Importance of Spray–Wall Interaction and Post-Deposition Liquid Motion in the Transport and Delivery of Pharmaceutical Nasal Sprays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review of Studies Evaluating Spray–Wall Interaction and Post-Deposition Liquid Motion
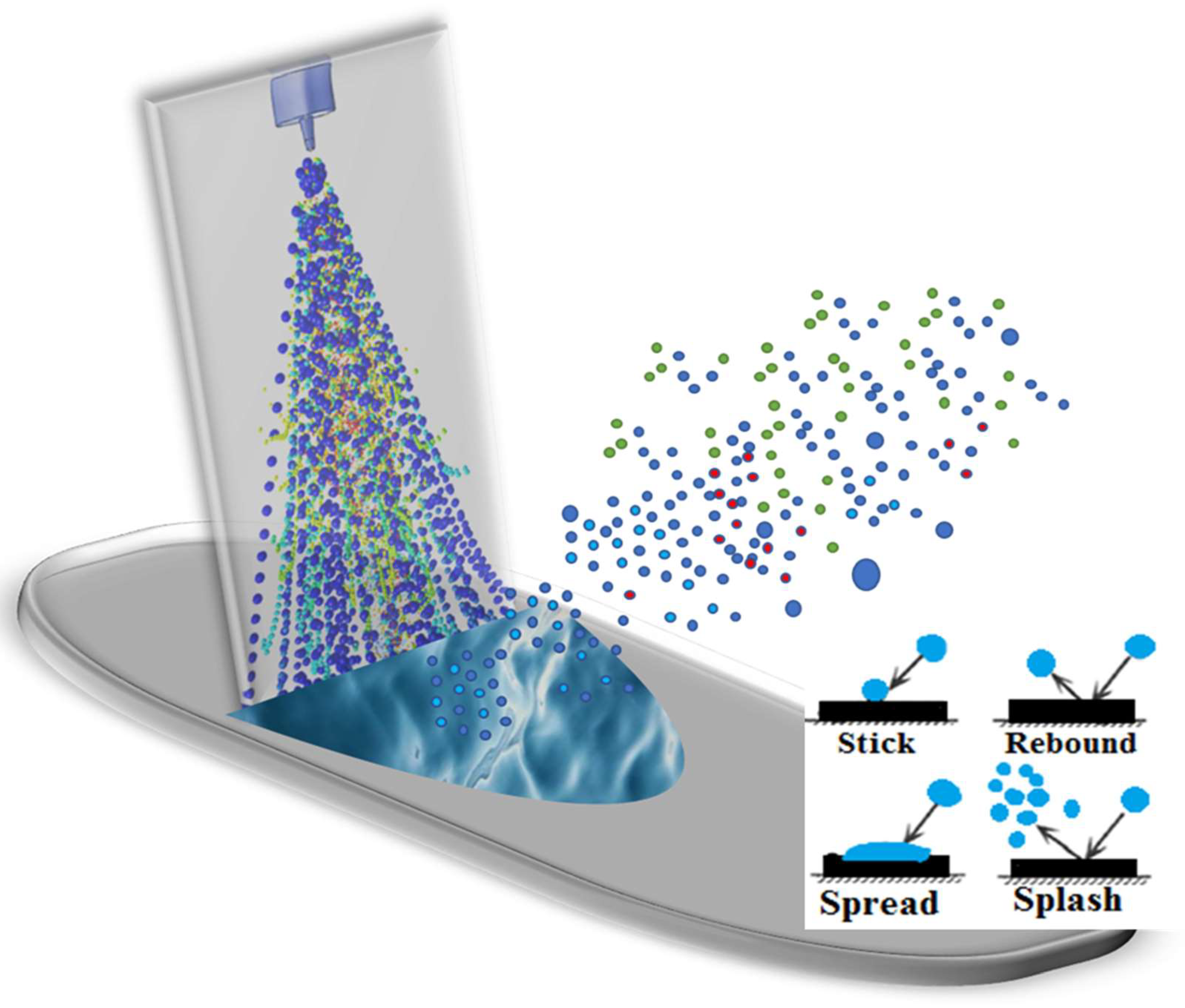
2.2. Spray–Wall Interaction (SWI) Model
2.3. Post-Deposition Liquid Motion (PDLM) Model
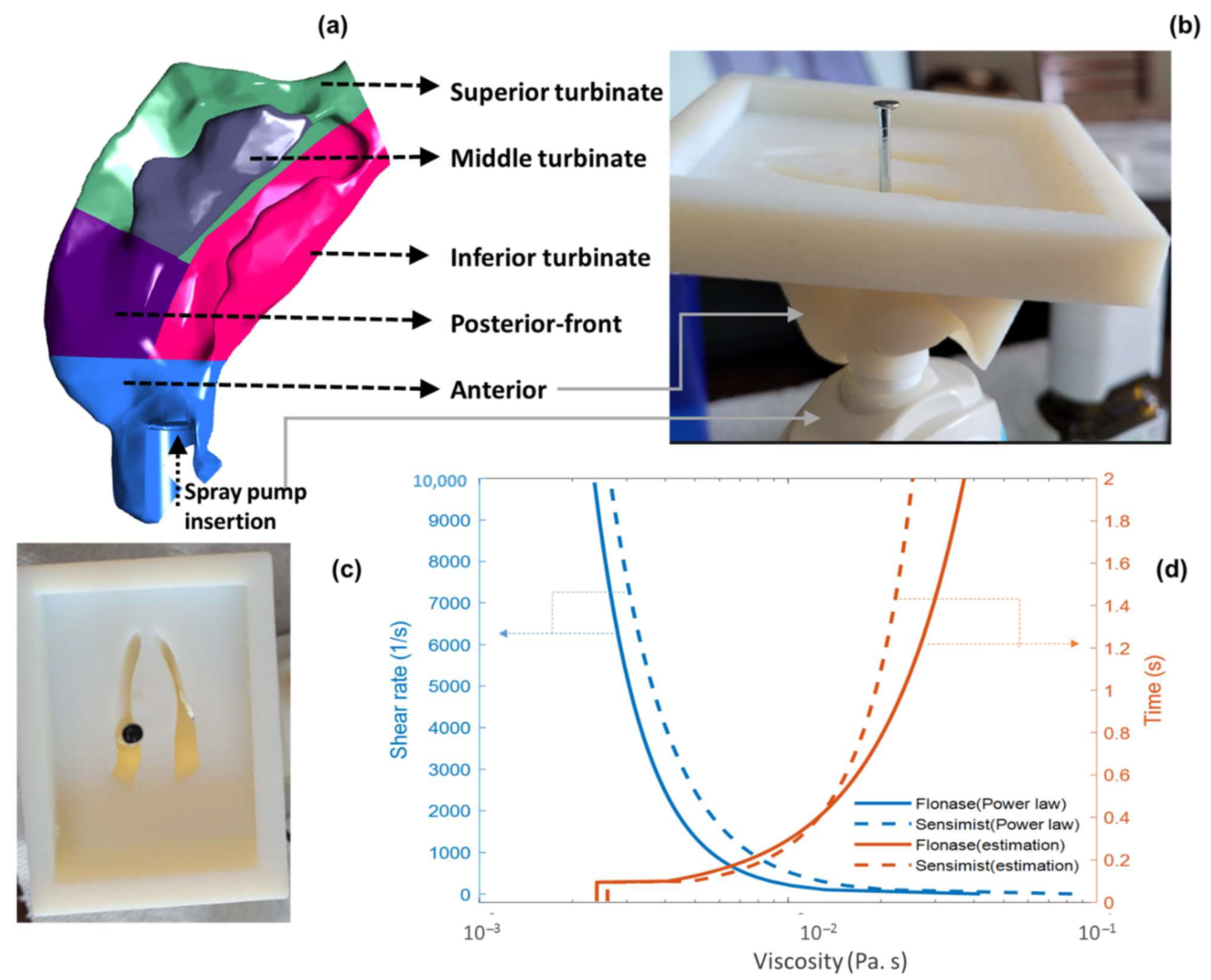
2.4. Nasal Airway Model
2.5. In Vitro Experimental Setup and Spray Delivery Measurements
2.6. CFD Simulation Setup with Specific Spray Parameters
2.7. Numerical Methodology
3. Results
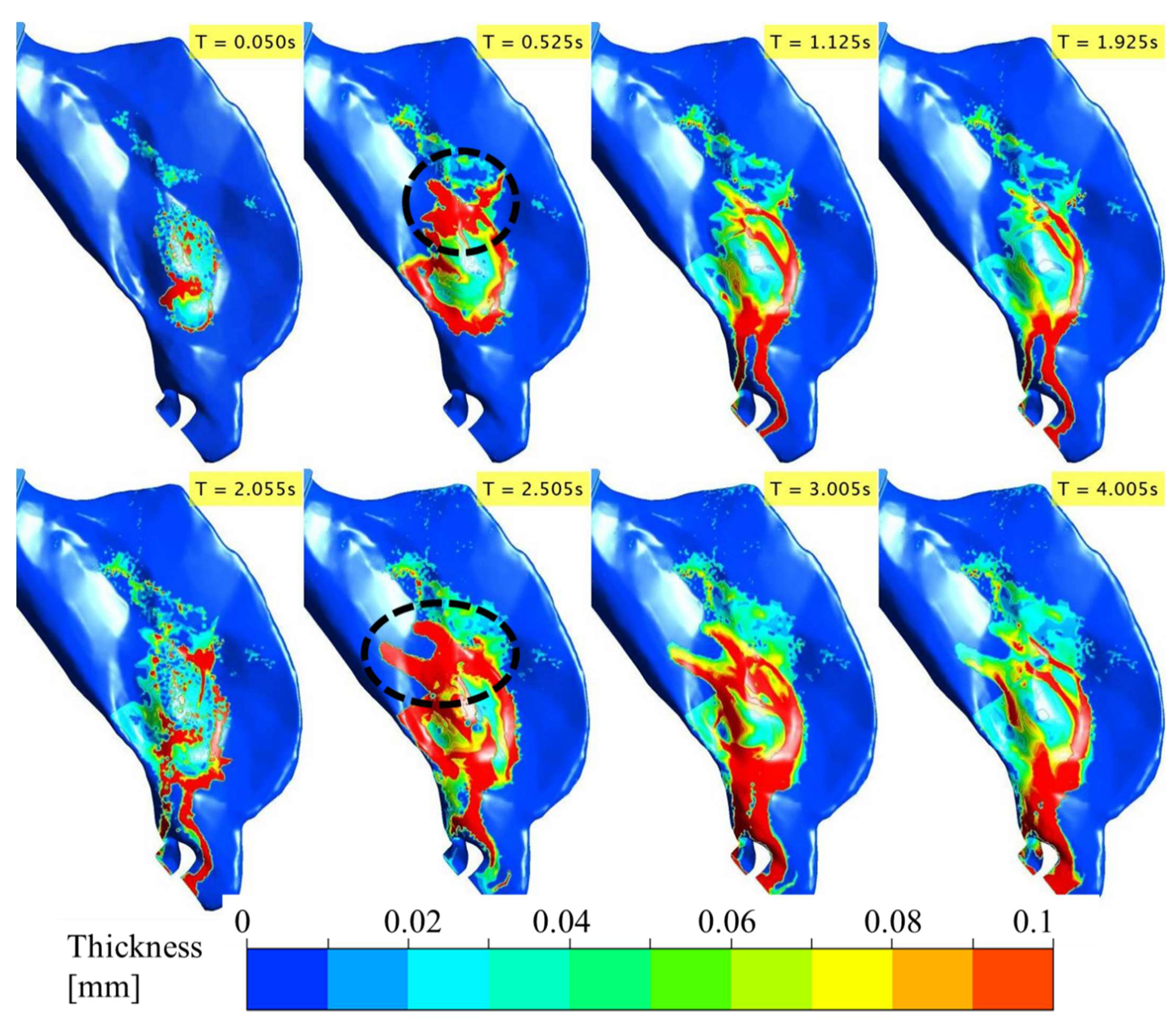
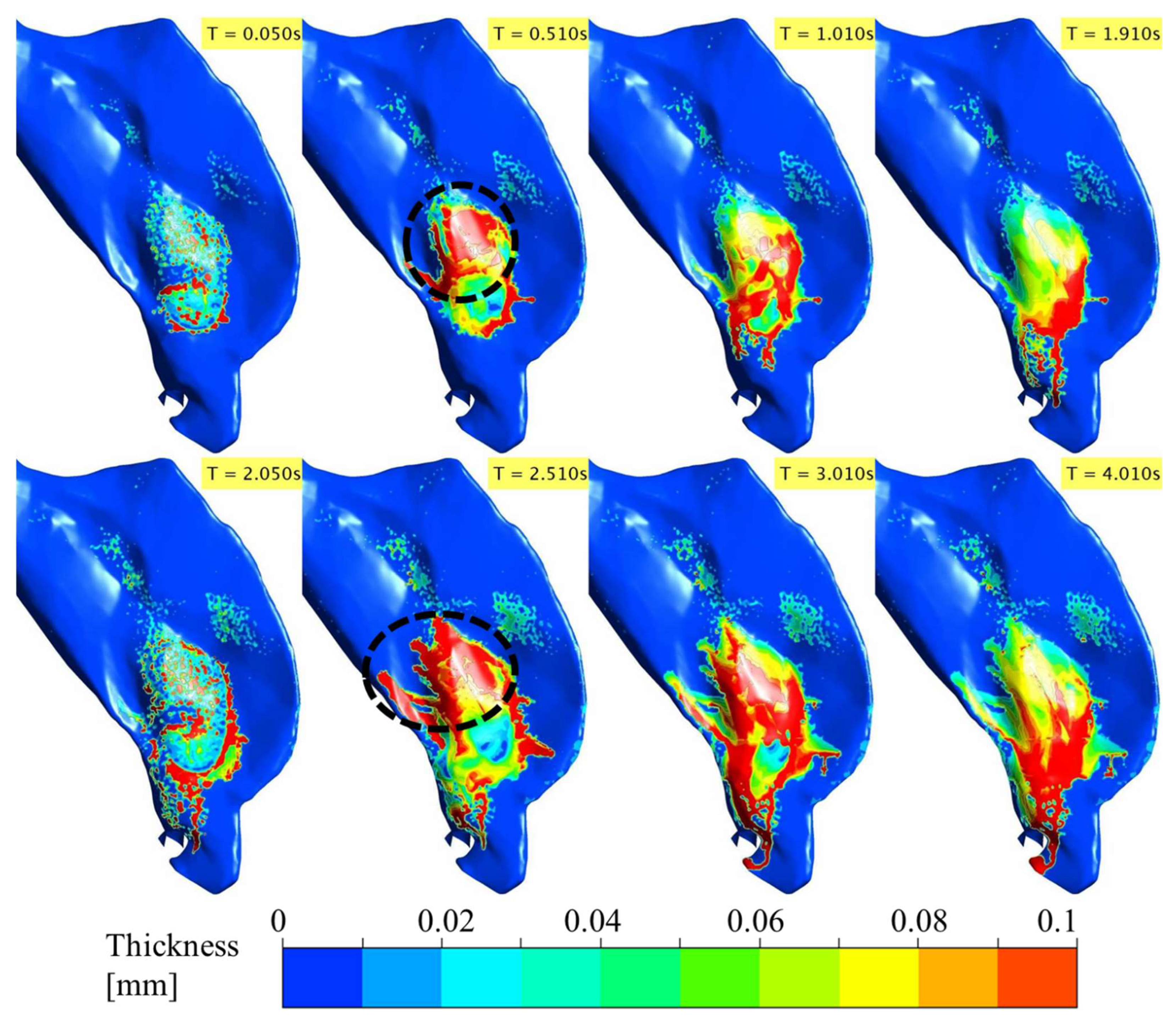
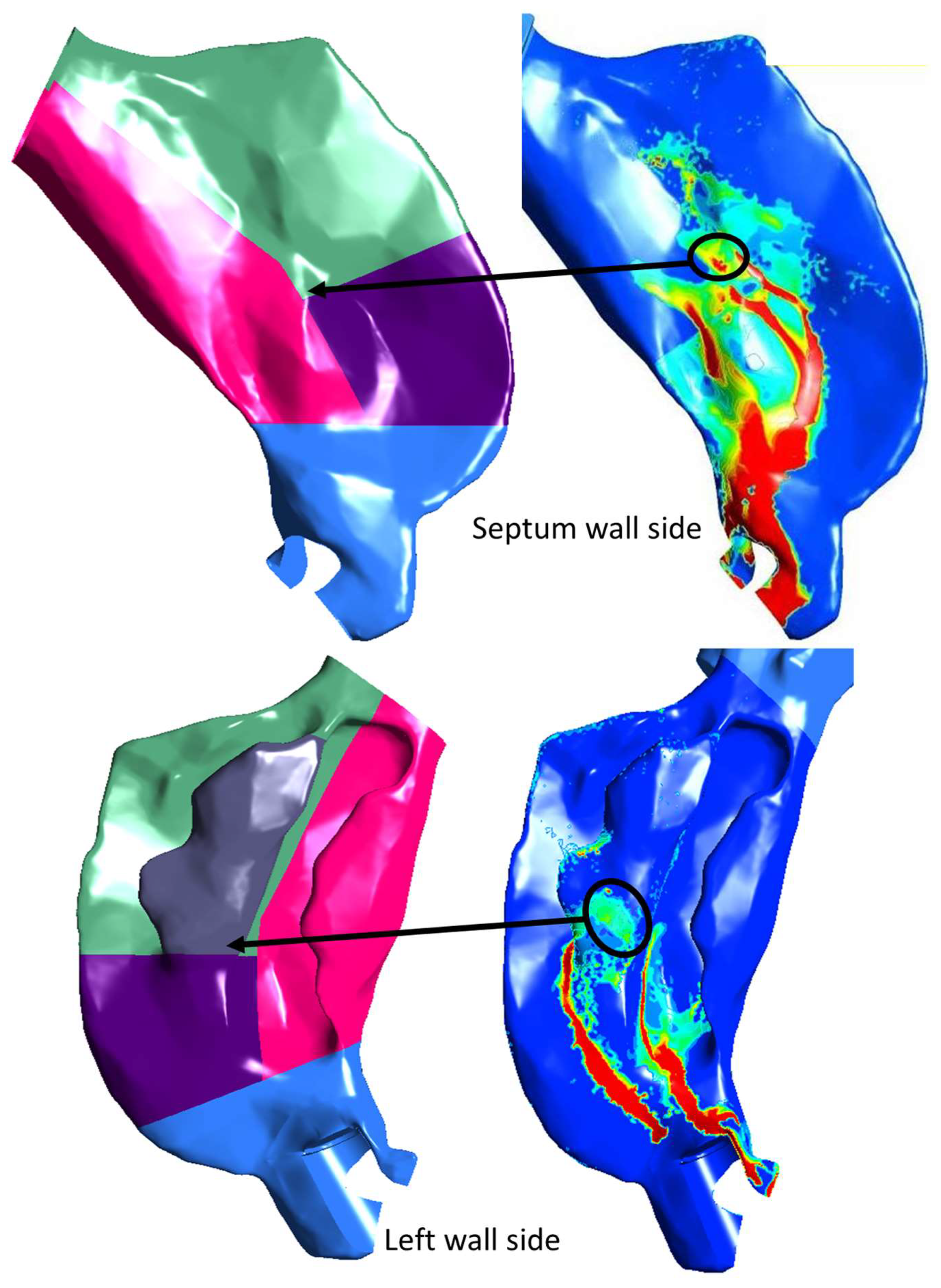
3.1. Spray–Wall Interaction and Post-Deposition Liquid Motion on the Nasal Surface
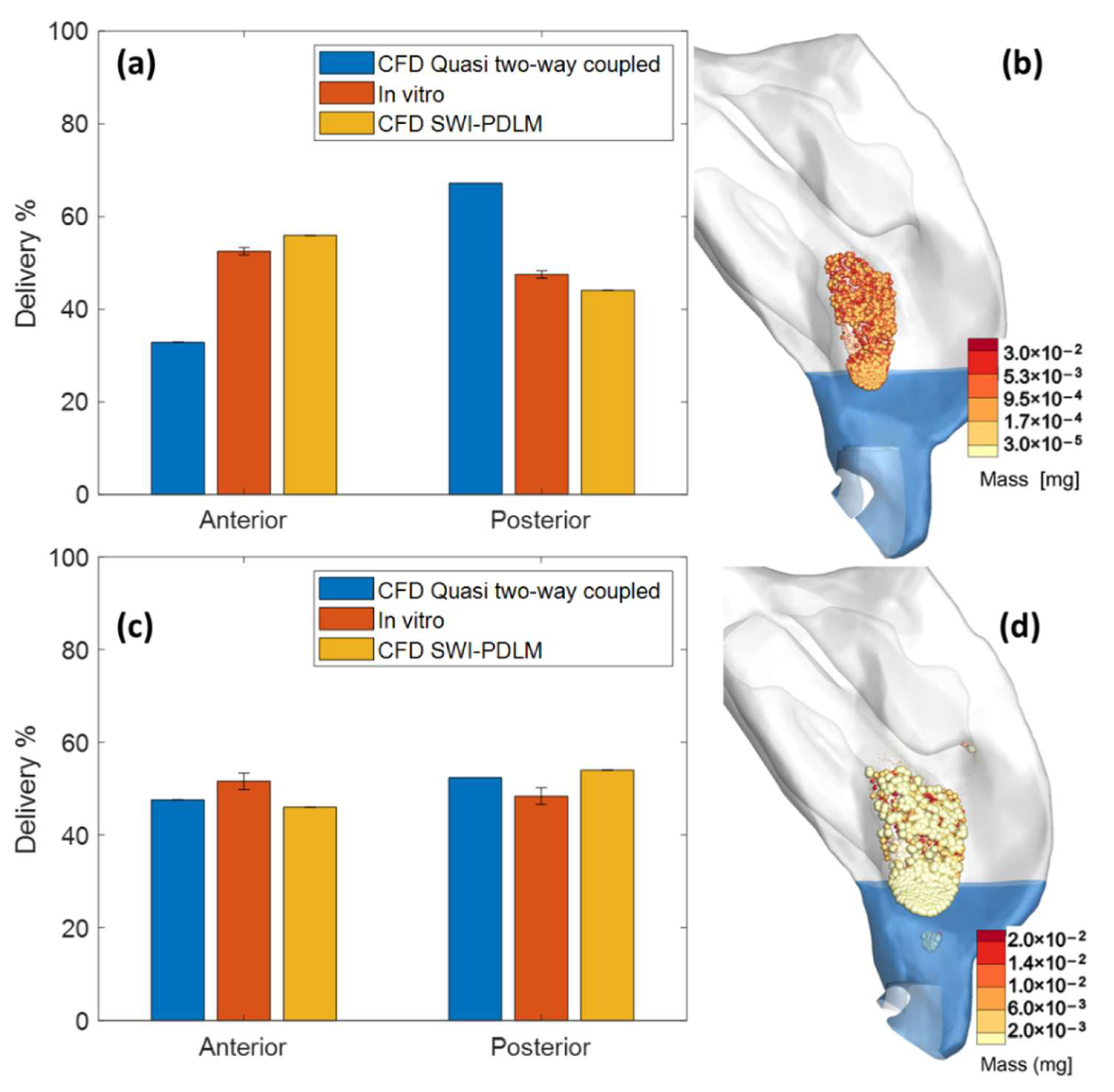
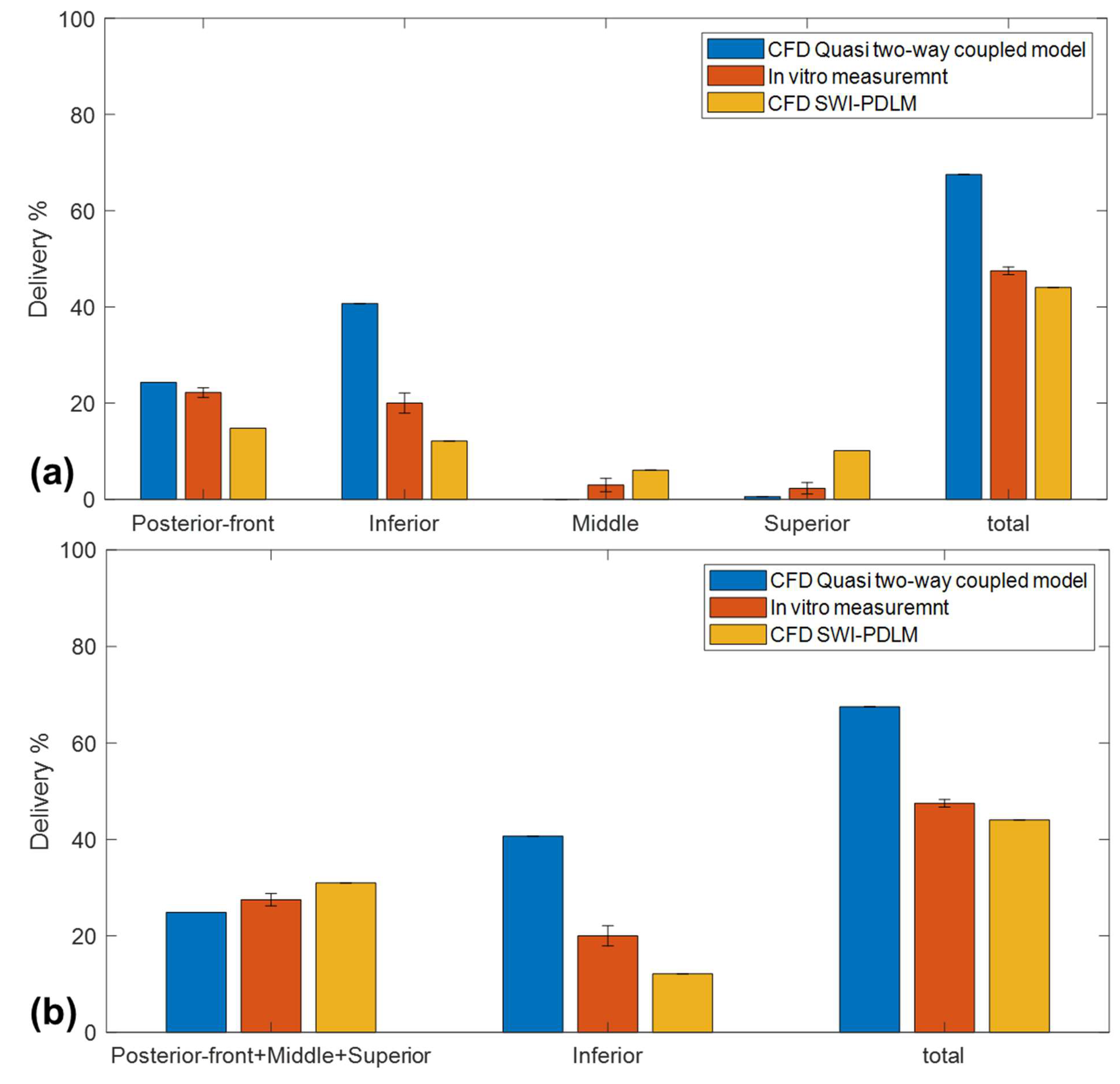
3.2. Comparison of Model Predicted Drug Delivery with In Vitro Measurements
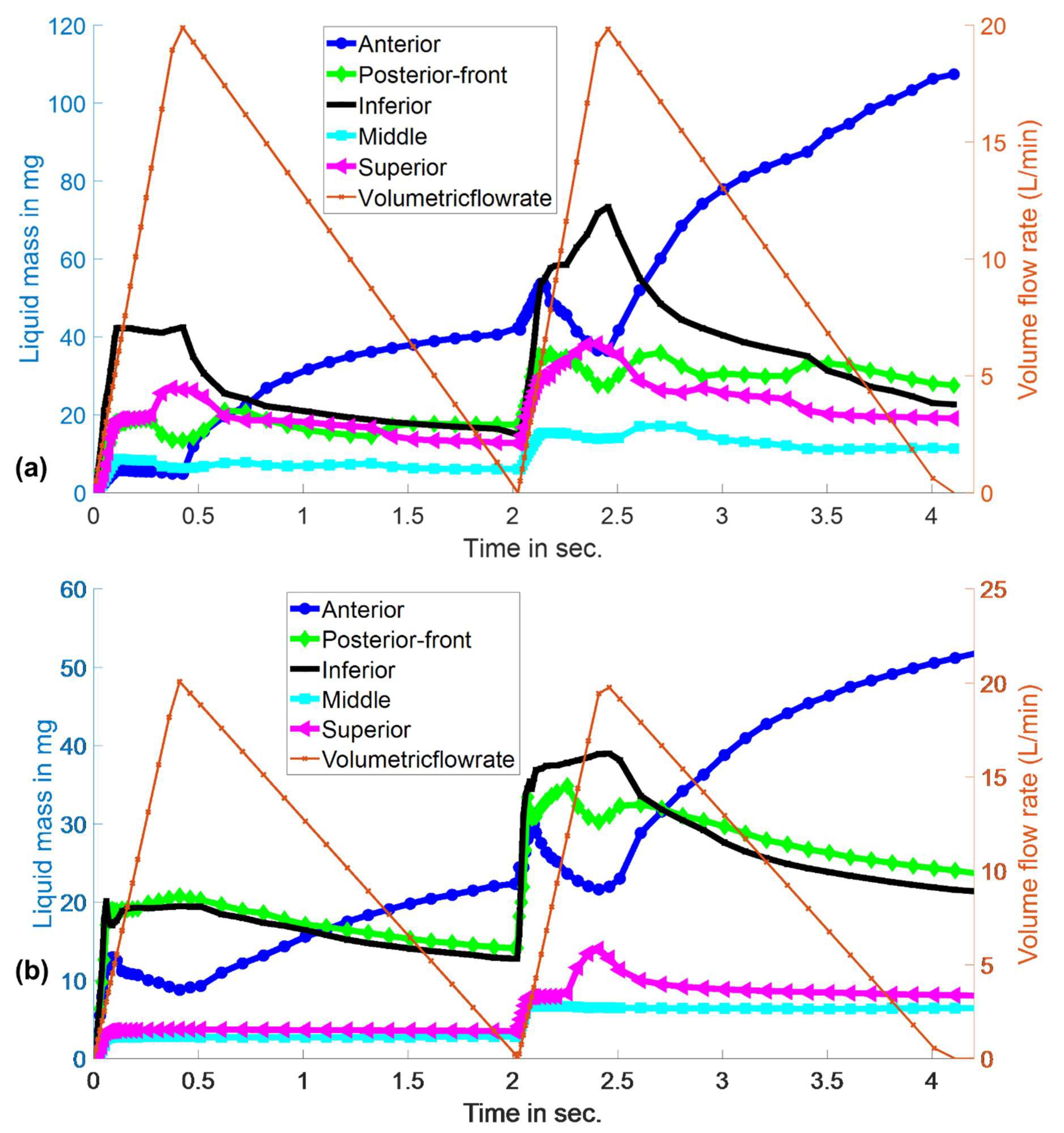
3.3. Evolution of Spray-Liquid Mass in Specific Regions of the Nasal Airway Surface
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Djupesland, P.G. Nasal drug delivery devices: Characteristics and performance in a clinical perspective—A review. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guellec, S.; Ehrmann, S.; Vecellio, L. In vitro–in vivo correlation of intranasal drug deposition. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 170, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykewicz, M.S.; Hamilos, D.L. Rhinitis and sinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S103–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias-Valle, L.; Psaltis, A.J. A Scholarly Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Intranasal Corticosteroids Preparations in the Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020, 100, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbell, J.S.; Segal, R.A.; Asgharian, B.; Wong, B.A.; Schroeter, J.D.; Southall, J.P.; Dickens, C.J.; Brace, G.; Miller, F.J. Characterization of deposition from nasal spray devices using a computational fluid dynamics model of the human nasal passages. J. Aerosol Med. -Depos. Clear. Eff. Lung 2007, 20, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inthavong, K.; Tian, Z.; Li, H.; Tu, J.; Yang, W.; Xue, C.; Li, C.G. A numerical study of spray particle deposition in a human nasal cavity. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, J.D.; Laube, B.L.; Dalby, R. Validity of in vitro tests on aqueous spray pumps as surrogates for nasal deposition, absorption, and biologic response. J. Aerosol Med. 2006, 19, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deruyver, L.; Rigaut, C.; Lambert, P.; Haut, B.; Goole, J. The importance of pre-formulation studies and of 3D-printed nasal casts in the success of a pharmaceutical product intended for nose-to-brain delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolanjiyil, A.V.; Hosseini, S.; Alfaifi, A.; Hindle, M.; Golshahi, L.; Longest, P.W. Importance of cloud motion and two-way momentum coupling in the transport of pharmaceutical nasal sprays. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 156, 105770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Shen, X.; Mao, S. Factors influencing drug deposition in the nasal cavity upon delivery via nasal sprays. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Dong, J.; Shang, Y.; Inthavong, K.; Tu, J. Effects of nasal drug delivery device and its orientation on sprayed particle deposition in a realistic human nasal cavity. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 77, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolanjiyil, A.V.; Hosseini, S.; Alfaifi, A.; Farkas, D.; Hindle, M.; Golshahi, L.; Longest, P.W. How Spray Metric Variability Impacts the Initial Deposition of Nasal Sprays. Respir. Drug Deliv. 2021, 1, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Manniello, M.D.; Hosseini, S.; Ali, A.; Esmaeili, A.R.; Kolanjiyil, A.V.; Walenga, R.; Babiskin, A.; Sandell, D.; Mohammadi, R.; Schuman, T.; et al. In vitro evaluation of regional nasal drug delivery using multiple anatomical nasal replicas of adult human subjects and two nasal sprays. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Goodey, A.P.; Fang, X.; Jacob, K. A comparison of the deposition patterns of different nasal spray formulations using a nasal cast. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundoor, V.; Dalby, R. Effect of formulation-and administration-related variables on deposition pattern of nasal spray pumps evaluated using a nasal cast. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.O.; Kimbell, J.S.; Pawar, S.; Rhee, J.S. Effects of anatomy and particle size on nasal sprays and nebulizers. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grmaš, J.; Stare, K.; Božič, D.; Injac, R.; Dreu, R. Elucidation of formulation and delivery device-related effects on in vitro performance of nasal spray with implication to rational product specification identification. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2017, 30, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Kiaee, M.; Martin, A.; Finlay, W.H. In vitro Assessment of an Idealized Nose for Nasal Spray Testing: Comparison with Regional Deposition in Realistic Nasal Replicas. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, N.; Donovan, M.D. In vitro assessment of spray deposition patterns in a pediatric (12 year-old) nasal cavity model. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, M.Y.; Cheng, Y.S.; Su, W.C.; Donovan, M.D. The influence of spray properties on intranasal deposition. J. Aerosol Med. 2007, 20, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Stine, K.J.; Kauffman, J.F.; Doub, W.H. Assessment of the influence factors on in vitro testing of nasal sprays using Box-Behnken experimental design. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 35, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnken, Z.N.; Smyth, H.D.; Davis, D.A.; Weitman, S.; Kuhn, J.G.; Williams, I.I.I.R.O. Personalized medicine in nasal delivery: The use of patient-specific administration parameters to improve nasal drug targeting using 3D-printed nasal replica casts. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salade, L.; Wauthoz, N.; Goole, J.; Amighi, K. How to characterize a nasal product. The state of the art of in vitro and ex vivo specific methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmet, H.; Inthavong, K.; Eguzkitza, B.; Lehmkuhl, O.; Houzeaux, G.; Vázquez, M. Nasal sprayed particle deposition in a human nasal cavity under different inhalation conditions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inthavong, K.; Ge, Q.J.; Se, C.M.K.; Yang, W.; Tu, J.Y. Simulation of sprayed particle deposition in a human nasal cavity including a nasal spray device. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.P.; Pitcairn, G.R.; Dalby, R.N. Drug delivery to the nasal cavity: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Crit. Rev. ™ Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2004, 21, 21–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, B.; Bommer, R.; Goole, J.; Hellfritzsch, M.; De Kruijf, W.; Lambert, P.; Caivano, G.; Regard, A.; Schiaretti, F.; Trenkel, M. A consensus research agenda for optimising nasal drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Holmes, T.; Gao, J.; Guilmette, R.; Li, S.; Surakitbanharn, Y.; Rowlings, C. Characterization of nasal spray pumps and deposition pattern in a replica of the human nasal airway. J. Aerosol Med. 2001, 14, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Doub, W.H. The influence of actuation parameters on in vitro testing of nasal spray products. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, A.; Blagbrough, I.S.; De Bank, P.A. In Vitro Evaluation of Nasal Aerosol Depositions: An Insight for Direct Nose to Brain Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, C.L.; Kuehl, P.J.; Chand, R.; McDonald, J.D. Nasal deposition of HFA-beclomethasone, aqueous fluticasone propionate and aqueous mometasone furoate in allergic rhinitis patients. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2015, 28, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayal, P.; Pillay, V.; Babu, R.J.; Singh, M. Box-Behnken experimental design in the development of a nasal drug delivery system of model drug hydroxyurea: Characterization of viscosity, in vitro drug release, droplet size, and dynamic surface tension. Aaps Pharmscitech 2005, 6, E573–E585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, M.C.; Inthavong, K.; Yang, W.; Lappas, P.; Tu, J. External characteristics of unsteady spray atomization from a nasal spray device. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Doub, W.H.; Guo, C. Evaluation of droplet velocity and size from nasal spray devices using phase Doppler anemometry (PDA). Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, J.; Pandey, P.; Tat, H.; Willson, J.; Donovan, B. Spray pattern and droplet size analyses for high-shear viscosity determination of aqueous suspension corticosteroid nasal sprays. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2008, 34, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inthavong, K.; Fung, M.C.; Yang, W.; Tu, J. Measurements of droplet size distribution and analysis of nasal spray atomization from different actuation pressure. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2015, 28, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.V.; Jin, F.; Lee, S.L.; Bai, T.; Chowdhury, B.; Caramenico, H.T.; Conner, D.P. Bioequivalence for locally acting nasal spray and nasal aerosol products: Standard development and generic approval. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. FDA. Draft Guidance for Industry: Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Nasal Aerosols and Nasal Sprays for Local Action; US Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, M.Y.; Sawant, N.; Overholtzer, E.; Donovan, M.D. A Simplified Geometric Model to Predict Nasal Spray Deposition in Children and Adults. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2767–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundoor, V.; Dalby, R.N. Assessment of nasal spray deposition pattern in a silicone human nose model using a color-based method. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Wei, X.; Wilkins, J.V., Jr.; Fergusson, C.P.; Mohammadi, R.; Vorona, G.; Golshahi, L. In Vitro Measurement of Regional Nasal Drug Delivery with Flonase,® Flonase® Sensimist,™ and MAD Nasal™ in Anatomically Correct Nasal Airway Replicas of Pediatric and Adult Human Subjects. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2019, 32, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Yuan, J.E.; Zhang, Y.; Nevorski, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Visualization and quantification of nasal and olfactory deposition in a sectional adult nasal airway cast. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laube, B.L.; Sharpless, G.; Vikani, A.R.; Harrand, V.; Zinreich, S.J.; Sedberry, K.; Knaus, D.; Barry, J.; Papania, M. Intranasal deposition of Accuspray™ aerosol in anatomically correct models of 2-, 5-, and 12-year-old children. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2015, 28, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rygg, A.; Hindle, M.; Longest, P.W. Absorption and clearance of pharmaceutical aerosols in the human nose: Effects of nasal spray suspension particle size and properties. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rygg, A.; Hindle, M.; Longest, P.W. Linking suspension nasal spray drug deposition patterns to pharmacokinetic profiles: A proof-of-concept study using computational fluid dynamics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Holbrook, L.T.; Kudlaty, K.; Fasanmade, O.; Wu, J.; Burke, A.; Langworthy, B.W.; Farzal, Z.; Mamdani, M.; Bennett, W.D. Numerical evaluation of spray position for improved nasal drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiaee, M.; Wachtel, H.; Noga, M.L.; Martin, A.R.; Finlay, W. An idealized geometry that mimics average nasal spray deposition in adults: A computational study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 107, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.; Sridhar, K.; Walenga, R.; Kleinstreuer, C. Computational analysis of a 3D mucociliary clearance model predicting nasal drug uptake. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 155, 105757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolanjiyil, A.V.; Hosseini, S.; Ali, A.; Farkas, D.R.; Walenga, R.; Babiskin, A.; Hindle, M.; Golshahi, L.; Longest, P.W. Validating CFD Predictions of Nasal Spray Deposition: Inclusion of Cloud Motion Effects for Two Spray Pump Designs. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.A.; Sami, M.; Xi, J. Liquid Film Translocation Significantly Enhances Nasal Spray Delivery to Olfactory Region: A Numerical Simulation Study. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Van Strien, J.; Singh, N.; Inthavong, K. Primary break-up and atomization characteristics of a nasal spray. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.T.; Monticello, T.M. Airflow, gas deposition, and lesion distribution in the nasal passages. Environ. Health Perspect. 1990, 85, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Laube, B.; Dalby, R. The effect of formulation variables and breathing patterns on the site of nasal deposition in an anatomically correct model. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djupesland, P.G.; Messina, J.C.; Mahmoud, R.A. Role of nasal casts for in vitro evaluation of nasal drug delivery and quantitative evaluation of various nasal casts. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josserand, C.; Thoroddsen, S.T. Drop impact on a solid surface. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2016, 48, 365–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowski, T.R.; Rapiejko, P.; Sova, J.; Dobrowolska, K. Impact of physicochemical properties of nasal spray products on drug deposition and transport in the pediatric nasal cavity model. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenbach, J.; Roisman, I.V.; Tropea, C. From drop impact physics to spray cooling models: A critical review. Exp. Fluids 2018, 59, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šikalo, Š.; Ganić, E. Phenomena of droplet–surface interactions. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2006, 31, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L. Drop impact dynamics: Splashing, spreading, receding, bouncing. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2006, 38, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Moita, A.; Panao, M. Advances and challenges in explaining fuel spray impingement: How much of single droplet impact research is useful? Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 554–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Mudawar, I. Review of mass and momentum interactions during drop impact on a liquid film. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 577–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthavong, K.; Shang, Y.; Wong, E.; Singh, N. Characterization of nasal irrigation flow from a squeeze bottle using computational fluid dynamics. In International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology; Wiley Online Library: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, K.; Wong, E.; Salati, H.; Fletcher, D.F.; Singh, N.; Inthavong, K. Liquid volume and squeeze force effects on nasal irrigation using Volume of Fluid modelling. Exp. Comput. Multiph. Flow 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Salati, H.; Fletcher, D.; Singh, N.; Inthavong, K. Effects of head tilt on squeeze-bottle nasal irrigation–A computational fluid dynamics study. J. Biomech. 2021, 123, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salati, H.; Bartley, J.; White, D.E. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation of Wall Shear Stress and Pressure Distribution from a Neti Pot During Nasal Saline Irrigation. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2021, 41, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygg, A.; Longest, P.W. Absorption and clearance of pharmaceutical aerosols in the human nose: Development of a CFD model. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2016, 29, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Inthavong, K.; Qiu, D.; Singh, N.; He, F.; Tu, J. Prediction of nasal spray drug absorption influenced by mucociliary clearance. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Inthavong, K.; Tu, J. Development of a computational fluid dynamics model for mucociliary clearance in the nasal cavity. J. Biomech. 2019, 85, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Schuman, T.A.; Walenga, R.; Wilkins Jr, J.V.; Babiskin, A.; Golshahi, L. Use of anatomically-accurate 3-dimensional nasal airway models of adult human subjects in a novel methodology to identify and evaluate the internal nasal valve. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 123, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtadernejad, S.; Lee, C.; Jadidi, M. An Introduction of Droplet Impact Dynamics to Engineering Students. Fluids 2020, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundo, C.; Sommerfeld, M.; Tropea, C. Experimental studies of the deposition and splashing of small liquid droplets impinging on a flat surface. In ICLASS-94, Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems; Begell House: Danbury, CT, USA, 1994; pp. 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Rusche, H.; Gosman, A. Modeling of gasoline spray impingement. At. Sprays 2002, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruiter, J.; Lagraauw, R.; Van Den Ende, D.; Mugele, F. Wettability-independent bouncing on flat surfaces mediated by thin air films. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Gosman, A. Mathematical modelling of wall films formed by impinging sprays. SAE Trans. 1996, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, C.; Marengo, M. The impact of drops on walls and films. Multiph. Sci. Technol. 1999, 11, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, D.; Tropea, C. Spray impact onto flat and rigid walls: Empirical characterization and modelling. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2007, 33, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossali, G.; Marengo, M.; Santini, M. Single-drop empirical models for spray impact on solid walls: A review. At. Sprays 2005, 15, 699–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Tian, R.; Mao, F. Analysis of special phenomena of droplet impact on horizontal liquid film at low velocity. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 136, 107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L.; Berger, G.M.; Mozes, S.D. The combined influence of a rough surface and thin fluid film upon the splashing threshold and splash dynamics of a droplet impacting onto them. Exp. Fluids 2006, 40, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioboo, R.; Bauthier, C.; Conti, J.; Voue, M.; De Coninck, J. Experimental investigation of splash and crown formation during single drop impact on wetted surfaces. Exp. Fluids 2003, 35, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z. Dynamics of Single Droplet Splashing on Liquid Film by Coupling FVM with VOF. Processes 2021, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari; Tropea, C. Influence of surface roughness in spray/wall interaction phenomena. In Proceedings of the ILASS—Europe 2010, 23rd Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Brno, Czech Republic, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Okawa, T.; Kubo, K.; Kawai, K.; Kitabayashi, S. Experiments on splashing thresholds during single-drop impact onto a quiescent liquid film. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2021, 121, 110279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Gosman, A. Development of methodology for spray impingement simulation. SAE Trans. 1995, 550–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’rourke, P.; Amsden, A. A particle numerical model for wall film dynamics in port-injected engines. SAE Trans. 1996, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, P.J.; Amsden, A. A spray/wall interaction submodel for the KIVA-3 wall film model. SAE Trans. 2000, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Xu, Z. Wall Film Dynamics Modeling for Impinging Sprays in Engines. SAE Tech. Pap. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, D.W.; Rutland, C.J. Multi-dimensional modeling of heat and mass transfer of fuel films resulting from impinging sprays. SAE Trans. 1998, 107, 44–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yarin, A.L.; Weiss, D.A. Impact of drops on solid surfaces: Self-similar capillary waves, and splashing as a new type of kinematic discontinuity. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 283, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossali, G.E.; Coghe, A.; Marengo, M. The impact of a single drop on a wetted solid surface. Exp. Fluids 1997, 22, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Mu, X.; Guo, Y.; Shen, S. Crown and drop rebound on thin curved liquid films. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 98, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, B.; Mao, F.; Wen, J.; Tian, R.; Lu, C. Experimental study of droplet impacting on inclined wetted wall in corrugated plate separator. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 137, 107155. [Google Scholar]
- Motzkus, C.; Gensdarmes, F.; Géhin, E. Study of the coalescence/splash threshold of droplet impact on liquid films and its relevance in assessing airborne particle release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, D.; Tropea, C. Comparison between Splash of a Droplet in Isolation and in a Spray. In Spray Workshop. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/ (accessed on 22 October 2021).
- Naber, J.; Reitz, R.D. Modeling engine spray/wall impingement. SAE Trans. 1988, 97, 118–140. [Google Scholar]
- Meredith, K.; de Vries, J.; Wang, Y.; Xin, Y. A comprehensive model for simulating the interaction of water with solid surfaces in fire suppression environments. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2719–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, K.; Boc, S.; Hindle, M.; Dodson, K.; Longest, W. High-Efficiency Nose-to-Lung Aerosol Delivery in an Infant: Development of a Validated Computational Fluid Dynamics Method. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2019, 32, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolanjiyil, A.V.; Hosseini, S.; Manniello, M.; Alfaifi, A.; Farkas, D.; Hindle, M.; Golshahi, L.; Longest, P.W. Effect of spray momentum on nasal spray droplet transport and deposition. Respir. Drug Deliv. 2020, 3, 691–696. [Google Scholar]
- Kippax, P.; Suman, J.D.; Williams, G. Enhancing the in vitro assessment of nasal sprays. Pharm. Technol. Eur. 2008, 20, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston, G.; Bakhshaee, M.; Hudson, N.; Richards, D. Rheological behavior of nasal sprays in shear and extension. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, S.; Sandweiss, V.; Tuazon, J.; Giordano, M.; Witchey-Lakshmanan, L.; Hart, J.; Sequeira, J. Comparison of the flow properties of aqueous suspension corticosteroid nasal sprays under differing sampling conditions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttin, E.; Schipper, N.G.; Verhoef, J.C.; Merkus, F.W. Nasal mucociliary clearance as a factor in nasal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 29, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Rosales, F.J.; Alves, M.; Oliveira, M.S. Microdevices for extensional rheometry of low viscosity elastic liquids: A review. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2013, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.Y.; Bhushan, B. Comparison of surface roughness measurements by stylus profiler, AFM and non-contact optical profiler. Wear 1995, 190, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šikalo, Š.; Wilhelm, H.-D.; Roisman, I.; Jakirlić, S.; Tropea, C. Dynamic contact angle of spreading droplets: Experiments and simulations. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 062103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolghasemibizaki, M.; Dilmaghani, N.; Mohammadi, R.; Castano, C.E. Viscous droplet impact on nonwettable textured surfaces. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10752–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
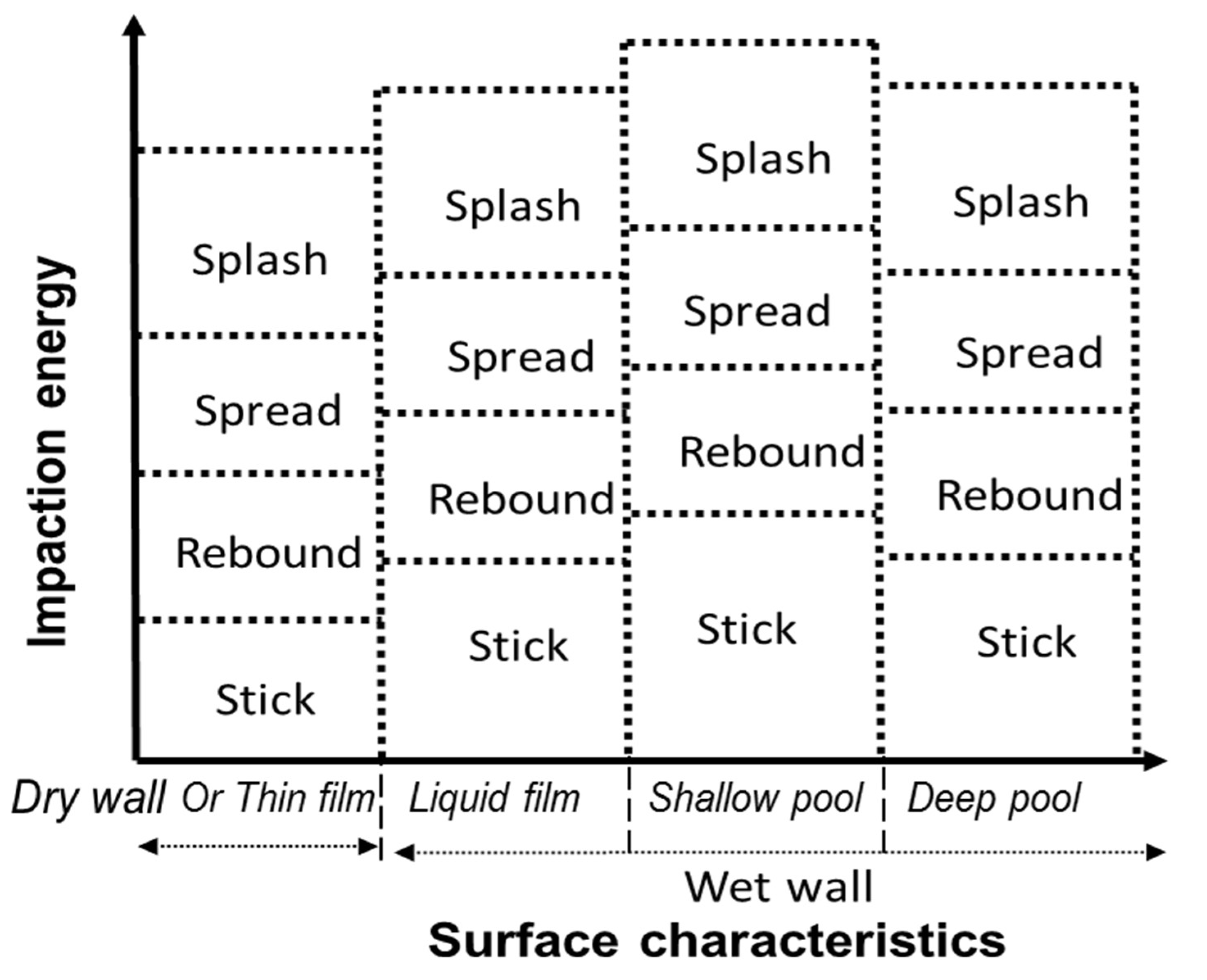
| Surface Characteristics | Impaction Regime | Transition Condition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry wall or thin film ) | Stick | We < 1 | |
| Rebound | We < 4 | ||
| Spread | K-f < Ktrans | ||
| Splash | K-f > Ktrans | ||
| Liquid film ) | Stick | We < 2 | where Ktrans = when ≤ 0.05 2100.0 + 2000.0 when 0.05 < ≤ 1.0 |
| Rebound | We < 20 | ||
| Spread | K-f < Ktrans | ||
| Splash | K-f > Ktrans | ||
| Shallow pool ) | Stick | We < 2 | where Ktrans = 4000.0 |
| Rebound | We < 20 | ||
| Spread | K-f < Ktrans | ||
| Splash | K-f > Ktrans | ||
| Deep pool ) | Stick | We < 2 | where Ktrans = 3390.0 |
| Rebound | We < 20 | ||
| Spread | K-f < Ktrans | ||
| Splash | K-f > Ktrans |
| Flonase and Flonase Sensimist Spray Droplet Transport and Deposition Models | ||
|---|---|---|
| Two-Way Coupled Euler–Lagrange Model + Spray–Wall Interaction + Post-Deposition Liquid Motion | Stand-Alone Two-Way Coupled Euler–Lagrange Model | |
| Two-way coupling effect modeled using | ‘Momentum transfer’ approach | ‘Quasi two-way coupled’ approach |
| Droplet–wall interaction | SWI model | Deposit-on-touch |
| Liquid motion | PDLM model | Not modeled |
| Flonase | Flonase Sensimist | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior (%) | Posterior (%) | Anterior (%) | Posterior (%) | |
| CFD SWI-PDLM model | 55.95 | 44.05 | 46.0 | 54.0 |
| CFD quasi two-way coupled model (with deposit-on-touch droplet boundary condition) | 32.50 | 67.50 | 47.6 | 52.4 |
| in vitro | 52.5 ± 0.8 | 47.5 ± 0.8 | 51.6 ± 1.8 | 48.4 ± 1.8 |
| Relative error (SWI_PDLM model) (%) | 6.6 | 7.3 | 10.8 | 11.5 |
| Relative error (quasi two-way coupled model) (%) | 38.1 | 42.1 | 7.8 | 8.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolanjiyil, A.V.; Alfaifi, A.; Aladwani, G.; Golshahi, L.; Longest, W. Importance of Spray–Wall Interaction and Post-Deposition Liquid Motion in the Transport and Delivery of Pharmaceutical Nasal Sprays. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050956
Kolanjiyil AV, Alfaifi A, Aladwani G, Golshahi L, Longest W. Importance of Spray–Wall Interaction and Post-Deposition Liquid Motion in the Transport and Delivery of Pharmaceutical Nasal Sprays. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(5):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050956
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolanjiyil, Arun V., Ali Alfaifi, Ghali Aladwani, Laleh Golshahi, and Worth Longest. 2022. "Importance of Spray–Wall Interaction and Post-Deposition Liquid Motion in the Transport and Delivery of Pharmaceutical Nasal Sprays" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 5: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050956
APA StyleKolanjiyil, A. V., Alfaifi, A., Aladwani, G., Golshahi, L., & Longest, W. (2022). Importance of Spray–Wall Interaction and Post-Deposition Liquid Motion in the Transport and Delivery of Pharmaceutical Nasal Sprays. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050956






