Evaluation of 3-Borono-l-Phenylalanine as a Water-Soluble Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
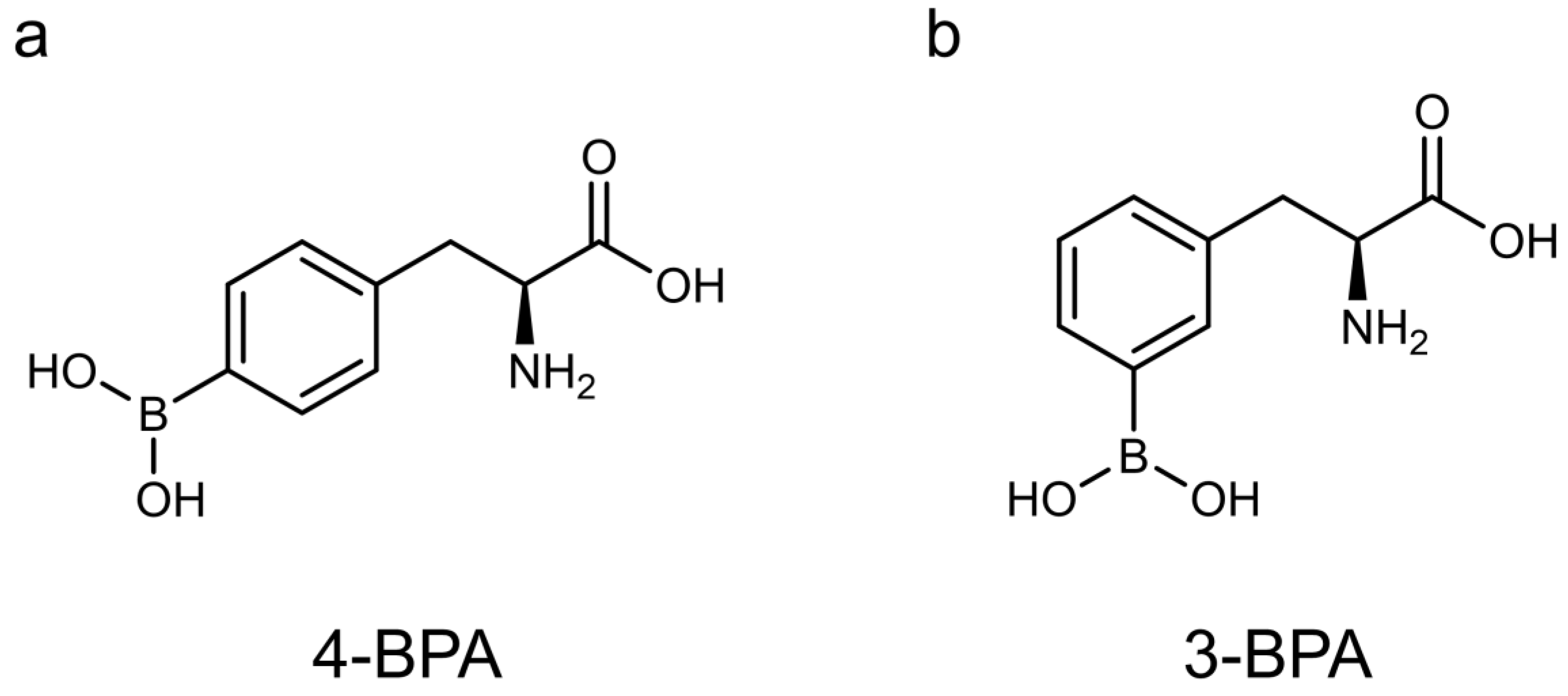
2.2. Synthesis of 3-BPA
2.3. Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of 3-BPA and 4-BPA
2.3.1. Water Solubility
2.3.2. Log p Measurement
2.4. In Vitro Experiments
2.4.1. Cell Lines
2.4.2. Western Blotting
2.4.3. Cell Staining
2.4.4. Cellular Uptake Study
2.5. In Vivo Experiment
2.5.1. Animal Preparation
2.5.2. In Vivo Biodistribution Study
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Properties of the 3-BPA and 4-BPA
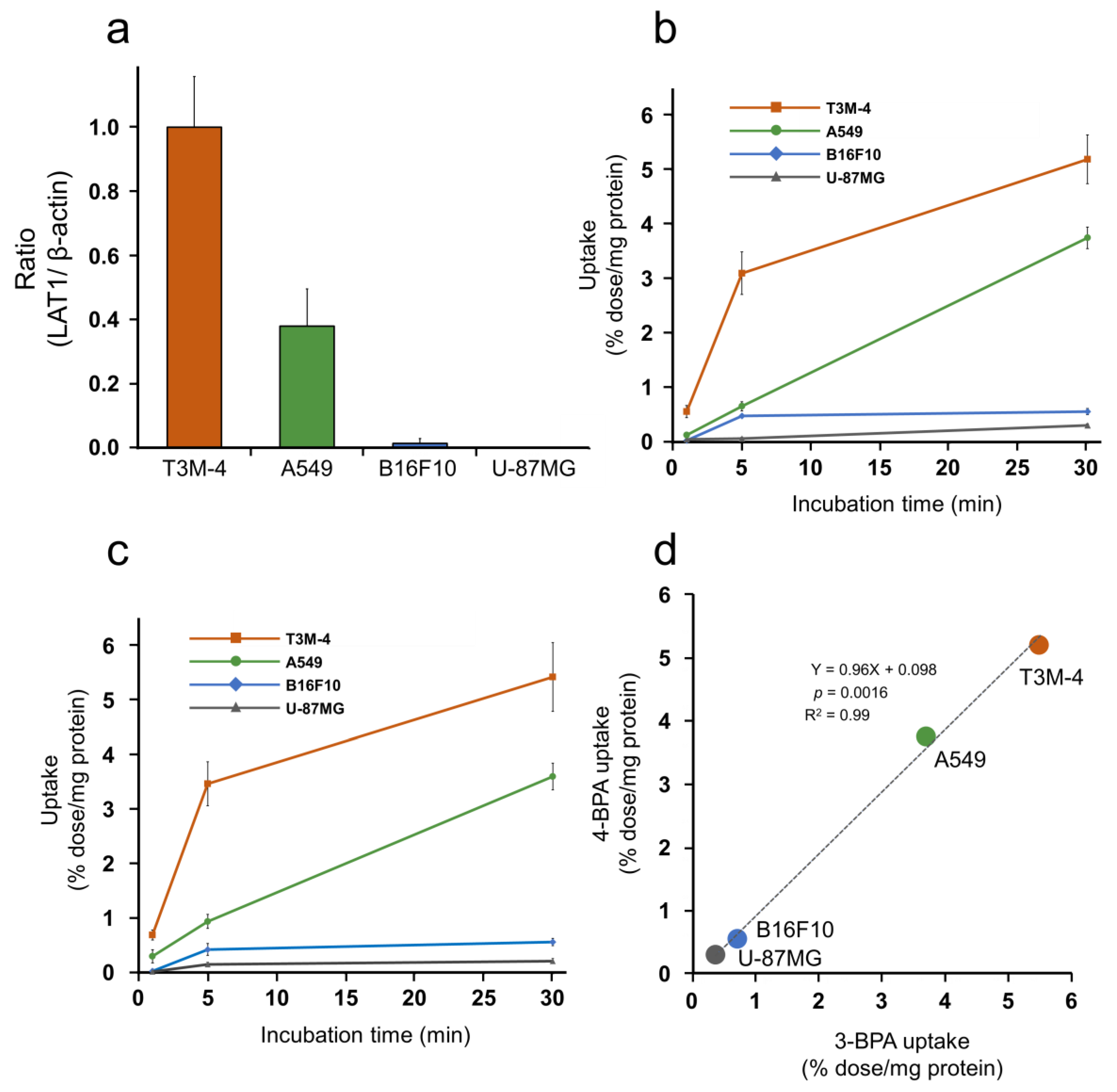
3.2. Cellular Uptake Study
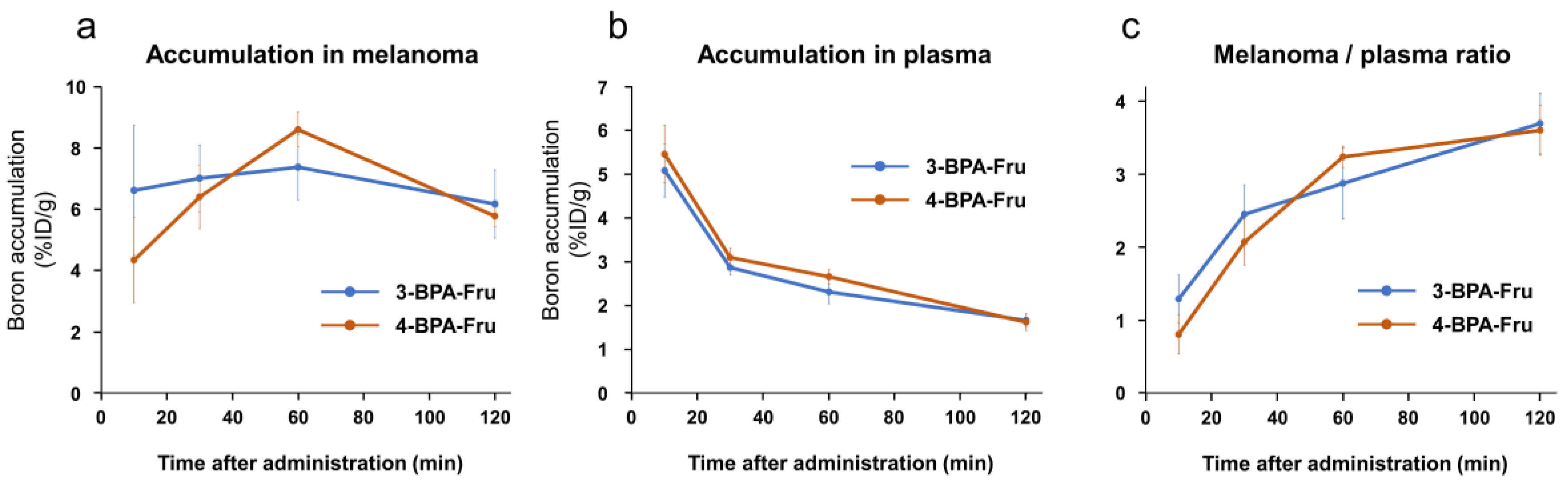
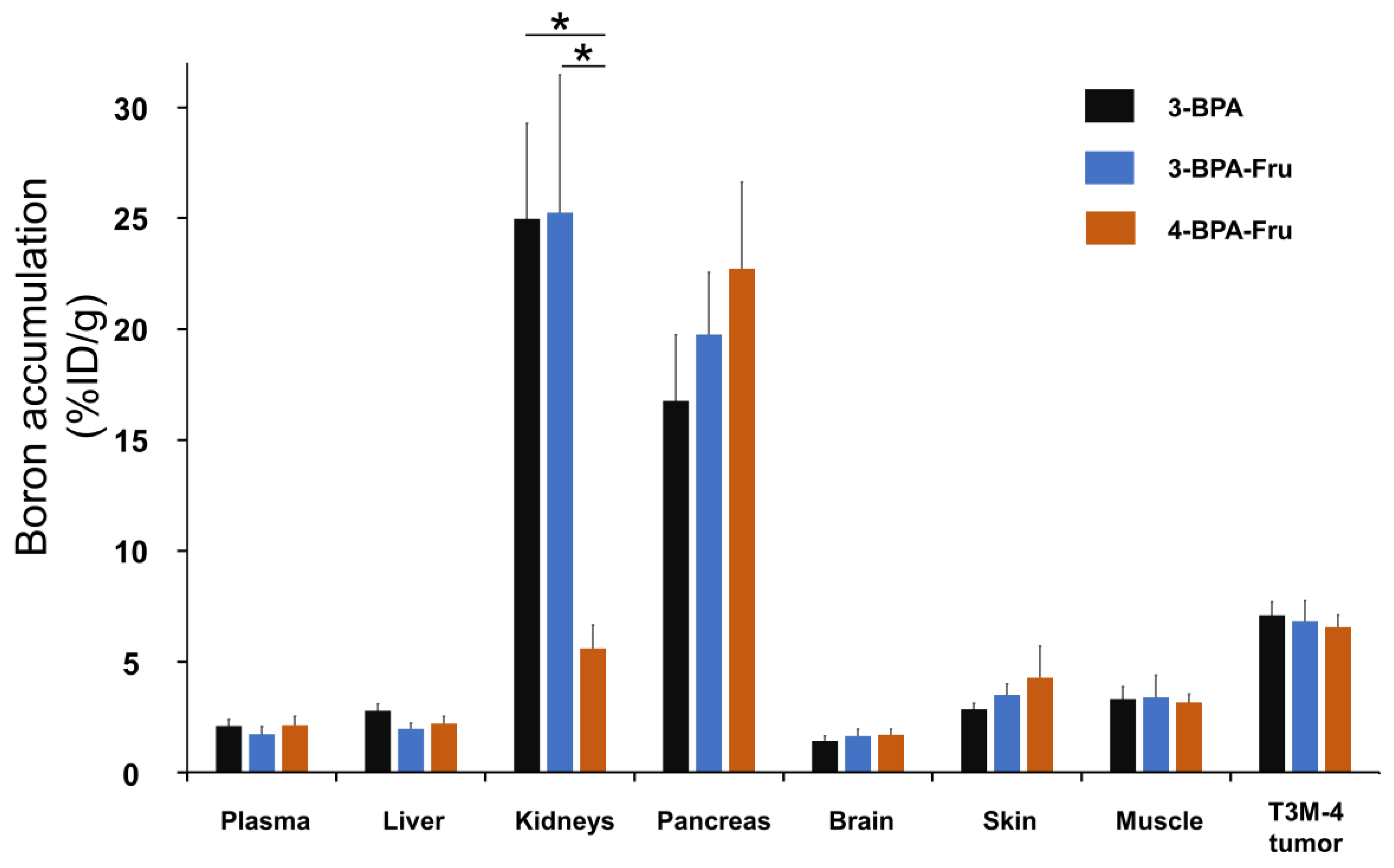
3.3. Biodistribution Study
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moss, R.L. Critical review, with an optimistic outlook, on boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 88, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedunchezhian, K.; Aswath, N.; Thiruppathy, M.; Thirugnanamurthy, S. Boron neutron capture therapy—A literature review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZE01–ZE04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, R.F.; Coderre, J.A.; Vicente, M.G.; Blue, T.E. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: Current status and future prospects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3987–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, M.J.; Turowski, B.; Zanella, F.E.; Paquis, P.; Siefert, A.; Hideghety, K.; Haselsberger, K.; Grochulla, F.; Postma, T.J.; Wittig, A.; et al. Radiologic findings in patients treated with boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma multiforme within EORTC trial 11961. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 61, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skold, K.; Gorlia, T.; Pellettieri, L.; Giusti, V.; H-Stenstam, B.; Hopewell, J.W. Boron neutron capture therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: An assessment of clinical potential. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, R.F.; Mi, P.; Yang, W. Boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy of cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H.R.; Reedy, A.J.; Lennarz, W.J. Synthesis of aromatic boronic acids. aldehydo boronic acids and a boronic acid analog of tyrosine1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 80, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, Y.; Ichihashi, M.; Hatta, S.; Honda, C.; Yamamura, K.; Nakagawa, T. New thermal neutron capture therapy for malignant melanoma: Melanogenesis-seeking 10B molecule-melanoma cell interaction from in vitro to first clinical trial. Pigment Cell Res. 1989, 2, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elowitz, E.H.; Bergland, R.M.; Coderre, J.A.; Joel, D.D.; Chadha, M.; Chanana, A.D. Biodistribution of p-boronophenylalanine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme for use in boron neutron capture therapy. Neurosurgery 1998, 42, 463–468, discussion 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanana, A.D.; Capala, J.; Chadha, M.; Coderre, J.A.; Diaz, A.Z.; Elowitz, E.H.; Iwai, J.; Joel, D.D.; Liu, H.B.; Ma, R.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: Interim results from the phase I/II dose-escalation studies. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 1182–1192, discussion 1192–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, I.; Ono, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Ohmae, M.; Maruhashi, A.; Imahori, Y.; Kirihata, M.; Nakazawa, M.; Yura, Y. Effectiveness of BNCT for recurrent head and neck malignancies. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, H.; Nagata, H.; Ishiguro, A.; Tsuzuranuki, S.; Nakano, S.; Nonaka, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Kimura, T.; Sugawara, A.; Okazaki, Y.; et al. Designation products: Boron neutron capture therapy for head and neck carcinoma. Oncologist 2021, 26, e1250–e1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detta, A.; Cruickshank, G.S. L-amino acid transporter-1 and boronophenylalanine-based boron neutron capture therapy of human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongthai, P.; Hagiwara, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Wei, L.; Ohgaki, R.; Kato, I.; Hamase, K.; Nagamori, S.; Kanai, Y. Boronophenylalanine, a boron delivery agent for boron neutron capture therapy, is transported by ATB0,+, LAT1 and LAT2. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwata, K. 4-Borono-2-18F-fluoro-L-phenylalanine PET for boron neutron capture therapy-oriented diagnosis: Overview of a quarter century of research. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2019, 33, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, Y. Amino acid transporter LAT1 (SLC7A5) as a molecular target for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 230, 107964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloway, A.H.; Tjarks, W.; Barnum, B.A.; Rong, F.G.; Barth, R.F.; Codogni, I.M.; Wilson, J.G. The chemistry of neutron capture therapy. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1515–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Yoshino, K.; Kakihana, H. Complex formation of p-boronophenylalanine with some monosaccharides. Pigment. Cell Res. 1989, 2, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Hirose, K.; Harada, T.; Sato, M.; Watanabe, T.; Anbai, A.; Hashimoto, M.; Takai, Y. Impact of oxygen status on 10B-BPA uptake into human glioblastoma cells, referring to significance in boron neutron capture therapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, J.; Ruokonen, I.; Lapatto, R.; Kallio, M. Inborn errors in metabolism and 4-boronophenylalanine-fructose-based boron neutron capture therapy. Radiat. Res. 2003, 160, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, R.; Capala, J.; Michanek, A.; Lindahl, S.A.; Salford, L.G.; Franzen, L.; Blomquist, E.; Westlin, J.E.; Bergenheim, A.T.; Swedish Brain Tumour Study Group. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for glioblastoma multiforme: A phase II study evaluating a prolonged high-dose of boronophenylalanine (BPA). Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 88, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, J.; Miyamoto, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Uchiyama, M.; Makishima, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Improvement in aqueous solubility of achiral symmetric cyclofenil by modification to a chiral asymmetric analog. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Tomoshige, S.; Makishima, M.; Muranaka, A.; Uchiyama, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Improvement in aqueous solubility of retinoic acid receptor (RAR) agonists by bending the molecular structure. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Hiramatsu, M.; Mita, Y.; Makishima, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Masumoto, Y.; Muranaka, A.; Uchiyama, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Meta-non-flat substituents: A novel molecular design to improve aqueous solubility in small molecule drug discovery. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, H.C.; Colas, C.; Finke, K.; Springer, S.; Stoner, L.; Zur, A.A.; Venteicher, B.; Campbell, J.; Hall, C.; Flint, A.; et al. Reevaluating the substrate specificity of the L-type amino acid transporter (LAT1). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7358–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ecker, G.F. Insights into the structure, function, and ligand discovery of the large neutral amino acid transporter 1, LAT1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, J.; Yoshino, K.; Kondoh, H.; Imajo, Y.; Mishima, Y. Biodistribution of boron concentration on melanoma-bearing hamsters after administration of p-, m-, o-boronophenylalanine. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2000, 91, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, J.; Kondoh, H.; Tsuboi, T.; Yoshino, K.; Imajo, Y.; Mishima, Y. Selective uptake of para-boronophenylalanine increases in amelanotic melanoma cells transfected by the tyrosinase gene. Melanoma Res. 2000, 10, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-J.; Lee, C.-Y.; Cheon, C.-H. General methods for synthesis of N-methyliminodiacetic acid boronates from unstableortho-phenolboronic acids. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.; Chen, J.; Richardson, D.; Thorpe, R.; Yuan, Y. A Highly stereoselective and scalable synthesis of L-allo-enduracididine. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4620–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgin, N.; Flinn, T.; Cobb, S.L. Synthesis and properties of MIDA boronate containing aromatic amino acids: New peptide building blocks. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okunushi, K.; Furihata, T.; Morio, H.; Muto, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Kaneko, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Ohno, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Reien, Y.; et al. JPH203, a newly developed anti-cancer drug, shows a preincubation inhibitory effect on L-type amino acid transporter 1 function. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 144, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafliger, P.; Graff, J.; Rubin, M.; Stooss, A.; Dettmer, M.S.; Altmann, K.H.; Gertsch, J.; Charles, R.P. The LAT1 inhibitor JPH203 reduces growth of thyroid carcinoma in a fully immunocompetent mouse model. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Okazaki, S.; Sampetrean, O.; Irie, J.; Itoh, H.; Saya, H. CD44 variant inhibits insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells by attenuating LAT1-mediated amino acid uptake. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, K.; Watanabe, N.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, S.; Ichihashi, M.; Kakihana, H.; Mishima, Y. Chemical properties of p-, m-, o-boronophenylalanine. In Cancer Neutron Capture Therapy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Cai, K.Z.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, C.G.; Xu, B.C. Small molecular weight aldose (d-Glucose) and basic amino acids (l-Lysine, l-Arginine) Increase the occurrence of PAHs in grilled pork sausages. Molecules 2018, 23, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchcock, D.I. The solubility of tyrosine in acid and in alkali. J. Gen. Physiol. 1924, 6, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hossain, A.; Roy, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mondal, S.; Dolui, B.K. Solubility of dl-serine and dl-phenylalanine in aqueous mixtures of dimethyl sulfoxide and solvation thermodynamics. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69839–69847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; Kondoh, H.; Hiratsuka, J.; Mishima, Y. Enhanced melanogenesis induced by tyrosinase gene-transfer increases boron-uptake and killing effect of boron neutron capture therapy for amelanotic melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 1998, 11, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, R.; Yamada, S.; Ishiwata, K.; Tada, M.; Ido, T.; Kubota, K. Cellular accumulation of 18F-labelled boronophenylalanine depending on DNA synthesis and melanin incorporation: A double-tracer microautoradiographic study of B16 melanomas in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 67, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aihara, T.; Morita, N.; Kamitani, N.; Kumada, H.; Ono, K.; Hiratsuka, J.; Harada, T. Boron neutron capture therapy for advanced salivary gland carcinoma in head and neck. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, T.; Hanaoka, K.; Naka, S.; Kanai, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Aoki, M.; Shimosegawa, E.; Kirihata, M.; Hatazawa, J. Practical calculation method to estimate the absolute boron concentration in tissues using 18F-FBPA PET. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2017, 31, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkinen, S.; Savolainen, S.; Melkko, P. In vitro studies on stability of L-p-boronophenylalanine-fructose complex (BPA-F). J. Radiat. Res. 2011, 52, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svantesson, E.; Capala, J.; Markides, K.E.; Pettersson, J. Determination of boron-containing compounds in urine and blood plasma from boron neutron capture therapy patients. The importance of using coupled techniques. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5358–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichihashi, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Mishima, Y. Specific killing effect of 10B1-para-boronophenylalanine in thermal neutron capture therapy of malignant melanoma: In vitro radiobiological evaluation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomoto, T.; Inoue, Y.; Yao, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kanamori, K.; Takemoto, H.; Matsui, M.; Tomoda, K.; Nishiyama, N. Poly(vinyl alcohol) boosting therapeutic potential of p-boronophenylalanine in neutron capture therapy by modulating metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Lang, L.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z. A metabolically stable boron-derived tyrosine serves as a theranostic agent for positron emission tomography guided noron neutron capture therapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 2870–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 3-BPA | 4-BPA | |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility (in water, 25 °C, n = 6) | * 125 ± 12 (g/L) | 0.72 ± 0.13 (g/L) |
| Log p (n = 12) | † −1.59 ± 0.03 | −1.80 ± 0.04 |
| RP-HPLC Retention time | 4.5 (min) | 3.7 (min) |
| Time after Administration (min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 (n = 4) | 30 (n = 4) | 60 (n = 7) | 120 (n = 4) | |
| Plasma | 5.1 ± 0.6 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.1 |
| Liver | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | 2.6 ± 0.3 |
| Kidneys | 58.3 ± 11.3 | 53.6 ± 7.1 | 36.4 ± 8.4 | 23.0 ± 1.9 |
| Pancreas | 52.5 ± 4.9 | 50.2 ± 4.5 | 33.1 ± 8.5 | 34.4 ± 2.9 |
| Brain | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.5 |
| Skin | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 2.7 ± 0.6 |
| Muscle | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 4.4 ± 0.5 |
| B16F10 melanoma | 6.6 ± 2.1 | 7.0 ± 1.1 | 7.4 ± 1.0 | 6.2 ± 1.1 |
| Tumor/Plasma | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.4 |
| Time after Administration (min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 (n = 4) | 30 (n = 4) | 60 (n = 4) | 120 (n = 4) | |
| Plasma | 5.5 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 1.6 ± 0.2 |
| Liver | 7.4 ± 0.7 | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Kidneys | 16.9 ± 2.5 | 10.8 ± 1.6 | 8.4 ± 3.7 | 4.7 ± 0.6 |
| Pancreas | 44.1 ± 7.0 | 44.8 ± 5.7 | 33.9 ± 6.5 | 12.9 ± 1.4 |
| Brain | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.2 |
| Skin | 5.2 ± 0.7 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.9 | 2.5 ± 0.3 |
| Muscle | 3.1 ± 0.7 | 4.2 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 2.8 ± 0.3 |
| B16F10 melanoma | 4.3 ± 1.4 | 6.4 ± 1.0 | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 5.8 ± 0.4 |
| Tumor/Plasma | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 3.6 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondo, N.; Hirano, F.; Temma, T. Evaluation of 3-Borono-l-Phenylalanine as a Water-Soluble Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Agent. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051106
Kondo N, Hirano F, Temma T. Evaluation of 3-Borono-l-Phenylalanine as a Water-Soluble Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Agent. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(5):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondo, Naoya, Fuko Hirano, and Takashi Temma. 2022. "Evaluation of 3-Borono-l-Phenylalanine as a Water-Soluble Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Agent" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 5: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051106
APA StyleKondo, N., Hirano, F., & Temma, T. (2022). Evaluation of 3-Borono-l-Phenylalanine as a Water-Soluble Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Agent. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051106






