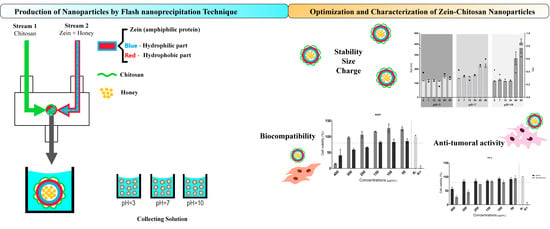
Single-Step Self-Assembly of Zein–Honey–Chitosan Nanoparticles for Hydrophilic Drug Incorporation by Flash Nanoprecipitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nanoparticles Assembly and Characterization
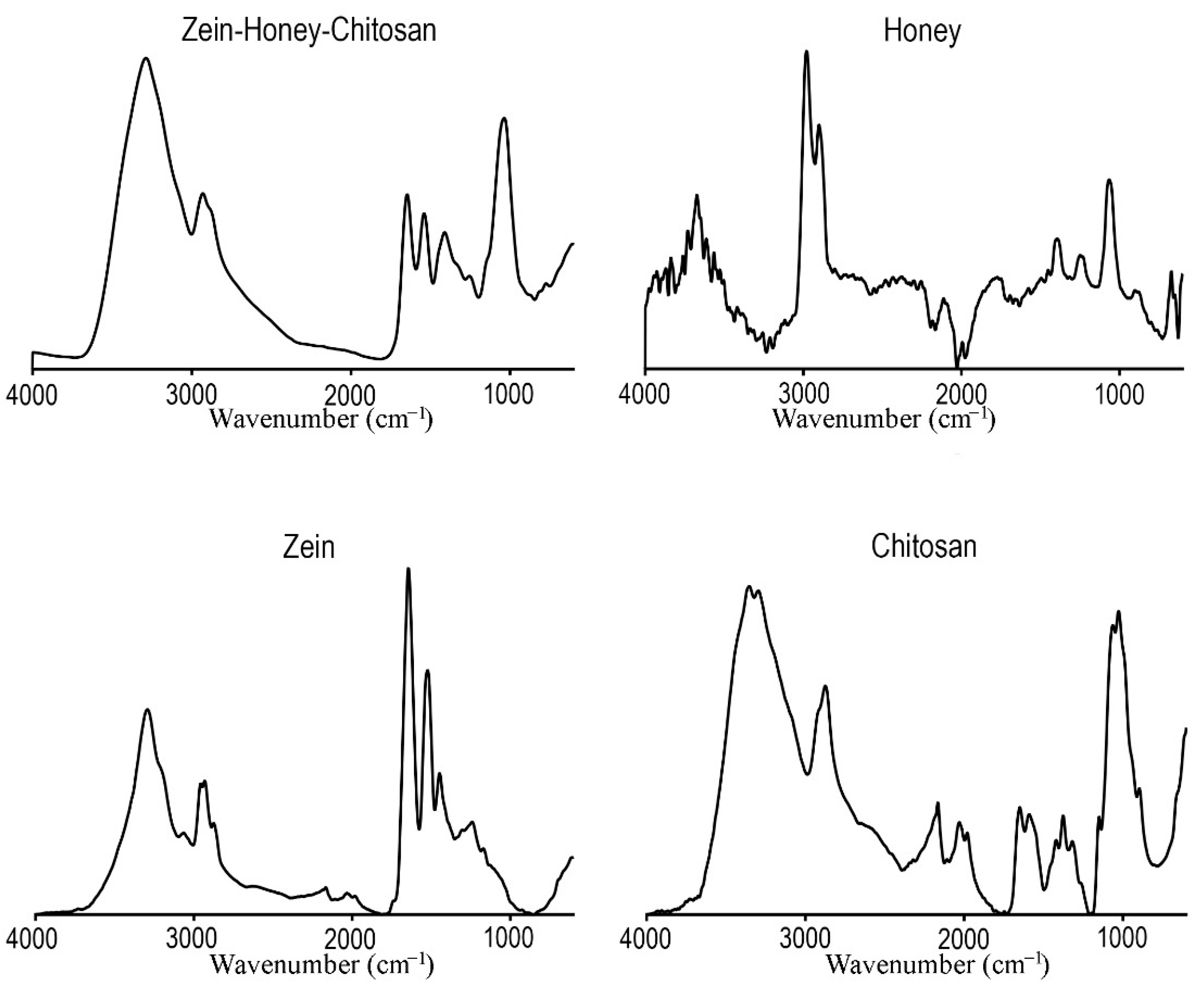
2.2.1. FTIR
2.2.2. Drug Encapsulation Efficiency and Release Profile
2.2.3. Characterization of Vitamin C Release Profile from Nanoparticles
2.3. In Vitro Assays
2.3.1. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
2.3.2. Nanoparticles Cellular Uptake
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Zein–Honey–Chitosan Nanoparticles
3.1.1. FTIR
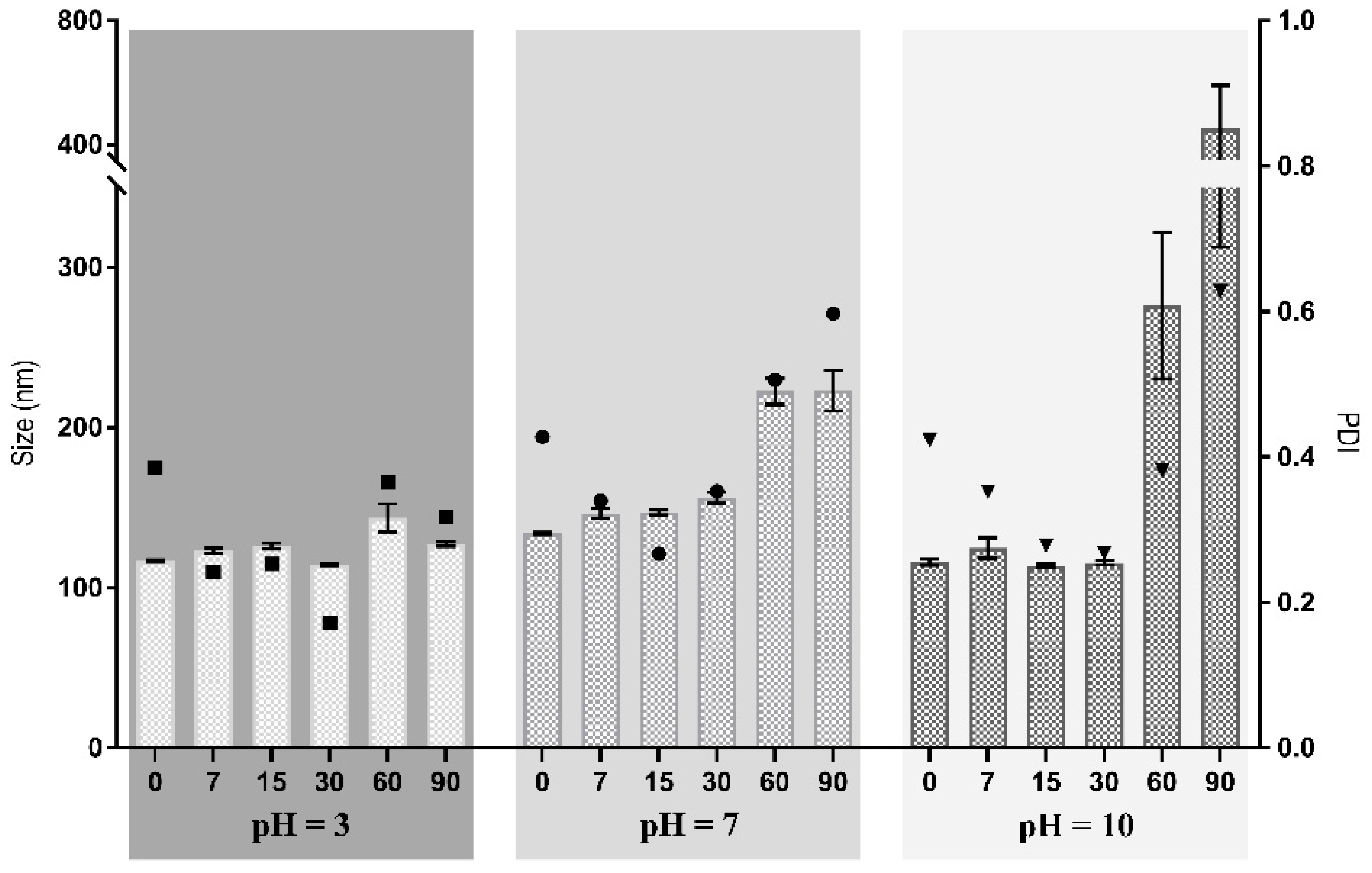
3.1.2. Evaluation of the Stability of Zein–Honey–Chitosan NPs
3.2. Vitamin C Release Profile
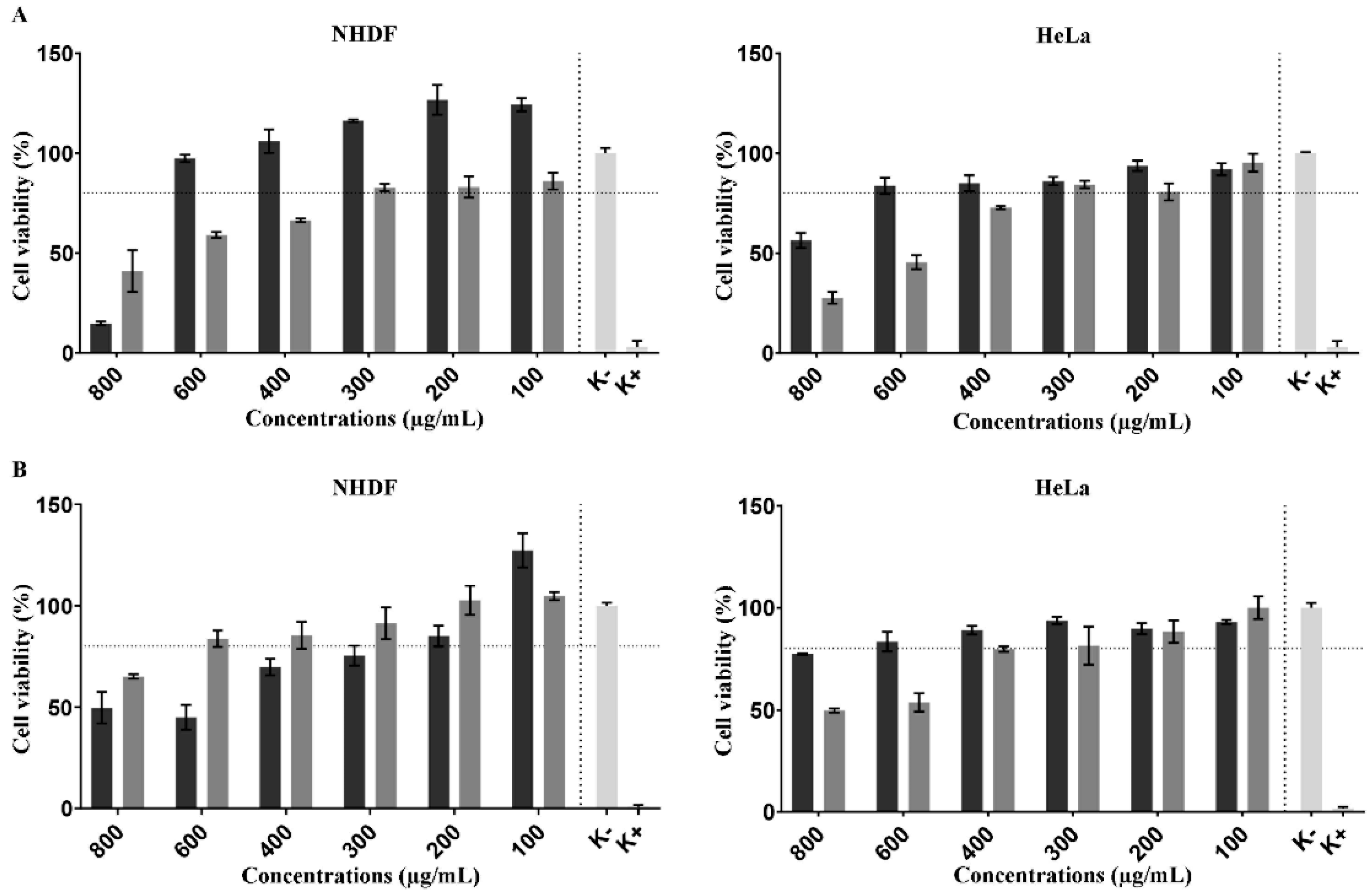
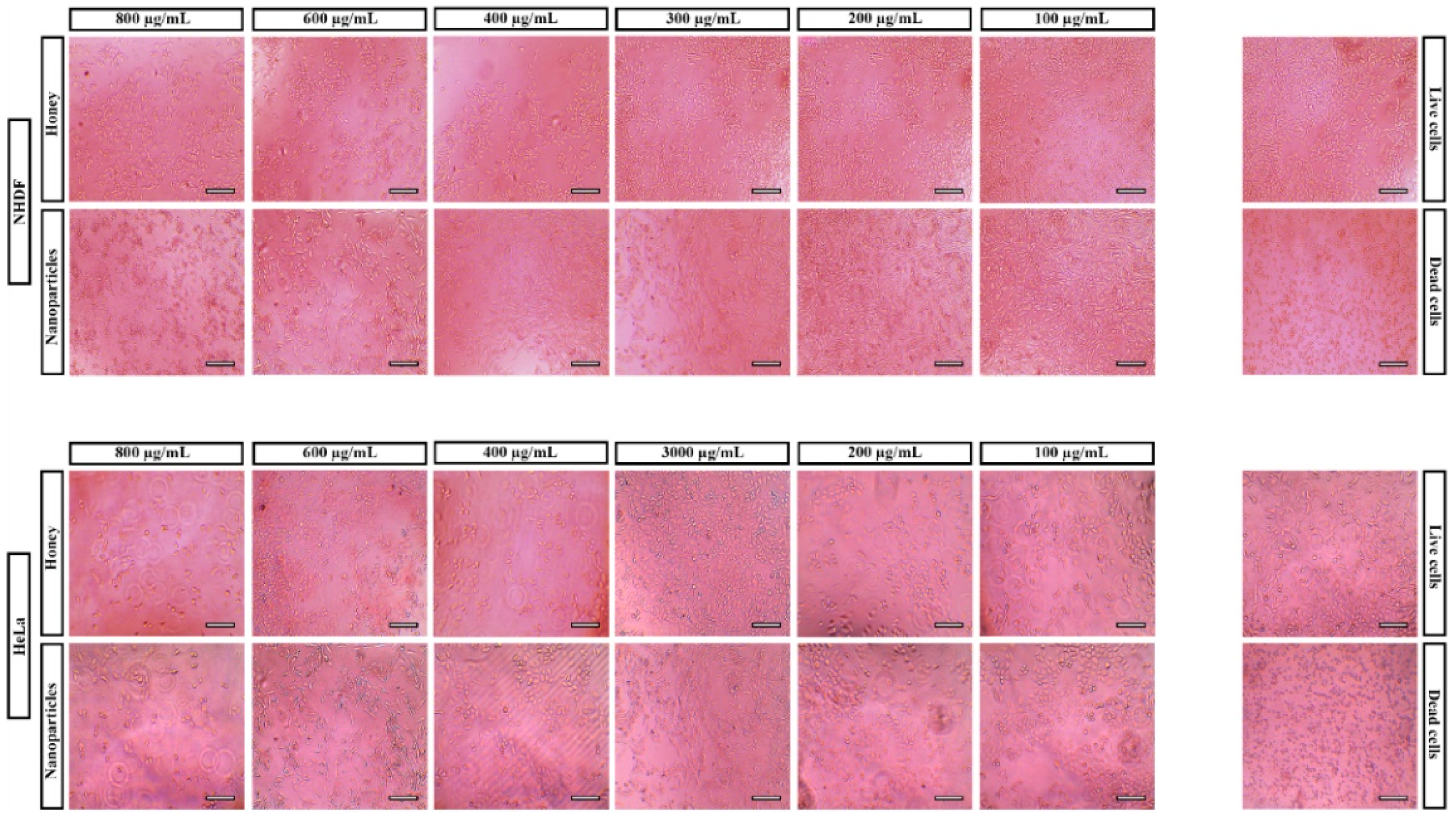
3.3. In Vitro Assays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beketov, E.E.; Isaeva, E.V.; Yakovleva, N.D.; Demyashkin, G.A.; Arguchinskaya, N.V.; Kisel, A.A.; Lagoda, T.S.; Malakhov, E.P.; Kharlov, V.I.; Osidak, E.O.; et al. Bioprinting of Cartilage with Bioink Based on High-Concentration Collagen and Chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, K.M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Al Nahyah, K.S. The relevance of nanotechnology, hepato-protective agents in reducing the toxicity and augmenting the bioavailability of isotretinoin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 28, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.C.; Borah, A.; Jacob, E.M.; Kumar, D.S. Nanotechnological approach to delivering nutraceuticals as promising drug candidates for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 550–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, S.; Ding, Q.; Fan, Q.; Dai, Y.; Guo, S.; Ye, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, M. Recent advances in cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles for inflammation therapy. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasekar, N.M.; Singh, S.; Jadhav, K.R.; Kadam, V.J. BCS class II drug loaded protein nanoparticles with enhanced oral bioavailability:in vitroevaluation andin vivopharmacokinetic study in rats. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Sun, K.; Sun, J. Combination prostate cancer therapy: Prostate-specific membranes antigen targeted, pH-sensitive nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin and tanshinone. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zheng, W.; Pu, J.; Chen, Q.; Shao, W. NIR-II Upconversion Photoluminescence of Er3+ Doped LiYF4 and NaY(Gd)F4 Core-Shell Nanoparticles. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 690833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, J.; Henriquez, G.; Narayan, M. Enhancing the Delivery of Chemotherapeutics: Role of Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles. Molecules 2018, 23, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaguera, C.; Castells-Sala, C.; Borrós, S. Unraveling Polymeric Nanoparticles Cell Uptake Pathways: Two Decades Working to Understand Nanoparticles Journey to Improve Gene Therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1288, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.J.; Jones, O.G. Stabilizing zein nanoparticle dispersions with ι-carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-P.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Wu, D.; Li, H.-L. Fabrication of sustained-release zein nanoparticles via modified coaxial electrospraying. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Rodríguez-Felix, F.; Juárez-Onofre, J.E.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Robles-García, M.A.; Borboa-Flores, J.; Wong-Corral, F.J.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Castro-Enríquez, D.D.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L. Zein-polysaccharide nanoparticles as matrices for antioxidant compounds: A strategy for prevention of chronic degenerative diseases. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Dong, C.; Zhao, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Mao, H.-Q.; Leong, K.W.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y. Scalable Production of Therapeutic Protein Nanoparticles Using Flash Nanoprecipitation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-F.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.-Z.; Zhang, J.-L.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Q.-Z.; Wei, X.-C.; Yuan, Y. The formation of zein-chitosan complex coacervated particles: Relationship to encapsulation and controlled release properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.-K.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Yin, S.-W.; Yang, X.-Q.; Wen, Q.-B.; Tang, C.-H.; Lai, F.-R. Continuous preparation of zein colloidal particles by Flash NanoPrecipitation (FNP). J. Food Eng. 2014, 127, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Hon, M.-H. The Effect of the Degree of Deacetylation of Chitosan Nanoparticles and its Characterization and Encapsulation Efficiency on Drug Delivery. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2010, 49, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoli, M.; Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Zein Nanoparticles and Strategies to Improve Colloidal Stability: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, R.D.O.; Hoffmann, S.; Pereira, S.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Schmitt, C.C.; Neumann, M.G. Self-assembled amphiphilic chitosan nanoparticles for quercetin delivery to breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 131, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, R.; Chow, C.; Drikas, M. Evaluation of chitosan as a natural coagulant for drinking water treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, B.; He, L.; An, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Fabrication of zein/quaternized chitosan nanoparticles for the encapsulation and protection of curcumin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13891–13900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Margulis-Goshen, K.; Magdassi, S.; Talmon, Y.; Macosko, C.W. Polyelectrolyte Stabilized Drug Nanoparticles via Flash Nanoprecipitation: A Model Study With β-Carotene. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4295–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divya, K.; Jisha, M.S. Chitosan nanoparticles preparation and applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 16, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, W.S.; Prud’Homme, R.K. Principles of nanoparticle formation by flash nanoprecipitation. Nano Today 2016, 11, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Santos, J.L.; Tian, H.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Leong, K.W.; Chen, Y.; Mao, H.-Q. Scalable fabrication of size-controlled chitosan nanoparticles for oral delivery of insulin. Biomaterials 2017, 130, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. Effects of amphiphilic diblock copolymer on drug nanoparticle formation and stability. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 10238–10248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, D.; Guo, X.; Song, H.; Cao, S.; Yan, Y. Fabrication of Charge-Conversion Nanoparticles for Cancer Imaging by Flash Nanoprecipitation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10752–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuropatnicki, A.K.; Kłósek, M.; Kucharzewski, M. Honey as medicine: Historical perspectives. J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhu, Z.; Qian, H.; Wohl, A.R.; Beaman, C.J.; Hoye, T.R.; Macosko, C.W. A simple confined impingement jets mixer for flash nanoprecipitation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 4018–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.D.D.S.; Oriani, V.B.; de Oliveira, G.M.; Hubinger, M.D. Solid lipid microparticles loaded with ascorbic acid: Release kinetic profile during thermal stability. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.D.; Baird, S.K. Honey is cytotoxic towards prostate cancer cells but interacts with the MTT reagent: Considerations for the choice of cell viability assay. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Qian, H.; Sun, S.; Sun, D.; Yin, H.; Cai, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of fluorescent dye. Chem. Central J. 2011, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.F.; Rodrigues, C.F.; A Reis, C.; Costa, E.C.; Ferreira, P.; Correia, I.J. Development of poly-2-ethyl-2-oxazoline coated gold-core silica shell nanorods for cancer chemo-photothermal therapy. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2611–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bteich, J.; McManus, S.A.; Ernsting, M.J.; Mohammed, M.Z.; Prud’Homme, R.K.; Sokoll, K.K. Using Flash Nanoprecipitation to Produce Highly Potent and Stable Cellax Nanoparticles from Amphiphilic Polymers Derived from Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Polyethylene Glycol, and Cabazitaxel. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3998–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D. Cancer Cell Surface Negative Charges: A Bio-Physical Manifestation of the Warburg Effect. Nano Life 2017, 7, 1771001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.; Smyth, H.D.; Ghosh, D. Physicochemical properties of mucus and their impact on transmucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, A.H.; Wipf, P. Nanoparticles in cellular drug delivery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2950–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.A.; Feng, S.-S. Effects of Particle Size and Surface Modification on Cellular Uptake and Biodistribution of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, A.B.; Tsourkas, A.; Saboury, B.; Cardoso, V.N.; Alavi, A. Emerging role of radiolabeled nanoparticles as an effective diagnostic technique. EJNMMI Res. 2012, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Naik, P.K.; Pradhan, D.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Mucoadhesive formulations: Innovations, merits, drawbacks, and future outlook. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, J.; Han, L.; Lin, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W. Zein-Polyglycerol Conjugates with Enhanced Water Solubility and Stabilization of High Oil Loading Emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11810–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Gao, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, Y. Synthesis of cross-linking chitosan-PVA composite hydrogel and adsorption of Cu(II) ions. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Lan, X.; Liang, C.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, R.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. Honey loaded alginate/PVA nanofibrous membrane as potential bioactive wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 219, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Jian, L.; Liao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Fabrication, characterization, physicochemical stability of zein-chitosan nanocomplex for co-encapsulating curcumin and resveratrol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiong, H. Aggregation modeling of the influence of pH on the aggregation of variably charged nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.L.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Hirsch, V.; Balog, S.; Urban, D.; Jud, C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Lattuada, M.; Petri-Fink, A. Nanoparticle colloidal stability in cell culture media and impact on cellular interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6287–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamahkar, E.; Özkahraman, B.; Süloğlu, A.K.; Idil, N.; Perçin, I. A novel multilayer hydrogel wound dressing for antibiotic release. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Teo, Y.Y.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Mushtaq, M.W. Rheological behavior of biodegradable N-succinyl chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels and their applications as drug carrier and in vitro theophylline release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, B.; Dharmaratne, P.; Yan, W.; Chan, B.C.; Lau, C.; Fung, K.-P.; Ip, M.; Leung, S.S. Development of thermosensitive hydrogel containing methylene blue for topical antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 203, 111776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.F.; Serro, A.P.; Colaço, R.; Chauhan, A. Optimization of intraocular lens hydrogels for dual drug release: Experimentation and modelling. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of Current Characterization and Evaluation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ak, G. Covalently coupling doxorubicin to polymeric nanoparticles as potential inhaler therapy: In vitro studies. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.M.; Calado, R.; Marto, J.; Bettencourt, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Gonçalves, L.M.D. Chitosan Nanoparticles as a Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery System for Ocular Administration. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbinatto, F.M.; de Castro, A.D.; Evangelista, R.C.; Cury, B.S. Insights into the swelling process and drug release mechanisms from cross-linked pectin/high amylose starch matrices. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Eshak, Z.; Ismail, W.I.W. Acacia honey induces apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma cell lines (MCF-7). J. Teknol. 2017, 79, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fauzi, A.N.; Norazmi, M.N.; Yaacob, N.S. Tualang honey induces apoptosis and disrupts the mitochondrial membrane potential of human breast and cervical cancer cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T. Zein/fucoidan-based composite nanoparticles for the encapsulation of pterostilbene: Preparation, characterization, physicochemical stability, and formation mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivolta, I.; Panariti, A.; Miserocchi, G. The effect of nanoparticle uptake on cellular behavior: Disrupting or enabling functions? Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
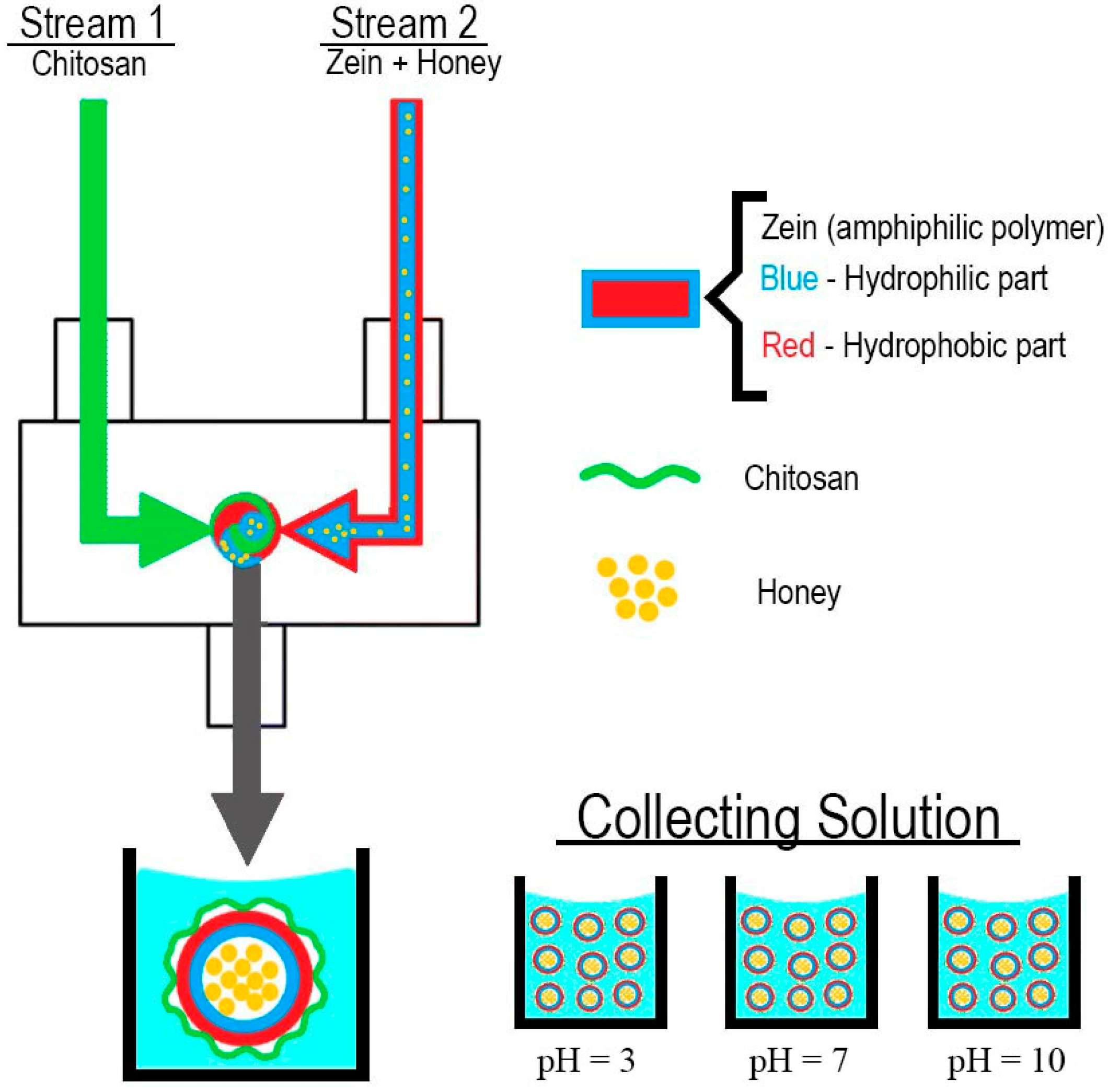


| Experiment | Stream 1 | Stream 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zein | Water |
| 2 | Zein | Water + honey |
| 3 | Zein + honey | Water |
| 4 | Zein + honey | Chitosan |
| Stream 1 | Stream 2 | Size (nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zein | Water | 126.20 ± 1.071 | 0.007 ± 0.027 | −12.40 ± 0.526 |
| Zein | Water + honey | 185.20 ± 1.564 | 0.107 ± 0.023 | −10.50 ± 0.537 |
| Zein + honey | Water | 125.60 ± 0.885 | 0.086 ± 0.014 | −12.80 ± 0.351 |
| Zein + honey | Chitosan | 148.10 ± 3.444 | 0.300 ± 0.028 | 48.30 ± 1.150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loureiro, J.; Miguel, S.P.; Seabra, I.J.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P. Single-Step Self-Assembly of Zein–Honey–Chitosan Nanoparticles for Hydrophilic Drug Incorporation by Flash Nanoprecipitation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050920
Loureiro J, Miguel SP, Seabra IJ, Ribeiro MP, Coutinho P. Single-Step Self-Assembly of Zein–Honey–Chitosan Nanoparticles for Hydrophilic Drug Incorporation by Flash Nanoprecipitation. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(5):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050920
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoureiro, Jorge, Sónia P. Miguel, Inês J. Seabra, Maximiano P. Ribeiro, and Paula Coutinho. 2022. "Single-Step Self-Assembly of Zein–Honey–Chitosan Nanoparticles for Hydrophilic Drug Incorporation by Flash Nanoprecipitation" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 5: 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050920
APA StyleLoureiro, J., Miguel, S. P., Seabra, I. J., Ribeiro, M. P., & Coutinho, P. (2022). Single-Step Self-Assembly of Zein–Honey–Chitosan Nanoparticles for Hydrophilic Drug Incorporation by Flash Nanoprecipitation. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050920