Multi-Modal Imaging to Assess the Follicular Delivery of Zinc Pyrithione
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulations
2.2. Spectral Characterisation
2.3. Cryo-Scanning Electron Microscopy (Cryo-SEM)
2.4. Human Skin Experiments
2.5. Multiphoton Microscopy and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (MPM-FLIM)
2.6. Dissolution Studies
2.7. Data and Image Analysis
3. Results
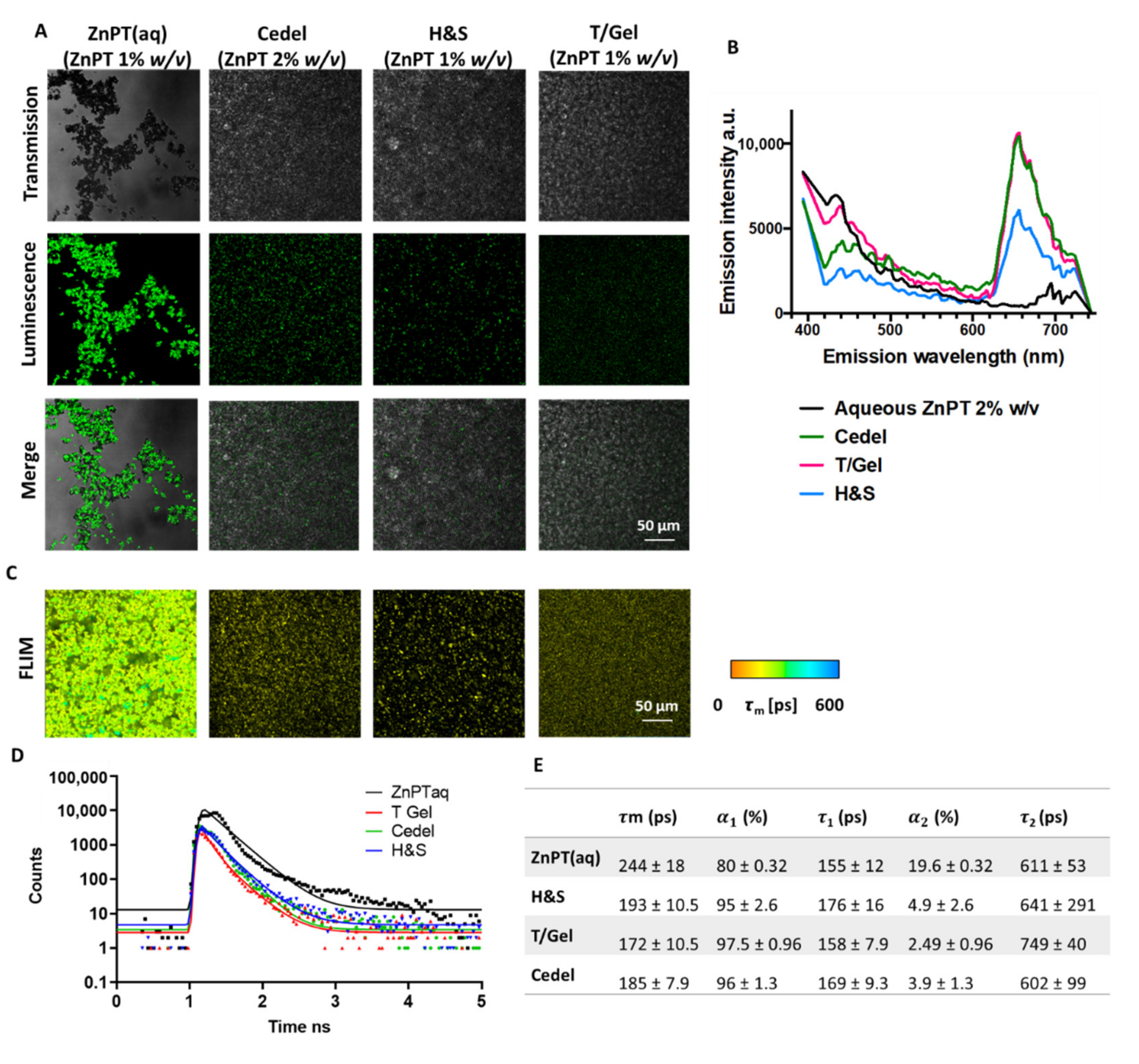
3.1. Spectral Characterisation of Commercial Formulations
3.2. Time-Resolved Imaging
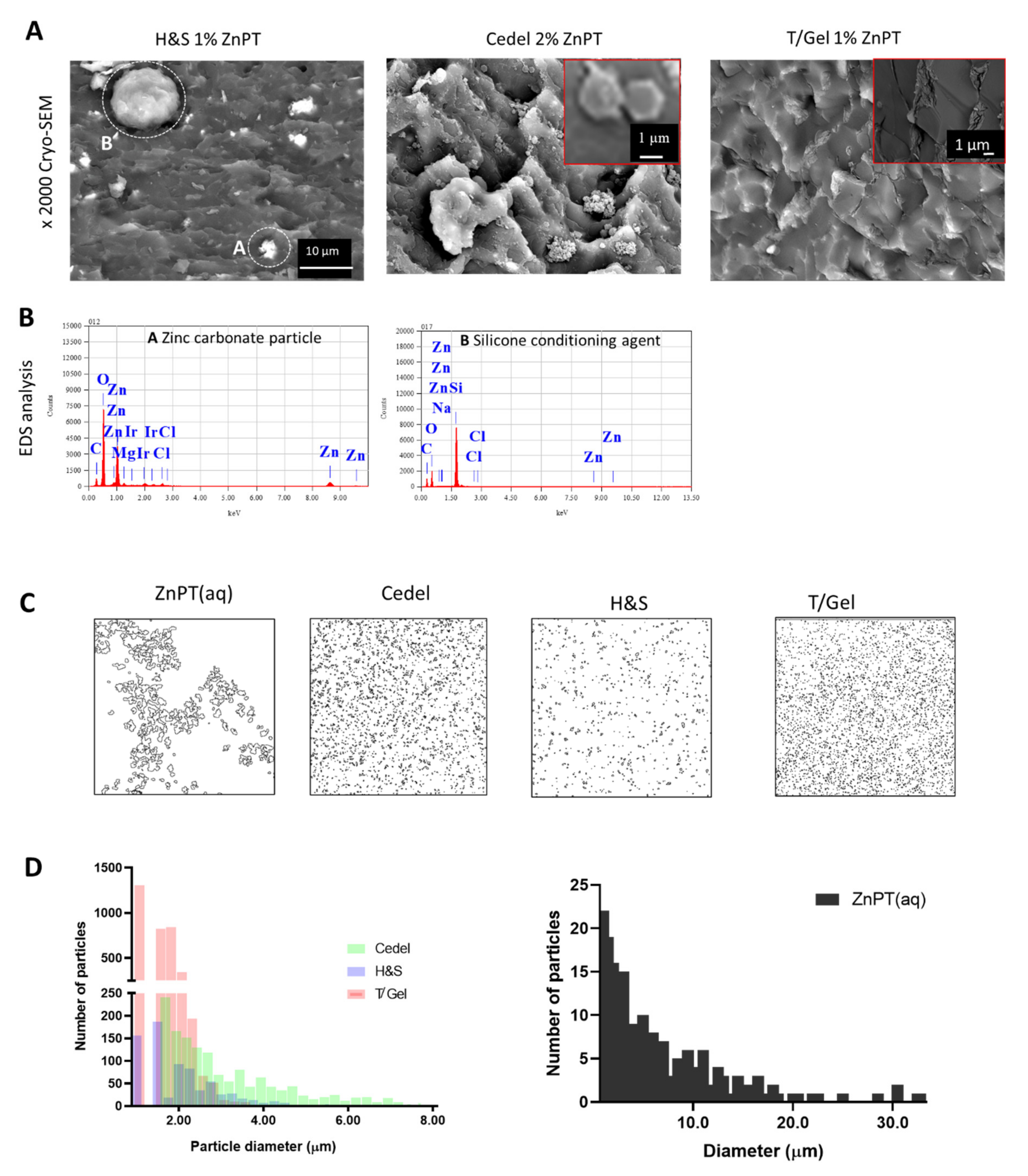
3.3. Microstructure and Particle Size
3.4. Dissolution of ZnPT
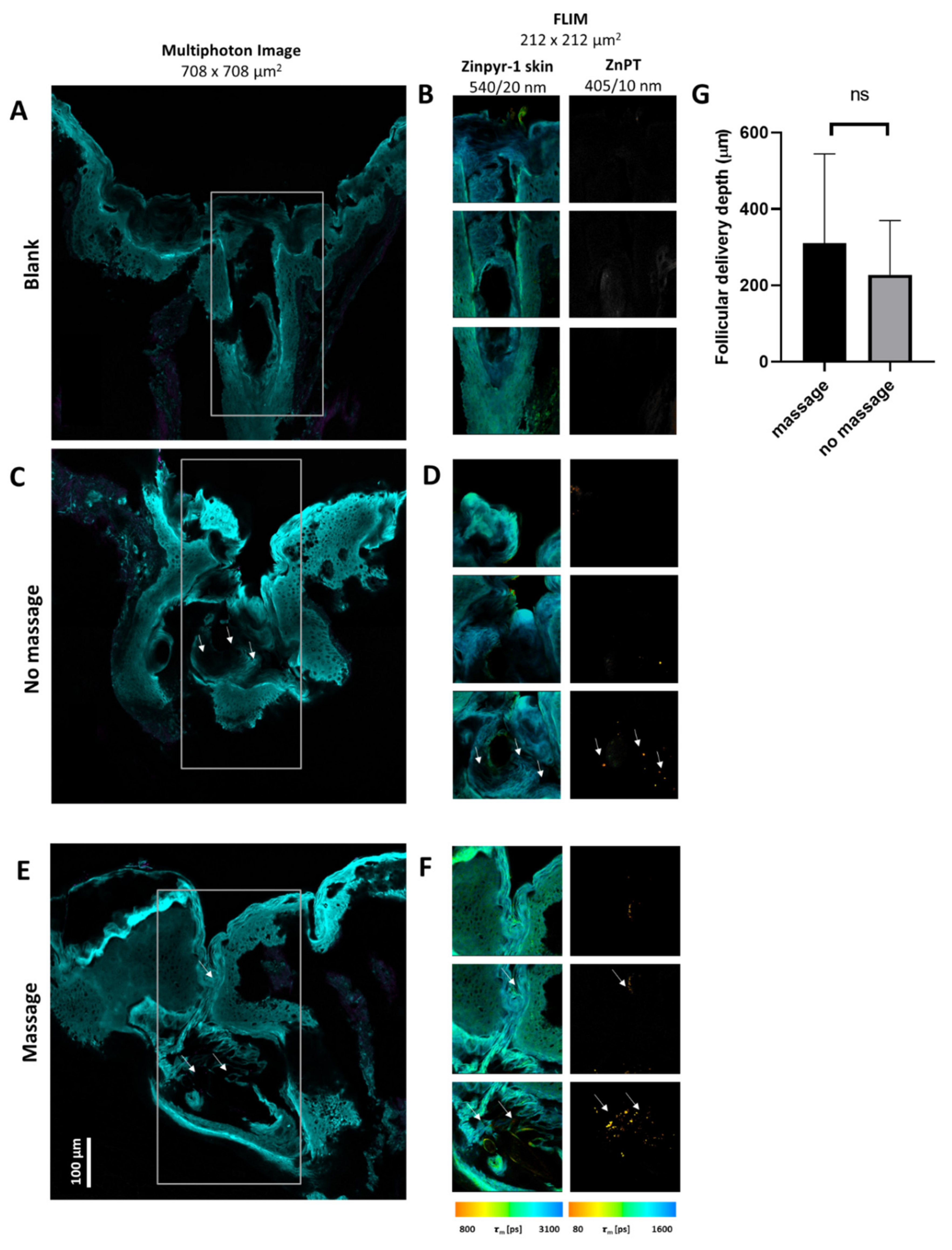
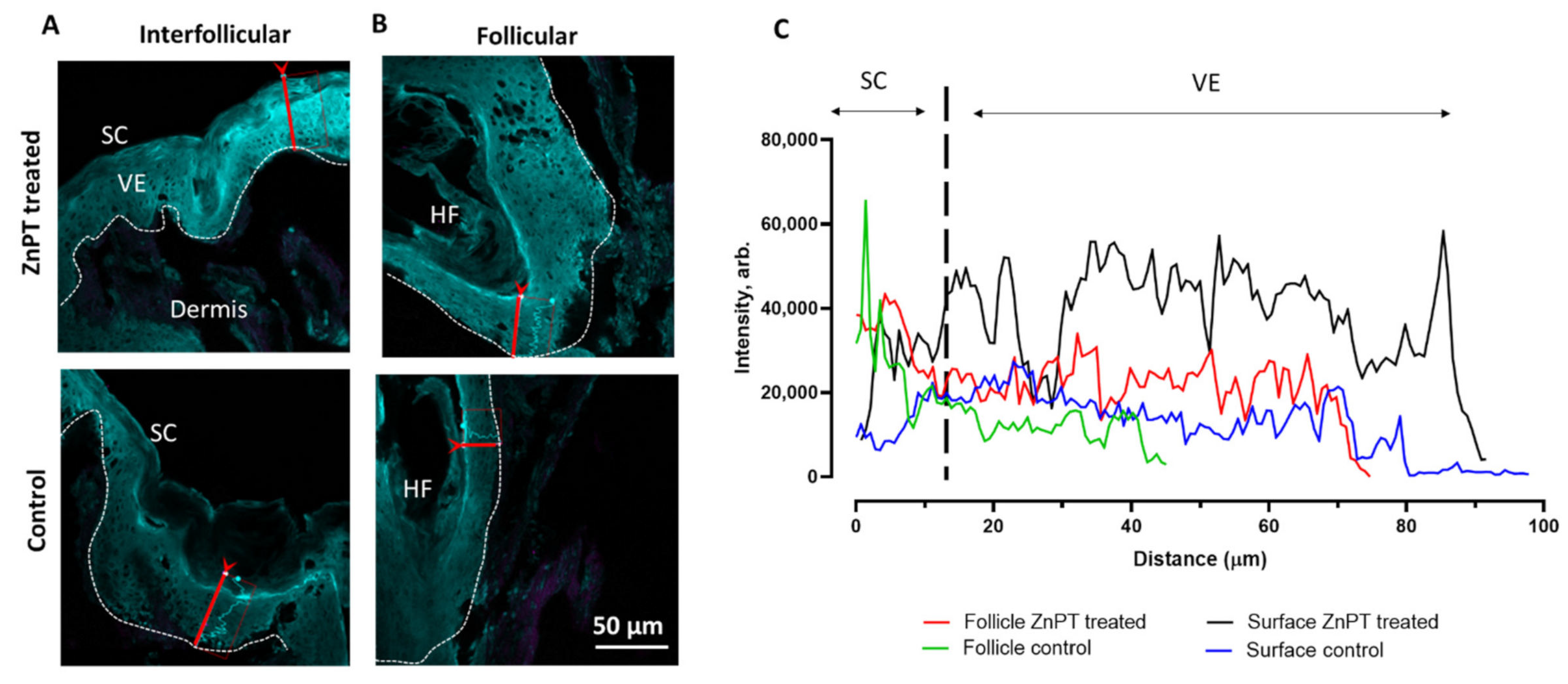
3.5. Detection of ZnPT in Hair Follicles from ZnPT (aq)
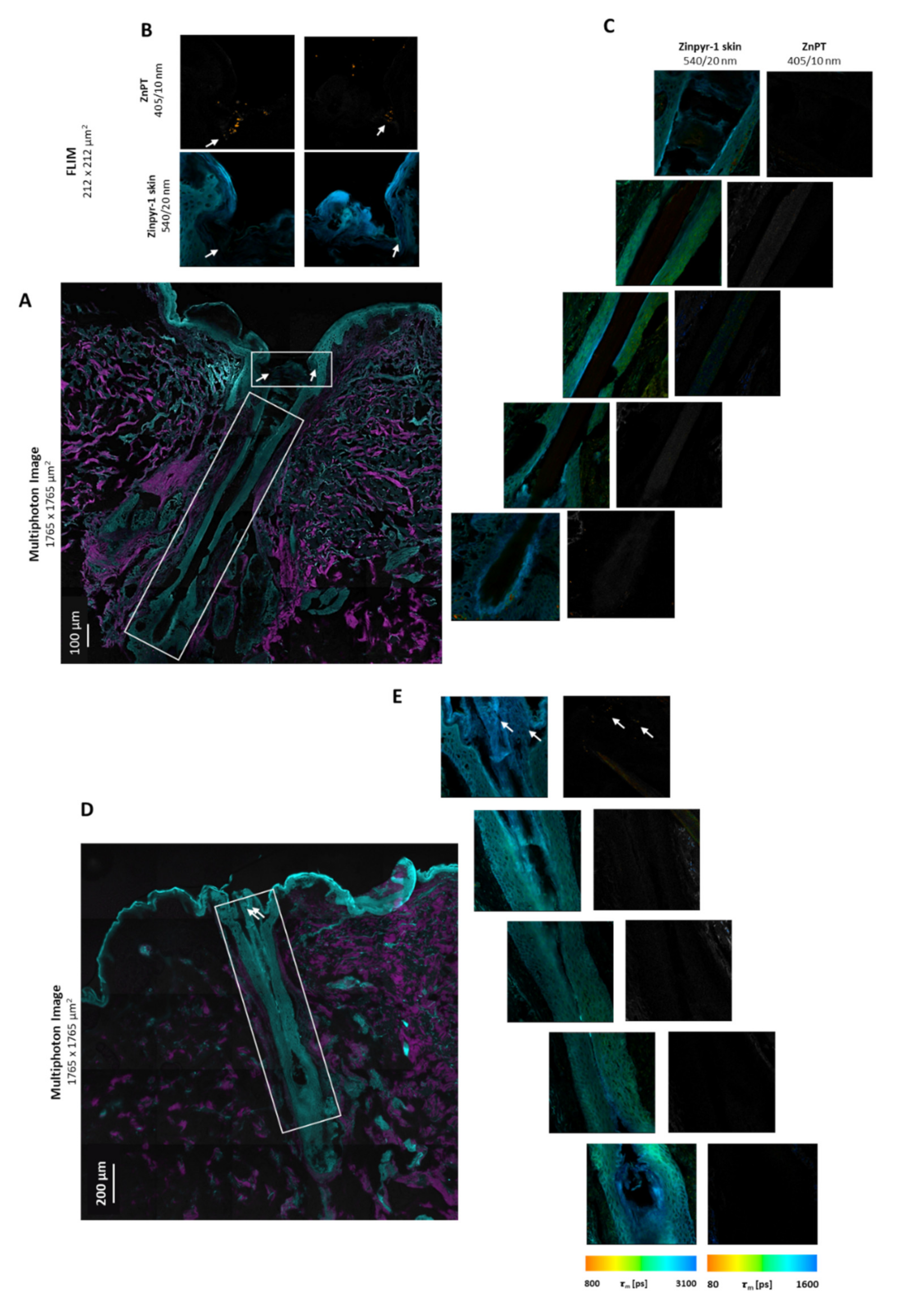
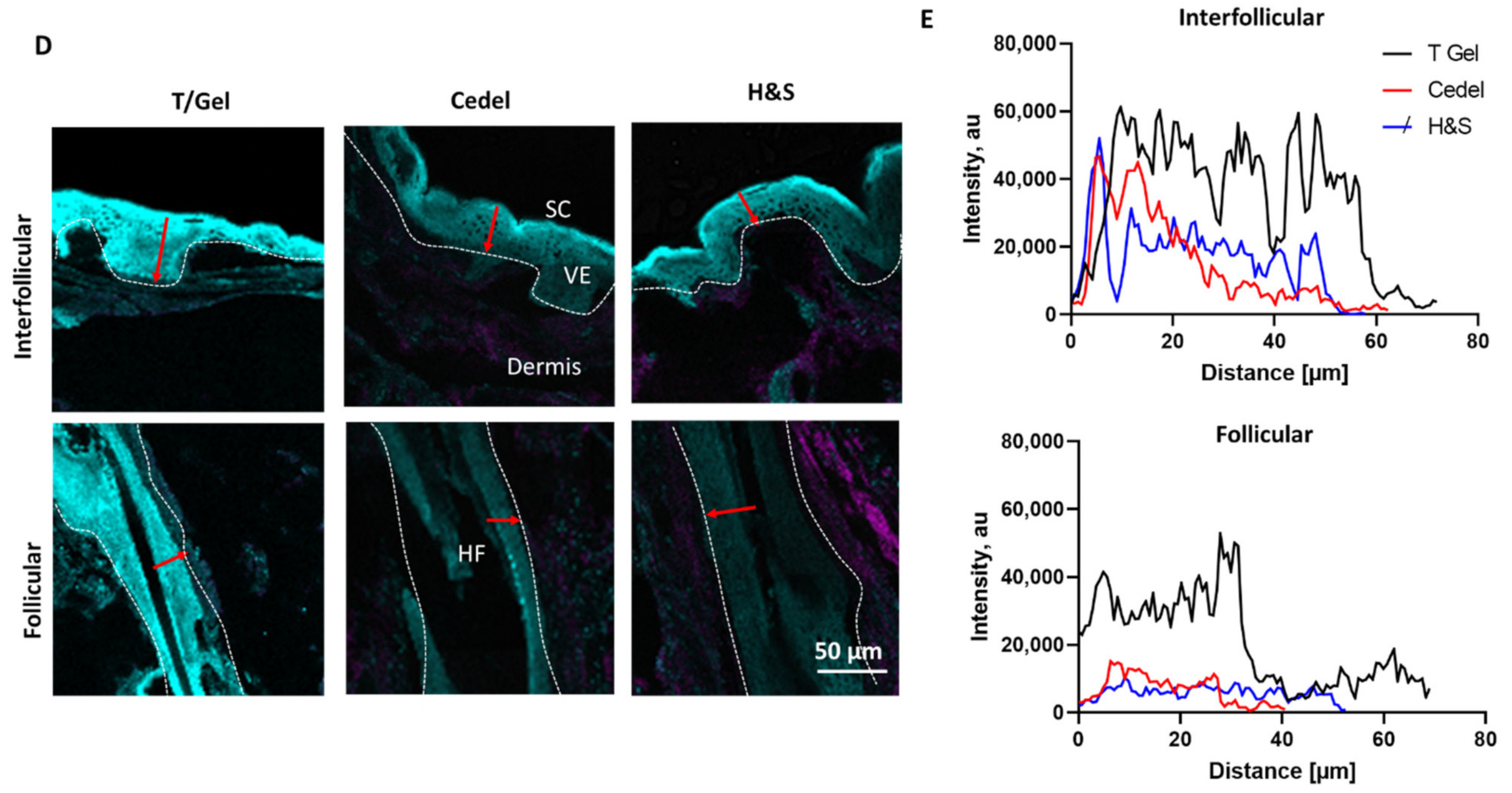
3.6. Detection of ZnPT in Hair Follicles from Commercial Products
3.7. ZnPT Dissolution on Skin Surface and Within Hair Follicles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| H&S | Head and Shoulders |
| MPM | multiphoton microscopy |
| FLIM | fluorescence lifetime imaging microscop |
| ZnPT | zinc pyrithione |
| SD | seborrheic dermatitis |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy. |
References
- Lonza Consumer Care. Zinc OmadineTM 48% Aqueous Dispersion FPS (Fine Particle Size) Safe & Effective Dandruff Relief; Lonza Consumer Care: South Plainfield, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Leger, D. Dandruff (pityriasis capitis simplex): Of yeasts and men. In The Science of Haircare, 2nd ed.; Bouillon, C., Wilkinson, J., Eds.; Tailor and Francis Boca Raton: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 609–631. [Google Scholar]
- McGinley, K.J.; Leyden, J.J.; Marples, R.R.; Path, M.R.C.; Kligman, A.M. Quantitative Microbiology of the Scalp in Non-Dandruff, Dandruff, and Seborrheic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1975, 64, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangion, S.E.; Holmes, A.M.; Roberts, M.S. Targeted Delivery of Zinc Pyrithione to Skin Epithelia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.R. Product Pharmacology and Medical Actives in Achieving Therapeutic Benefits. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2005, 10, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Commision. Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1902 of 29 October 2021; Official Journal of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Piérard, G.E.; Xhauflaire-Uhoda, E.; Piérard-Franchimont, C. The key role of corneocytes in pityrosporoses. Dermatology 2006, 212, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, L.E.; Otberg, N.; Tietz, H.J.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. In vivo imaging of Malassezia yeasts on human skin using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Laser Phys. Lett. 2005, 2, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.R.; Johnson, E.S.; Dawson, T.L. Shampoos for Normal Scalp Hygiene and Dandruff. In Cosmetic Dermatology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chwartz, J.R.; Shah, R.; Krigbaum, H.; Sacha, J.; Vogt, A.; Blume-Peytavi, U. New insights on dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis: The role of the scalp follicular infundibulum in effective treatment strategies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165 (Suppl. S2), 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, T.; Black, J.G. The use of autoradiography to study the localization of germicides in the skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 1969, 81, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, N.L.; Singh, B.; Jones, A.; Moger, J. Imaging microscopic distribution of antifungal agents in dandruff treatments with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 66003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandiford, L.; Holmes, A.M.; Mangion, S.E.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Zvyagin, A.V.; Roberts, M.S. Optical Characterisation of Zinc Pyrithione. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breunig, H.G.; Studier, H.; Konig, K. Multiphoton excitation characteristics of cellular fluorophores of human skin in vivo. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7857–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, K.; Riemann, I. High-resolution multiphoton tomography of human skin with subcellular spatial resolution and picosecond time resolution. J. Biomed. Opt. 2003, 8, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, W. Fluorescence lifetime imaging—Techniques and applications. J. Microsc. 2012, 247, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite-Silva, V.R.; Sanchez, W.Y.; Studier, H.; Liu, D.C.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Holmes, A.M.; Ryan, E.M.; Haridass, I.N.; Chandrasekaran, N.C.; Becker, W.; et al. Human skin penetration and local effects of topical nano zinc oxide after occlusion and barrier impairment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. eV 2016, 104, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leite-Silva, V.R.; Liu, D.C.; Sanchez, W.Y.; Studier, H.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Holmes, A.; Becker, W.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.; Roberts, M.S. Effect of flexing and massage on in vivo human skin penetration and toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, Y.H.; Haridass, I.N.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.E.; Roberts, M.S. Bathing Does Not Facilitate Human Skin Penetration or Adverse Cellular Effects of Nanoparticulate Zinc Oxide Sunscreens after Topical Application. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, Y.H.; Holmes, A.; Haridass, I.N.; Sanchez, W.Y.; Studier, H.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.E.; Roberts, M.S. Support for the Safe Use of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Sunscreens: Lack of Skin Penetration or Cellular Toxicity after Repeated Application in Volunteers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, A.M.; Kempson, I.; Turnbull, T.; Paterson, D.; Roberts, M.S. Imaging the penetration and distribution of zinc and zinc species after topical application of zinc pyrithione to human skin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 343, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, A.M.; Song, Z.; Moghimi, H.R.; Roberts, M.S. Relative Penetration of Zinc Oxide and Zinc Ions into Human Skin after Application of Different Zinc Oxide Formulations. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, A.K.; Nash, J.F.; Smith Iii, E.D.; Kasting, G.B. Formulation and Artificial Sebum Effects on the Percutaneous Absorption of Zinc Pyrithione through Excised Human Skin. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 32, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhling, K.; Hirvonen, L.M.; Levitt, J.A.; Chung, P.-H.; Tregido, C.; le Marois, A.; Rusakov, D.A.; Zheng, K.; Ameer-Beg, S.; Poland, S.; et al. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM): Basic Concepts and Recent Applications. In Advanced Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Applications; Becker, W., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 119–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi, T.; Nakai, Y.; Torii, Y. Photoluminescence of bis(8-hydroxyquinoline) zinc (Znq2) and magnesium (Mgq2). Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 2012, 10, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Knorr, F.; Schäfer, U.; Lehr, C.-M.; Dähne, L.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Selective follicular targeting by modification of the particle sizes. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Weigmann, H.; Rickmeyer, C.; Barthelmes, H.; Schaefer, H.; Mueller, G.; Sterry, W. Penetration of titanium dioxide microparticles in a sunscreen formulation into the horny layer and the follicular orifice. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 1999, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorr, F.; Lademann, J.; Patzelt, A.; Sterry, W.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A. Follicular transport route-research progress and future perspectives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Pharm. Verfahr. eV 2009, 71, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, A.M.; Lim, J.; Studier, H.; Roberts, M.S. Varying the morphology of silver nanoparticles results in differential toxicity against micro-organisms, HaCaT keratinocytes and affects skin deposition. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Z.; Li, Y.F. Resonance light scattering technique used for biochemical and pharmaceutical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 500, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, C. Chemical and Physical Behaviour of Human Hair, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Trueb, R.M. Shampoos: Ingredients, efficacy and adverse effects. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. JDDG 2007, 5, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, C. Shampoos. Clin. Derm. 1996, 14, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.R. Zinc Pyrithione: A Topical Antimicrobial With Complex Pharmaceutics. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2016, 15, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.R.; Bacon, R.A.; Shah, R.; Mizoguchi, H.; Tosti, A. Therapeutic efficacy of anti-dandruff shampoos: A randomized clinical trial comparing products based on potentiated zinc pyrithione and zinc pyrithione/climbazole. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, W.; Su, B.; Holub, O.; Weisshart, K. FLIM and FCS detection in laser-scanning microscopes: Increased efficiency by GaAsP hybrid detectors. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, A.K.; Miller, M.A.; Smith Iii, E.D.; Kasting, G.B. A quantitative radioluminographic imaging method for evaluating lateral diffusion rates in skin. J. Control. Release 2015, 216, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otberg, N.; Richter, H.; Knuttel, A.; Schaefer, H.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Laser spectroscopic methods for the characterization of open and closed follicles. Laser Phys. Lett. 2004, 1, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Knorr, F.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Hair follicles, their disorders and their opportunities. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2008, 5, e173–e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, A.; Hadam, S.; Heiderhoff, M.; Audring, H.; Lademann, J.; Sterry, W.; Blume-Peytavi, U. Morphometry of human terminal and vellus hair follicles. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Meinke, M.; Sterry, W.; Patzelt, A. Which skin model is the most appropriate for the investigation of topically applied substances into the hair follicles? Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 23, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Teichmann, A.; Otberg, N.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Luengo, J.; Weiss, B.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.M.; Wepf, R.; et al. Nanoparticles—An efficient carrier for drug delivery into the hair follicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Pharm. Verfahr. eV 2007, 66, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, S.; Jardas, J.; Polson, G.; Beaty, D.; Kaufman, C. Non-Spherical and Non-Platelet Forms of Pyrithione Salts and Methods of Making Same; ArchChemicals Inc.: Alpharetta, GA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantar, T.H.; Foley, P.; Tucker, C.J.; Felix, M.S.; Rozeveld, S.J.; Harris, J.D.; Crowder, C.E.; Howard, K.E. A green synthesis of bis[1-(hydroxy-κO)-2(1H)-pyridinethionato-κS2]-(T-4)-zinc (zinc pyrithione) nanoparticles via mechanochemical milling. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, S.H.; Jardas, J.J. Sonic Method of Enhancing Chemical Reactions to Provide Uniform, Non-Agglomerated Particles. U.S. Patent No. 6,682,724, 27 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sahle, F.F.; Giulbudagian, M.; Bergueiro, J.; Lademann, J.; Calderon, M. Dendritic polyglycerol and N-isopropylacrylamide based thermoresponsive nanogels as smart carriers for controlled delivery of drugs through the hair follicle. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Product | Particle Delivery Observations | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 min Massage | No Massage | |
| Head and Shoulders (1% w/v) | Average deposition depth of 57 ± 65 µm (n = 3) | Deposition at 117 µm (n = 1) or not observed (n = 2) |
| Cedel (1% w/v) | Average depth 441 ± 543 µm (n = 2) or not observed (n = 1) | Depth of 61 µm (n = 1) or no particles observed (n = 2) |
| T/Gel (2% w/v) | Surface deposition (n = 2) or no deposition observed (n = 1) | Deposition at 154 µm (n = 1) or no deposition observed (n = 2) |
| Aqueous suspension (2% w/v) | Average deposition depth of 310 ± 243 µm (n = 3) | Average deposition depth of 228 ± 142 µm (n = 3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mangion, S.E.; Sandiford, L.; Mohammed, Y.; Roberts, M.S.; Holmes, A.M. Multi-Modal Imaging to Assess the Follicular Delivery of Zinc Pyrithione. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051076
Mangion SE, Sandiford L, Mohammed Y, Roberts MS, Holmes AM. Multi-Modal Imaging to Assess the Follicular Delivery of Zinc Pyrithione. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(5):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051076
Chicago/Turabian StyleMangion, Sean E., Lydia Sandiford, Yousuf Mohammed, Michael S. Roberts, and Amy M. Holmes. 2022. "Multi-Modal Imaging to Assess the Follicular Delivery of Zinc Pyrithione" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 5: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051076
APA StyleMangion, S. E., Sandiford, L., Mohammed, Y., Roberts, M. S., & Holmes, A. M. (2022). Multi-Modal Imaging to Assess the Follicular Delivery of Zinc Pyrithione. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051076








