Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP-2) Aggregates Can be Solubilized by Albumin—Investigation of BMP-2 Aggregation by Light Scattering and Electrophoresis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
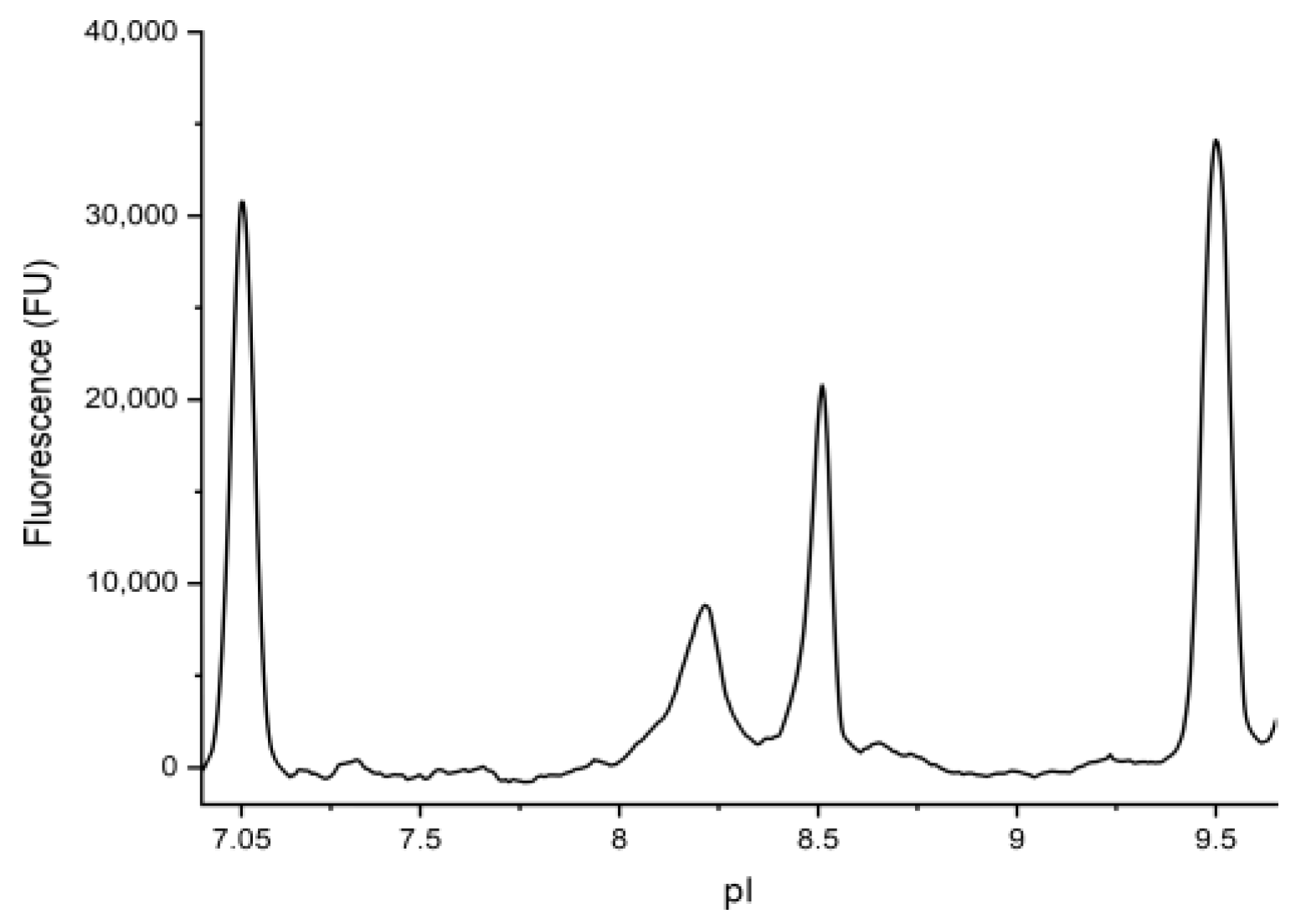
2.1. Imaged Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (icIEF) of BMP-2
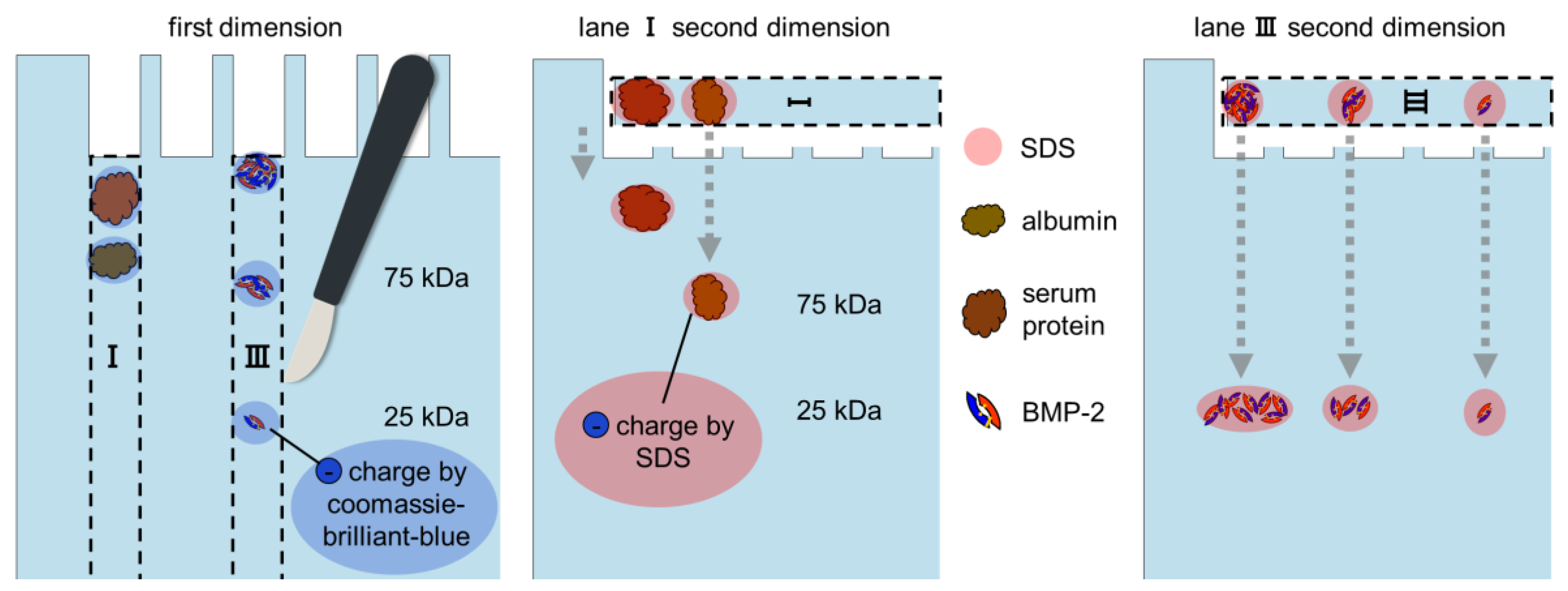
2.2. 2D Blue Native/SDS-PAGE, Anodic Native and Cathodic Native PAGE
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Asymmetric Flow Field-Flow Fractionation with Multi-Angle Light Scattering (AF4/MALS)
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) Measurements
2.6. Computation of BMP-2 Isoelectric Point and Electrostatic Potential Map
3. Results
3.1. Imaged Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (icIEF) of BMP-2
3.2. Theoretical Isoelectric Point and Electrostatic Potential Map of BMP-2
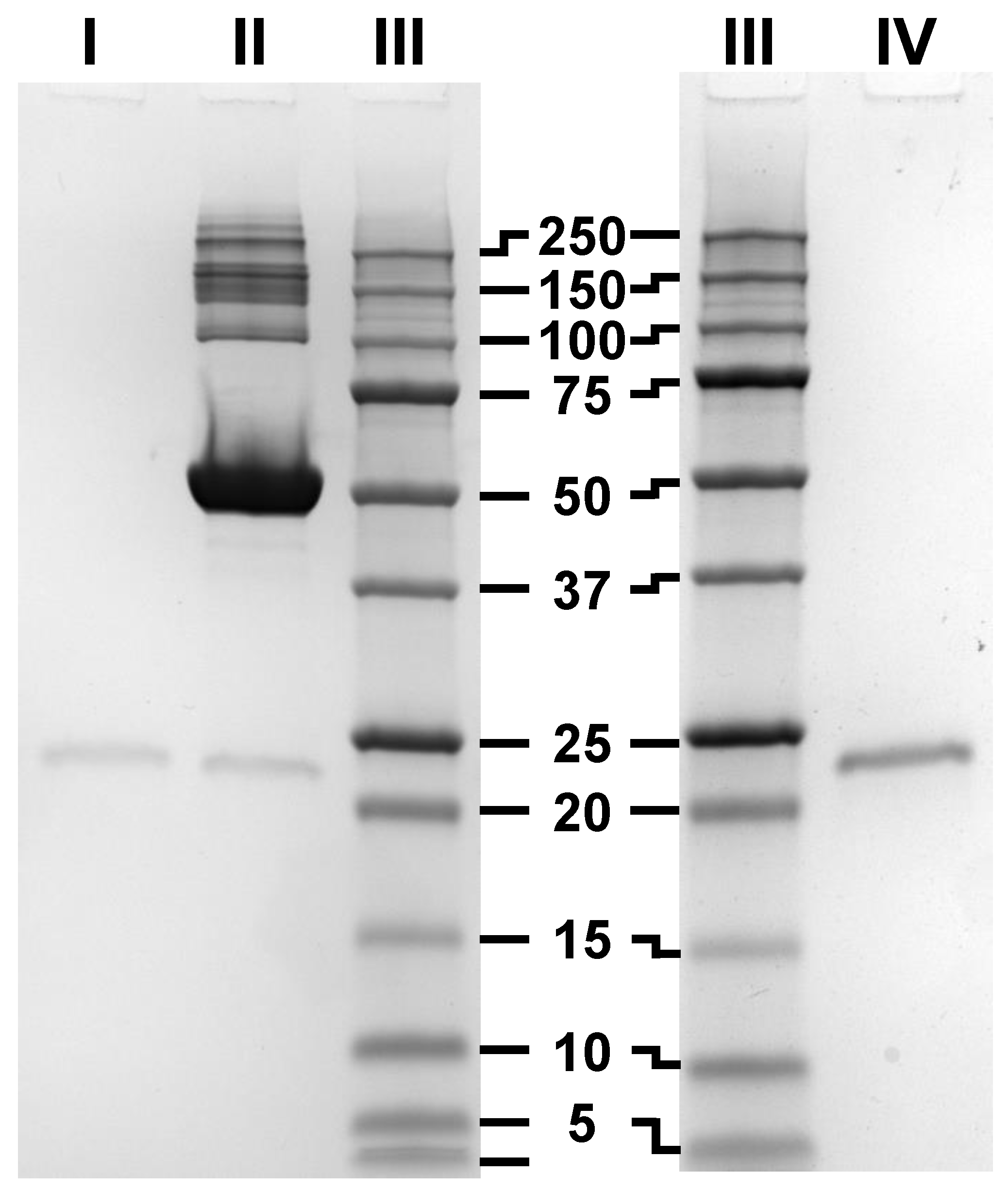
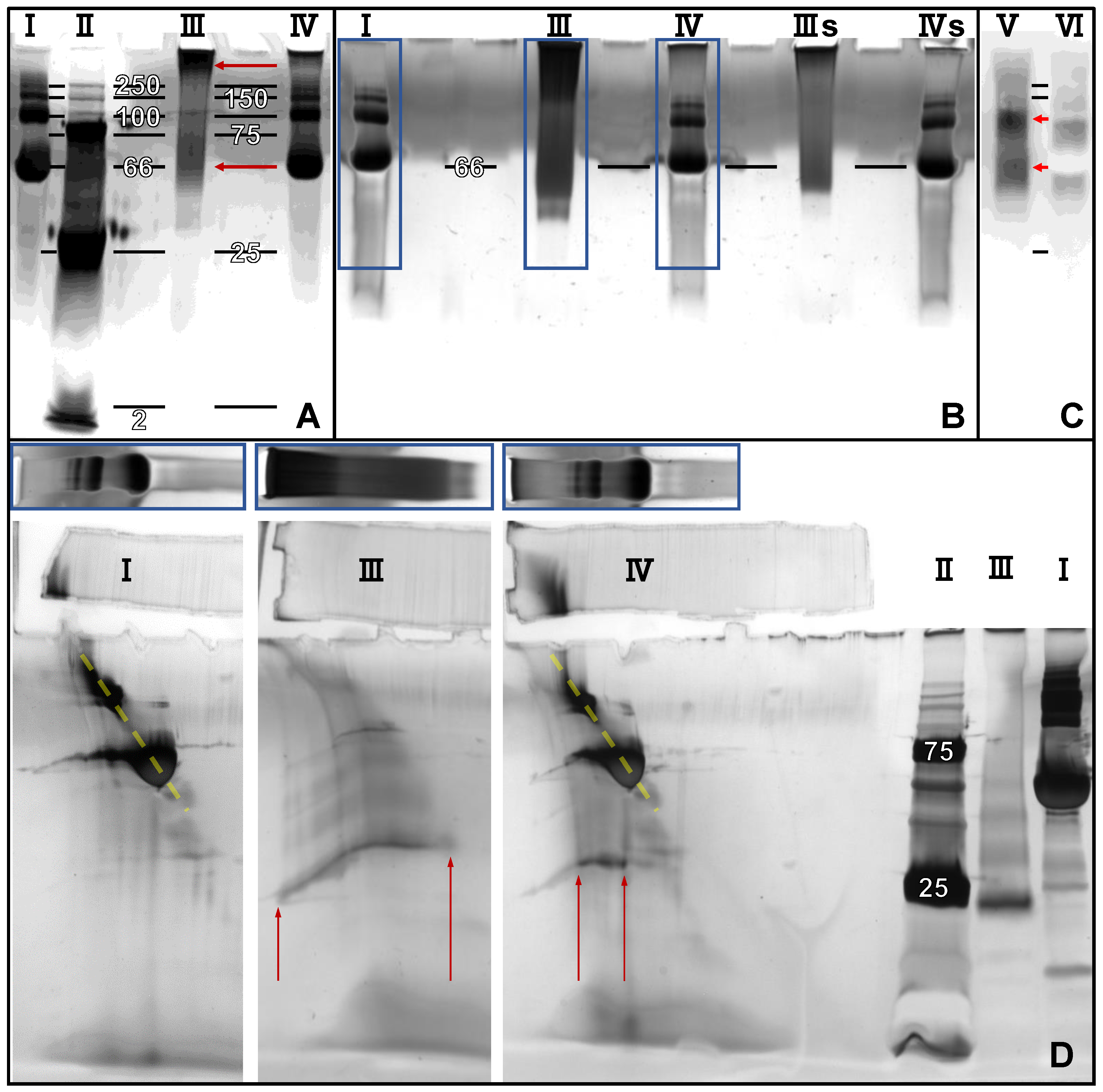
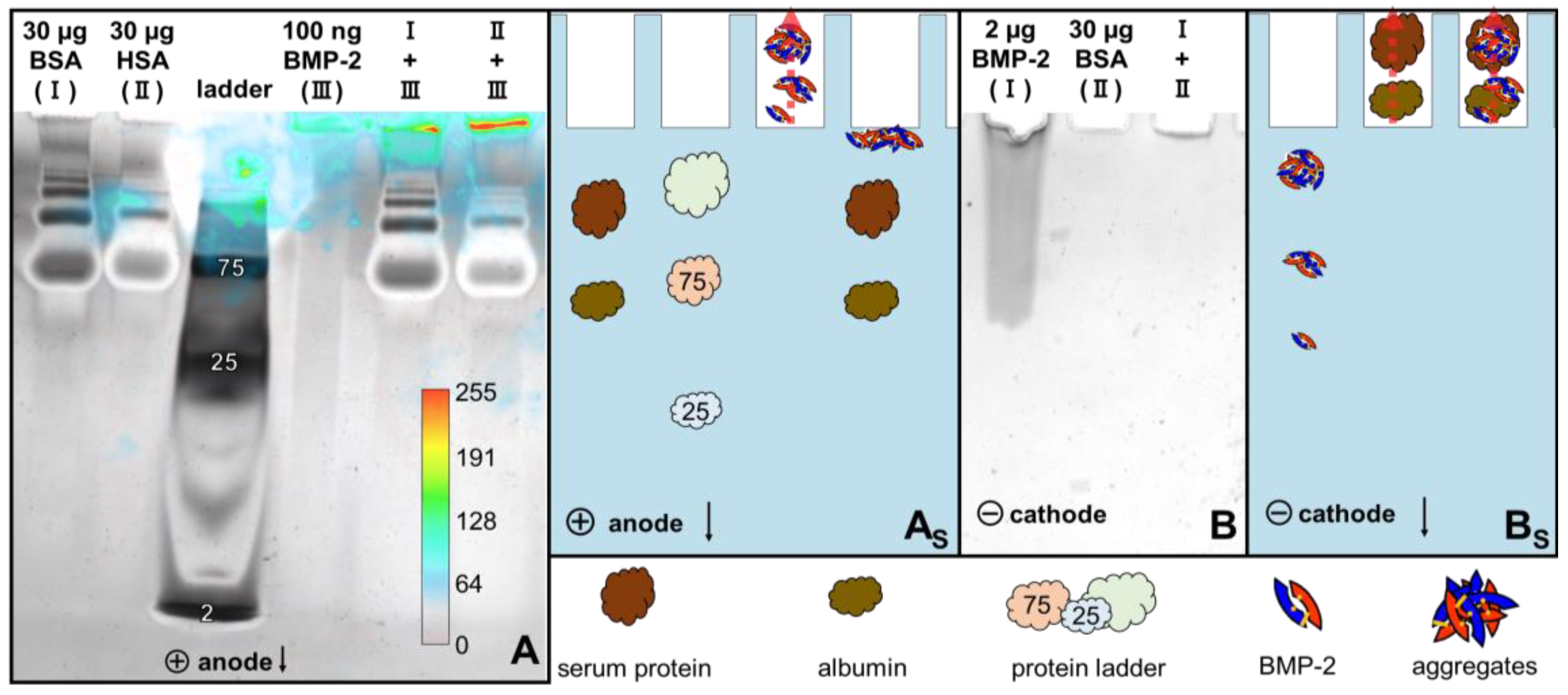
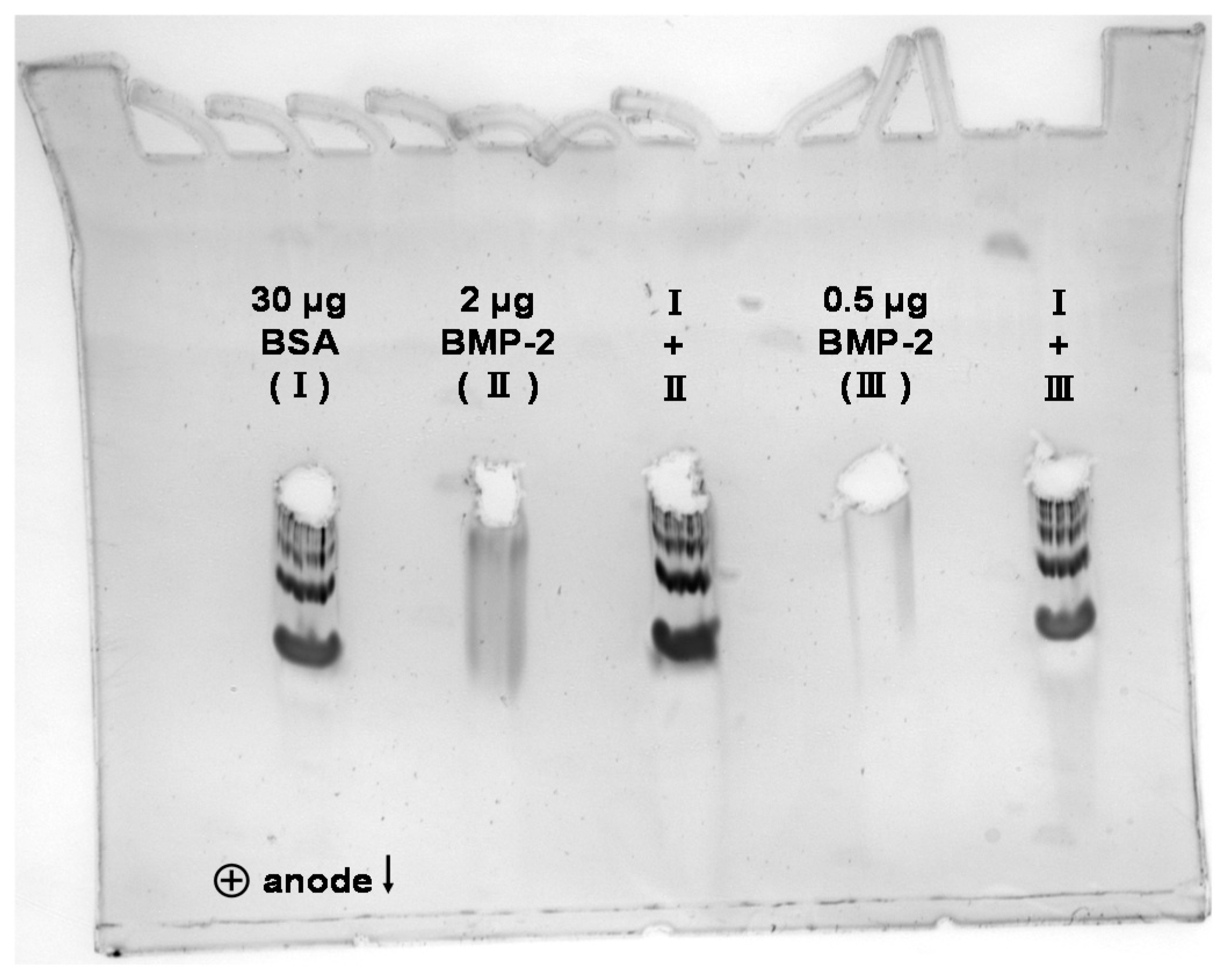
3.3. SDS-PAGE, Blue Native-PAGE and 2D Blue Native/SDS-PAGE of BMP-2 and BSA
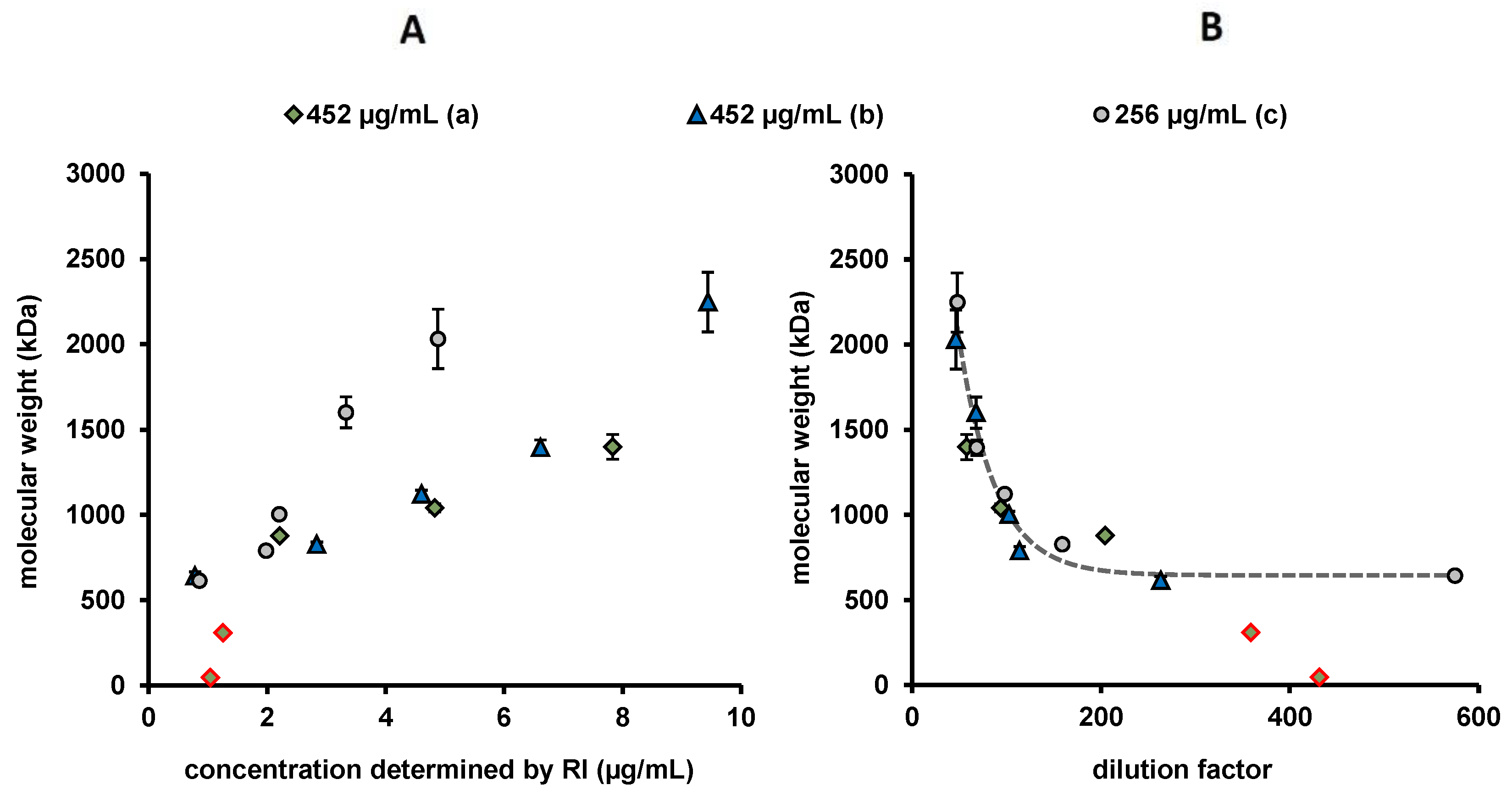
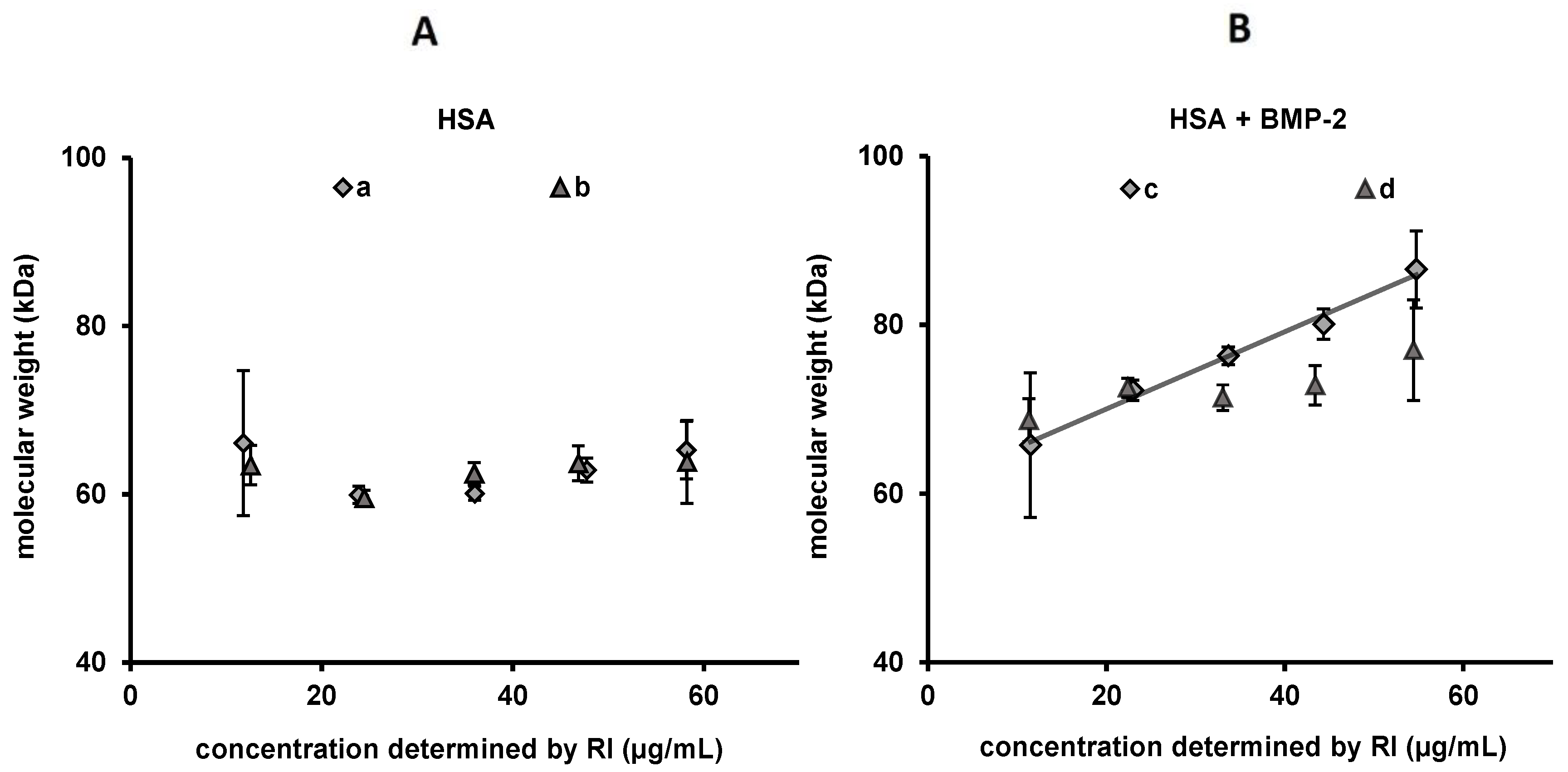
3.4. Recovery and Molar Mass Determinations (AF4/MALS) in MES Buffer pH 5 and PBS pH 7.4
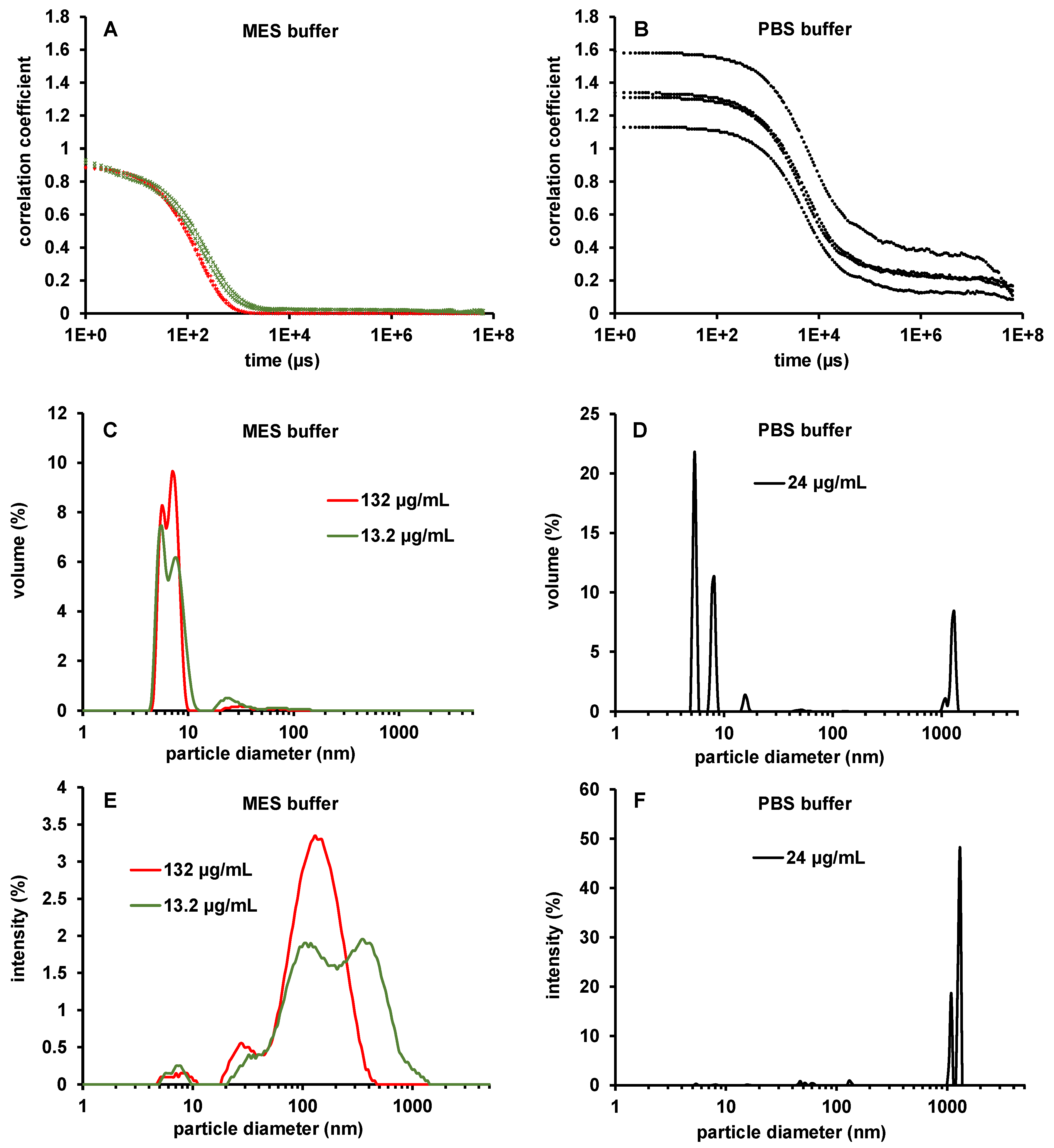
3.5. DLS and NTA Measurements of BMP-2 in MES Buffer pH 5 and in PBS pH 7.2
4. Discussion
4.1. Isoelectric Point and Charge
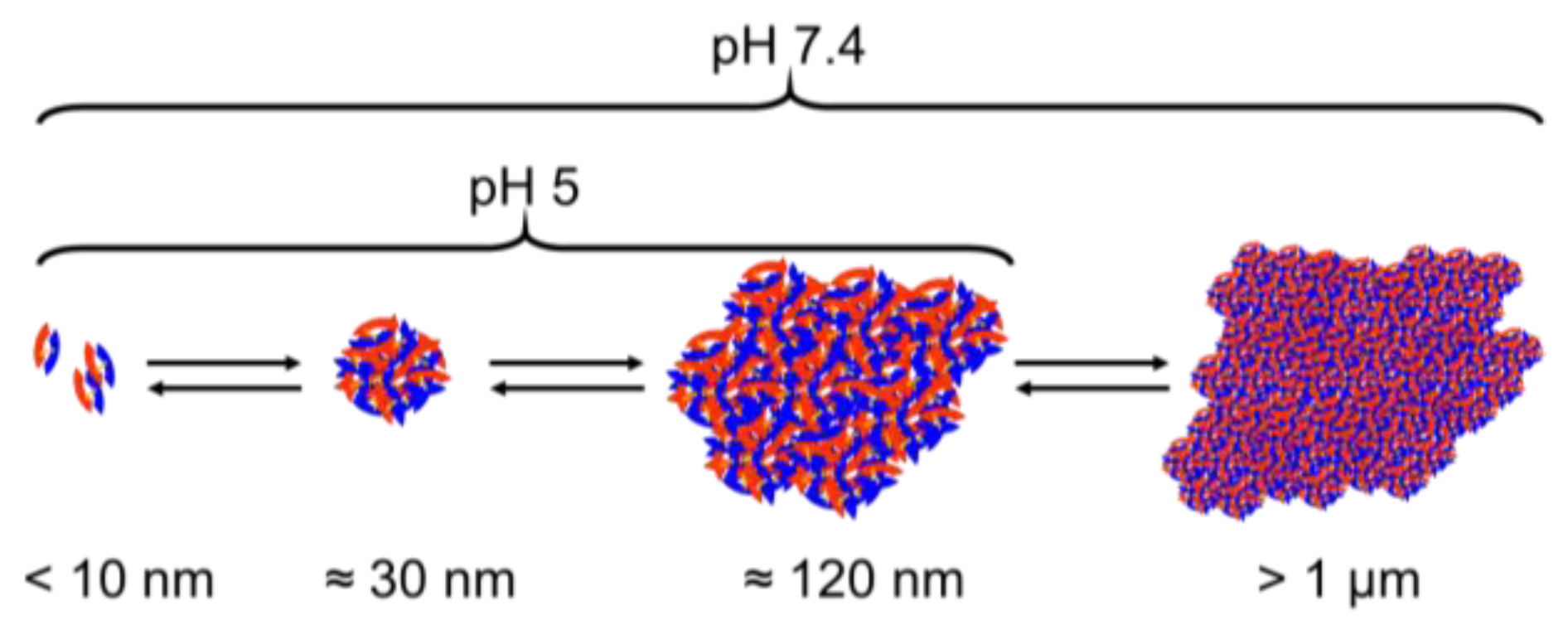
4.2. Aggregation
4.3. BMP 2 Solubilization by Albumin
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lissenberg-Thunnissen, S.N.; de Gorter, D.J.J.; Sier, C.F.M.; Schipper, I.B. Use and efficacy of bone morphogenetic proteins in fracture healing. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C. Agonists and antagonists of TGF-beta family ligands. Cold. Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, T.J.; Rathore, S.; Rouse, J.; Denton, M. Biomolecules in tissue engineered medical products (TEMPs): A case study of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). J. ASTM Int. 2004, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uludag, H.; D’Augusta, D.; Golden, J.; Timony, G.; Li, J.; Riedel, R.; Wozney, J.M. Implantation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic proteins with biomaterial carriers: A correlation between protein pharmacokinetics and osteoinduction in the rat ectopic model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 50, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheufler, C.; Sebald, W.; Hülsmeyer, M. Crystal structure of human bone morphogenetic protein-2 at 2.7 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 287, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.; Sofia, S.; Friess, W. Integrity and stability studies of precipitated rhBMP-2 microparticles with a focus on ATR-FTIR measurements. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, L.; Capelle, M.A.H.; Machaidze, G.; Arvinte, T.; Jordan, O.; Gurny, R. Physical instability, aggregation and conformational changes of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaas, B.; Burmeister, L.; Li, Z.; Satalov, A.; Behrens, P.; Hoffmann, A.; Rinas, U. Stability and biological activity of E. coli derived soluble and precipitated bone morphogenetic protein-2. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.-W.; Jung, Y.C.; Yoon, B.-I.; Woo, H.-M.; Kang, B.-J. Application of alginate microbeads as a carrier of bone morphogenetic protein-2 for bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.M.; Hodgkinson, T.; Sanchez, M.S.; Dalby, M.J.; Tanner, K.E. Hybrid core-shell scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 25008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-J.; Xia, H.; Chen, L.; Ying, Q.-S.; Yu, X.; Li, L.-H.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhang, Y. Efficient delivery of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP-2) with dextran sulfate-chitosan microspheres. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3265–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maisani, M.; Sindhu, K.R.; Fenelon, M.; Siadous, R.; Rey, S.; Mantovani, D.; Chassande, O. Prolonged delivery of BMP-2 by a non-polymer hydrogel for bone defect regeneration. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Tong, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, T.; Wang, X. In vitro evaluation of a bone morphogenetic protein-2 nanometer hydroxyapatite collagen scaffold for bone regeneration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5830–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Tong, F. In vitro and in vivo protein release and anti-ischemia/reperfusion injury properties of bone morphogenetic protein-2-loaded glycyrrhetinic acid-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(l-lysine) nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7613–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, B.-B.; Koh, J.-T.; Song, S.-C. Tuning physical properties and BMP-2 release rates of injectable hydrogel systems for an optimal bone regeneration effect. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begam, H.; Nandi, S.K.; Kundu, B.; Chanda, A. Strategies for delivering bone morphogenetic protein for bone healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochmann, A.; Nitzsche, H.; von Einem, S.; Schwarz, E.; Mäder, K. The influence of covalently linked and free polyethylene glycol on the structural and release properties of rhBMP-2 loaded microspheres. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawe, A.; Friess, W. Stabilization of a hydrophobic recombinant cytokine by human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2987–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, W.W.; Wang, M. Bicomponent fibrous scaffolds made through dual-source dual-power electrospinning: Dual delivery of rhBMP-2 and Ca-P nanoparticles and enhanced biological performances. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiaratchi, M.H.; Chou, C.; Servies, N.; Smeekens, J.M.; Cheng, A.; Esancy, C.; Wu, R.; McDevitt, T.C.; Guldberg, R.E.; Krishnan, L. Competitive protein binding influences heparin-based modulation of spatial growth factor delivery for bone regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundermann, J.; Oehmichen, S.; Sydow, S.; Burmeister, L.; Quaas, B.; Hänsch, R.; Rinas, U.; Hoffmann, A.; Menzel, H.; Bunjes, H. Varying the sustained release of BMP-2 from chitosan nanogel-functionalized PCL fiber mats by different PCL surface modifications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, K.; Henriksen, J.R.; Andresen, T.L. Adsorption of cationic peptides to solid surfaces of glass and plastic. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiala, G.J.; Schamel, W.W.A.; Blumenthal, B. Blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) for analysis of multiprotein complexes from cellular lysates. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, e2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Säftel, W.; Winkler, U.; Stabenau, H. Separation of Native Basic Proteins by Cathodic, Discontinuous Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. Bio-Rad Tech Note 2376. Available online: http://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/Bulletin_2376.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Keller, S.; Nickel, J.; Zhang, J.-L.; Sebald, W.; Mueller, T.D. Molecular recognition of BMP-2 and BMP receptor IA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandakrishnan, R.; Aguilar, B.; Onufriev, A.V. H++ 3.0: Automating pK prediction and the preparation of biomolecular structures for atomistic molecular modeling and simulations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W537–W541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, N.A.; Sept, D.; Joseph, S.; Holst, M.J.; McCammon, J.A. Electrostatics of nanosystems: Application to microtubules and the ribosome. Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10037–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gervais, D.; King, D. Capillary isoelectric focusing of a difficult-to-denature tetrameric enzyme using alkylurea-urea mixtures. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 465, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Alexov, E. On the dielectric “constant” of proteins: Smooth dielectric function for macromolecular modeling and its implementation in DelPhi. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, A.; Glibowicka, M.; Nadeau, V.G.; Chen, G.; Deber, C.M. Detergent binding explains anomalous SDS-PAGE migration of membrane proteins. Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otter, T.; King, S.M.; Witman, G.B. A two-step procedure for efficient electrotransfer of both high-molecular-weight (>400,000) and low-molecular-weight (<20,000) proteins. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, A.; Boström, M.; Medda, L.; Cugia, F.; Barse, B.; Parsons, D.F.; Ninham, B.W.; Monduzzi, M. Measurements and theoretical interpretation of points of zero charge/potential of BSA protein. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11597–11604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, R. Dynamic Light Scattering Training, Malvern Panalytical. Available online: https://www.chem.uci.edu/~dmitryf/manuals/Fundamentals/DLS%20concept.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Kozlowski, L.P. Proteome-pI: Proteome isoelectric point database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1112–D1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjellqvist, B.; Basse, B.; Olsen, E.; Celis, J.E. Reference points for comparisons of two-dimensional maps of proteins from different human cell types defined in a pH scale where isoelectric points correlate with polypeptide compositions. Electrophoresis 1994, 15, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halligan, B.D.; Ruotti, V.; Jin, W.; Laffoon, S.; Twigger, S.N.; Dratz, E.A. ProMoST (Protein Modification Screening Tool): A web-based tool for mapping protein modifications on two-dimensional gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W638–W644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josuran, R. Prot pi. Available online: https://www.protpi.ch/ (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Gao, T.; Kousinioris, N.; Winn, S.R.; Wozney, J.M.; Uludag, H. Enhanced retention of rhBMP-2 in vivo by thermoreversible polymers. Materialwiss. Werkst. 2001, 32, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaas, B.; Burmeister, L.; Li, Z.; Nimtz, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Rinas, U. Properties of dimeric, disulfide-linked rhBMP-2 recovered from E. coli derived inclusion bodies by mild extraction or chaotropic solubilization and subsequent refolding. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, T.; Clarke, S. Deamidation, isomerization, and racemization at asparaginyl and aspartyl residues in peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, D. Development of an Aqueous Suspension of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (rhBMP-2). Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Walsh, A.; Ehrick, R.; Xu, W.; May, K.; Liu, H. Chromatographic analysis of the acidic and basic species of recombinant monoclonal antibodies. MAbs 2012, 4, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaman, M.R.; Williamson, A.R. Isoelectric focusing of proteins in the native and denatured states. Anomalous behaviour of plasma albumin. Biochem. J. 1971, 122, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Righetti, P.G. Determination of the isoelectric point of proteins by capillary isoelectric focusing. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1037, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po, H.N.; Senozan, N.M. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: Its history and limitations. J. Chem. Educ. 2001, 78, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbatiello, S.E.; Porter, T.J. Anion-mediated precipitation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP-2) is dependent upon the heparin binding N-terminal region. In Proceedings of the Protein Society Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 13–16 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zangi, R.; Zhou, R.; Berne, B.J. Urea’s action on hydrophobic interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Ren, F.; Lu, G.; Lu, X. The interaction of chitosan and BMP-2 tuned by deacetylation degree and pH value. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 107, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, T.E.; Nunez, A.C.; Sunde, M.; Easterbrook-Smith, S.B. Serum albumin prevents protein aggregation and amyloid formation and retains chaperone-like activity in the presence of physiological ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21530–21540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utesch, T.; Daminelli, G.; Mroginski, M.A. Molecular dynamics simulations of the adsorption of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on surfaces with medical relevance. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13144–13153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquetti, I.; Desai, S. Molecular modeling the adsorption behavior of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on hydrophobic and hydrophilic substrates. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 706, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, G.; Di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| BMP-2 (mg/mL) | HSA (mg/mL) | Buffer |
|---|---|---|
| 0.452 | - | MES |
| 0.226 | - | MES |
| 0.226 | - | PBS |
| - | 1.15 | PBS |
| 0.200 | 1.15 | PBS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sundermann, J.; Zagst, H.; Kuntsche, J.; Wätzig, H.; Bunjes, H. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP-2) Aggregates Can be Solubilized by Albumin—Investigation of BMP-2 Aggregation by Light Scattering and Electrophoresis. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121143
Sundermann J, Zagst H, Kuntsche J, Wätzig H, Bunjes H. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP-2) Aggregates Can be Solubilized by Albumin—Investigation of BMP-2 Aggregation by Light Scattering and Electrophoresis. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(12):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121143
Chicago/Turabian StyleSundermann, Julius, Holger Zagst, Judith Kuntsche, Hermann Wätzig, and Heike Bunjes. 2020. "Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP-2) Aggregates Can be Solubilized by Albumin—Investigation of BMP-2 Aggregation by Light Scattering and Electrophoresis" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 12: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121143
APA StyleSundermann, J., Zagst, H., Kuntsche, J., Wätzig, H., & Bunjes, H. (2020). Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP-2) Aggregates Can be Solubilized by Albumin—Investigation of BMP-2 Aggregation by Light Scattering and Electrophoresis. Pharmaceutics, 12(12), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121143







