Deleterious Effects of Ethanol, Δ(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and Their Combination on the Spatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility in Adolescent and Adult Male Rats in the Barnes Maze Task
Abstract
1. Introduction
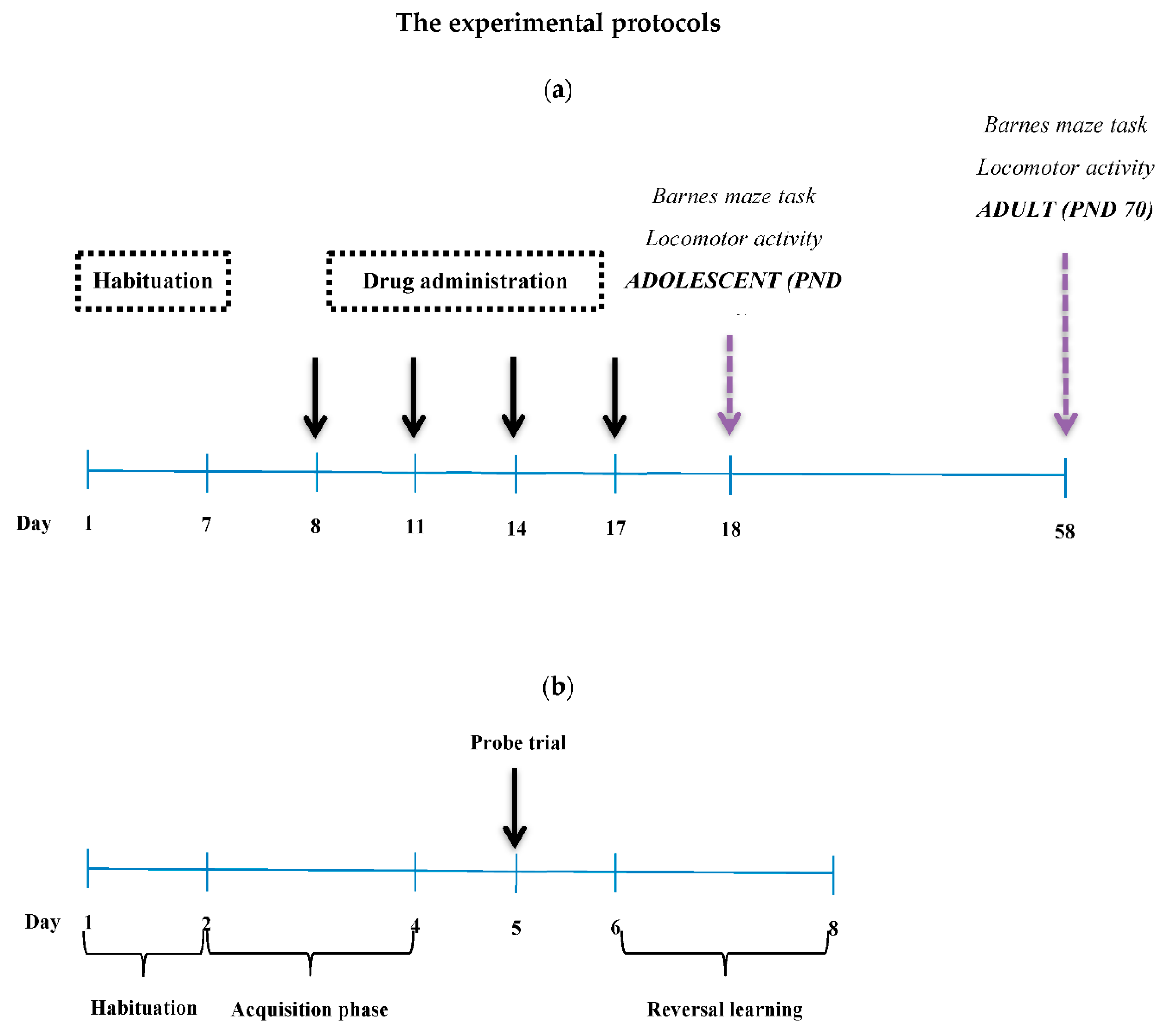
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
2.2.1. Barnes Maze Task
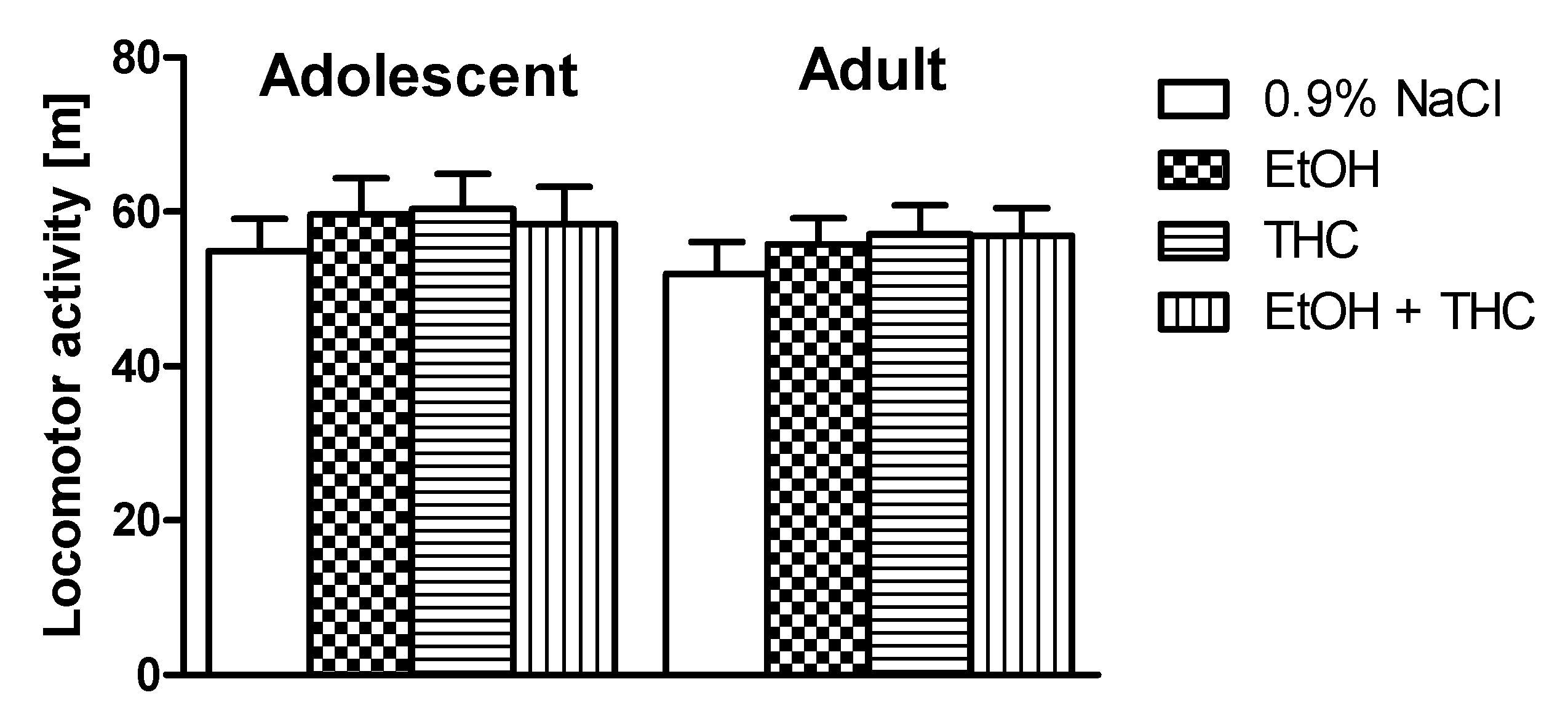
2.2.2. Horizontal Locomotor Activity Test
2.2.3. Experiment 1
2.2.4. Experiment 2
2.2.5. Experiment 3
2.2.6. Experiment 4
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
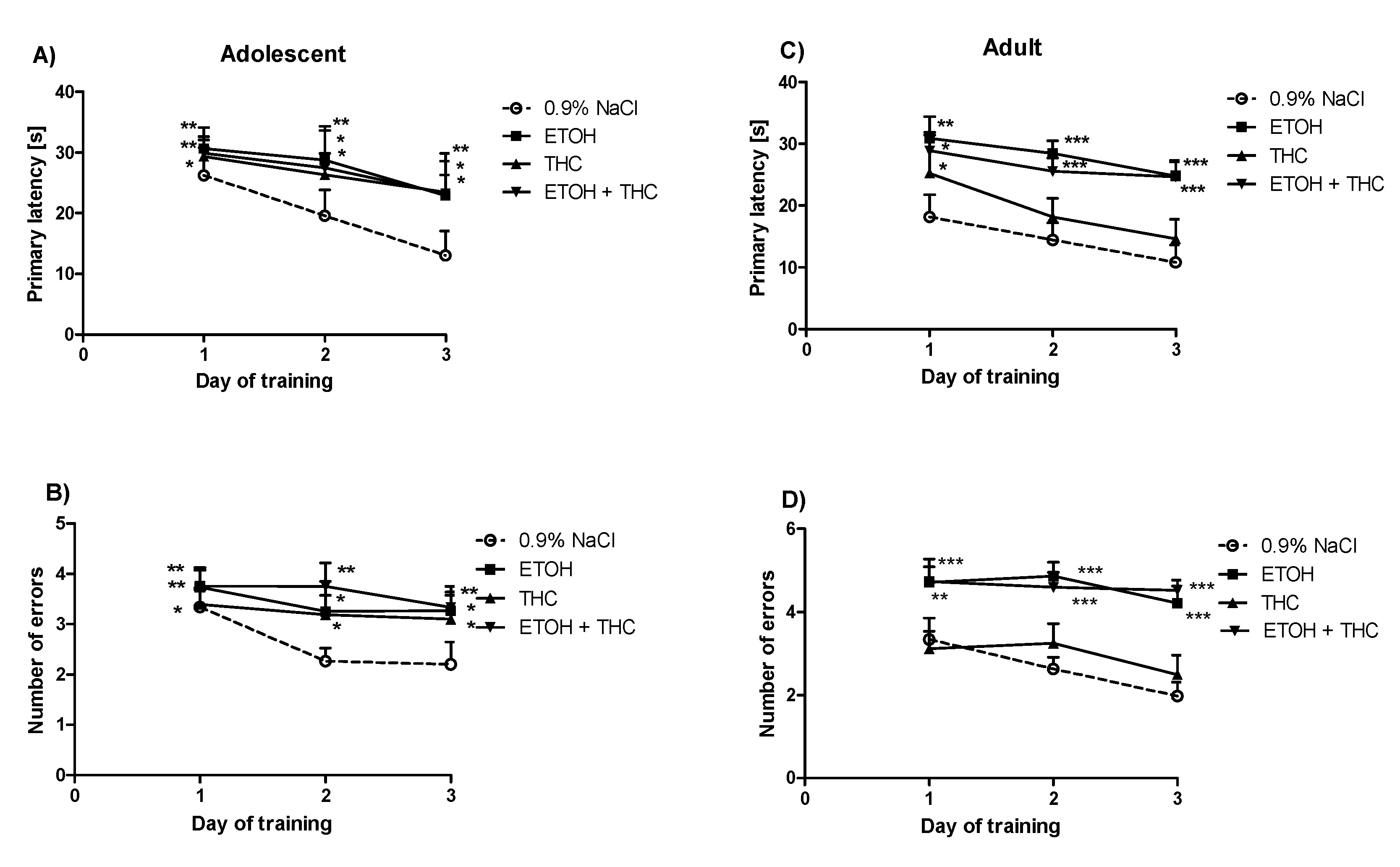
3.1. Experiment 1
3.2. Experiment 2
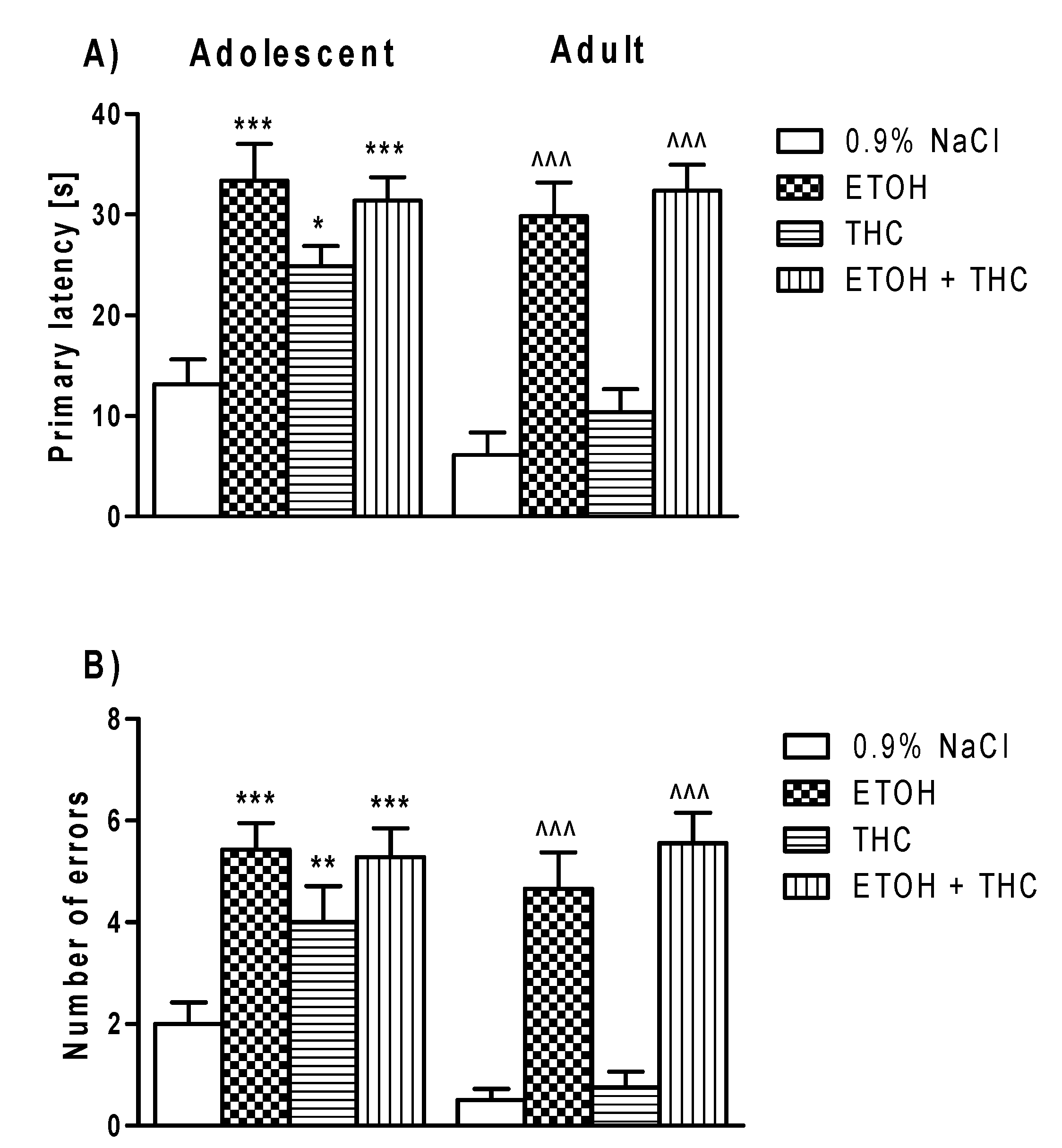
3.3. Experiment 3
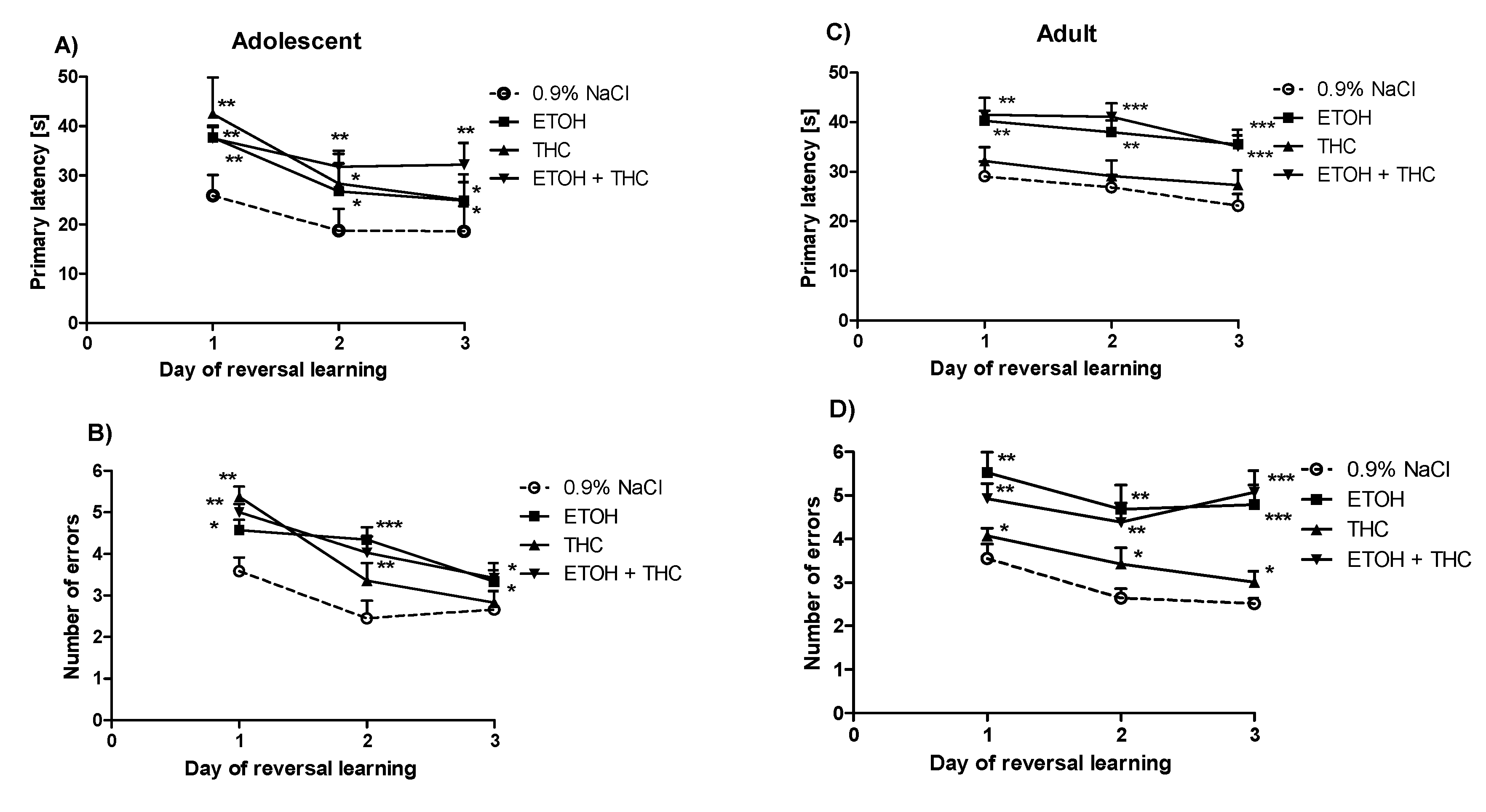
3.4. Experiment 4
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Midanik, L.T.; Tam, T.W.; Weisner, C. Concurrent and simultaneous drug and alcohol use: Results of the 2000 National Alcohol Survey. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007, 90, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewit, D.J.; Adlaf, E.M.; Offord, D.R.; Ogborne, A.C. Age at First Alcohol Use: A Risk Factor for the Development of Alcohol Disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewit, D.J.; Hance, J.; Offord, D.R.; Ogborne, A. The Influence of Early and Frequent Use of Marijuana on the Risk of Desistance and of Progression to Marijuana-Related Harm. Prev. Med. 2000, 31, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, S.; Komaki, A.; Shahidi, S.; Sarihi, A.; Mirazi, N.; Salehi, I. Effects of cannabinoid and glutamate receptor antagonists and their interactions on learning and memory in male rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 131, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenreich, H.; Kunert, H.J.; Moeller, M.R.; Poser, W.; Schilling, L.; Gigerenzer, G.; Hoehe, M.R.; Rinn, T. Specific attentional dysfunction in adults following early start of cannabis use. Psychopharmacology 1999, 142, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, G.; Davies, S.N. Cannabinoid function in learning, memory and plasticity. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2005, 168, 445–477. [Google Scholar]
- Fife, T.D.; Moawad, H.; Moschonas, C.; Shepard, K.M.; Hammond, N. Clinical perspectives on medical marijuana (cannabis) for neurologic disorders. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2015, 5, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, H.R.; Matsumoto, I.; Callaghan, P.D.; Long, L.E.; Arnold, J.C.; Gunasekaran, N.; Thompson, M.R.; Dawson, B.; Mallet, P.E.; Kashem, M.A.; et al. Adolescent rats find repeated Delta(9)-THC less aversive than adult rats but display greater residual cognitive deficits and changes in hippocampal protein expression following exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, N.L.T.; Greenleaf, A.L.R.; Acheson, S.K.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S.; Kuhn, C.M. Role of cannabinoid receptor type 1 desensitization in greater tetrahydrocannabinol impairment of memory in adolescent rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, T.; Vigano’, D.; Realini, N.; Guidali, C.; Braida, D.; Capurro, V.; Castiglioni, C.; Cherubino, F.; Romualdi, P.; Candeletti, S.; et al. Chronic delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol during adolescence provokes sex-dependent changes in the emotional profile in adult rats: Behavioral and biochemical correlates. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 2760–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellgren, M.; Spano, S.M.; Hurd, Y.L. Adolescent Cannabis Exposure Alters Opiate Intake and Opioid Limbic Neuronal Populations in Adult Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 32, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopponi, S.; Soverchia, L.; Ubaldi, M.; Cippitelli, A.; Serpelloni, G.; Ciccocioppo, R. Chronic THC during adolescence increases the vulnerability to stress-induced relapse to heroin seeking in adult rats. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsauer, P.; Daniel, J.M.; Filipeanu, C.M.; Leonard, S.T.; Hulst, J.L.; Rodgers, S.P.; Lassen-Greene, C.L.; Sutton, J.L. Long-term behavioral and pharmacodynamic effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in female rats depend on ovarian hormone status. Addict. Boil. 2011, 16, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, S.; Takahashi, R.N. SR 141716A prevents delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced spatial learning deficit in a Morris-type water maze in mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Boil. Psychiatry 2002, 26, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, F.; Ottani, A.; Vivoli, R.; Giuliani, D. Learning Impairment Produced in Rats by the Cannabinoid Agonist HU 210 in a Water-Maze Task. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1999, 64, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, T.; Realini, N.; Braida, D.; Guidi, S.; Capurro, V.; Viganò, D.; Guidali, C.; Pinter, M.; Sala, M.; Bartesaghi, R.; et al. Changes in hippocampal morphology and neuroplasticity induced by adolescent THC treatment are associated with cognitive impairment in adulthood. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvel, S.A.; Hamm, R.J.; Martin, B.R.; Lichtman, A.H. Differential effects of delta 9-THC on spatial reference and working memory in mice. Psychopharmacology 2001, 157, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, J.; Andrysiak, T.; Ungerleider, J.; Löfroth, G.; Hefner, E.; Alfheim, I.; Mooller, M. Cognition and long-term use of ganja (Cannabis). Science 1981, 213, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, N.A.; Taib, C.N.M.; Moklas, M.A.M.; Basir, R. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9-THC) Induce Neurogenesis and Improve Cognitive Performances of Male Sprague Dawley Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 33, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwiese, B.J.; Acheson, S.K.; Levin, E.D.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Differential effects of ethanol on memory in adolescent and adult rats. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyapali, G.K.; Turner, D.A.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H. Age and Dose-Dependent Effects of Ethanol on the Induction of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. Alcohol 1999, 19, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzwelder, N.A.; Risher, M.L.; Abdelwahab, S.H.; D’Abo, A.; Rezvani, A.H.; Levin, E.D.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S.; Acheson, S.K. Effects of ethanol, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or their combination on object recognition memory and object preference in adolescent and adult male rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 527, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, P.J.; Kuhn, C.M.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Differential Effects of Ethanol in Adolescent and Adult Rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shram, M.J.; Bahroos, M.; Beleskey, J.I.; Tampakeras, M.; Lê, A.D.; Tomkins, D.M. Motor Impairing Effects of Ethanol and Diazepam in Rats Selectively Bred for High and Low Ethanol Consumption in a Limited-Access Paradigm. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheson, S.K.; Stein, R.M.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Impairment of semantic and figural memory by acute ethanol: Age-dependent effects. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccocioppo, R.; Martin-Fardon, R.; Weiss, F. Effect of selective blockade of mu(1) or delta opioid receptors on reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 27, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.B.; Ilgen, M.; White, A.M.; Best, P.J. Acute Ethanol Administration Impairs Spatial Performance While Facilitating Nonspatial Performance in Rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 1999, 72, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Braun, C.J.; Hoplight, B.; Switzer, R.C., III; Knapp, D.J. Binge ethanol consumption causes differential brain damage in young adolescent rats compared with adult rats. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, W.A. Are binge drinkers more at risk of developing brain damage? Alcohol 1993, 10, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.M.; Ghia, A.J.; Levin, E.D.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Binge pattern ethanol exposure in adolescent and adult rats: Differential impact on subsequent responsiveness to ethanol. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.M.; Matthews, U.B.; Best, P.J. Ethanol, memory, and hippocampal function: A review of recent findings. Hippocampus 2000, 10, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoglia, A.E.; Holstein, S.E.; Eastman, V.R.; Hodge, C.W. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor inhibition blunts adolescent-typical increased binge alcohol and sucrose consumption in male C57BL/6J mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2016, 143, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson-Redmond, A.N.; Guindon, J.; Morgan, D.J. Roles for the endocannabinoid system in ethanol-motivated behavior. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Boil. Psychiatry 2015, 65, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, D.J.; Henderson-Redmond, A.N.; Gonek, M.; Zee, M.L.; Farnsworth, J.C.; Amin, R.A.; Andrews, M.-J.; Davis, B.J.; Mackie, K.; Morgan, D.J. Mice expressing a “hyper-sensitive” form of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1) show modestly enhanced alcohol preference and consumption. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzschentke, T.M. Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference paradigm: A comprehensive review of drug effects, recent progress and new issues. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 613–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.M.; White, A.M.; Kuhn, C.M.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Differential effects of delta9-THC on learning in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 83, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm-Sapyta, N.L.; Cha, Y.M.; Chaudhry, S.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S.; Kuhn, C.M. Differential anxiogenic, aversive, and locomotor effects of THC in adolescent and adult rats. Psychopharmacology 2007, 191, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, S.E.; Orozco, S. Ethanol increases plasma Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) levels and subjective effects after marihuana smoking in human volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2001, 64, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, F.E.; Reiserer, R.S.; Tomarken, A.J.; McDonald, M.P. Spatial and nonspatial escape strategies in the Barnes maze. Learn. Mem. 2006, 13, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Csaszar, E.; Szodorai, E.; Patil, S.; Pollak, A.; Lubec, G. The differential hippocampal phosphoproteome of Apodemus sylvaticus paralleling spatial memory retrieval in the Barnes maze. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 264, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Sunyer, B.; Höger, H.; Lubec, G. Evaluation of spatial memory of C57BL/6J and CD1 mice in the Barnes maze, the Multiple T-maze and in the Morris water maze. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 198, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, N.G.; Law, W.X.; Weingarten, M.J.; Carnevale, L.N.; Das, A.; Liang, N.C. Combined ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol and moderate alcohol administration: Effects on ingestive behaviors in adolescent male rats. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaekers, J.G.; Kauert, G.; Van Ruitenbeek, P.; Theunissen, E.; Schneider, E.; Moeller, M.R. High-Potency Marijuana Impairs Executive Function and Inhibitory Motor Control. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, M.; Singh, M.E.; McGregor, I.S.; Mallet, P.E. Chronic cannabinoid exposure produces lasting memory impairment and increased anxiety in adolescent but not adult rats. J. Psychopharmacol. 2004, 18, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas-Roig, J.; Benito, E.; Agís-Balboa, R.C.; Piscitelli, F.; Hoyer-Fender, S.; Di Marzo, V.; Havemann-Reinecke, U. Chronic exposure to cannabinoids during adolescence causes long-lasting behavioral deficits in adult mice. Addict. Boil. 2016, 22, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.H.; Krutz, B.; Sifringer, M.; Stefovska, V.; Bittigau, P.; Pragst, F.; Marsicano, G.; Lutz, B.; Ikonomidou, C. Cannabinoids enhance susceptibility of immature brain to ethanol neurotoxicity. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardingham, G.; Bading, H. The Yin and Yang of NMDA receptor signalling. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, J.A.; López-Sánchez, R.C.; Rendón-Ramírez, A. Lipids and Oxidative Stress Associated with Ethanol-Induced Neurological Damage. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Rojas, C.; Mira, R.G.; Torres, A.K.; Jara, C.; Pérez, M.J.; Vergara, E.H.; Cerpa, W.; Quintanilla, R. Alcohol consumption during adolescence: A link between mitochondrial damage and ethanol brain intoxication. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert-Chatelain, E.; Desprez, T.; Serrat, R.; Bellocchio, L.; Soria-Gomez, E.; Busquets-Garcia, A.; Pagano Zottola, A.C.; Delamarre, A.; Cannich, A.; Vincent, P.; et al. A cannabinoid link between mitochondria and memory. Nature 2016, 539, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyser, C.J.; Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on delayed match to sample performance in rats: Alterations in short-term memory associated with changes in task specific firing of hippocampal cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 264, 294–307. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman, A.H.; Dimen, K.R.; Martin, B.R. Systemic or intrahippocampal cannabinoid administration impairs spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 1995, 119, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallet, P.E.; Beninger, R.J. Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, but not the endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand anandamide, produces conditioned place avoidance. Life Sci. 1998, 62, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Mills, S.; Winstone, J.; Leishman, E.; Wager-Miller, J.; Bradshaw, H.; Mackie, K. Chronic Adolescent Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Treatment of Male Mice Leads to Long-Term Cognitive and Behavioral Dysfunction, Which Are Prevented by Concurrent Cannabidiol Treatment. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, E.M.; Da Silva, E.A.; Concilio, G.V.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Masur, J. Reversible effects of acute and long-term administration of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on memory in the rat. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1991, 28, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.M.; Jones, K.H.; Kuhn, C.M.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Sex differences in the effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on spatial learning in adolescent and adult rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2007, 18, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilkei-Gorzo, A.; Albayram, O.; Draffehn, A.; Michel, K.; Piyanova, A.; Oppenheimer, H.; Ginzbrg, M.D.; Rácz, I.; Ulas, T.; Imbeault, S.; et al. A chronic low dose of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) restores cognitive function in old mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abood, M.E.; Rizvi, G.; Sallapudi, N.; McAllister, S.D. Activation of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor protects cultured mouse spinal neurons against excitotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 309, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, A.J.; Grimaldi, M. Cannabinoid receptor activation and elevated cyclic AMP reduce glutamate neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Spatz, M.; Shohami, E. Endocannabinoids and neuroprotection. Sci. Signal. 2002, 2002, re5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Thayer, S.A. Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Protect Cultured Rat Hippocampal Neurons from Excitotoxicity. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Koch, M. Chronic Pubertal, but not Adult Chronic Cannabinoid Treatment Impairs Sensorimotor Gating, Recognition Memory, and the Performance in a Progressive Ratio Task in Adult Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Schömig, E.; Leweke, F.M. Acute and chronic cannabinoid treatment differentially affects recognition memory and social behavior in pubertal and adult rats. Addict. Boil. 2008, 13, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Piser, T.M.; Seybold, V.S.; Thayer, S.A. Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Inhibit Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission in Rat Hippocampal Cultures. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 4322–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisskopf, M.; Castillo, P.E.; Zalutsky, R.; Nicoll, R. Mediation of hippocampal mossy fiber long-term potentiation by cyclic AMP. Science 1994, 265, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Cannabinoids Reveal the Necessity of Hippocampal Neural Encoding for Short-Term Memory in Rats. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8932–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, L.E.; Thorpe, A.J.; Lichtman, A.H. Hippocampal CB1 Receptors Mediate the Memory Impairing Effects of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2072–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BeLue, R.C.; Howlett, A.; Westlake, T.M.; Hutchings, D.E. The ontogeny of cannabinoid receptors in the brain of postnatal and aging rats. Neurotoxicology Teratol. 1995, 17, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.C.; Hinds, T.R.; Impey, S.; Storm, D.R. Hippocampal neurotoxicity of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 5322–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landfield, P.W.; Cadwallader, L.B.; Vinsant, S. Quantitative changes in hippocampal structure following long-term exposure to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol: Possible mediation by glucocorticoid systems. Brain Res. 1988, 443, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallet, A.C. Neurotoxicology of cannabis and THC: A review of chronic exposure studies in animals. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglick, A.; Kalant, H. Learning impairment in the radial-arm maze following prolonged cannabis treatment in rats. Psychopharmacology 1982, 77, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiglick, A.; Kalant, H. Behavioral effects of prolonged administration of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the rat. Psychopharmacology 1983, 80, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglick, A.; Kalant, H. Residual effects of chronic cannabis treatment on behavior in mature rats. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijnzeel, A.W.; Knight, P.; Panunzio, S.; Xue, S.; Bruner, M.M.; Wall, S.C.; Pompilus, M.; Febo, M.; Setlow, B. Effects in rats of adolescent exposure to cannabis smoke or THC on emotional behavior and cognitive function in adulthood. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2773–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novier, A.; Diaz-Granados, J.L.; Matthews, D.B. Alcohol use across the lifespan: An analysis of adolescent and aged rodents and humans. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 133, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetreno, R.P.; Crews, F.T. Binge ethanol exposure during adolescence leads to a persistent loss of neurogenesis in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus that is associated with impaired adult cognitive functioning. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Dolan, S.L.; Denburg, N.; Hindes, A.; Anderson, S.W.; Nathan, P.E. Decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 2001, 39, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, M.J.; Lindquist, D.H. Significant long-term, but not short-term, hippocampal-dependent memory impairment in adult rats exposed to alcohol in early postnatal life. Dev. Psychobiol. 2014, 56, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidt, L.; Kapczinski, F.; Fries, G.R.; Stertz, L.; Cabral, J.C.C.; De Almeida, R.M.M. Ethanol during adolescence decreased the BDNF levels in the hippocampus in adult male Wistar rats, but did not alter aggressive and anxiety-like behaviors. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2015, 37, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izenwasser, S. Differential Effects of Psychoactive Drugs in Adolescents and Adults. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 2005, 17, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedema, H.P.; Carter, M.D.; Dugan, B.P.; Gurnsey, K.; Olsen, A.; Bradberry, C.W. The acute impact of ethanol on cognitive performance in rhesus macaques. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 21, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawel, K.; Labuz, K.; Gibula-Tarlowska, E.; Jenda, M.; Marszałek-Grabska, M.; Filarowska, J.; Silberring, J.; Kotlinska, J.H. Cholinesterase inhibitors, donepezil and rivastigmine, attenuate spatial memory and cognitive flexibility impairment induced by acute ethanol in the Barnes maze task in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibula-Tarlowska, E.; Kotlinska, J.H. Kissorphin improves spatial memory and cognitive flexibility impairment induced by ethanol treatment in the Barnes maze task in rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2020, 31, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmin, A.; Liljequist, S.; Meis, J.; Chefer, V.; Shippenberg, T.; Bakalkin, G. Repeated moderate-dose ethanol bouts impair cognitive function in Wistar rats. Addict. Boil. 2011, 17, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszałek-Grabska, M.; Gibula-Tarlowska, E.; Bodzoń-Kułakowska, A.; Suder, P.; Gawel, K.; Talarek, S.; Listos, J.; Kędzierska, E.; Danysz, W.; Kotlinska, J.H. ADX-47273, a mGlu5 receptor positive allosteric modulator, attenuates deficits in cognitive flexibility induced by withdrawal from ‘binge-like’ ethanol exposure in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 338, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernier, J.A.; White, A.M.; Swartzwelder, H.S.; Crews, F.T. Cognitive deficits and CNS damage after a 4-day binge ethanol exposure in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 72, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.; McDonald, R. Hippocampus, amygdala, and memory deficits in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1990, 37, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Boettiger, C.A. Impulsivity, frontal lobes and risk for addiction. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 93, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hungund, B.; Szakall, I.; Adam, A.; Basavarajappa, B.S.; Vadasz, C. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice exhibit markedly reduced voluntary alcohol consumption and lack alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J. Neurochem. 2003, 84, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibula-Tarlowska, E.; Wydra, K.; Kotlinska, J.H. Deleterious Effects of Ethanol, Δ(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and Their Combination on the Spatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility in Adolescent and Adult Male Rats in the Barnes Maze Task. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070654
Gibula-Tarlowska E, Wydra K, Kotlinska JH. Deleterious Effects of Ethanol, Δ(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and Their Combination on the Spatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility in Adolescent and Adult Male Rats in the Barnes Maze Task. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(7):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070654
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibula-Tarlowska, Ewa, Karolina Wydra, and Jolanta H. Kotlinska. 2020. "Deleterious Effects of Ethanol, Δ(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and Their Combination on the Spatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility in Adolescent and Adult Male Rats in the Barnes Maze Task" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 7: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070654
APA StyleGibula-Tarlowska, E., Wydra, K., & Kotlinska, J. H. (2020). Deleterious Effects of Ethanol, Δ(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and Their Combination on the Spatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility in Adolescent and Adult Male Rats in the Barnes Maze Task. Pharmaceutics, 12(7), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070654




