Novel Non-Congeneric Derivatives of the Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor ICL-CCIC-0019
Abstract
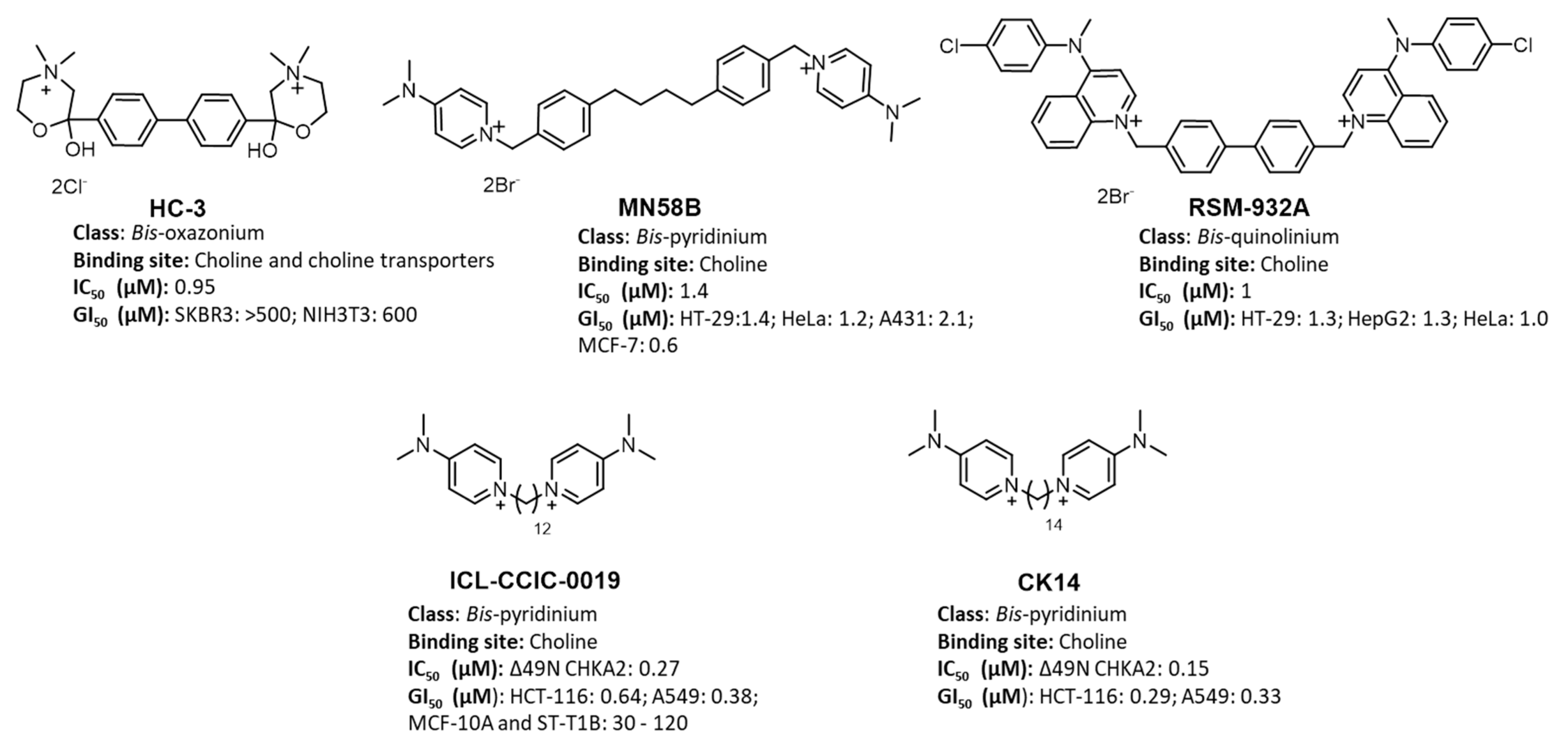
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- (2)
2. Materials and Methods
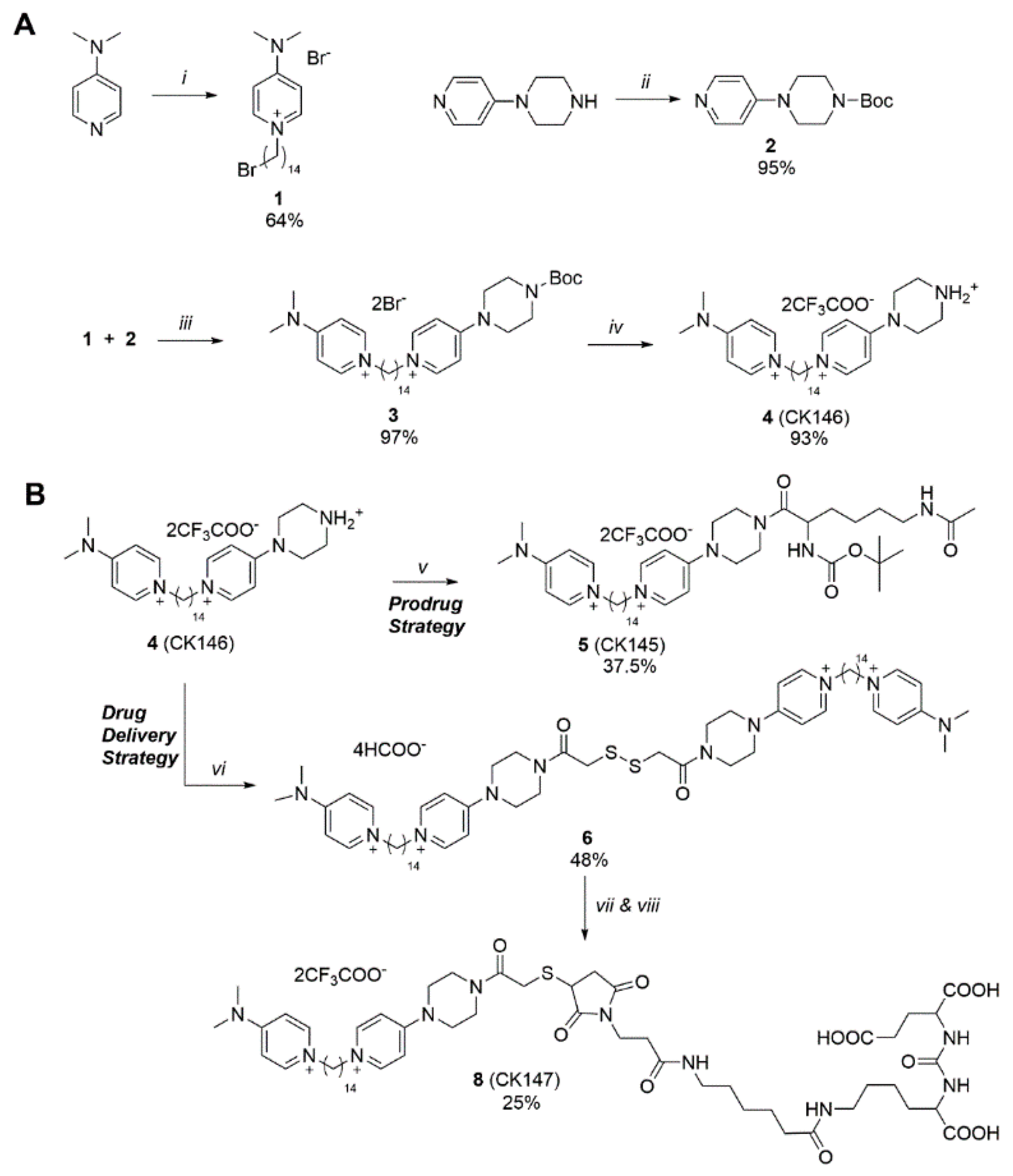
2.1. Chemical Synthesis
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Anti-Proliferative Assay (Sulforhodamine B Assay)
2.4. Lipid Kinase Screening
2.5. In Vitro ‘Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion’ (ADME) Study
2.6. Immunoblotting Analysis (General)
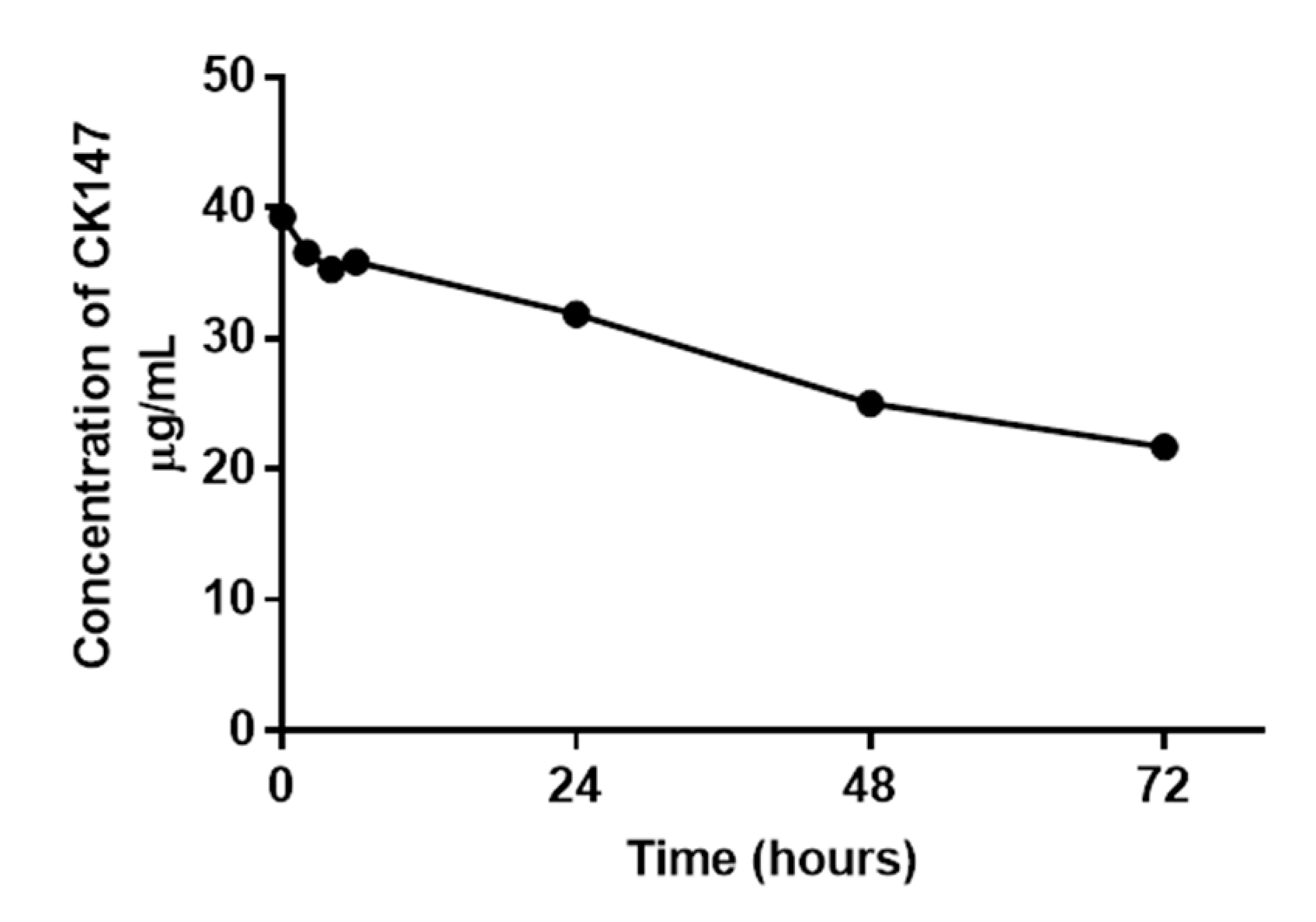
2.7. Conjugate Stability Test of CK147 (8)
2.8. Cellular Uptake and Metabolism Study of CK145 (5)
2.9. Cellular Uptake and Metabolism Study of ICL-CCIC-0019, CK146 (4), CK147 (8) and CK148 (7) in Presence and Absence of Serum
2.10. [18F]D4-FCH Uptake In Vitro Study
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Novel CHKA Inhibitors
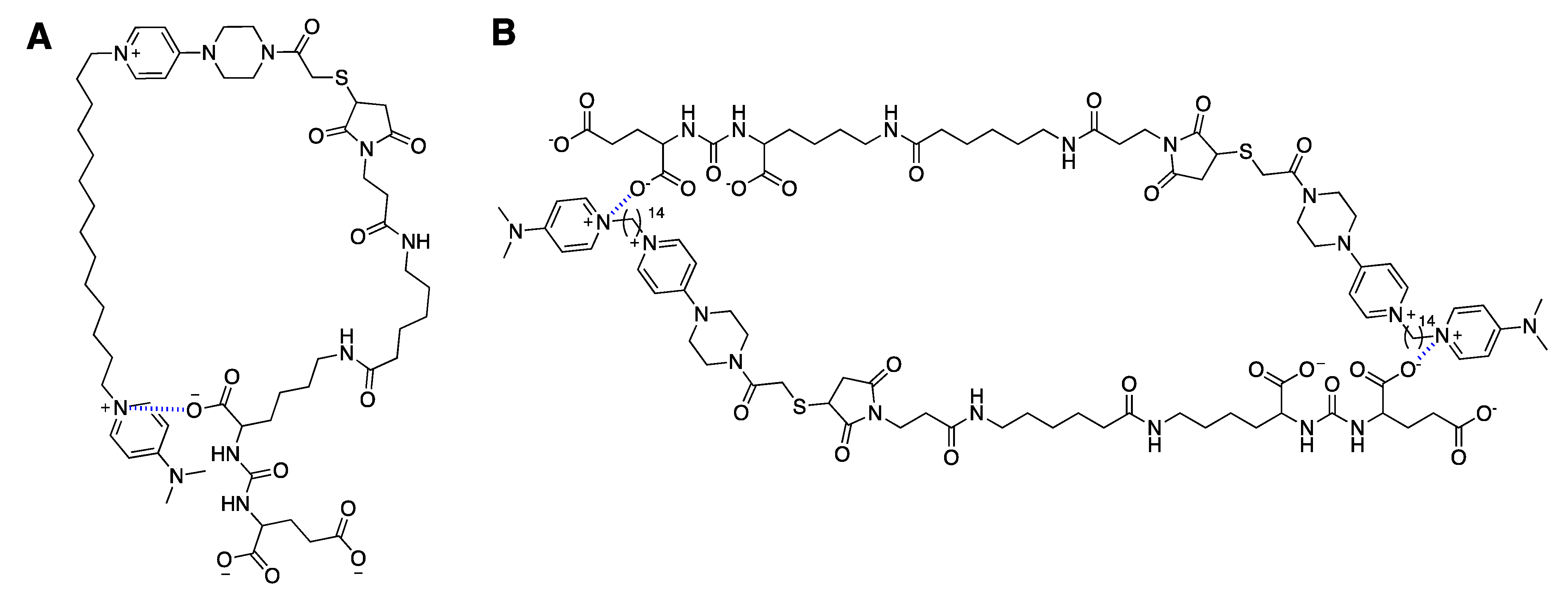
3.2. Conjugate Stability Test of CK147 (8)
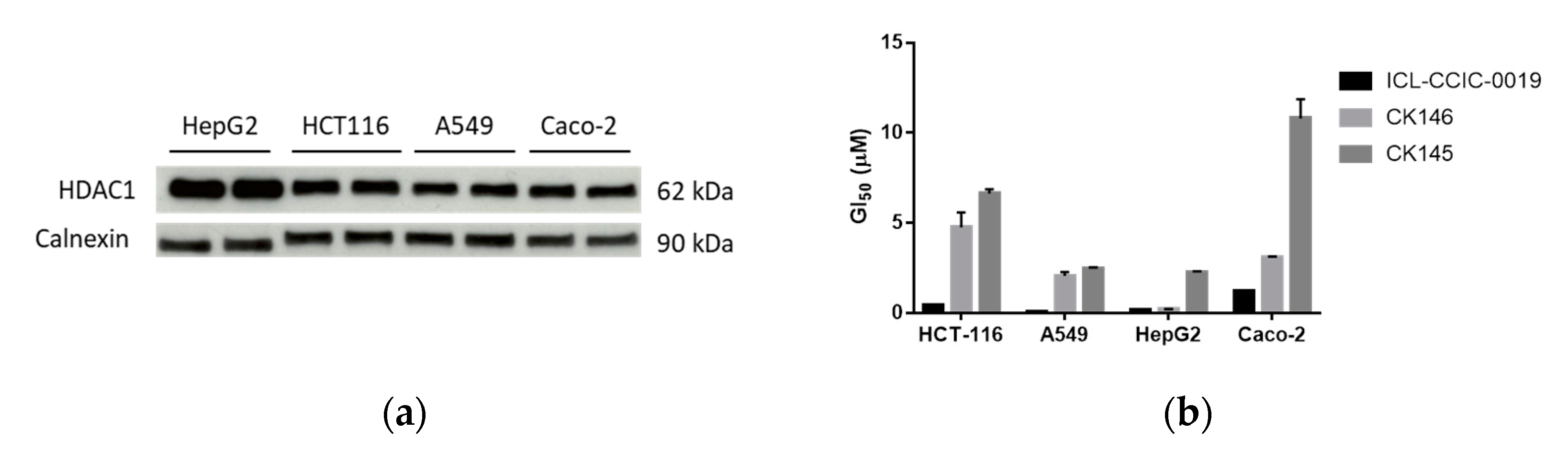
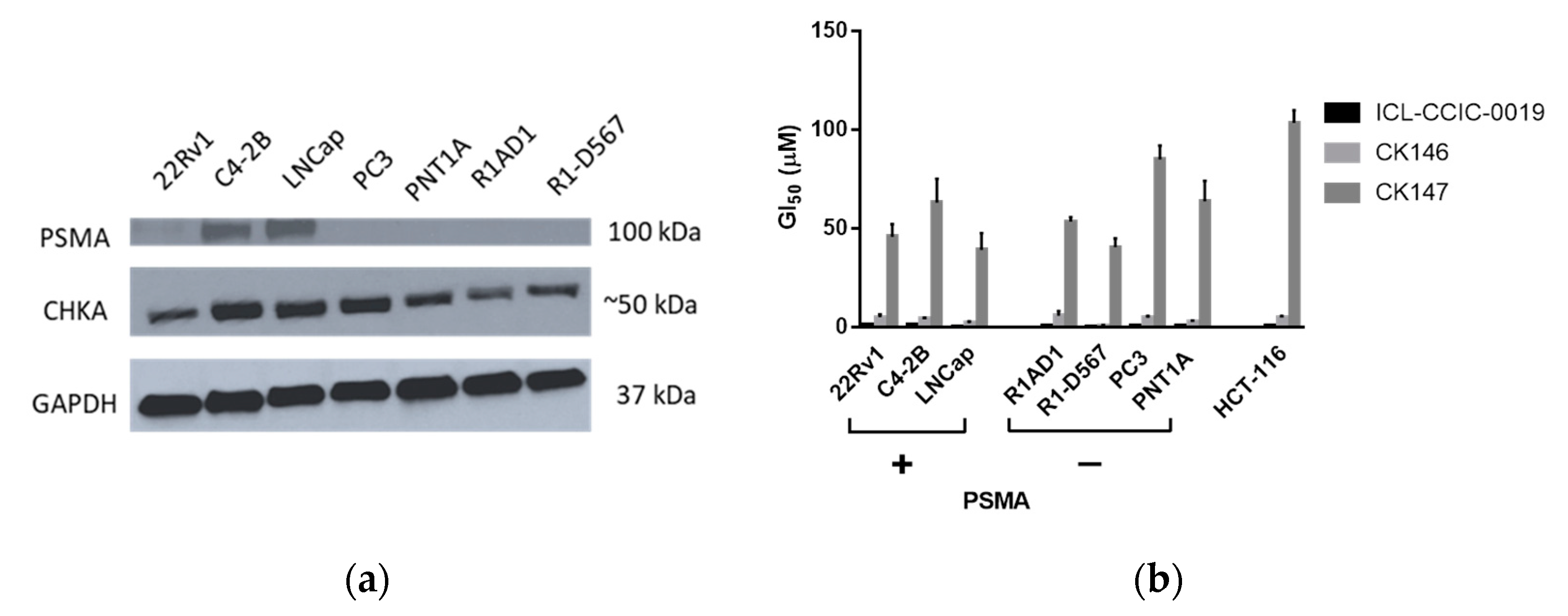
3.3. Antiproliferative Activity Assays
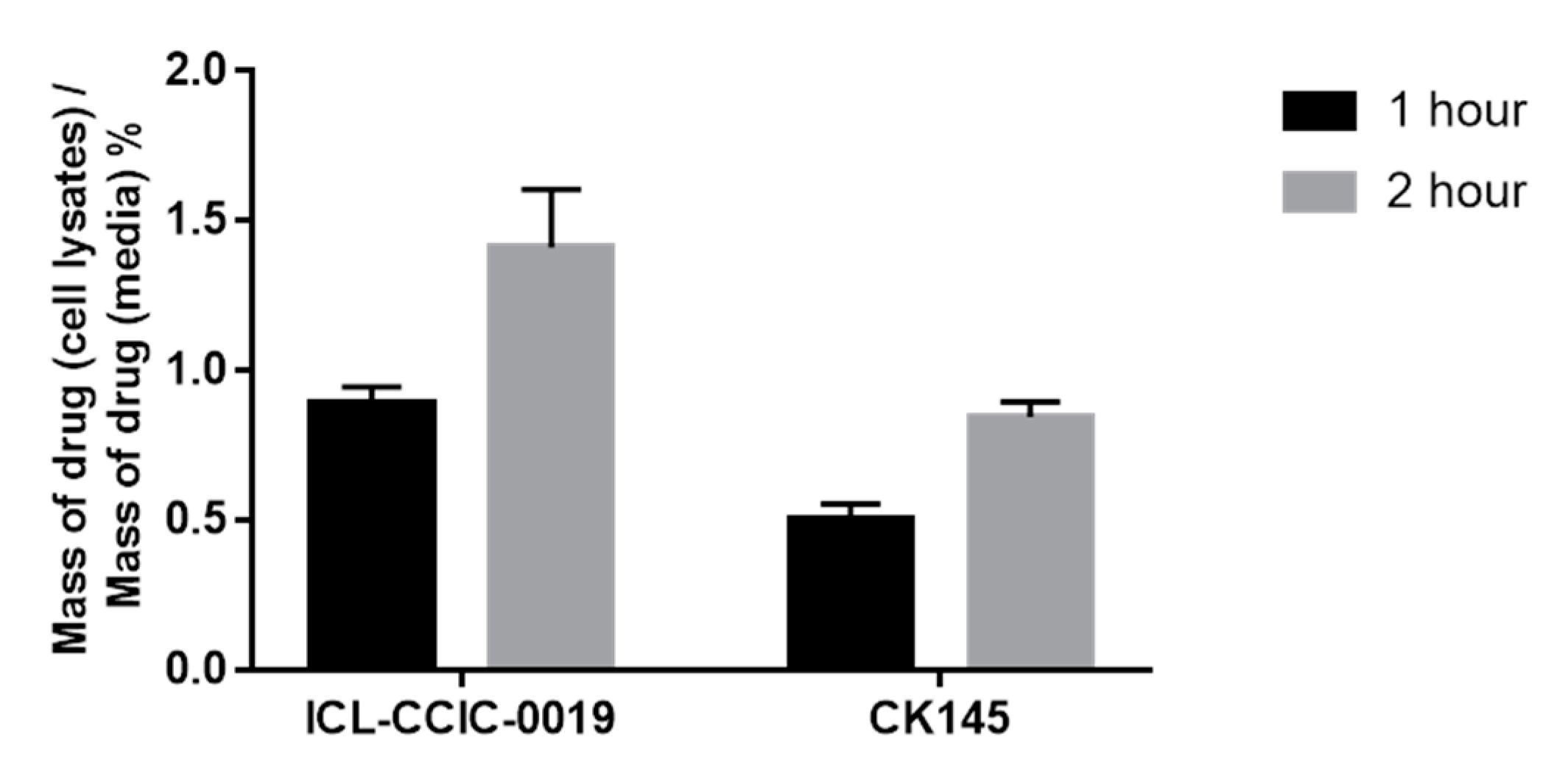
3.4. Cellular Uptake and In Vitro Metabolism
3.5. ADME Study
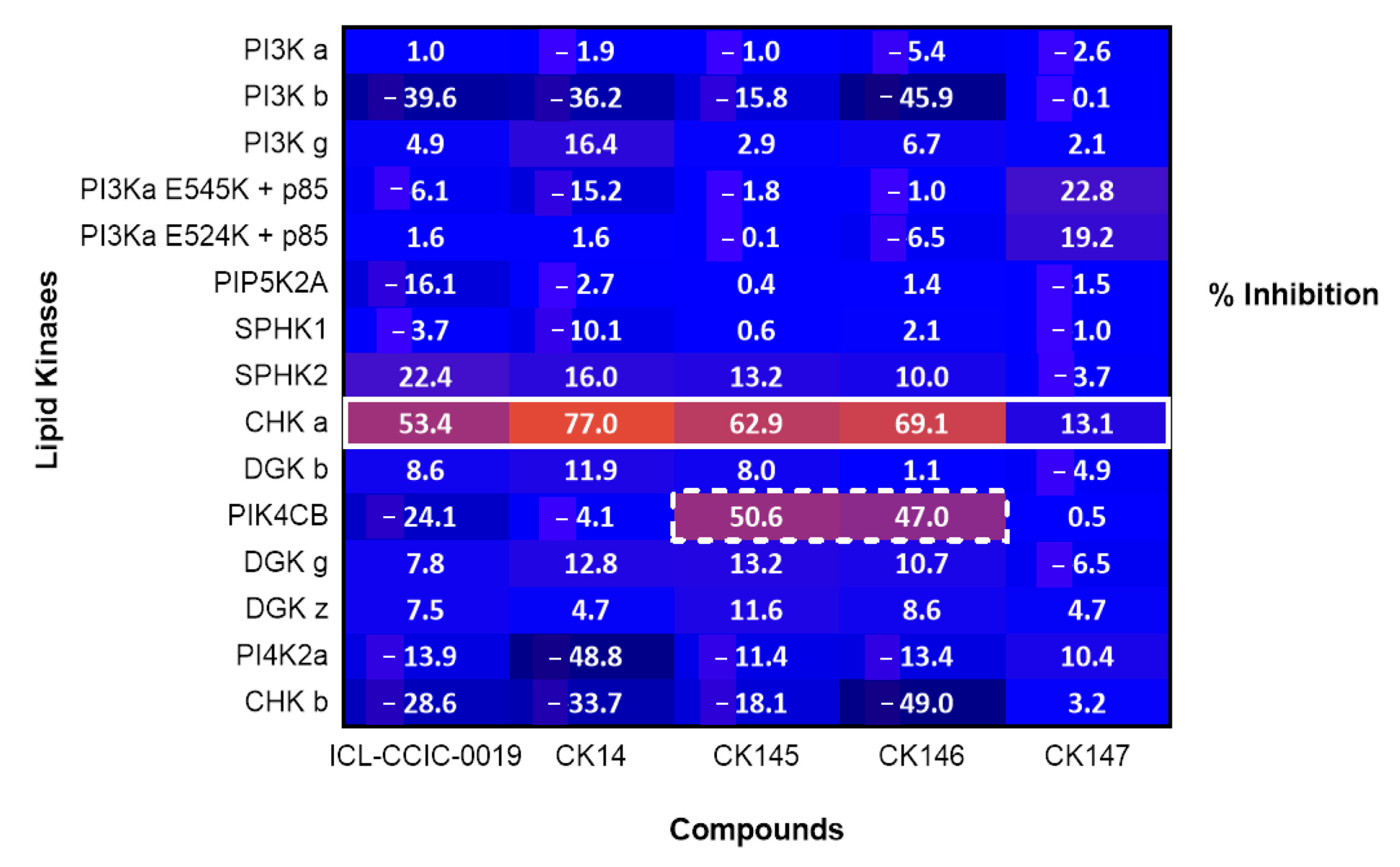
3.6. Lipid Kinase Screening
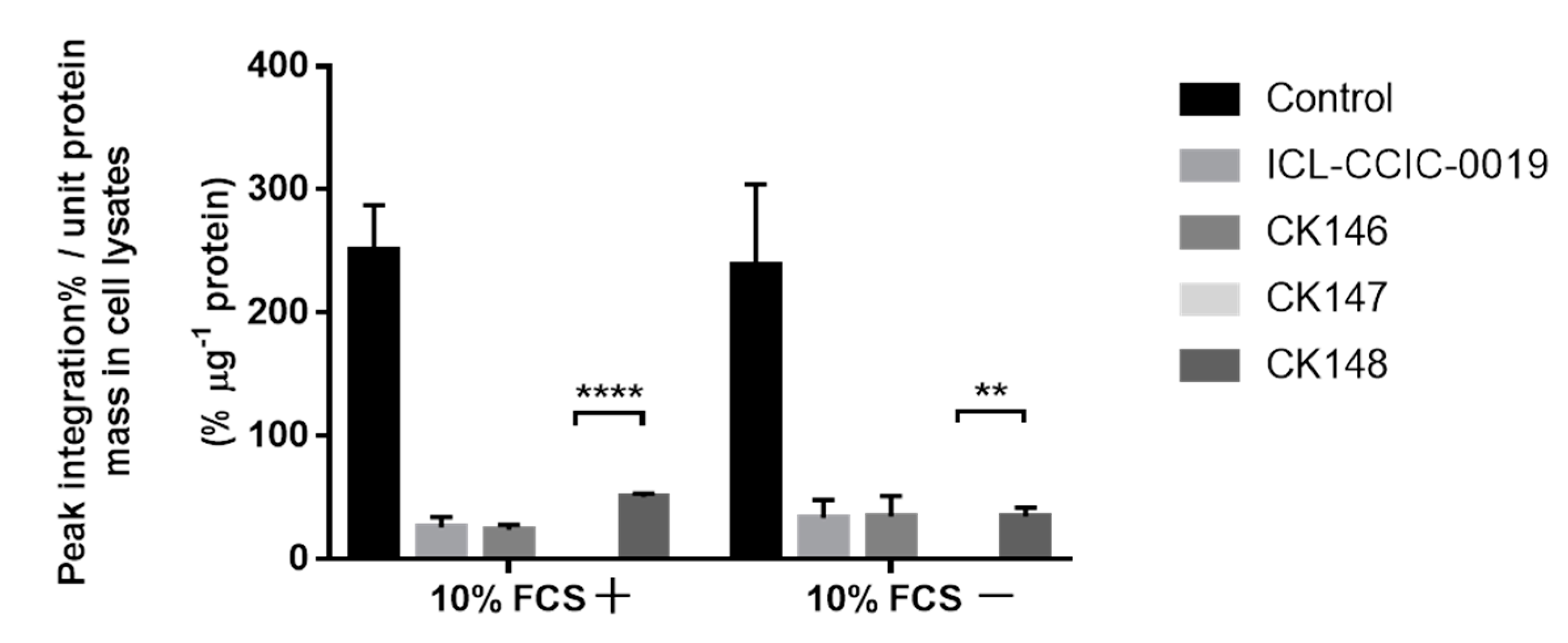
3.7. [18F]D4-FCH Uptake In Vitro Study
4. Discussion
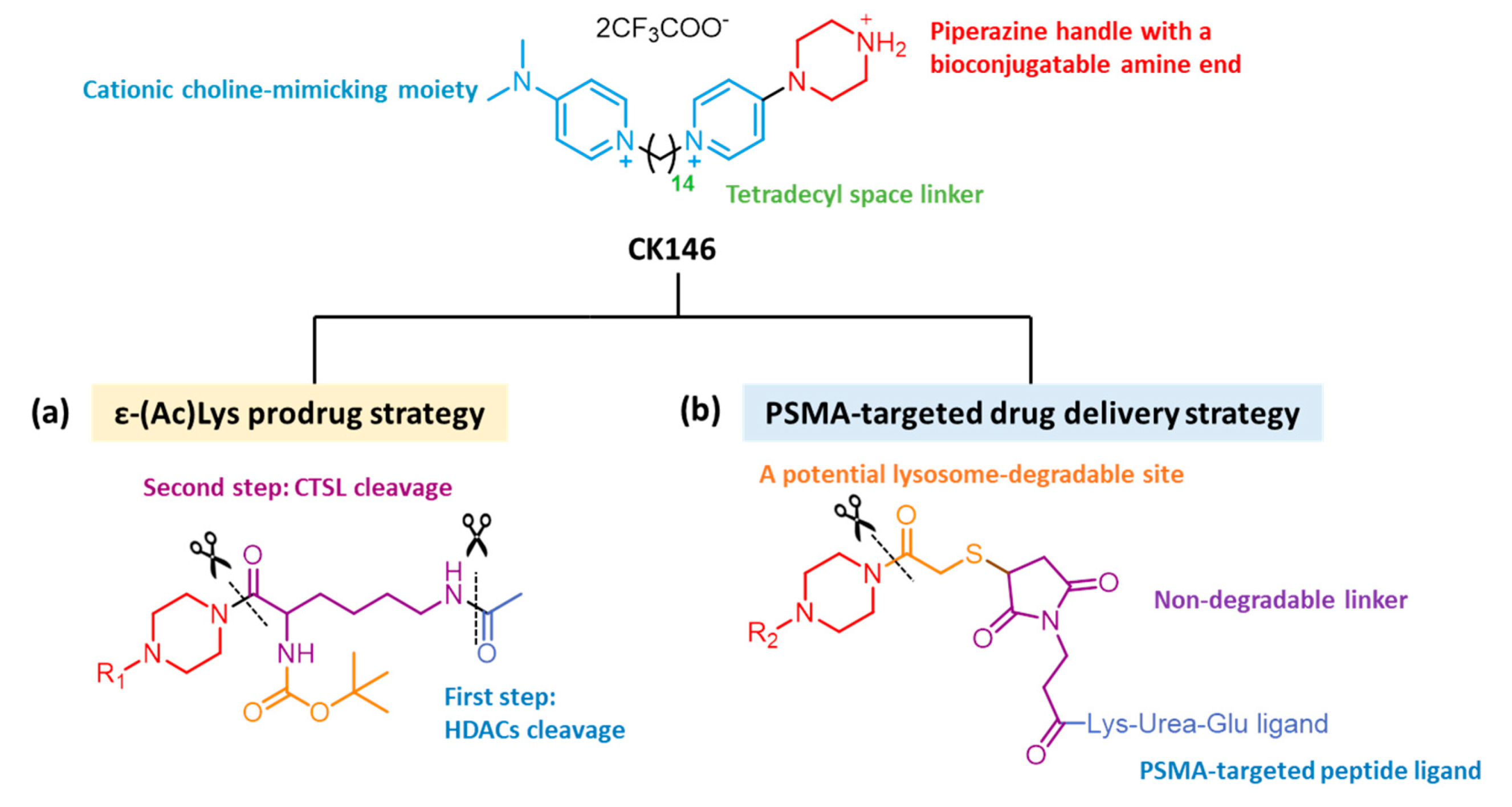
4.1. Prodrug Strategy
4.2. Drug Delivery Strategy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, C.R.; Schulze, A. Lipid metabolism in cancer. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Du, G. Dysregulated lipid metabolism in cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Ronen, S.M. Choline metabolism in malignant transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoyama, C.; Liao, H.; Ishidate, K. Structure and function of choline kinase isoforms in mammalian cells. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.; Too, W.C.S.; Wong, M.T.; Lavie, A.; McSorley, T.; Konrad, M. Balance of human choline kinase isoforms is critical for cell cycle regulation. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Molina, A.R.; Rodríguez-González, A.; Gutiérrez, R.; Martínez-Piñeiro, L.; Sánchez, J.J.; Bonilla, F.; Rosell, R.; Lacal, J.C. Overexpression of choline kinase is a frequent feature in human tumor-derived cell lines and in lung, prostate, and colorectal human cancers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 296, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Raman, V.; Mori, N.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. RNA Interference-Mediated Choline Kinase Suppression in Breast Cancer Cells Induces Differentiation and Reduces Proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11034–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iorio, E.; Mezzanzanica, D.; Alberti, P.; Spadaro, F.; Ramoni, C.; D’Ascenzo, S.; Millimaggi, D.; Pavan, A.; Dolo, V.; Canevari, S.; et al. Alterations of Choline Phospholipid Metabolism in Ovarian Tumor Progression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9369–9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Molina, A.R.; Gutiérrez, R.; Ramos, M.A.; Silva, J.M.; Silva, J.; Bonilla, F.; Sánchez, J.J.; Lacal, J.C. Increased choline kinase activity in human breast carcinomas: Clinical evidence for a potential novel antitumor strategy. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4317–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernando, E.; Sarmentero-Estrada, J.; Koppie, T.; Iniesta, C.B.; De Molina, A.R.; Cejas, P.; Ozu, C.; Le, C.; Sánchez, J.J.; González-Barón, M.; et al. A critical role for choline kinase-α in the aggressiveness of bladder carcinomas. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iorio, E.; Ricci, A.; Bagnoli, M.; Pisanu, M.E.; Castellano, G.; Di Vito, M.; Venturini, E.; Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Mezzanzanica, D.; et al. Activation of Phosphatidylcholine Cycle Enzymes in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wu, G.; van der Veen, J.N.; Hermansson, M.; Vance, D.E. Phosphatidylcholine metabolism and choline kinase in human osteoblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2014, 1841, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Molina, A.R.; Sarmentero-Estrada, J.; Iniesta, C.B.; Tarón, M.; de Molina, V.R.; Cejas, P.; Skrzypski, M.; Gallego-Ortega, D.; de Castro, J.; Casado, E.; et al. Expression of choline kinase alpha to predict outcome in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Massie, C.; Orafidiya, F.; Pértega-Gomes, N.; Warren, A.Y.; Esmaeili, M.; Selth, L.; Zecchini, H.I.; Luko, K.; Qureshi, A.; et al. Choline Kinase Alpha as an Androgen Receptor Chaperone and Prostate Cancer Therapeutic Target. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Ruiz, B.; Serrán-Aguilera, L.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; Conejo-García, A. Recent advances in the design of choline kinase α inhibitors and the molecular basis of their inhibition. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 41, 902–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, L.A. Synthesis and biological activity of a 2-bromoethylamine (mustard) derivative of hemicholinium-3 and hemicholinium-15. J. Med. Chem. 1983, 26, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, J.G.; Lee, T.M.; Nyanda, A.M.; Bhattacharyya, B.; Long, J.P. Structure-activity relationship studies in the hemicholinium (’HC-3′) series. Drug Des. Deliv. 1987, 1, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Pérez, V.; McSorley, T.; Too, W.C.S.; Konrad, M.; Campos, J.M. Novel 4-Amino Bis-pyridinium and Bis-quinolinium Derivatives as Choline Kinase Inhibitors with Antiproliferative Activity against the Human Breast Cancer SKBR-3 Cell Line. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.M. The Choline Transporter Resurfaces: New Roles for Synaptic Vesicles? Mol. Interv. 2004, 4, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.; Nunez, M.; Conejo-García, A.; Sanchez-Martin, R.M.; Hernández-Alcoceba, R.; Rodríguez-González, A.; Lacal, J.C.; Gallo, M.; Espinosa, A. QSAR-Derived Choline Kinase Inhibitors: How Rational can Antiproliferative Drug Design Be? Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 1095–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alcoceba, R.; Fernández, F.; Lacal, J.C. In vivo antitumor activity of choline kinase inhibitors: A novel target for anticancer drug discovery. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 3112–3118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Saffar, N.M.; Troy, H.; De Molina, A.R.; Jackson, L.E.; Madhu, B.; Griffiths, J.R.; Leach, M.; Workman, P.; Lacal, J.C.; Judson, I.R.; et al. Noninvasive Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Pharmacodynamic Markers of the Choline Kinase Inhibitor MN58b in Human Carcinoma Models. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacal, J.C.; Campos, J. Preclinical Characterization of RSM-932A, a Novel Anticancer Drug Targeting the Human Choline Kinase Alpha, an Enzyme Involved in Increased Lipid Metabolism of Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 14, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Martin, R.M.; Campos, J.; Conejo-García, A.; Cruz-López, O.; Báñez-Coronel, M.; Rodríguez-González, A.; Gallo, M.A.; Lacal, J.C.; Espinosa, A. Symmetrical Bis-Quinolinium Compounds: New Human Choline Kinase Inhibitors with Antiproliferative Activity against the HT-29 Cell Line. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3354–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Alcoceba, R.; Saniger, L.; Campos, J.; Núñez, M.C.; Khaless, F.; Gallo, M.A.; Espinosa, A.; Lacal, J.C. Choline kinase inhibitors as a novel approach for antiproliferative drug design. Oncogene 1997, 15, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trousil, S.; Carroll, L.; Kalusa, A.; Aberg, O.; Kaliszczak, M.; Aboagye, E. Design of symmetrical and nonsymmetrical N,N-dimethylaminopyridine derivatives as highly potent choline kinase alpha inhibitors. MedChemComm 2013, 4, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trousil, S.; Kaliszczak, M.; Schug, Z.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Tomasi, G.; Favicchio, R.; Brickute, D.; Fortt, R.; Twyman, F.J.; Carroll, L.; et al. The novel choline kinase inhibitor ICL-CCIC-0019 reprograms cellular metabolism and inhibits cancer cell growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 37103–37120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malito, E.; Sekulic, N.; Too, W.C.S.; Konrad, M.; Lavie, A. Elucidation of Human Choline Kinase Crystal Structures in Complex with the Products ADP or Phosphocholine. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 364, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, J.; Núñez, C.; Díaz, J.J.; Sánchez, R.M.; Gallo, M.A.; Espinosa, A. Anticancer bisquaternary heterocyclic compounds: A rasional design. Il Farm. 2003, 58, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Tempel, W.P.J.F., Jr.; MacKenzie, F.; Dimov, S.; Vedadi, M.; Park, H.-W. Crystal Structures of Human Choline Kinase Isoforms in Complex with Hemicholinium-3: Single amino acid near the active site influences inhibitor sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16330–16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahún-Roncero, M.; Rubio-Ruiz, B.; Saladino, G.; Conejo-García, A.; Espinosa, A.; Velázquez-Campoy, A.; Gervasio, F.L.; Entrena, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R. The Mechanism of Allosteric Coupling in Choline Kinase α1 Revealed by the Action of a Rationally Designed Inhibitor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4582–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahún-Roncero, M.; Rubio-Ruiz, B.; Conejo-Garcia, A.; Velázquez-Campoy, A.; Entrena, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R. Determination of Potential Scaffolds for Human Choline Kinase α1 by Chemical Deconvolution Studies. ChemBioChem 2013, 14, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serran-Aguilera, L.; Nuti, R.; Lopez-Cara, L.; Rios-Marco, P.; Carrasco, M.; Marco, C.; Entrena, A.; Macchiarulo, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R. Choline kinase active site provides features for designing versatile inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 14, 2684–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrán-Aguilera, L.; Nuti, R.; López-Cara, L.C.; Mezo, M.G.; Macchiarulo, A.; Entrena, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R. Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening to Discover New Active Compounds for Human Choline Kinase α1. Mol. Inform. 2015, 34, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zech, S.G.; Kohlmann, A.; Zhou, T.; Li, F.; Squillace, R.M.; Parillon, L.E.; Greenfield, M.T.; Miller, D.P.; Qi, J.; Thomas, R.M.; et al. Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors of Choline Kinase Identified by Fragment-Based Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Ruiz, B.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Jimenez, M.P.C.; Espinosa, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; Marco, C.; Conejo-García, A.; Entrena, A. Choline kinase inhibition and docking studies of a series of 6-(benzylthio)-9H-purin-9-yl-pyridinium derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Duvvuri, S.; Mitra, A.K. Membrane transporter/receptor-targeted prodrug design: Strategies for human and veterinary drug development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1437–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, F.; Müller, I.A.; Ryppa, C.; Warnecke, A. Prodrug Strategies in Anticancer Chemotherapy. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 20–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Johnson, A.; Mokalled, M.H.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. Genetic dissection of histone deacetylase requirement in tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7751–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolden, J.E.; Peart, M.J.; Johnstone, R. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.A.; Baruch, A.; Chehade, K.; Meyer-Morse, N.; Giraudo, E.; Tsai, F.-Y.; Greenbaum, D.C.; Hager, J.H.; Bogyo, M.; Hanahan, D. Cathepsin cysteine proteases are effectors of invasive growth and angiogenesis during multistage tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jedeszko, C.; Sloane, B.F. Cysteine cathepsins in human cancer. Biol. Chem. 2004, 385, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Heston, W.D. Tumor target prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 91, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.H.; Greene, T.G.; Tino, W.T.; Boynton, A.L.; Aldape, H.C.; Misrock, S.L.; Murphy, G.P. Analysis of glycosylation of prostate-specific membrane antigen derived from LNCaP cells, prostatic carcinoma tumors, and serum from prostate cancer patients. Prostate. Suppl. 1996, 7, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witney, T.; Alam, I.S.; Turton, D.R.; Smith, G.; Carroll, L.; Brickute, D.; Twyman, F.J.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Tomasi, G.; Awais, R.O.; et al. Evaluation of Deuterated 18F- and 11C-Labeled Choline Analogs for Cancer Detection by Positron Emission Tomography. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, N.; Lee, S.; Sampson, N.; Hayman, M.J. Selective cancer targeting with prodrugs activated by histone deacetylases and a tumour-associated protease. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNamara, C.W.; Lee, M.C.S.; Lim, C.S.; Lim, S.H.; Roland, J.; Nagle, A.; Simon, O.; Yeung, B.K.; Chatterjee, A.K.; McCormack, S.L.; et al. Targeting Plasmodium PI(4)K to eliminate malaria. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 504, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borawski, J.; Troke, P.; Puyang, X.; Gibaja, V.; Zhao, S.; Mickanin, C.; Leighton-Davies, J.; Wilson, C.J.; Myer, V.; CornellaTaracido, I.; et al. Class III Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase Alpha and Beta Are Novel Host Factor Regulators of Hepatitis C Virus Replication. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10058–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, T.; Moneriz, C.; Diez, A.; Bautista, J.M.; Del Pulgar, T.G.; Cebrián, A.; Lacal, J.C. Antiplasmodial Activity and Mechanism of Action of RSM-932A, a Promising Synergistic Inhibitor of Plasmodium falciparum Choline Kinase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5878–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torretta, A.; Lopez-Cara, L.C.; Parisini, E. Crystal Structure of the Apo and the ADP-Bound Form of Choline Kinase from Plasmodium falciparum. Crystals 2020, 10, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacal, J.; Zimmerman, T.; Campos, J. Choline Kinase: An Unexpected Journey for a Precision Medicine Strategy in Human Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Zhang, K.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Quick, J.; Tam, Y.K.; Lin, P.J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Nair, J.K.; Zlatev, I.; et al. A Glu-urea-Lys Ligand-conjugated Lipid Nanoparticle/siRNA System Inhibits Androgen Receptor Expression In Vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Kim, M.; Zheng, L.; Deperalta, G.; Jacobson, F. Structural Characterization of Cross-Linked Species in Trastuzumab Emtansine (Kadcyla). Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vraneš, M.; Panić, J.; Tot, A.; Popsavin, M.; Jocić, A.; Gadžurić, S. Physicochemical characterization of choline based ionic liquids with chelating anions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
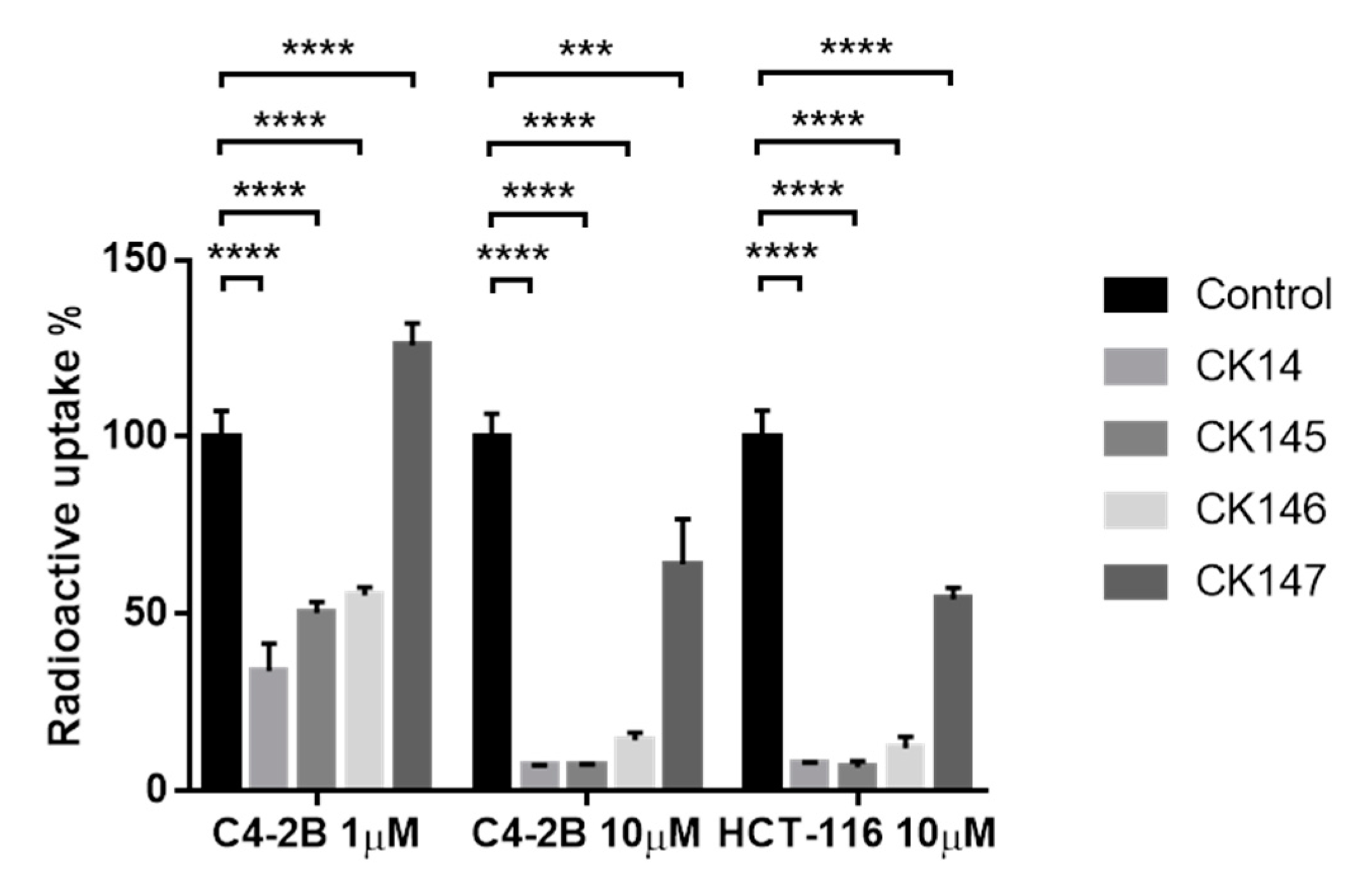
| Parameters | ICL-CCIC-0019 | CK14 | CK146 | CK145 | CK147 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetic Solubility | Solubility (μM) | 161 | 154 | 158 | 178 | 186 |
| Human Microsomal Metabolic Stability 1 | Half-life (min) | >100 | >100 | >100 | 7.4 | >100 |
| Clint (µL/min/mg) | <14 | <14 | <14 | 188 | <14 | |
| Predicted in vivo clearance (mL/min/kg) | <10 | <10 | <10 | 19 | <10 | |
| PCT_LBF % | <45 | <45 | <45 | 92 | <45 | |
| Remaining % | 92 | 101 | 127 | 2 | 105 | |
| Permeability and Efflux | Papp A-B (×10−6 cm/s) | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Papp B-A (×10−6 cm/s) | 0.9 | 8.7 | 0.3 | 0.3 | <0.1 | |
| Efflux ratio (Papp B-A/Papp A-B) | >8.6 | >87 | >2.6 | >2.8 | No data 1 | |
| Matrix Stability | FaSSGF stability Half-life (h) | >10 | >10 | >10 | 9.2 | >10 |
| Remaining % | 117 | 95 | 92 | 74 | 97 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Brickute, D.; Braga, M.; Barnes, C.; Lu, H.; Allott, L.; Aboagye, E.O. Novel Non-Congeneric Derivatives of the Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor ICL-CCIC-0019. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071078
Wang N, Brickute D, Braga M, Barnes C, Lu H, Allott L, Aboagye EO. Novel Non-Congeneric Derivatives of the Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor ICL-CCIC-0019. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071078
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ning, Diana Brickute, Marta Braga, Chris Barnes, Haonan Lu, Louis Allott, and Eric O. Aboagye. 2021. "Novel Non-Congeneric Derivatives of the Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor ICL-CCIC-0019" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071078
APA StyleWang, N., Brickute, D., Braga, M., Barnes, C., Lu, H., Allott, L., & Aboagye, E. O. (2021). Novel Non-Congeneric Derivatives of the Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor ICL-CCIC-0019. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071078







