Simple Summary
This article belongs to the Special Issue mRNA Therapeutics: A Themed Issue in Honor of Professor Katalin Karikó.
Abstract
Advances in the using in vitro transcribed (IVT) modRNA in the past two decades, especially the tremendous recent success of mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, have brought increased attention to IVT mRNA technology. Despite its well-known use in infectious disease vaccines, IVT modRNA technology is being investigated mainly in cancer immunotherapy and protein replacement therapy, with ongoing clinical trials in both areas. One of the main barriers to progressing mRNA therapeutics to the clinic is determining how to deliver mRNA to target cells and protect it from degradation. Over the years, many different vehicles have been developed to tackle this issue. Desirable vehicles must be safe, stable and preferably organ specific for successful mRNA delivery to clinically relevant cells and tissues. In this review we discuss various mRNA delivery platforms, with particular focus on attempts to create organ-specific vehicles for therapeutic mRNA delivery.
1. Introduction
mRNA therapeutics are an innovative pharmaceutical technology with the capacity to create a new type of drugs that will make personalized medicine possible [1]. Currently, there are a few methods used to therapeutically manipulate protein levels in tissues, including small molecules such as statins and other inhibitors, or recombinant proteins, such an insulin. Additionally, over the last few decades there is an increase in gene therapeutic approaches being tested in clinical trials. One such approach uses micro RNA (miRs) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) as seen in the FDA-approved drug Patisiran. Another method utilizes various viral vectors such as the adeno associated viruses (AAV) for therapeutic protein expression (Table 1). However, the use of viral vectors for gene delivery in clinical setting have various limitations, therefore there is a need for a more robust gene delivery method. Because mRNA is the link between DNA and protein creation in our cells, it has been of interest to researchers in biology and medical sciences since its discovery in the early 1960s [2]. The first therapeutic use of mRNA was in the early 1990s: Wolff et al showed that mRNA can lead to functional protein translation in murine skeletal muscle, and a couple of years later, mRNA was used to treat Brattleboro rats suffering from diabetes insipidus, with partial success of injected mRNA encoding for the missing hormone arginine vasopressin (AVP) [3,4]. While early work on mRNA showed promising results, two fundamental barriers prevent mRNA therapeutics from moving forward into clinical use. The first barrier is that mRNA elicits an innate immune response. mRNA has been shown to trigger Toll-like receptors (TLRs) TLR7 and TLR8 (which recognize single-strain RNA) in the endosome and activate RIG-1 and MDA-5 receptors (leading to protein translation shutdown) in the cytoplasm [5,6,7]. The second barrier is that mRNA rapidly degrades in the body via ribonucleases (RNases) [8,9], so that exogenous mRNA in transfected cells has a very short half-life. The immune reactivity and curtailed half-life of mRNA both limit its translatability.

Table 1.
Tools for therapeutic manipulation of protein levels in tissues.
To overcome these barriers, two researchers, Dr. Katalin Karikó and Dr. Drew Weissman, asked the fundamental question: what mechanism is responsible for the immunological response, triggered by TLR7 and TLR8, to mRNA? Their landmark work [10]. showed that uridine, an mRNA ribonucleotide, activates the two TLRs in the endosome. Furthermore, they demonstrated that replacing uridine (U) with naturally occurring pseudouridine (Ψ) attenuates the innate immune response. This modified mRNA (modRNA), in which U is replaced with Ψ, has shown high ability to avoid cleavage by RNase and to reduce RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) activity [10,11]. These results indicate that modRNA has higher translation in comparison to mRNA containing either other nucleotide modifications or uridine. Our lab and others have confirmed their study and produced similar results [12,13]. Recently, modRNA has been successfully used to deliver SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein and vaccinate millions of people around the world during the COVID-19 pandemic [14,15]. New approaches seek to locally or systemically deliver modRNA in vivo without degrading the mRNA. In this review, we summarize different vehicles that have been used to deliver mRNA. We will cover the advantages and disadvantages of each vehicle and point out future directions in this exciting and important field.
2. mRNA Delivery Methods
Since RNA was first discovered, researchers have employed many methods of delivering it to cells. Initial techniques used naked RNA, which, as mentioned above, is prone to RNase degradation and evokes a strong proinflammatory response. More sophisticated methods sought to enable cell entry and, on a systemic level, allow sufficient circulation time for the therapeutic mRNA to reach its destination and be released into target cells.
To date, lipidbased nanoparticles (LNPs) are the only RNA therapeutic carriers approved for clinical use [14,15,16]; therefore, LNPs will be the main focus of this review. However, there are other formulations used for RNA delivery, including polymers and carbohydrate polymers [17]. Gene delivery polymers contain polycations such as polyethylenimine (PEI) [18]. Due to its positive charge and abundant amines, PEI has good affinity for nucleic acids which results in a formation of complexes with a positive surface charge [19]. In vivo, PEI was successfully used for aerosol gene delivery into the lungs [20]. Although PEI formulations allow high transfection efficiency in vitro and in vivo, they are also significantly cytotoxic, partly because of their poor degradability, which prevents PEI-based carriers from broader use in pre-clinical and clinical settings [19,21].
Polyesters are another group of materials being used for RNA delivery. A library of 480 biodegradable polyesters was screened in vitro and formulations most efficiently transfected IGROV1 cells with luciferase (Luc) mRNA were subsequently tested in vivo. Adding pluronic F127 decreased the overall charge of the nanoparticle and increased its stability. Further, manipulating F127 content resulted in lung-specific mRNA delivery that potentially could be used to treat pulmonary disease [22].
A miniature biodegradable polymeric matrix, LOcal Drug EluteR (LODERTM), was developed for prolonged siRNA delivery into the pancreatic tumor environment and, combined with chemotherapy, was tested in a phase 1/2a clinical trial [23]. LODER matrix is a copolymer of poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) with high molecular weight and allows slow, prolonged siRNA release in the tumor environment over several months [24].
Naturally occurring chitosan is a carbohydrate polymer that can be used for gene delivery. Chitosan features biodegradability, biocompatibility and cationic charge that allows nucleic acid binding; however, it also has limitations such as poor water solubility and limited target capability [25].
3. Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs)
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are spherical vesicles made of lipids. Lipids are organic, water-insoluble lipid compounds that can form defined structures such as cell membranes due to their unique features. Lipids have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail that allow LNPs to undergo self-assembly into well-defined structures, such as cell membranes [26]. LNP-RNA systems form via hydrophobic interactions in an aqueous environment combined with electrostatic interactions between negatively charged RNA and cationic or ionizable lipids [27,28]. Though LNP-RNA formulations initially used cationic lipids to allow electrostatic interactions with RNA, their toxicity instigated a gradual shift to ionizable lipids [17,29,30]. Ionizable lipids are positively charged at low pH (which allows RNA binding) and become neutral at physiological pH, a change that helps reduce the toxicity of LNP-RNA complexes in vivo.
Additional modifications tuned the properties of LNPs. For example, in addition to ionizable lipids, LNPs contain phospholipids that serve as helper lipids, cholesterol to improve cell entry and polyethylene glycol (PEG) to improve stability and circulation time by preventing serum protein binding (Figure 1a,b) [27,31,32,33].
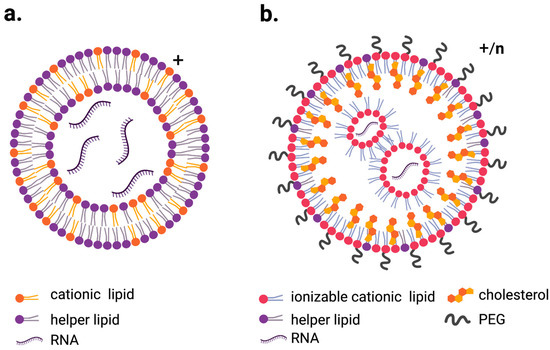
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the most commonly used LNPs for RNA delivery. (a). LNP containing cationic lipid (lipoplex) with overall positive charge, (b). ionizable lipid LNPs which exhibit positive charge while at low pH and more neutral charge when exposed to physiological pH. Figures created with BioRender.com.
Each LNP component can be altered to adjust the properties of the final vehicles. PEG content is inversely proportional to LNP size; changing PEG content from 1% to 5% produces LNPs 100nm to 20nm in size [34]. Similarly, raising PEG content from 0.5% to 5% results in particle sizes between 150nm and 50nm. In the same study, particles containing 0.5% PEG carrying Luc-coding mRNA showed the highest expression when injected subretinally, suggesting that particle size may be an important factor in allowing mRNA translation efficiency [35]. The primary reasons for using PEGylation in LNPs were to stabilize particles and prevent excessive serum protein binding and opsonization, which causes rapid clearance from the circulation [36,37]. However, the presence of PEG on LNP surfaces may induce anti-PEG IgM production especially after repeated administrations [38]. Because excessive immune response against PEGylated LNPs is detrimental for gene delivery, it was important to retain their stabilizing properties while avoiding anti-PEG IgM production. Manipulating PEG acryl chain length results in faster shedding from LNPs after administration. Systemic delivery of LNPs with shorter acryl chain PEGs led to lower anti-PEG IgM production following repeated administration [39]. Additionally, different naturally occurring cholesterol analogues have been shown to significantly alter LNP morphology, changes that may affect translation efficiency and thus be relevant to LNP design [40].
We will describe other application-specific modifications to LNP formulations in detail below.
3.1. Cationic LNPs
As mentioned above, cationic lipids are used to formulate LNPs containing nucleic acids [17]. Cationic amino groups within these lipids interact with nucleic acids’ negatively charged phosphate groups, resulting in engraftment in an LNP. In 1989, a lipoplex structure containing synthetic cationic lipid DOTMA (N-[1-(2,3-dioleyloxy)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonium chloride) and helper lipid DOPE (dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine) was used to generate Luc mRNA LNPs that successfully transfected several cell types [41]. Further, in vitro transfections have long used cationic lipids including commercially available Lipofectamine, which is widely used for RNA and DNA in vitro transfections despite its known cytotoxicity [42]. While separated, both cationic and anionic lipids in cell membranes display a cylindrical shape, which supports bilayer structure formation. However, when these lipids interact together via negatively and positively charged headgroups, they form cone-shaped structures that promote hexagonal HII phase formation. This hexagonal phase disorganizes bilayer structures and correlates with membrane fusion as well as the disruption that is partially responsible for cationic lipid toxicity [43]. When systemically delivered, LNPs with permanent surface charge interact with serum proteins, and this interaction causes rapid clearance from the circulation [44,45]. Indeed, cationic LNPs have been shown to generate toxicity towards phagocytic cells in vitro. [46]. Additionally, systemically delivering cationic LNPs induces a strong immune response by activating the interferon type I response and instigating expression of INFγ, TNFα and the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-2. [47]. Excessive immune reaction to LNPs is not desirable because uncontrolled cytokine release can lead to life-threating conditions; however, carefully designed immune response activation can be used as an adjuvant in RNA-LNP-based vaccines [48,49]. Though using cationic lipids has disadvantages, as detailed above, the positive charge very efficiently entraps nucleic acids. This approach lead to the development of pH-sensitive ionizable cationic LNPs for more effective RNA delivery [50].
3.2. Ionizable Cationic Lipids LNPs
Currently, the LNPs that are most widely used in systemic nucleic acid delivery typically contain ionizable cationic lipids, helper (structural) phospholipids, cholesterol and PEG. Ionizable LNPs were created to avoid the toxicity of the permanently cationic lipids originally used in LNP-RNA systems, in order to enable their therapeutic applications. Patisiran (brand name Onpattro), the only FDA-approved LNP-RNA therapeutic prior to anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, utilizes ionizable lipids in its LNP formulation [51]. Design of ionizable cationic lipids is balanced twofold using their pKa value. The pKa value is supposed to be sufficiently high so at low pH lipids are positively charged which enable binding with negatively charged RNA molecules and formation of LNPs. Thus, at low endosomal pH positive charge of ionizable lipid allow interactions with endogenous anionic lipids hence leads to disruption of endosomal structure and release of LNPs cargo into cytoplasm. Simultaneously, the pKa value of the ionizable lipids should be sufficiently low so at physiological pH the surface charge of LNPs will remain relatively neutral. This allows to modulate toxicity and immunogenicity of resulting LNPs and increases their circulation time [27,40,52].
At the cellular level, the limiting factor in efficiently translating LNP-RNA is the RNA cargo release into target cells’ cytoplasm. One mechanistic explanation for the endosomal escape process is molecular structure hypothesis. According to this hypothesis, cationic ionizable lipids become protonated in increasingly acidic endosomal environments, a process that allows interaction with anionic lipids in the endosomal bilayer. That interaction forms non-bilayer hexagonal structures that disrupt the bilayer, releasing LNP cargo into cytoplasm [43,52,53]. Different cell types present varying endosomal escape mechanisms when transfected with LNP-mRNA containing cationic ionizable lipids. A study analyzing 30 different cancer cell lines concluded that the most efficiently transfecting cells exhibit rapid LNP uptake and either processing to lysosomes or rapid exocytosis. In contrast, low-transfecting cells show slower endosomal LNP trafficking to lysosomes [54]. Another study showed very low recovery of LNP-delivered mRNA in epithelial cells and determined that LNP-mRNA undergoes endocytosis and is then packed into extracellular vehicles (EV), which are subsequently secreted and detected in plasma and organs. When delivered intravenously, these EVs containing intact exogenous mRNA engendered lower levels of proinflammatory cytokines, as compared to LNP-mRNA, in mouse plasma [55]. The immunogenicity of RNA molecules might be one reason for low translation efficiency. That limitation can be resolved by using RNA containing modified nucleosides such as 1-methylpseudouridine as we previously mentioned [1,10,11].
Introducing and evolving ethanol loading procedures facilitated effective production of homogenous, small-size (diameter < 100nm) LNPs with high entrapment efficiency (>80%) [34,56,57,58]. Over the years, many ionizable lipids have been developed, with a variety of features depending on the desired purpose.
Prior to developing SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, both BioNTech and Moderna worked on LNP-encapsulated mRNA therapeutics with a range of properties optimized for different aims [59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. In a study published in 2015, LNP containing an ionizable cationic lipid carrying Luc modRNA was injected in vivo using six different delivery routes (intradermally, intramuscularly, subcutaneously, intraperitoneally, intravenously and intratracheally). The LNPs were 70-100nm in size and comprised cationic ionizable lipid, phospholipid, cholesterol and PEG at 50:10:38.5:1.5 mol/mol ratio. Expression kinetics analysis showed different expression patterns depending on the delivery route. Local intramuscular injection produced Luc expression at the injection site as well as diffusion to the liver. Additionally, systemic delivery via intravenous or intraperitoneal injection also resulted in strong protein production in the liver [67]. These findings suggest it will be important to tune LNP properties to enable the highest expression rates in the targeted tissue, according to the therapeutic goals.
Research published in 2019 compared various LNP formulations for intramuscular administration of mRNA vaccines. As noted above, in LNPs ionizable lipids’ properties depend on pH, and their pKa value defines their behavior at various pH levels. This study tested LNPs containing ionizable lipids with different pKa and found that with regard to protein expression, the best lipids for intramuscular administration have higher pKa than those that are best for IV administration, a result that suggests LNPs should be specifically designed their intended purposes [68]. For example, vaccines must boost innate immune stimulation with good tolerability. Of the lipid formulations tested, the authors concluded that the optimal pKa for immunogenicity was between 6.6 and 6.8; however, an ionizable lipids’s pKa is not the only factor that plays a role in optimization. Another 2019 publication focused on designing ionizable lipids for LNP formulations intended to serve as antigen mRNA delivery vehicles as well as adjuvants. This extensive study prepared a library of over 1000 lipid formulations and tested their ability to cause antigen protein expression and induce immune response for anti-tumor vaccines. The authors concluded that the formulations containing ionizable lipids with cyclic amine head groups, unsaturated lipid tails and dihydroimidazole linkers most efficiently inhibited tumor growth and increased survival in both melanoma and human papillomavirus E7 mouse models [69].
To date, ionizable lipid LNPs are the preferred carriers for clinical therapeutic RNA delivery. The anti-SARS-Cov-2 modRNA vaccines are the most prominent example, with millions of doses already administered worldwide [14,15]. Additionally, a previously mentioned Patisiran, carrying an siRNA targeting 3′ untranslated region of transthyretin mRNA was FDA-approved treatment for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis in 2018 [16].
Having proved that LNP-RNA therapeutics are safe and efficient, the next step for the field is to focus on designing cell- and organ-specific treatments for minimally invasive clinical delivery routes. Indeed, several trials have been already completed in pursuit of these goals, and many more are ongoing.
3.3. Organ-Specific LNPs
The abovementioned vaccine studies used intramuscular injections of LNP-RNA for systemic immune response, as well as systemic delivery to the liver in the case of Patisiran, but how could we direct LNP-RNA into other organs for protein replacement therapy? Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) in blood serum has been shown to bind to intravenously injected LNPs. Crucial to transporting and metabolizing lipids, ApoE regulates lipoprotein and cholesterol levels in the plasma via high-affinity binding to the family of LDL receptors [70,71]. The liver is the main organ for clearing ApoE-binding lipoproteins; hence, systemically delivered LNPs would bind ApoE and preferentially home to the liver [36,72]. A study performed on apoE−/− mice using cationic and ionizable lipid LNPs carrying siRNA demonstrated that the hepatic uptake of ionizable, but not cationic, LNPs is ApoE dependent, suggesting that LNP charge plays a role in LNP tissue tropism [73].
While excessive liver homing is a notable disadvantage of intravenously injected ionizable LNPs, a selective organ targeting (SORT) strategy could overcome this issue [74]. In this system, various lipid classes were designed for tissue-specific gene delivery and editing using CRISPR-Cas technology. Based on previous work, researchers speculated that the key to organ-specific delivery would be manipulating the internal and/or external charge of formulated LNPs [75,76,77]. Along with standard LNP components including an ionizable cationic lipid, phospholipids, cholesterol and PEG, the authors proposed adding SORT molecules which allow lung-, spleen- or liver-specific gene delivery. Indeed, adding increasingly higher percentages of permanently positively charged 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane lipid (DOTAP) shifted tissue tropism from the liver to the lungs. Based on that outcome, researchers tested numerous other molecules with different charges, including a negatively charged 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (18PA) SORT molecule that, at 10-40% incorporation in an LNP formulation, resulted in spleen-specific Luc expression. Incorporating SORT molecules, including DLin-MC3-DMA which was used in Patisiran [51], into several classes of ionizable LNPs produced similar outcomes, indicating this system is compatible with commonly used ionizable lipid-LNPs and can be altered according to therapeutic goals [74]. These same authors recently published another study, where they created multi-tailed ionizable phospholipids (iPhos) that facilitated endosomal release of RNA cargo. These lipids can function together with additional variously charged helper lipids to allow organ-specific delivery, an approach similar to the SORT system [78].
In addition to organ-specific delivery, researchers have pursued targeting specific cell subsets in the liver by engineering ionizable lipid nanoparticles for selective RNA delivery into hepatocytes and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSEC). For hepatocyte-specific delivery, the authors manipulated particle size by adjusting PEG content, whereas incorporating mannose favored targeted LSEC RNA delivery [79].
One of the most therapeutically important targets for gene delivery is tumor tissue. Cancer remains the main cause of death worldwide, accounting for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020 [80] and various gene therapy applications, including RNA-based approaches [81], have been employed for cancer treatment in pre-clinical trials. However, as with traditional chemotherapy, the main concern remains targeted delivery to tumor tissue. To meet this challenge, a LNP-mRNA delivery system was designed to deliver CRISPR components (cLNP) into glioblastoma and disseminated ovarian tumors [82]. LNPs are typically constructed using ionizable cationic lipids; however, this study designed a library of novel-class ionizable amino lipids and compared them to the clinically used Dlin-MC3-DMA LNP formulation containing ionizable cationic lipid. In a glioblastoma model, local, intratumoral cLNP delivery inhibited tumor growth and increased survival, results that show its efficiency in PLK1 (polo-like kinase) gene editing. Because PLK1 is an enzyme involved in the cell cycle, its inhibition causes cell cycle arrest and death of dividing cells. Even though intratumor injection beneficially affected designed LNPs, the most promising path to potential clinical use is to develop tissue-targeted LNPs suitable for minimally invasive delivery methods. In pursuit of this goal, the authors created LNPs coated with cell-targeting antibodies, a system called ASSET [83]. Intraperitoneally delivering targeted LNPs against OV8 peritoneal xenografts limited tumor growth and improved survival in tumor-bearing mice. As OV8 tumor cells overexpress epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), the targeted LNPs contained anti-EGFR antibody [84]. However, the limitation of this approach is that only some cancer cells exhibit a distinct expression profile on their surfaces that can be targeted using antibodies. Another approach to delivering LNP-mRNA to tumors and imaging them in vivo deployed theranostic LNPs containing PEGylated BODIPY dyes (PBD) [85], which structurally similar to the PEGs traditionally used in LNPs. Analysis of the novel LNP library revealed that the intravenously administered 4A3-SC8&PEG2k5d formulation was preferentially expressed in liver and subcutaneous tumors. Yet this formulation contains pH-activable dye that allows high tumor-to-liver contrast fluorescence, as the authors themselves noted [86,87]. Therefore, the high signal observed in tumors might be a product of the low-pH tumor environment and not necessarily LNP accumulation in the tumor tissue.
So far, systemic delivery into tumors remains an unmet challenge, though many researchers are exploring the use of lipoplexes, which are cationic liposomes, to carry nucleic acid as another approach to cancer immunotherapy and cancer vaccines. In a study that used RNA-lipoplexes (RNA-LPX) to convey cancer antigens into dendritic cells [75], the authors manipulated lipid to RNA ratios and compared Luc expression in different organs after systemic delivery. Decreasing cationic lipid content in RNA-LPX formulations resulted in a predominant signal in the spleen. Most importantly, in CD11c-DTR mice, which allow CD11c+ cell depletion, the spleen signal was not detectable after Luc-LPX administration, indicating that this formulation preferentially targeted antigen-presenting cells (APC). More detailed analysis showed that dendritic cells showed the highest protein expression even though macrophages internalized more RNA from injected RNA-LPXs. When treated with RNA-LPX bearing influenza virus hemagglutinin, both cell types induced TLR7-dependent overexpression of INFα. Systemic delivery of RNA-LPX vaccines carrying tumor-specific antigens (OVA for B16-OVA melanoma and gp70 for CT26 colon carcinoma), produced complete, long-lasting protection against subcutaneous tumor challenge, and re-challenge in the case of CT26. Additionally, RNA-LPX vaccines protected the mice from lung metastasis when delivered after intravenous tumor implantation and significantly increased their survival. The authors concluded that the observed tumor rejection occurred via INFα-dependent T-cell activation [75].
The formulation used in this study was also employed in a project focusing on immune system desensitization in multiple sclerosis [88]. Antigen-specific tolerization is a promising approach for treating autoimmune diseases without impairing the immune system’s primary functions [89]. In this study, the authors used nucleoside-modified mRNA with 1-methylpseudouridine (m1Ψ) to avoid TRL7-dependent INFα release by APCs caused by single-strain RNA stimulation [10,11,90]. Systemic delivery of m1Ψ-RNA-LPX coding for disease-related autoantigens generated improvements in several mouse models of multiple sclerosis. Contrary to the RNA-LPX study, m1Ψ-RNA-LPX caused neither INFα secretion nor significant APC activation, and the authors concluded that the beneficial effect was related to reduced effector T-cell levels and elevated regulatory T-cell populations. Importantly, the authors showed that Luc expression in the spleen was much higher and more prolonged when Luc was delivered using m1Ψ-RNA-LPX rather than RNA-LPX, suggesting that not only the vehicle but also RNA composition itself has tremendous impact on treatment outcome.
Another study utilizing modified mRNA LNPs investigated therapeutic delivery of interleukin 10 (IL-10) into Ly6C+ inflammatory leukocytes in a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [91]. In addition to using modified RNA for prolonged, robust therapeutic protein expression, researchers achieved cell specificity with an LNP formulation utilizing the previously described ASSET system which coats LNP surface with cell-specific antibodies. Here the authors used anti-Ly6c antibody and showed that systemic delivery of anti-inflammatory IL-10 into Ly6C+ leukocytes significantly reduced the severity of intestinal inflammation in treated mice [91].
Thoughtfully designing and tuning LNP properties is one approach for tissue-specific delivery of therapeutic RNA. Another possibility would be to create a ‘self-controlling’ RNA expression system that only allows protein translation in specific cell subsets despite RNA uptake by other cell types. The Specific Modified mRNA Translation System (SMRTs) was designed to permit specific expression of therapeutic genes in cardiomyocytes (CM) but not in non-CMs in the heart [92]. This system takes advantage of the CM-specific micro RNAs (miRs) miR-1 and miR-208 [93,94]. SMRTs is an on/off system that contains two modRNA molecules which together create a circuit; the first contains a L7AE gene and a CM-specific miR recognition element; the second contains a gene of interest and a L7AE-recognition element, a K-motif. This design allows expression of the gene of interest in CM and prevents expression in other cell types.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Until recently, LNPs were mostly designed for small interference RNAs (siRNAs), which are significantly smaller than mRNA. More tailored LNP formulations may therefore need to be developed to allow such a big molecule to be carried and translated efficiently [95,96,97].
To date, the only broadly used organ-specific delivery approach is based on the overall charge of the LNPs (Figure 2). Positively charged mRNA-LNPs translate mostly, but not specifically, in the lung, neutral charge leads to expression in the liver and a negative charge allows expression in the spleen. This approach still needs improvements to prevent leakage to other organs in order to achieve true organ-specific expression of the therapeutic transgenes. Moreover, approaches to deliver LNP-RNA therapeutics to other organs need to be explored.

Figure 2.
Approaches for organ specific modifications of LNPs used for RNA delivery. Attempts for organ specific modifications of LNPs include manipulation of LNP charge that promotes lung-, spleen- or liver- specific delivery of therapeutic RNA. Attaching cell specific antibody on the surface of LNP allows delivery of the RNA into target cells. Figures created with BioRender.com.
Tumor targeting can be improved by adding tumor-specific antibodies to the surface of LNPs. However, due to the lack of cancer-specific surface markers, this approach cannot be widely utilized. One attempt to boost tumor-specific RNA-LNP delivery is to increase its circulation time in order to expand its ability to accumulate in tumor tissue. PEGylation is one method that can promote LNP accumulation in tumor tissue after systemic delivery. Adding PEG to the LNP surface prevents protein binding and opsonization which increase circulation time but may also be related to the more favorable nanoparticle size that helps extravasation into tumor tissue [98]. Another direction for designing more effective tumor-specific RNA-LNPs is to employ unique tumor environment characteristics. Since solid tumors have lower pH than surrounding tissues [99,100], for example, incorporating pH-responsive systems into RNA-LNPs may help tumor-specific delivery [101].
In last decade, lipid-based carriers for RNA delivery received significantly increased attention in this rapidly growing field. LNPs used in mRNA vaccines against SARS-Cov2 are a safe and efficient vehicle for therapeutic gene delivery, and their success will certainly support the development of LNPs for other applications, such as protein replacement therapies or gene editing, in the future.
Author Contributions
M.M.Ż.; writing—original draft preparation, review and editing, visualization, L.Z.; writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, funding acquisition. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Institutes of Health (NIH/NHLBI: R01 HL142768-01 and R01 HL14913701).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sahin, U.; Karikó, K.; Türeci, Ö. MRNA-based therapeutics-developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.D.S.; Meselson, D.M. An unstable intermediate carrying information from genes to ribosomes for protein synthesis. Def. At. Support Agency Rep. DASA-532 B 1957, 186, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.A.; Malone, R.W.; Williams, P.; Chong, W.; Acsadi, G.; Jani, A.; Felgner, P.L. Direct Gene Transfer into Mouse Muscle in Vivo. Science 1990, 247, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirikowski, G.F.; Sanna, P.P.; Maciejewski-Lenoir, D.; Bloom, F.E. Reversal of diabetes insipidus in Brattleboro tats: Intrahypothalamic injection of vasopressin mRNA. Science 1992, 255, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, F.; Hemmi, H.; Hochrein, H.; Ampenberger, F.; Kirschning, C.; Akira, S.; Lipford, G.; Wagner, H.; Bauer, S. Species-Specific Recognition of Single-Stranded RNA via Toll-like Receptor 7 and 8. Science 2004, 303, 1526–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pichlmair, A.; Schulz, O.; Tan, C.-P.; Rehwinkel, J.; Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Way, M.; Schiavo, G.; e Sousa, C.R. Activation of MDA5 Requires Higher-Order RNA Structures Generated during Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10761–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlee, M.; Roth, A.; Hornung, V.; Hagmann, C.A.; Wimmenauer, V.; Barchet, W.; Coch, C.; Janke, M.; Mihailovic, A.; Wardle, G.; et al. Recognition of 5′ Triphosphate by RIG-I Helicase Requires Short Blunt Double-Stranded RNA as Contained in Panhandle of Negative-Strand Virus. Immunity 2009, 31, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigby, R.; Rehwinkel, J. RNA degradation in antiviral immunity and autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dyer, K.D.; Rosenberg, H.F. The RNase a superfamily: Generation of diversity and innate host defense. Mol. Divers. 2006, 10, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karikó, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Welsh, F.A.; Ludwig, J.; Kato, H.; Akira, S.; Weissman, D. Incorporation of Pseudouridine Into mRNA Yields Superior Nonimmunogenic Vector with Increased Translational Capacity and Biological Stability. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA Recognition by Toll-like Receptors: The Impact of Nucleoside Modification and the Evolutionary Origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultana, N.; Magadum, A.; Hadas, Y.; Kondrat, J.; Singh, N.; Youssef, E.; Calderon, D.; Chepurko, E.; Dubois, N.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. Optimizing Cardiac Delivery of Modified mRNA. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eyler, D.E.; Franco, M.K.; Batool, Z.; Wu, M.Z.; Dubuke, M.L.; Dobosz-Bartoszek, M.; Jones, J.; Polikanov, Y.S.; Roy, B.; Koutmou, K.S. Pseudouridinylation of mRNA coding sequences alters translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23068–23074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.-C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, K.H.; Popova, P.; Hadrup, S.R.; Astakhova, K.; Taskova, M. Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivery of Therapeutic RNA Oligonucleotides. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2265–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski-Daspit, A.S.; Kauffman, A.C.; Bracaglia, L.G.; Saltzman, W.M. Polymeric vehicles for nucleic acid delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulkoski, D.; Bak, A.; Wilson, J.T.; Krishnamurthy, V.R. Recent advances in polymeric materials for the delivery of RNA therapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioia, S.; Conese, M. Polyethylenimine-mediated gene delivery to the lung and therapeutic applications. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2008, 2, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Symonds, P.; Murray, J.C.; Hunter, A.; Debska, G.; Szewczyk, A. A two-stage poly(ethylenimine)-mediated cytotoxicity: Implications for gene transfer/therapy. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Q.; Siegwart, D.J. Systemic mRNA Delivery to the Lungs by Functional Polyester-based Carriers. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4307–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Khvalevsky, E.Z.; Hubert, A.; Gabai, R.M.; Hen, N.; Segal, A.; Domb, A.J.; Harari, G.; Ben-David, E.; Raskin, S.; et al. RNAi therapy targeting KRAS in combination with chemotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24560–24570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramot, Y.; Rotkopf, S.; Gabai, R.M.; Khvalevsky, E.Z.; Muravnik, S.; Marzoli, G.A.; Domb, A.J.; Shemi, A.; Nyska, A. Preclinical Safety Evaluation in Rats of a Polymeric Matrix Containing an siRNA Drug Used as a Local and Prolonged Delivery System for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 44, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Tan, Y.F.; Wong, Y.S.; Liew, M.W.J.; Venkatraman, S. Recent Advances in Chitosan-Based Carriers for Gene Delivery. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullis, P.R.; Hope, M.J. Lipid Nanoparticle Systems for Enabling Gene Therapies. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bessodes, M.; Dhotel, H.; Mignet, N. Lipids for Nucleic Acid Delivery: Cationic or Neutral Lipoplexes, Synthesis, and Particle Formation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1943, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Guo, P.; Wen, W.-C.; Wong, H. Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for RNA Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 3140–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.J.; Tam, Y.K. Controlling Protein Expression by Delivery of RNA Therapeutics Using Lipid Nanoparticles. In Nucleic Acid Nanotheranostics: Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 277–310. [Google Scholar]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaczmarek, J.C.; Kowalski, P.; Anderson, D.G. Advances in the delivery of RNA therapeutics: From concept to clinical reality. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlatkovic, I. Non-Immunotherapy Application of LNP-mRNA: Maximizing Efficacy and Safety. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliveau, N.; Huft, J.; Lin, P.J.; Chen, S.; Leung, A.K.; Leaver, T.J.; Wild, A.W.; Lee, J.B.; Taylor, R.J.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Potent Limit-size Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryals, R.C.; Patel, S.; Acosta, C.; McKinney, M.; Pennesi, M.E.; Sahay, G. The effects of PEGylation on LNP based mRNA delivery to the eye. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Duncan, R.G.; Brigham, B.; Fishman, S.; Nair, J.K.; Akinc, A.; Barros, S.A.; Kasperkovitz, P.V. Shielding of Lipid Nanoparticles for siRNA Delivery: Impact on Physicochemical Properties, Cytokine Induction, and Efficacy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaridou, E.; Heyes, J.; Lutwyche, P. Lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery: Current perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154–155, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, A.; McClintock, K.; Phelps, J.R.; Maclachlan, I. Hypersensitivity and loss of disease site targeting caused by antibody responses to PEGylated liposomes. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Hihara, T.; Kubara, K.; Kondo, K.; Hyodo, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Ishida, T.; Ishihara, H. PEG shedding-rate-dependent blood clearance of PEGylated lipid nanoparticles in mice: Faster PEG shedding attenuates anti-PEG IgM production. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eygeris, Y.; Patel, S.; Jozic, A.; Sahay, G. Deconvoluting Lipid Nanoparticle Structure for Messenger RNA Delivery. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4543–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, R.W.; Felgner, P.L.; Verma, I.M. Cationic liposome-mediated RNA transfection [cationic lipid vesicies/N-[1-(2,3-dioleyloxy)propyl]-NNN-timethylammonium chloride (DOTMA)/translationj. Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6077–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dokka, S.; Toledo, D.; Shi, X.; Castranova, V.; Rojanasakul, Y. Oxygen Radical-Mediated Pulmonary Toxicity Induced by Some Cationic Liposomes. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, S.C.; Akinc, A.; Chen, J.; Sandhu, A.P.; Mui, B.L.; Cho, C.K.; Sah, D.W.Y.; Stebbing, D.; Crosley, E.J.; Yaworski, E.; et al. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, D.; Scherphof, G. Effect of fetal calf serum and serum protein fractions on the uptake of liposomal phosphatidylcholine by rat hepatocytes in primary monolayer culture. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 1979, 551, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonn, A.; Semple, S.; Cullis, P. Association of blood proteins with large unilamellar liposomes in vivo. Relation to circulation lifetimes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 18759–18765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filion, M.C.; Phillips, N.C. Toxicity and immunomodulatory activity of liposomal vectors formulated with cationic lipids toward immune effector cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 1997, 1329, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kedmi, R.; Ben-Arie, N.; Peer, D. The systemic toxicity of positively charged lipid nanoparticles and the role of Toll-like receptor 4 in immune activation. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6867–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonez, C.; Bessodes, M.; Scherman, D.; Vandenbranden, M.; Escriou, V.; Ruysschaert, J.-M. Cationic lipid nanocarriers activate Toll-like receptor 2 and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, S.; Kawai, A.; Shibuya, M.; Munakata, L.; Omata, D.; Suzuki, R.; Yoshioka, Y. Lipid Nanoparticle Acts as a Potential Adjuvant for Influenza Split Vaccine without Inducing Inflammatory Responses. Vaccines 2020, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Hyodo, M.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. A pH-sensitive cationic lipid facilitates the delivery of liposomal siRNA and gene silencing activity in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinc, A.; Maier, M.A.; Manoharan, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Jayaraman, M.; Barros, S.; Ansell, S.; Du, X.; Hope, M.J.; Madden, T.D.; et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J.; Cullis, P.R.; van der Meel, R. Lipid Nanoparticles Enabling Gene Therapies: From Concepts to Clinical Utility. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018, 28, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlich, M.; Palomba, R.; Costabile, G.; Mizrahy, S.; Pannuzzo, M.; Peer, D.; Decuzzi, P. Cytosolic delivery of nucleic acids: The case of ionizable lipid nanoparticles. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 6, e10213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.; Peel, S.E.; Schantz, A.; England, R.M.; Beano, M.; Bates, S.M.; Desai, A.S.; Puri, S.; Ashford, M.B.; Jones, A.T. Endocytic Profiling of Cancer Cell Models Reveals Critical Factors Influencing LNP-Mediated mRNA Delivery and Protein Expression. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1950–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, M.; Nawaz, M.; Papadimitriou, A.; Angerfors, A.; Camponeschi, A.; Na, M.; Hölttä, M.; Skantze, P.; Johansson, S.; Sundqvist, M.; et al. Linkage between endosomal escape of LNP-mRNA and loading into EVs for transport to other cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeffs, L.B.; Palmer, L.R.; Ambegia, E.G.; Giesbrecht, C.; Ewanick, S.; MacLachlan, I. A Scalable, Extrusion-Free Method for Efficient Liposomal Encapsulation of Plasmid DNA. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semple, S.C.; Klimuk, S.K.; Harasym, T.O.; Dos Santos, N.; Ansell, S.M.; Wong, K.F.; Maurer, N.; Stark, H.; Cullis, P.R.; Hope, M.J.; et al. Efficient encapsulation of antisense oligonucleotides in lipid vesicles using ionizable aminolipids: Formation of novel small multilamellar vesicle structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2001, 1510, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terada, T.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Huynh, A.; Chen, S.; Van Der Meel, R.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P.R. Characterization of Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Ionizable Cationic Lipids Using Design-of-Experiments Approach. Langmuir 2021, 37, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.; Pelc, R.; Muramatsu, H.; Andersen, H.; DeMaso, C.R.; Dowd, K.A.; Sutherland, L.L.; Scearce, R.M.; Parks, R.; et al. Zika virus protection by a single low-dose nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccination. Nature 2017, 543, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; LaBranche, C.C.; Ferrari, G.; Cain, D.W.; Tombácz, I.; Parks, R.J.; Muramatsu, H.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Karikó, K.; et al. Characterization of HIV-1 Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Vaccines in Rabbits and Rhesus Macaques. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Naradikian, M.S.; Parkhouse, K.; Cain, D.W.; Jones, L.; Moody, M.A.; Verkerke, H.P.; Myles, A.; Willis, E.; et al. Nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines induce potent T follicular helper and germinal center B cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1571–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richner, J.; Himansu, S.; Dowd, K.A.; Butler, S.L.; Salazar, V.; Fox, J.; Julander, J.G.; Tang, W.; Shresta, S.; Pierson, T.C.; et al. Modified mRNA Vaccines Protect against Zika Virus Infection. Cell 2017, 168, 1114–1125.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahl, K.; Senn, J.J.; Yuzhakov, O.; Bulychev, A.; Brito, L.A.; Hassett, K.J.; Laska, M.E.; Smith, M.; Almarsson, O.; Thompson, J.; et al. Preclinical and Clinical Demonstration of Immunogenicity by mRNA Vaccines against H10N8 and H7N9 Influenza Viruses. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, F.; Lindgren, G.; Lin, A.; Thompson, E.A.; Ols, S.; Röhss, J.; John, S.; Hassett, K.; Yuzhakov, O.; Bahl, K.; et al. Efficient Targeting and Activation of Antigen-Presenting Cells In Vivo after Modified mRNA Vaccine Administration in Rhesus Macaques. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2635–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.; Ashwanikumar, N.; Robinson, E.; DuRoss, A.; Sun, C.; Murphy-Benenato, K.E.; Mihai, C.; Almarsson, Ö.; Sahay, G. Boosting Intracellular Delivery of Lipid Nanoparticle-Encapsulated mRNA. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5711–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, S.; Yuzhakov, O.; Woods, A.; Deterling, J.; Hassett, K.; Shaw, C.A.; Ciaramella, G. Multi-antigenic human cytomegalovirus mRNA vaccines that elicit potent humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Tuyishime, S.; Muramatsu, H.; Kariko, K.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Madden, T.D.; Hope, M.J.; Weissman, D. Expression kinetics of nucleoside-modified mRNA delivered in lipid nanoparticles to mice by various routes. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassett, K.J.; Benenato, K.E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B.M.; Ketova, T.; et al. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular Administration of mRNA Vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, L.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Delcassian, D.; Chahal, J.; Han, J.; Shi, Y.; Sadtler, K.; Gao, W.; Lin, J.; et al. Delivery of mRNA vaccines with heterocyclic lipids increases anti-tumor efficacy by STING-mediated immune cell activation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Apoprotein E as a lipid transport and signaling protein in the blood, liver, and artery wall. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S156–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauser, P.S.; Narayanaswami, V.; Ryan, R.O. Apolipoprotein E: From lipid transport to neurobiology. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastiani, F.; Yanez Arteta, M.; Lerche, M.; Porcar, L.; Lang, C.; Bragg, R.A.; Elmore, C.S.; Krishnamurthy, V.R.; Russell, R.A.; Darwish, T.; et al. Apolipoprotein E Binding Drives Structural and Compositional Rearrangement of mRNA-Containing Lipid Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6709–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinc, A.; Querbes, W.; De, S.; Qin, J.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Jayaprakash, K.N.; Jayaraman, M.; Rajeev, K.G.; Cantley, W.L.; Dorkin, J.R.; et al. Targeted Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics with Endogenous and Exogenous Ligand-Based Mechanisms. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Farbiak, L.; Johnson, L.T.; Dilliard, S.A.; Siegwart, D.J. Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas gene editing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranz, L.; Diken, M.; Haas, H.; Kreiter, S.; Loquai, C.; Reuter, K.C.; Meng, M.; Fritz, D.; Vascotto, F.; Hefesha, H.; et al. Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2016, 534, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.B.; Zhang, S.; Kos, P.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, K.; Perelman, S.S.; Zhu, H.; Siegwart, D.J. Non-Viral CRISPR/Cas Gene Editing In Vitro and In Vivo Enabled by Synthetic Nanoparticle Co-Delivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 56, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fehring, V.; Schaeper, U.; Ahrens, K.; Santel, A.; Keil, O.; Eisermann, M.; Giese, K.; Kaufmann, J. Delivery of Therapeutic siRNA to the Lung Endothelium via Novel Lipoplex Formulation DACC. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Yu, X.; Johnson, L.T.; Farbiak, L.; Siegwart, D.J. Membrane-destabilizing ionizable phospholipids for organ-selective mRNA delivery and CRISPR—Cas gene editing. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jeong, M.; Hur, S.; Cho, Y.; Park, J.; Jung, H.; Seo, Y.; Woo, H.A.; Nam, K.T.; Lee, K.; et al. Engineered ionizable lipid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of RNA therapeutics into different types of cells in the liver. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Kanasty, R.L.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Vegas, A.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Anderson, D.G. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, D.; Gutkin, A.; Kedmi, R.; Ramishetti, S.; Veiga, N.; Jacobi, A.M.; Schubert, M.S.; Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Cohen, Z.R.; Behlke, M.A.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing using targeted lipid nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedmi, R.; Veiga, N.; Ramishetti, S.; Goldsmith, M.; Rosenblum, D.; Dammes, N.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Nahary, L.; Leviatan-Ben-Arye, S.; Harlev, M.; et al. A modular platform for targeted RNAi therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, N.; Kimmig, R.; Lang, S.; Singh, M.; Brandau, S. Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibodies overcome resistance of ovarian cancer cells to targeted therapy and natural cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12000–12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, S.; Wei, T.; Cheng, Q.; Siegwart, D.J. Theranostic dendrimer-based lipid nanoparticles containing PEGylated BODIPY dyes for tumor imaging and systemic mRNA delivery in vivo. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Kos, P.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, K.; Miller, J.B.; Elkassih, S.; Siegwart, D.J. Activatable Water-Soluble Probes Enhance Tumor Imaging by Responding to Dysregulated pH and Exhibiting High Tumor-to-Liver Fluorescence Emission Contrast. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zuo, H.; Yan, Y.; Occhialini, G.; Zhou, K.; Wan, Y.; Siegwart, D.J. High-Contrast Fluorescence Detection of Metastatic Breast Cancer Including Bone and Liver Micrometastases via Size-Controlled pH-Activatable Water-Soluble Probes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krienke, C.; Kolb, L.; Diken, E.; Streuber, M.; Kirchhoff, S.; Bukur, T.; Akilli-Öztürk, O.; Kranz, L.M.; Berger, H.; Petschenka, J.; et al. A noninflammatory mRNA vaccine for treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science 2021, 371, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Turley, D.M.; Podojil, J.R. Antigen-specific tolerance strategies for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Ludwig, J.; Weissman, D. Generating the optimal mRNA for therapy: HPLC purification eliminates immune activation and improves translation of nucleoside-modified, protein-encoding mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veiga, N.; Goldsmith, M.; Granot, Y.; Rosenblum, D.; Dammes, N.; Kedmi, R.; Ramishetti, S.; Peer, D. Cell specific delivery of modified mRNA expressing therapeutic proteins to leukocytes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magadum, A.; Kurian, A.A.; Chepurko, E.; Sassi, Y.; Hajjar, R.J.; Zangi, L. Specific Modified mRNA Translation System. Circulation 2020, 142, 2485–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Yalcin, A.; Meyer, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of Tissue-Specific MicroRNAs from Mouse. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callis, T.E.; Pandya, K.; Seok, H.Y.; Tang, R.; Tatsuguchi, M.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.-F.; Deng, Z.; Gunn, B.; Shumate, J.; et al. MicroRNA-208a is a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and conduction in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2772–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tam, Y.K.; Madden, T.D.; Hope, M.J. Pieter Cullis’ quest for a lipid-based, fusogenic delivery system for nucleic acid therapeutics: Success with siRNA so what about mRNA? J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, K.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Yang, J.H.; Heartlein, M.W.; DeRosa, F.; Mir, F.F.; Fenton, O.S.; Anderson, D.G. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations for mRNA Delivery in Vivo with Fractional Factorial and Definitive Screening Designs. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 7300–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Luo, X.; Deng, B.; Wang, J.; McComb, D.W.; Shi, Y.; Gaensler, K.M.L.; Tan, X.; Dunn, A.; Kerlin, B.; et al. An Orthogonal Array Optimization of Lipid-like Nanoparticles for mRNA Delivery in Vivo. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8099–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashby, B. pH Studies in human malignant tumours. Lancet 1966, 288, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, I.F.; Rotin, D. Acid pH in tumors and its potential for therapeutic exploitation. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 4373–4384. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Dong, Z.; Tao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. The acidic tumor microenvironment: A target for smart cancer nano-theranostics. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 5, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).