Acoustic and Elastic Properties of a Blood Clot during Microbubble-Enhanced Sonothrombolysis: Hardening of the Clot with Inertial Cavitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Human Blood Clots
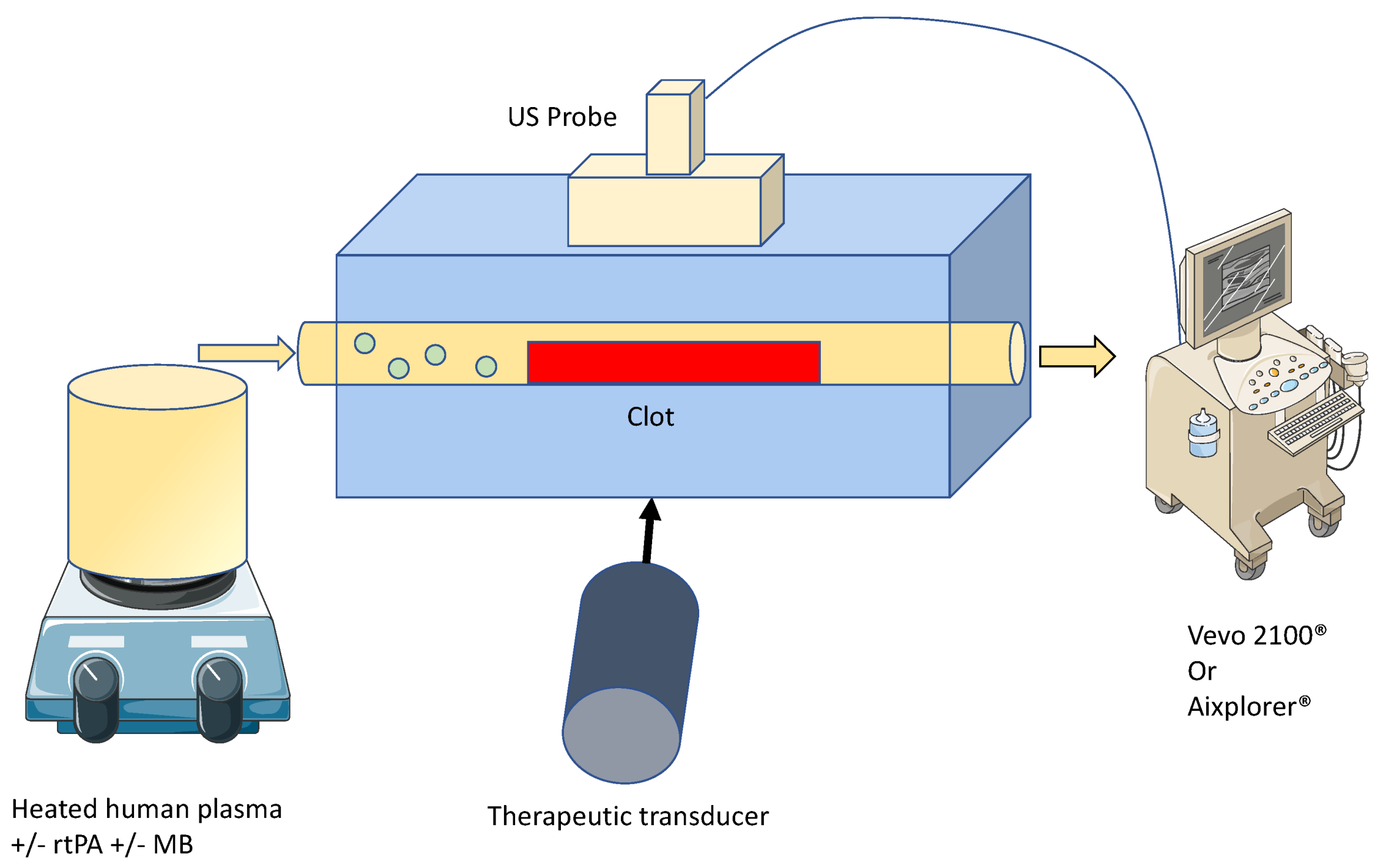
2.2. Ultrasound Thrombolysis Setup
2.3. In-Vitro rtPA Delivery
2.4. Sonothrombolysis
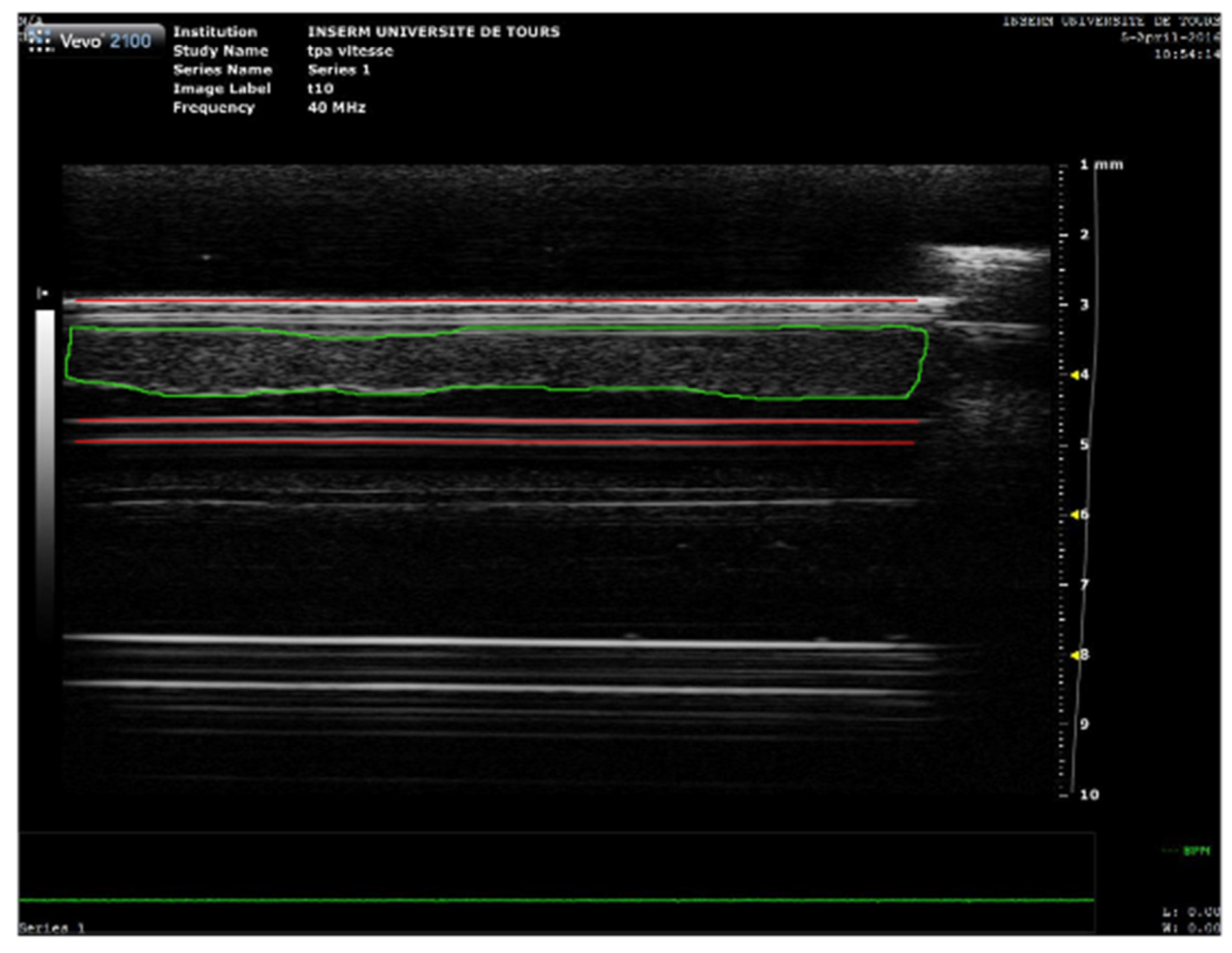
2.5. High Frequency Ultrasound Imaging and SoS Measurement
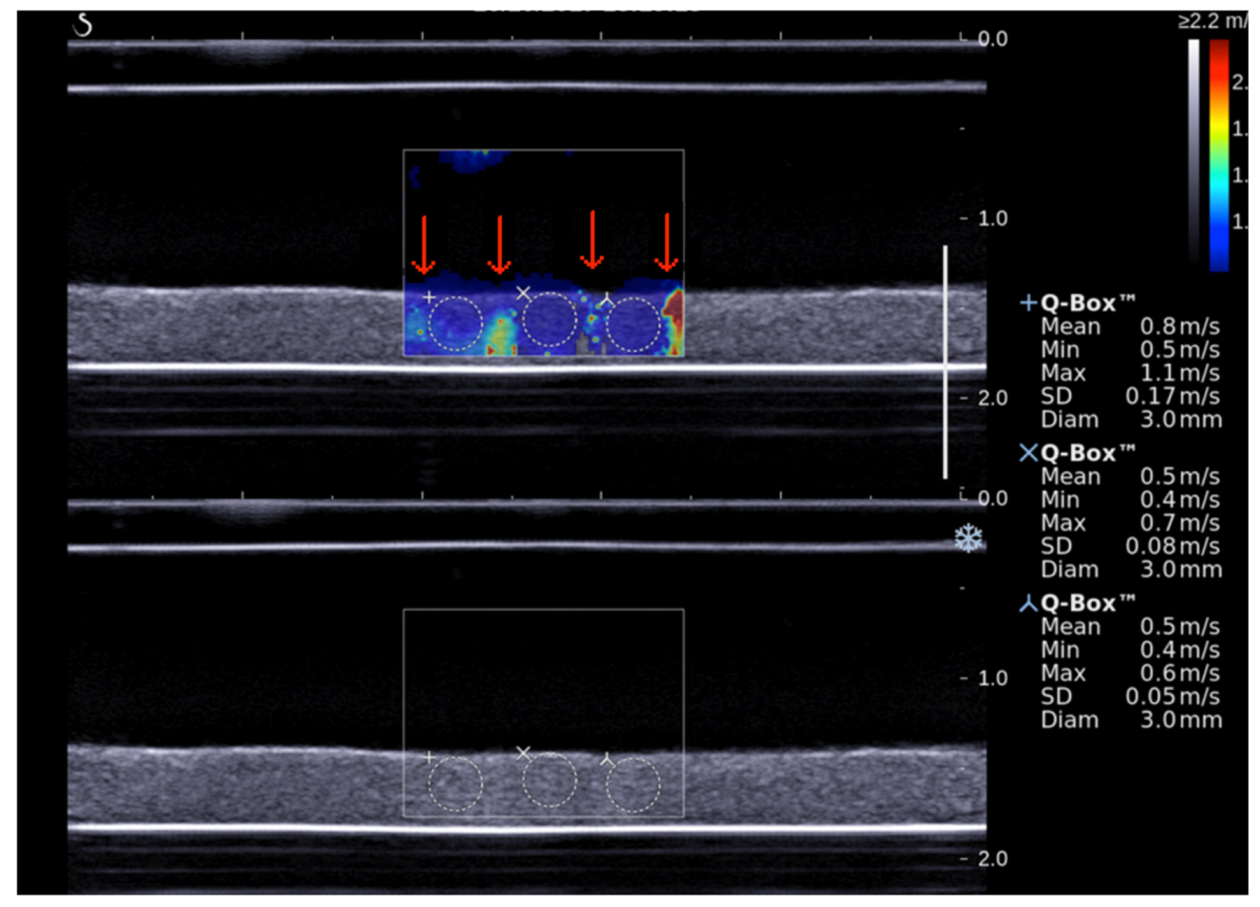
2.6. Shear Wave Elastography Imaging
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
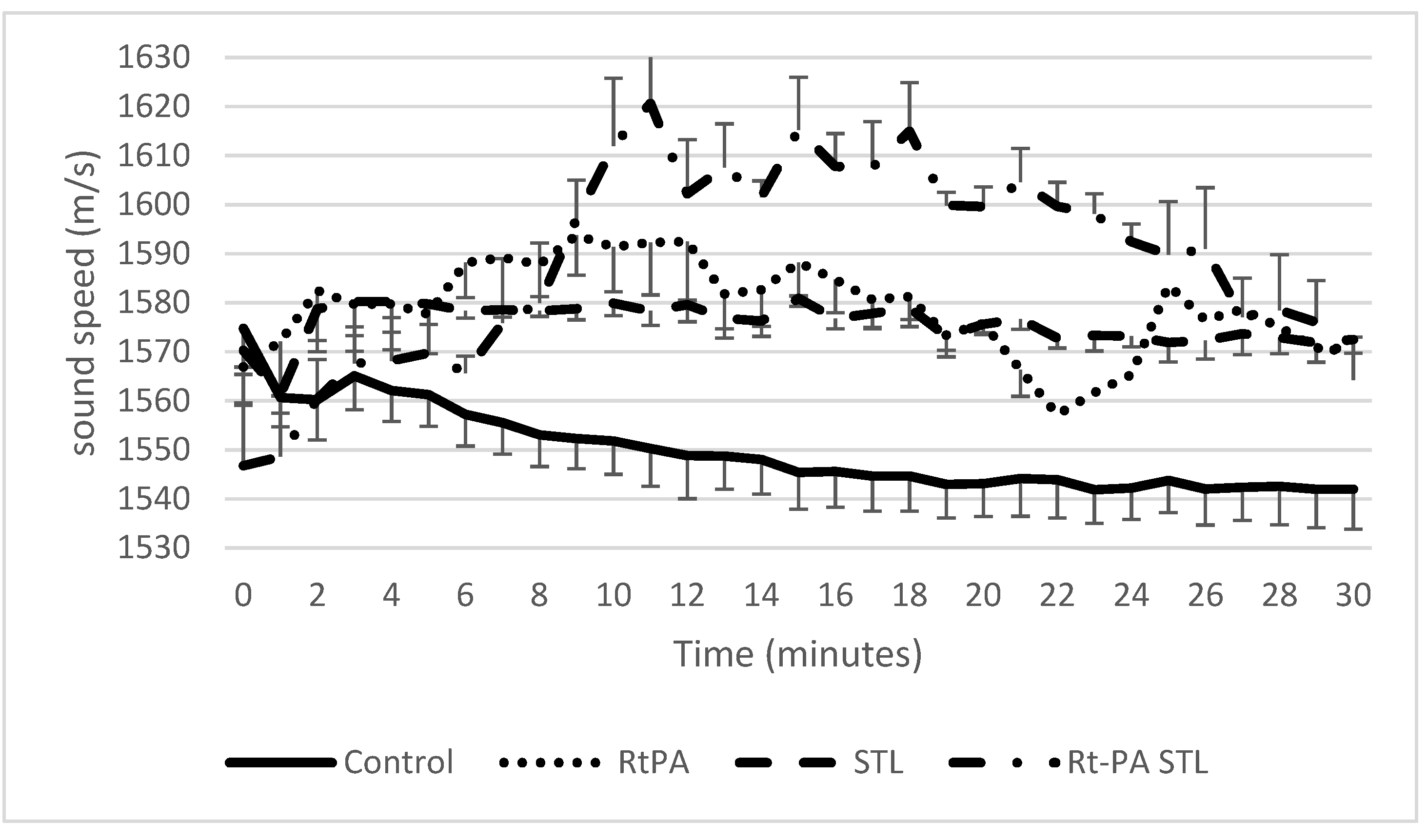
3.1. Sound Speed Measurement during Sonothrombolysis
3.2. Assessment of SWS during Sonothrombolysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Saver, J.L. Time Is Brain—Quantified. Stroke 2006, 37, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Acute Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saver, J.L.; Goyal, M.; Bonafe, A.; Diener, H.-C.; Levy, E.I.; Pereira, V.M.; Albers, G.W.; Cognard, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Hacke, W.; et al. Stent-Retriever Thrombectomy after Intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA Alone in Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bracard, S.; Ducrocq, X.; Mas, J.L.; Soudant, M.; Oppenheim, C.; Moulin, T.; Guillemin, F. Mechanical thrombectomy after intravenous alteplase versus alteplase alone after stroke (THRACE): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Bluhmki, E.; Brozman, M.; Dávalos, A.; Guidetti, D.; Larrue, V.; Lees, K.R.; Medeghri, Z.; Machnig, T.; et al. Thrombolysis with Alteplase 3 to 4.5 Hours after Acute Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tachibana, K.; Tachibana, S. Albumin Microbubble Echo-Contrast Material as an Enhancer for Ultrasound Accelerated Thrombolysis. Circulation 1995, 92, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, S.; Dinia, L.; Del Sette, M.; Anzola, P.; Mazzoli, T.; Cenciarelli, S.; Gandolfo, C. Sonothrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libgot-Callé, R.; Ossant, F.; Gruel, Y.; Lermusiaux, P.; Patat, F. High Frequency Ultrasound Device to Investigate the Acoustic Properties of Whole Blood during Coagulation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennisson, J.-L.; Lerouge, S.; Cloutier, G. Assessment by transient elastography of the viscoelastic properties of blood during clotting. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auboire, L.; Escoffre, J.-M.; Fouan, D.; Jacquet, J.-R.; Ossant, F.; Grégoire, J.-M.; Bouakaz, A. Evaluation of high resolution ultrasound as a tool for assessing the 3D volume of blood clots during in vitro thrombolysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishida, H.; Shibuya, M.; Endo, M.; Koyanagi, H. Simple Evaluation Method of Biocompatibility of Artificial Oxygenator Hollow Fiber. Artif. Organs 2008, 20, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Flaud, P.; Tanter, M. Shear Wave Elastography Quantification of Blood Elasticity during Clotting. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoffre, J.; Kaddur, K.; Rols, M.; Bouakaz, A. In Vitro Gene Transfer by Electrosonoporation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1746–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanswell, P.; Tebbe, U.; Neuhaus, K.-L.; Gläsle-Schwarz, L.; Wojcik, J.; Seifried, E. Pharmacokinetics and fibrin specificity of alteplase during accelerated infusions in acute myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1992, 19, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auboire, L.; Tranquart, F.; Ossant, F.; Sennoga, C.; Bouakaz, A. Impact of Sonothrombolysis on in vitro Blood Clot: Pictographic Validation with Electron Microscopy. Ultraschall Med. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2015, 38, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, B.; Bohren, Y.; Gaud, E.; Bussat, P.; Arditi, M.; Yan, F.; Tranquart, F.; Allémann, E. Sonothrombolysis: The Contribution of Stable and Inertial Cavitation to Clot Lysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahirnyak, V.M.; Yoon, S.W.; Holland, C.K. Acousto-mechanical and thermal properties of clotted blood. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 3766–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y.; Shau, Y.-W.; Wang, C.-L. An Artifact in Supersonic Shear Wave Elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvazyan, A.P.; Rudenko, O.; Swanson, S.D.; Fowlkes, J.; Emelianov, S. Shear wave elasticity imaging: A new ultrasonic technology of medical diagnostics. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1998, 24, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Flaud, P.; Tanter, M. Correlation between Classical Rheometry and Supersonic Shear Wave Imaging in Blood Clots. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 2123–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jen, C.J.; McIntire, L.V. The structural properties and contractile force of a clot. Cell Motil. 1982, 2, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, K.; Itoh, K.; Ookawara, S.; Taniguchi, N.; Omoto, K. The Effects of Levovist and DD-723 in Activating Platelets and Damaging Hepatic Cells of Rats. J. Ultrasound Med. 2005, 24, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.; Le Guennec, J.Y.; Bougnoux, P.; Tranquart, F.; Bouakaz, A. Characterization of cell membrane response to ultrasound activated microbubbles. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2008, 55, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plag, C.; Mofid, Y.; Mateéo, T.; Callé, R.; Ossant, F. High frequency ultrasound imaging of whole blood gelation and retraction duringin vitrocoagulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 4196–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, A.L.; Alwis, I.; MacLean, J.A.A.; Priyananda, P.; Hawkett, B.; Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Jackson, S.P. Endogenous fibrinolysis facilitates clot retraction in vivo. Blood 2017, 130, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.V.; Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W.; Alber, M.S. Structural basis for the nonlinear mechanics of fibrin networks under compression. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6739–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braaten, J.V.; A Goss, R.; Francis, C.W. Ultrasound Reversibly Disaggregates Fibrin Fibers. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalker, T.J.; Welsh, J.D.; Tomaiuolo, M.; Wu, J.; Colace, T.V.; Diamond, S.L.; Brass, L.F. A systems approach to hemostasis: Thrombus consolidation regulates intrathrombus solute transport and local thrombin activity. Blood 2014, 124, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Bridge, K.; Philippou, H.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Clot properties and cardiovascular disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Shekhar, K.P.; Kleven, R.T.; Rivera, H.A.; Lewis, R.; Karani, K.B.; Vos, H.J.; Abruzzo, T.A.; Haworth, K.J.; Holland, C.K. Effect of Clot Stiffness on Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Lytic Susceptibility in Vitro. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2710–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebeskind, D.S.; Sanossian, N.; Yong, W.H.; Starkman, S.; Tsang, M.; Moya, A.L.; Zheng, D.D.; Abolian, A.M.; Kim, D.; Ali, L.K.; et al. CT and MRI Early Vessel Signs Reflect Clot Composition in Acute Stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Undas, A. Fibrin clot properties and their modulation in thrombotic disorders. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
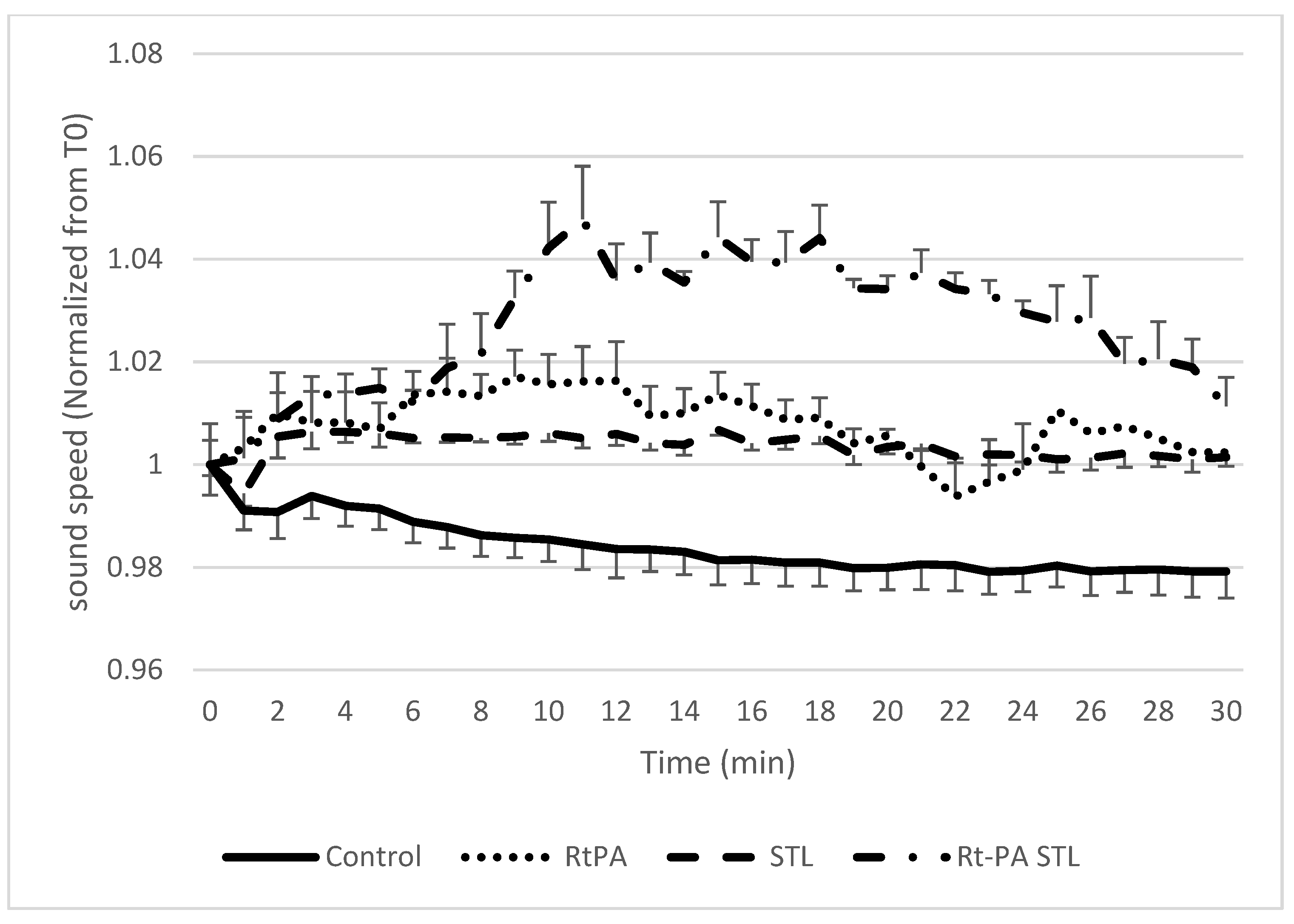
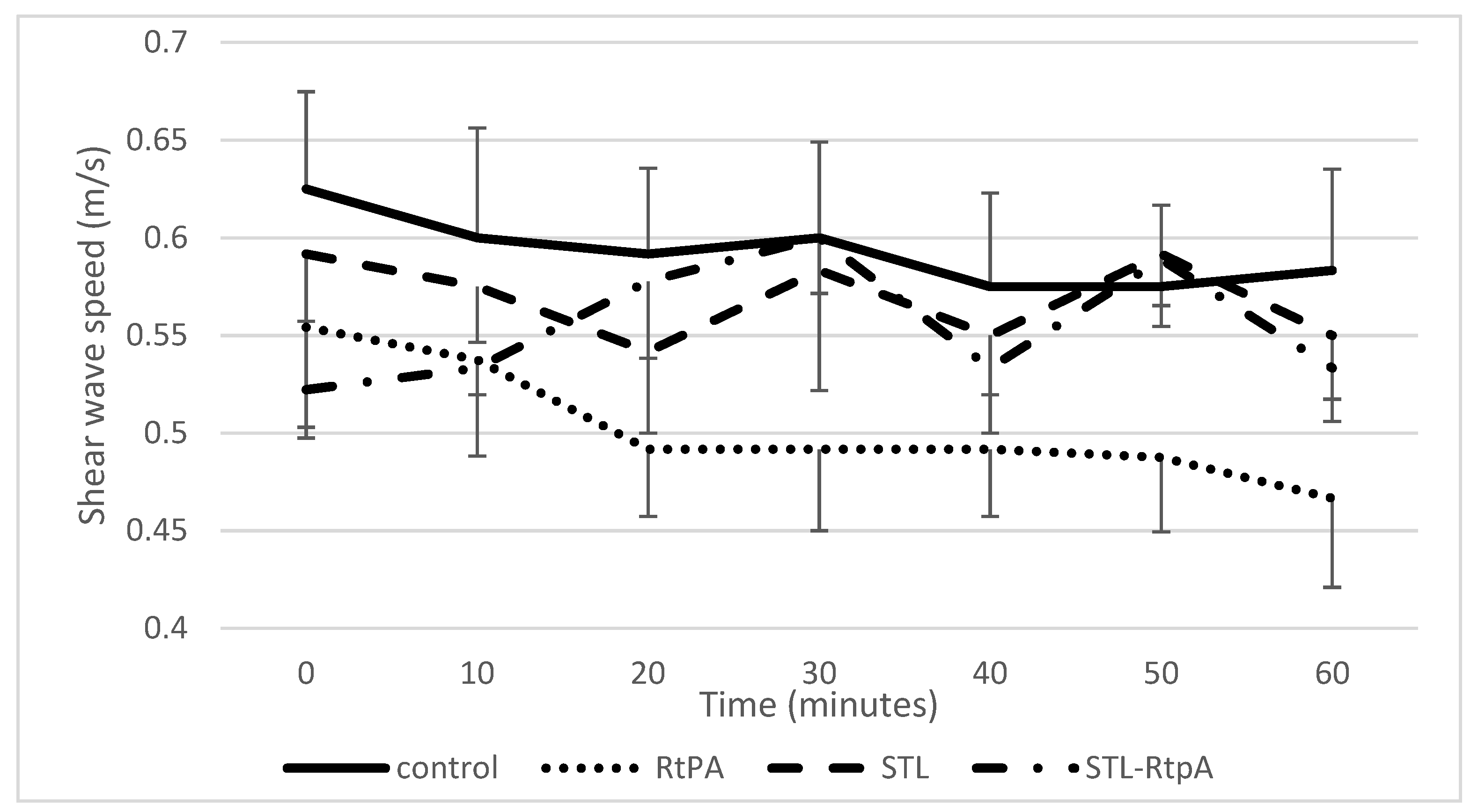
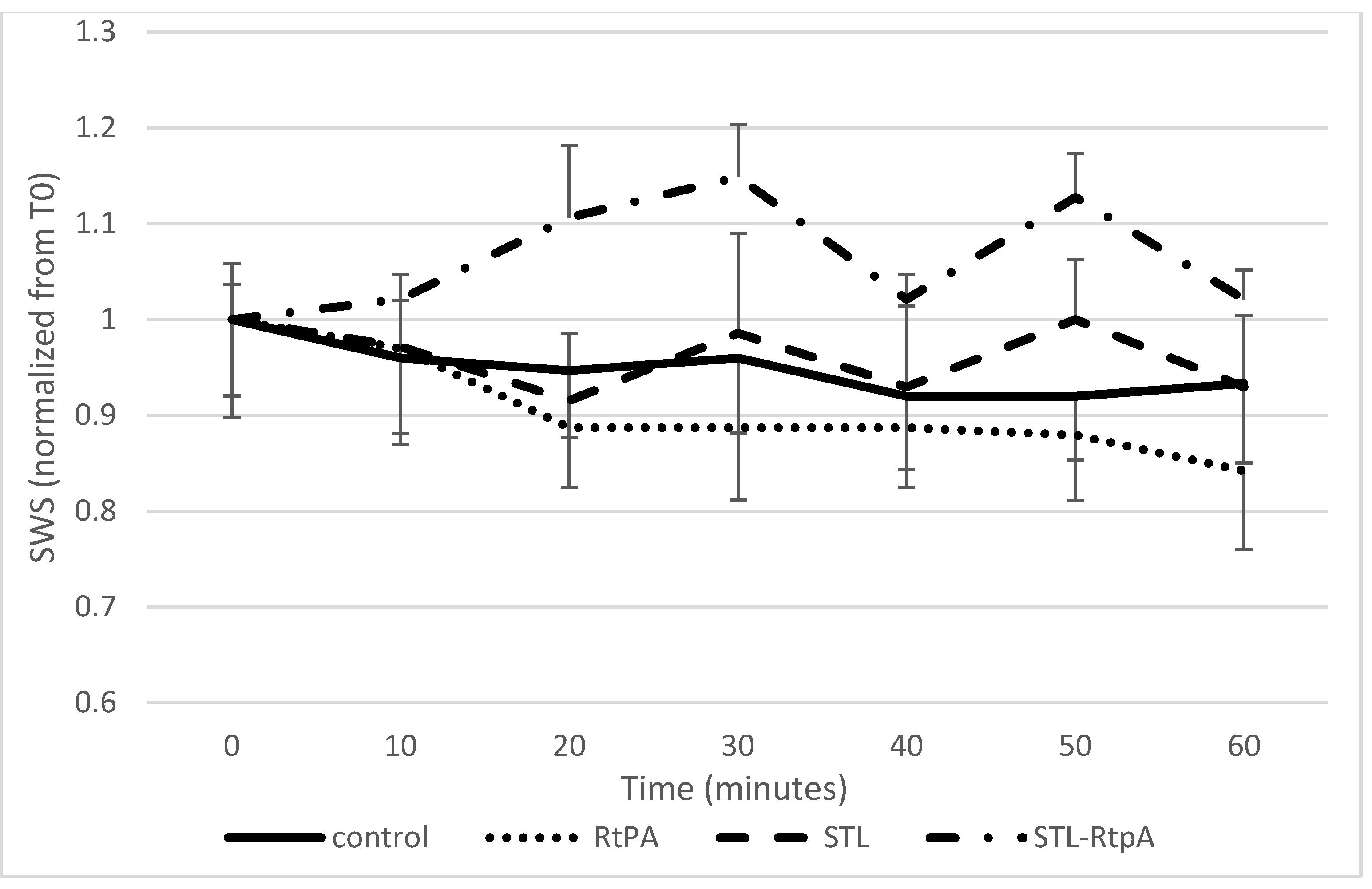
| High Frequency Ultrasound Imaging (SoS Setup) | Shear Wave Elastography Imaging (SWS Setup) | |
| Internal diameter of tube (mm) | 1.6 | 3.2 |
| Volume of recalcified human plasma (mL) | 15 | 45 |
| Constant flow (mL/min) | 30 | 100 |
| Duration of treatment (min) | 30 | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Auboire, L.; Fouan, D.; Grégoire, J.-M.; Ossant, F.; Plag, C.; Escoffre, J.-M.; Bouakaz, A. Acoustic and Elastic Properties of a Blood Clot during Microbubble-Enhanced Sonothrombolysis: Hardening of the Clot with Inertial Cavitation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101566
Auboire L, Fouan D, Grégoire J-M, Ossant F, Plag C, Escoffre J-M, Bouakaz A. Acoustic and Elastic Properties of a Blood Clot during Microbubble-Enhanced Sonothrombolysis: Hardening of the Clot with Inertial Cavitation. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(10):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101566
Chicago/Turabian StyleAuboire, Laurent, Damien Fouan, Jean-Marc Grégoire, Fréderic Ossant, Camille Plag, Jean-Michel Escoffre, and Ayache Bouakaz. 2021. "Acoustic and Elastic Properties of a Blood Clot during Microbubble-Enhanced Sonothrombolysis: Hardening of the Clot with Inertial Cavitation" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 10: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101566
APA StyleAuboire, L., Fouan, D., Grégoire, J.-M., Ossant, F., Plag, C., Escoffre, J.-M., & Bouakaz, A. (2021). Acoustic and Elastic Properties of a Blood Clot during Microbubble-Enhanced Sonothrombolysis: Hardening of the Clot with Inertial Cavitation. Pharmaceutics, 13(10), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101566







