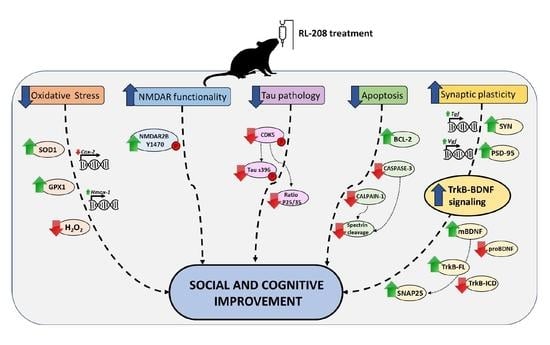
A Novel NMDA Receptor Antagonist Protects against Cognitive Decline Presented by Senescent Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Pharmacological Characterization of RL-208
2.2.1. Microsomal Stability in Human, Rat and Mice Microsomes
2.2.2. Cytochrome Inhibition
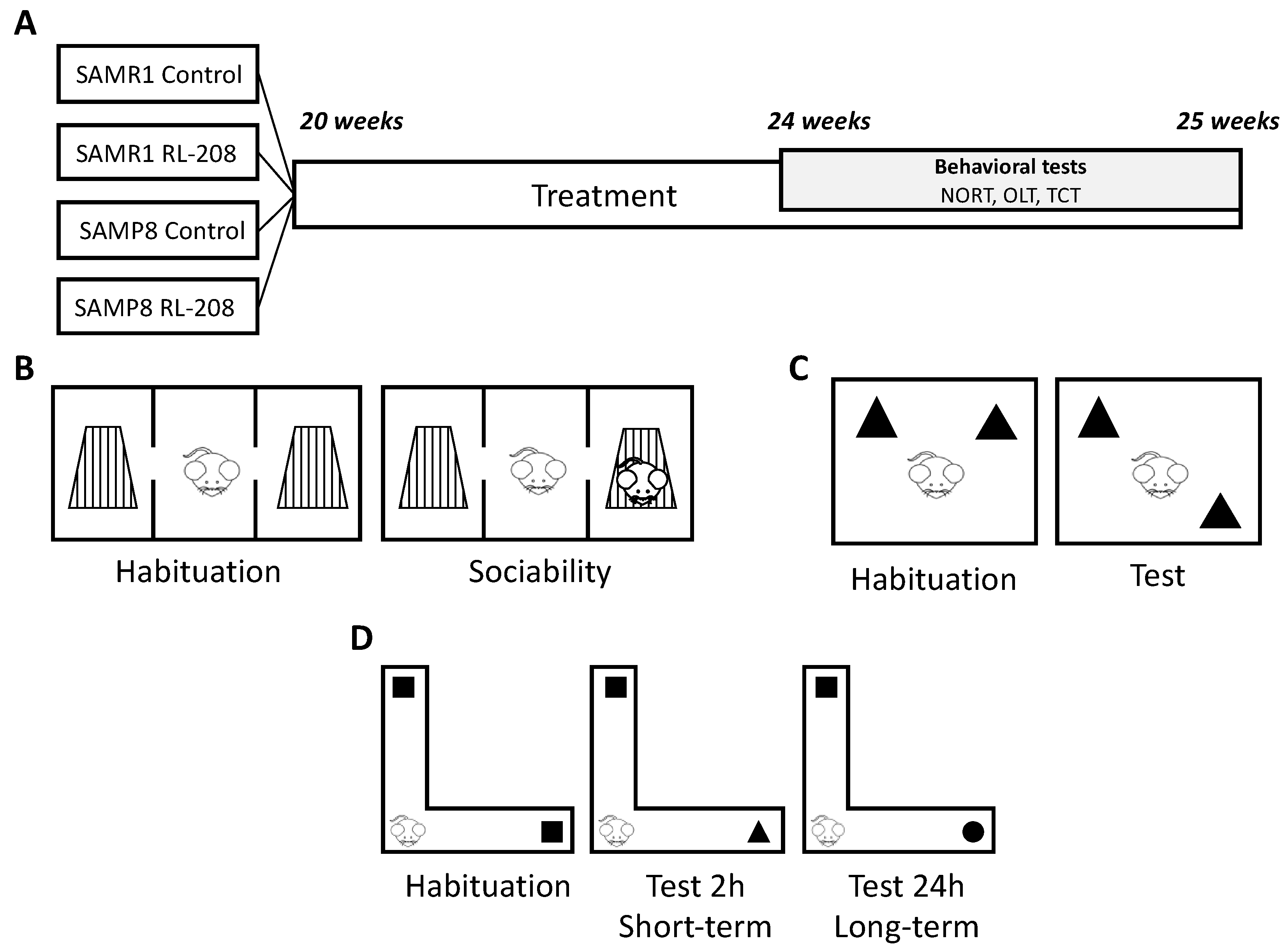
2.3. Animals
2.4. Behavioural and Cognitive Tests
2.4.1. Three-Chamber Test
2.4.2. Object Location Test
2.4.3. Novel Object Recognition Test
2.5. Brain Processing
2.6. Protein Level Determination by Western Blotting
2.7. Detection of Oxidative Stress in the Hippocampus
2.8. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Determination
2.9. Measurement of proBDNF and mBDNF Protein Levels in the Hippocampus
2.10. Data Acquisition and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Microsomal Stability and Cytochrome Inhibition
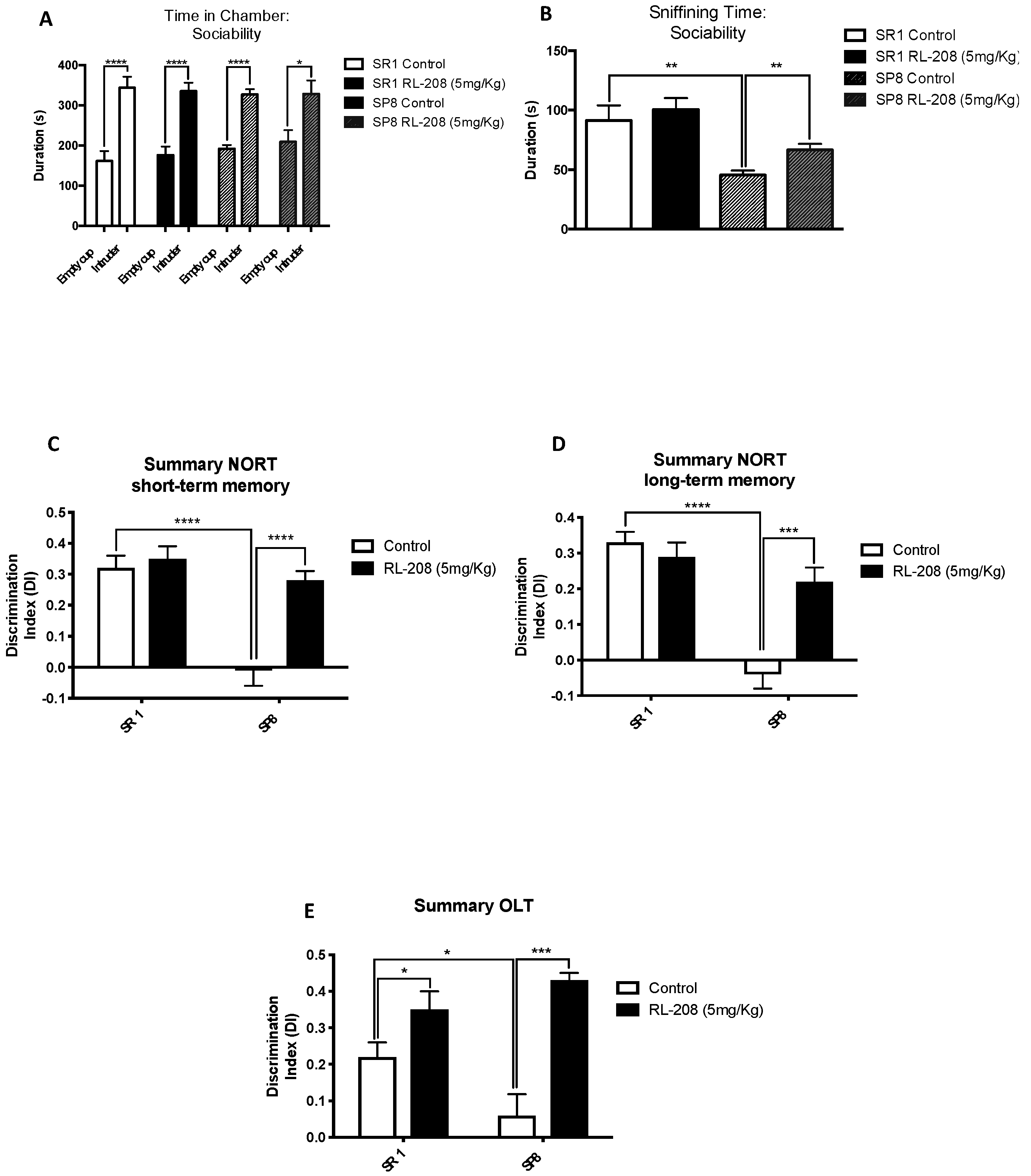
3.2. Improvement on Social Behaviour and Cognition after Treatment with RL-208
3.3. Changes in NMDAR and Apoptotic Pathways Induced by RL-208
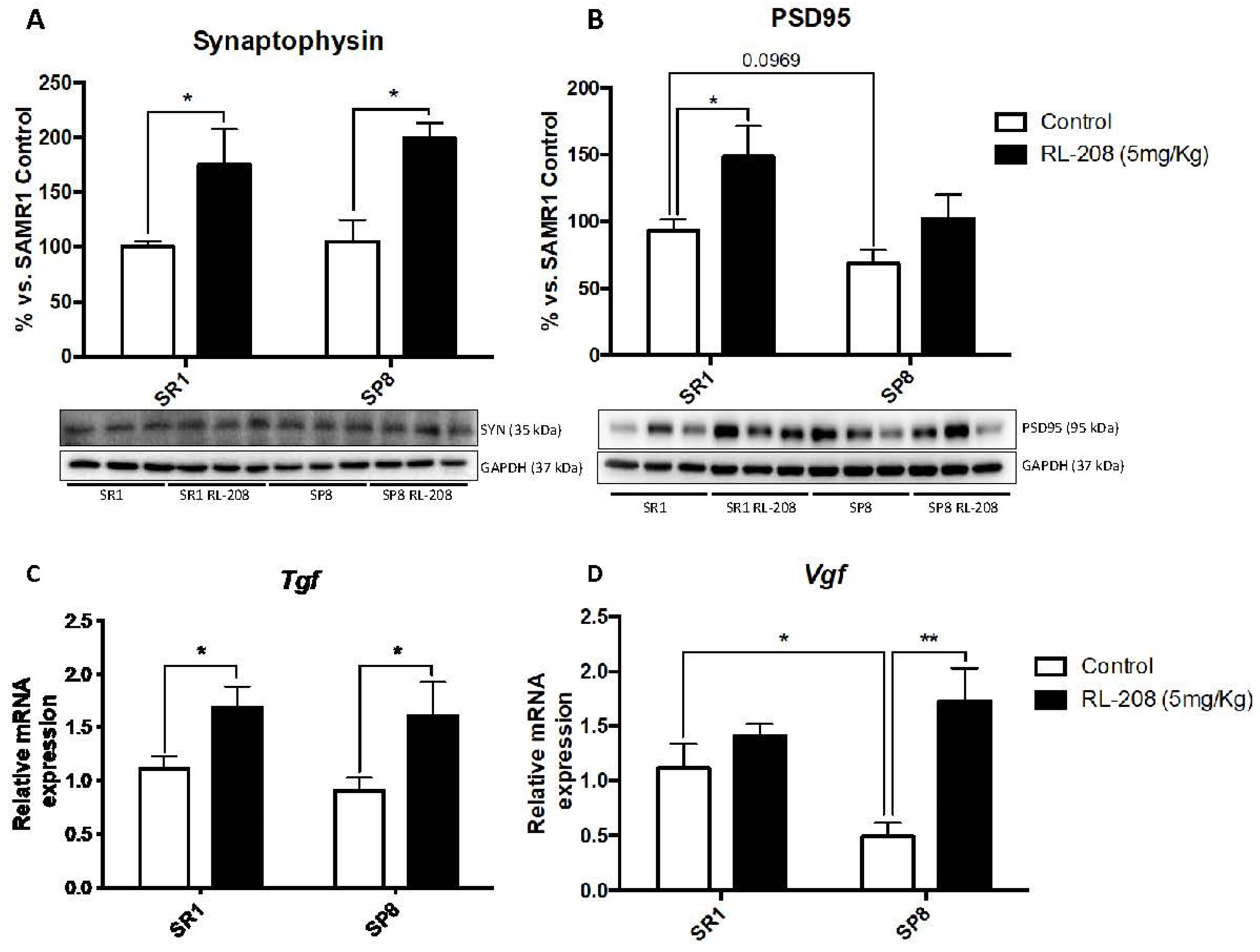
3.4. Increased Neurotrophins and Synaptic Markers Protein Levels after Treatment with RL-208
3.5. Changes in Protein Levels and Gene Expression of Antioxidant and Pro-oxidant Enzymes and ROS Levels after Treatment with RL-208
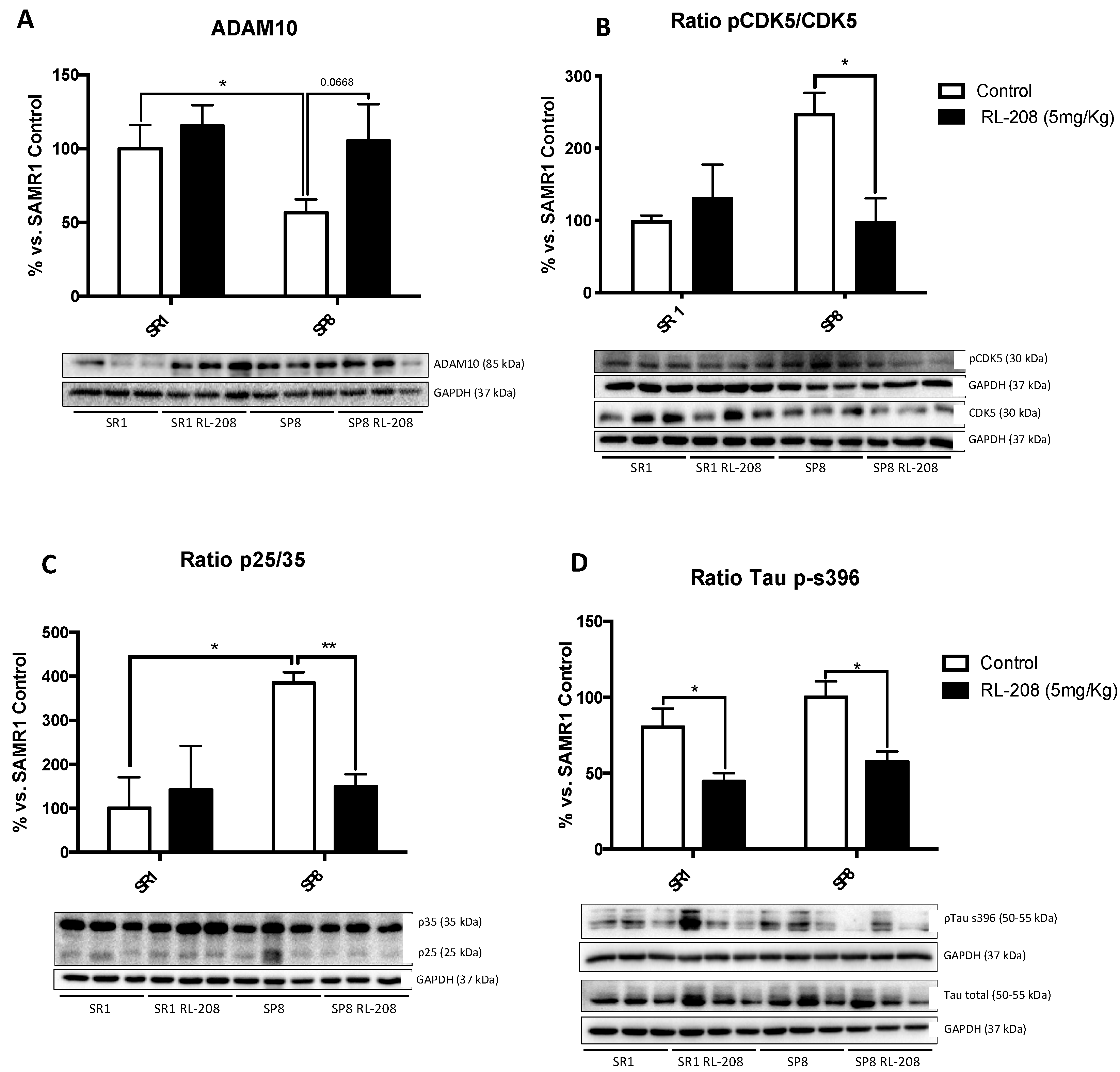
3.6. Changes in CDK5/p25-35 Pathway Activation and Tau Phosphorylation after Treatment with RL-208
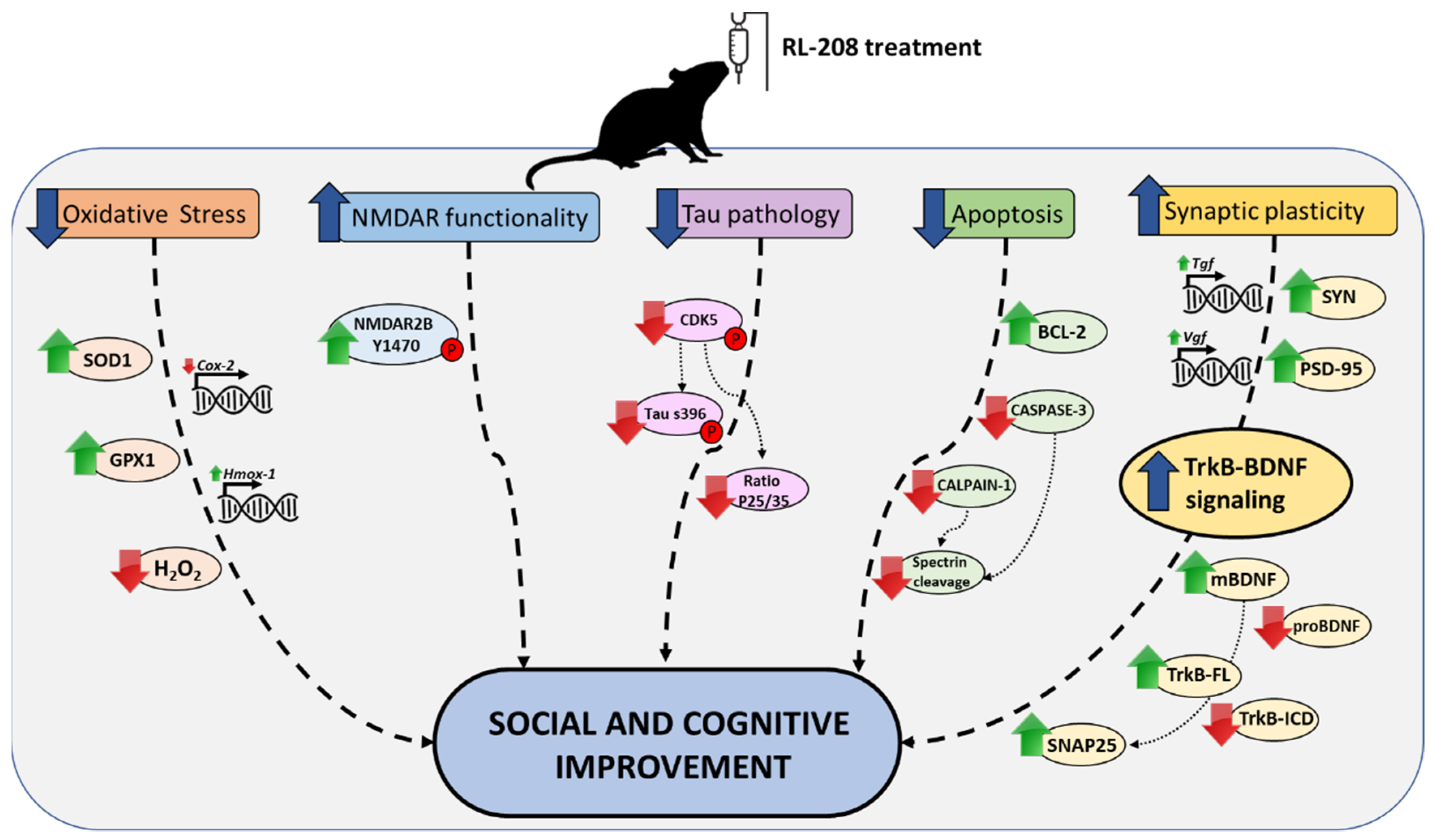
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, P.H.; Cheng, S.J.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Chou, C.H. Risk factors for the progression of mild cognitive impairment in different types of neurodegenerative disorders. Behav. Neurol. 2018, 2018, 6929732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griñán-Ferré, C.; Corpas, R.; Puigoriol-Illamola, D.; Palomera-Ávalos, V.; Sanfeliu, C.; Pallàs, M. Understanding Epigenetics in the Neurodegeneration of Alzheimer’s Disease: SAMP8 Mouse Model. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2018 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 367–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.J.; Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Prina, M. World Alzheimer Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence. Incid. Cost Trends 2015, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, M.; Comas-Herrera, A.; Knapp, M.; Guerchet, M.; Karagiannidou, M. World Alzheimer report 2016: Improving healthcare for people living with dementia: Coverage, quality and costs now and in the future. Alzheimer’s Dis. Int. Lond. 2016, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, R. Ageing and the brain. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, J.D.; Cummings, J.L. Novel targets for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010, 10, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.W. Role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 4, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calsolaro, V.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Current evidence and future directions. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrnhoefer, D.E.; Wong, B.K.Y.; Hayden, M.R. Convergent pathogenic pathways in Alzheimer’s and Huntington disease: Shared targets for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, G.; Bapat, D.; Das, D.; Gowaikar, R.; Amritkar, R.E.; Rangarajan, G.; Ravindranath, V.; Ambika, G. Synapse loss and progress of Alzheimer’s disease-A network model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhou, P.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Q. Neurotransmitter receptors and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 97, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Feng, J.; Wu, M. Dysfunction of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Iorio, G.; Baroni, G.; Lorusso, M.; Montemitro, C.; Spano, M.C.; Di Giannantonio, M. Efficacy of Memantine in Schizophrenic Patients: A Systematic Review. J. Amino Acids 2017, 2017, 7021071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.S.V.; Lipton, S.A. The chemical biology of clinically tolerated NMDA receptor antagonists. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 1611–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: Implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, G.; Platt, B.; Micheau, J. Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 140, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danysz, W.; Parsons, C.G. Alzheimer’s disease, β-amyloid, glutamate, NMDA receptors and memantine-Searching for the connections. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, F.G.; Velasco, P.T.; Lambert, M.P.; Viola, K.; Fernandez, S.J.; Ferreira, S.T.; Klein, W.L. Aβ oligomers induce neuronal oxidative stress through an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent mechanism that is blocked by the Alzheimer drug memantine. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11590–11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, L.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Y. The role of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blundell, J.; Adamec, R. The NMDA receptor antagonist CPP blocks the effects of predator stress on pCREB in brain regions involved in fearful and anxious behavior. Brain Res. 2007, 1136, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.W.; Glasgow, N.G.; Povysheva, N.V. Recent insights into the mode of action of memantine and ketamine. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 20, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomidou, C.; Turski, L. Why did NMDA receptor antagonists fail clinical trials for stroke and traumatic brain injury? Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, K.W. Glutamate-based therapeutic approaches: Clinical trials with NMDA antagonists. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, S.A. Failures and Successes of NMDA Receptor Antagonists: Molecular Basis for the Use of Open-Channel Blockers like Memantine in the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Neurologic Insults. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D.; Deshpande, V.K.; Shi, Y.; Lahiri, D.K.; Greig, N.H.; Rogers, J.T.; Huang, X. N-Methyl D-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Antagonists and Memantine Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease, Vascular Dementia and Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, W.F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhong, X.; Sha, L.; He, M.; Zheng, Z.H.; Wei, M.J. Memantine improves spatial learning and memory impairments by regulating NGF signaling in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neuroscience 2014, 273, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.; Kishi, T.; Iwata, N. Memantine monotherapy for Alzheimer’s Disease:A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, R.; Phillips, M.B.; Turcu, A.L.; Gratacòs-Batlle, E.; León-García, L.; Sureda, F.X.; Soto, D.; Johnson, J.W.; Vázquez, S. Pharmacological and Electrophysiological Characterization of Novel NMDA Receptor Antagonists. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2722–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallàs, M. Senescence-Accelerated Mice P8: A Tool to Study Brain Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease in a Mouse Model. ISRN Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 917167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Takeshita, S.; Irino, M.; Higuchi, K.; Matsushita, T.; Tomita, Y.; Yasuhira, K.; Hamamoto, H.; Shimizu, K.; et al. A new murine model of accelerated senescence. Mech Ageing Dev. 1981, 17, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, S.; Endo, S. Early onset of behavioral alterations in senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8). Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 308, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griñan-Ferré, C.; Palomera-Ávalos, V.; Puigoriol-Illamola, D.; Camins, A.; Porquet, D.; Plá, V.; Aguado, F.; Pallàs, M. Behaviour and cognitive changes correlated with hippocampal neuroinflammaging and neuronal markers in female SAMP8, a model of accelerated senescence. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 80, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Poon, H.F. The senescence-accelerated prone mouse (SAMP8): A model of age-related cognitive decline with relevance to alterations of the gene expression and protein abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Armbrecht, H.J.; Farr, S.A.; Kumar, V.B. The senescence accelerated mouse (SAMP8) as a model for oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquerda-Canals, G.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Güell-Bosch, J.; Villegas, S. Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griñan-Ferré, C.; Pérez-Cáceres, D.; Gutiérrez-Zetina, S.M.; Camins, A.; Palomera-Avalos, V.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D.; Rodrigo, M.T.; Pallàs, M. Environmental Enrichment Improves Behavior, Cognition, and Brain Functional Markers in Young Senescence-Accelerated Prone Mice (SAMP8). Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2435–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaceur, A.; Meliani, K. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. III. Spatial vs. non-spatial working memory. Behav. Brain Res. 1992, 51, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaceur, A.; Delacour, J. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav. Brain Res. 1988, 31, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigoriol-Illamola, D.; Griñán-Ferré, C.; Vasilopoulou, F.; Leiva, R.; Vázquez, S.; Pallàs, M. 11β-HSD1 Inhibition by RL-118 Promotes Autophagy and Correlates with Reduced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Enhancing Cognitive Performance in SAMP8 Mouse Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8904–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griñán-Ferré, C.; Sarroca, S.; Ivanova, A.; Puigoriol-Illamola, D.; Aguado, F.; Camins, A.; Sanfeliu, C.; Pallàs, M. Epigenetic mechanisms underlying cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease hallmarks in 5XFAD mice. Aging 2016, 8, 664–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhan, S.E.; Caro, M.; Hadzimichalis, N. NMDA receptor activity in neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Huang, Y.; Lin, C.; Lane, H.; Tsai, G. NMDA Neurotransmission Dysfunction in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimers Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 5169–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Z.Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, X.T.; Wang, C.; Fan, W.M.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Ma, C.L. NMDAR-Mediated Hippocampal Neuronal Death is Exacerbated by Activities of ASIC1a. Neurotox. Res. 2015, 28, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, S.A. Paradigm shift in neuroprotection by NMDA receptor blockade: Memantine and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.W.; Kotermanski, S.E. Mechanism of action of memantine. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Coria, H.; Green, K.N.; Billings, L.M.; Kitazawa, M.; Albrecht, M.; Rammes, G.; Parsons, C.G.; Gupta, S.; Banerjee, P.; LaFerla, F.M. Memantine improves cognition and reduces Alzheimer’s-like neuropathology in transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkeviciene, R.; Banerjee, P.; Tanila, H. Memantine improves spatial learning in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, A.; Shitaka, Y.; Yarimizu, J.; Matsuoka, N. Characterization of cognitive deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease and effects of donepezil and memantine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 703, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakas, C.; Granic, I.; Halmy, L.G.; Banerjee, P.; Luiten, P.G.M. The basal forebrain cholinergic system in aging and dementia. Rescuing cholinergic neurons from neurotoxic amyloid-β42 with memantine. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholtzowa, H.; Wadghiri, Y.Z.; Douadi, M.; Sigurdsson, E.M.; Li, Y.S.; Quartermain, D.; Banerjee, P.; Wisniewski, T. Memantine leads to behavioral improvement and amyloid reduction in Alzheimer’s-disease-model transgenic mice shown as by micromagnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Han, S.; Li, J.; Ding, S.; Wang, W.; Yin, Y. IGF-1-Involved Negative Feedback of NR2B NMDA Subunits Protects Cultured Hippocampal Neurons Against NMDA-Induced Excitotoxicity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumida, H.; Takagi, H.; Fujisawa, H.; Iwata, N.; Nakashima, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Iwama, S.; Namba, T.; Komatu, Y.; Kaibuchi, K.; et al. NMDA receptor antagonist prevents cell death in the hippocampal dentate gyrus induced by hyponatremia accompanying adrenal insufficiency in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 287, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volianskis, A.; France, G.; Jensen, M.S.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Jane, D.E.; Collingridge, G.L. Long-term potentiation and the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Brain Res. 2015, 1621, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidfar, M.; Kim, Y.K.; Wiborg, O. Effectiveness of memantine on depression-like behavior, memory deficits and brain mRNA levels of BDNF and TrkB in rats subjected to repeated unpredictable stress. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.W.; Klyubin, I.; Anwy, R.; Rowan, M.J. GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptor antagonists prevent Aβ-mediated synaptic plasticity disruption in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20504–20509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, T.; Ziegler, A.C.; Dimitrion, P.; Zuo, L. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 2525967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Kalani, A.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Tota, S.; Nath, C.; Tyagi, N. Mechanism of Oxidative Stress and Synapse Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Understanding the Therapeutics Strategies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.G.; Takeuchi, K.; Rodenas-Ruano, A.; Takayasu, Y.; Murphy, J.; Bennett, M.V.I.; Zukin, R.S. Regulation of NMDA receptor Ca2+ signalling and synaptic plasticity. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, R.C.; Brennan, A.M.; Shen, Y.; Baldwin, Y.; Swanson, R.A. Activation of neuronal NMDA receptors induces superoxide-mediated oxidative stress in neighboring neurons and astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12973–12978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, P.K.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Shukla, R.; Nath, C. Mechanism of synapse redox stress in Okadaic acid (ICV) induced memory impairment: Role of NMDA receptor. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 76, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tönnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Alvarez, J.F.; Uribe-Arias, A.; Raigoza, D.M.; Cardona-Gómez, G.P. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5, a node protein in diminished tauopathy: A systems biology approach. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, C. Memantine Differentially Regulates Tau Phosphorylation Induced by Chronic Restraint Stress of Varying Duration in Mice. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 4168472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Sengupta, A.; Haque, N.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Memantine inhibits and reverses the Alzheimer type abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau and associated neurodegeneration. FEBS Lett. 2004, 566, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Blanchard, J.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Memantine attenuates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Companys-Alemany, J.; Turcu, A.L.; Bellver-Sanchis, A.; Loza, M.I.; Brea, J.M.; Canudas, A.M.; Leiva, R.; Vázquez, S.; Pallàs, M.; Griñán-Ferré, C. A Novel NMDA Receptor Antagonist Protects against Cognitive Decline Presented by Senescent Mice. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030284
Companys-Alemany J, Turcu AL, Bellver-Sanchis A, Loza MI, Brea JM, Canudas AM, Leiva R, Vázquez S, Pallàs M, Griñán-Ferré C. A Novel NMDA Receptor Antagonist Protects against Cognitive Decline Presented by Senescent Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(3):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030284
Chicago/Turabian StyleCompanys-Alemany, Júlia, Andreea L. Turcu, Aina Bellver-Sanchis, Maria I Loza, José M. Brea, Anna M Canudas, Rosana Leiva, Santiago Vázquez, Mercè Pallàs, and Christian Griñán-Ferré. 2020. "A Novel NMDA Receptor Antagonist Protects against Cognitive Decline Presented by Senescent Mice" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 3: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030284
APA StyleCompanys-Alemany, J., Turcu, A. L., Bellver-Sanchis, A., Loza, M. I., Brea, J. M., Canudas, A. M., Leiva, R., Vázquez, S., Pallàs, M., & Griñán-Ferré, C. (2020). A Novel NMDA Receptor Antagonist Protects against Cognitive Decline Presented by Senescent Mice. Pharmaceutics, 12(3), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030284