Aconitum Alkaloid Songorine Exerts Potent Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-A Receptor Agonist Action In Vivo and Effectively Decreases Anxiety without Adverse Sedative or Psychomotor Effects in the Rat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Care
2.2. In Vivo Electrophysiology
2.2.1. Surgery
2.2.2. Extracellular Recordings
2.2.3. Microiontophoretic Drug Delivery
2.2.4. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.3. Elevated Zero Maze (EOM) Test
2.3.1. Initial Group Assignment
2.3.2. Apparatus
2.3.3. Test Protocol
2.3.4. Pharmacological Treatments and Experimental Design
2.3.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.4. Psychomotor Vigilance Task
2.4.1. Apparatus and Test Protocol
2.4.2. Pharmacological Treatments and Experimental Design
2.4.3. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. In Vivo Electrophysiology
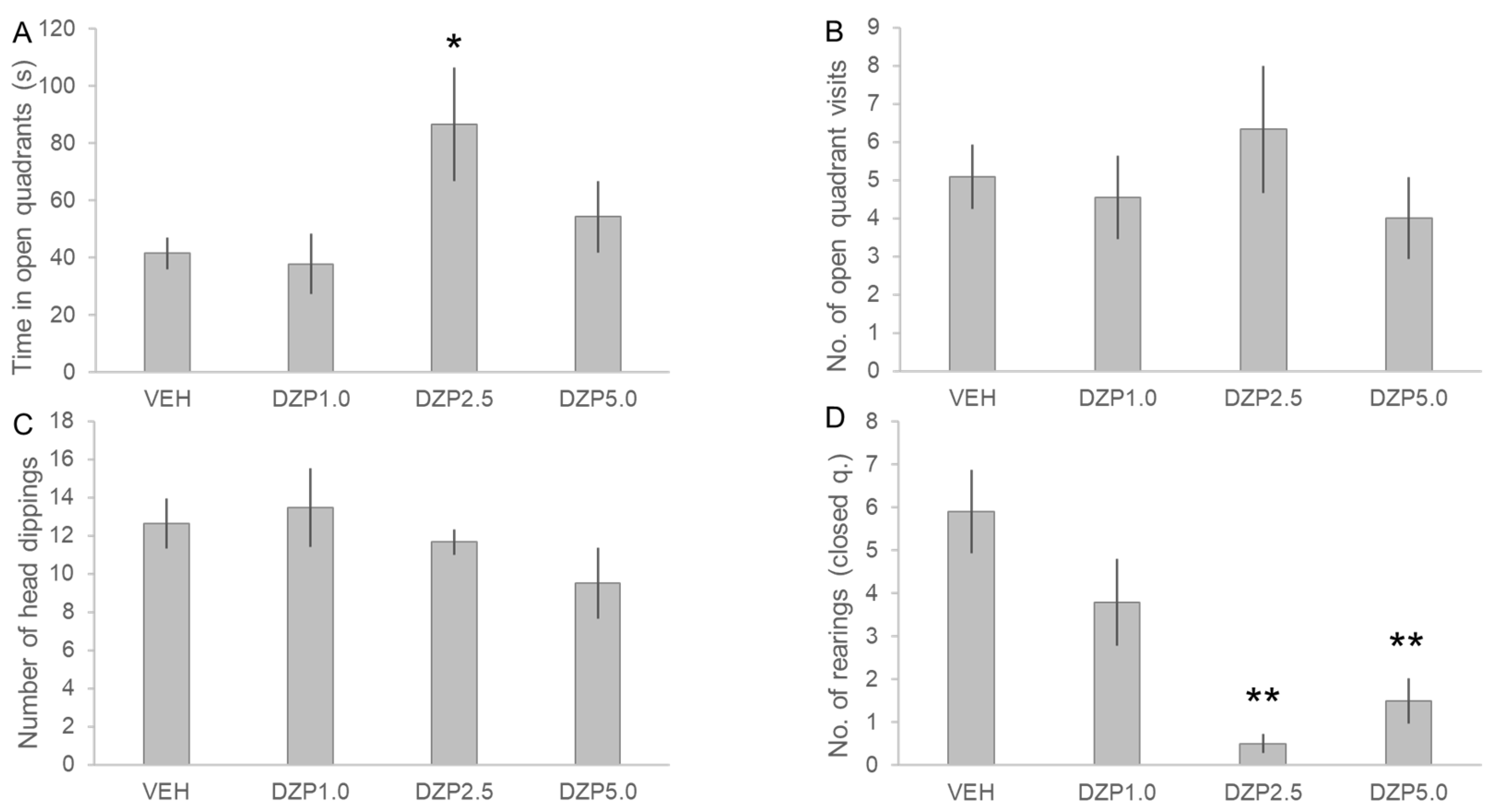
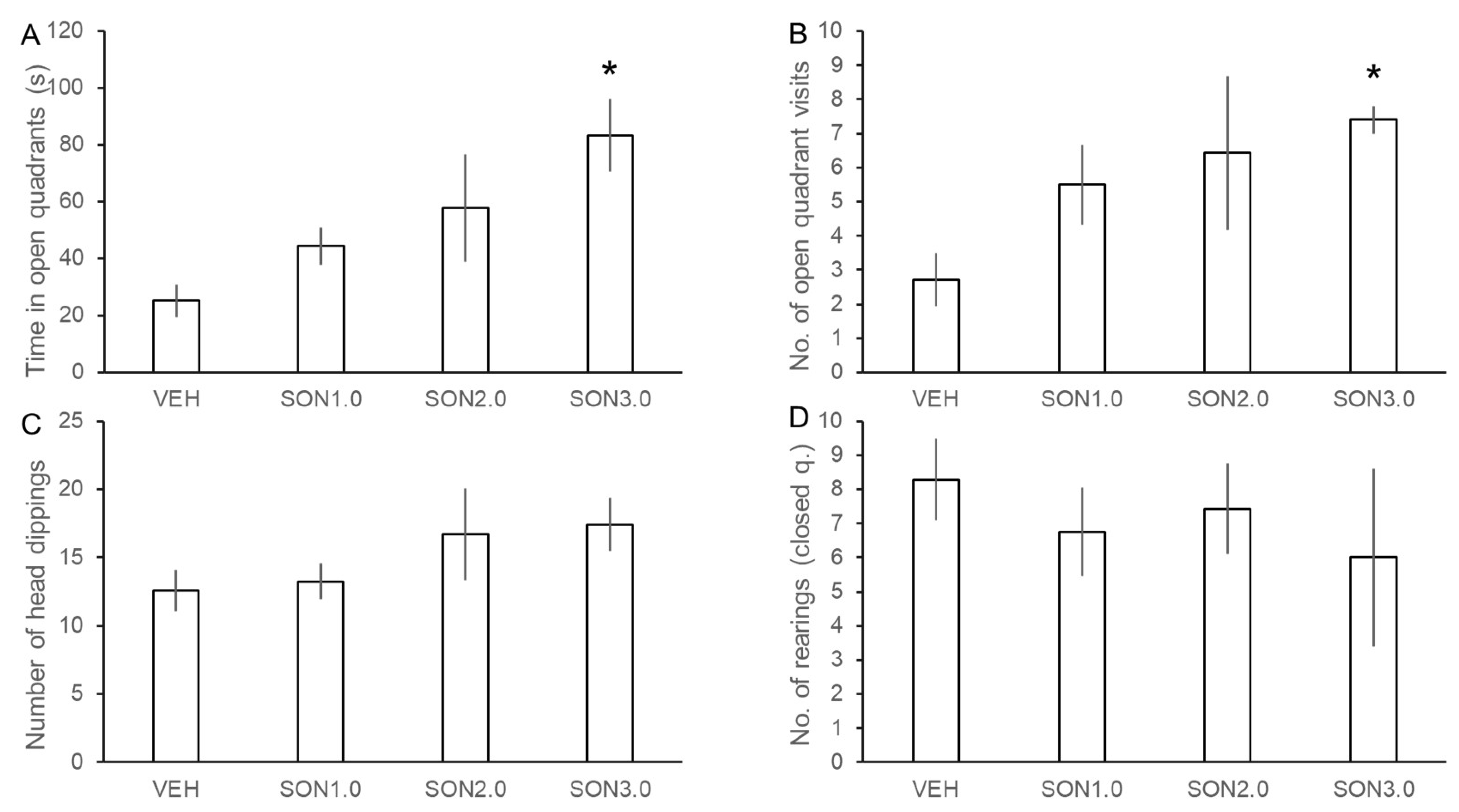
3.2. Assessment of the Anxiolytic Effects of SON
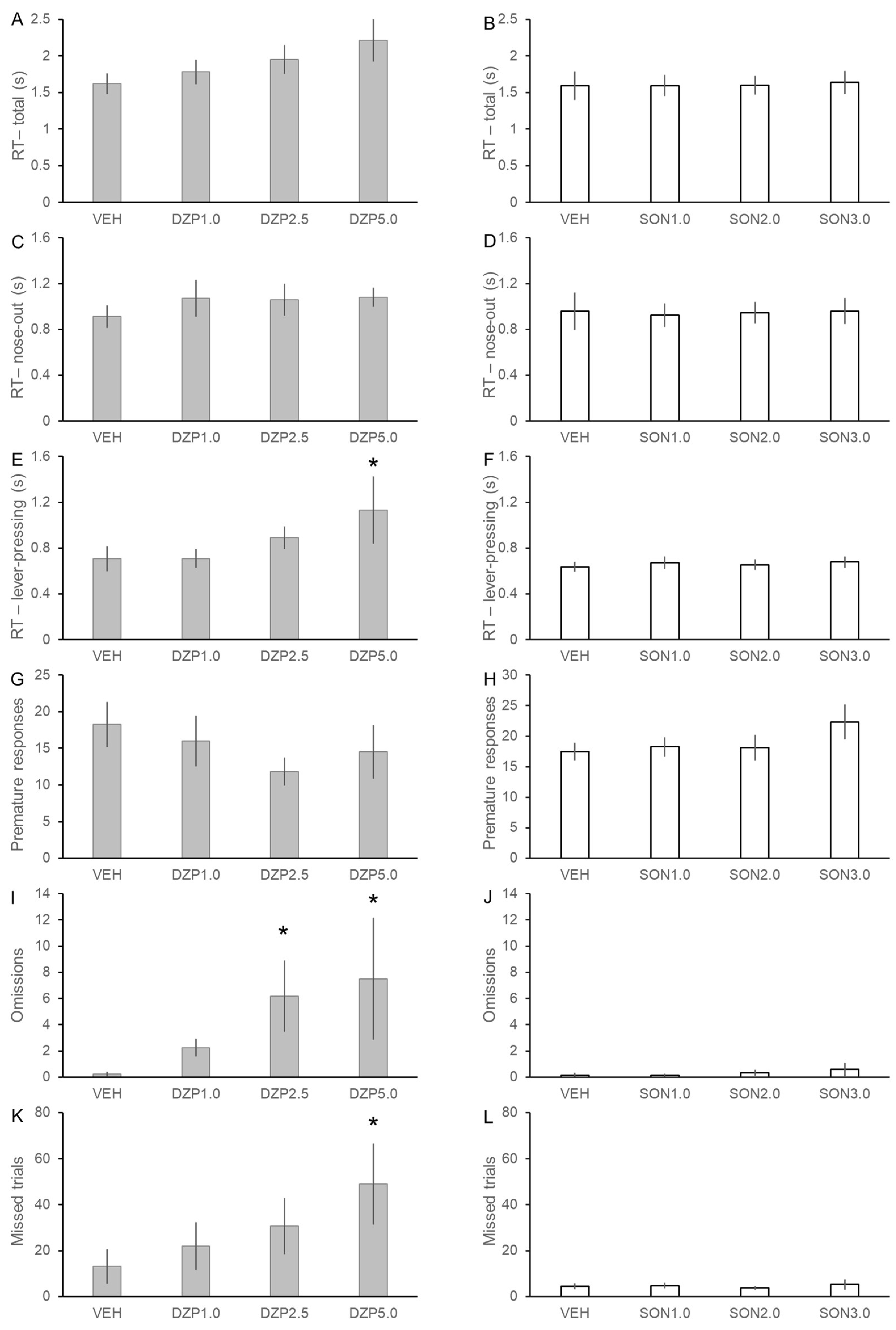
3.3. Assessment of the Effects of SON in the Psychomotor Vigilance Task
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bisset, N.G. Arrow Poisons in China. Part II. Aconitum—Botany, Chemistry, and Pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1981, 4, 247–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y.; Tomlinson, B.; Tse, L.K.; Chan, J.C.; Chan, W.W.; Critchley, J.A. Aconitine Poisoning Due to Chinese Herbal Medicines: A Review. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1994, 36, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Nabavi, S.M.; Sureda, A.; Mehterov, N.; Gulei, D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Taniguchi, H.; Atanasov, A.G. Therapeutic Potential of Songorine, a Diterpenoid Alkaloid of the Genus Aconitum. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 153, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.; Yang, L.; Cui, R.; Yang, W.; Li, B. Neuropharmacological Effects of Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Xia, H.; Wu, Y.; Shao, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, T.; Shi, J. Structure, Property, Biogenesis, and Activity of Diterpenoid Alkaloids Containing a Sulfonic Acid Group from Aconitum carmichaelii. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1954–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyuz’Kov, G.N.; Chaikovskii, A.V.; Ligacheva, A.A.; Zhdanov, V.V.; Udut, E.V.; Danilets, M.G.; Miroshnichenko, L.A.; Simanina, E.V.; Suslov, N.I.; Losev, E.A.; et al. Role of Receptors to Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) on Mesenchymal Precursor Cells in the Realization of Regenerative Effects of Alkaloid Songorine. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 157, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagdullaev, T.; Yu, A.; Gagel, A.I. Influence of a Number of Diterpen Alkaloids on the Calcium Homeostasis of Rat Cardiomyocytes. Structure-Activity Relationship. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1998, 34, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Siyiti, M.; Zhang, J.; Yao, M.; Zhao, F. Anti-inflammatory and Anti-rheumatic Activities in Vitro of Alkaloids Separated from Aconitum soongoricum Stapf. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Y.-F.; Liu, X.-T.; Li, Y.-C.; Zhu, H.-M.; Sun, M.-R.; Li, P.; Liu, B.; Yang, H. Songorine Promotes Cardiac Mitochondrial Biogenesis via Nrf2 Induction during Sepsis. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Mao, B.; Guan, H.; Bai, Y.; Chi, B.; Shan, Y.; Lian, Q.; Ge, R. Determination of Songorine in Rat Plasma by UPLC-MS/MS: Assay Development and Application to Pharmacokinetic Study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 1002, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zong, X.; Wu, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Li, N. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Eighteen Major Alkaloids of Aconitum carmichaelii in Rats by UHPLC-QQQ-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterova, Y.V.; Povet’eva, T.N.; Suslov, N.I.; Shults, E.E.; Ziuz’kov, G.N.; Aksinenko, S.G.; Afanas’eva, O.G.; Krapivin, A.V.; Kharina, T.G. Anxiolytic Activity of Diterpene Alkaloid Songorine. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 159, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterova, Y.V.; Povet’eva, T.N.; Suslov, N.I.; Zyuz’kov, G.N.; Zhdanov, V.V.; Fedorova, Y.S.; Kul’pin, P.V.; Shaposhnikov, K.V. Correction of Cholinergic Abnormalities in Mnestic Processes with Diterpene Alkaloid Songorine. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 165, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.-Q.; Yang, H.-H.; Yue, J.-M.; Hu, G.-Y. Songorine, a Diterpenoid Alkaloid of the Genus Aconitum, Is a Novel GABA(A) Receptor Antagonist in Rat Brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 337, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.A.; Skelton, M.R.; Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Comparison of the Elevated plus and Elevated Zero Mazes in Treated and Untreated Male Sprague-Dawley Rats: Effects of Anxiolytic and Anxiogenic Agents. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 97, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, R.W.; Ferguson, S.A.; Sargent, C.; Zhou, X.; Kosmadopoulos, A.; Roach, G.D. Using Interstimulus Interval to Maximise Sensitivity of the Psychomotor Vigilance Test to Fatigue. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2017, 99, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinges, D.F.; Powell, J.W. Microcomputer Analyses of Performance on a Portable, Simple Visual RT Task during Sustained Operations. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1985, 17, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Budai, D.; Molnár, Z. Novel Carbon Fiber Microeletrodes for Extracellular Electrophysiology. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2001, 45, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bali, Z.K.; Budai, D.; Hernádi, I. Separation of Electrophysiologically Distinct Neuronal Populations in the Rat Hippocampus for Neuropharmacological Testing under in Vivo Conditions. Acta Biol. Hung. 2014, 65, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csupor, D.; Forgo, P.; Csedő, K.; Hohmann, J. C19 and C20 Diterpene Alkaloids from Aconitum Toxicum RCHB. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harro, J.; Lang, A.; Vasar, E. Long-Term Diazepam Treatment Produces Changes in Cholecystokinin Receptor Binding in Rat Brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 180, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughy, J.; Sarter, M. Behavioral Vigilance in Rats: Task Validation and Effects of Age, Amphetamine, and Benzodiazepine Receptor Ligands. Psychopharmacology 1995, 117, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeeva, G.; Valiullina, F.; Khazipov, R. Excitatory Actions of GABA in the Intact Neonatal Rodent Hippocampus in Vitro. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Colonnese, M.T. GABAergic Interneurons Excite Neonatal Hippocampus in Vivo. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Effects of the Aconitum Alkaloid Songorine on Synaptic Transmission and Paired-Pulse Facilitation of CA1 Pyramidal Cells in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentai, N.; Csathó, Á.; Trunk, A.; Fiocchi, S.; Parazzini, M.; Ravazzani, P.; Thuroczy, G.; Hernádi, I. No Effects of Acute Exposure to Wi-Fi Electromagnetic Fields on Spontaneous EEG Activity and Psychomotor Vigilance in Healthy Human Volunteers. Radiat. Res. 2015, 184, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, V.; Knakker, B.; Trunk, A.; Lendvai, B.; Hernádi, I. Dissociating Cholinergic Influence on Alertness and Temporal Attention in Primates in a Simple Reaction Time Paradigm. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 52, 3776–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.M.; Roma, P.G.; Hienz, R.D. A Rodent Model of the Human Psychomotor Vigilance Test: Performance Comparisons. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 259, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, B.S.; Salinsky, M.C.; Elsas, S.M. Vigilance, Alertness, or Sustained Attention: Physiological Basis and Measurement. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 1885–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servan-Schreiber, D.; Bruno, R.M.; Carter, C.S.; Cohen, J.D. Dopamine and the Mechanisms of Cognition: Part I. A Neural Network Model Predicting Dopamine Effects on Selective Attention. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 43, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashchinkina, E.; Panhelainen, A.; Aitta-aho, T.; Korpi, E.R. GABAA Receptor Drugs and Neuronal Plasticity in Reward and Aversion: Focus on the Ventral Tegmental Area. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
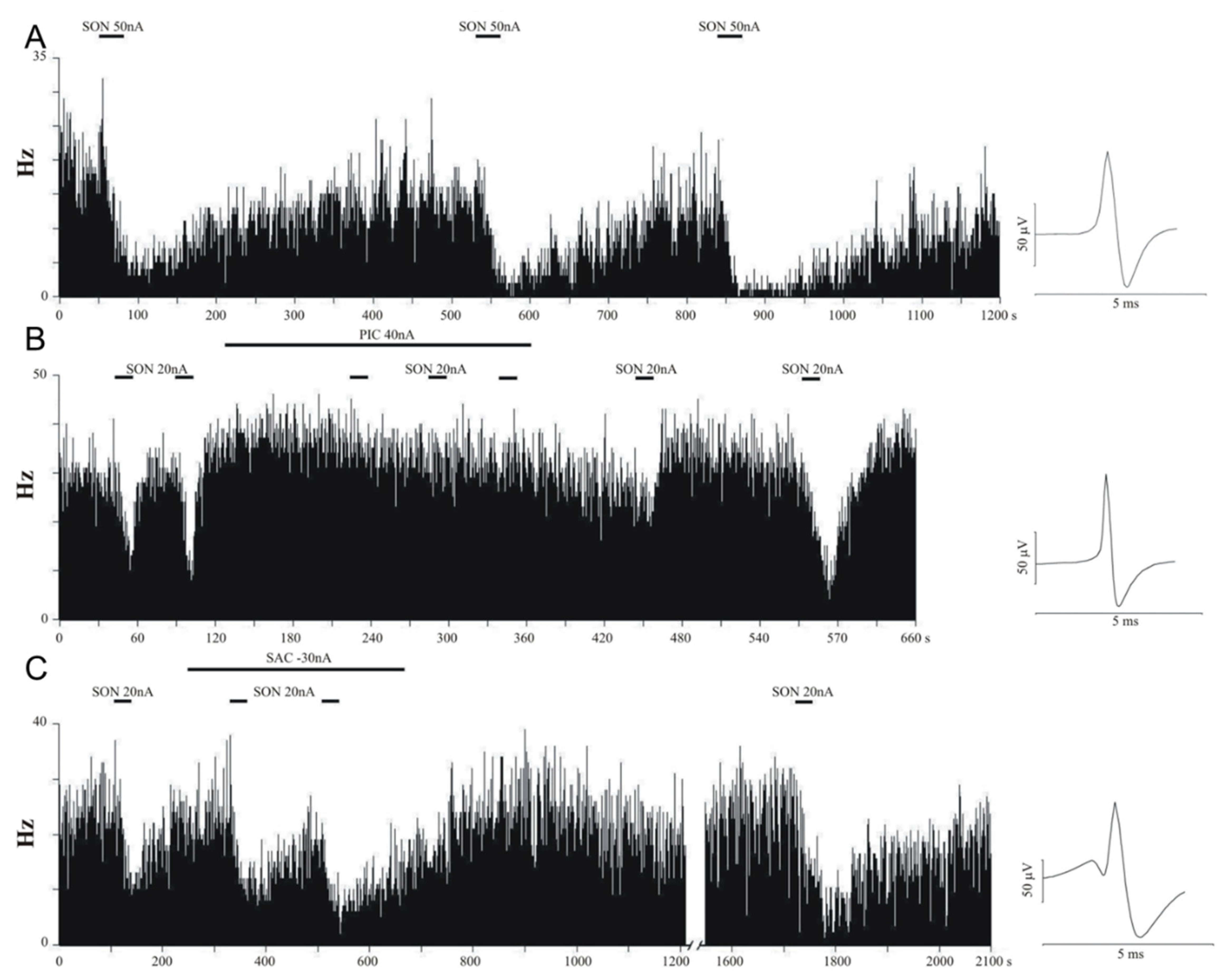
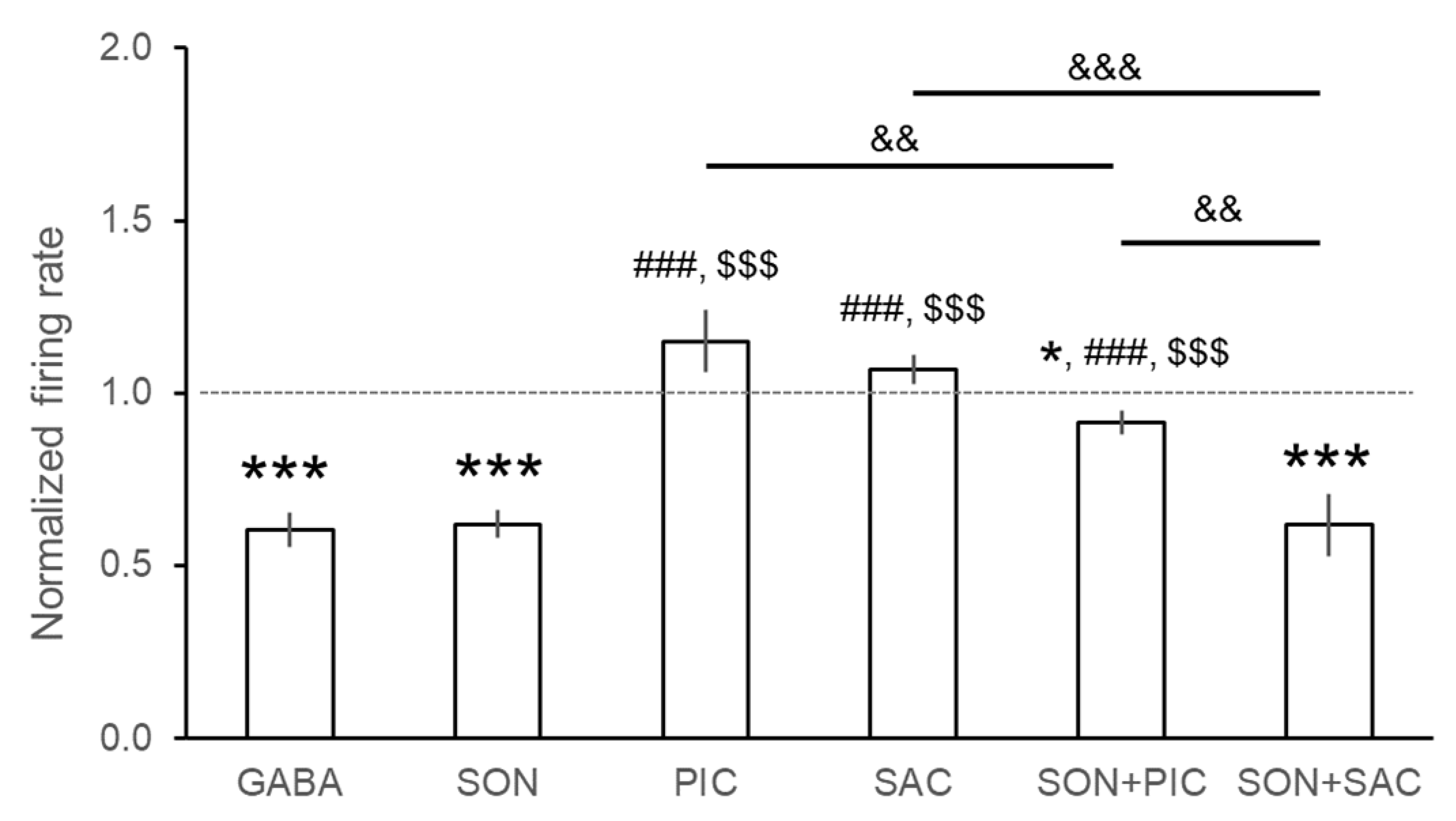
| Compound | Effect | nneuron | %neuron | ntrials | %trials | Normalized Firing Rate (Mean ± S.E.M.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABA | ↑ | 3/123 | 2.4% | 7/296 | 2.4% | 0.604 ± 0.049 *** |
| Ø | 27/123 | 22.0% | 36/296 | 12.2% | ||
| ↓ | 93/123 | 75.6% | 253/296 | 85.5% | ||
| SON | ↑ | 1/112 | 0.9% | 2/201 | 1.0% | 0.621 ± 0.041 *** |
| Ø | 21/112 | 18.8% | 36/201 | 17.9% | ||
| ↓ | 90/112 | 80.4% | 163/201 | 81.1% | ||
| PIC | ↑ | 24/56 | 42.9% | 39/90 | 43.3% | 1.150 ± 0.091 |
| Ø | 32/56 | 57.1% | 51/90 | 56.7% | ||
| ↓ | - | - | - | - | ||
| SAC | ↑ | 11/49 | 22.5% | 20/75 | 26.7% | 1.069 ± 0.042 |
| Ø | 35/49 | 71.4% | 48/75 | 64.0% | ||
| ↓ | 3/49 | 6.1% | 7/75 | 9.3% | ||
| SON + PIC | ↑ | 1/56 | 1.8% | 2/99 | 2.0% | 0.915 ± 0.034 * |
| Ø | 42/56 | 75.0% | 68/99 | 68.7% | ||
| ↓ | 13/56 | 23.2% | 29/99 | 29.3% | ||
| SON + SAC | ↑ | 2/37 | 5.4% | 5/89 | 5.6% | 0.617 ± 0.089 *** |
| Ø | 5/37 | 13.5% | 13/89 | 14.6% | ||
| ↓ | 30/37 | 81.1% | 71/89 | 79.8% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bali, Z.K.; Bruszt, N.; Kőszegi, Z.; Nagy, L.V.; Atlasz, T.; Kovács, P.; Csupor, D.; Csupor-Löffler, B.; Hernádi, I. Aconitum Alkaloid Songorine Exerts Potent Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-A Receptor Agonist Action In Vivo and Effectively Decreases Anxiety without Adverse Sedative or Psychomotor Effects in the Rat. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102067
Bali ZK, Bruszt N, Kőszegi Z, Nagy LV, Atlasz T, Kovács P, Csupor D, Csupor-Löffler B, Hernádi I. Aconitum Alkaloid Songorine Exerts Potent Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-A Receptor Agonist Action In Vivo and Effectively Decreases Anxiety without Adverse Sedative or Psychomotor Effects in the Rat. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(10):2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102067
Chicago/Turabian StyleBali, Zsolt Kristóf, Nóra Bruszt, Zsombor Kőszegi, Lili Veronika Nagy, Tamás Atlasz, Péter Kovács, Dezső Csupor, Boglárka Csupor-Löffler, and István Hernádi. 2022. "Aconitum Alkaloid Songorine Exerts Potent Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-A Receptor Agonist Action In Vivo and Effectively Decreases Anxiety without Adverse Sedative or Psychomotor Effects in the Rat" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10: 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102067
APA StyleBali, Z. K., Bruszt, N., Kőszegi, Z., Nagy, L. V., Atlasz, T., Kovács, P., Csupor, D., Csupor-Löffler, B., & Hernádi, I. (2022). Aconitum Alkaloid Songorine Exerts Potent Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-A Receptor Agonist Action In Vivo and Effectively Decreases Anxiety without Adverse Sedative or Psychomotor Effects in the Rat. Pharmaceutics, 14(10), 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102067








