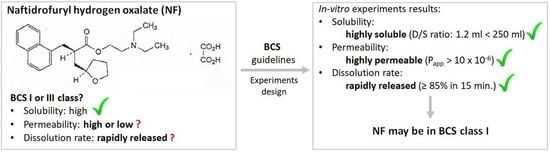
Solubility, Permeability, and Dissolution Rate of Naftidrofuryl Oxalate Based on BCS Criteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Dosage Form | Dosage [mg] | No. of Patients | T1/2 [h] | Tmax [h] | Cmax [ng/mL] | AUC [ng/mL*h] | BA [%] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| oral | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 30 | [20] |
| oral (gelatin capsules) | 50 | n/d | 0.68 | 1.1 | 350 | nd | 76 | [21] |
| oral (capsules) | 100 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 203 | nd | nd | [13] |
| intravenous | 40 | 18 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [16] |
| oral (gelatin capsules) | 300 | 12 | 1.79 | 0.94 | 922 | 2022 | nd | [21] |
| oral (fasted) oral (nonfasted) | 100 | 12 | 1.3 1.6 | 0.8 2 | 238 181 | 500 583 | 19.7 23.0 | [14] |
| oral (tablets) | 100 300 300 | 9 | nd | 1 0.9 1.2 | 209 590 645 | 630 1271 1955 | 121 77 114 | [6] |
| oral (tablets) | 200 | 30 | 3.41 | 2.75 | 279 | 1797 | nd | [22] |
| oral (tablets) | 200 | 12 | 4.4 | 1.3 | 174 | 1504 | nd | [23] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and References
2.2. Solubility Test
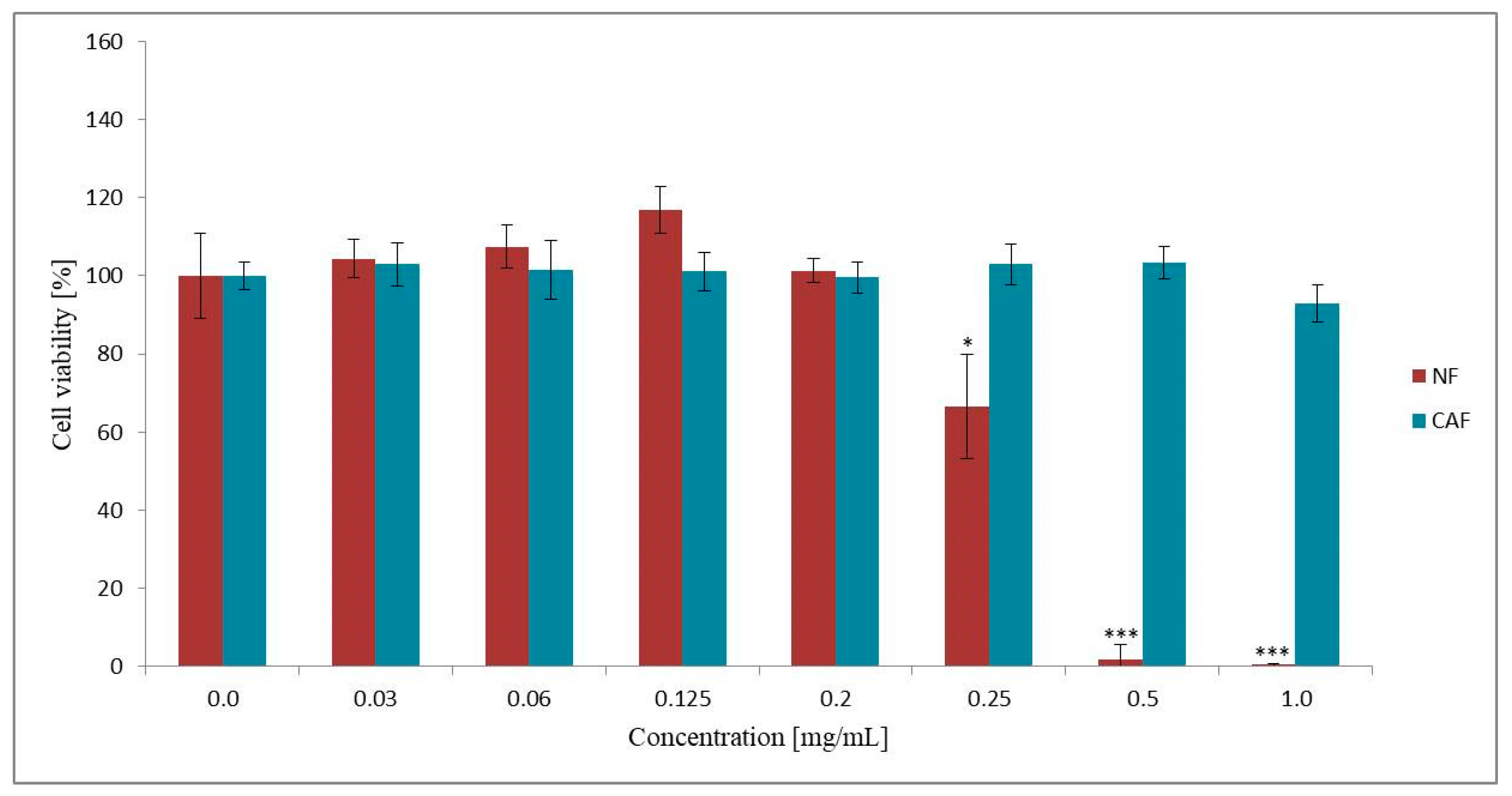
2.3. Cytotoxicity Analysis
2.4. The Culture of Caco-2 Colon Cancer Cells
2.5. Permeability Test
2.6. In-House NF Capsules Preparation
2.7. In Vitro Dissolution Test and Data Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Solubility Test
3.2. Permeability Assay on Caco-2 Cell Line
3.2.1. Effect of NF and CAF on Caco-2 Cells Viability
3.2.2. Caco-2 Permeability Assay
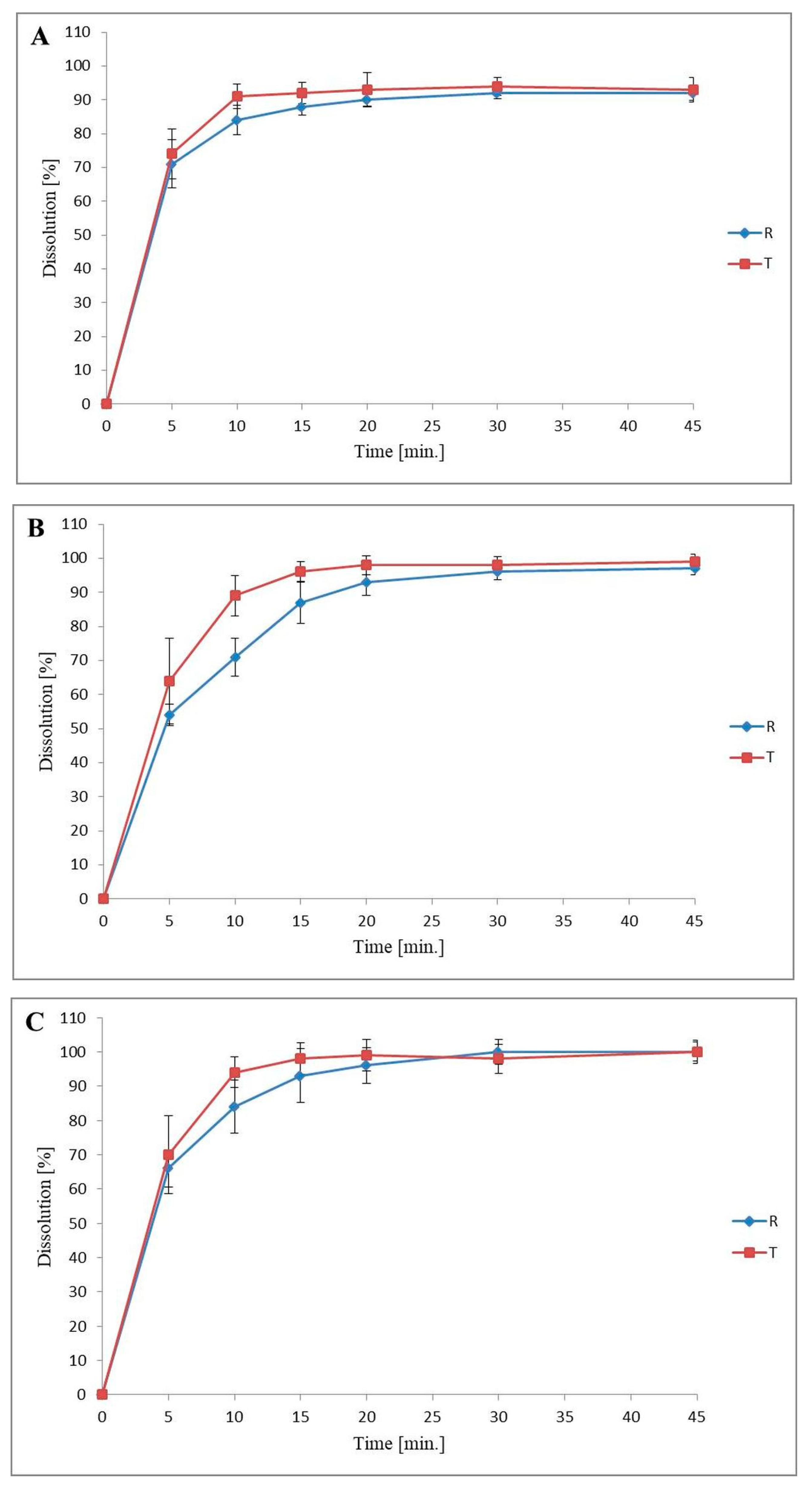
3.3. Dissolution Profiles Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in Vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manallack, D.T.; Prankerd, R.J.; Yuriev, E.; Oprea, T.I.; Chalmers, D.K. The significance of acid/base properties in drug discovery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panakanti, R.; Narang, A.S. Impact of Excipient Interactions on Drug Bioavailability from Solid Dosage Forms. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2639–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Chen, B.; Yao, Y.; Hossain, M.; Nagatomo, T.; Yao, H.; Kong, L.; Sun, H. Practical access to four stereoisomers of naftidrofuryl and their binding affinity towards 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3441–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines. European Pharmacopoeia, 10th ed.; European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines: Strasbourg, France, 2019; pp. 3322–3323. [Google Scholar]
- Waaler, P.; Graffner, C.; Müller, B. Biopharmaceutical studies of naftidrofuryl in hydrocolloid matrix tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 87, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiernsperger, N.F. Serotonin, 5-HT2 receptors, and their blockade by naftidrofuryl: A targeted therapy of vascular diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1994, 23, S37–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheggen, R.; Schrör, K. Effect of naftidrofuryl on platelet-induced vasospasm in vitro. Role of antiserotonergic actions. Arzneimittelforschung 1993, 43, 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Wellington, K. Naftidrofuryl. Drugs Aging 2005, 22, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, A.; Lehert, P.; Opsomer, L. Naftidrofuryl in the treatment of subacute stroke. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1990, 16, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Song, H.; Hao, Z.; Wu, T.; Mccleery, J. Naftidrofuryl for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 12, CD002955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck Serono Ltd. Praxilene 100 mg Capsules; Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/990/smpc#companyDetails (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Brodie, R.; Chasseaud, L.; Taylor, T.; Hunter, J.; Ciclitira, P. Determination of naftidrofuryl in the plasma of humans by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1979, 164, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishigaki, R.; Umemura, K.; Okui, K.; Hayashi, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakurai, Y. The pharmacokinetical analysis of the fate of naphtidrofuryl oxalate (LS121) in human subjects. II. Estimation of the first-pass effect after oral administration. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1986, 106, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrett, E.R. Bioanalyses and Pharmacokinetics of Nafronyl in the Dog. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, D.; Mühlberg, W.; Rieck, W.; Horn, H.J.; Schmitt-Rüth, R. Pharmacokinetics of naftidrofuryl in multimorbidity in geriatric patients. Z. Gerontol. 1984, 17, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, K.; Hildebrand, M.; Beyer, K.-H. Metabolism of nafronyl in man. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1989, 14, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, S.M.; Belal, T.S.; Barary, M.H.; Ibrahim, M.E.A. A validated HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of naftidrofuryl oxalate and its degradation product (metabolite), naftidrofuryl acid: Applications to pharmaceutical tablets and biological samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 5, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, A.C.; Osselton, M.D.; Widdop, B.; Watts, J. Clarke’s Analysis of Drugs and Poisons, 4th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK; Gurnee, IL, USA, 2011; pp. 1746–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Riederer, P.; Laux, G.; Pöldinger, W. Neuro-Psychopharmaka Ein Therapie-Handbuch; Springer: Wien, Austria, 1999; p. 660. [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley, L.M.; Taylor, T.; Wilkinson, P.A.; Brodie, R.R.; Chasseaud, L.F.; Alun-Jones, V.; Hunter, J.O. Plasma concentrations and relative bioavailability of naftidrofuryl from different salt forms. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1986, 7, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulot, T.; Gamand, S.; Dupain, T.; Ahtoy, P.; Bromet, M. Influence of age on the pharmacokinetics of naftidrofuryl after single oral administration in elderly versus young healthy volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung 1998, 48, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Legallicier, B.; Barbier, S.; Bolloni, L.; Fillastre, J.-P.; Godin, M.; Kuhn, T.; Porte, F.; Chretien, P.; Dupainc, T.; Bromet-Petitd, M. Pharmacokinetics of Naftidrofuryl in Patients with Renal Impairment. Arzneimittelforschung 2011, 55, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). ICH M9 Guideline on Biopharmaceutics Classification System-Based Biowaivers. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-m9-biopharmaceutics-classification-system-based-biowaivers-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Waiver of In Vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70963/download (accessed on 26 December 2017).
- Dahan, A.; Miller, J.M.; Amidon, G.L. Prediction of Solubility and Permeability Class Membership: Provisional BCS Classification of the World’s Top Oral Drugs. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The British Pharmacopoeia Commission. British Pharmacopoeia; The British Pharmacopoeia Commission: London, England, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tavelin, S.; Gråsjö, J.; Taipalensuu, J.; Ocklind, G.; Artursson, P.; Wise, C. Applications of Epithelial Cell Culture in Studies of Drug Transport. Methods Mol Biol. 2002, 188, 233–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubatsch, I.; E Ragnarsson, E.G.; Artursson, P. Determination of drug permeability and prediction of drug absorption in Caco-2 monolayers. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms. Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70936/download (accessed on 25 August 1997).
- Volpe, D.A.; Faustino, P.J.; Ciavarella, A.B.; Asafu-Adjaye, E.B.; Ellison, C.D.; Yu, L.X.; Hussain, A.S. Classification of Drug Permeability with a Caco-2 Cell Monolayer Assay. Clin. Res. Regul. Aff. 2007, 24, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanová, L.; Stetinova, V.; Kholova, D.; Kvetina, J.; Smetana, J.; Svoboda, Z. Caco-2 cells and Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) for prediction of transepithelial transport of xenobiotics (model drug: Caffeine). Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2009, 30, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yee, S. In Vitro Permeability across Caco-2 Cells (Colonic) Can Predict In Vivo (Small Intestinal) Absorption in Man—Fact or Myth. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, T.R. Potential for pharmaceutical excipients to impact absorption: A mechanistic review for BCS Class 1 and 3 drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institusional affiliations. |
 ) determined “cumulative fraction transported” of naftidrofuryl oxalate (NF) and caffeine (CAF) versus time in bidirectional A–B and B–A transport across Caco-2 cell monolayer. NF concentrations in donor compartments were established at 0.125 mg/mL (A) and 0.200 mg/mL (B). CAF transport was analyzed at an initial concentration of 0.5 mg/mL (C).
) determined “cumulative fraction transported” of naftidrofuryl oxalate (NF) and caffeine (CAF) versus time in bidirectional A–B and B–A transport across Caco-2 cell monolayer. NF concentrations in donor compartments were established at 0.125 mg/mL (A) and 0.200 mg/mL (B). CAF transport was analyzed at an initial concentration of 0.5 mg/mL (C).
 ) determined “cumulative fraction transported” of naftidrofuryl oxalate (NF) and caffeine (CAF) versus time in bidirectional A–B and B–A transport across Caco-2 cell monolayer. NF concentrations in donor compartments were established at 0.125 mg/mL (A) and 0.200 mg/mL (B). CAF transport was analyzed at an initial concentration of 0.5 mg/mL (C).
) determined “cumulative fraction transported” of naftidrofuryl oxalate (NF) and caffeine (CAF) versus time in bidirectional A–B and B–A transport across Caco-2 cell monolayer. NF concentrations in donor compartments were established at 0.125 mg/mL (A) and 0.200 mg/mL (B). CAF transport was analyzed at an initial concentration of 0.5 mg/mL (C).
| Ingredients | Quantity (Per One Capsule) | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Naftidrofuryl oxalate | 100 mg | active ingredient |
| Talc | rest of the unit filling weight | filler |
| Magnesium stearate | up to 0.5% of the unit filling weight | lubricant |
| Dose (D) (mg) | pH | Solubility (S) (mg/mL) | D/S Ratio (mL) | D0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 1.2 | 279.00 ± 15.69 | 0.69 | 0.003 |
| 4.5 | 169.00 ± 6.79 | 1.19 | 0.005 | |
| 6.8 | 290.40 ± 19.83 | 0.67 | 0.003 |
| Papp × 10−6 (cm/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Substance | Concentration (mg/mL) | Apical-to-Basolaterial Transport | Basolaterial-to-Apical Transport |
| NF | 0.125 | 131.9 ± 34.8 | 84.1 ± 4.7 |
| NF | 0.200 | 100.8 ± 15.1 | 78.8 ± 1.0 |
| CAF | 0.500 | 161.3 ± 19.7 | 126.5 ± 2.4 |
| Time Point [min.] | 0.1 M HCl pH 1.2 (%RSD) | Acetate Buffer pH 4.5 (%RSD) | Phosphate Buffer pH 6.8 (%RSD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | T | R | T | R | T | |
| 5 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 5.8 | 19.8 | 8.3 | 16.3 |
| 10 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 9.2 | 4.8 |
| 15 | 2.9 | 3.5 | 7.1 | 3.2 | 8.5 | 4.7 |
| 20 | 2.1 | 5.4 | 4.1 | 2.9 | 5.3 | 4.6 |
| 30 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 3.6 | 4.3 |
| 45 | 2.3 | 3.9 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 3.3 |
| Requirement | 0.1 M HCl pH = 1.2 | Acetate Buffer pH = 4.5 | Phosphate Buffer pH = 6.8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Difference factor f1 (profiles are similar when f1 ≤ 15) | 2 | 11 | 6 |
| Similarity factor f2 (profiles are similar when f2 ≥ 50) | 71 | 51 | 65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kus-Slowinska, M.; Wrzaskowska, M.; Ibragimow, I.; Czaklosz, P.I.; Olejnik, A.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H. Solubility, Permeability, and Dissolution Rate of Naftidrofuryl Oxalate Based on BCS Criteria. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121238
Kus-Slowinska M, Wrzaskowska M, Ibragimow I, Czaklosz PI, Olejnik A, Piotrowska-Kempisty H. Solubility, Permeability, and Dissolution Rate of Naftidrofuryl Oxalate Based on BCS Criteria. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(12):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121238
Chicago/Turabian StyleKus-Slowinska, Marta, Monika Wrzaskowska, Izabela Ibragimow, Piotr Igor Czaklosz, Anna Olejnik, and Hanna Piotrowska-Kempisty. 2020. "Solubility, Permeability, and Dissolution Rate of Naftidrofuryl Oxalate Based on BCS Criteria" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 12: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121238
APA StyleKus-Slowinska, M., Wrzaskowska, M., Ibragimow, I., Czaklosz, P. I., Olejnik, A., & Piotrowska-Kempisty, H. (2020). Solubility, Permeability, and Dissolution Rate of Naftidrofuryl Oxalate Based on BCS Criteria. Pharmaceutics, 12(12), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121238