MAP Kinase Pathways in Brain Endothelial Cells and Crosstalk with Pericytes and Astrocytes Mediate Contrast-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Materials and Reagents
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Establishment of the In Vitro BBB Model
2.5. Transendothelial Electrical Resistance (TEER)
2.6. Paracellular Permeability of Sodium Fluorescein (Na-F)
2.7. CM Treatment in the In Vitro BBB Models
2.8. Collection of Conditioned Medium and Treatment in the In Vitro BBB Models
2.9. Cell Viability
2.10. Immunostaining
2.11. Immunoblotting
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
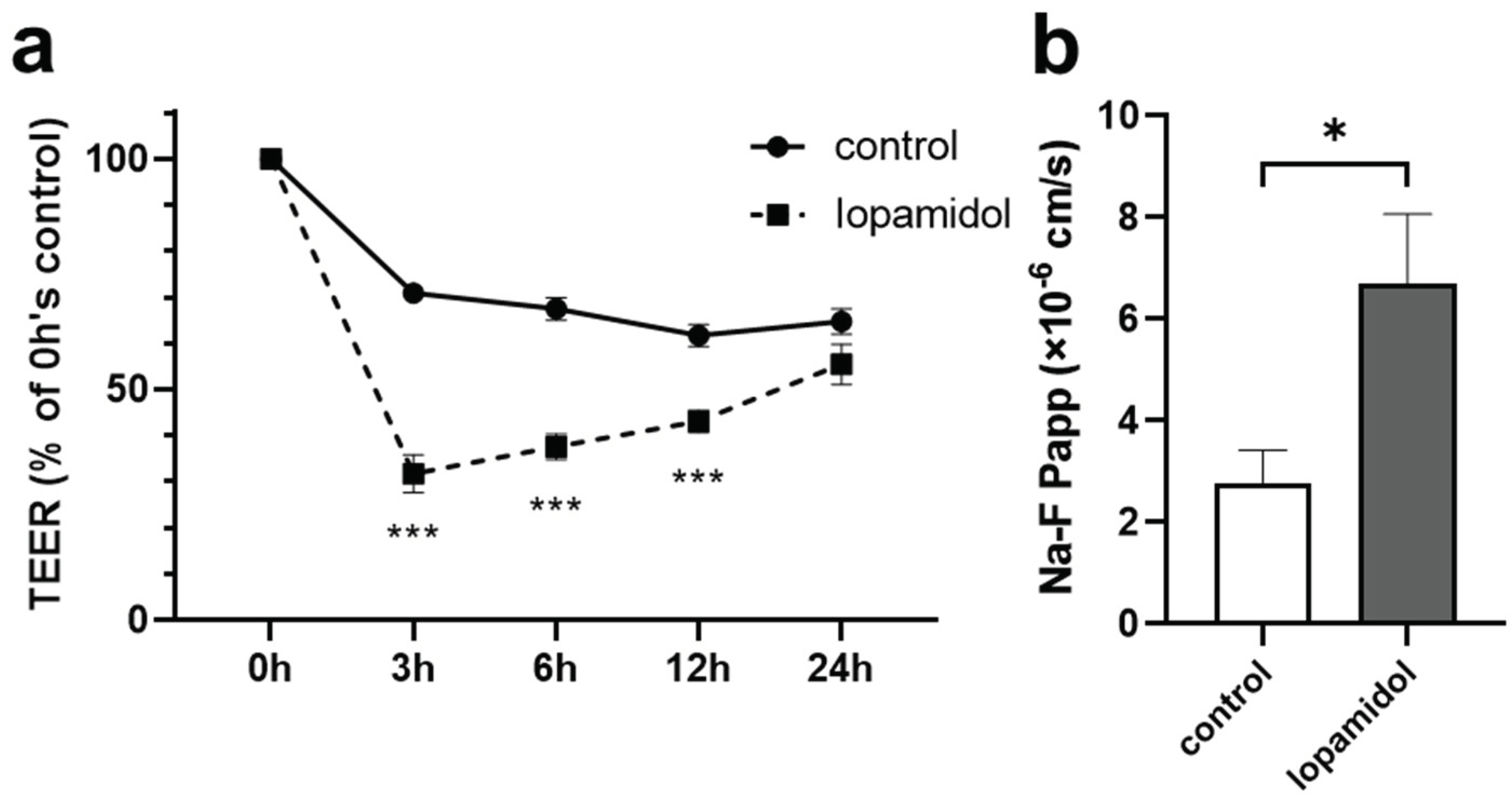
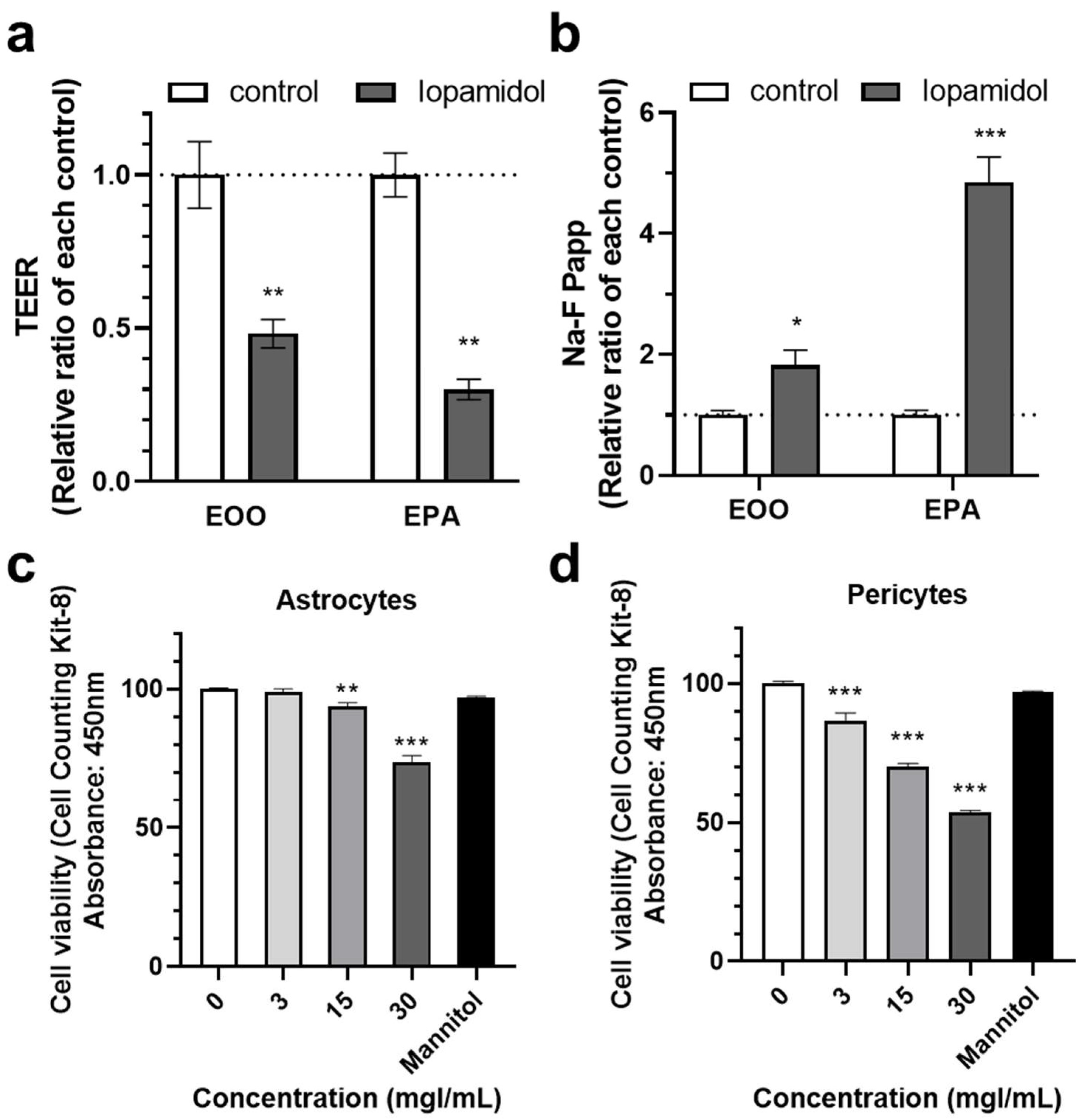
3.1. Effects of Short-Term Exposure to CM on Barrier Function
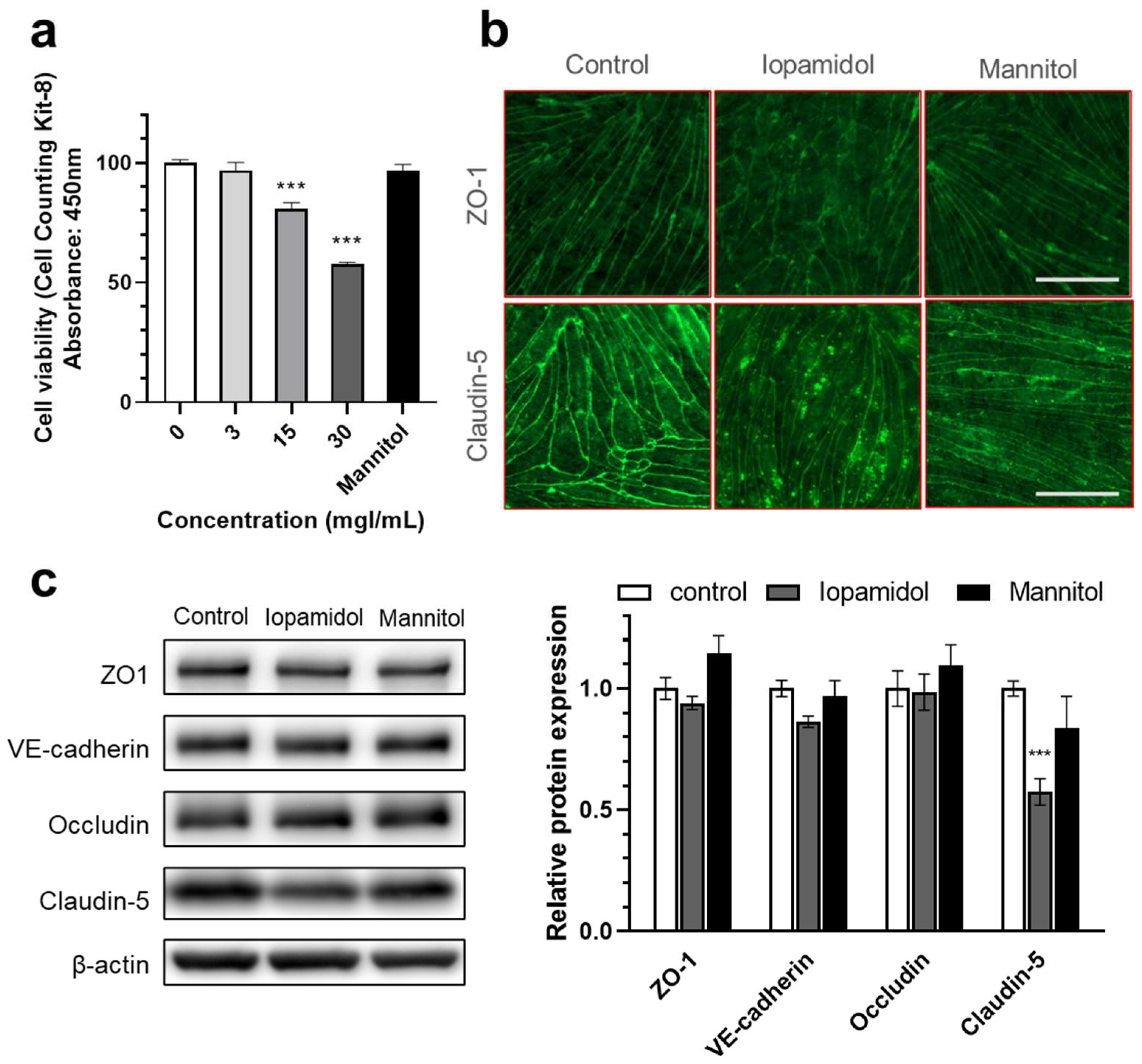
3.2. Effects of Iopamidol on Cell Viability and Expression of TJ Proteins in RBECs
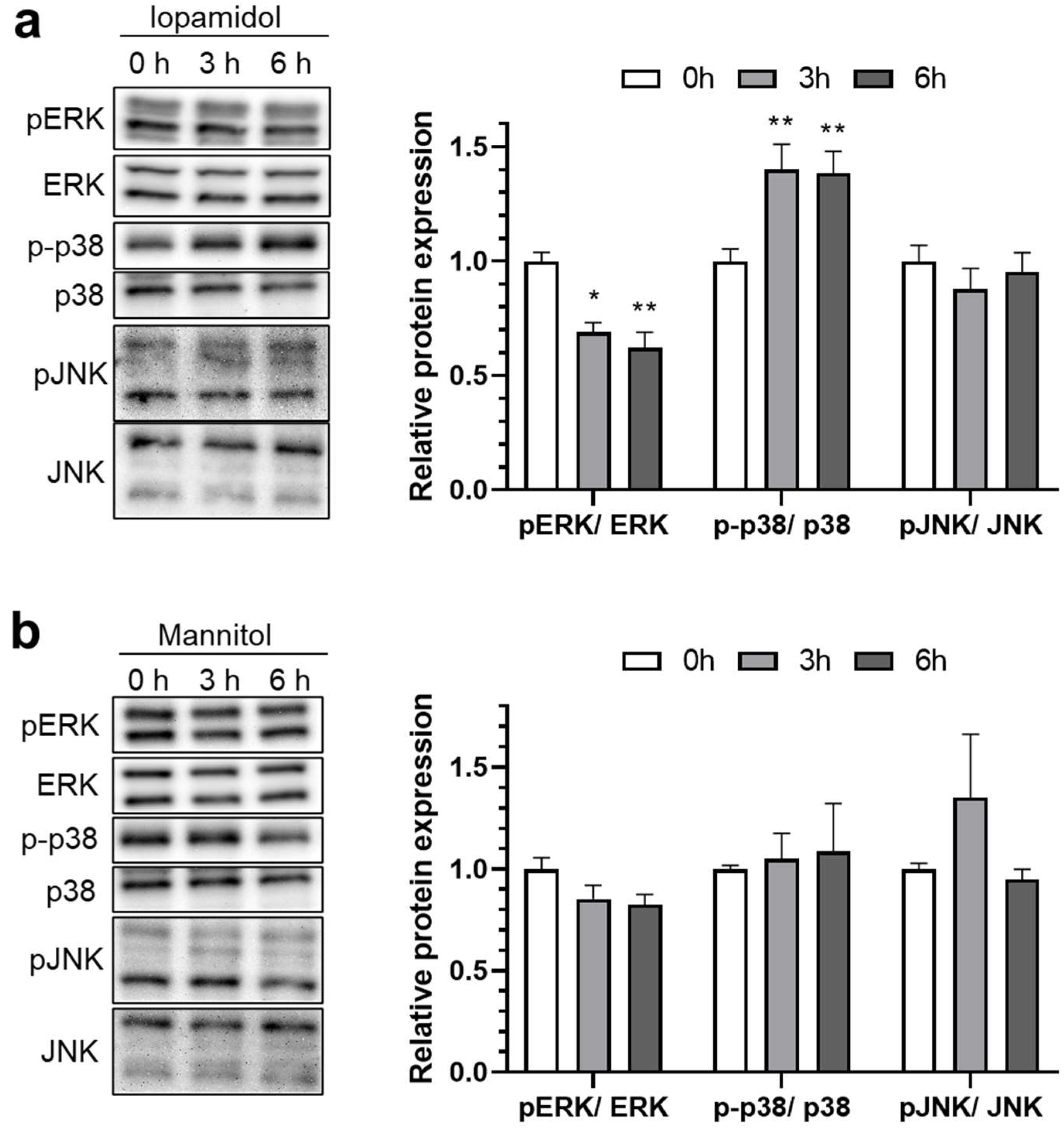
3.3. Influence of Iopamidol on the Phosphorylation of MAP Kinases in RBECs
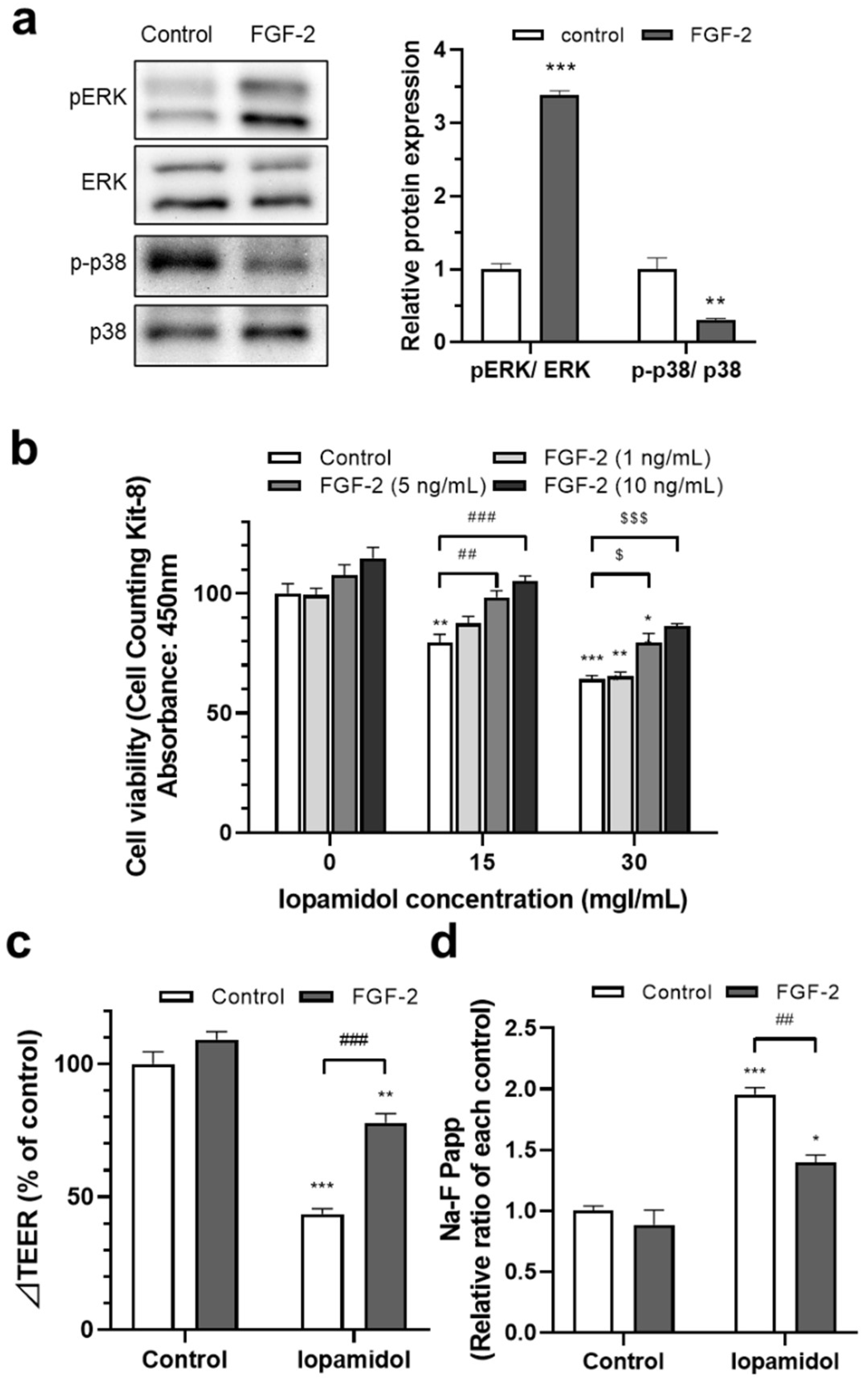
3.4. Effects of FGF-2 on Viability and Barrier Function in Iopamidol-Treated RBECs
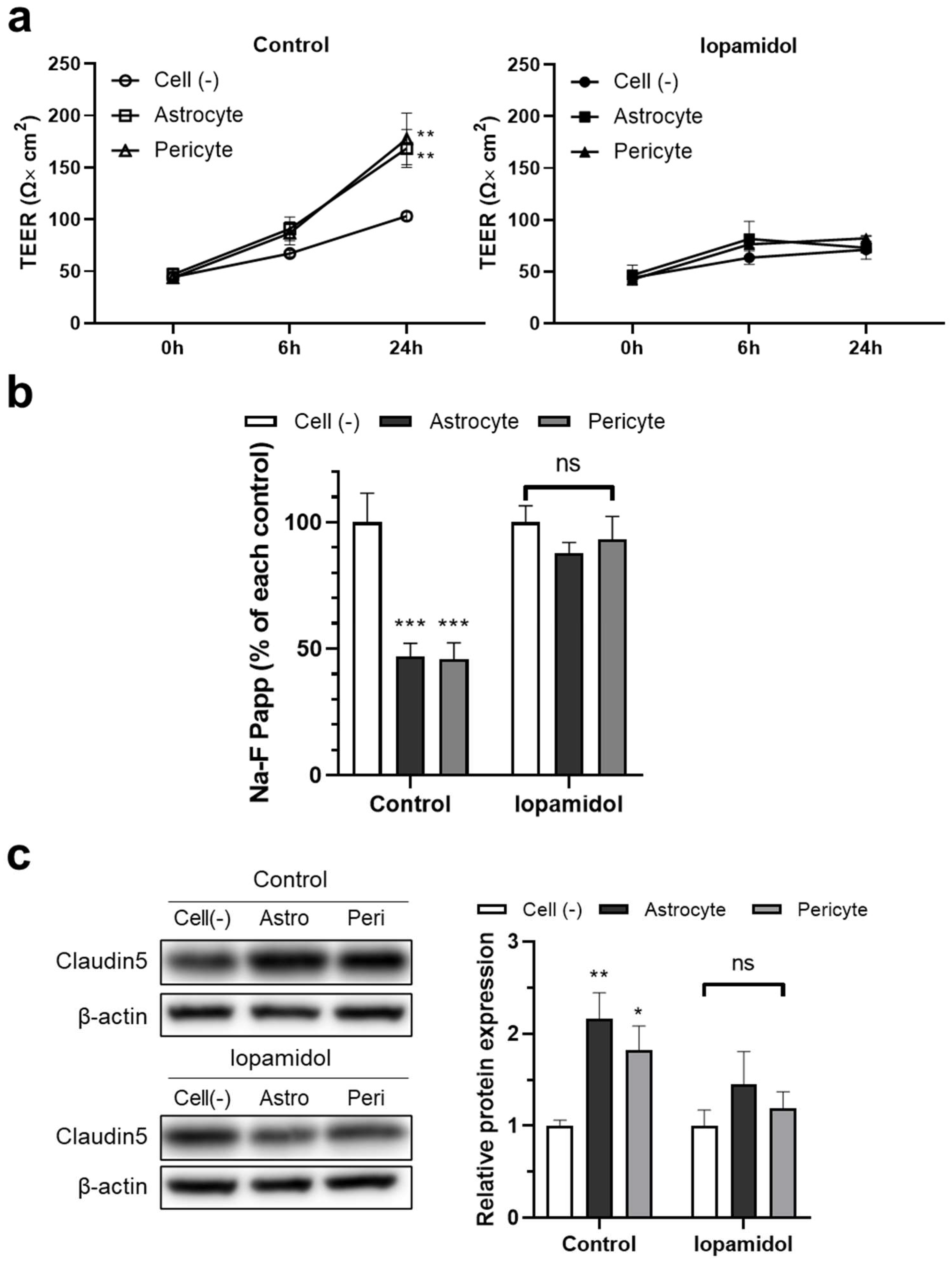
3.5. Effects of Iopamidol on NVU Types
3.6. Effects of Iopamidol on the Astrocyte- or Pericyte-Induced Enhancement of Barrier Function in RBECs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehran, R.; Nikolsky, E. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Definition, epidemiology, and patients at risk. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, S11–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyman, S.N.; Rosen, S.; Khamaisi, M.; Idée, J.-M.; Rosenberger, C. Reactive oxygen species and the pathogenesis of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. Investig. Radiol. 2010, 45, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoditti, E.; Massaro, M.; Montinari, M.R. Endothelial safety of radiological contrast media: Why being concerned. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2013, 58, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beierwaltes, W.H. Endothelial dysfunction in the outer medullary vasa recta as a key to contrast media-induced nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2013, 304, F31–F32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Persson, P.B.; Hansell, P.; Liss, P. Pathophysiology of contrast medium–induced nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paúl, L.; Vicente, J.M.; Pastorín, R.; Casasco, A. A case of temporary nonthrombotic hemiplegia and aphasia due to neurotoxicity from angiographic contrast material? Radiologia 2009, 51, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, R.; Simon, N.; Markus, R.; Muller, D.W.; Kathir, K. Contrast-induced encephalopathy following cardiac catheterization. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 90, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lantos, G. Cortical blindness due to osmotic disruption of the blood-brain barrier by angiographic contrast material: CT and MRI studies. Neurology 1989, 39, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-T.; Lee, K.-P.; Chen, C.-H.; Sung, P.-S.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Tsai, L.-K.; Tang, S.-C.; Jeng, J.-S. Contrast-induced encephalopathy after endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 3756–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.T.; Davis, T.P. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A.; Kovac, A.; Morofuji, Y. Neurovascular unit crosstalk: Pericytes and astrocytes modify cytokine secretion patterns of brain endothelial cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdő, F.; Denes, L.; de Lange, E. Age-associated physiological and pathological changes at the blood-brain barrier: A review. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkler, E.A.; Bell, R.D.; Zlokovic, B.V. Central nervous system pericytes in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosselet, F. Modelling of the blood-brain barrier. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, S.; Deli, M.A.; Kawaguchi, H.; Shimizudani, T.; Shimono, T.; Kittel, A.; Tanaka, K.; Niwa, M. A new blood-brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 54, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, S.; Deli, M.A.; Nakao, S.; Honda, M.; Hayashi, K.; Nakaoke, R.; Kataoka, Y.; Niwa, M. Pericytes from brain microvessels strengthen the barrier integrity in primary cultures of rat brain endothelial cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 27, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deli, M.A.; Szabó, C.A.; Dung, N.T.K.; Joó, F. Immunohistochemical and electron microscopy detections on primary cultures of rat cerebral endothelial cells. In Drug Transport across the Blood—Brain Barrier: In Vivo and In Vitro Techniques; Harwood Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, F.R.; Valkai, S.; Kincses, A.; Petneházi, A.; Czeller, T.; Veszelka, S.; Ormos, P.; Deli, M.A.; Dér, A. A versatile lab-on-a-chip tool for modeling biological barriers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrière, N.; Demeuse, P.; Garcia, E.; Regina, A.; Debray, M.; Andreux, J.-P.; Couvreur, P.; Scherrmann, J.-M.; Temsamani, J.; Couraud, P.-O.; et al. Puromycin-based purification of rat brain capillary endothelial cell cultures. Effect on the expression of blood-brain barrier-specific properties. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barna, L.; Walter, F.R.; Harazin, A.; Bocsik, A.; Kincses, A.; Tubak, V.; Jósvay, K.; Zvara, Á.; Campos-Bedolla, P.; Deli, M.A. Simvastatin, edaravone and dexamethasone protect against kainate-induced brain endothelial cell damage. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veszelka, S.; Tóth, A.; Walter, F.R.; Tóth, A.E.; Gróf, I.; Mészáros, M.; Bocsik, A.; Hellinger, É.; Vastag, M.; Rákhely, G.; et al. Comparison of a Rat Primary Cell-Based Blood-Brain Barrier Model with Epithelial and Brain Endothelial Cell Lines: Gene Expression and Drug Transport. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoheisel, D.; Nitz, T.; Franke, H.; Wegener, J.; Hakvoort, A.; Tilling, T.; Galla, H.J. Hydrocortisone reinforces the blood-brain properties in a serum free cell culture system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 247, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morofuji, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; So, G.; Hiu, T.; Horai, S.; Hayashi, K.; Tanaka, K.; Suyama, K.; Deli, M.A.; Nagata, I.; et al. Pitavastatin strengthens the barrier integrity in primary cultures of rat brain endothelial cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiu, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Hayashi, K.; Kitagawa, N.; Tsutsumi, K.; Kawakubo, J.; Honda, M.; Suyama, K.; Nagata, I.; Niwa, M. Tissue plasminogen activator enhances the hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced impairment of the blood-brain barrier in a primary culture of rat brain endothelial cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Hayashi, K.; Kitagawa, N.; Tsutsumi, K.; Nagata, I.; Niwa, M. Adrenomedullin improves the blood-brain barrier function through the expression of claudin-5. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2006, 26, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deli, M.A.; Abrahám, C.S.; Kataoka, Y.; Niwa, M. Permeability studies on in vitro blood-brain barrier models: Physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 59–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, K.A.; Avdeef, A.; Abbott, N.J. In vitro trans-monolayer permeability calculations: Often forgotten assumptions. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, L.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y. Atorvastatin attenuates contrast-induced nephropathy by modulating inflammatory responses through the regulation of JNK/p38/Hsp27 expression. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 131, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintavalle, C.; Brenca, M.; De Micco, F.; Fiore, D.; Romano, S.; Romano, M.F.; Apone, F.; Bianco, A.; Zabatta, M.A.; Troncone, G.; et al. In vivo and in vitro assessment of pathways involved in contrast media-induced renal cells apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, C.; Sharma, V.; Park, J.; Schirmer, C.M.; Zand, R. Contrast-induced encephalopathy after cerebral angiogram: A case series and review of literature. Case Rep. Neurol. 2021, 13, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lv, S. Hypotonic contrast media is more toxic than isotonic contrast media on endothelial cells in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4334–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Holt, C.M.; Malik, N.; Shepherd, L.; Morcos, S.K. Effects of radiographic contrast media on proliferation and apoptosis of human vascular endothelial cells. Br. J. Radiol. 2000, 73, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peachell, P.T.; Morcos, S.K. Effect of radiographic contrast media on histamine release from human mast cells and basophils. Br. J. Radiol. 1998, 71, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrow, R.; Roobottom, C.A.; Wells, I.P.; Hurlock, N. Effects of radiographic contrast media on leukocyte phagocytosis. Acad. Radiol. 1994, 1, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avruch, J. MAP kinase pathways: The first twenty years. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.-J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsunaga, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Morofuji, Y.; Dohgu, S.; Watanabe, D.; Horie, N.; Izumo, T.; Niwa, M.; Walter, F.R.; Santa-Maria, A.R.; et al. MAP Kinase Pathways in Brain Endothelial Cells and Crosstalk with Pericytes and Astrocytes Mediate Contrast-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081272
Matsunaga Y, Nakagawa S, Morofuji Y, Dohgu S, Watanabe D, Horie N, Izumo T, Niwa M, Walter FR, Santa-Maria AR, et al. MAP Kinase Pathways in Brain Endothelial Cells and Crosstalk with Pericytes and Astrocytes Mediate Contrast-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(8):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081272
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsunaga, Yuki, Shinsuke Nakagawa, Yoichi Morofuji, Shinya Dohgu, Daisuke Watanabe, Nobutaka Horie, Tsuyoshi Izumo, Masami Niwa, Fruzsina R. Walter, Ana Raquel Santa-Maria, and et al. 2021. "MAP Kinase Pathways in Brain Endothelial Cells and Crosstalk with Pericytes and Astrocytes Mediate Contrast-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 8: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081272
APA StyleMatsunaga, Y., Nakagawa, S., Morofuji, Y., Dohgu, S., Watanabe, D., Horie, N., Izumo, T., Niwa, M., Walter, F. R., Santa-Maria, A. R., Deli, M. A., & Matsuo, T. (2021). MAP Kinase Pathways in Brain Endothelial Cells and Crosstalk with Pericytes and Astrocytes Mediate Contrast-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption. Pharmaceutics, 13(8), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081272









