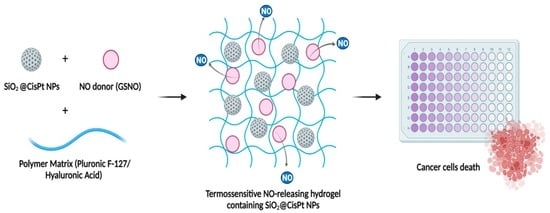
Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells of Pluronic F-127/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Containing Nitric Oxide Donor and Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of SiO2 NPs
2.3. Synthesis of SiO2@CisPt NPs and Evaluation of Cisplatin Encapsulation Efficiency
2.4. Synthesis of GSNO
2.5. Preparation of Pluronic F-127 Hydrogels
2.6. Characterization of the Prepared Materials
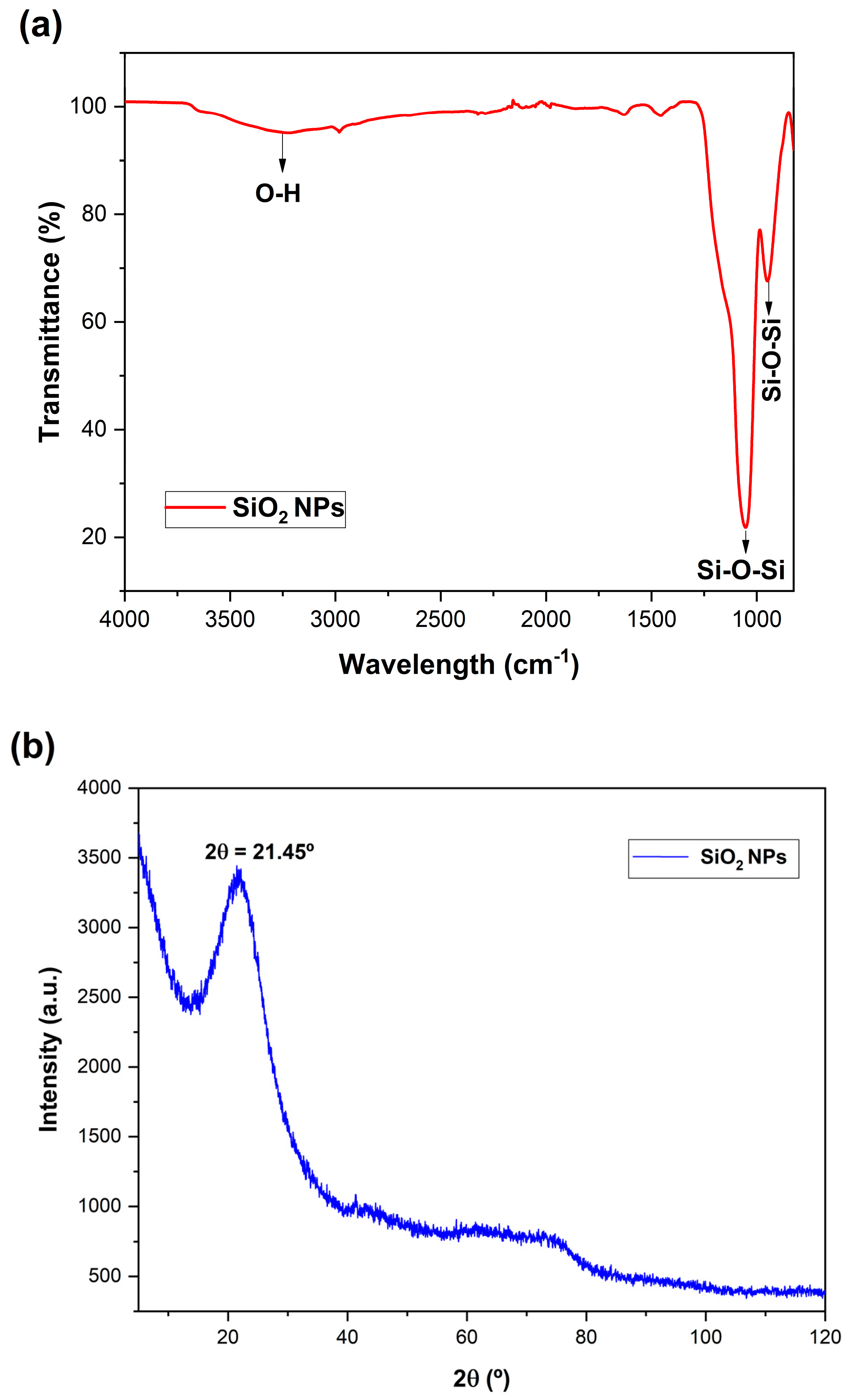
2.6.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.6.2. Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
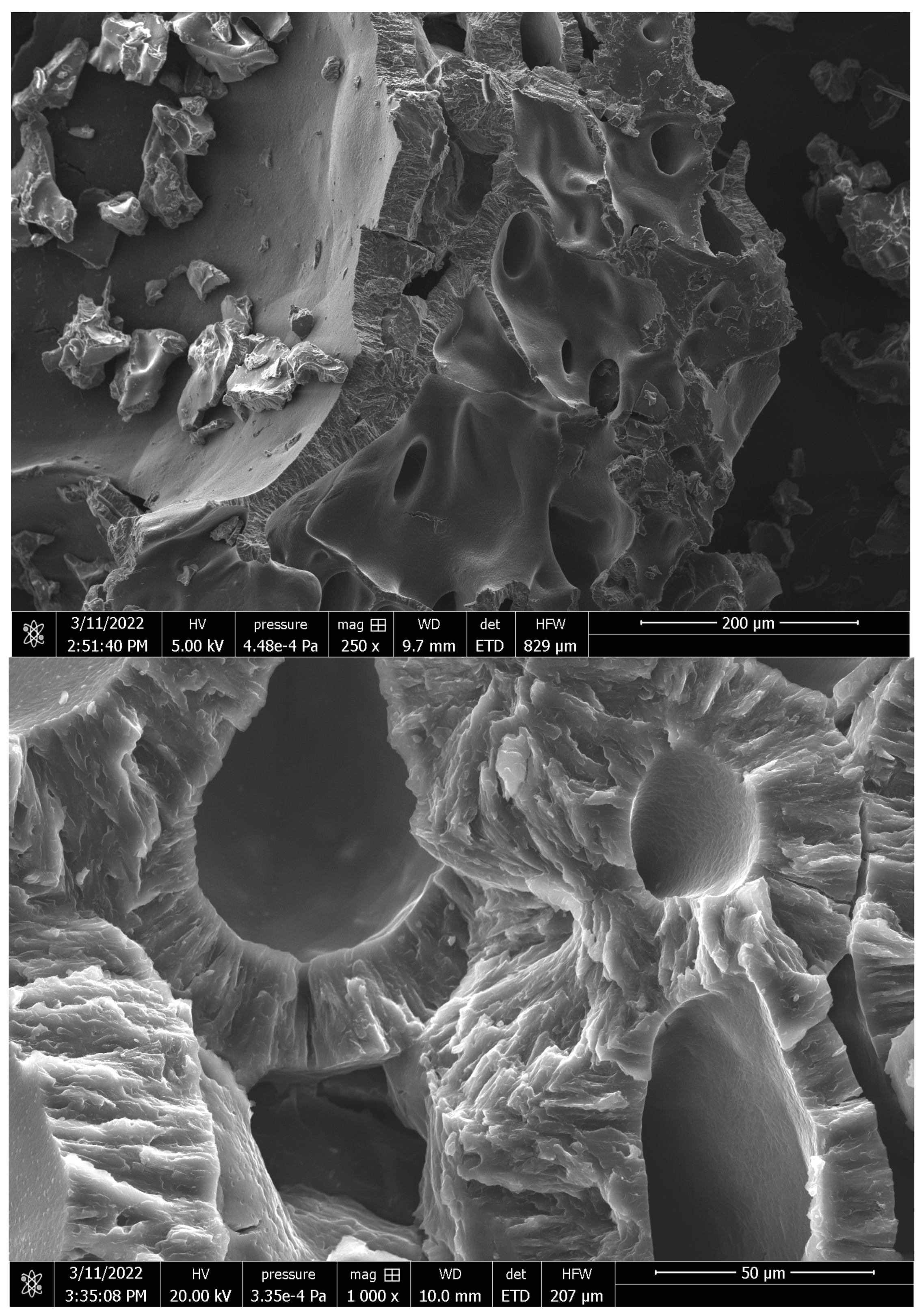
2.6.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Kinetics of NO Release from GSNO-Containing PL
2.8. In Vitro Diffusion of GSNO from PL-HA-SiO2@CisPt-GSNO
2.9. Mathematical Models
2.10. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assays
3. Results and Discussion
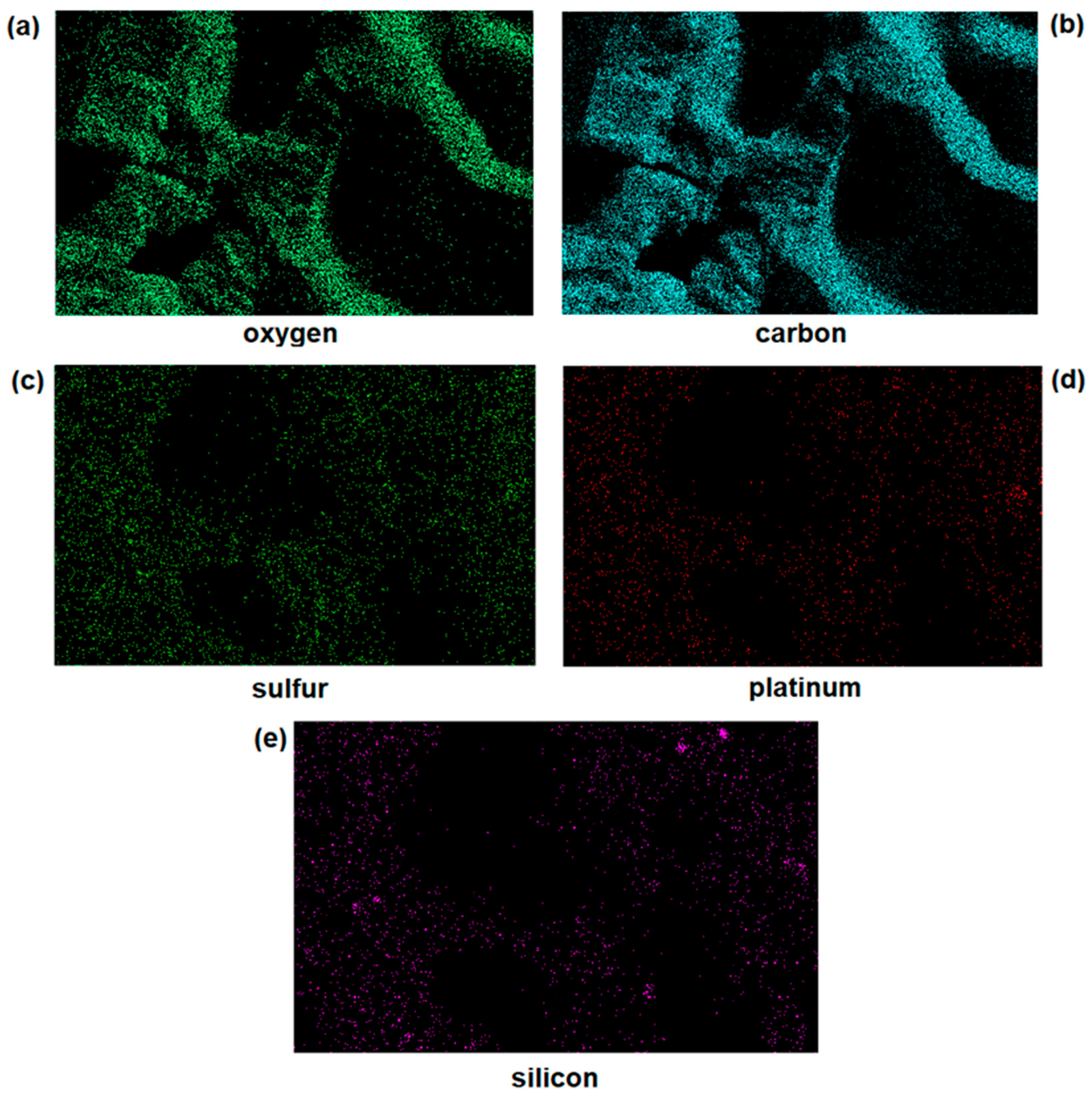
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of SiO2@CisPt NPs
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Pluronic-F127-Based Hydrogels
3.3. Kinetics of NO Release from GSNO-Containing PL
3.4. In Vitro Diffusion of GSNO from PL-HA-SiO2@CisPt-GSNO
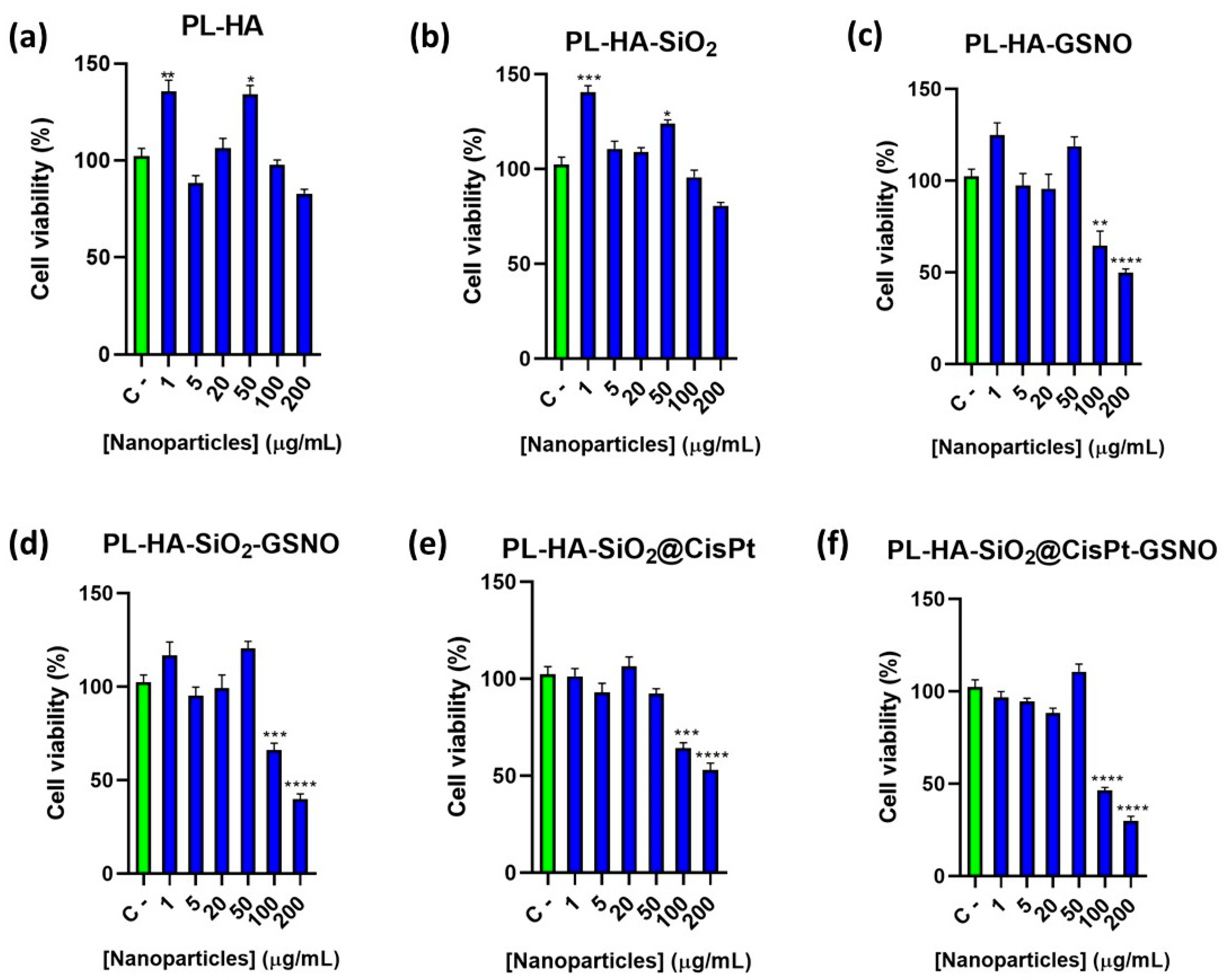
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of the Hydrogels against MDA-MB-231 Tumor Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, S.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Chen Ru Sun, K.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, J.; Wei, W. Global patterns of breast cancer incidence and mortality: A population-based cancer registry data analysis from 2000 to 2020. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Fu, M.; Yang, X.; Jia, G.; Shi, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, X.; Zhai, G. Paclitaxel and quercetin co-loaded functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles overcoming multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotaleb, M.; Kubatka, P.; Caprnda, M.; Varghese, E.; Zolakova, B.; Zubor, P.; Büsselberg, D. Chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer: An update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepantafar, M.; Maheronnaghsh, R.; Mohammadi, H.; Radmanesh, F.; Hasani-sadrabadi, M.M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Baharvand, H. Engineered Hydrogels in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.-Z.; Liu, Z.-Z.; Gu, S.-S.; Liu, X.-Q. Multiple local therapeutics based on nano-hydrogel composites in breast cancer treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1521–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegrino, M.; de Araujo Lima, B.; do Nascimento, M.; Lombello, C.; Brocchi, M.; Seabra, A. Biocompatible and Antibacterial Nitric Oxide-Releasing Pluronic F-127/Chitosan Hydrogel for Topical Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriky, B.; Kelly, A.; Isreb, M.; Babenko, M.; Mahmoudi, N.; Rogers, S.; Shebanova, O.; Snow, T.; Gough, T. Pluronic F127 Thermosensitive Injectable Smart Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery System Development. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 565, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ding, J. Injectable hydrogels as unique biomedical materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouda, L.; Mikos, A.G. Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, S.M.; Seabra, A.B.; Loh, W.; Ganzarolli de Oliveira, M. Thermal and photochemical nitric oxide release from S-nitrosothiols incorporated in Pluronic F127 gel: Potential uses for local and controlled nitric oxide release. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3543–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrino, M.T.; de Araújo, D.R.; Seabra, A.B. S-nitrosoglutathione-containing chitosan nanoparticles dispersed in Pluronic F-127 hydrogel: Potential uses in topical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Dai, Y.; Gao, H. Development and Application of Hyaluronic Acid in Tumor Targeting Drug Delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Q.; et al. CD44 targets Na+/H+ exchanger 1 to mediate MDA-MB-231 cells’ metastasis via the regulation of ERK1/2. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, P.G.; Mulay, P.; Venkat, R.; Ramalingam, C. Multifaceted Application of Silica Nanoparticles. A Review. Silicon 2019, 12, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuehr, D.J.; Haque, M.M. Nitric Oxide Synthase Enzymology in the Twenty Years after the Nobel Prize. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 176, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, J.C.; Pelegrino, M.T.; Nascimento, M.H.M.; Tortella, G.R.; Rubilar, O.; Seabra, A.B. Small molecules for great solutions: Can nitric oxide-releasing nanomaterials overcome drug resistance in chemotherapy? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 113740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokrollahi, A.; Zamani, R. Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic nanoparticle, functionalized with 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2019, 49, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Chen, F.; Sun, K.; An, P.; Sun, C.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, B. A novel pH-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle (HMSN) system encapsulating doxorubicin (DOX) and glucose oxidase (GOX) for potential cancer treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, H. The synergistic effect and mechanism of doxorubicin-ZnO nanocomplexes as a multimodal agent integrating diverse anticancer therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.H.M.; Franco, M.K.K.D.; Yokaichyia, F.; de Paula, E.; Lombello, C.B.; de Araujo, D.R. Hyaluronic acid in Pluronic F-127/F-108 hydrogels for postoperative pain in arthroplasties: Influence on physico-chemical properties and structural requirements for sustained drug-release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzedo, A.L.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Nascimento, M.H.; Lombello, C.B.; Nakazato, G.; Seabra, A.B. Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of alginate hydrogel containing nitric oxide donor and silver nanoparticles for topical applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 2117–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Peterson, D.A.; Kimura, H.; Schubert, D. Mechanism of Cellular 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Reduction. J. Neurochem. 1997, 69, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; He, Q.; Gao, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles loading doxorubicin reverse multidrug resistance: Performance and mechanism. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattheolabakis, G.; Taoufik, E.; Haralambous, S.; Roberts, M.L.; Avgoustakis, K. In vivo investigation of tolerance and antitumor activity of cisplatin-loaded PLGA-mPEG nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Cellular uptake, antitumor response and tumor penetration of cisplatin-loaded milk protein nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Deac, I.G.; Cadar, O.; Levei, E.A. Effect of Silica Embedding on the Structure, Morphology and Magnetic Behavior of Zn0.6Mn0.4Fe2O4)δ/(SiO2)(100−δ) Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufiq, A.; Nikmah, A.; Hidayat, A.; Sunaryono, S.; Mufti, N.; Hidayat, N.; Susanto, H. Synthesis of magnetite/silica nanocomposites from natural sand to create a drug delivery vehicle. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, B.; Yektadoost, E.; Behzadi, E.; Azmoodeh, E.; Attar, F.; Sari, S.; Akhtari, K.; Falahati, M. Interaction of silica nanoparticles with tau proteins and PC12 cells: Colloidal stability, thermodynamic, docking, and cellular studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Lu, W.; Meng, L.; Feng, X.; Xuan, J.; Liu, F.; Feng, Z. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition, antioxidant activity against alveolar epithelial cells and antibacterial effect against Klebsiella pneumoniae enabled by synthesized silica nanoparticles through laser ablation technique. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.; Park, J.; Singha, K.; Park, H.; Kim, W.J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based cisplatin prodrug delivery and anticancer effect under reductive cellular environment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Islas, E.; Manríquez-Ramírez, M.E.; Sosa-Muñoz, A.; Almaguer, P.; Arias, C.; Guevara, P.; Hernández-Cortez, G.; Aguirre-Cruz, M.L. Preparation and characterization of silica-based nanoparticles for cisplatin release on cancer brain cells. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 14, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X.; Fan, D.; Hui, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Preparation of silica nanoparticles based multifunctional therapeutic systems via one-step mussel inspired modification. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 296, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, A.B.; Durán, N. Nanoparticulated Nitric Oxide Donors and their Biomedical Applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Freeman, B. Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cellet, T.S.P.; Pereira, G.M.; Muniz, E.C.; Silva, R.; Rubira, A.F. Hydroxyapatite nanowhiskers embedded in chondroitin sulfate microspheres as colon targeted drug delivery systems. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6837–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.C.; Gomes, B.C.R.; Pelegrino, M.T.; Seabra, A.B. Nitric oxide-releasing chitosan nanoparticles alleviate the effects of salt stress in maize plants. Nitric Oxide 2016, 61, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Xiao, H.; Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Gu, J.; et al. Enhanced Cisplatin Chemotherapy by Iron Oxide Nanocarrier-Mediated Generation of Highly Toxic Reactive Oxygen Species. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Q.; Lü, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, D.; Shen, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xie, D.; Cho, W.C.; et al. Targeted Inhibition of miR-221/222 Promotes Cell Sensitivity to Cisplatin in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimoldi, I.; Facchetti, G.; Lucchini, G.; Castiglioni, E.; Marchianò, S.; Ferri, N. In vitro anticancer activity evaluation of new cationic platinum(II) complexes based on imidazole moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.Z.; Ho, W.Y.; Yeap, S.K.; Ali, N.M.; Boo, L.; Alitheen, N.B. Regulation of Cellular and Cancer Stem Cell-Related Putative Gene Expression of Parental and CD44+CD24− Sorted MDA-MB-231 Cells by Cisplatin. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunović, M.G.; Matić, M.M.; Obradović, A.D.; Jevtić, V.V.; Stojković, D.L.; Ognjanović, B.I. Antiproliferative, antimigratory, and prooxidative potential of novel platinum(IV) complexes and resveratrol on breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) and choriocarcinoma (JEG-3) cell lines. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, R.; Molina-Ruiz, F.J.; Barcena, J.A.; Padilla, C.A.; Muntane, J. Regulation of cell survival, apoptosis, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by nitric oxidedependent post-translational modifications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1312–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, R. Oxygen radicals, nitric oxide, and peroxynitrite: Redox pathways in molecular medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5839–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Lyu, X.; Wang, Z.; Jin, H.; Lu, S.; Xing, D.; Hu, X. Cocktail polyprodrug nanoparticles concurrently release cisplatin and peroxynitrite-generating nitric oxide in cisplatin-resistant cancers. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai Dai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Shen, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Nitric oxide-releasing platinum(iv) prodrug efficiently inhibits proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14051–14054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, J.C.; Pelegrino, M.T.; Boudier, A.; Seabra, A.B. Recent progress in the toxicity of nitric oxide-releasing nanomaterials. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 7530–7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavida, B.; Baritaki, S.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Vega, M.I.; Chatterjee, D.; Yeung, K. Novel therapeutic applications of nitric oxide donors in cancer: Roles in chemo and immunosensitization to apoptosis and inhibition of metastases. Nitric Oxide 2008, 19, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Niu, D.; He, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Tian, H.; Shi, J.; et al. Dual intratumoral redox/enzyme-responsive NO-releasing nanomedicine for the specific, high-efficacy, and low-toxic cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | Equation |
|---|---|
| Higuchi | Qt= KH · t0.5 |
| Hixson–Crowell | Q01/3 − Qt1/3 = KS · t |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | Ln = ln KK + n · ln t |
| Pluronic F-127 (µg·mL−1) | Hyaluronic Acid (µg·mL−1) | GSNO (µmol·L−1) | SiO2 NPs (µg·mL−1) | CisPt (µmol·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.125 | 5 | 1 | 1.900 |
| 250 | 0.625 | 25 | 5 | 9.560 |
| 1000 | 2.50 | 100 | 20 | 38.36 |
| 2000 | 6.25 | 250 | 50 | 95.65 |
| 5000 | 12.5 | 500 | 100 | 191.5 |
| 10,000 | 25.0 | 1000 | 200 | 382.9 |
| DLS Parameter | SiO2 NPs | SiO2@CisPt NPs |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) | 197.53 ± 6.0 | 317.9 ± 2.6 |
| Polydispersity index (PDI) | 0.144 ± 0.044 | 0.353 ± 0.04 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −27.37 ± 0.51 | −20.2 ± 0.75 |
| Mathematical Models | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higuchi | Hixson–Crowell | Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||||
| R2 | KH (%·h−1/2) | R2 | Ks (%·h−1) | R2 | KK (%·h−n) | n |
| 0.969 | 30.81 | 0.925 | 10.45 | 0.978 | 39.11 | 0.936 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Melo Santana, B.; Pieretti, J.C.; Gomes, R.N.; Cerchiaro, G.; Seabra, A.B. Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells of Pluronic F-127/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Containing Nitric Oxide Donor and Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122837
de Melo Santana B, Pieretti JC, Gomes RN, Cerchiaro G, Seabra AB. Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells of Pluronic F-127/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Containing Nitric Oxide Donor and Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122837
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Melo Santana, Bianca, Joana Claudio Pieretti, Rafael Nunes Gomes, Giselle Cerchiaro, and Amedea Barozzi Seabra. 2022. "Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells of Pluronic F-127/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Containing Nitric Oxide Donor and Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122837
APA Stylede Melo Santana, B., Pieretti, J. C., Gomes, R. N., Cerchiaro, G., & Seabra, A. B. (2022). Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells of Pluronic F-127/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Containing Nitric Oxide Donor and Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122837