Biosynthetic Nanobubble-Mediated CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing of Cdh2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Bacterium Culture and Extraction of GVs
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of GVs-PEI-DNA (GPD)
2.4. In Vitro Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Transfection
2.5. sgRNA Sequences and Vector Construct
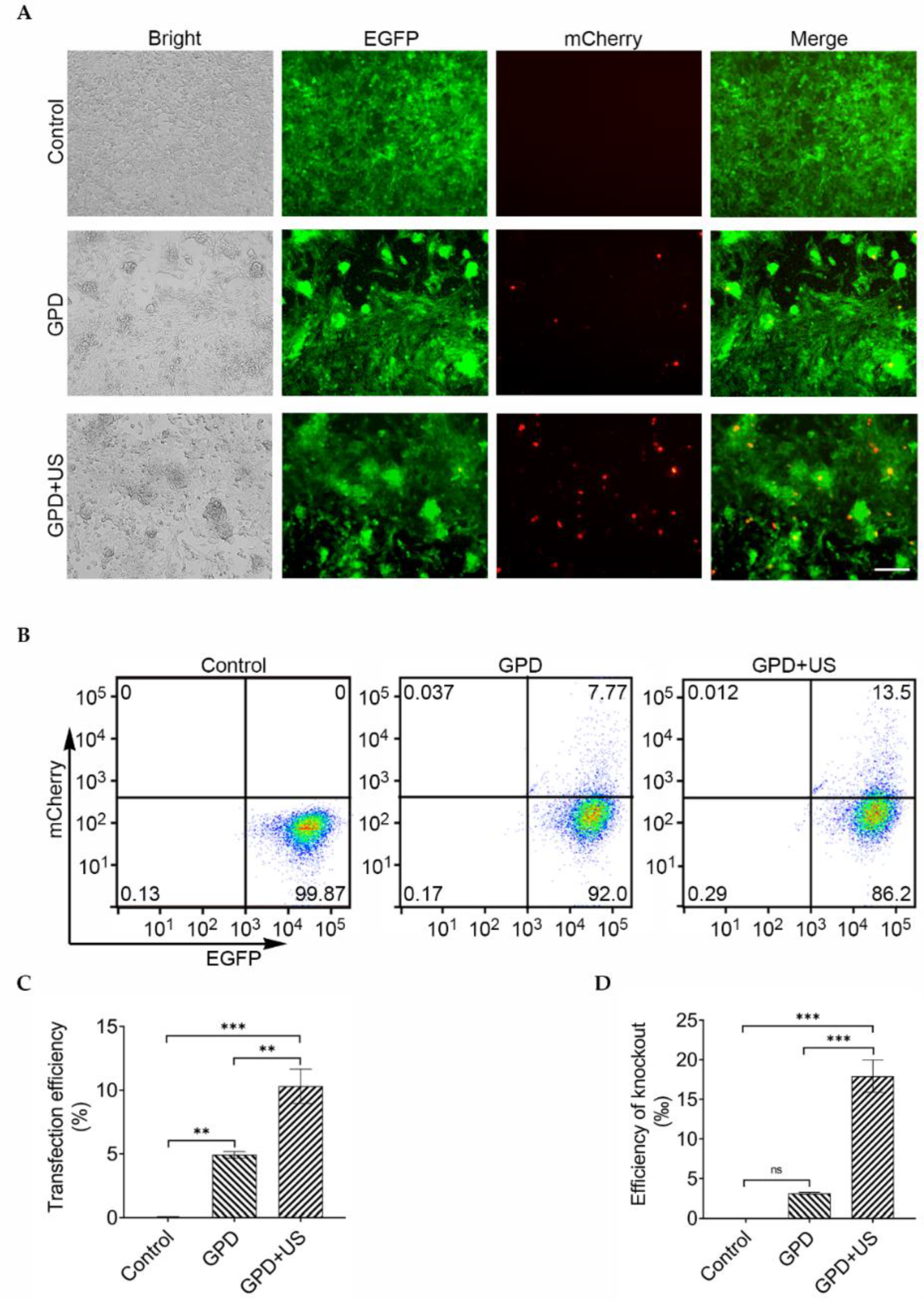
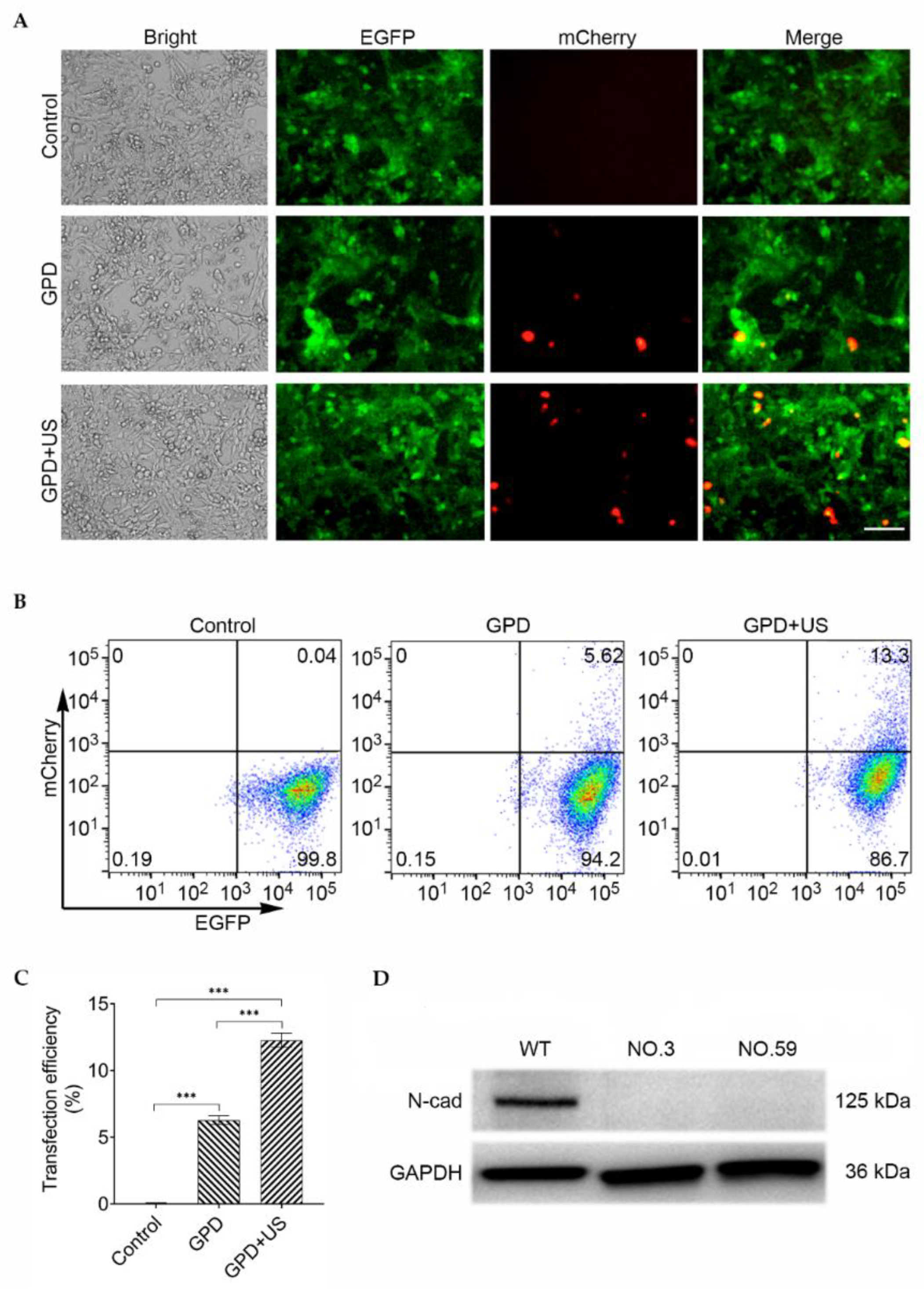
2.6. Determination of Gene Transfection and Editing Efficiencies
2.7. CCK-8 Assay
2.8. Western Blotting Assay
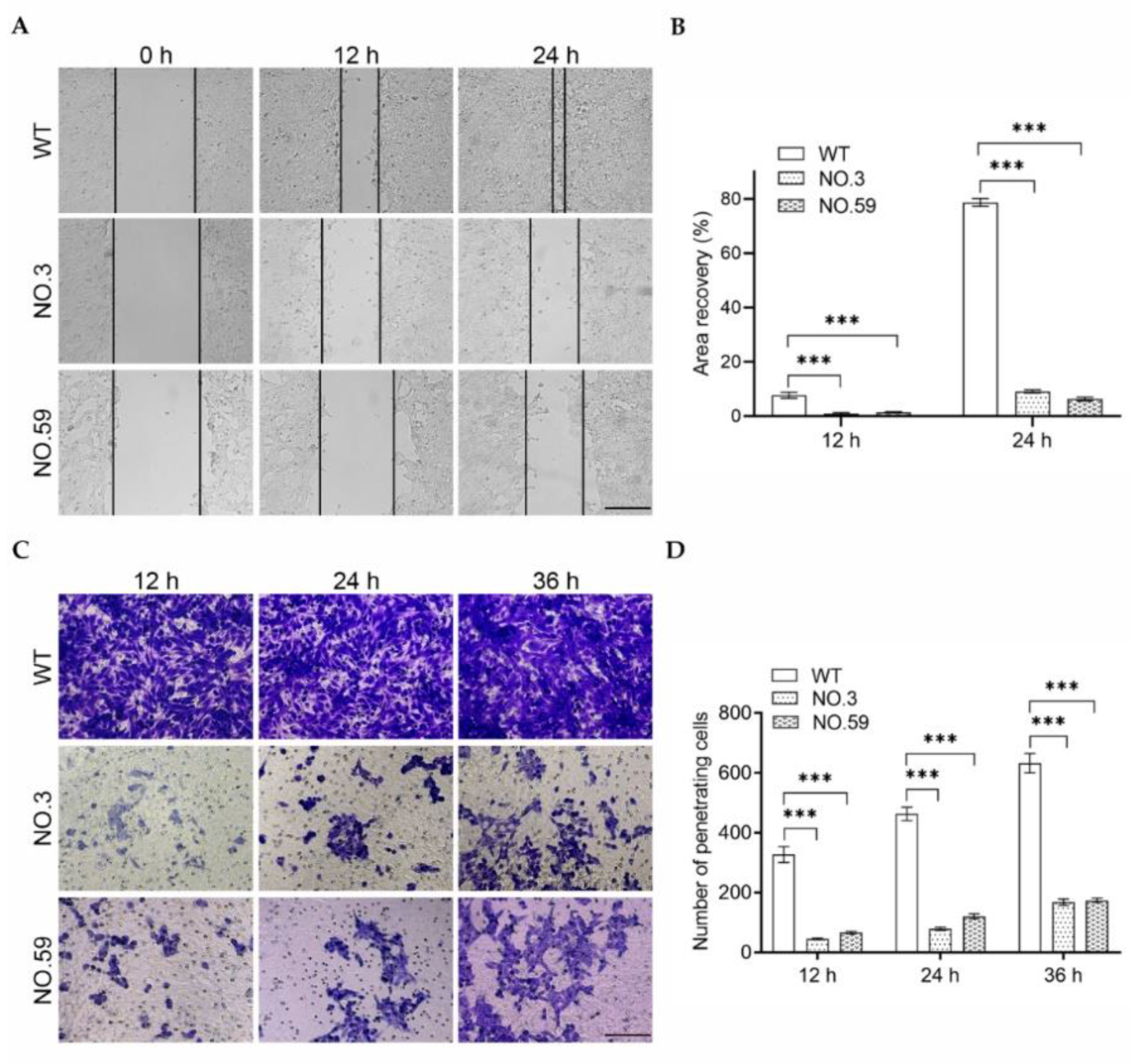
2.9. In Vitro Wound Healing Assay and Cell Migration Experiments
2.10. Animals and Tumor Model
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
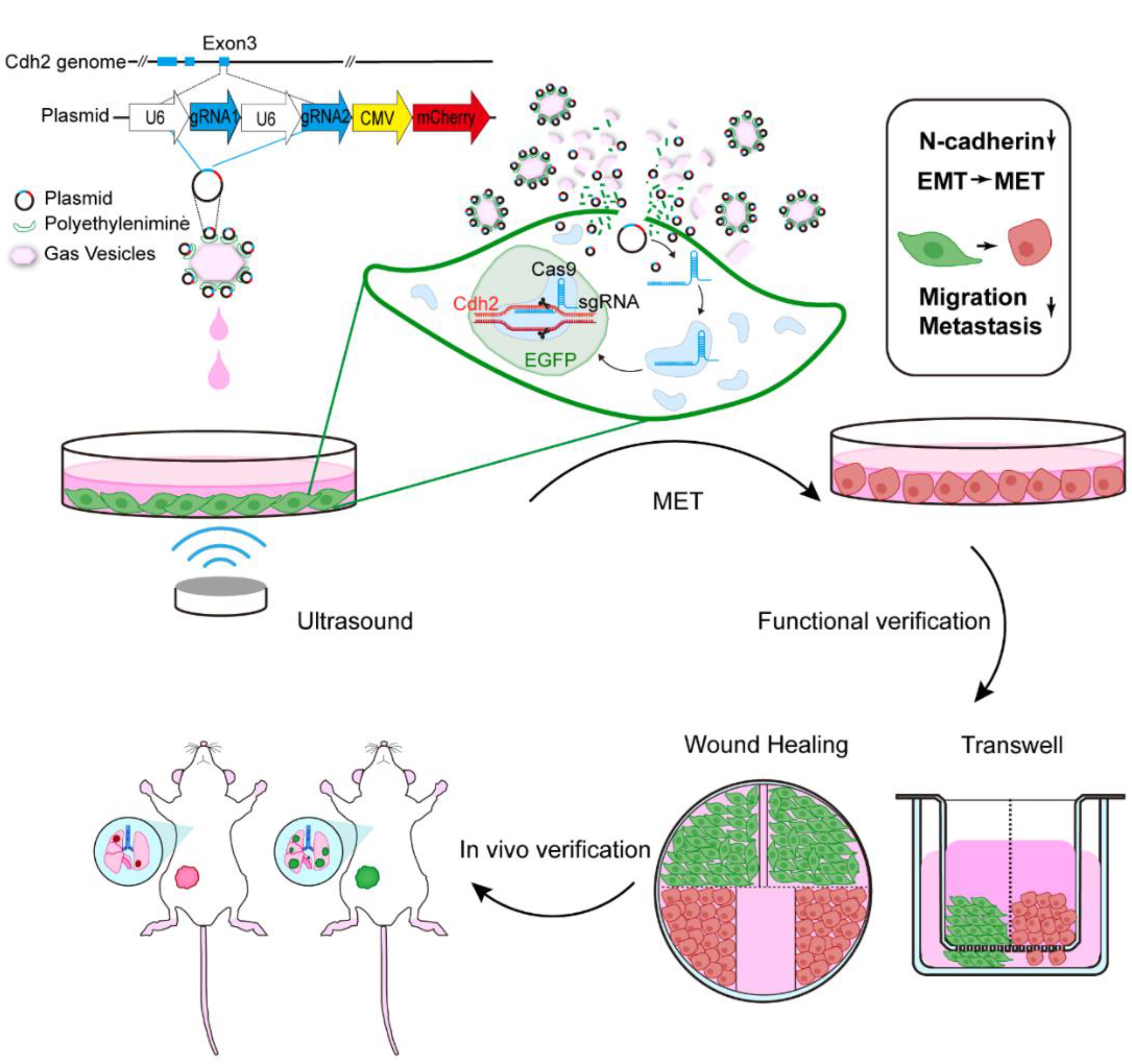
3.1. In Vitro Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Editing of EGFP
3.2. In Vitro Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Editing of Cdh2
3.3. Invasion Behavior Assay of Cdh2 KO Cells
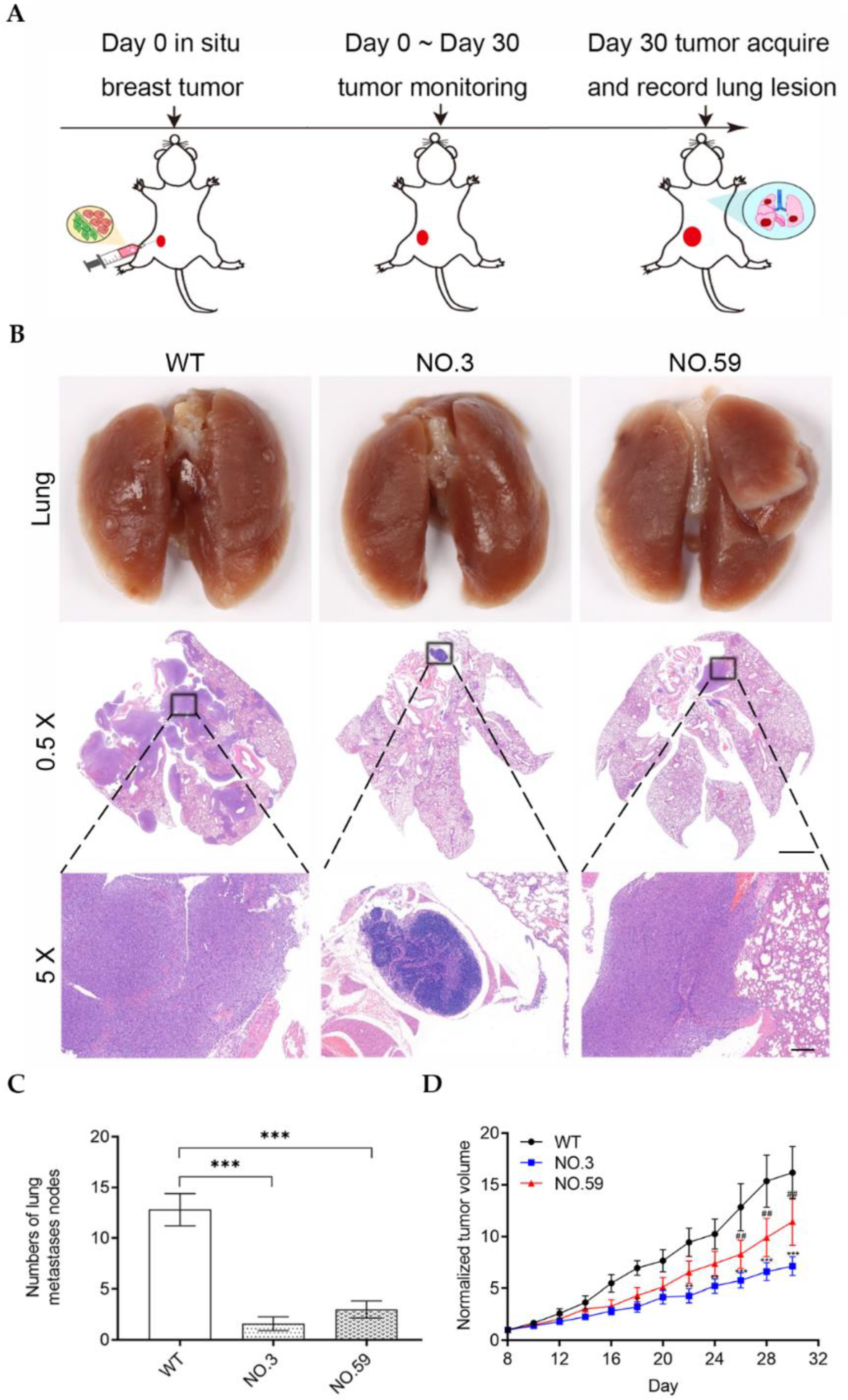
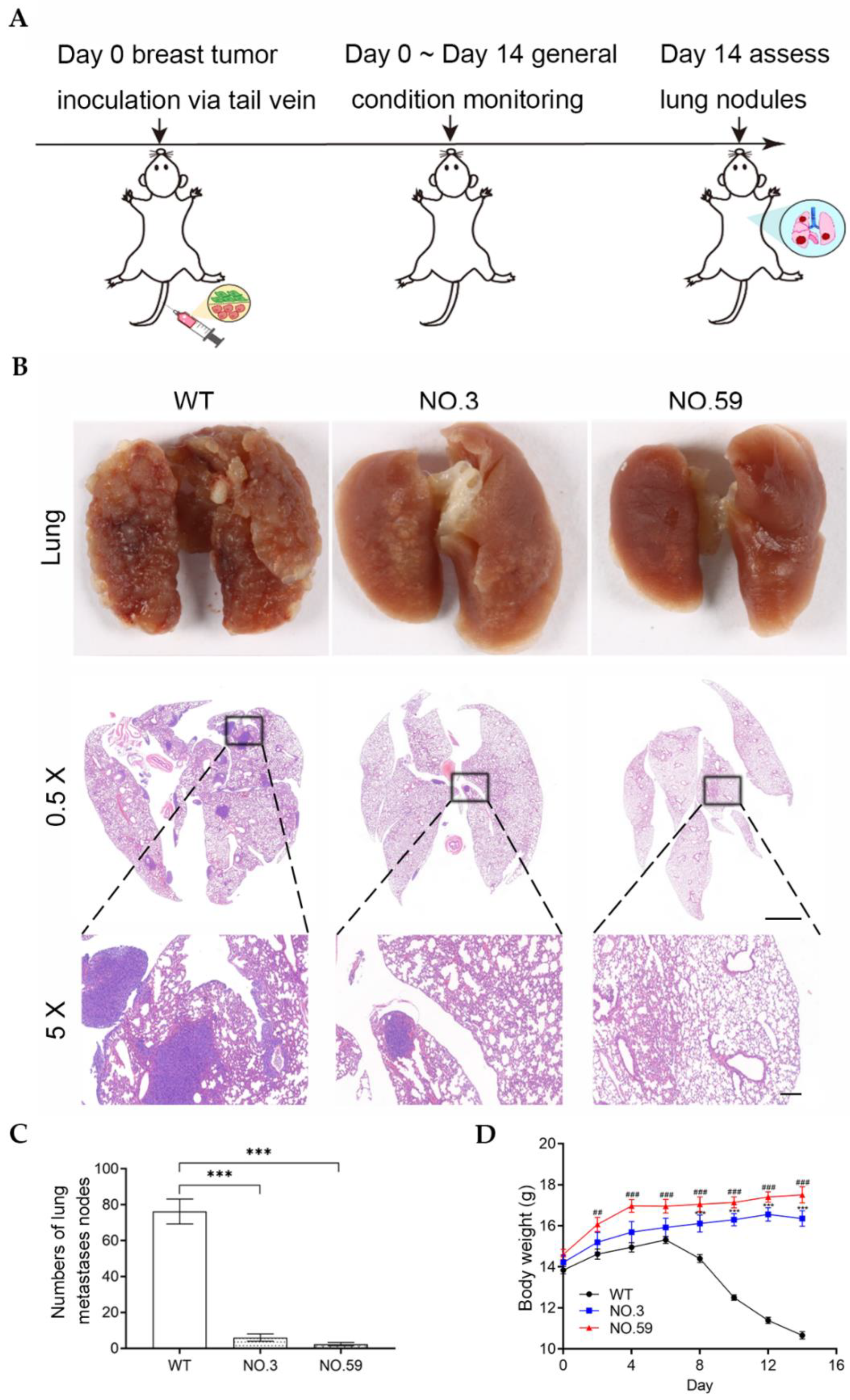
3.4. In Vivo Tumor Metastasis of Cdh2-Edited Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, D.; Cao, M.; Li, H.; He, S.; Chen, W. Cancer burden and trends in China: A review and comparison with Japan and South Korea. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.; Frei, R.; Lawson, K.R. The cytoplasmic domain of N-cadherin modulates MMP9 induction in oral squamous carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Kwiatkowski, N.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Xie, S.; Yuzugullu, H.; Von, T.; Li, H.; Lin, Z.; et al. CDK7-dependent transcriptional addiction in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, B.T.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Gilcrease, M.Z.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Lee, J.S.; Fridlyand, J.; Sahin, A.; Agarwal, R.; Joy, C.; et al. Characterization of a naturally occurring breast cancer subset enriched in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell characteristics. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4116–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Epithelial Mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, P.; Yang, L.; Esvelt, K.M.; Aach, J.; Guell, M.; DiCarlo, J.E.; Norville, J.E.; Church, G.M. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 2013, 339, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahel, D.K.; Mittal, A.; Chitkara, D. CRISPR/Cas System for genome editing: Progress and prospects as a therapeutic tool. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, S.; Hu, B.; Deng, Q.; Jiang, N.; Cui, J. Efficient gene therapy with a combination of ultrasoundtargeted microbubble destruction and PEI/DNA/NLS complexes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7685–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, F.; Wang, Y. Polyethyleneimine-anchored liposomes as scavengers for improving the efficiency of protein-bound uremic toxin clearance during dialysis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2022, 110, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Ren, P.; You, M.; Zhang, J.; Fang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yan, F.; Zheng, H.; et al. Localized delivery of shRNA against PHD2 protects the heart from acute myocardial infarction through ultrasound-targeted cationic microbubble destruction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Han, Z.; Shao, L.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation of in vivo antitumor effects of low-frequency ultrasound-mediated miRNA-133a microbubble delivery in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.L.; Rush, R.A. Non-viral gene therapy for neurological diseases, with an emphasis on targeted gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 157, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, R.K. Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction in gene therapy: A new tool to cure human diseases. Genes Dis. 2017, 4, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, F. Distribution, formation and regulation of gas vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, F. Haloarchaea and the formation of gas vesicles. Life 2015, 5, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.G.; Goodwill, P.W.; Neogy, A.; Yin, M.; Foster, F.S.; Schaffer, D.V.; Conolly, S.M. Biogenic gas nanostructures as ultrasonic molecular reporters. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, A.K. Haloarchaea: Worth exploring for their biotechnological potential. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, K.; Lin, S.; Boyer, E.; Simeonov, D.R.; Subramaniam, M.; Gate, R.E.; Haliburton, G.E.; Ye, C.J.; Bluestone, J.A.; Doudna, J.A.; et al. Generation of knock-in primary human T cells using Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10437–10442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L.; Su, B.; Mou, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. CRISPR-edited stem cells in a patient with HIV and acute lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangoul, H.; Altshuler, D.; Cappellini, M.D.; Chen, Y.S.; Domm, J.; Eustace, B.K.; Foell, J.; de la Fuente, J.; Grupp, S.; Handgretinger, R.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing for Sickle Cell Disease and beta-Thalassemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, A.; Fonteyne, L.; Giesert, F.; Hoppmann, P.; Meier, A.B.; Bozoglu, T.; Baehr, A.; Schneider, C.M.; Sinnecker, D.; Klett, K.; et al. Somatic gene editing ameliorates skeletal and cardiac muscle failure in pig and human models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, P.; Chen, C.; Kaminski, R.; Gordon, J.; Liao, S.; Robinson, J.A.; Smith, M.D.; Liu, H.; Sariyer, I.K.; Sariyer, R.; et al. CRISPR based editing of SIV proviral DNA in ART treated non-human primates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zincarelli, C.; Soltys, S.; Rengo, G.; Rabinowitz, J.E. Analysis of AAV serotypes 1–9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, P.S.; Meyerson, M. Targeted genomic rearrangements using CRISPR/Cas technology. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.R.; Geis, N.A.; Katus, H.A.; Bekeredjian, R. Ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction for drug and gene delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 1121–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, S.; Liang, X. Applications of micro/nanotechnology in ultrasound-based drug delivery and therapy for tumor. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 525–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjaminsen, R.V.; Mattebjerg, M.A.; Henriksen, J.R.; Moghimi, S.M.; Andresen, T.L. The possible “proton sponge” effect of polyethylenimine (PEI) does not include change in lysosomal pH. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Huang, S.; Yi, Y.; Bao, S. Ultrasound microbubble-mediated CRISPR/Cas9 knockout of C-erbB-2 in HEC-1A cells. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Gu, C.; Li, N.; Ying, Y.; Cao, L.F.; Xiao, Q.F.; Ni, D.; Zhuang, Y.B.; Zhang, Q. New biomarker for lung cancer—Focus on circSETD3. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.Y.; Kuang, X.Y.; Shao, N.; Wang, S.M.; Lin, Y. Downregulation of NPTX1 induces cell cycle progression through Wntβ-catenin signaling in breast cancer. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, R.; Luo, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, L.; Cai, J.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, F.; Liu, J. Biosynthetic Nanobubble-Mediated CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing of Cdh2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071382
Gao R, Luo Q, Li Y, Song L, Cai J, Xiong Y, Yan F, Liu J. Biosynthetic Nanobubble-Mediated CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing of Cdh2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(7):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071382
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ruru, Qiong Luo, Yang Li, Liming Song, Junnan (Stephen) Cai, Ying Xiong, Fei Yan, and Jianhua Liu. 2022. "Biosynthetic Nanobubble-Mediated CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing of Cdh2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 7: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071382
APA StyleGao, R., Luo, Q., Li, Y., Song, L., Cai, J., Xiong, Y., Yan, F., & Liu, J. (2022). Biosynthetic Nanobubble-Mediated CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing of Cdh2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis. Pharmaceutics, 14(7), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14071382







