Green by Design: Convergent Synthesis, Computational Analyses, and Activity Evaluation of New FXa Inhibitors Bearing Peptide Triazole Linking Units
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. FXa In Vitro Inhibition Assay
2.3. Computational Analyses
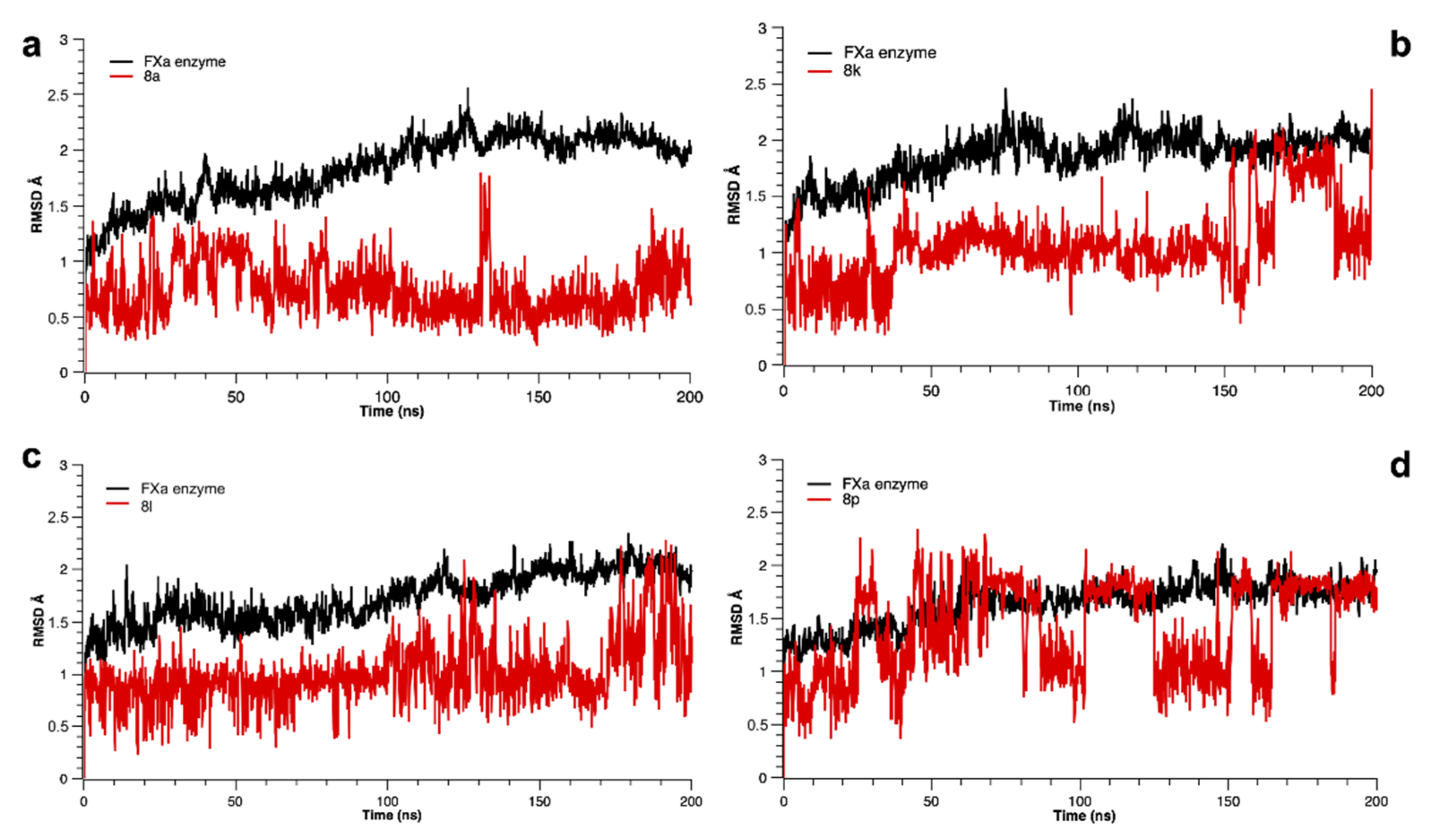
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulations (MD)
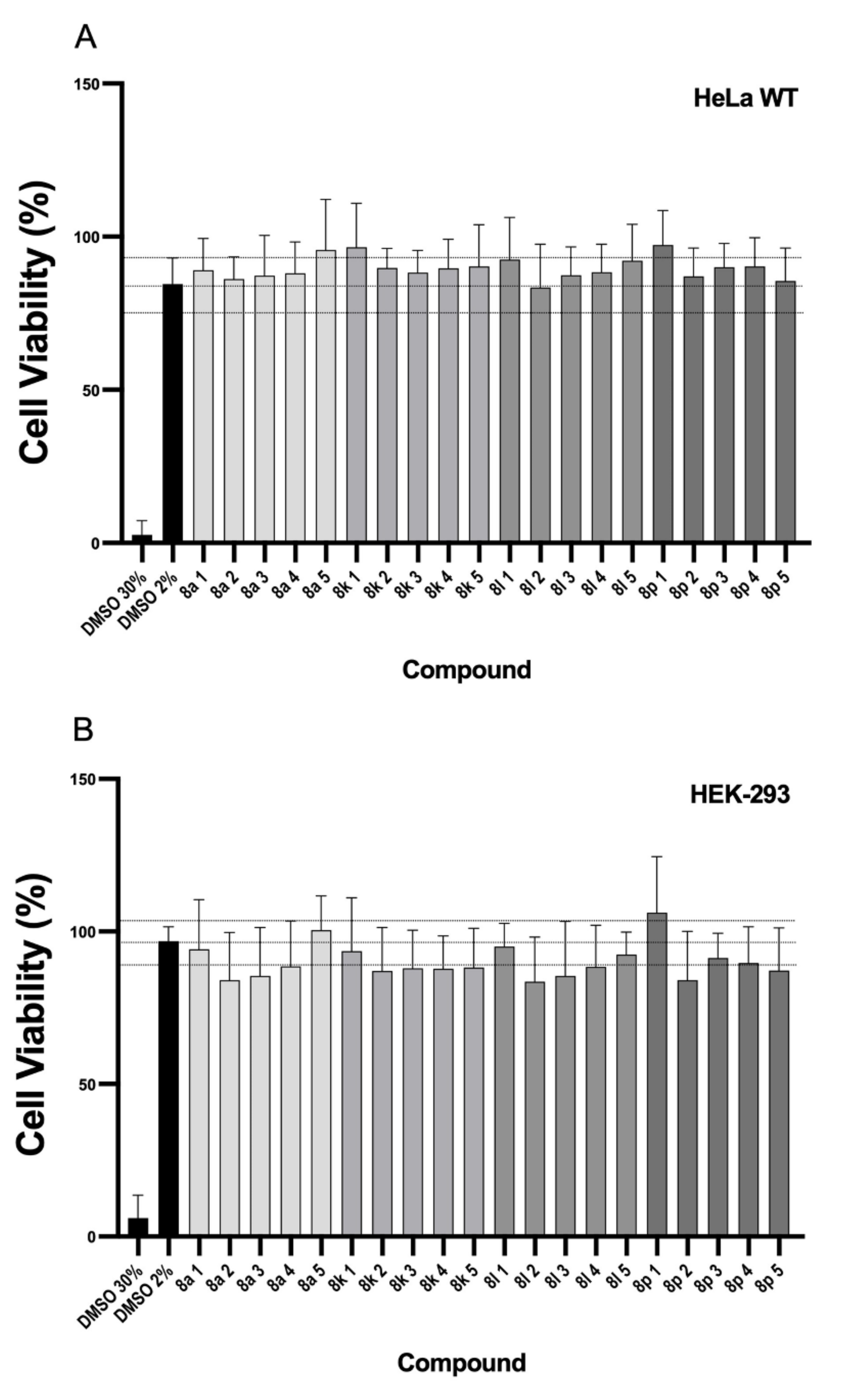
2.5. Cell Viability Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Optimization
- (i)
- Synthesis of the aryl-amide motive P1 by chemoselective copper-catalyzed Ullmann-Goldberg reactions in a benign solvent.
- (ii)
- Synthesis of the triazole linker and P2 motif by a multicomponent click chemistry reaction catalyzed by carbon-supported copper nanoparticles CuNPs/C.
- (iii)
- Efficient microwave-assisted synthesis of final products through peptide coupling.
3.2. In Vitro FXa Inhibition Analysis
3.3. Computational Analysis
3.3.1. Molecular Docking
3.3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.4. Cell Viability Analysis
3.5. Drug Likeness Prediction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinto, D.J.P.; Qiao, J.X.; Knabb, R.M. The emergence of factor Xa inhibitors for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases: A patent review. Expert Opin. Pat. 2012, 22, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, D.; Robinson, A. Factor Xa inhibitors: A novel therapeutic class for the treatment of nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 10, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, R.C. COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 50, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salabei, J.K.; Fishman, T.J.; Asnake, Z.T.; Ali, A.; Iyer, U.G. COVID-19 Coagulopathy: Current knowledge and guidelines on anticoagulation. Hearth Lung J. Cardiopulm. Acute Care 2021, 50, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, F.; Sepe, L.; Fusina, F.; Prezioso, C.; Baronio, M.; Caminiti, F.; Di Maio, A.; Faggian, B.; Franceschetti, M.E.; Massari, M.; et al. Thromboprophylaxis with enoxaparin is associated with a lower death rate in patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection. A cohort study. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 27, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.-S.; Leung, W.K. Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients on novel oral anticoagulants: Risk, prevention and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.H.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Samama, C.M.; Douketis, J. Direct Oral Anticoagulants: New Drugs and New Concepts. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 1333–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pansuriya, T.; Nguyen, T.; Sadat, M.A.; Raza, S.A.; Sarva, S.T. A 78-Year-Old Man with a Pulmonary Embolism Who Developed Skin Necrosis 7 Days After Treatment with the Direct Oral Anticoagulant Factor Xa Inhibitor Apixaban. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e929002-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Mowafy, K.; Elsaadany, N.; Awad, S.; Soliman, R.; Soliman, R. Rivaroxaban-induced skin necrosis: A case report. Eur. J. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 3, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrig, S.; Straub, A.; Pohlmann, J.; Lampe, T.; Pernerstorfer, J.; Schlemmer, K.-H.; Reinemer, P.; Perzborn, E. Discovery of the Novel Antithrombotic Agent 5-Chloro-N-({(5S)-2-oxo-3-[4-(3-oxomorpholin-4-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl}methyl)thiophene-2-carboxamide (BAY 59-7939): An Oral, Direct Factor Xa Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5900–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.J.P.; Orwat, M.J.; Koch, S.; Rossi, K.A.; Alexander, R.S.; Smallwood, A.; Wong, P.C.; Rendina, A.R.; Luettgen, J.M.; Knabb, R.M.; et al. Discovery of 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro- 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (Apixaban, BMS-562247), a Highly Potent, Selective, Efficacious, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of Blood Coagulation F. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5339–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, W.R.; Cladera, E.; Harris, M.S.; Zhang, E.; Narasimhan, L.; Thorn, J.M.; Leadley, R.J. Co-crystal Structure and Inhibition of Factor Xa by PD0313052 Identifies Structurally Stabilized Active Site Residues of Factor Xa and Prothrombinase. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 9280–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.S.; Roy, K.K.; Saxena, A.K. Profiling the Structural Determinants for the Selectivity of Representative Factor-Xa and Thrombin Inhibitors Using Combined Ligand-Based and Structure-Based Approaches. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1966–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, D.; Visscher, K.M.; Vosmeer, C.R.; Cheung, K.L.; Reitsma, P.H.; Geerke, D.P.; Bos, M.H.A. Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, N.R.; Patel, D.V.; Murumkar, P.R.; Yadav, M.R. Contemporary developments in the discovery of selective factor Xa inhibitors: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 671–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, B.; Stubbs, M.T.; Bergner, A.; Hauptmann, J.; Bode, W.; Stürzebecher, J.; Moroder, L. Design of Benzamidine-Type Inhibitors of Factor Xa. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 4240–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, P.Y.S.; Clark, C.G.; Li, R.; Pinto, D.J.P.; Orwat, M.J.; Galemmo, R.A.; Fevig, J.M.; Teleha, C.A.; Alexander, R.S.; Smallwood, A.M.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Novel Guanidine/Benzamidine Mimics: Potent and Orally Bioavailable Factor Xa Inhibitors as Novel Anticoagulants. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4405–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, C.; Huang, M. Halogen bonding for the design of inhibitors by targeting the S1 pocket of serine proteases. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 28189–28197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazaré, M.; Will, D.W.; Matter, H.; Schreuder, H.; Ritter, K.; Urmann, M.; Essrich, M.; Bauer, A.; Wagner, M.; Czech, J.; et al. Probing the Subpockets of Factor Xa Reveals Two Binding Modes for Inhibitors Based on a 2-Carboxyindole Scaffold: A Study Combining Structure-Activity Relationship and X-ray Crystallography. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4511–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Kochanny, M.J.; Ye, B.; Rumennik, G.; Light, D.R.; Biancalana, S.; Whitlow, M. Crystal Structures of Two Potent Nonamidine Inhibitors Bound to Factor Xa. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 15514–15523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.J.P.; Smallheer, J.M.; Cheney, D.L.; Knabb, R.M.; Wexler, R.R. Factor Xa Inhibitors: Next-Generation Antithrombotic Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6243–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Fuaad, A.A.H.; Azmi, F.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Peptide Conjugation via CuAAC ‘Click’ Chemistry. Molecules 2013, 18, 13148–13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holub, J.M.; Kirshenbaum, K. Tricks with clicks: Modification of peptidomimetic oligomers via copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne [3 + 2] cycloaddition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brik, A.; Alexandratos, J.; Lin, Y.-C.; Elder, J.H.; Olson, A.J.; Wlodawer, A.; Goodsell, D.S.; Wong, C.-H. 1,2,3-Triazole as a Peptide Surrogate in the Rapid Synthesis of HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurugan, P.; Matosiuk, D.; Jozwiak, K. Click Chemistry for Drug Development and Diverse Chemical–Biology Applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4905–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Ameta, C.; Ameta, R.; Punjabi, P.B. Chapter 2—Click chemistry: A tool for green chemical organic synthesis. In Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science; Inamuddin, B.R., Asiri, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 13–48. ISBN 978-0-12-819539-0. [Google Scholar]
- Erythropel, H.C.; Zimmerman, J.B.; de Winter, T.M.; Petitjean, L.; Melnikov, F.; Lam, C.H.; Lounsbury, A.W.; Mellor, K.E.; Janković, N.Z.; Tu, Q.; et al. The Green ChemisTREE: 20 years after taking root with the 12 principles. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1929–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, J.B. Chapter 1: Introduction: The Five Ws of Pharmaceutical Green Chemistry. In Green Chemistry Strategies for Drug Discovery; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 1–12. ISBN 978-1-84973-961-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R.A. Fundamentals of green chemistry: Efficiency in reaction design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taj, M.B.; Raheel, A.; Alelwani, W.; Babteen, N.; Kattan, S.; Alnajeebi, A.; Sharif, M.; Ahmad, R.H.; Hazeeq, A.; Tirmizi, S.A.; et al. One-Pot CuO-Catalyzed Green Synthesis of N(N′)-Arylbenzamidines as Potential Enzyme Inhibitors. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 55, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavi Sastry, G.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Release 2020-4: Schrödinger Suite 2020-4 Protein Preparation Wizard, Epik, Impact, Prime; Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Release 2020-4: LigPrep; Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Release 2021-4: Epik; Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Release 2020-4: Glide; Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, V.; Hoyos, P.; Castoldi, L.; Domínguez de María, P.; Alcántara, A.R. 2-Methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF): A Biomass-Derived Solvent with Broad Application in Organic Chemistry. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.G.; Dankwardt, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Singh, S.P. Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indoles and Related Heterocycles in Renewable Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appukkuttan, P.; Dehaen, W.; Fokin, V.V.; Van der Eycken, E. A Microwave-Assisted Click Chemistry Synthesis of 1,4-Disubstituted 1,2,3-Triazoles via a Copper(I)-Catalyzed Three-Component Reaction. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4223–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, F.; Moglie, Y.; Radivoy, G.; Yus, M. Click chemistry from organic halides, diazonium salts and anilines in water catalysed by copper nanoparticles on activated carbon. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 6385–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso, F.; Moglie, Y.; Radivoy, G. Copper Nanoparticles in Click Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2516–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perutz, M.F.; Kirby, A.J.; Williams, D.H. The role of aromatic rings as hydrogen-bond acceptors in molecular recognition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Phys. Eng. Sci. 1993, 345, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, H.; Nazaré, M.; Güssregen, S.; Will, D.W.; Schreuder, H.; Bauer, A.; Urmann, M.; Ritter, K.; Wagner, M.; Wehner, V. Evidence for C—Cl/C—Br⋅⋅⋅π Interactions as an Important Contribution to Protein–Ligand Binding Affinity. Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2911–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Romo, F.; Lagos, F.C.; Duarte, Y.; Castillo, F.; Moglie, Y.; Maestro, A.M.; Charbe, N.; Zacconi, C.F. Innovative Three-Step Microwave-Promoted Synthesis of N-Propargyltetrahydroquinoline and 1,2,3-Triazole Derivatives as a Potential Factor Xa (FXa) Inhibitors: Drug Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2020, 25, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kundu, S.; Wu, S. A Structure Based Study of Selective Inhibition of Factor IXa over Factor Xa. Molecules 2021, 26, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Bankoti, N.; Michael, D.; Sekar, K.; Row, T.N.G. C-halogen…pi interactions in nucleic acids: A database study. J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 132, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugo, O. How root-mean-square distance (r.m.s.d.) values depend on the resolution of protein structures that are compared. J. Appl. Cryst. 2003, 36, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Release 2020-4: QikProp; Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]

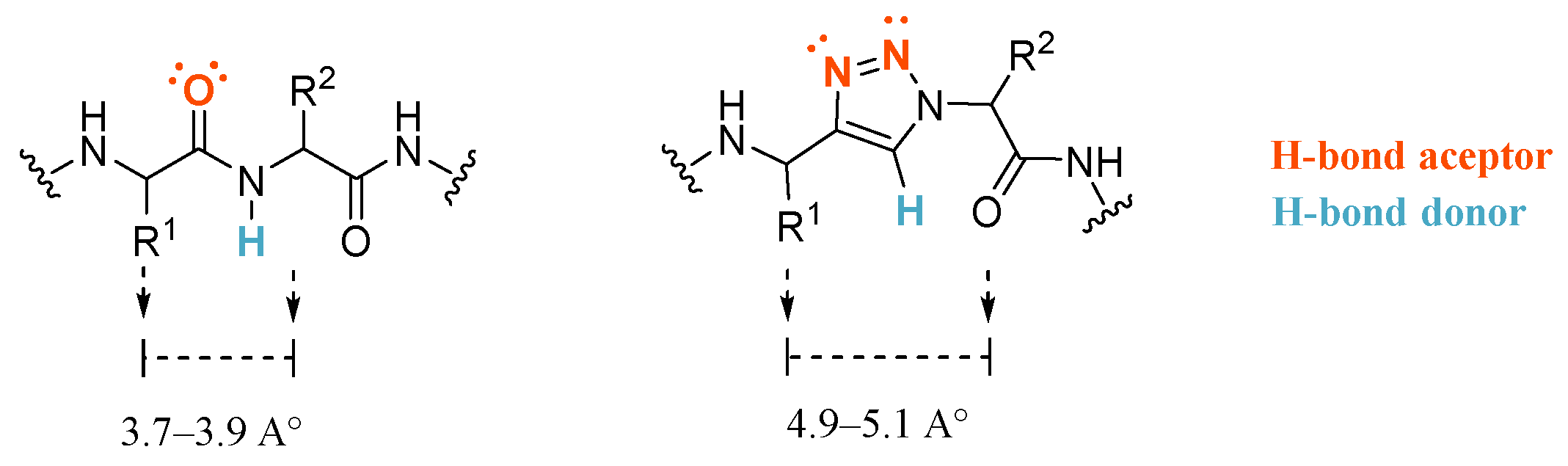
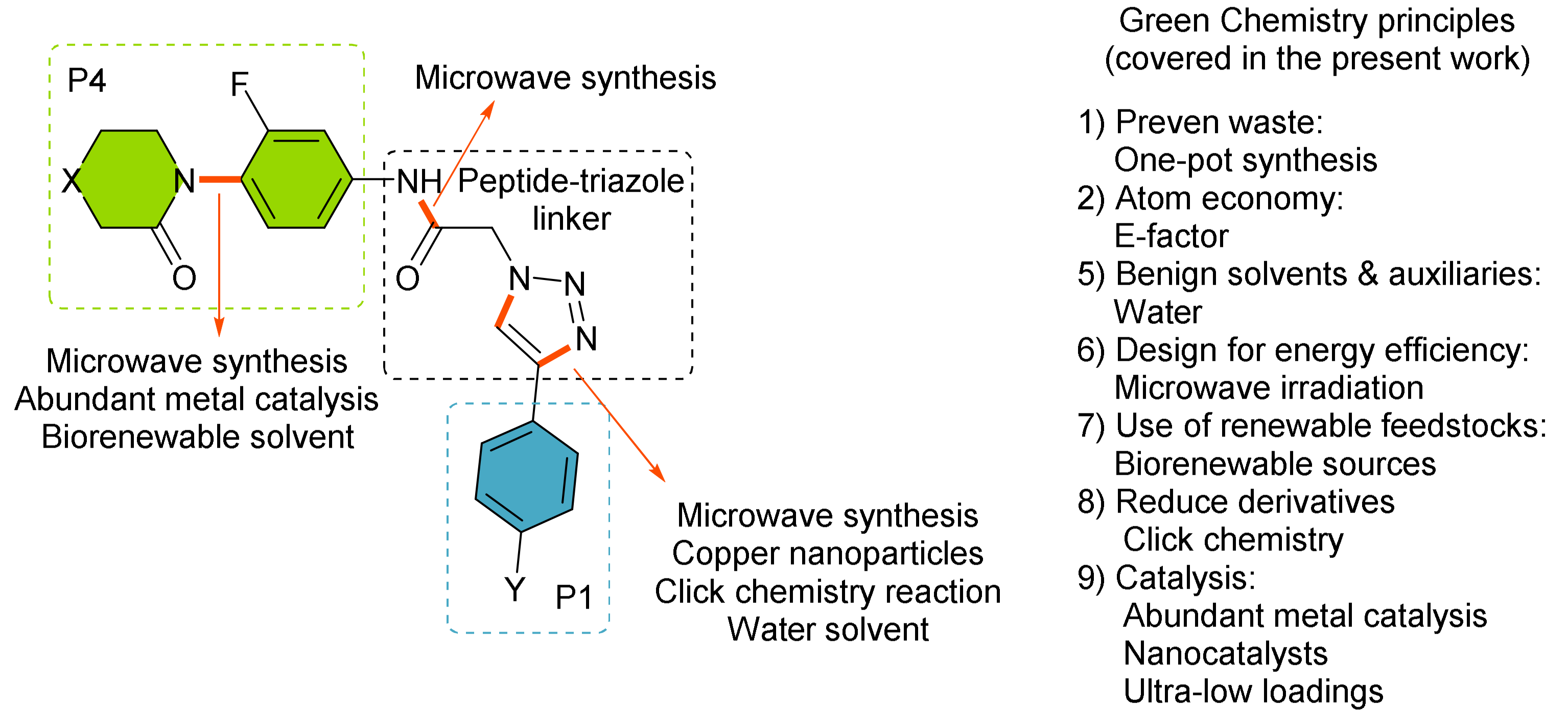
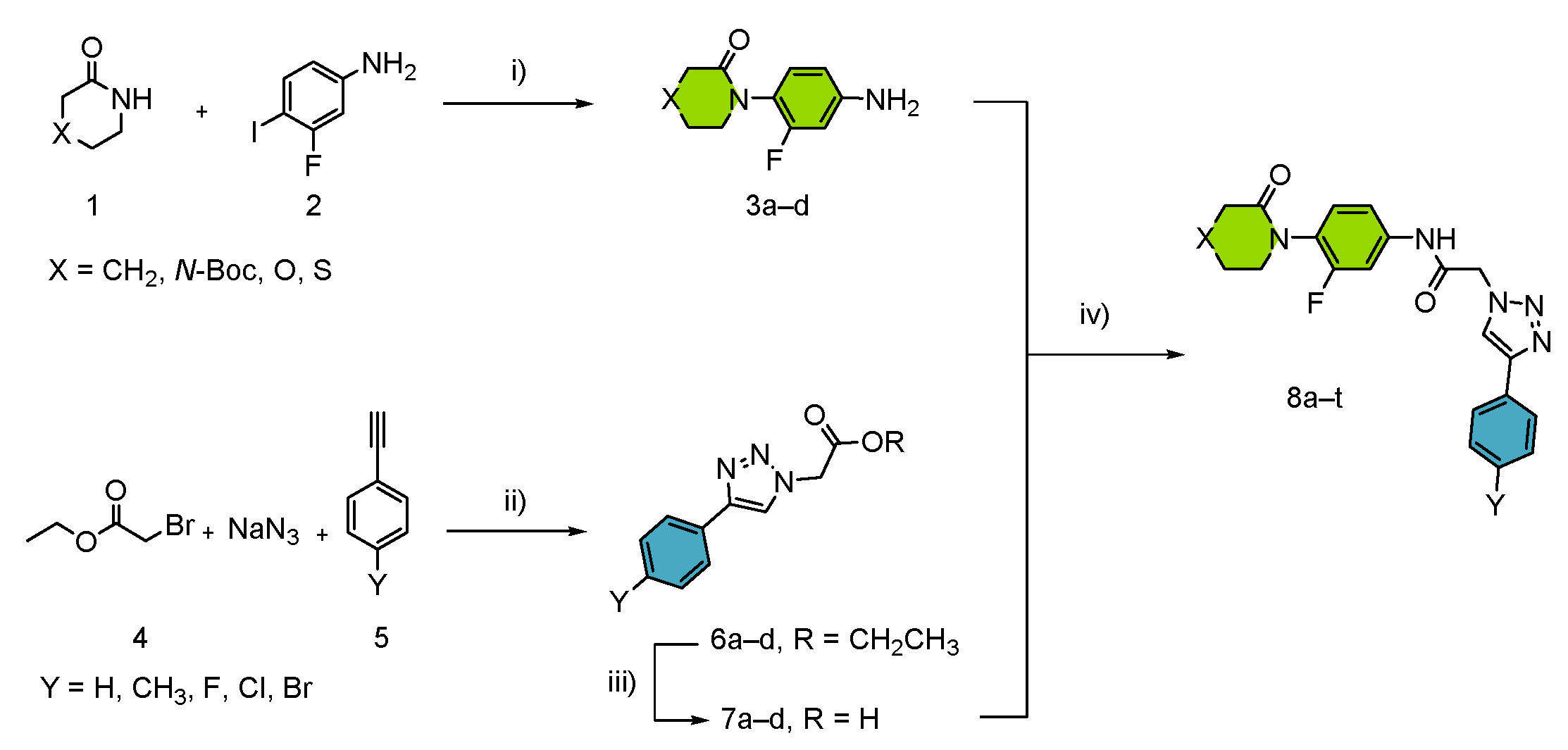

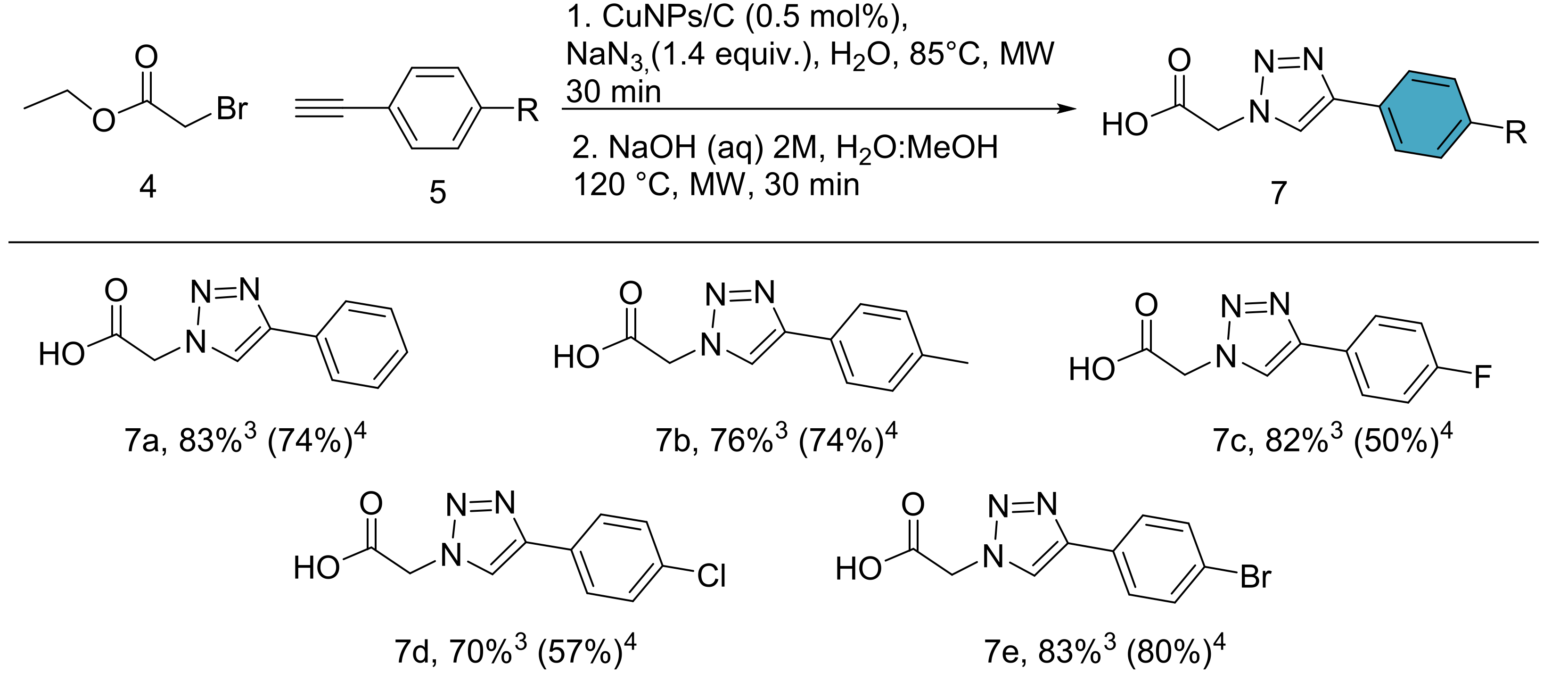
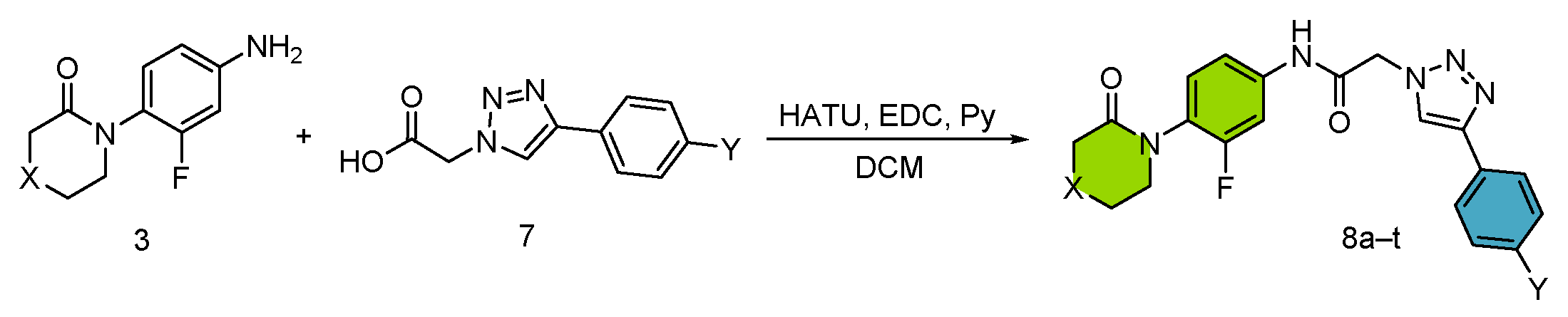

| Entry | Nomenclature | X | Y | Yield (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8a | CH2 | H | 50 |
| 2 | 8b | N-Boc | H | 70 |
| 3 | 8c | O | H | 43 |
| 4 | 8d | S | H | 82 |
| 5 | 8e | CH2 | F | 19 |
| 6 | 8f | N-Boc | F | 62 |
| 7 | 8g | O | F | 52 |
| 8 | 8h | S | F | 42 |
| 9 | 8i | CH2 | Cl | 19 |
| 10 | 8j | N-Boc | Cl | 69 |
| 11 | 8k | O | Cl | 27 |
| 12 | 8l | S | Cl | 51 |
| 13 | 8m | CH2 | Br | 27 |
| 14 | 8n | N-Boc | Br | 56 |
| 15 | 8o | O | Br | 66 |
| 16 | 8p | S | Br | 83 (44) 3 |
| 17 | 8q | CH2 | CH3 | 30 |
| 18 | 8r | N-Boc | CH3 | 57 |
| 19 | 8s | O | CH3 | 31 |
| 20 | 8t | S | CH3 | 57 |
| Entry | %Inhibition FXa 1 | IC50 (μM) |
| 8a | 68 | 41.2 ± 1.2 |
| 8b | 24 | - |
| 8c | 17 | - |
| 8d | 33 | - |
| 8e | 17 | - |
| 8f | 44 | - |
| 8g | 36 | - |
| 8h | 25 | - |
| 8i | 29 | - |
| 8j | 23 | - |
| 8k | 59 | 76.2 ± 16.9 |
| 8l | 50 | 52.9 ± 5.5 |
| 8m | 29 | - |
| 8n | 22 | - |
| 8o | 37 | - |
| 8p | 65 | 17.2 ± 0.8 |
| 8q | 21 | - |
| 8r | 27 | - |
| 8s | 37 | - |
| 8t | 31 | - |
| Gabexate mesylate | 93 | 0.34 ± 0.10 |
| Apixaban | 97 | 0.0028 ± 0.0001 |
| Rivaroxaban | 94 | 0.0007 ± 0.0001 |
| Compound | logPo/w | mol MW | H Bond Donors | H Bond Acceptors | logS | logBB | PMDCK | PHOA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8a | 3.37 | 393.42 | 1.0 | 8.0 | −5.89 | −0.88 | 473.25 | 100.00 |
| 8k | 2.82 | 429.84 | 1.0 | 9.7 | −5.56 | −0.82 | 879.37 | 92.01 |
| 8l | 3.82 | 445.90 | 1.0 | 8.5 | −6.85 | −0.76 | 1663.45 | 100.00 |
| 8p | 3.90 | 490.35 | 1.0 | 8.5 | −6.89 | −0.70 | 1982.33 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, D.F.; Durán-Osorio, F.; Duarte, Y.; Olivares, P.; Moglie, Y.; Dua, K.; Zacconi, F.C. Green by Design: Convergent Synthesis, Computational Analyses, and Activity Evaluation of New FXa Inhibitors Bearing Peptide Triazole Linking Units. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010033
Rodríguez DF, Durán-Osorio F, Duarte Y, Olivares P, Moglie Y, Dua K, Zacconi FC. Green by Design: Convergent Synthesis, Computational Analyses, and Activity Evaluation of New FXa Inhibitors Bearing Peptide Triazole Linking Units. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Diego F., Francisca Durán-Osorio, Yorley Duarte, Pedro Olivares, Yanina Moglie, Kamal Dua, and Flavia C. Zacconi. 2022. "Green by Design: Convergent Synthesis, Computational Analyses, and Activity Evaluation of New FXa Inhibitors Bearing Peptide Triazole Linking Units" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010033
APA StyleRodríguez, D. F., Durán-Osorio, F., Duarte, Y., Olivares, P., Moglie, Y., Dua, K., & Zacconi, F. C. (2022). Green by Design: Convergent Synthesis, Computational Analyses, and Activity Evaluation of New FXa Inhibitors Bearing Peptide Triazole Linking Units. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010033








