Development of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Improving Oral Absorption of Enoxaparin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles (LPHNs)
2.3. In Vitro Characteristics
2.3.1. Size, Zeta Potential, and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.3.2. Particle Morphology
2.3.3. In Vitro Drug Release
2.4. Intestinal Absorption
2.5. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats
2.6. In Vivo Efficacy in Mice
2.7. Safety Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles
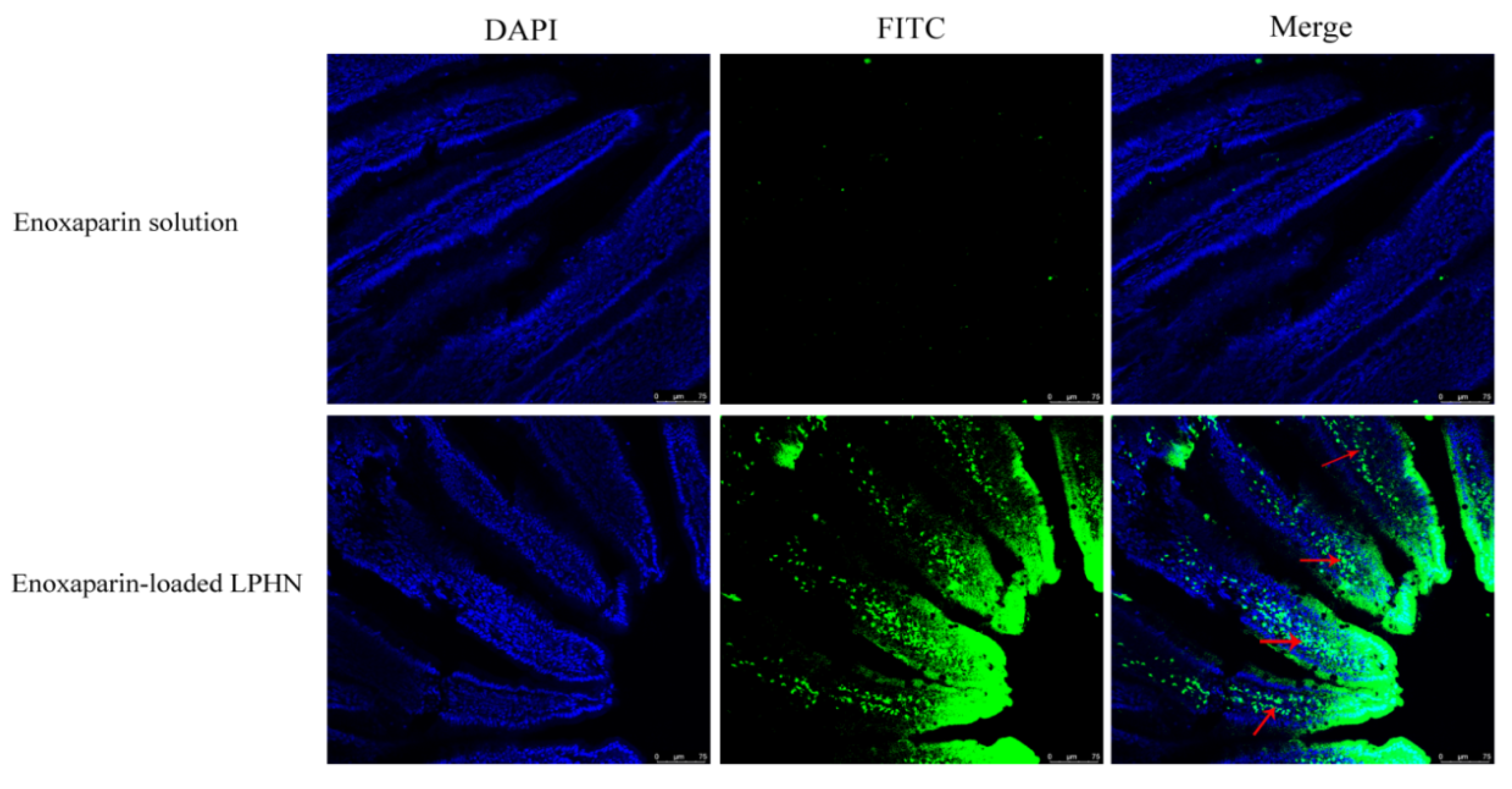
3.2. Intestinal Absorption
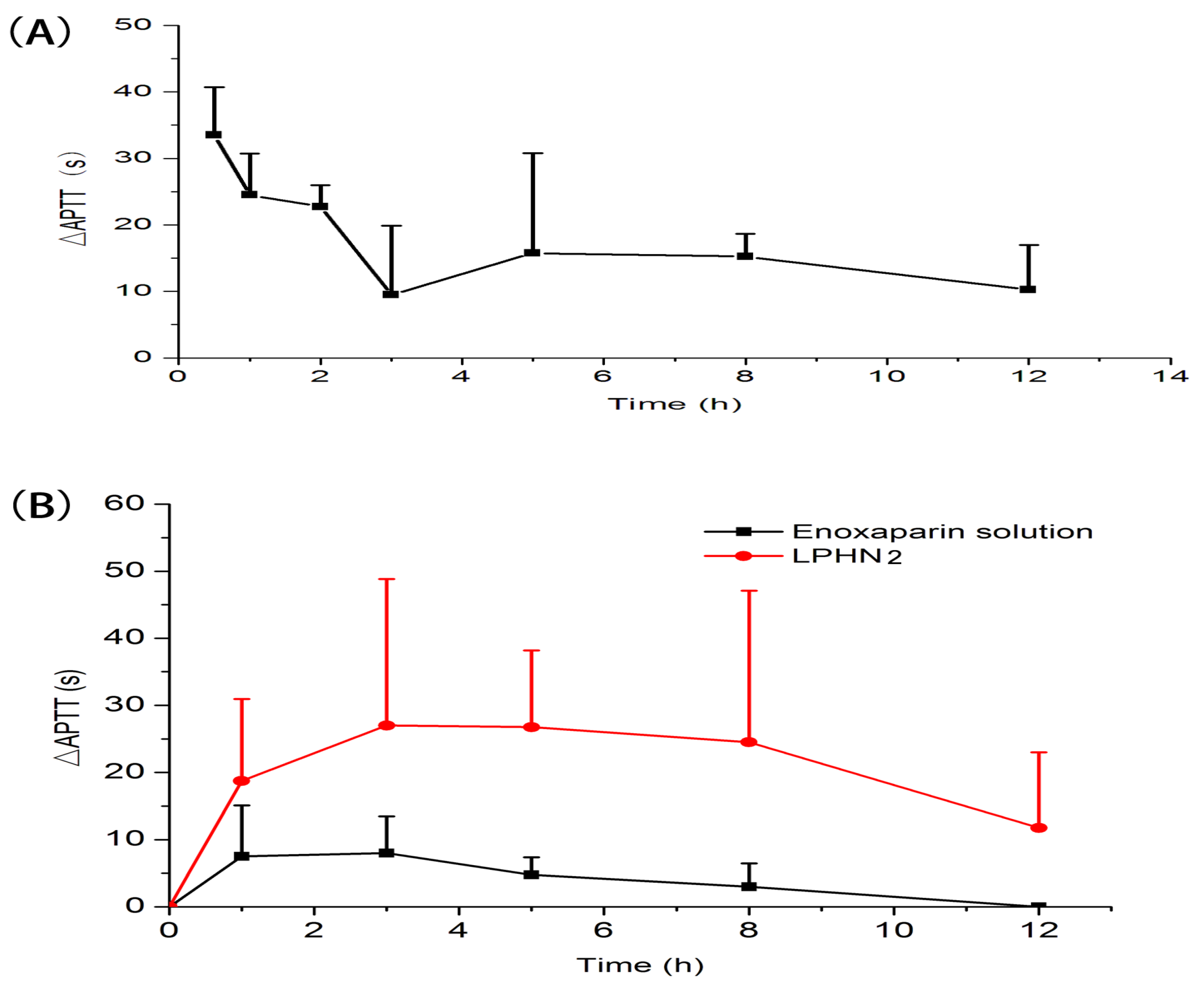
3.3. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats
3.4. In Vivo Efficacy
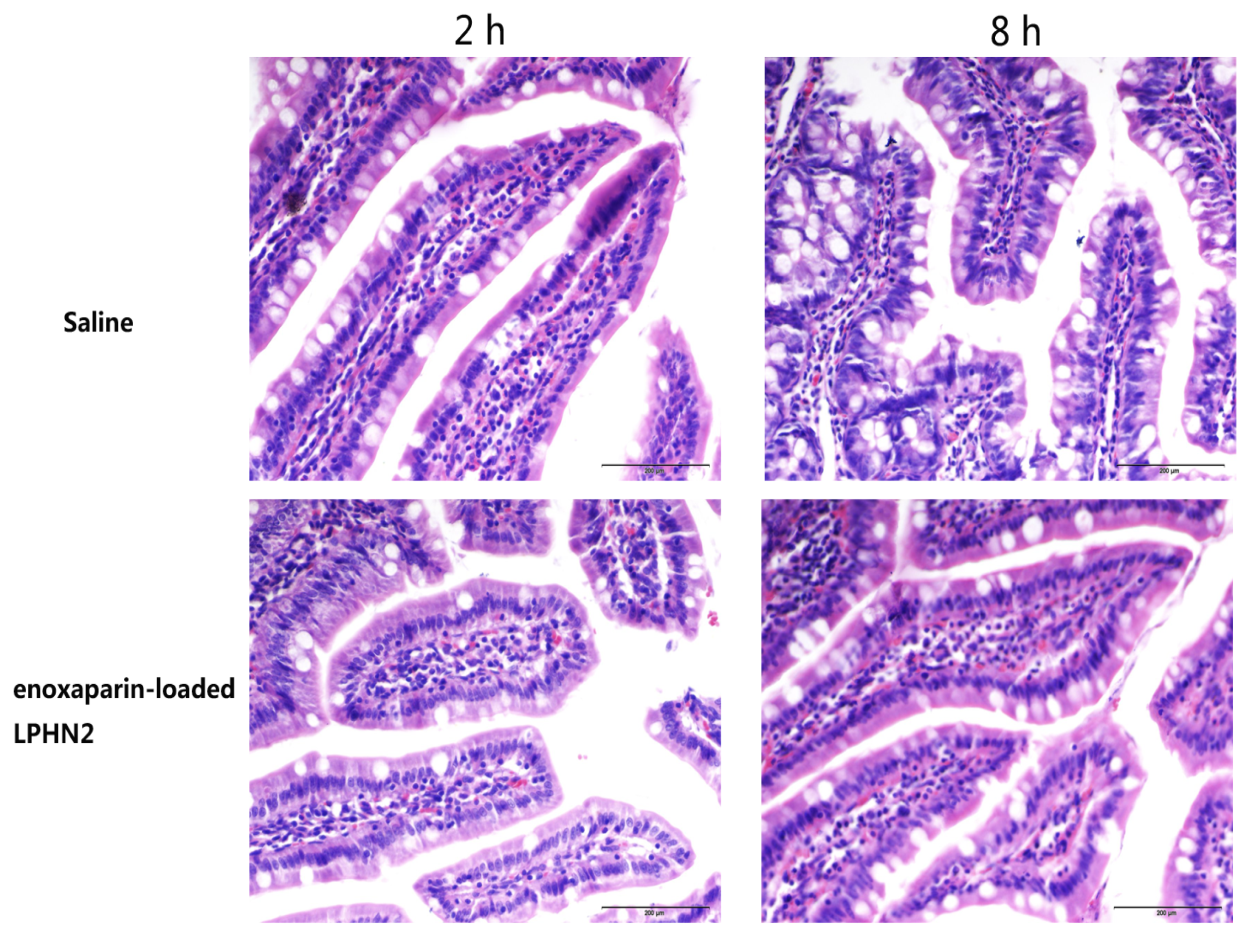
3.5. Safety Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirsh, J.; Warkentin, T.E.; Shaughnessy, S.G.; Anand, S.S.; Halperin, J.L.; Raschke, R.; Granger, C.; Ohman, E.M.; Dalen, J.E. Heparin and Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Mechanisms of Action, Pharmacokinetics, Dosing, Monitoring, Efficacy, and Safety. Chest 2001, 119, 64S–94S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, E.; Mulloy, B.; Barrowcliffe, T.W. Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y.; Gou, J.; Yang, X.; Tang, B. Development and evaluation of thermo-sensitive hydrogel system with nanocomplexes for prolonged subcutaneous delivery of enoxaparin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Mao, S. Exploration of hydrophobic modification degree of chitosan-based nanocomplexes on the oral delivery of enoxaparin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Duan, X.; Li, Y.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Mao, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of chitosan graft glyceryl monooleate as peroral delivery carrier of enoxaparin. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlekar, N.A.; Youan, B.B. The quest for non-invasive delivery of bioactive macromolecules: A focus on heparins. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2006, 113, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.R.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M. Strategies to Overcome Heparins’ Low Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Tang, B. Advanced delivery strategies facilitating oral absorption of heparins. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valimaki, S.; Khakalo, A.; Ora, A.; Johansson, L.S.; Rojas, O.J.; Kostiainen, M.A. Effect of PEG-PDMAEMA Block Copolymer Architecture on Polyelectrolyte Complex Formation with Heparin. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2891–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Osman, R.; Awad, G.A.; Mortada, N.D.; Geneidy, A.S. Low molecular weight heparins for current and future uses: Approaches for micro- and nano-particulate delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, A.; Lagarce, F.; Tessier-Marteau, A.; Thomas, O.; Legras, P.; Macchi, L.; Saulnier, P.; Benoit, J.P. Oral fondaparinux: Use of lipid nanocapsules as nanocarriers and in vivo pharmacokinetic study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, E.H.; Vaishali, B.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Tricaprylin microemulsion for oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin conjugates. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2005, 105, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, R.; Paliwal, S.R.; Agrawal, G.P.; Vyas, S.P. Biomimetic solid lipid nanoparticles for oral bioavailability enhancement of low molecular weight heparin and its lipid conjugates: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, W.-T.; Lu, Y.-P.; Tao, Q.; Guo, M.; Lu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Yu, S.-Q. Hydroxypropyl-Sulfobutyl-β-Cyclodextrin Improves the Oral Bioavailability of Edaravone by Modulating Drug Efflux Pump of Enterocytes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yu, S. Complexation of Z-ligustilide with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin to improve stability and oral bioavailability. Acta Pharm. 2014, 64, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagre, A.P.; Jain, K.; Jain, N.K. Alginate coated chitosan core shell nanoparticles for oral delivery of enoxaparin: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, Y.; Ubrich, N.; Ghazouani, F.E.; Maincent, P.; Lamprecht, A. Low molecular weight heparin loaded pH-sensitive microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 335, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Xing, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, C.; Liang, G. pH-responsive thiolated chitosan nanoparticles for oral low-molecular weight heparin delivery: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Chen, C.Y.; Chai, G.H.; Du, Y.Z.; Hu, F.Q. Improved transport and absorption through gastrointestinal tract by PEGylated solid lipid nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.L.; Bendayan, R.; Rauth, A.M.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.Y. Chemotherapy with anticancer drugs encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, J.; Anand Sonia, S.; Halperin Jonathan, L.; Fuster, V. Mechanism of Action and Pharmacology of Unfractionated Heparin. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boushra, M.; Tous, S.; Fetih, G.; Korzekwa, K.; Lebo, D.B.; Xue, H.Y.; Wong, H.L. Development and evaluation of viscosity-enhanced nanocarrier (VEN) for oral insulin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Ma, K.; He, B.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel system with paclitaxel nanocrystals: High drug-loading, sustained drug release and extended local retention guaranteeing better efficacy and lower toxicity. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2014, 174, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Huang, K.; Gui, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Pluronic-based micelle encapsulation potentiates myricetin-induced cytotoxicity in human glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4991–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Jiang, M. Effects of the multilayer structures on Exenatide release and bioactivity in microsphere/thermosensitive hydrogel system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Tang, B.; Chao, Y.; Xu, H.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Cysteine-Functionalized Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Oral Delivery of Docetaxel: A Permeability and Pharmacokinetic Study. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Ubrich, N.; Marchand-Arvier, M.; Vigneron, C.; Hoffman, M.; Lecompte, T.; Maincent, P. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Oral Heparin–Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles in Rabbits. Circulation 2002, 105, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffart, V.; Ubrich, N.; Lamprecht, A.; Bachelier, K.; Vigneron, C.; Lecompte, T.; Hoffman, M.; Maincent, P. Microencapsulation of Low Molecular Weight Heparin into Polymeric Particles Designed with Biodegradable and Nonbiodegradable Polycationic Polymers. Drug Deliv. 2003, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, S.; Bendas, E.R.; Badawy, S. The clinical efficacy of cosmeceutical application of liquid crystalline nanostructured dispersions of alpha lipoic acid as anti-wrinkle. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. e.V 2014, 86, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkireddy, H.R.; Urmann, M.; Besenius, M.; Werner, U.; Haack, T.; Brun, P.; Alie, J.; Illel, B.; Hortala, L.; Vogel, R.; et al. Oral delivery of diabetes peptides—Comparing standard formulations incorporating functional excipients and nanotechnologies in the translational context. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 196–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhaire, H.; Gimel, J.-C.; Roger, E.; Benoît, J.-P.; Lagarce, F. How to design the surface of peptide-loaded nanoparticles for efficient oral bioavailability? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.C. Mucus and mucins in diseases of the intestinal and respiratory tracts. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Amount of P407 | Size (nm) | PI | ζ Potential (mV) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% (SLNs) | 159.40 ± 1.59 | 0.293 ± 0.010 | −21.83 ± 3.94 | 43.21 ± 3.79 |
| 20% (LPHN1) | 149.70 ± 1.71 | 0.264 ± 0.030 | −17.47 ± 1.20 | 43.14 ± 7.52 |
| 30% (LPHN2) | 149.75 ± 2.45 | 0.293 ± 0.009 | −14.71 ± 1.93 | 65.72 ± 14.33 |
| 40% (LPHN3) | 153.19 ± 0.79 | 0.274 ± 0.002 | −20.04 ± 1.59 | 59.47 ± 11.66 |
| Formulations | Tmax (h) | AUC0–12 h(s·h) | Fabs (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enoxaparin solution (i.v.) | - | 182.3 ± 44.2 | 100.0 |
| Enoxaparin solution (p.o.) | 0.5 | 37.6 ± 10.0 | 2.1 |
| Enoxaparin-loaded LPHN2 (p.o.) | 3 | 258.3 ± 93.1 | 14.2* |
| Formulations | Inhibition Effect (% protection) |
|---|---|
| Saline (i.v.) | 8.3 |
| Enoxaparin solution (i.v.) | 58.3 |
| Enoxaparin solution (p.o.) | 16.7 |
| Enoxaparin-loaded LPHN2 (p.o.) | 50.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, B.; Qian, Y.; Fang, G. Development of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Improving Oral Absorption of Enoxaparin. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070607
Tang B, Qian Y, Fang G. Development of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Improving Oral Absorption of Enoxaparin. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(7):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070607
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Bo, Yu Qian, and Guihua Fang. 2020. "Development of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Improving Oral Absorption of Enoxaparin" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 7: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070607
APA StyleTang, B., Qian, Y., & Fang, G. (2020). Development of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Improving Oral Absorption of Enoxaparin. Pharmaceutics, 12(7), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070607




