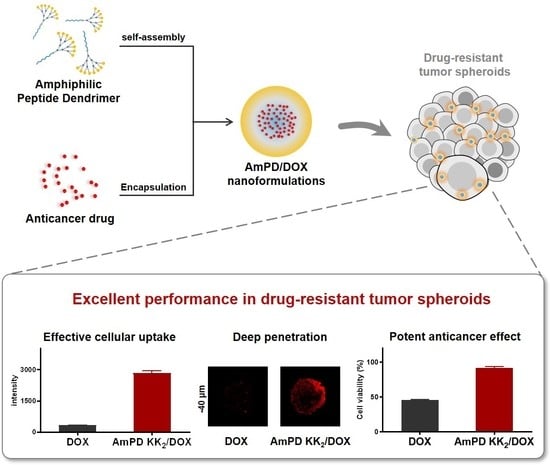
A Self-Assembling Amphiphilic Peptide Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of AmPD KK2
2.3. Synthesis of AmPD KK2K4
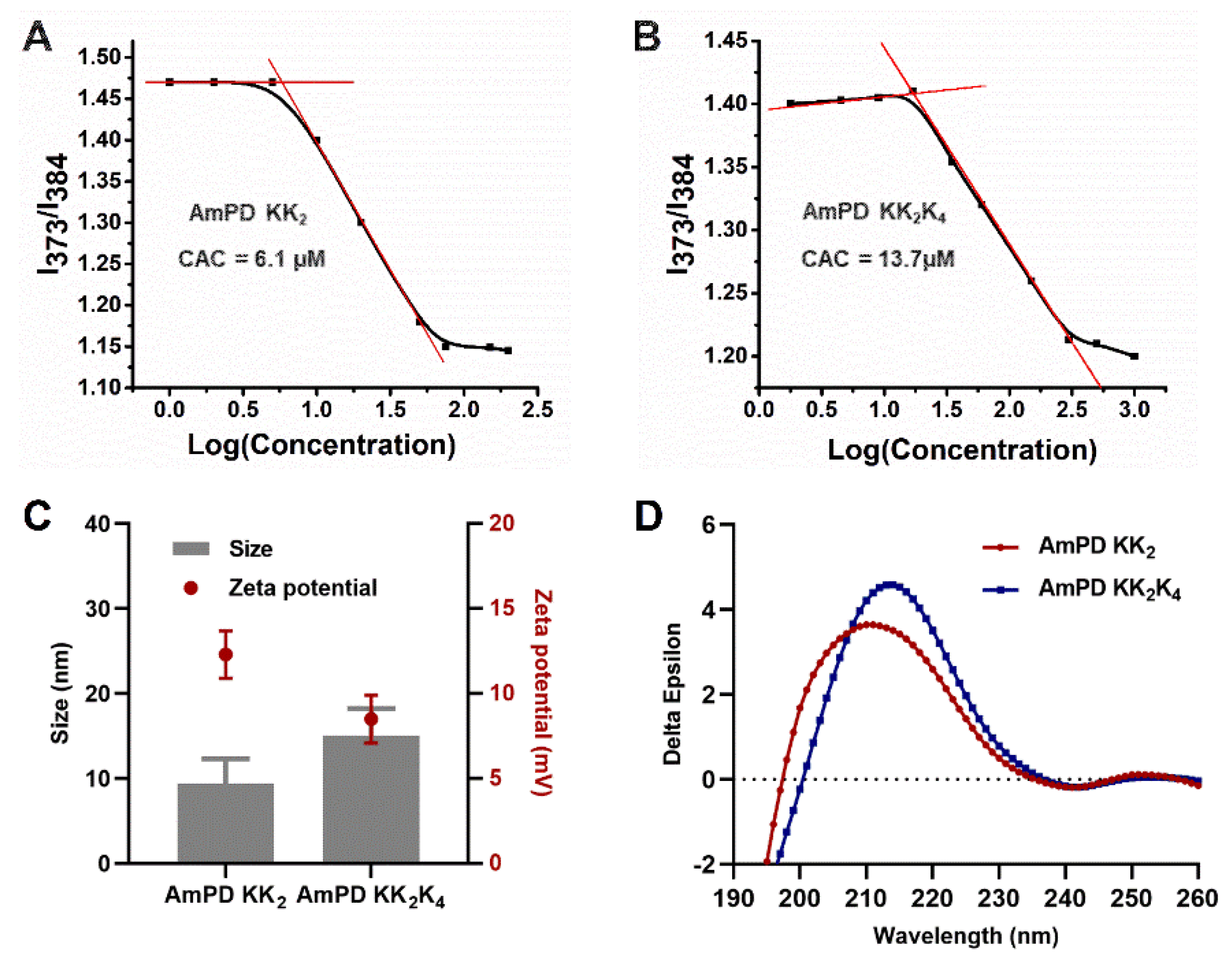
2.4. Critical Aggregation Concentration (CAC) of AmPDs Nanoassemblies
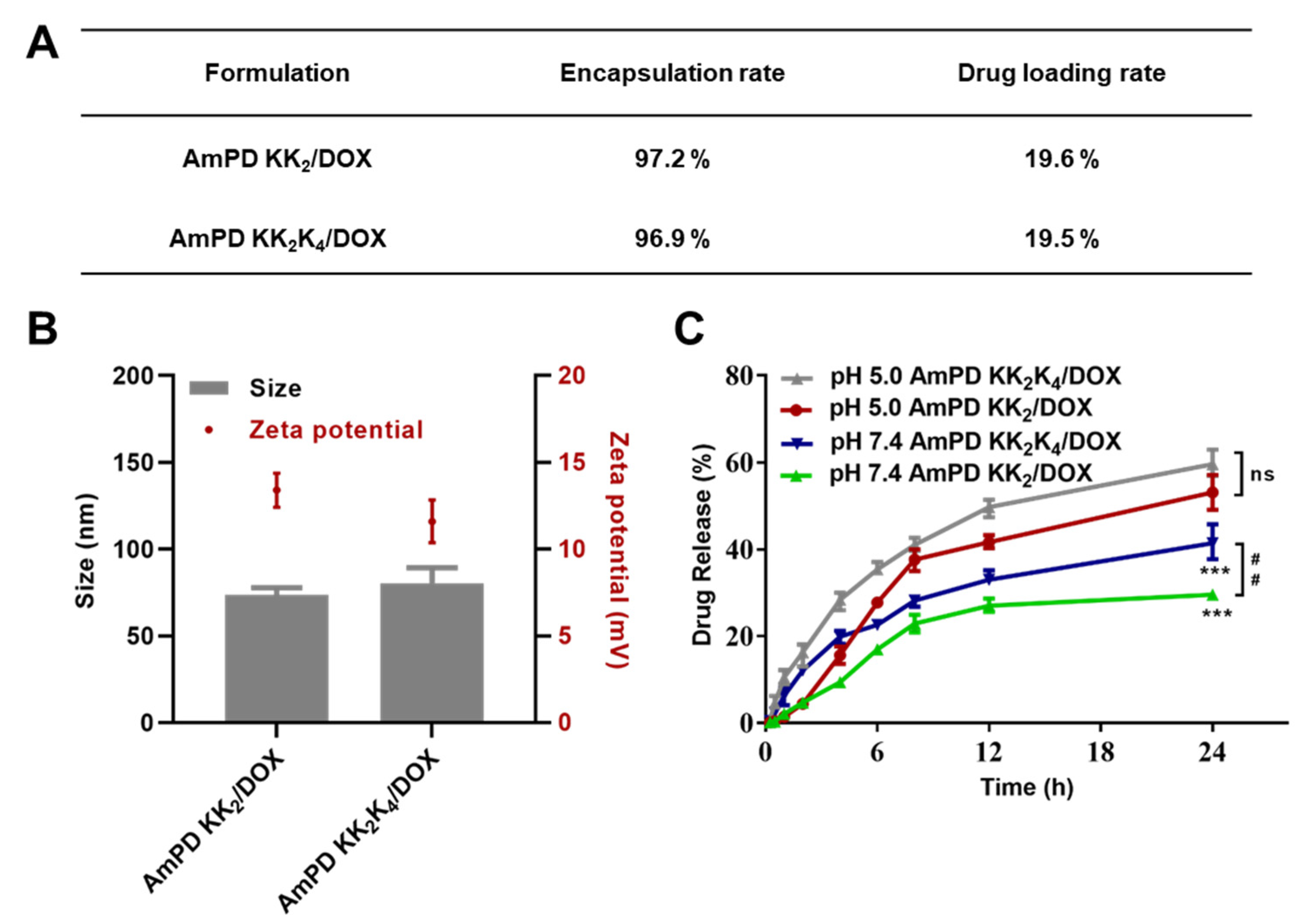
2.5. Preparation of Doxorubicin-Loading Nanoformulations
2.6. Size Distribution, and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.7. In Vitro Drug Release
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. In Vitro Anticancer Activity
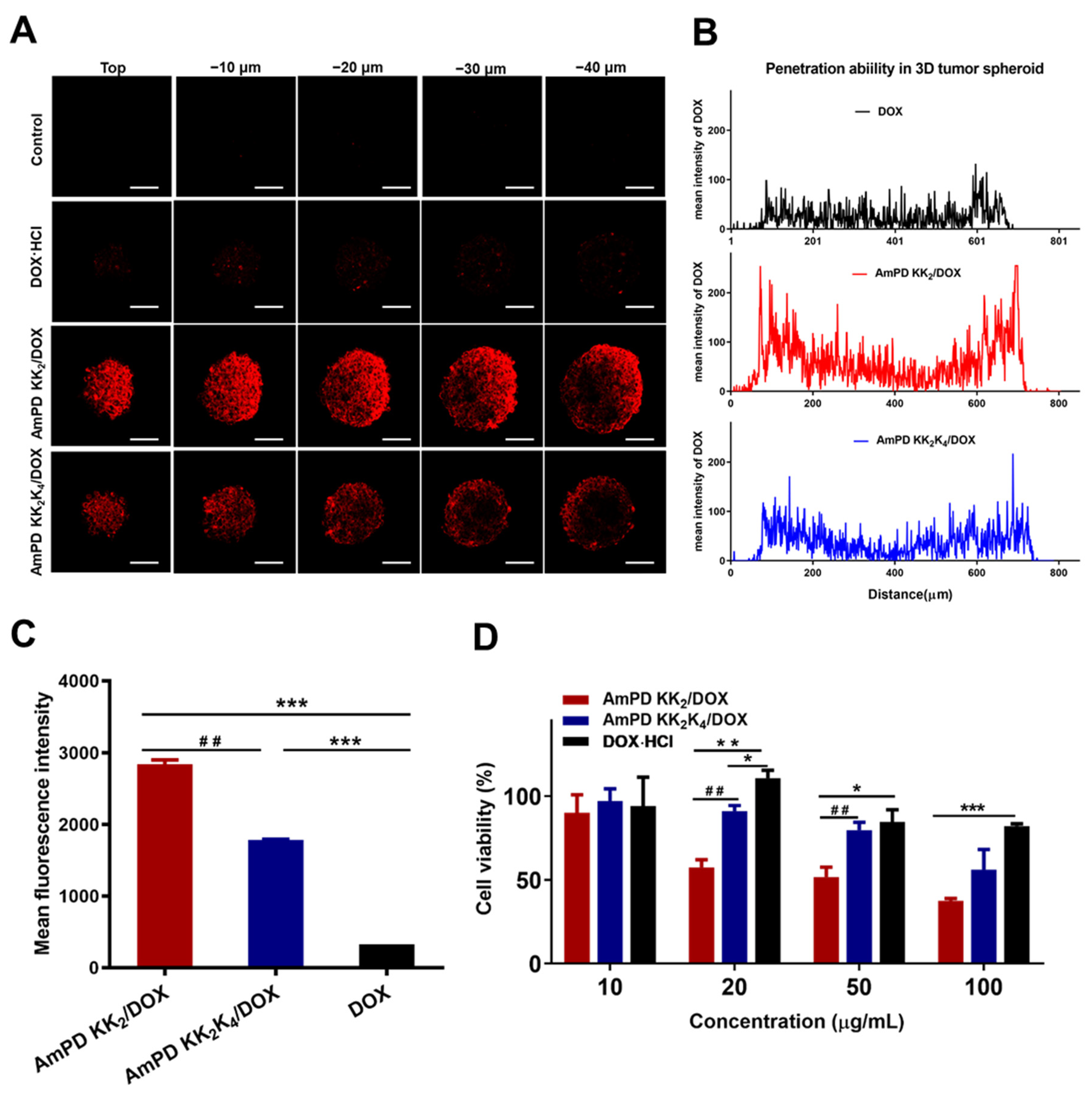
2.10. In Vitro Cellular Uptake
2.11. Drug Penetration in 3D-Cultured Tumor Spheroids
2.12. In Vitro Anticancer Activity in 3D-Cultured Tumor Spheroids
2.13. Statistical Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of the Amphiphilic Peptide Dendrimers (AmPDs)
3.2. Characterization of Self-Assembly Behaviours of AmPDs
3.3. Drug Encapsulation and Drug Release Profiles of DOX-Loaded AmPD Nanoformulations
3.4. Potent Anticancer Efficacy of AmPD/DOX Nanoformulations via Effective Intracellular Uptake
3.5. Deep Drug Penetration and Cellular Uptake in 3D-Cultured Tumor Spheroids
3.6. Enhanced Antiproliferative Effect in 3D-Cultured Tumor Spheroids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hulvat, M.C. Cancer Incidence and Trends. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 100, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Baselga, J.; Hyman, D.M. A view on drug resistance in cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfarouk, K.O.; Stock, C.-M.; Taylor, S.; Walsh, M.; Muddathir, A.K.; Verduzco, D.; Bashir, A.H.H.; Mohammed, O.Y.; ElHassan, G.O.; Harguindey, S.; et al. Resistance to cancer chemotherapy: Failure in drug response from ADME to P-gp. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourzac, K. Nanotechnology carrying drugs. Nature 2012, 491, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, J.S.O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minko, T. Nanotechnology and drug resistance preface. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1665–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.A.; Fawell, S.; Floc’H, N.; Flemington, V.; McKerrecher, D.; Smith, P.D. Challenges and Opportunities in Cancer Drug Resistance. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3297–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y. Nanotechnology applied to overcome tumor drug resistance. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Posocco, P.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Q.; Huo, S.; Liang, Z.; Fermeglia, M.; et al. Anticancer drug nanomicelles formed by self-assembling amphiphilic dendrimer to combat cancer drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2978–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petros, R.A.; DeSimone, J.M. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenson, S.; Tomalia, D.A. Dendrimers in biomedical applications—Reflections on the field. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2106–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Mackay, J.A.; Frechet, J.; Szoka, F.C. Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Ding, L.; Tintaru, A.; Peng, L. Self-Assembling Supramolecular Dendrimers for Biomedical Applications: Lessons Learned from Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2936–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Liu, X.; Bolcato-Bellemin, A.-L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Erbacher, P.; Qu, F.; Rocchi, P.; Behr, J.-P.; Peng, L. An Amphiphilic Dendrimer for Effective Delivery of Small Interfering RNA and Gene Silencing In Vitro and In Vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8478–8484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, T.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Q.; Sengupta, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Adaptive amphiphilic dendrimer-based nanoassemblies as robust and versatile siRNA delivery systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11822–11827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Tintaru, A.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Ziarelli, F.; Tang, J.; Guo, H.; Rosas, R.; et al. A Fluorinated Bola-Amphiphilic Dendrimer for On-Demand Delivery of siRNA, via Specific Response to Reactive Oxygen Species. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8594–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, L.; Laurini, E.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Weng, Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, P.; Marson, D.; et al. A dual targeting dendrimer-mediated siRNA delivery system for effective gene silencing in cancer therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16264–16274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapra, R.; Verma, R.P.; Maurya, G.P.; Dhawan, S.; Babu, J.; Haridas, V. Designer Peptide and Protein Dendrimers: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11391–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z. Virion-Like Membrane-Breaking Nanoparticles with Tumor-Activated Cell-and-Tissue Dual-Penetration Conquer Impermeable Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1707240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Shi, K.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.; Rocchi, P.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X. Self-assembly of amphiphilic phospholipid peptide dendrimer-based nanovectors for effective delivery of siRNA therapeutics in prostate cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lin, W.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. Amphiphilic peptide dendrimer-based nanovehicles for safe and effective siRNA delivery. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 6, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Li, C.; Li, L.; She, W.; Wang, G.; Gu, Z. Arginine functionalized peptide dendrimers as potential gene delivery vehicles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4917–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, I.F.; Rotin, D. Acid pH in tumors and its potential for therapeutic exploitation. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 4373–4384. [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby, R.A.; Gillies, R. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.A.; Chimenti, M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. Dysregulated pH: A perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishiguro, T.; Ohata, H.; Sato, A.; Yamawaki, K.; Enomoto, T.; Okamoto, K. Tumor-derived spheroids: Relevance to cancer stem cells and clinical applications. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Lian, B.; Ma, C.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; et al. A Self-Assembling Amphiphilic Peptide Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071092
Zhu D, Zhang H, Huang Y, Lian B, Ma C, Han L, Chen Y, Wu S, Li N, Zhang W, et al. A Self-Assembling Amphiphilic Peptide Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071092
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Dandan, Huanle Zhang, Yuanzheng Huang, Baoping Lian, Chi Ma, Lili Han, Yu Chen, Shengmei Wu, Ning Li, Wenjie Zhang, and et al. 2021. "A Self-Assembling Amphiphilic Peptide Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071092
APA StyleZhu, D., Zhang, H., Huang, Y., Lian, B., Ma, C., Han, L., Chen, Y., Wu, S., Li, N., Zhang, W., & Liu, X. (2021). A Self-Assembling Amphiphilic Peptide Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071092