Synovial and Systemic Pharmacokinetics of Florfenicol and PK/PD Integration against Streptococcus suis in Pigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.5. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
2.6. In Vitro Killing-Time Curves of Florfenicol against SS3
2.7. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Integration
3. Results
3.1. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Florfenicol in Plasma and Synovial Fluid after Intramuscular Administration
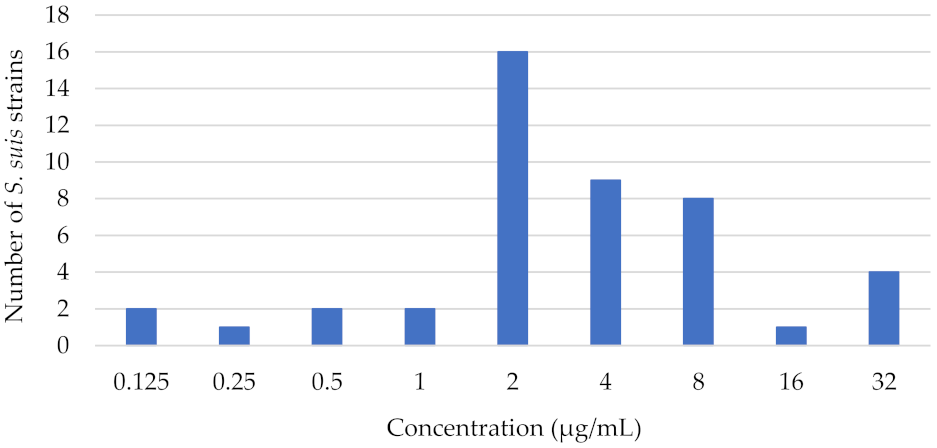
3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Florfenicol against S. suis
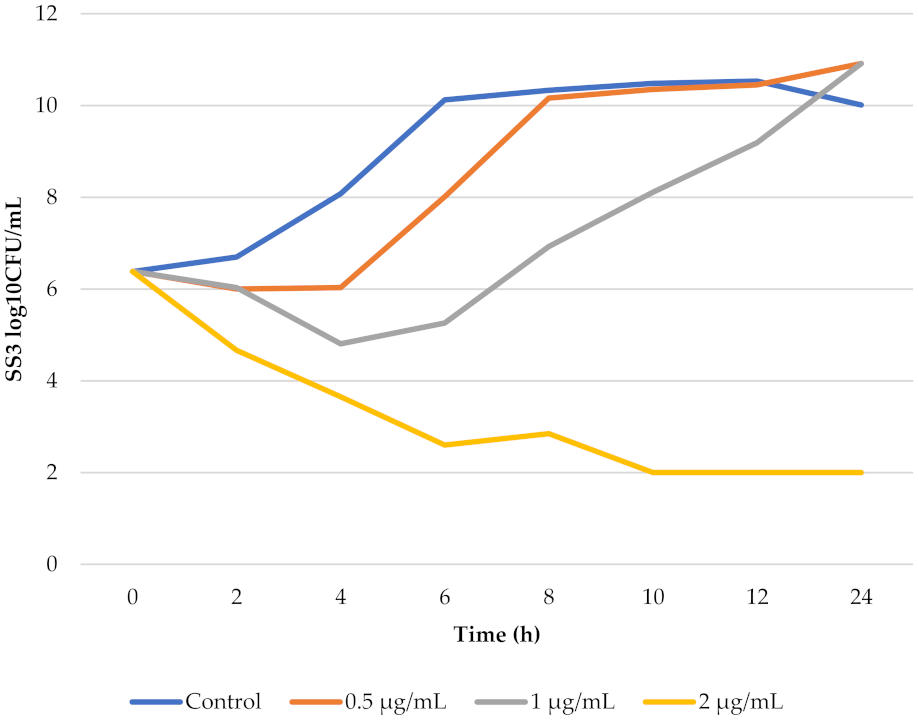
3.3. In Vitro Killing-Time Curves of Florfenicol against SS3
3.4. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Integration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Switała, M.; Hrynyk, R.; Smutkiewicz, A.; Jaworski, K.; Pawlowski, P.; Okoniewski, P.; Grabowski, T.; Debowy, J. Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol, thiamphenicol, and chloramphenicol in turkeys. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 30, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, R.S.; Patterson, S.K.; Meier, A.E.; Gibson, J.K.; Lee, H.L.; Maddox, C.W. Relationship between Phenotypic and Genotypic Florfenicol Resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4047–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yang, B.; Khaliq, H.; Li, K.; Ahmed, S.; Sajid, A.; Zhang, B.; Chen, P.; et al. PK-PD Integration Modeling and Cutoff Value of Florfenicol against Streptococcus suis in Pigs. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliam, J.N.; Streeter, R.N.; Papich, M.G.; Washburn, K.E.; Payton, M.E. Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in serum and synovial fluid after regional intravenous perfusion in the distal portion of the hind limb of adult cows. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.J.; Fung, K.-F. Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in pigs following intravenous, intramuscular or oral administration and the effects of feed intake on oral dosing. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 29, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorspoels, J.; D’Haese, E.; de Craene, B.A.; Vervaet, C.; De Riemaecker, D.; Deprez, P.; Nelis, H.; Remon, J.P. Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol after treatment of pigs with single oral or intramuscular doses or with medicated feed for three days. Vet. Rec. 1999, 145, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Washburn, K.E.; Fajt, V.R.; Rice, S.; Coetzee, J.F. Synovial fluid pharmacokinetics of tulathromycin, gamithromycin and florfenicol after a single subcutaneous dose in cattle. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Fung, K.-F.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, J. Pharmacokinetics of Florfenicol in Healthy Pigs and in Pigs Experimentally Infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-Z.; Fung, K.-F.; Chen, Z.-L.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Zhang, J. Tissue pharmacokinetics of florfenicol in pigs experimentally infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 27, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, P.; Rassouli, A.; Illambas, J.; Potter, T.; Pelligand, L.; Rycroft, A.; Lees, P. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic integration and modelling of florfenicol in calves. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. The pathogenesis of the meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis: The unresolved questions. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 76, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D. Streptococcus Suis Infection. 2005. Available online: http://www.medicine-on-line.com/en/documents/revisited/r0001_en.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Wei, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, A.; He, H.; Hua, Y.; Xia, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Characterization of Streptococcus suis isolates from the diseased pigs in China between 2003 and 2007. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 137, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, T.C.S.; Paes, A.C.; Megid, J.; Ribolla, P.E.M.; dos Paduan, K.S.; Gottschalk, M. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis isolated from clinically healthy swine in Brazil. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 78, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Qiu, H.; Gao, H. In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from clinically healthy sows in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 131, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, J.J.; Feder, I.; Okwumabua, O.; Chengappa, M.M. Streptococcus Suis: Past and Present. Vet. Res. Commun. 1997, 21, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Kang, S.G.; Nabin, R.; Kang, M.L.; Yoo, H.S. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of florfenicol against bacteria isolated from bovine and porcine respiratory disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 106, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.T. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus suis, and Bordetella bronchiseptica isolated from pigs in the United States and Canada, 2011 to 2015. JSHAP 2017, 25, 106–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lubbers, B.V.; Diaz-Campos, D.V.; Schwarz, S.; Bowden, R.; Burbick, C.R.; Fajt, V.R.; Fielder, M.; Gunnett, L.; Holliday, N.M.; Kerdraon, C.; et al. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilutation Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi, Z.; Karancsi, Z.; Jerzsele, Á. Farmakokinetika/farmakodinámia (PK/PD) megközelítés az állatgyógyászatban. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2018, 140, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Toutain, P.-L.; Bousquet-Melou, A.; Damborg, P.; Ferran, A.A.; Mevius, D.; Pelligand, L.; Veldman, K.T.; Lees, P. En Route towards European Clinical Breakpoints for Veterinary Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: A Position Paper Explaining the VetCAST Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, E.I.; Friberg, L.E. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Antibacterial Drugs. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 1053–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.-Z.; Fan, H.-G.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.-S.; Ma, K.; Yu, S.-M.; Tan, L.-J.; Wang, H.-B. Cardiopulmonary, Biochemical and Haematological Effects of the Tiletamine/Zolazepam-Xylazine-Tramadol Combination to Provide Anaesthesia in Miniature Pigs. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Gao, J.D.; Cao, X.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Sun, G.Z.; Yang, J.J. Lung microdialysis study of florfenicol in pigs after single intramuscular administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 40, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottbøll, L.; Skovgaard, K.; Barington, K.; Friis, C.; Rottbøll, L.A.H.; Jensen, H.E. Intrabronchial Microdialysis: Effects of Probe Localization on Tissue Trauma and Drug Penetration into the Pulmonary Epithelial Lining Fluid. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 117, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ahmed, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Pharmacokinetic of florfenicol in pulmonary epithelial lining fluid of swine and effects of anesthetic agent on drug plasma disposition kinetics. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2018, 70, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.M.; Martin, L.G.; Papich, M.G. Comparison of Active Drug Concentrations in the Pulmonary Epithelial Lining Fluid and Interstitial Fluid of Calves Injected with Enrofloxacin, Florfenicol, Ceftiofur, or Tulathromycin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobell, R.D.; Varma, K.J.; Johnson, J.C.; Sams, R.A.; Gerken, D.F.; Ashcraft, S.M. Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol following intravenous and intramuscular doses to cattle. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 17, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretzlaff, K.N.; Neff-Davis, C.A.; Ott, R.S.; Koritz, G.D.; Gustafsson, B.K.; Davis, L.E. Florfenicol in non-lactating dairy cows: Pharmacokinetics, binding to plasma proteins, and effects on phagocytosis by blood neutrophils. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1987, 10, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, P.L.; Bousquet-Melou, A. Volumes of distribution. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J.W.; Dudley, M.N.; Cars, O.; Derendorf, H.; Drusano, G.L. Standardization of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) terminology for anti-infective drugs: An update. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, P.-L.; Sidhu, P.K.; Lees, P.; Rassouli, A.; Pelligand, L. VetCAST Method for Determination of the Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Cut-Off Values of a Long-Acting Formulation of Florfenicol to Support Clinical Breakpoints for Florfenicol Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing in Cattle. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, P.L.; Pelligand, L.; Lees, P.; Bousquet-Mélou, A.; Ferran, A.A.; Turnidge, J.D. The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic paradigm for antimicrobial drugs in veterinary medicine: Recent advances and critical appraisal. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 44, 172–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.; Kerouault, B.; Martin, C. Chloramphenicol and florfenicol susceptibility of fish-pathogenic bacteria isolated in France: Comparison of minimum inhibitory concentration, using recommended provisory standards for fish bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errecalde, J.O.; Carmely, D.; Marino, E.L.; Mestorino, N. Pharmacokinetics of amoxycillin in normal horses and horses with experimental arthritis. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorey, L.; Pelligand, L.; Cheng, Z.; Lees, P. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic integration and modelling of florfenicol for the pig pneumonia pathogens Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and Pasteurella multocida. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hout, J.; Heuvelink, A.; Gonggrijp, M. Monitoring of antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis in the Netherlands, 2013–2015. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 194, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Garch, F.; de Jong, A.; Simjee, S.; Moyaert, H.; Klein, U.; Ludwig, C.; Marion, H.; Haag-Diergarten, S.; Richard-Mazet, A.; Thomas, V.; et al. Monitoring of antimicrobial susceptibility of respiratory tract pathogens isolated from diseased cattle and pigs across Europe, 2009–2012: VetPath results. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 194, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Garcia, J.; Wang, J.; Restif, O.; Holmes, M.A.; Mather, A.E.; Weinert, L.A.; Wileman, T.M.; Thomson, J.R.; Langford, P.R.; Wren, B.W.; et al. Patterns of antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus suis isolates from pigs with or without streptococcal disease in England between 2009 and 2014. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESVAC–Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2018–Healthy Livestock. Available online: https://healthylivestock.net/esvac-sales-of-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-in-31-european-countries-in-2018/ (accessed on 10 December 2021).

| Plasma | In steady-state condition in plasma AUC24h = AUC0-∞ LD = Vss/F × target concentration Vss = Cl/F × MRT target concentration = C24av in steady-state condition in plasma C24av = AUC0-∞/24 h | LD = C24av × Vss |
| Synovial fluid | Ratio = AUC0-∞ of plasma / AUC0-∞ of synovial fluid | |
| C24av of synovial fluid = No. of ratio × C24av of plasma | ||
| Parameters | Unit | Plasma | Synovial Fluid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | µg/mL | 3.58 ± 1.51 | 2.73 ± 1.2 |
| Tmax | h | 1.64 ± 1.74 | 3.4 ± 1.67 |
| T1/2 | h | 17.24 ± 9.35 | 21.01 ± 13.19 |
| AUC24h | μg/mL·h | 54.66 ± 23.34 | 31.24 ± 6.82 |
| AUC0-∞ | μg/mL·h | 87.14 ± 31.50 | 54.80 ± 13.35 |
| Cl/F | L/h/kg | 0.19 ± 0.08 | 0.29 ± 0.08 |
| MRT0-∞ | h | 24.0 ± 13.59 | 27.39 ± 17.16 |
| Effect | 1 AUC24h/MIC Breakpoints | Average Plasma Concentration Required (in Fold of the MIC) | MIC of S. suis in Synovial Fluid (µg/mL) | MIC of S. suis in Plasma (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteriostatic | 37.89 | 1.58 | ≤1.42 | ≤2.30 |
| Bactericidal | 44.02 | 1.83 | ≤1.22 | ≤1.96 |
| Eradication | 46.42 | 1.93 | ≤1.16 | ≤1.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Somogyi, Z.; Mag, P.; Kovács, D.; Kerek, Á.; Szabó, P.; Makrai, L.; Jerzsele, Á. Synovial and Systemic Pharmacokinetics of Florfenicol and PK/PD Integration against Streptococcus suis in Pigs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010109
Somogyi Z, Mag P, Kovács D, Kerek Á, Szabó P, Makrai L, Jerzsele Á. Synovial and Systemic Pharmacokinetics of Florfenicol and PK/PD Integration against Streptococcus suis in Pigs. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010109
Chicago/Turabian StyleSomogyi, Zoltán, Patrik Mag, Dóra Kovács, Ádám Kerek, Pál Szabó, László Makrai, and Ákos Jerzsele. 2022. "Synovial and Systemic Pharmacokinetics of Florfenicol and PK/PD Integration against Streptococcus suis in Pigs" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010109
APA StyleSomogyi, Z., Mag, P., Kovács, D., Kerek, Á., Szabó, P., Makrai, L., & Jerzsele, Á. (2022). Synovial and Systemic Pharmacokinetics of Florfenicol and PK/PD Integration against Streptococcus suis in Pigs. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010109








