Enhanced Intestinal Absorption of Insulin by Capryol 90, a Novel Absorption Enhancer in Rats: Implications in Oral Insulin Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Intestinal Absorption of Insulin Using the In Situ Closed-Loop Method
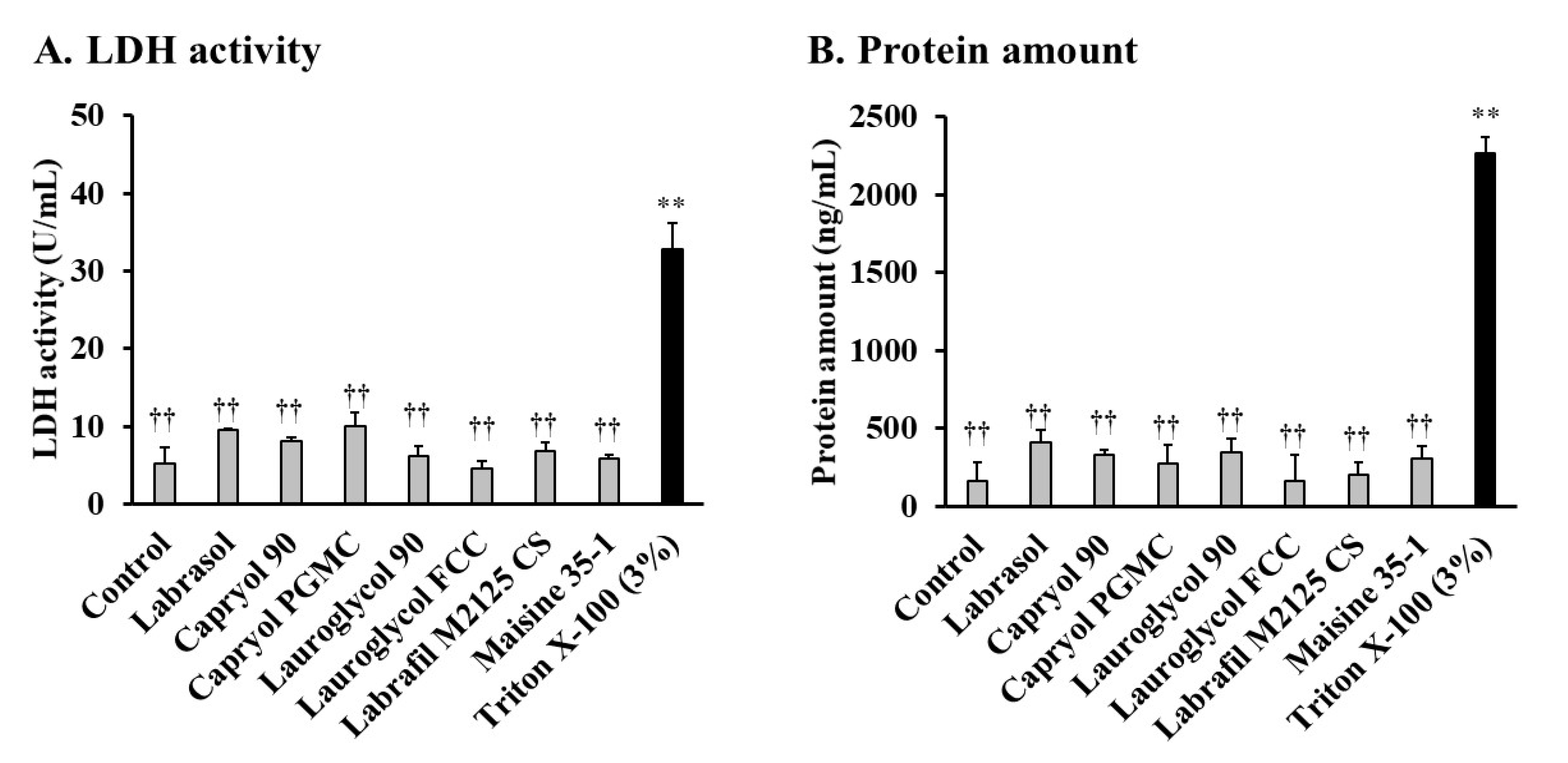
2.3. Estimation of Intestinal Membrane Damage
2.4. Circular Dichroism Studies
2.5. Preparation of Rat Mucosal Tissue Homogenates
2.6. Degradation of Insulin in Intestinal Mucosal Homogenates
2.7. Measurement of Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) and Transport of Insulin Using Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
2.8. Analytical Methods
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
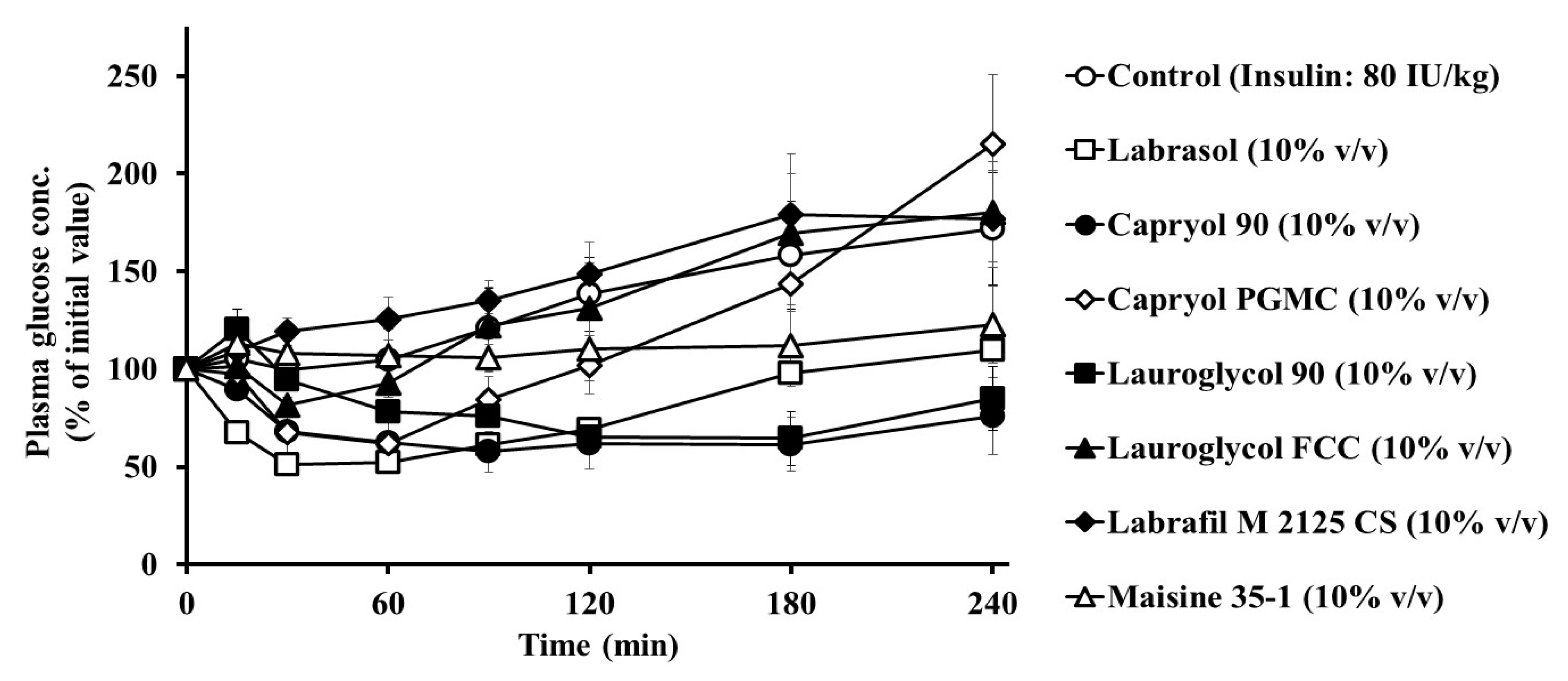
3.1. Effects of Labrasol® and Its Related Formulations on the Intestinal Absorption of Insulin and Their Intestinal Membrane Toxicity
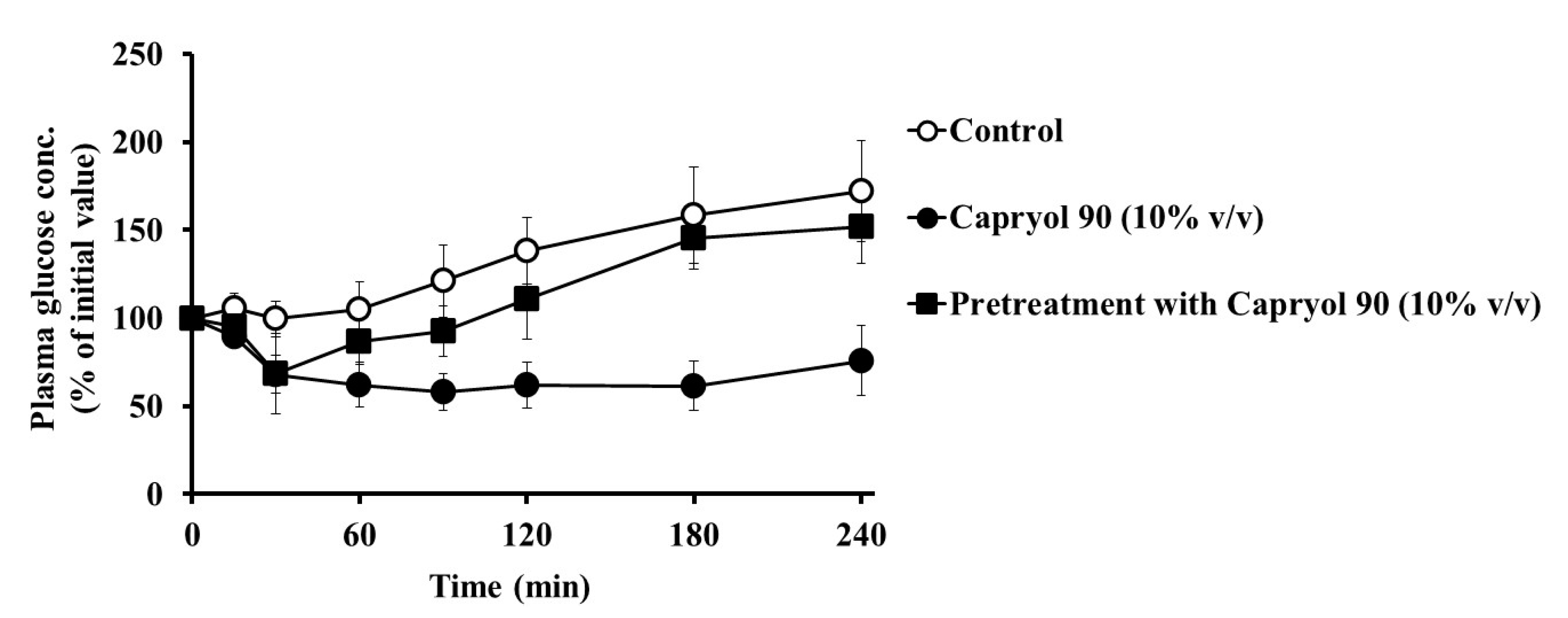
3.2. Absorption Enhancing Characteristics of Capryol 90
3.3. Effect of Capryol 90 on the Association Properties of Insulin
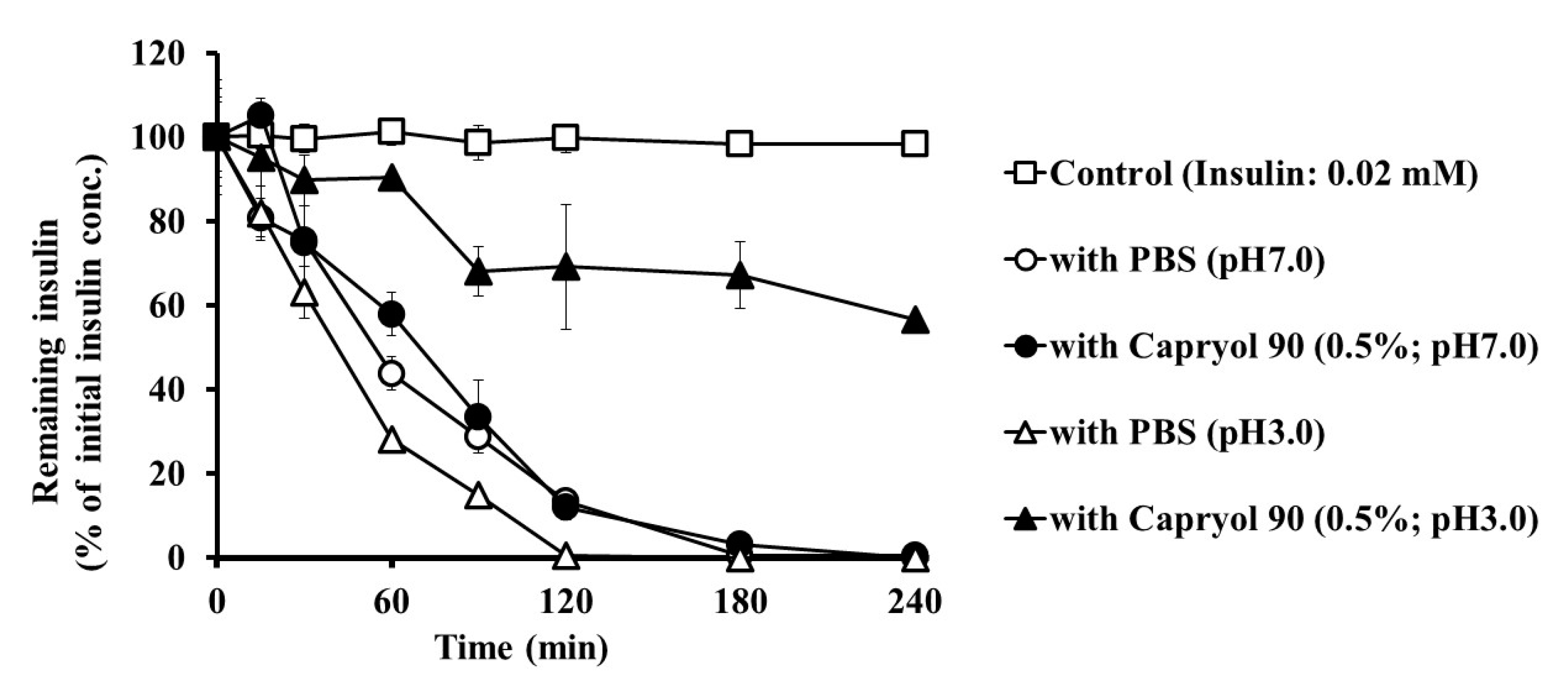
3.4. Effect of Capryol 90 on the Stability of Insulin in Intestinal Homogenates
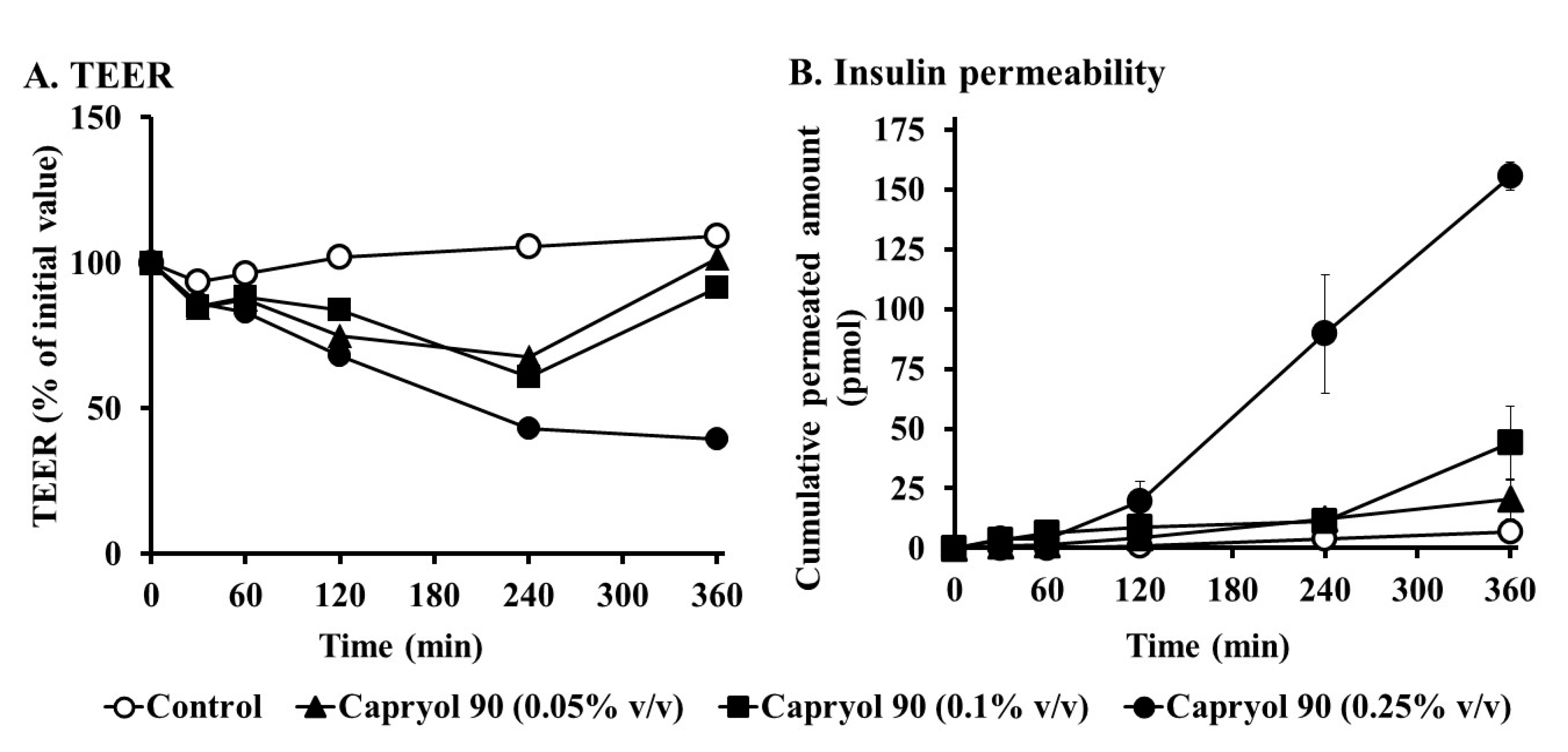
3.5. Effects of Capryol 90 on TEER and Insulin Transport in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Park, K. Oral protein delivery: Current status and future prospect. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Quan, Y.-S.; Kotani, A.; Okada, N.; Fujita, T.; Muranishi, S.; Yamamoto, A. Enhanced permeability of insulin across the rat intestinal membrane by various absorption enhancers: Their intestinal mucosal toxicity and absorption-enhancing mechanism of n-Lauryl-β-d-maltopyranoside. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetih, G.; Habib, F.; Okada, N.; Fujita, T.; Attia, M.; Yamamoto, A. Nitric oxide donors can enhance the intestinal transport and absorption of insulin and [Asu1,7]-eel calcitonin in rats. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; He, L.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Fujita, T.; Yamamoto, A. Improvement of intestinal absorption of water-soluble macromolecules by various polyamines: Intestinal mucosal toxicity and absorption-enhancing mechanism of spermine. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fujimori, T.; Kawaguchi, N.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Nishimi, M.; Dong, Z.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Polyamidoamine dendrimers as novel potential absorption enhancers for improving the small intestinal absorption of poorly absorbable drugs in rats. J. Control. Release 2011, 149, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Rikyuu, K.; Tsuji, T.; Fujita, T.; Murakami, M.; Muranishi, S. Effects of various protease inhibitors on the intestinal absorption and degradation of insulin in rats. Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Kotani, A.; Kishida, T.; Tatsumi, H.; Okamoto, A.; Fujita, T.; Murakami, M.; Muranishi, S.; Yamamoto, A. Effects of various protease inhibitors on the stability and permeability of [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin in the rat intestine: Comparison with leucine enkephalin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindmark, T.; Söderholm, J.D.; Olaison, G.; Alván, G.; Ocklind, G.; Artursson, P. Mechanism of absorption enhancement in humans after rectal administration of ampicillin in suppositories containing sodium caprate. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, T.A.S.; Teijeiro-Osorio, D.; Rosa, M.; Coulter, I.S.; Alonso, M.J.; Brayden, D.J. Current status of selected oral peptide technologies in advanced preclinical development and in clinical trials. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaimtrakarn, S.; Rama Prasad, Y.V.; Ohno, T.; Konishi, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Shibata, N.; Takada, K. Absorption enhancing effect of Labrasol on the intestinal absorption of insulin in rats. J. Drug Target. 2002, 10, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Rama Prasad, Y.V.; Tawa, R.; Konishi, T.; Ishida, M.; Shibata, N.; Takada, K. Diethyl ether fraction of Labrasol having a stronger absorption enhancing effect on gentamicin than Labrasol itself. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 234, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tawa, R.; Konishi, T.; Shibata, N.; Takada, K. A novel emulsifier, Labrasol, enhances gastrointestinal absorption of gentamicin. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreilgaard, M.; Pedersen, E.J.; Jaroszewski, J.W. NMR characterisation and transdermal drug delivery potential of microemulsion systems. J. Control. Release 2000, 69, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.; Jannin, V.; Chevrier, S.; Chavant, Y.; Demarne, F.; Carrière, F. In vitro digestion of the self-emulsifying lipid excipient labrasol® by gastrointestinal lipases and influence of its colloidal structure on lipolysis rate. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 3077–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Prasad, Y.V.; Minamimoto, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Shibata, N.; Mori, S.; Matsuura, A.; Takada, K. In situ intestinal absorption studies on low molecular weight heparin in rats using Labrasol as absorption enhancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 271, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, K.A.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. The effects of common solubilizing agents on the intestinal membrane barrier functions and membrane toxicity in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartney, F.; Jannin, V.; Chevrier, S.; Boulghobra, H.; Hristov, D.R.; Ritter, N.; Miolane, C.; Chavant, Y.; Demarne, F.; Brayden, D.J. Labrasol® is an efficacious intestinal permeation enhancer across rat intestine: Ex vivo and in vivo rat studies. J. Control. Release 2019, 310, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Hayakawa, E.; Lee, V.H.L. Insulin and proinsulin proteolysis in mucosal homogenates of the albino rabbit: Implications in peptide delivery from nonoral routes. Life Sci. 1990, 47, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukai, H.; Kawagoe, A.; Sato, E.; Morishita, M.; Katsumi, H.; Yamamoto, A. Propylene glycol caprylate as a novel potential absorption enhancer for improving the intestinal absorption of insulin: Efficacy, safety, and absorption-enhancing mechanisms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Cebrian, M.; Zornoza, T.; Granero, L.; Polache, A. Intestinal absorption enhancement via the paracellular route by fatty acids, chitosans and others: A target for drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.G.; Adamczyk, B.E.; Chalasani, K.B.; Maher, S.; O’Toole, E.B.; Fox, J.S.; Leonard, T.W.; Brayden, D.J. Oral delivery of macromolecules: Rationale underpinning Gastrointestinal Permeation Enhancement Technology (GIPET®). Ther. Deliv. 2011, 2, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlSheyyab, R.Y.; Al-taani, B.M.; Obeidat, R.M.; Alsmadi, M.M.; Masaedeh, R.K.; Sabat, R.N. Delivery of peptidic gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonists. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, N.; Takahashi, K.; Mizuno, N.; Utoguchi, N.; Watanabe, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Mayumi, T. Improvement of intestinal absorption of macromolecules by nitric oxide donor. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, I.M. Rat lingual lipase: Effect of proteases, bile, and pH on enzyme stability. Am. J. Physiol. 1985, 249, G496–G500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waizumi, K.; Eguchi, T. Novel observation of nucleation and growth of insulin crystals via liquid droplets generated by liquid–liquid phase separation. Chem. Lett. 2005, 34, 1654–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, M.J.; Timasheff, S.N.; Strycharz, G.D. Optical activity of insulin. I. On the nature of the circular dichroism bands. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 824–831. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, J.; Carpenter, F.H. Zinc Binding, circular dichroism, and equilibrium sedimentation studies on insulin (Bovine) and several of its derivatives. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 4566–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadima, W.; Øgendal, L.; Bauer, R.; Kaarsholm, N.; Brodersen, K.; Hansen, J.F.; Porting, P. The influence of ionic strength and pH on the aggregation properties of zinc-free insulin studied by static and dynamic laser light scattering. Biopolymers 1993, 33, 1643–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Weiss, M.A. Toward the solution structure of human insulin: Sequential 2D 1H NMR assignment of a des-pentapeptide analogue and comparison with crystal structure. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 10545–10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.; Spencer, D.B.; Miller, A.; Bakaysa, D.L.; McCune, K.S.; Maple, S.R.; Pekar, A.H.; Brems, D.N. Acid stabilization of insulin. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 8075–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.; Khurana, R.; Coats, A.; Frokjaer, S.; Brange, J.; Vyas, S.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Effect of environmental factors on the kinetics of insulin fibril formation: Elucidation of the molecular mechanism. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 6036–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.; Frokjaer, S.; Brange, J.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Probing the mechanism of insulin fibril formation with insulin mutants. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 8397–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Ling, Y.; Dong, J.; Xia, R.; Sun, X.H. Nanoparticles: Oral delivery for protein and peptide drugs. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Shan, W.; Liu, M.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. A novel ligand conjugated nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Shan, W.; Wu, L.; Zhou, R.; Liu, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Multifunctional nanoparticles enable efficient oral delivery of biomacromolecules via improving payload stability and regulating the transcytosis pathway. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34039–34049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Chitosan coating of zein-carboxymethylated short-chain amylose nanocomposites improves oral bioavailability of insulin in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2019, 313, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Bin, W.; Tu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Liao, S.; Sun, C. A delivery system for oral administration of proteins/peptides through bile acid transport channels. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aungst, B.J. Intestinal permeation enhancers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.C.; Nguyen, J.V.; Broughall, M.; Griffin, A.; Fix, J.A.; Daddona, P.E. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of effects of sodium caprate on enteral peptide absorption and on mucosal morphology. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 191, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alama, T.; Katayama, H.; Hirai, S.; Ono, S.; Kajiyama, A.; Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Enhanced oral delivery of alendronate by sucrose fatty acids esters in rats and their absorption-enhancing mechanisms. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Uehara, S.; Sawangrat, K.; Morishita, M.; Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Improvement of intestinal absorption of curcumin by cyclodextrins and the mechanisms underlying absorption enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaya, Y.; Takaya, M.; Hinatsu, Y.; Alama, T.; Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Enhanced oral delivery of bisphosphonate by novel absorption enhancers: Improvement of intestinal absorption of alendronate by N-acyl amino acids and N-acyl taurates and their absorption-enhancing mechanisms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3680–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; He, L.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Fujita, T.; Yamamoto, A. Improvement of intestinal absorption of insulin and water-soluble macromolecular compounds by chitosan oligomers in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariscal, L.; Betanzos, A.; Nava, P.; Jaramillo, B.E. Tight junction proteins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2003, 81, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y.; Nguyen, D.; Bui, V.; Nguyen, H.; Hoa, N. Ethanol modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, G965–G974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madara, J.L. Regulation of the movement of solutes across tight junctions. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Product Name | Chemical Definition | Hydrophobic Group |
|---|---|---|
| Labrasol® | Caprylocaproyl macrogol-8 glycerides | caproic acid (≤2.0%), caprylic acid (50–80%), capric acid (20.0–50.0%), lauric acid (≤3.0%), myristic acid (≤1.0%) |
| Caprylocaproyl polyoxyl-8 glycerides | ||
| Capryol 90 | Propylene glycol monocaprylate (type ii) | caprylic acid (≥90%), capric acid (≤3.0%), lauric acid (≤3.0%), myristic acid (≤3.0%), palmitic acid (≤1.0%) |
| Capryol PGMC | Propylene glycol monocaprylate (type i) | caprylic acid (≥99%), capric acid (≤3.0%), lauric acid (≤3.0%) |
| Lauroglycol 90 | Propylene glycol monolaurate (type ii) | caprylic acid (≤0.5%), capric acid (≤2.0%), lauric acid (≥95.0%), myristic acid (≤3.0%), palmitic acid (≤1.0%) |
| Lauroglycol FCC | Propylene glycol monolaurate (type i) | caprylic acid (≤0.5%), capric acid (≤2.0%), lauric acid (≥95.0%), myristic acid (≤3.0%), palmitic acid (≤1.0%) |
| Labrafil M 2125 CS | Linoleoyl macrogol-6 glycerides | palmitic acid (4.0–20.0%), stearic acid (≤6.0%),oleic acid (20.0–35.0%), linoleic acid (50.0–65.0%), linolenic acid (≤2.0%), arachidic acid (≤1.0%), eicosenoic acid (≤1.0%) |
| Linoleoyl polyoxyl-6 glycerides | ||
| Maisine 35-1 | Glycerol monolinoleate | palmitic acid (4.0–20.0%), stearic acid (≤6.0%), oleic acid (10.0–35.0%), linoleic acid (≥50.0%), linolenic acid (≤2.0%), arachidic acid (≤1.0%), eicosenoic acid (≤1.0%) |
| Glyceryl monolinoleate |
| Formulation | Concentration (% v/v) | AAC0→4h (%⋅min) | PA% | Enhancement Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 636 ± 636 | 0.10 ± 0.10 | - |
| + Labrasol® | 10 | 5700 ± 130 ** | 0.87 ± 0.02 ** | 9.0 |
| + Capryol 90 | 5 | 1040 ± 550 | 0.16 ± 0.08 | 1.6 |
| 10 | 8050 ± 703 ** | 1.23 ± 0.11 ** | 12.7 | |
| 15 | 9870 ± 2740 ** | 1.51 ± 0.42 ** | 15.5 | |
| + Capryol PGMC | 10 | 2750 ± 1100 | 0.42 ± 0.17 | 4.3 |
| + Lauroglycol 90 | 10 | 5700 ± 1350 ** | 0.87 ± 0.21 ** | 9.0 |
| + Lauroglycol FCC | 10 | 844 ± 286 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 1.3 |
| + Labrafil M 2125 CS | 10 | 10 ± 10 | 0.002 ± 0.002 | 0.02 |
| + Maisine 35-1 | 10 | 1110 ± 1100 | 0.17 ± 0.17 | 1.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ukai, H.; Iwasa, K.; Deguchi, T.; Morishita, M.; Katsumi, H.; Yamamoto, A. Enhanced Intestinal Absorption of Insulin by Capryol 90, a Novel Absorption Enhancer in Rats: Implications in Oral Insulin Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050462
Ukai H, Iwasa K, Deguchi T, Morishita M, Katsumi H, Yamamoto A. Enhanced Intestinal Absorption of Insulin by Capryol 90, a Novel Absorption Enhancer in Rats: Implications in Oral Insulin Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(5):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050462
Chicago/Turabian StyleUkai, Hiroki, Kazuki Iwasa, Takamasa Deguchi, Masaki Morishita, Hidemasa Katsumi, and Akira Yamamoto. 2020. "Enhanced Intestinal Absorption of Insulin by Capryol 90, a Novel Absorption Enhancer in Rats: Implications in Oral Insulin Delivery" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 5: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050462
APA StyleUkai, H., Iwasa, K., Deguchi, T., Morishita, M., Katsumi, H., & Yamamoto, A. (2020). Enhanced Intestinal Absorption of Insulin by Capryol 90, a Novel Absorption Enhancer in Rats: Implications in Oral Insulin Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 12(5), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050462





