A Comparison of the Antinociceptive Properties of SJP-005 and Morphine in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Housing and Handling of Animals
2.2. Study 1
2.3. Study 2
2.4. Safety and Adverse Effects
3. Results
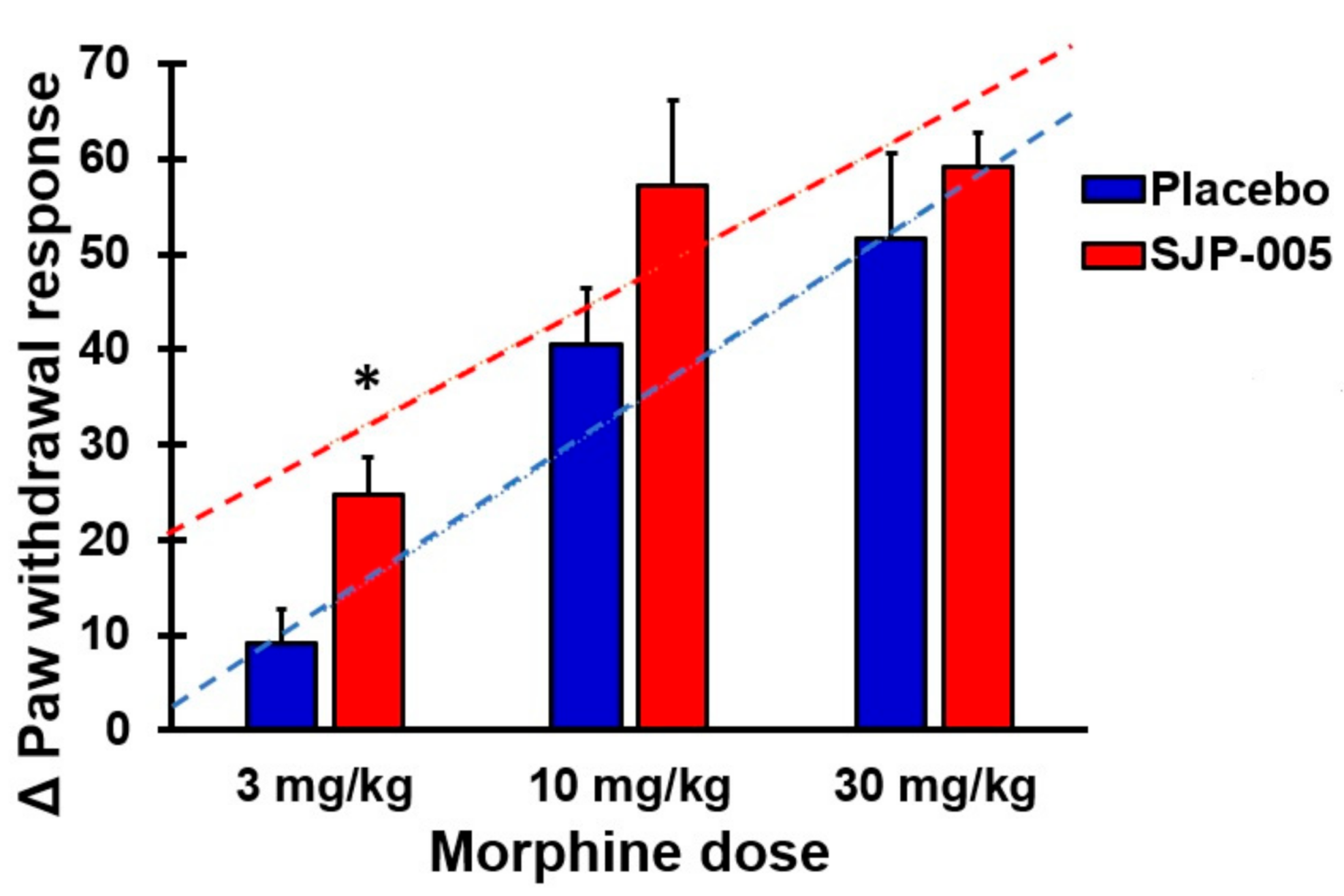
3.1. Study 1
3.2. Study 2
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Assessment | Paw Withdrawal Response (g) | Paw Volume (mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Animal | Pre-Dose | Post-Dose | Pre-Dose | Post-Dose | Edema |
| Group 1: Morphine (3 mg/kg) | 5401 | 6.7 | 10.3 | 1.89 | 2.91 | 1.02 |
| 5402 | 37.3 | 37.3 | 2.10 | 3.04 | 0.94 | |
| 5403 | 12.0 | 37.3 | 1.98 | 3.18 | 1.20 | |
| 5404 | 22.3 | 37.3 | 2.07 | 3.08 | 1.01 | |
| 5405 | 9.0 | 26.0 | 2.08 | 3.42 | 1.34 | |
| 5406 | 10.3 | 37.3 | 2.25 | 3.34 | 1.09 | |
| 5407 | 26.0 | 22.3 | 2.23 | 2.89 | 0.66 | |
| 5408 | 15.0 | 16.3 | 2.25 | 3.52 | 1.27 | |
| 5409 | 22.3 | 26.0 | 2.36 | 3.19 | 0.82 | |
| 5410 | 18.7 | 22.3 | 2.14 | 3.30 | 1.16 | |
| Group 2: Morphine (10 mg/kg) | 5411 | 16.3 | 60.0 | 1.81 | 2.59 | 0.78 |
| 5412 | 18.7 | 48.7 | 1.94 | 3.22 | 1.28 | |
| 5413 | 12.7 | 60.0 | 2.03 | 2.81 | 0.78 | |
| 5414 | 10.3 | 60.0 | 2.06 | 2.80 | 0.74 | |
| 5415 | 6.0 | 60.0 | 2.08 | 2.89 | 0.81 | |
| 5416 | 5.3 | 73.3 | 2.03 | 2.66 | 0.64 | |
| 5417 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 1.97 | 2.82 | 0.84 | |
| 5418 | 12.7 | 60.0 | 2.06 | 3.12 | 1.07 | |
| 5419 | 30.0 | 73.3 | 1.99 | 3.07 | 1.09 | |
| 5420 | 16.3 | 37.3 | 2.14 | 2.89 | 0.75 | |
| Group 3: Morphine (30 mg/kg) | 5421 | 18.7 | 48.7 | 2.11 | 3.04 | 0.92 |
| 5422 | 18.7 | 73.3 | 2.14 | 3.33 | 1.20 | |
| 5423 | 48.7 | 60.0 | 2.09 | 3.12 | 1.03 | |
| 5424 | 7.3 | 37.3 | 1.94 | 2.77 | 0.83 | |
| 5425 | 3.3 | 100.0 | 2.03 | 3.03 | 1.00 | |
| 5426 | 18.7 | 60.0 | 2.26 | 2.85 | 0.59 | |
| 5427 | 12.0 | 100.0 | 2.11 | 2.89 | 0.79 | |
| 5428 | 15.0 | 60.0 | 2.17 | 2.83 | 0.66 | |
| 5429 | 60.0 | 100.0 | 2.19 | 3.36 | 1.17 | |
| 5430 | 19.3 | 100.0 | 2.08 | 2.52 | 0.43 | |
| Group 4: SJP-005 + Morphine (3 mg/kg) | 5431 | 45.0 | 60.0 | 2.24 | 2.89 | 0.65 |
| 5432 | 6.0 | 48.7 | 2.27 | 2.91 | 0.63 | |
| 5433 | 23.3 | 33.7 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | |
| 5434 | 12.7 | 22.3 | 2.16 | 3.59 | 1.43 | |
| 5435 | 26.3 | 48.7 | 2.17 | 3.05 | 0.89 | |
| 5436 | 22.3 | 48.7 | 2.35 | 3.28 | 0.93 | |
| 5437 | 30.0 | 48.7 | 2.13 | 2.99 | 0.86 | |
| 5438 | 16.3 | 60.0 | 2.16 | 2.90 | 0.73 | |
| 5439 | 16.3 | 37.3 | 2.12 | 2.86 | 0.73 | |
| 5440 | 22.3 | 60.0 | 1.94 | 2.95 | 1.01 | |
| Group 5: SJP-005 + Morphine (10 mg/kg) | 5441 | 16.3 | 100.0 | 2.10 | 2.94 | 0.84 |
| 5442 | 7.3 | 73.3 | 2.23 | 2.80 | 0.57 | |
| 5443 | 15.7 | 100.0 | 2.31 | 2.73 | 0.43 | |
| 5444 | 16.3 | 48.7 | 2.14 | 2.77 | 0.63 | |
| 5445 | 45.0 | 73.3 | 2.14 | 2.79 | 0.65 | |
| 5446 | 18.7 | 26.0 | 2.33 | 3.79 | 1.46 | |
| 5447 | 15.0 | 60.0 | 2.26 | 3.17 | 0.91 | |
| 5448 | 8.3 | 100.0 | 2.23 | 3.24 | 1.00 | |
| 5449 | 4.7 | 60.0 | 2.15 | 3.24 | 1.09 | |
| 5450 | 22.3 | 100.0 | 2.24 | 3.08 | 0.84 | |
| Group 6: SJP-005 + Morphine (30 mg/kg) | 5451 | 9.0 | 100.0 | 2.07 | 3.20 | 1.13 |
| 5452 | 16.3 | 73.3 | 2.10 | 2.87 | 0.77 | |
| 5453 | 48.7 | 60.0 | 2.08 | 2.95 | 0.87 | |
| 5454 | 7.7 | 100.0 | 2.11 | 3.03 | 0.92 | |
| 5455 | 30.0 | 60.0 | 2.21 | 3.10 | 0.90 | |
| 5456 | 18.7 | 60.0 | 2.24 | 3.08 | 0.84 | |
| 5457 | 15.0 | 100.0 | 2.06 | 3.00 | 0.94 | |
| 5458 | 6.0 | 37.3 | 1.72 | 2.44 | 0.72 | |
| 5459 | 15.0 | 73.3 | 2.09 | 3.29 | 1.20 | |
| 5460 | 6.7 | 100.0 | 1.83 | 2.62 | 0.79 | |
| Group 7: SJP-005 + Placebo (saline 5 mL/kg) | 5461 | 15.7 | 10.3 | 2.05 | 3.22 | 1.17 |
| 5462 | 15.0 | 6.0 | 2.30 | 3.00 | 0.71 | |
| 5463 | 12.7 | 11.3 | 2.19 | 3.08 | 0.90 | |
| 5464 | 16.3 | 9.0 | 2.26 | 3.45 | 1.19 | |
| 5465 | 20.0 | 22.3 | 2.26 | 3.47 | 1.21 | |
| 5466 | 26.0 | 15.0 | 2.28 | 3.20 | 0.92 | |
| 5467 | 12.7 | 10.3 | 2.06 | 2.78 | 0.72 | |
| 5468 | 7.7 | 4.0 | 2.07 | 3.50 | 1.43 | |
| 5469 | 48.7 | 12.7 | 1.99 | 3.63 | 1.63 | |
| 5470 | 8.0 | 9.7 | 1.86 | 3.15 | 1.29 | |
Appendix B
| Assessment | Reaction Time (Seconds) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | + Placebo (Week 1) | + SJP-005 (Week 2) | ||
| Group | Animal | Baseline | 30 Min | 30 Min |
| Group 1: Placebo (saline 5 mL/kg) | 4401 | 4.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| 4402 | 4.6 | 3.6 | 3.0 | |
| 4403 | 1.4 | 3.2 | 4.0 | |
| 4404 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 3.9 | |
| 4405 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 3.9 | |
| 4406 | 3.9 | 1.8 | 1.4 | |
| 4407 | 3.7 | 2.4 | 2.2 | |
| 4408 | 5.2 | 4.6 | 1.8 | |
| 4409 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 2.4 | |
| 4410 | 4.8 | 3.5 | 2.2 | |
| Group 2: Morphine (3 mg/kg) | 4411 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 2.3 |
| 4412 | 4.1 | 5.5 | 3.1 | |
| 4413 | 4.0 | 8.6 | 3.0 | |
| 4414 | 6.1 | 4.2 | 3.9 | |
| 4415 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 5.2 | |
| 4416 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 2.4 | |
| 4417 | 3.1 | 4.0 | 3.5 | |
| 4418 | 4.2 | 3.7 | 2.7 | |
| 4419 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 1.4 | |
| 4420 | 4.5 | 8.4 | 4.8 | |
| Group 3: Morphine (10 mg/kg) | 4421 | 3.4 | 12.8 | 6.4 |
| 4422 | 3.3 | 9.0 | 2.5 | |
| 4423 | 4.5 | 6.2 | 3.0 | |
| 4424 | 4.1 | 11.4 | 6.2 | |
| 4425 | 3.3 | 10.2 | 4.0 | |
| 4426 | 5.9 | 7.0 | 9.9 | |
| 4427 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 6.1 | |
| 4428 | 3.7 | 8.3 | 2.9 | |
| 4429 | 6.7 | 5.4 | 5.8 | |
| 4430 | 4.1 | 14.1 | 6.7 | |
| Group 4: Morphine (30 mg/kg) | 4431 | 4.5 | 30.0 | 10.6 |
| 4432 | 4.4 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 4433 | 4.6 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 4434 | 4.4 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 4435 | 3.2 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 4436 | 3.4 | 30.0 | - | |
| 4437 | 2.8 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 4438 | 3.2 | 30.0 | 9.5 | |
| 4439 | 4.2 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 4440 | 4.3 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
References
- Schuckit, M.A. Treatment of Opioid-Use Disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Opioid Overdose Crisis; National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): North Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019.
- Scholl, L.; Seth, P.; Kariisa, M.; Wilson, N.; Baldwin, G. Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths—United States, 2013–2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, M.; Lintzeris, N.; Maier, C.; Savage, S. Recommendations for the prevention, detection, treatment and management of prescription opioid analgesic dependence: Outcomes from the Opioid Analgesic Dependence Education Nexus (OPEN) meeting. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2016, 14, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkman, G.A.; Kramers, C.; van Dongen, R.T.; van den Brink, W.; Schellekens, A. Trends in use and misuse of opioids in the Netherlands: A retrospective, multi-source database study. Lancet Public Health 2019, 4, E498–E505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. European Drug Report 2019: Trends and Developments; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, S.R.; Kirsh, K.L.; Passik, S.D. Challenges in using opioids to treat pain in persons with substance use disorders. Addict. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2008, 4, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalana, H.; Sachdeva, J.K.; Kundal, T.; Malhari, A.S.; Choudhary, R. A double blind, placebo controlled, randomised study comparing quetiapine with placebo, along with oral naltrexone, in the treatment of opioid dependent patients. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2015, 4, 9158–9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, E.C.; Lofwall, M.R.; Jaffe, J.H. Opioid Related Disorders. In Kaplan & Sadock’s Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry, 9th ed.; Sadock, B.J., Sadock, V.A., Ruiz, P., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; p. 1382. [Google Scholar]
- Puhl, A.C.; Milton, F.A.; Cvoro, A.; Sieglaff, D.H.; Campos, J.C.L.; Bernardes, A.; Figueira, C.S.; Lindemann, J.L.; Deng, T.; Neves, F.A.R.; et al. Mechanisms of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ regulation by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2015, 13, e004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtell, R.K.; Jones, J.D.; Heinzerling, K.G.; Beardsley, P.M.; Comer, S.D. Glial and neuroinflammatory targets for treating substance use disorders. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 180, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verster, J.C.; Scholey, A.; Dahl, T.A.; Iversen, J.M. Functional observation after morphine withdrawal: Effects of SJP-005. Psychopharmacology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, P.; Khodavar, M.J.; Mansouri, M.T.; Ghorbanzadeh, B. Investigation on the effect of ketotifen upon morphine tolerance and dependence in mice. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2018, 13, e16303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dvorakova, L.S.; Vetter, I. Methods used to evaluate pain behaviors in rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.J. The up-and-down method for small samples. Am. Statist. Assoc. 1965, 60, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfe, G.; Macdonald, A.D. The evaluation of the analgesic action of pethidine hydrocholoride (Demerol). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1944, 80, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Knezevic, N.N.; Tverdohleb, T.; Nikibin, F.; Knezevic, I.; Candido, K.D. Management of chronic neuropathic pain with single and compounded topical analgesics. Pain Manag. 2017, 7, 537–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catapres (Clonidine Hydrochloride) Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/017407s034lbl.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Gish, E.C.; Miller, J.L.; Honey, B.L.; Johnson, P.N. Lofexidine, an {alpha}2-receptor agonist for opioid detoxification. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stones, R.W.; Bradbury, L.; Anderson, D. Randomized placebo controlled trial of lofexidine hydrochloride for chronic pelvic pain in women. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 16, 1719–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, Z.D.; Johnson, K.W.; Pavlicova, M.; Glass, A.; Vosburg, S.K.; Sullivan, M.A.; Manubay, J.M.; Martinez, D.M.; Jones, J.D.; Saccone, P.A.; et al. The effects of ibudilast, a glial activation inhibitor, on opioid withdrawal symptoms in opioid-dependent volunteers. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, V.E.; Jones, J.D.; Manubay, J.; Sullivan, M.A.; Mogali, S.; Segoshi, A.; Madera, G.; Johnson, K.W.; Comer, S.D. Effects of ibudilast on the subjective, reinforcing, and analgesic effects of oxycodone in recently detoxified adults with opioid dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, Y.H.; Swift, J.E.; Gazerani, P.; Rolan, P. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial to determine the efficacy and safety of ibudilast, a potential glial attenuator, in chronic migraine. J. Pain Res. 2016, 9, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Bertollo, C.M.; Rocha, L.T.; Nascimento, E.B., Jr.; Costa, K.A.; Coelho, M.M. Antinociceptive and antiedematogenic activities of fenofibrate, an agonist of PPAR alpha, and pioglitazone, an agonist of PPAR gamma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 561, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Kiguchi, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ozaki, M.; Kishioka, S. Pioglitazone attenuates tactile allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in mice subjected to peripheral nerve injury. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 108, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, S.; Maeda, T.; Kiguchi, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Fukazawa, Y.; Ozaki, M.; Kishioka, S. Pioglitazone attenuates tactile allodynia and microglial activation in mice with peripheral nerve injury. Drug Discov. Ther. 2008, 2, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Zhu, S.; Ji, Q.; Hui, K.; Duan, M.; Xu, J.; Li, W. Repeated administration of pioglitazone attenuates development of hyperalgesia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 18, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottabathini, R.; Kumar, A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Garg, S.; Ekavali, E. Ameliorative potential of pioglitazone and ceftriaxone alone and in combination in rat model of neuropathic pain: Targeting PPARγ and GLT-1 pathways. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragomi, P.; Rahimian, R.; Kazemi, M.H.; Gharedaghi, M.H.; Khalifeh-Soltani, A.; Azary, S.; Javidan, A.N.; Moradi, K.; Sakuma, S.; Dehpour, A.R. Antinociceptive and antidiarrheal effects of pioglitazone in a rat model of diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: Role of nitric oxide. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 41, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Kwok, Y.H.; Sumracki, N.M.; Swift, J.E.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Johnson, K.; Williams, D.B.; Tuke, J.; Rolan, P.E. Glial attenuation with ibudilast in the treatment of medication overuse headache: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial of efficacy and safety. Headache 2015, 55, 1192–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pre-Dose Paw Volume (mL) | Post-Dose Paw Volume (mL) | Edema (mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Treatment | Mean (SE) | Mean (SE) | Mean (SE) |
| 1 | Morphine 3 mg/kg bw + placebo | 2.1 (0.05) | 3.2 (0.07) | 1.1 (0.07) |
| 2 | Morphine 10 mg/kg bw + placebo | 2.0 (0.03) | 2.9 (0.06) | 0.9 (0.06) |
| 3 | Morphine 30 mg/kg bw + placebo | 2.1 (0.03) | 3.0 (0.08) | 0.9 (0.08) |
| 4 | Morphine 3 mg/kg bw + SJP-005 | 2.2 (0.04) | 3.0 (0.07) | 0.9 (0.07) |
| 5 | Morphine 10 mg/kg bw + SJP-005 | 2.2 (0.02) | 3.1 (0.10) | 0.8 (0.09) |
| 6 | Morphine 30 mg/kg bw + SJP-005 | 2.1 (0.05) | 3.0 (0.08) | 0.9 (0.05) |
| 7 | Placebo + SJP-005 | 2.1 (0.05) | 3.2 (0.08) | 1.1 (0.10) |
| Pre-Dose Paw Withdrawal | Post-Dose Paw Withdrawal | Pre- vs. Post-Dose | Placebo vs. SJP-005 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Treatment | Mean (SE) | Mean (SE) | p-Value | p-Value |
| 1 | Morphine 3 mg/kg bw + placebo | 18.0 (3.0) | 27.2 (3.1) | 0.025 * | 0.179 |
| 2 | Morphine 10 mg/kg bw + placebo | 18.8 (5.1) | 59.3 (3.3) | 0.000 * | 0.491 |
| 3 | Morphine 30 mg/kg bw + placebo | 22.2 (5.7) | 73.9 (7.7) | 0.000 * | 1.000 |
| 4 | Morphine 3 mg/kg bw + SJP-005 | 22.1 (3.4) | 46.8 (3.9) | 0.000 * | - |
| 5 | Morphine 10 mg/kg bw + SJP-005 | 17.0 (3.6) | 74.1 (8.2) | 0.000 * | - |
| 6 | Morphine 30 mg/kg bw + SJP-005 | 17.3 (4.2) | 76.4 (7.1) | 0.000 * | - |
| 7 | Placebo + SJP-005 | 18.3 (3.8) | 11.1 (1.6) | 0.068 | - |
| Week 1 (Morphine Only) | Week 2 (Morphine + SJP-005) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Morphine Dose | Pre-Dose | Post-Dose | % Analgesia | Post-Dose | % Analgesia |
| 1 | 0 mg/kg bw | 4.1 (0.3) | 3.4 (0.3) | - | 2.7 (0.3) | - |
| 2 | 3 mg/kg bw | 4.3 (0.3) | 5.2 (0.6) | 53 | 3.2 (0.4) | 19 |
| 3 | 10 mg/kg bw | 4.2 (0.4) | 9.1 (0.9) * | 168 | 5.4 (0.7) | 100 |
| 4 | 30 mg/kg bw | 3.9 (0.2) | 30.0 (0.0) * | 782 | 25.6 (2.9)* | 848 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verster, J.C.; Scholey, A.; Dahl, T.A.; Iversen, J.M. A Comparison of the Antinociceptive Properties of SJP-005 and Morphine in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020243
Verster JC, Scholey A, Dahl TA, Iversen JM. A Comparison of the Antinociceptive Properties of SJP-005 and Morphine in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerster, Joris C, Andrew Scholey, Thomas A Dahl, and Jacqueline M Iversen. 2021. "A Comparison of the Antinociceptive Properties of SJP-005 and Morphine in Rats" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020243
APA StyleVerster, J. C., Scholey, A., Dahl, T. A., & Iversen, J. M. (2021). A Comparison of the Antinociceptive Properties of SJP-005 and Morphine in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 13(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020243






