Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PN Admixtures
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Visual Control and Microscopic Inspection
2.4. pH Measurement
2.5. Osmolality Measurement
2.6. Measurement of Particle Size and Zeta Potential
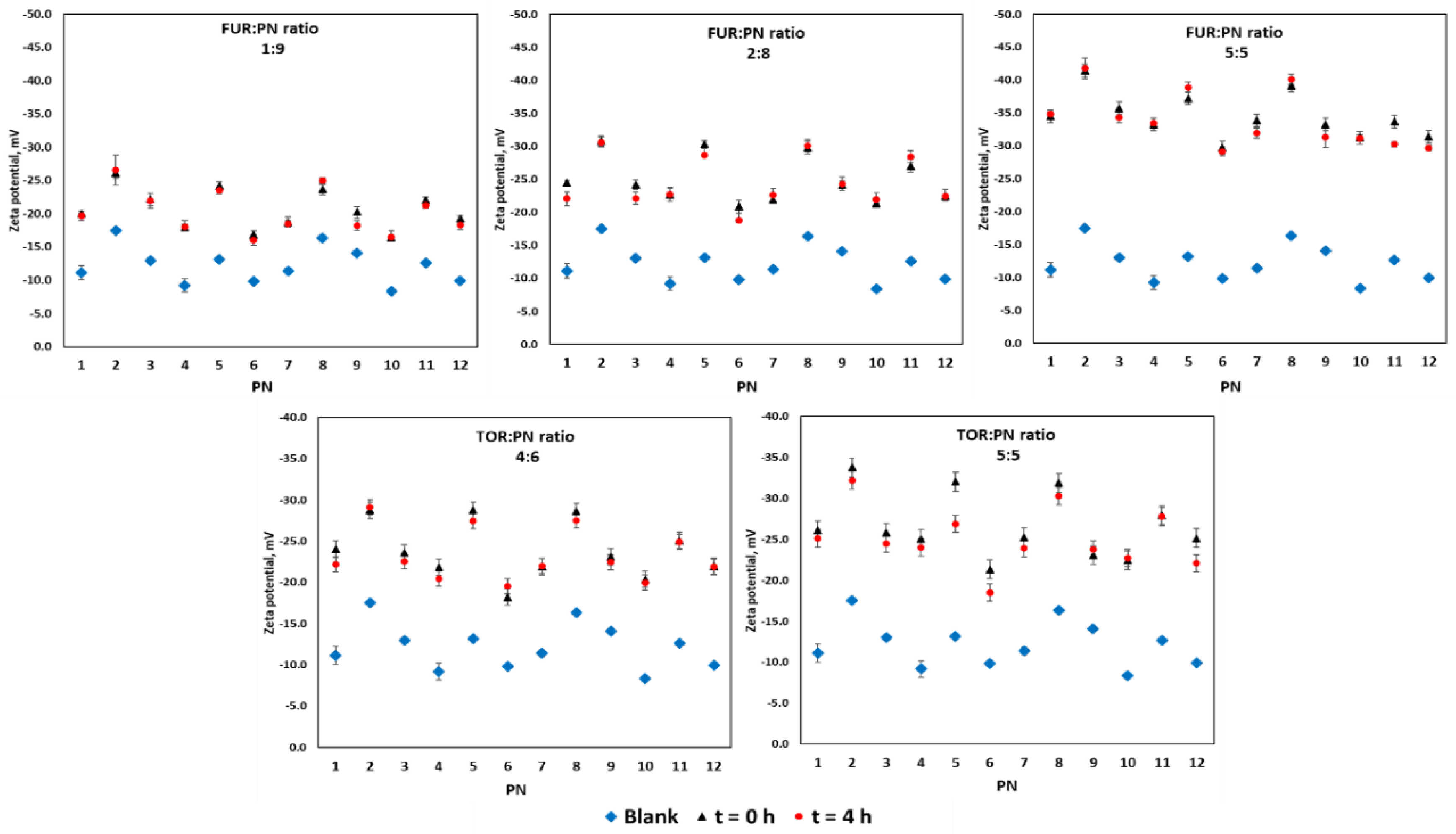
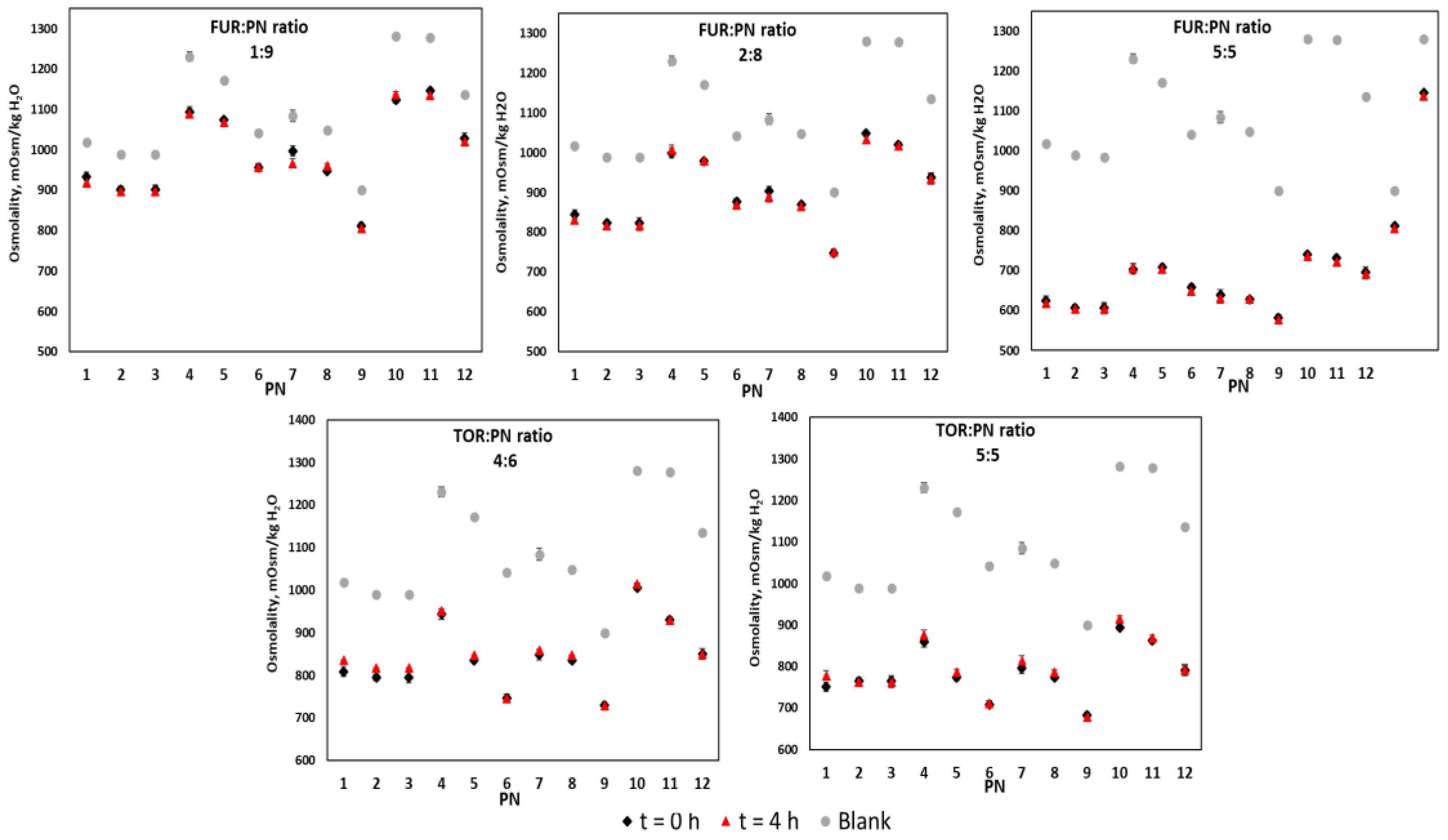
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaloga, G.P. Parenteral nutrition in adult inpatients with functioning gastrointestinal tracts: Assessment of outcomes. Lancet 2006, 367, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villet, S.; Chiolero, R.L.; Bollmann, M.D.; Revelly, J.P.; Cayeux RN, M.C.; Delarue, J.; Berger, M.M. Negative impact of hypocaloric feeding and energy balance on clinical outcome in ICU patients. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthucheary, Z.A.; Rawal, J.; McPhail, M.; Connolly, B.; Ratnayake, G.; Chan, P.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Padhke, R.; Dew, T.; Sidhu, P.S.; et al. Acute Skeletal Muscle Wasting in Critical Illness. JAMA 2013, 310, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, K.M.; Robinson, M.K.; Casey, J.D.; Gunasekera, N.S.; Moromizato, T.; Rawn, J.D.; Christopher, K.B. Nutritional Status and Mortality in the Critically Ill*. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.; Schuetz, P.; Bounoure, L.; Austin, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.; Cederholm, T.; Fletcher, J.; Laviano, A.; Norman, K.; Poulia, K.A.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutritional support for polymorbid internal medicine patients. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, P.; Blaser, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Alhazzani, W.; Calder, P.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Hiesmayr, M.; Mayer, K.; Montejo, J.C.; Pichard, C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 48–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gostyńska, A.; Stawny, M.; Dettlaff, K.; Jelińska, A. Clinical nutrition of critically ill patients in the context of the latest ESPEN guidelines. Medicina 2019, 55, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staven, V.; Wang, S.; Grønlie, I.; Tho, I. Development and evaluation of a test program for Y-site compatibility testing of total parenteral nutrition and intravenous drugs. Nutr. J. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhill, K.; Hornsby, E.; Gorman, G. Investigations of physical compatibilities of commonly used intravenous medications with and without parenteral nutrition in pediatric cardiovascular intensive care unit patients. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.E.; Heldman, L.S.; Goo, E.D.; Whippo, P.E.; Perkinson, J.C. Fatal microvascular pulmonary emboli from precipitation of a total nutrient admixture solution. J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 1996, 20, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S.; Wassel, R.T.; Lee, L.; Nambiar, S. Intravenous ceftriaxone and calcium in the neonate: Assessing the risk for cardiopulmonary adverse events. Pediatrics 2009, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Ling, P.-R.; Silvestri, A.P.; Bistrian, B.R. Fine vs. coarse complete all-in-one admixture infusions over 96 hours in rats: Fat globule size and hepatic function. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Ling, P.-R.; Bistrian, B.R. Pathological consequences to reticuloendothelial system organs following infusion of unstable all-in-one mixtures in rats. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, A.; Capuzzo, M.; Guidet, B.; Moreno, R.; Metnitz, B.; Bauer, P.; Metnitz, P. Errors in administration of parenteral drugs in intensive care units: Multinational prospective study. BMJ 2009, 338, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekadu, T.; Teweldemedhin, M.; Esrael, E.; Asgedom, S.W. Prevalence of intravenous medication administration errors: A cross-sectional study. Integr. Pharm. Res. Pract. 2017, 6, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agalu, A.; Ayele, Y.; Bedada, W.; Woldie, M. Medication administration errors in an intensive care unit in Ethiopia. Int. Arch. Med. 2012, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Timmermann, M.; Schulzke, S.; Kiss, C.; Sidler, M.A.; Furlano, R.I. Developing and implementing all-in-one standard paediatric parenteral nutrition. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisetty, S.; Osborn, D.; Sinn, J.; Lui, K.; Kent, A.; Trivedi, A.; Yaacoub, D.; Morris, S.; Marshall, P.; Birch, P.; et al. Standardised neonatal parenteral nutrition formulations—An Australasian group consensus 2012. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopotowska, J.E.; Kuiper, R.; van Kan, H.J.; de Pont, A.C.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Lie-A-Huen, L.; Vroom, M.B.; Smorenburg, S.M. On-ward participation of a hospital pharmacist in a Dutch intensive care unit reduces prescribing errors and related patient harm: An intervention study. Crit. Care 2010, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselli, D.; Rueda, J.D.; Silva, M.D.; Salcedo, J. Economic evaluation of four drug administration systems in intensive care units in Colombia. Value Heal. Reg. Issues 2014, 5, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crews, J.; Rueda-de-Leon, E.; Remus, D.; Sayles, R.; Mateus, J.; Shakeel, F. Total Parenteral Nutrition Standardization and Electronic Ordering to Reduce Errors. Pediatr. Qual. Saf. 2018, 3, e093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.W.; Han, S.Y. Loop Diuretics in Clinical Practice. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2015, 13, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Täger, T.; Fröhlich, H.; Grundtvig, M.; Seiz, M.; Schellberg, D.; Goode, K.; Kazmi, S.; Hole, T.; Katus, H.A.; Atar, D.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of loop diuretics on mortality in the treatment of patients with chronic heart failure—A multicenter propensity score matched analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 289, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormans, T.P.J.; van Meyel, J.J.M.; Gerlag, P.G.G.; Tan, Y.; Russel, F.G.M.; Smits, P. Diuretic efficacy of high dose furosemide in severe heart failure: Bolus injection versus continuous infusion. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 28, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Alvarez, G.; Sharpe, M.D.; Martin, C.M. Frusemide Administration in Critically Ill Patients by Continuous Compared to Bolus Therapy. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2007, 107, c70–c76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, K. Management of loop diuretic resistance in the intensive care unit. Am. J. Heal. Pharm. 2009, 66, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, D.; Rey, N.; Ramos, G.; Punzalan, F. Continuous infusion versus bolus injection of loop diuretics in congestive heart failure. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Staven, V.; Iqbal, H.; Wang, S.; Grønlie, I.; Tho, I. Physical compatibility of total parenteral nutrition and drugs in Y-site administration to children from neonates to adolescents. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoud, L.; Fonzo-Christe, C.; Klingmüller, M.; Bonnabry, P. Compatibility of intravenous medications with parenteral nutrition: In vitro evaluation. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2013, 37, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trissel, L.A.; Gilbert, D.L.; Martinez, J.F.; Baker, M.B.; Walter, W.V.; Mirtallo, J.M. Compatibility of medications with 3-in-1 parenteral nutrition admixtures. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1999, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watrobska, D.-S.; Pietka, M.; Klek, S. Evaluation of Y-site compatibility of home total parenteral nutrition and intravenous loop diuretics. Med. Baltim. 2019, 98, e15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Parenteral preparations 2017. In European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), 9th ed.; EDQM: Strasbourg, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczak, S.; Stawny, M.; Dettlaff, K.; Kieliszek, M.; Słomińska, D.; Jelińska, A. Physicochemical Compatibility and Stability of Linezolid with Parenteral Nutrition. Molecules 2019, 24, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USP. Globule Size Distribution in Lipid Injectable Emulsions; The United states Pharmacopeia 33/National Formulary: Rockville, MD, USA, 2009; Volume 28, pp. 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bourlieu, C.; Rousseau, F.; Briard-Bion, V.; Madec, M.N.; Bouhallab, S. Hydrolysis of native milk fat globules by microbial lipases: Mechanisms and modulation of interfacial quality. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, C.J.; Groves, M.J. The influence of free fatty acid formation on the pH of phospholipid-stabilized triglyceride emulsions. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.F. Lipid injectable emulsions: Pharmacopeial and safety issues. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlebach, S. Basics in clinical nutrition: Drugs and nutritional admixtures. E. Spen. Eur. e-J. Clin. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 4, e134–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltri, M.; Lee, C.K.K. Compatibility of neonatal parenteral nutrient solutions with selected intravenous drugs. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 1996, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trissel, L.A.; Gilbert, D.L.; Martinez, J.F.; Baker, M.B.; Walter, W.V.; Mirtallo, J.M. Compatibility of Parenteral Nutrient Solutions with Selected Drugs During Simulated Y-Site Administration; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 1997; Volume 54, pp. 1295–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.A.; Sawyer, J.E. Y-Site Compatibility of Medications with Parenteral Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. JPPT 2009, 14, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Boullata, J.I.; Gilbert, K.; Sacks, G.; Labossiere, R.J.; Crill, C.; Goday, P.; Kumpf, V.J.; Mattox, T.W.; Plogsted, S.; Holcombe, B.; et al. A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 334–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, E.; Messerli, M.; Stanga, Z.; Mühlebach, S. Pharmaceutical Aspects of Artificial Nutrition. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
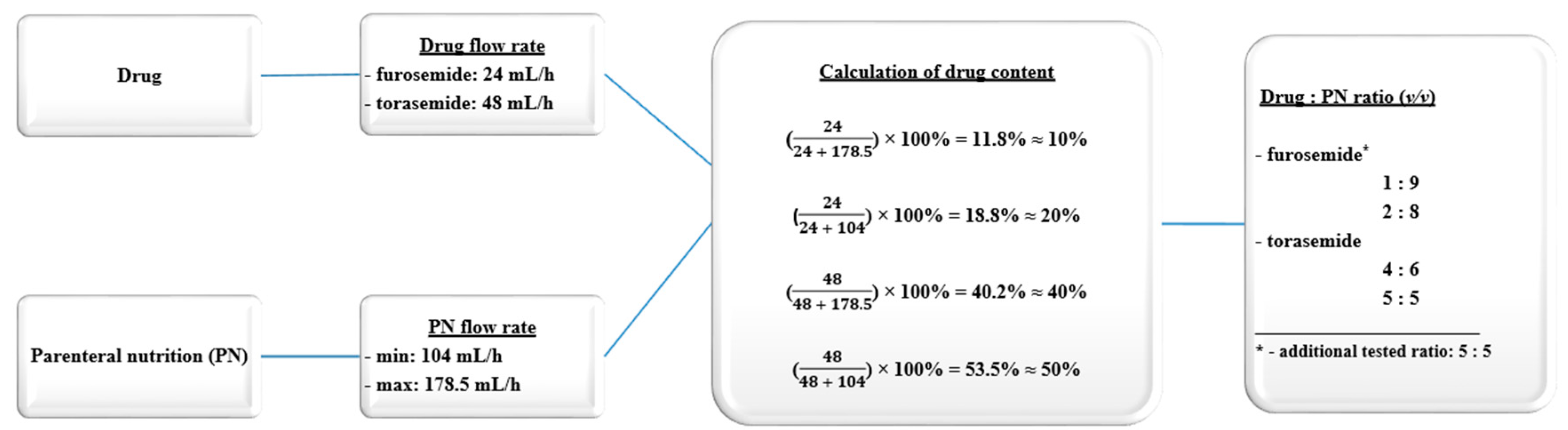

| Components | Unit | Low Lipid Content | High Lipid Content | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN 1 | PN 2 | PN 3 | PN 4 | PN 5 | PN 6 | PN 7 | PN 8 | PN 9 | PN 10 | PN 11 | PN 12 | ||
| Aminoplasmal B 10%E | mL | 375.0 | 875.0 | 375.0 | 875.0 | ||||||||
| Glucose 40% | 625.0 | ||||||||||||
| Lipofundin MCT/LCT 20% | 62.5 | 312.5 | |||||||||||
| Water for injection | 1240.3 | 1288.9 | 1341.7 | 762.5 | 809.7 | 848.6 | 990.3 | 1038.9 | 1095.8 | 512.5 | 559.7 | 602.8 | |
| Natrium Chloratum 10% | 37.5 | 36.9 | 0.0 | 28.2 | 28.2 | 0.0 | 41.3 | 41.3 | 0.0 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 0.0 | |
| Kalium Chloratum 15% | 64.0 | 64.0 | 0.0 | 57.8 | 57.8 | 0.0 | 64.0 | 64.0 | 0.0 | 57.8 | 57.8 | 0.0 | |
| Calcium Gluconate 10% | 44.0 | 5.6 | 44.0 | 44.0 | 5.6 | 44.0 | 44.0 | 5.6 | 44.0 | 44.0 | 5.6 | 44.0 | |
| Magnesium sulfuricum 20% | 11.4 | 1.9 | 11.4 | 9.7 | 0.4 | 9.7 | 11.4 | 1.9 | 11.4 | 9.7 | 0.4 | 9.7 | |
| Sodium Glycerophasphate | 40.3 | 35.3 | 36.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||
| Total volume | 2500.0 | 2500.1 | 2499.9 | 2500.0 | 2499.4 | 2500.1 | 2500.0 | 2500.7 | 2500.3 | 2500.6 | 2500.0 | 2500.6 | |
| PN Admixture | MDD ± SD (nm) | FUR:PN Ratio | MDD ± SD (nm) | TOR:PN Ratio | MDD ± SD (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN with FUR | PN with TOR | ||||||
| t = 0 h | t = 4 h | t = 0 h | t = 4 h | ||||
| PN 1 | 219.7 ± 1.9 | 1:9 | 206.9 ± 7.2 | 209.4 ± 4.5 | 4:6 | 211.3 ± 2.8 | 211.9 ± 5.0 |
| 2:8 | 206.2 ± 5.5 | 206.6 ± 5.6 | |||||
| 5:5 | 212.0 ± 3.9 | 211.9 ± 4.5 | |||||
| 5:5 | 205.2 ± 6.6 | 202.5 ± 5.4 | |||||
| PN 2 | 219.2 ± 1.1 | 1:9 | 207.6 ± 10.0 | 210.6 ± 7.0 | 4:6 | 212.5 ± 6.4 | 216.2 ± 5.1 |
| 2:8 | 206.7 ± 6.5 | 207.5 ± 6.6 | |||||
| 5:5 | 212.8 ± 4.6 | 213.5 ± 4.3 | |||||
| 5:5 | 203.6 ± 6.6 | 201.3 ± 10.2 | |||||
| PN 3 | 217.4 ± 3.9 | 1:9 | 210.1 ± 4.9 | 209.8 ± 4.9 | 4:6 | 212.6 ± 3.6 | 212.1 ± 4.3 |
| 2:8 | 207.5 ± 6.3 | 209.0 ± 5.5 | |||||
| 5:5 | 212.4 ± 2.8 | 213.0 ± 3.4 | |||||
| 5:5 | 207.0 ± 6.4 | 210.6 ± 7.6 | |||||
| PN 4 | 222.0 ± 1.5 | 1:9 | 218.5 ± 0.8 | 219.5 ± 2.6 | 4:6 | 223.6 ± 4.4 | 220.5 ± 3.8 |
| 2:8 | 217.4 ± 1.9 | 217.8 ± 2.7 | |||||
| 5:5 | 220.3 ± 2.1 | 221.0 ± 1.6 | |||||
| 5:5 | 215.6 ± 2.3 | 215.8 ± 3.5 | |||||
| PN 5 | 221.0 ± 1.0 | 1:9 | 219.7 ± 2.1 | 214.4 ± 1.5 | 4:6 | 220.9 ± 5.3 | 216.3 ± 0.9 |
| 2:8 | 215.9 ± 5.1 | 213.3 ± 2.3 | |||||
| 5:5 | 220.9 ± 4.5 | 218.9 ± 2.3 | |||||
| 5:5 | 212.1 ± 4.9 | 214.5 ± 5.7 | |||||
| PN 6 | 221.4 ± 1.1 | 1:9 | 224.1 ± 2.2 | 216.5 ± 1.2 | 4:6 | 221.5 ± 3.4 | 220.9 ± 6.7 |
| 2:8 | 217.3 ± 4.9 | 219.7 ± 2.6 | |||||
| 5:5 | 222.5 ± 3.2 | 221.0 ± 1.9 | |||||
| 5:5 | 213.3 ± 5.1 | 213.8 ± 6.1 | |||||
| PN 7 | 220.0 ± 1.4 | 1:9 | 212.0 ± 5.9 | 211.6 ± 5.0 | 4:6 | 215.5 ± 4.3 | 215.1 ± 4.7 |
| 2:8 | 209.3 ± 4.7 | 208.7 ± 5.3 | |||||
| 5:5 | 215.9 ± 4.7 | 214.4 ± 2.8 | |||||
| 5:5 | 201.4 ± 8.6 | 203.4 ± 6.0 | |||||
| PN 8 | 220.6 ± 1.6 | 1:9 | 222.8 ± 2.0 | 213.3 ± 6.6 | 4:6 | 213.0 ± 6.0 | 215.4 ± 4.4 |
| 2:8 | 222.4 ± 3.7 | 211.9 ± 7.5 | |||||
| 5:5 | 217.0 ± 3.6 | 214.7 ± 3.4 | |||||
| 5:5 | 210.4 ± 5.7 | 206.7 ± 6.3 | |||||
| PN 9 | 219.4 ± 2.6 | 1:9 | 213.1 ± 4.5 | 211.6 ± 3.8 | 4:6 | 213.5 ± 6.0 | 213.2 ± 2.0 |
| 2:8 | 211.0 ± 6.0 | 210.1 ± 6.0 | |||||
| 5:5 | 214.7 ± 3.0 | 215.0 ± 2.9 | |||||
| 5:5 | 205.4 ± 7.7 | 205.2 ± 6.4 | |||||
| PN 10 | 225.1 ± 3.3 | 1:9 | 222.8 ± 2.9 | 224.2 ± 0.5 | 4:6 | 225.2 ± 2.4 | 221.8 ± 5.7 |
| 2:8 | 221.3 ± 1.7 | 219.9 ± 1.3 | |||||
| 5:5 | 224.5 ± 3.4 | 220.2 ± 3.2 | |||||
| 5:5 | 218.5 ± 2.6 | 216.9 ± 0.3 | |||||
| PN 11 | 223.4 ± 0.4 | 1:9 | 219.2 ± 1.1 | 221.8 ± 2.4 | 4:6 | 221.1 ± 2.6 | 220.9 ± 1.6 |
| 2:8 | 217.9 ± 2.2 | 217.3 ± 5.0 | |||||
| 5:5 | 220.6 ± 2.0 | 219.7 ± 2.0 | |||||
| 5:5 | 216.0 ± 4.0 | 214.0 ± 5.3 | |||||
| PN 12 | 220.7 ± 2.0 | 1:9 | 218.4 ± 6.7 | 222.8 ± 3.3 | 4:6 | 220.8 ± 2.4 | 220.3 ± 2.0 |
| 2:8 | 220.1 ± 3.2 | 220.0 ± 3.3 | |||||
| 5:5 | 220.9 ± 2.8 | 222.1 ± 1.8 | |||||
| 5:5 | 218.1 ± 2.1 | 218.0 ± 1.8 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomczak, S.; Stawny, M.; Jelińska, A. Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111092
Tomczak S, Stawny M, Jelińska A. Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(11):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111092
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomczak, Szymon, Maciej Stawny, and Anna Jelińska. 2020. "Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 11: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111092
APA StyleTomczak, S., Stawny, M., & Jelińska, A. (2020). Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics, 12(11), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111092








