sottomettere per l’Autorizzazione di Sperimentazioni Cliniche e Relativi Emendamenti Sostanziali. 2019. Available online: https://www.aifa.gov.it/documents/20142/0/comunicazione_agg_mod_SC-ES_2019_08_01.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
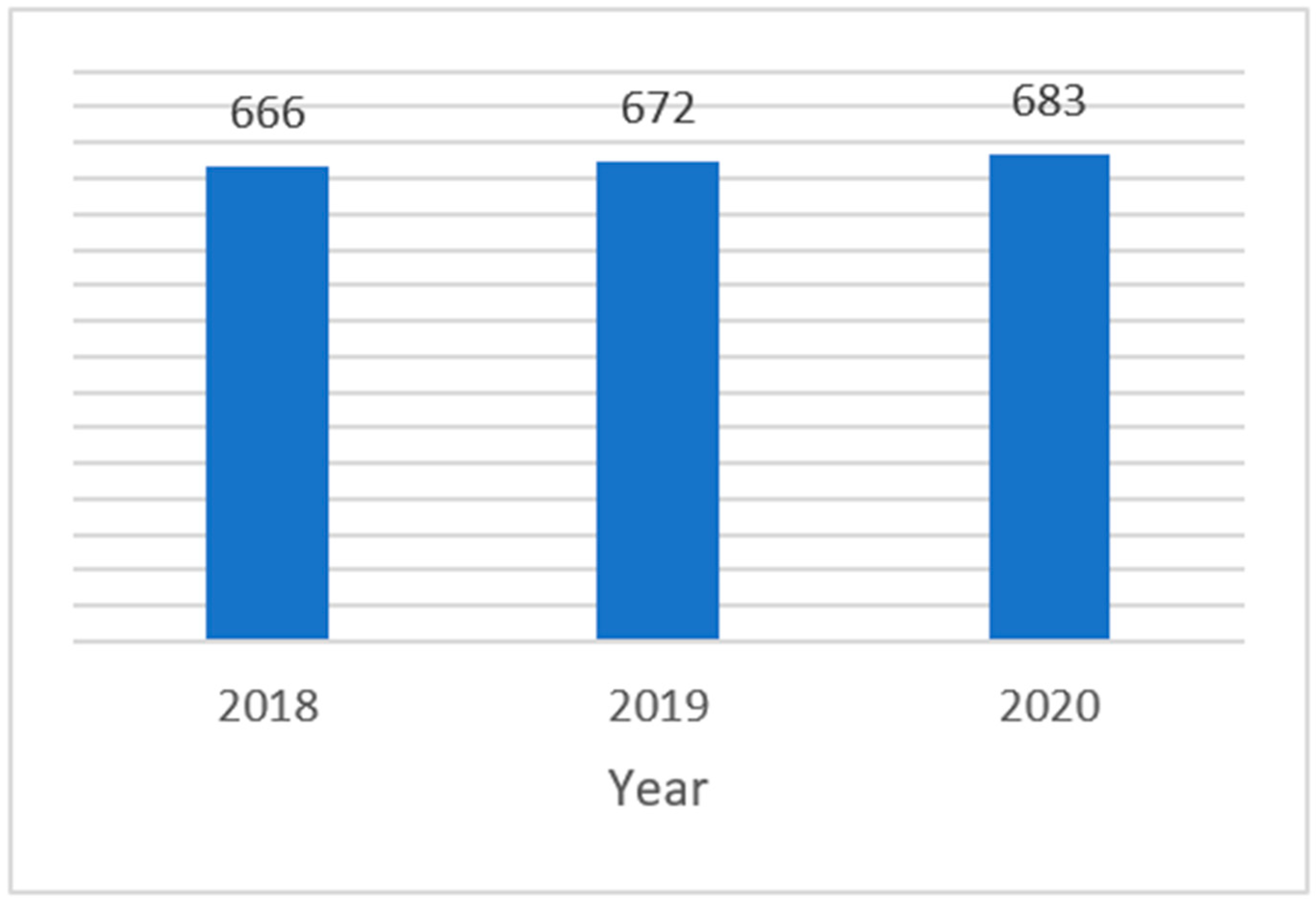
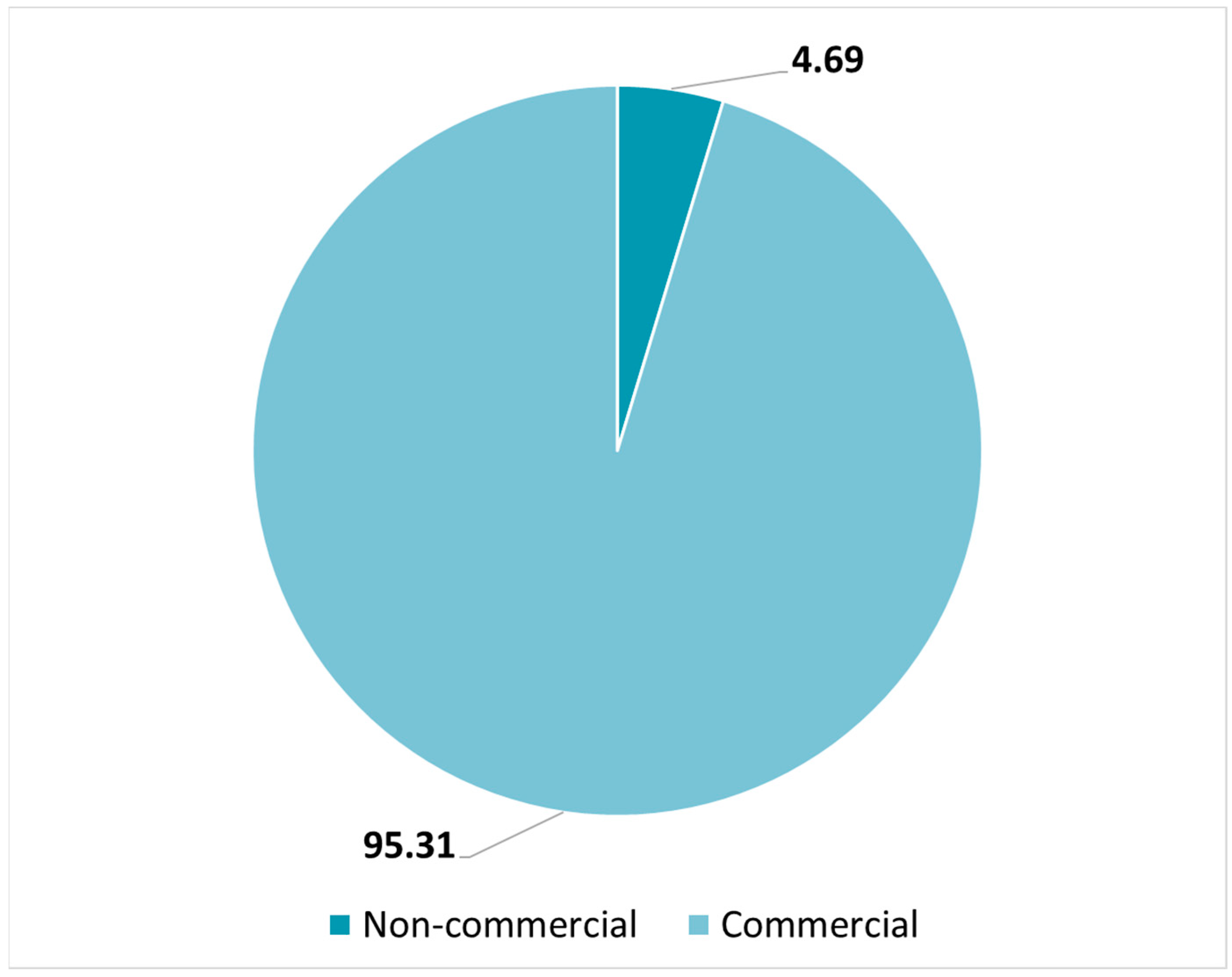
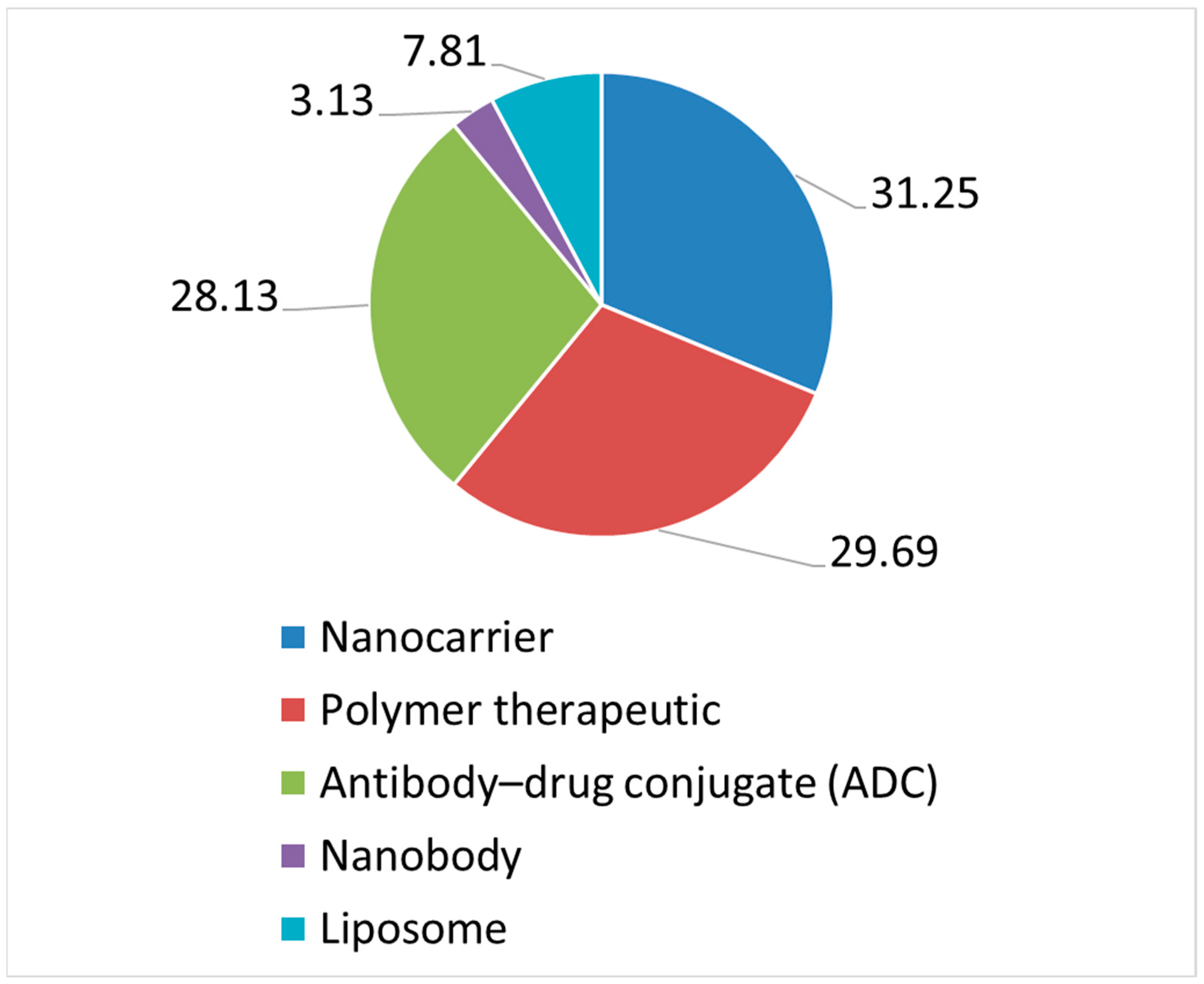
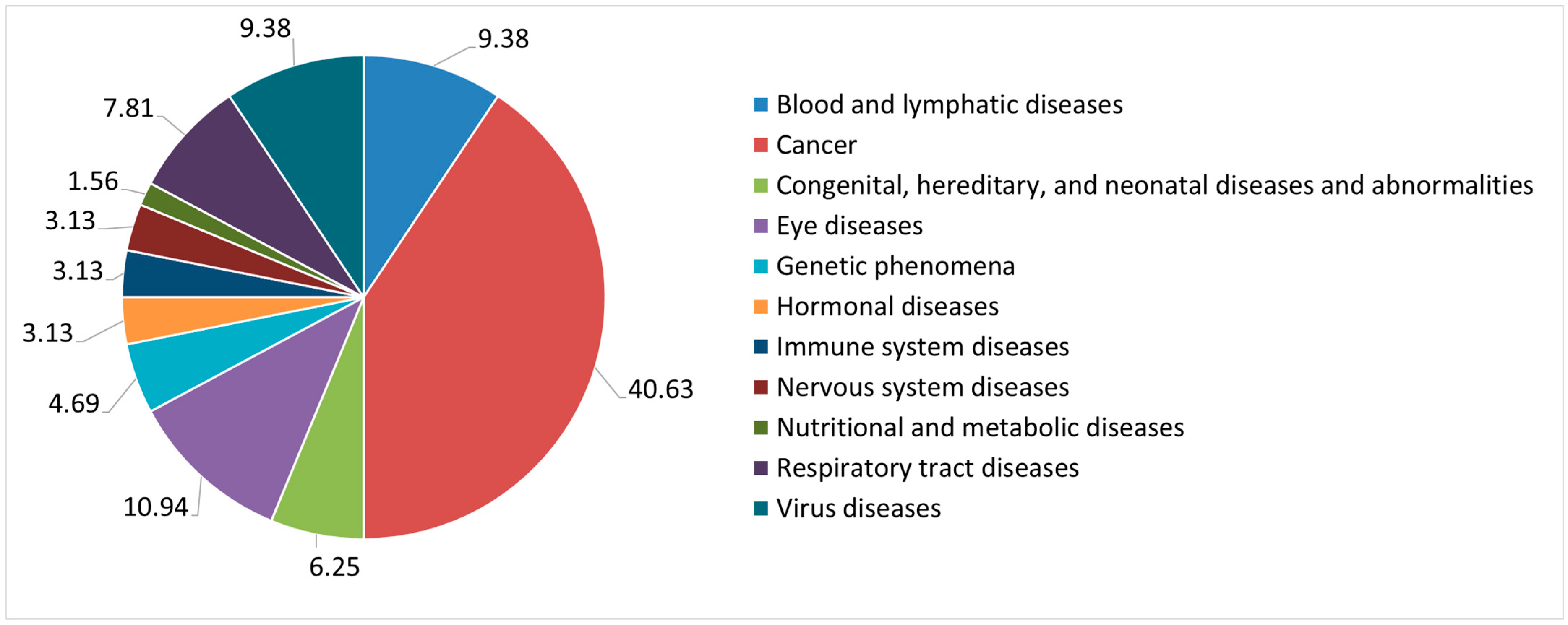
| Year | CTs Submitted | CTs Authorized | CTs in Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 716 | 666 | 433 |
| 2019 | 722 | 672 | 449 |
| 2020 | 815 | 683 | 359 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dri, D.A.; Gaucci, E.; Torrieri, I.; Carafa, M.; Marianecci, C.; Gramaglia, D. Critical Analysis and Quality Assessment of Nanomedicines and Nanocarriers in Clinical Trials: Three Years of Activity at the Clinical Trials Office. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071438
Dri DA, Gaucci E, Torrieri I, Carafa M, Marianecci C, Gramaglia D. Critical Analysis and Quality Assessment of Nanomedicines and Nanocarriers in Clinical Trials: Three Years of Activity at the Clinical Trials Office. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(7):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071438
Chicago/Turabian StyleDri, Diego Alejandro, Elisa Gaucci, Ilaria Torrieri, Maria Carafa, Carlotta Marianecci, and Donatella Gramaglia. 2022. "Critical Analysis and Quality Assessment of Nanomedicines and Nanocarriers in Clinical Trials: Three Years of Activity at the Clinical Trials Office" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 7: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071438
APA StyleDri, D. A., Gaucci, E., Torrieri, I., Carafa, M., Marianecci, C., & Gramaglia, D. (2022). Critical Analysis and Quality Assessment of Nanomedicines and Nanocarriers in Clinical Trials: Three Years of Activity at the Clinical Trials Office. Pharmaceutics, 14(7), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071438









