Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Modified inside and out for ON:OFF pH-Modulated Cargo Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
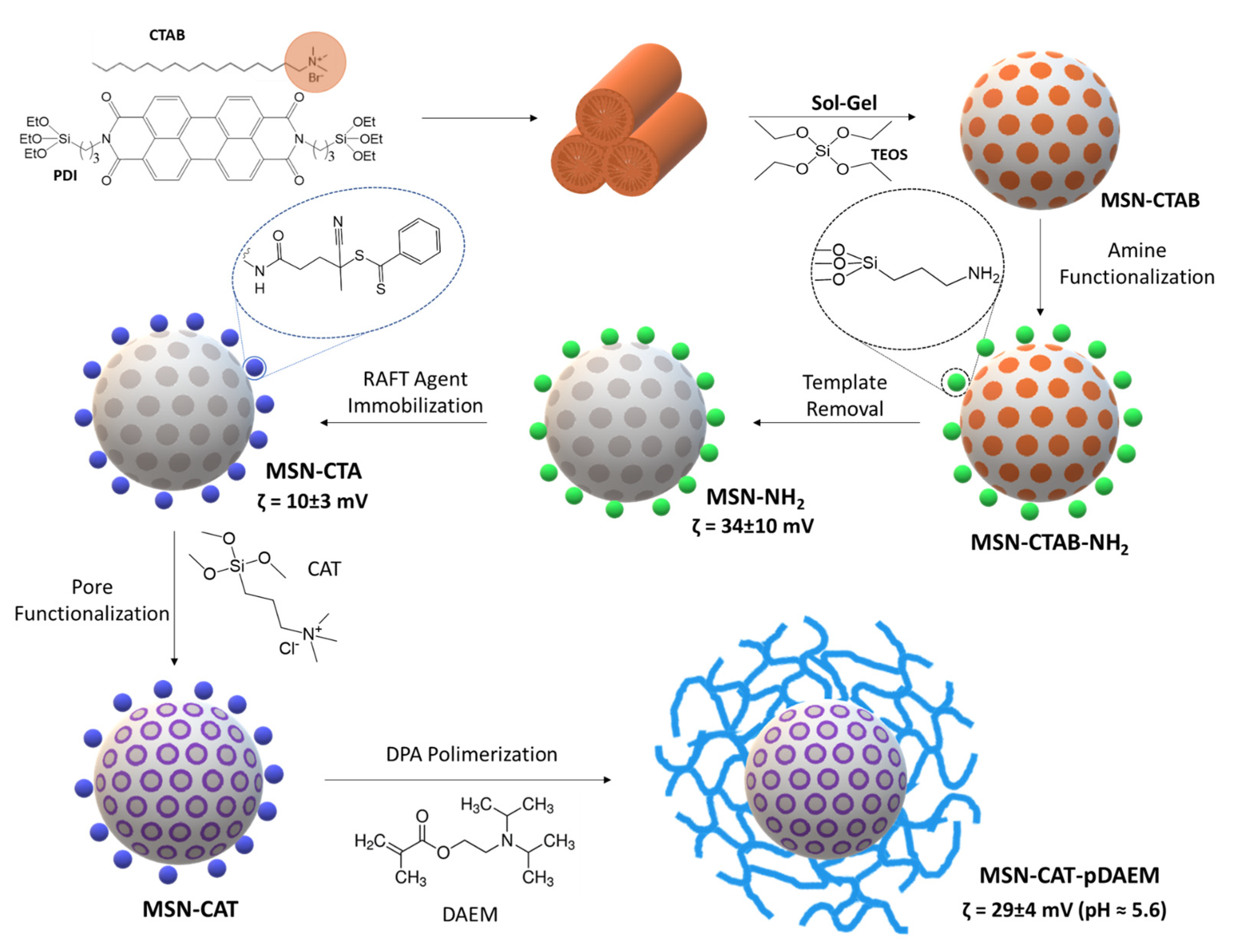
2.2.1. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNs)
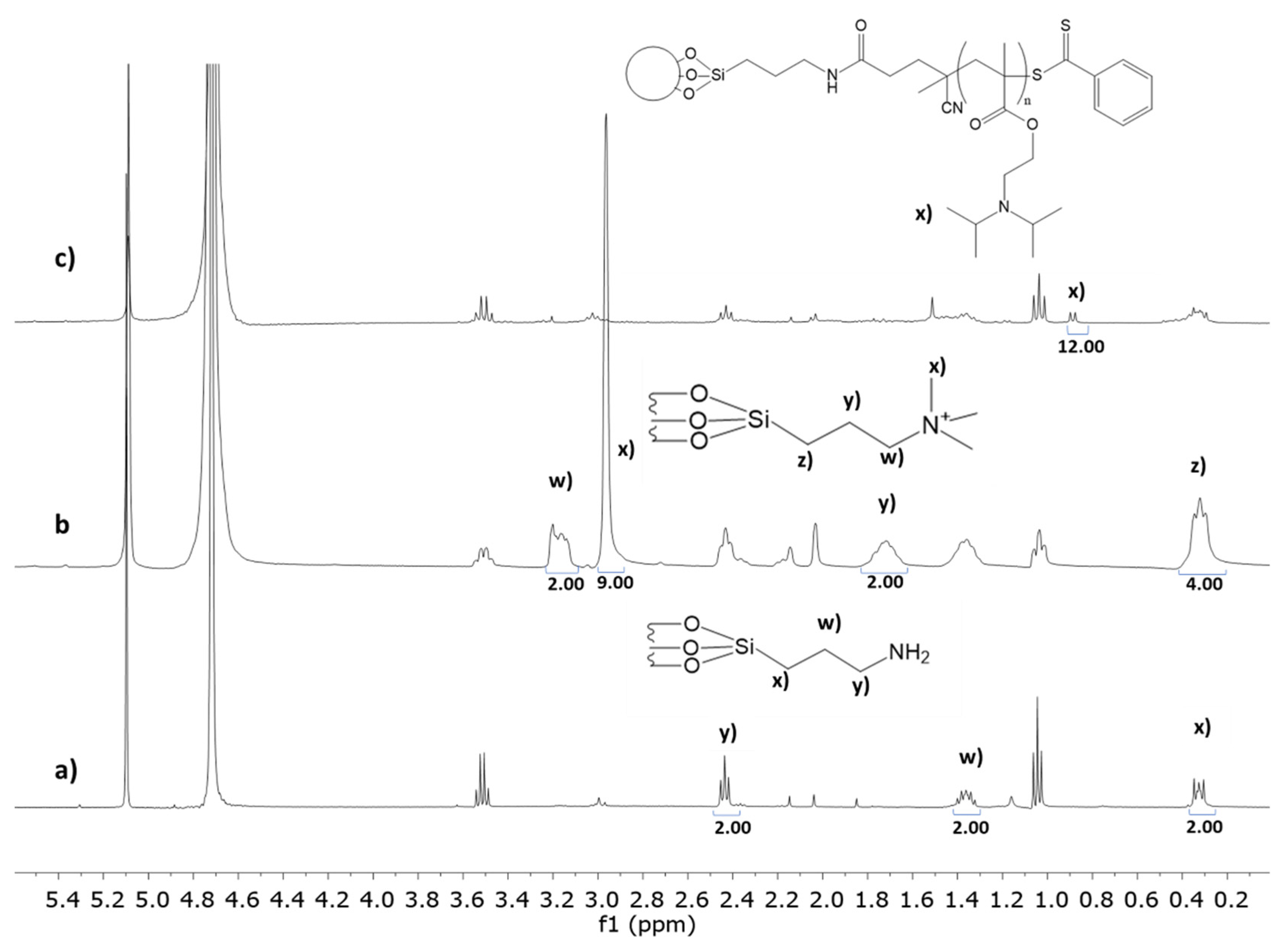
2.2.2. MSNs Amine Functionalization (MSN-NH2)
2.2.3. Surface Modification with a RAFT Agent (MSN-CTA)
2.2.4. Pore Functionalization (MSN-CAT-CTA)
2.2.5. Polymer Grafting to the MSN Surface (MSN-pDAEM)
2.2.6. Loading and Release of SRB
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.3.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
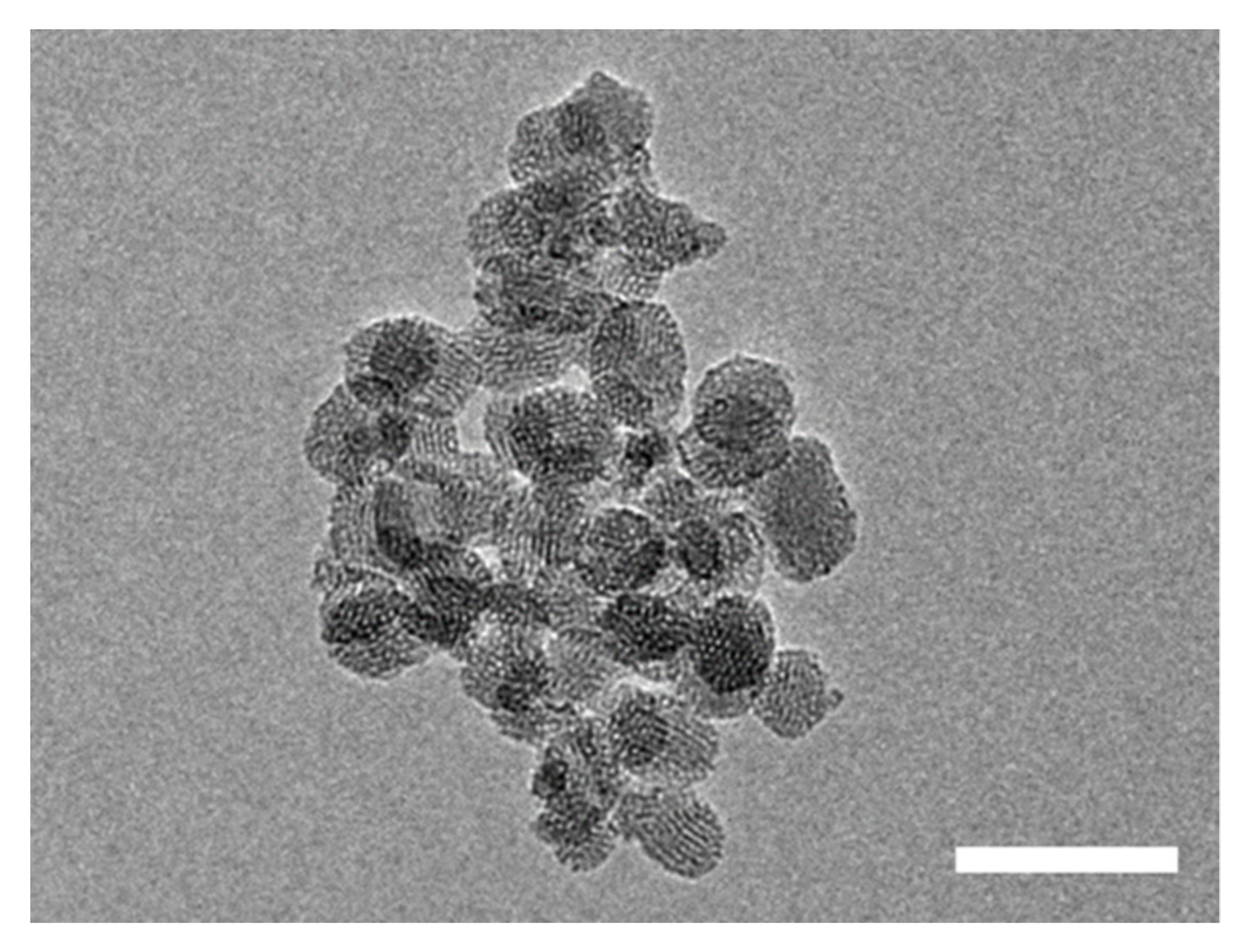
2.3.2. Transmission Electronic Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.3. Adsorption–Desorption Isotherms
2.3.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.3.5. Zeta-Potential
2.3.6. Fluorescence Measurements
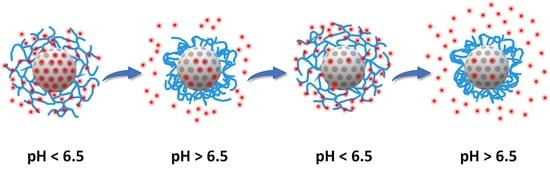
3. Results and Discussion
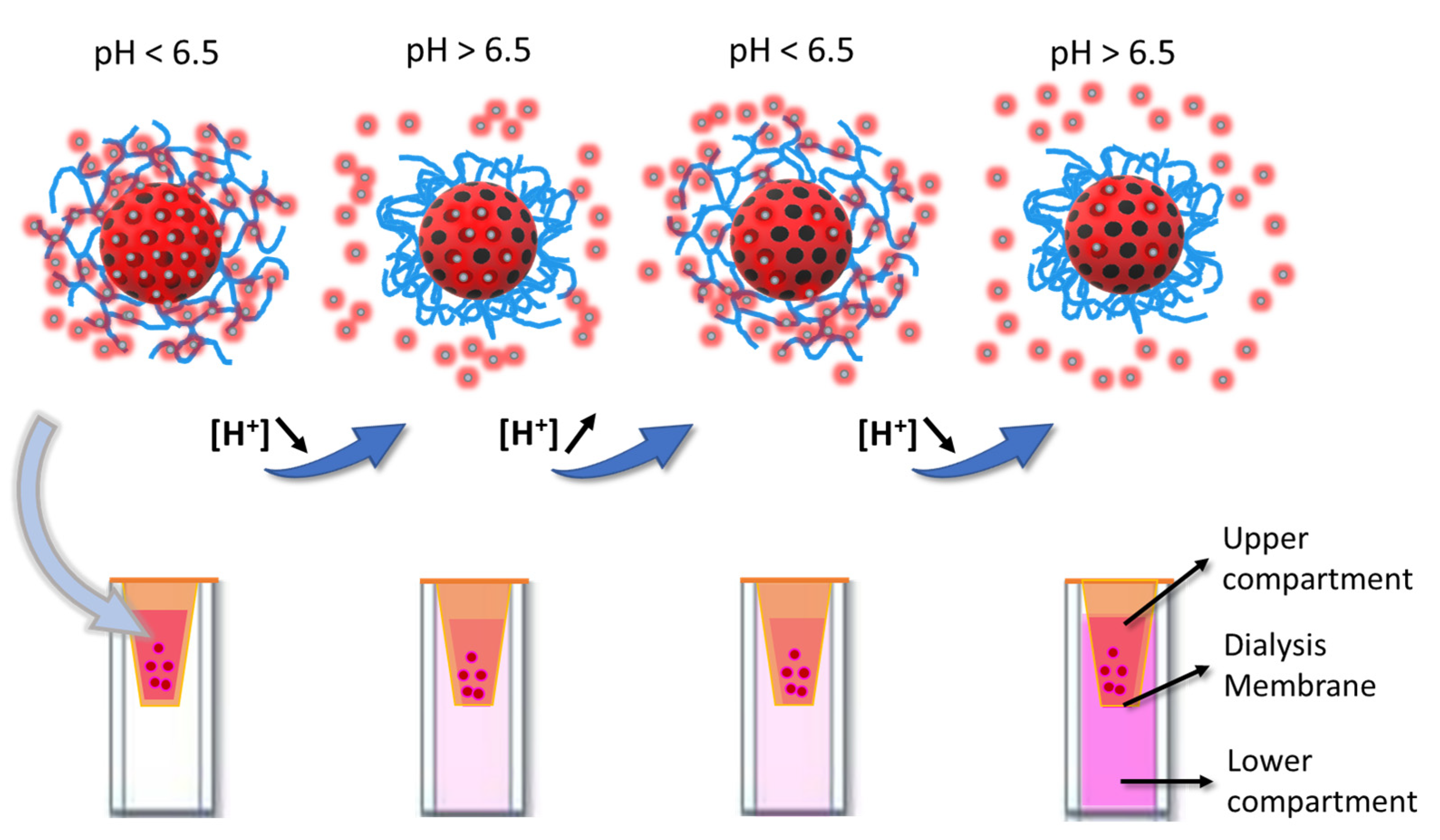
3.1. Nanocarrier Assembly
3.2. Cargo Relase Modulation
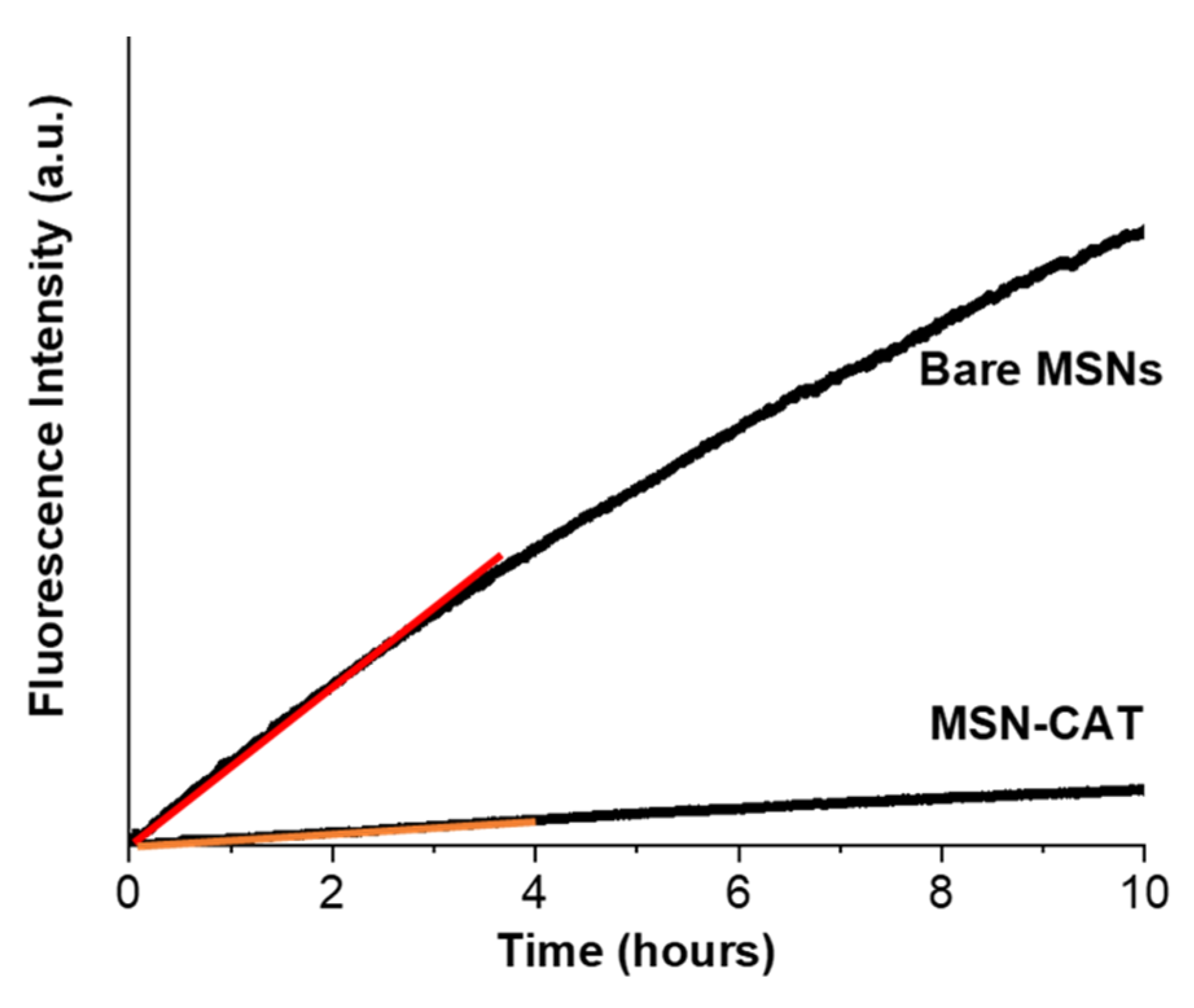
3.2.1. Functionalized Pore Strategy
3.2.2. Core-Shell System
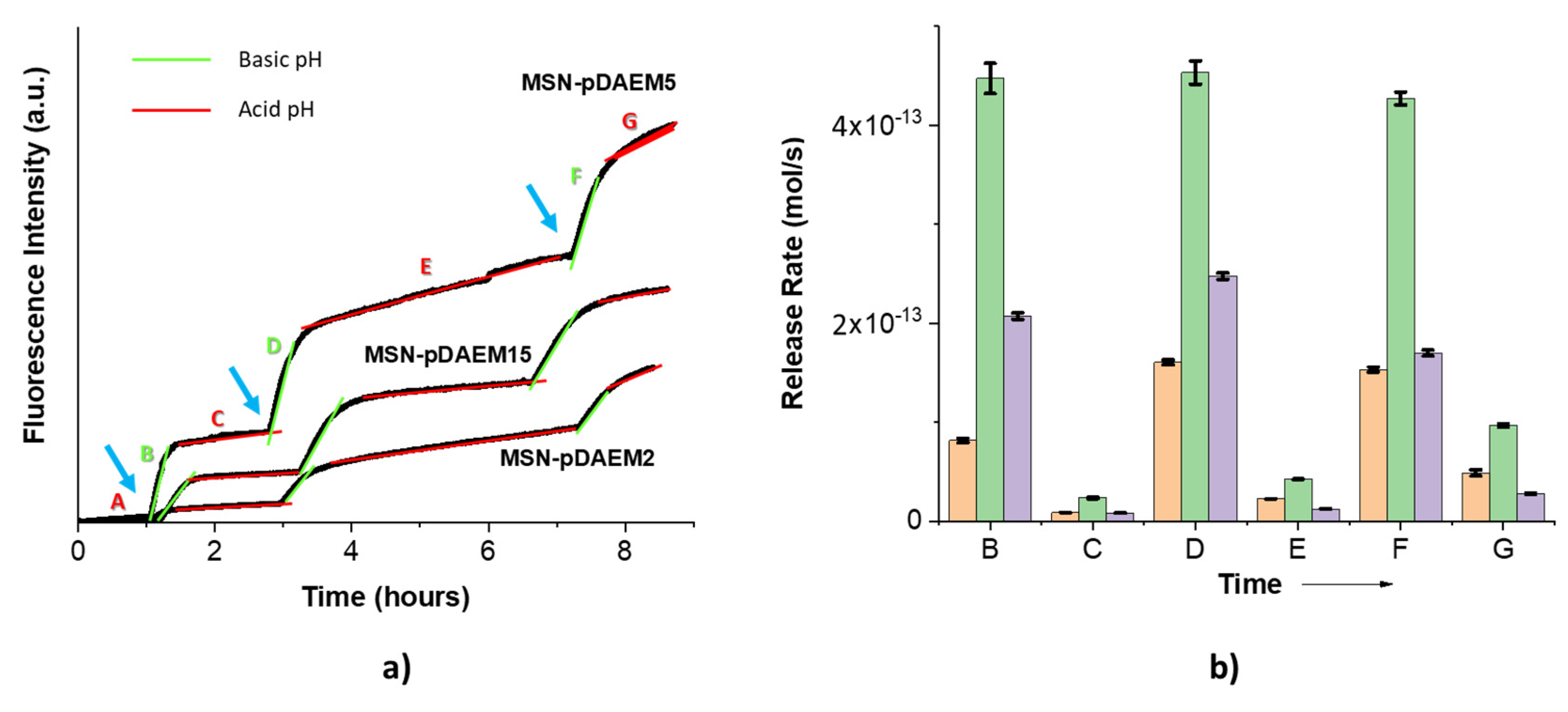
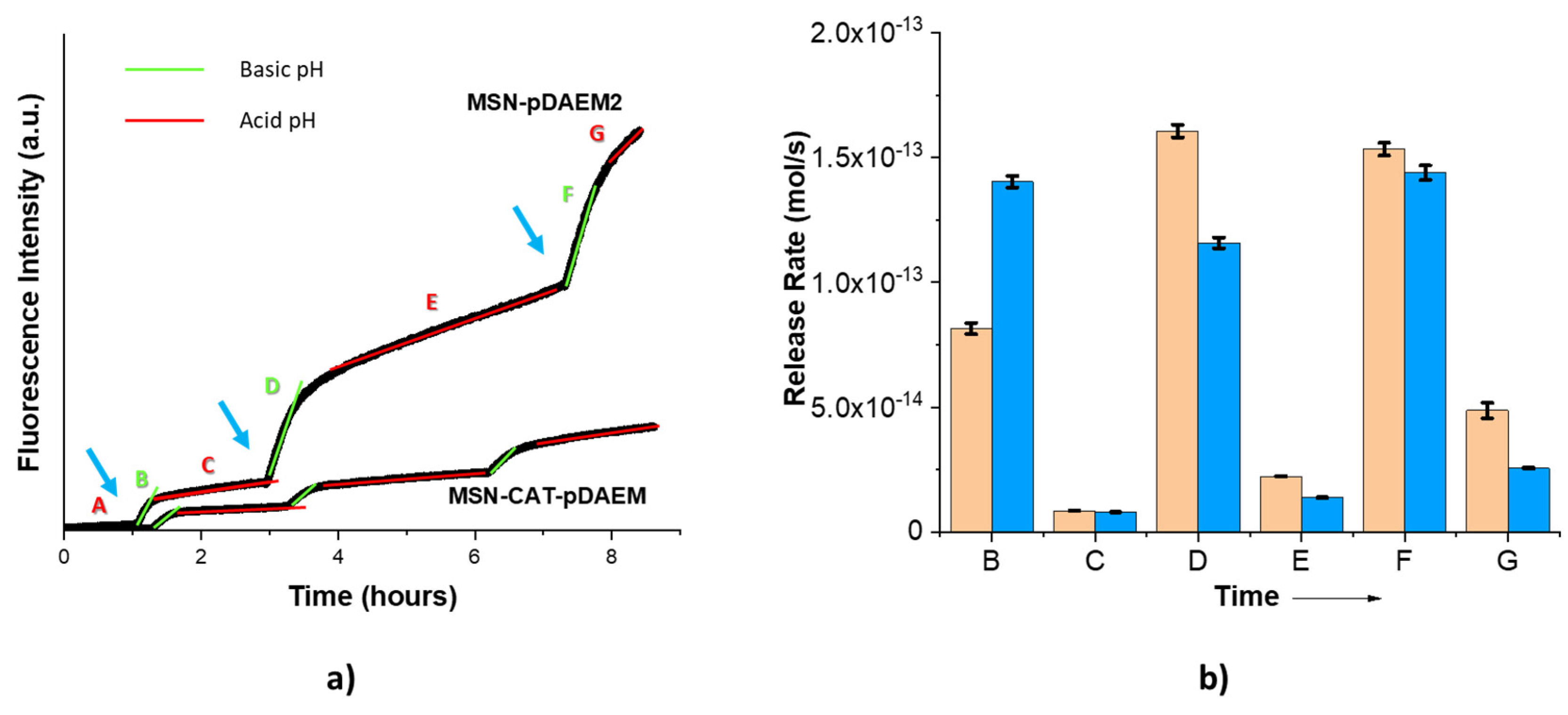
3.2.3. Dual Release Control Mechanism: Functionalized Pores and Polymer Shell
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skinner, B.F. The Generic Nature of the Concepts of Stimulus and Response. J. Gen. Psychol. 1935, 12, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, J.R.; Wagner, A.M.; Shin, S.R.; Hassan, S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Peppas, N.A. Modular fabrication of intelligent material-tissue interfaces for bioinspired and biomimetic devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bu, X.; Yip, S.; Liang, X.; Ho, J.C. Self-Assembly of Colloidal Particles for Fabrication of Structural Color Materials toward Advanced Intelligent Systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shim, M.S.; Levinson, N.S.; Sung, H.; Xia, Y. Stimuli-Responsive Materials for Controlled Release of Theranostic Agents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4206–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejo, T.; Uson, L.; Arruebo, M. Reversible stimuli-responsive nanomaterials with on-off switching ability for biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2019, 314, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.S.; Ribeiro, T.; Fernandes, F.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Baleizão, C. Intrinsically fluorescent silica nanocontainers: A promising theranostic platform. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.; Coutinho, E.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Hybrid mesoporous silica nanocarriers with thermovalve-regulated controlled release. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13485–13494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Crucho, C.I.C.; Alves, S.P.C.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Hybrid Mesoporous Nanoparticles for pH-Actuated Controlled Release. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Jung, K.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Boyer, C. Recent advances in stimuli-responsive polymer systems for remotely controlled drug release. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 99, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Zeng, X.; Tian, D.; Li, H. Temperature-Responsive Switch Constructed from an Anthracene-Functionalized Pillar[5]arene-Based Host–Guest System. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.S.; Charreyre, M.-T.; Favier, A.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Temperature-responsive copolymers without compositional drift by RAFT copolymerization of 2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl trimethylammonium chloride and 2-(diethylamino)ethyl acrylate. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 2106–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.; Santos, A.F.M.; Diogo, H.P.; Alves, S.P.C.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Correia, N.T.; Dionísio, M.; Viciosa, M.T. Bulk dynamics of the thermoresponsive random copolymer of di(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (MEO2MA) and oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (OEGMA). Polymer (Guildf). 2018, 148, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, L.A.; Vela Ramirez, J.E.; Haddadin, O.M.; Ross, K.A.; Narasimhan, B.; Peppas, N.A. pH-Responsive Microencapsulation Systems for the Oral Delivery of Polyanhydride Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Tan, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhuo, R. Dual-stimuli-responsive polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles used for controlled drug delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Tsuruta, K.; Kawamura, A.; Ohara, M.; Shoji, K.; Kawano, R.; Miyata, T. Design of protein-responsive micro-sized hydrogels for self-regulating microfluidic systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Tong, W.; Gao, C. Non-covalent assembly of poly(allylamine hydrochloride)/triethylamine microcapsules with ionic strength-responsiveness and auto-fluorescence. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 496, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.P.; Moura, L.; Fokkink, R.; Farinha, J.P.S. Preparation and Characterization of Low Dispersity Anionic Multiresponsive Core–Shell Polymer Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5802–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, G.; Sumer, B.D.; Gao, J. Multicolored pH-Tunable and Activatable Fluorescence Nanoplatform Responsive to Physiologic pH Stimuli. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7803–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. pH-Responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.; Bhargava, A.; Chhipa, H.; Jain, N. Nano-Fertilizers and Their Smart Delivery System; Rai, M., Ribeiro, C., Mattoso, L., Duran, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 9783319140247. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Zhong, N.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z. Fabrication of pH-Controlled-Release Ferrous Foliar Fertilizer with High Adhesion Capacity Based on Nanobiomaterial. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6800–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rayo, S.; Imran, A.; Bruun Hansen, H.C.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Magid, J. Layered Double Hydroxides: Potential Release-on-Demand Fertilizers for Plant Zinc Nutrition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8779–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.; Santos, C.; da Costa, A.P.; Silva, M.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Smart polymeric nanoparticles for boron scavenging. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, D.A.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Marino, C.E.B. Smart coating based on double stimuli-responsive microcapsules containing linseed oil and benzotriazole for active corrosion protection. Corros. Sci. 2018, 130, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, M.S.; Buonocore, G.G.; Giuliani, C.; Messina, E.; Di Carlo, G.; Lavorgna, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Ingo, G.M. Long-Lasting Efficacy of Coatings for Bronze Artwork Conservation: The Key Role of Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocarriers in Protecting Corrosion Inhibitors from Photodegradation. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 7380–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.; Varney, J.; Thompson, N.; Moghlssl, O.; Gould, M.; Payer, J. International Measures of Prevention, Application, and Economics of Corrosion Technologies Study; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zea, C.; Alcántara, J.; Barranco-García, R.; Morcillo, M.; de la Fuente, D. Synthesis and Characterization of Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Smart Corrosion Protection. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Mao, W.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, J. pH-Responsive zeolitic imidazole framework nanoparticles with high active inhibitor content for self-healing anticorrosion coatings. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 555, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.J.; Smyth, P.; Mcdaid, W.J.; Lavery, D.; Thom, J.; Cotton, G.; Scott, C.J.; Themistou, E. Single-Domain Antibody-Functionalized pH-Responsive Amphiphilic Block Copolymer Nanoparticles for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Targeted Cancer Therapy. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.A.; Mozhdehi, D.; Dzuricky, M.J.; Isaacs, F.J.; Brustad, E.M.; Chilkoti, A. Active Targeting of Cancer Cells by Nanobody Decorated Polypeptide Micelle with Bio-orthogonally Conjugated Drug. Nano Lett. 2018, 19, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, A.M.; Ribeiro, T.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Ribeiro, B.; Frade, R.F.M.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Multifunctional Hybrid Silica Nanoparticles with a Fluorescent Core and Active Targeting Shell for Fluorescence Imaging Biodiagnostic Applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4579–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Ochoa, M.; Parupudi, T.; Zhao, X.; Yazdi, I.K. A low-cost flexible pH sensor array for wound assessment. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2016, 229, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Xu, Z.P.; Li, L. Manipulating extracellular tumour pH: An effective target for cancer therapy. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22182–22192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chan, J.M.; Farokhzad, O.C. pH-Responsive Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Lo, L.-W.; Mou, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-S. Synthesis and Characterization of Positive-Charge Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Oral Drug Delivery of an Anti-Inflammatory Drug. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3283–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnathambi, S.; Tamanoi, F. Recent Development to Explore the Use of Biodegradable Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica (BPMO) Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanoi, F.; Chinnathambi, S.; Laird, M.; Komatsu, A.; Birault, A.; Takata, T.; Doan, T.L.-H.; Mai, N.X.D.; Raitano, A.; Morrison, K.; et al. Construction of Boronophenylalanine-Loaded Biodegradable Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles for BNCT Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, T.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Calderon, S.; Fidalgo, A.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; André, V.; Duarte, M.T.; Ferreira, P.J.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Baleizão, C. Silica nanocarriers with user-defined precise diameters by controlled template self-assembly. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekaru, H.; Lu, J.; Tamanoi, F. Development of Mesoporous Silica-based Nanoparticles with Controlled Release Capability for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 95, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, S.V.; Ribeiro, T.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Baleizão, C.; Ferreira, P.J. On the Structure of Amorphous Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Aberration-Corrected STEM. Small 2018, 1802180, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, T.; Raja, S.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Fernandes, F.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Dyes and Pigments NIR and visible perylenediimide-silica nanoparticles for laser scanning bioimaging. Dye. Pigment. 2014, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Hybrid smart mesoporous silica nanoparticles for theranostics. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2311–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Ribeiro, T.; Rodrigues, A. Process for the Production of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Diameters Under 100 Nanometers and Precise Control of the Particle Size. International Patent Application No. PCT/PT20 17/000003; International Publication No. WO 2017/131542 Al, 3 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Castanheira, E.J.; Alves, S.P.C.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P. Grafting with RAFT—gRAFT Strategies to Prepare Hybrid Nanocarriers with Core-shell Architecture. Polymers 2020, 12, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crucho, C.I.C.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Functional Group Coverage and Conversion Quantification in Nanostructured Silica by 1 H NMR. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujii, Y.; Ejaz, M.; Sato, K.; Goto, A.; Fukuda, T. Mechanism and Kinetics of RAFT-Mediated Graft Polymerization of Styrene on a Solid Surface. 1. Experimental Evidence of Surface Radical Migration. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 8872–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutcherlapati, S.N.R.; Koyilapu, R.; Boddu, U.M.R.; Datta, D.; Perali, R.S.; Swamy, M.J.; Jana, T. Glycopolymer-Grafted Nanoparticles: Synthesis Using RAFT Polymerization and Binding Study with Lectin. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7309–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, A.; Charreyre, M.T. Experimental requirements for an efficient control of free-radical polymerizations via the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) process. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 653–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppeta, J.; Rogers, C. Dual emission laser induced fluorescence for direct planar scalar behavior measurements. Exp. Fluids 1998, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Ray, A.K.; Kundu, S.; Sasikumar, S.; Dasgupta, K. Heavy-water-based solutions of rhodamine dyes: Photophysical properties and laser operation. Appl. Phys. B 2002, 75, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Lopes, A.B.C.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Modified inside and out for ON:OFF pH-Modulated Cargo Release. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050716
Gonçalves JLM, Lopes ABC, Baleizão C, Farinha JPS. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Modified inside and out for ON:OFF pH-Modulated Cargo Release. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050716
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, José L. M., Ana Beatriz C. Lopes, Carlos Baleizão, and José Paulo S. Farinha. 2021. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Modified inside and out for ON:OFF pH-Modulated Cargo Release" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050716
APA StyleGonçalves, J. L. M., Lopes, A. B. C., Baleizão, C., & Farinha, J. P. S. (2021). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Modified inside and out for ON:OFF pH-Modulated Cargo Release. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050716