Highly Water-Soluble Solid Dispersions of Honokiol: Preparation, Solubility, and Bioavailability Studies and Anti-Tumor Activity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the HK SD Formulation
2.3. Characterization of the HK SD Formulations
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.3. X-Ray Diffractometry (XRD)
2.3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC).
2.3.5. Gas Chromatography (GC) Measurement
2.4. Solubility Tests of the HK SD Formulations
2.4.1. High Performance Liquid Chromatograph (HPLC) Method for HK
2.4.2. Solubility Tests
2.5. Dissolution Tests
2.6. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
2.6.1. Animal Dosing
2.6.2. Determination of HK Content in Plasma Samples
2.7. MTT Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
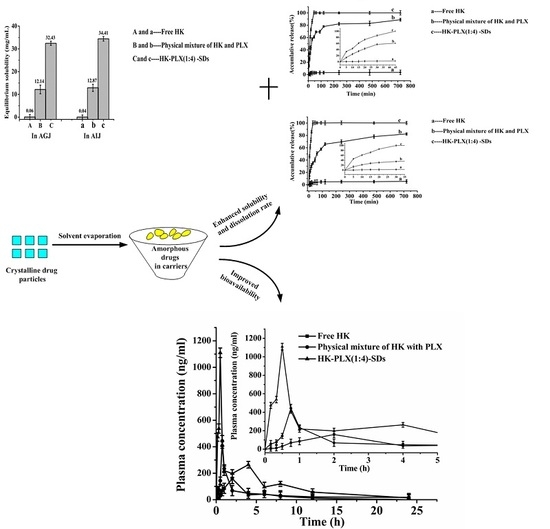
3.1. Solubility Enhancement
3.1.1. Solubility of Different Solid Dispersions of HK
3.1.2. Solubility of PMs and SD of HK
3.2. Characterization of HK Formulations
3.2.1. SEM Results
3.2.2. Physicochemical Properties Characterization
3.2.3. Residual Solvent Determination
3.3. Dissolution Study
3.4. Pharmacokinetic Behavior of HK Formulations
3.5. MTT Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jermain, S.V.; Brough, C.; Williams, R.O. Amorphous solid dispersions and nanocrystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery—An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skořepová, E.; Bím, D.; Hušák, M.; Klimeš, J.; Chatziadi, A.; Ridvan, L.; Boleslavská, T.; Beránek, J.; Šebek, P.; Rulíšek, L. Increase in Solubility of Poorly-Ionizable Pharmaceuticals by Salt Formation: A Case of Agomelatine Sulfonates. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 5283–5294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, K.; Li, K.; Cong, Y.; Pu, S.; Jin, Y.; Lin, J. Preparation, characterisation and antitumour activity of β-, γ- and HP-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes of oxaliplatin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 152, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapat, M.D.; Patel, N.J.; Bariya, A.; Patel, S.S.; Butani, S.B. Formulation and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery system for nimodipine, a BCS class II drug. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Cui, F.D.; Choi, M.K.; Lin, H.; Chung, S.J.; Shim, C.K.; Kim, D.D. Liposome formulation of paclitaxel with enhanced solubility and stability. Drug Deliv. 2007, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, M.; Men, K.; Shi, H.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, J.; Song, J.; Long, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X. Curcumin-loaded biodegradable polymeric micelles for colon cancer therapy in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale. 2011, 3, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Kavuru, P.; Wojtas, L.; Zaworotko, M.J.; Shytle, R.D. Cocrystals of Quercetin with Improved Solubility and Oral Bioavailability. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, A.; Wehner, L.; Pereyra, C.; Ossa, E.J.M. Mangiferin nanoparticles precipitation by supercritical antisolvent process. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2016, 112, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bley, H.; Fussnegger, B.; Bodmeier, R. Characterization and stability of solid dispersions based on PEG/polymer blends. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Li, C.; Lenon, G.B.; Xue, C.C.L.; Li, W. Preparation and characterisation of solid dispersions of tanshinone IIA, cryptotanshinone and total tanshinones. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ni, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Ren, P.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fu, S.; Wu, J. Honokiol-loaded polymeric nanoparticles: An active targeting drug delivery system for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Hou, X.; Cong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Lei, J.; Meng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, G. Co-delivery of honokiol, a constituent of Magnolia species, in a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for improved oral transport of lipophilic sirolimus. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yang, D.; Hu, K.; Zhou, H.; Guo, Y.; Du, G.; Lu, Y. Certification of a new certified reference material of honokiol. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5849–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Tang, Y.; Hu, W.; Tian, R.; Jia, Y.; Deng, P.; Zhang, L. Investigation of inclusion complex of honokiol with sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, H.; Wang, X. Honokiol nanosuspensions: Preparation, increased oral bioavailability and dramatically enhanced biodistribution in the cardio-cerebro-vascular system. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Cai, L.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Deng, L.Y.; Zheng, H.; Deng, C.Y.; Wen, J.L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Wei, Q.; Chen, L.J. Improved solubility and pharmacokinetics of PEGylated liposomal honokiol and human plasma protein binding ability of honokiol. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 410, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardo, A.; Julija, Z.; Andrea, B.; Luca, V. Antioxidant Activity of Magnolol and Honokiol: Kinetic and Mechanistic Investigations of Their Reaction with Peroxyl Radicals. J.Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 10651–10659. [Google Scholar]
- Schaper, K.J.; Kunz, B.; Raevsky, O.A. Analysis of water solubility data on the basis of HYBOT descriptors. Mol. Inform. 2010, 22, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Su, X.; Xu, M.; Hu, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro/vivo evaluation of polymer-assisting formulation of atorvastatin calcium based on solid dispersion technique. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Shah, M.K.; Patel, N.; Jain, S.; Vora, N.; Lin, S. Preparation and characterization of pyrimethamine solid dispersions and an evaluation of the physical nature of pyrimethamine in solid dispersions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, R.; Islam, M.S.; Tanwir, A.; Chowdhury, J. In vitro dissolution study of atorvastatin binary solid dispersion. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2013, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chutimaworapan, S.; Ritthidej, G.C.; Yonemochi, E.; Oguchi, T.; Yamamoto, K. Effect of Water-Soluble Carriers on Dissolution Characteristics of Nifedipine Solid Dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godugu, C.; Doddapaneni, R.; Singh, M. Honokiol nanomicellar formulation produced increased oral bioavailability and anticancer effects in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Yuan, P.; Tian, R.; Hu, W.; Tang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, L. Encapsulation of honokiol into self-assembled pectin nanoparticles for drug delivery to HepG2 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passerini, N.; Albertini, B.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Cavallari, C.; Rodriguez, L. Preparation and characterisation of ibuprofen-poloxamer 188 granules obtained by melt granulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 15, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.; Tran, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Woo, K.B.; Yong, J.C.; Choi, H.G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Preparation and characterization of fast dissolving flurbiprofen and esomeprazole solid dispersion using spray drying technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaidat, R.M.; Tashtoush, B.M.; Awad, A.A.; Al Bustami, R.T. Using Supercritical Fluid Technology (SFT) in Preparation of Tacrolimus Solid Dispersions. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiry, J.; Kok, M.G.; Collard, L.; Frère, A.; Krier, F.; Fillet, M.; Evrard, B. Bioavailability enhancement of itraconazole-based solid dispersions produced by hot melt extrusion in the framework of the Three Rs rule. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.E.; Jang, W.S.; Byeon, J.C.; Park, J.S. Solid dispersion of dutasteride using the solvent evaporation method: Approaches to improve dissolution rate and oral bioavailability in rats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2018, 90, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.T.; Pervez, H.; Shehzad, M.T.; Mahmood, Z.; Razi, M.T.; Ranjha, N.M.; Khanum, N. Improved physicochemical characteristics of artemisinin-nicotinamide solid dispersions by solvent evaporation and freeze dried methods. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 25, 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Song, I.S.; Choi, M.K. Preparation and characterization of quercetin-loaded solid dispersion by solvent evaporation and freeze-drying method. Mass Spectrom. Lett. 2016, 7, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriani, L.; Haqi, A.; Zaini, E. Preparation and characterization of solid dispersion freeze-dried efavirenz-polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2016, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suksiriworapong, J.; Rungvimolsin, T.; A-gomol, A.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Chantasart, D. Development and Characterization of Lyophilized Diazepam-Loaded Polymeric Micelles. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014, 15, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalkowsky, S.H. Solubility and Solubilization in Aqueous Media; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 236–320. [Google Scholar]










| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | Free HK | Physical Mixture of HK and PLX | HK–PLX (1:4) SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 159.02 ± 5.65 | 443.81 ± 9.14 * | 1109.87 ± 7.24 * |
| Tmax (h) | 2 ± 0.15 | 0.75 ± 0.09 * | 0.5 ± 0.08 * |
| t1/2 (h) | 0.74 ± 0.15 | 0.51 ± 0.12 | 0.37 ± 0.05 * |
| MRT(0–t) (h) | 3.93 ± 1.25 | 6.94 ± 2.22 * | 5.70 ± 0.76 * |
| MRT(0–∞) (h) | 5.11 ± 2.13 | 12.15 ± 3.15 * | 6.44 ± 1.15 |
| AUC(0–t) (ng/mL·h) | 580.45 ± 11.15 | 848.34 ± 12.24 * | 2558.22 ± 8.15 * |
| AUC(0–∞) (ng/mL·h) | 637.91 ± 13.42 | 1004.11 ± 15.38 * | 2588.70 ± 10.54 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X. Highly Water-Soluble Solid Dispersions of Honokiol: Preparation, Solubility, and Bioavailability Studies and Anti-Tumor Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110573
Wang L, Wu W, Wang L, Wang L, Zhao X. Highly Water-Soluble Solid Dispersions of Honokiol: Preparation, Solubility, and Bioavailability Studies and Anti-Tumor Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(11):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110573
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Weiwei Wu, Lingling Wang, Lu Wang, and Xiuhua Zhao. 2019. "Highly Water-Soluble Solid Dispersions of Honokiol: Preparation, Solubility, and Bioavailability Studies and Anti-Tumor Activity Evaluation" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 11: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110573
APA StyleWang, L., Wu, W., Wang, L., Wang, L., & Zhao, X. (2019). Highly Water-Soluble Solid Dispersions of Honokiol: Preparation, Solubility, and Bioavailability Studies and Anti-Tumor Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceutics, 11(11), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110573