Electrospinning of Cyclodextrin Functional Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
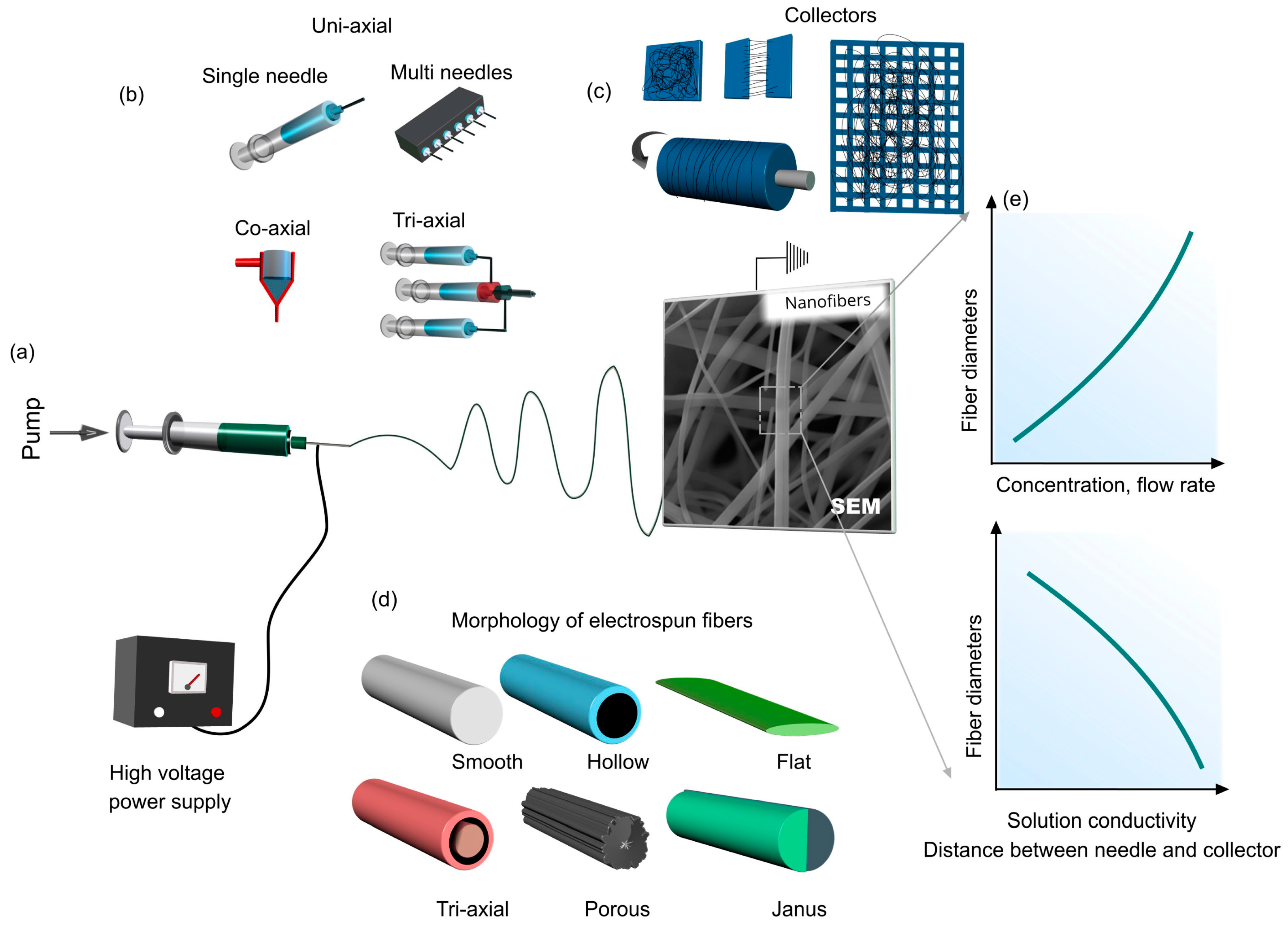
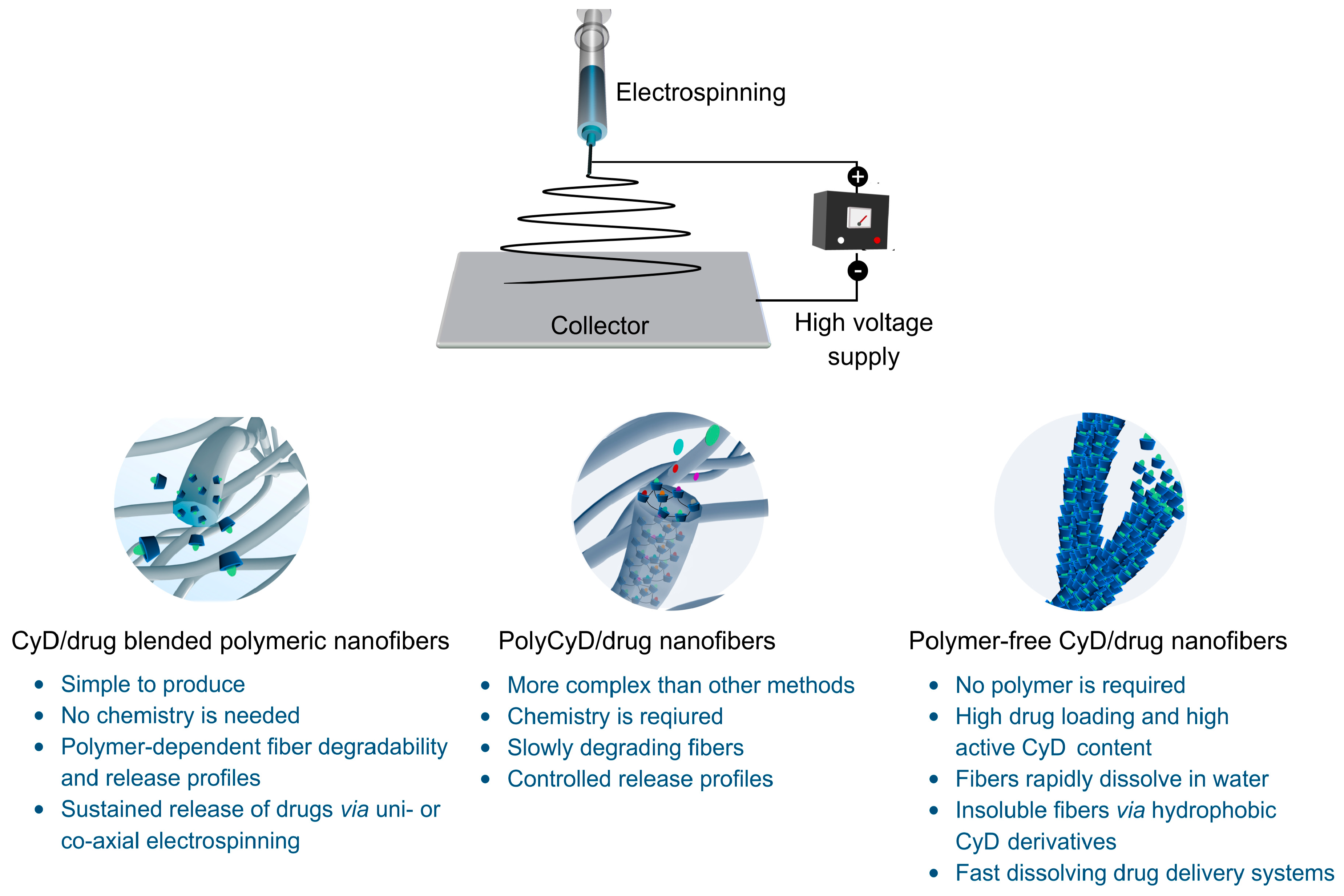
2. Electrospinning
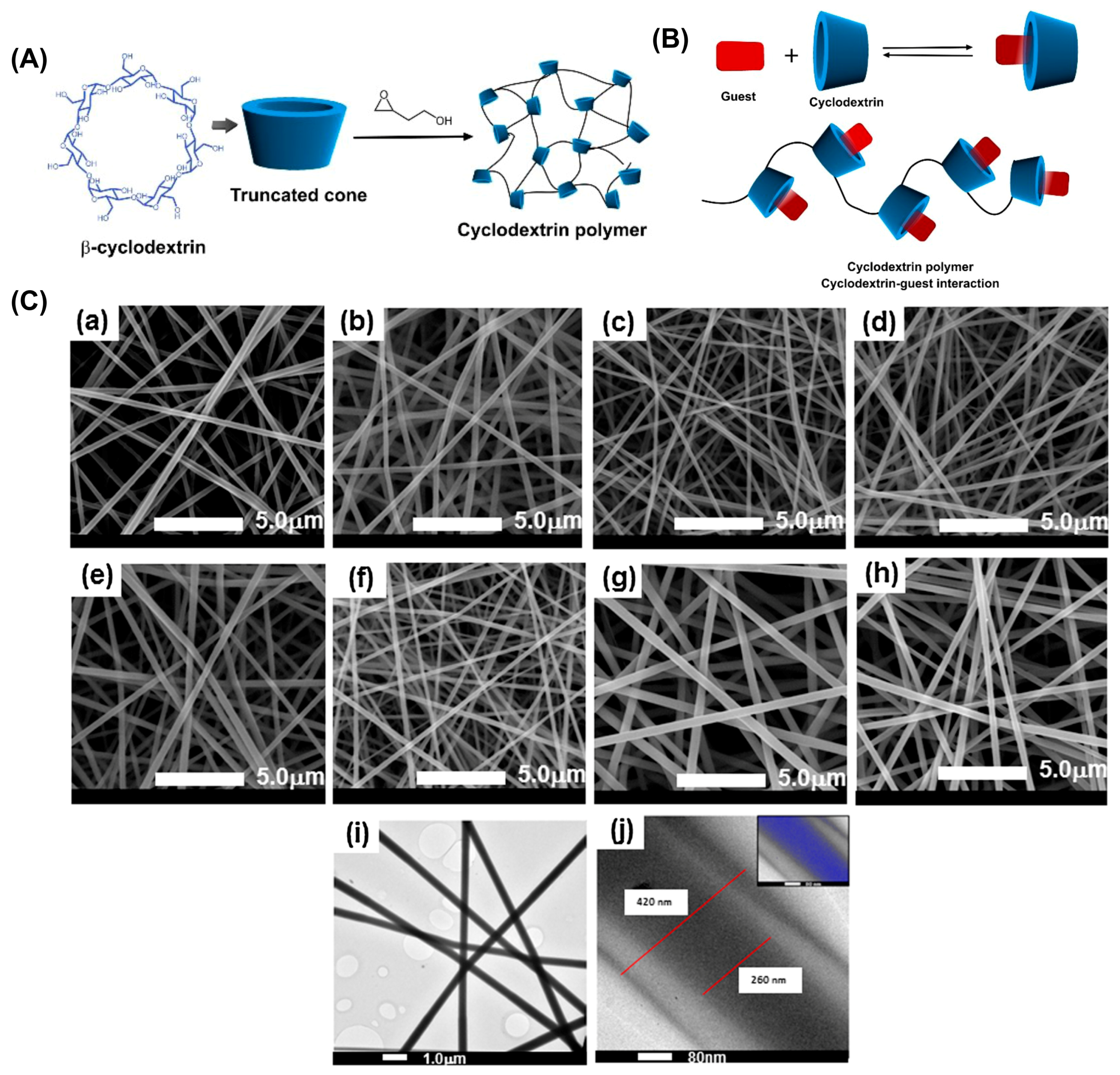
3. Cyclodextrins
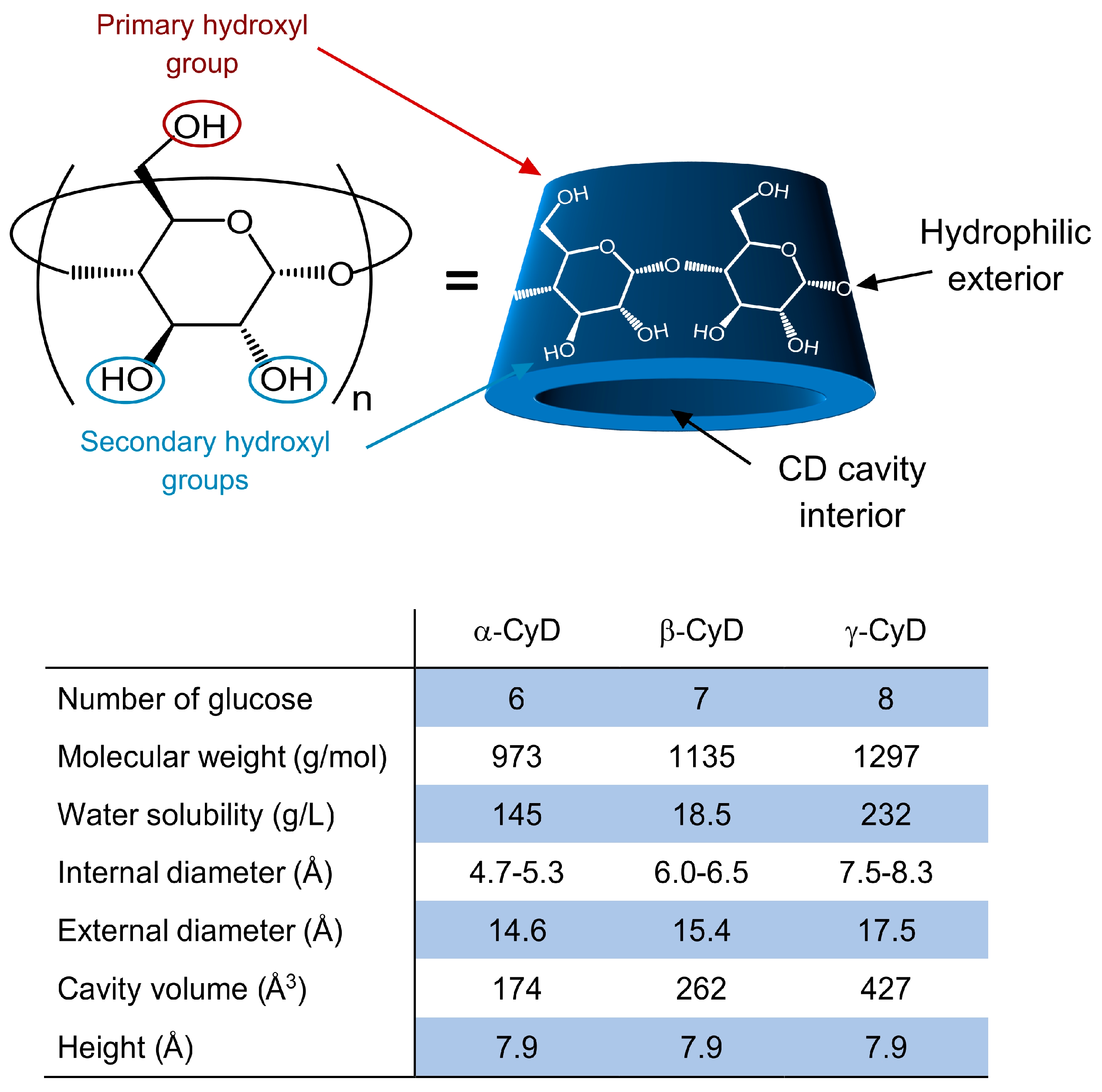
3.1. Structure and Properties of Cyclodextrins
3.2. Toxicological Issues of Cyclodextrins
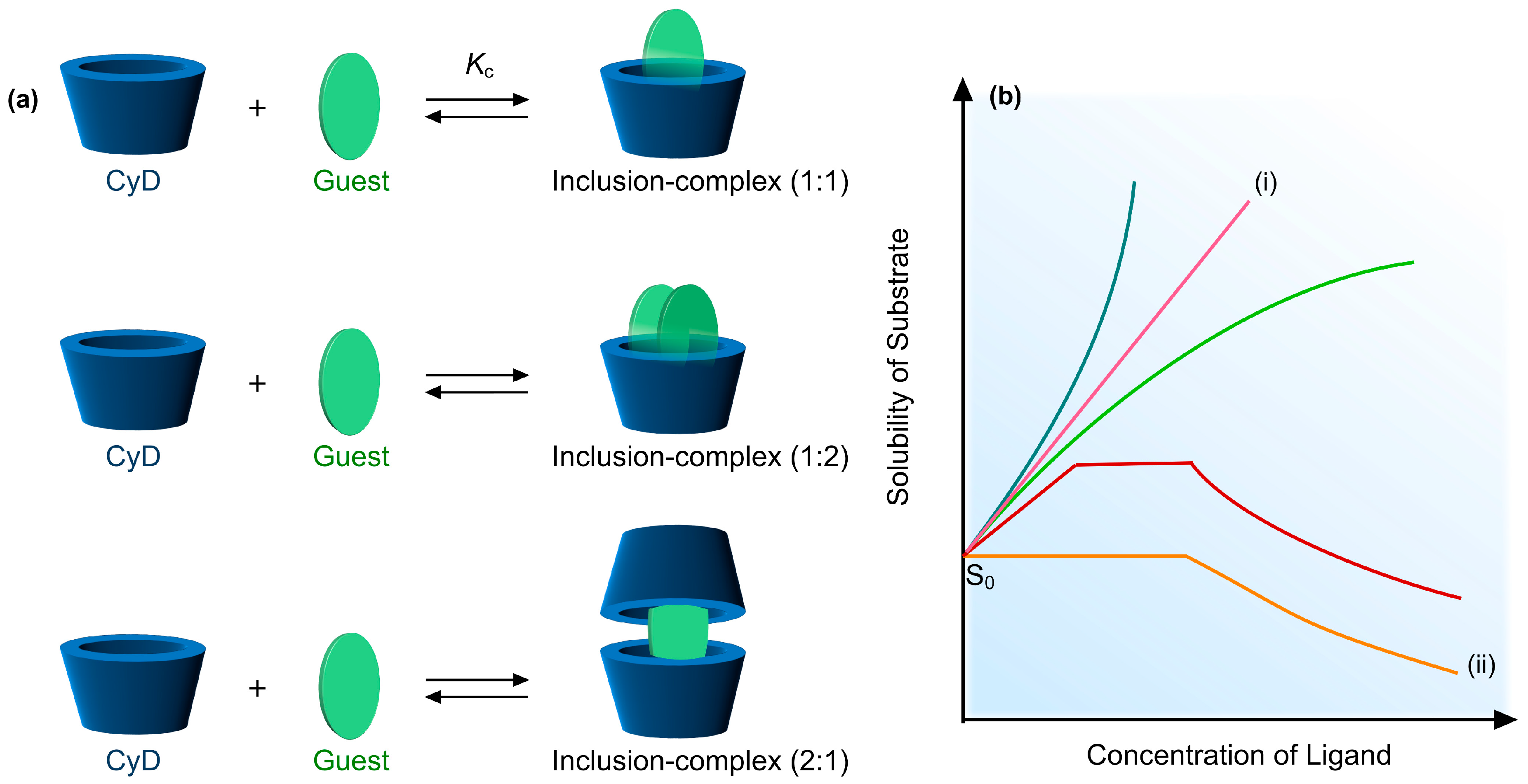
3.3. Mechanism of Cyclodextrin Inclusion-Complexation and Drug Solubility
3.4. Drug Stability and Release from Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes
4. Cyclodextrin Functional Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Systems
4.1. Cyclodextrin-Drug Encapsulated Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications
4.2. Poly-Cyclodextrin Functional Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Systems
4.3. Polymer-Free Cyclodextrin Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Systems
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ac-β-CyDP | Peracetyl-β-CyD polymer |
| AITC | Allyl isocyanate |
| AV | Aloe Vera |
| CEO | Cinnamon essential oil |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
| CUR | Curcumin |
| CyD | Cyclodextrins |
| CZ | Clotrimazole |
| DDS | Drug Delivery System |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| EEO | Eucalyptus essential oil |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| FDA | Federal Drug Administration |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatograph mass spectrometry |
| HCPT | Hydroxycamptothecin |
| HPC | Hydroxypropyl cellulose |
| HP-β-CyD | Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin |
| IC | Inclusion-Complex |
| MX | Meloxicam |
| M-β-CyD | Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin |
| NAP | Naproxen |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PEO | Poly(ethylene oxide) |
| PLACL | Poly (l-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone) |
| PLLA | Poly (l-lactic acid) |
| PMAA | Poly(methylacrylic acid) |
| PolyCyD | Polycyclodextrin |
| PROP | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| RA | Retinyl acetate |
| RH | Relative humidity |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| SAg | Silver sulfadiazine |
| SFS | Sulfisoxazole |
| TAM | Tamoxifen |
| TCN | Tetracycline |
| VRC | Voriconazole |
References
- Zeng, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Liang, Q.; Bian, X.; Yang, L.; Jing, X. Biodegradable electrospun fibers for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 92, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, E.-R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.G.; Sanders, E.H.; Wnek, G.E. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, L.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Guan, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Jing, X. Influence of the drug compatibility with polymer solution on the release kinetics of electrospun fiber formulation. J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katti, D.S.; Robinson, K.W.; Ko, F.K.; Laurencin, C.T. Bioresorbable nanofiber-based systems for wound healing and drug delivery: Optimization of fabrication parameters. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 70B, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenguo, C.; Yue, Z.; Jiang, C. Electrospun nanofibrous materials for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2010, 11, 014108. [Google Scholar]
- Deng-Guang, Y.; Xia-Xia, S.; Chris, B.-W.; Kenneth, W.; Li-Min, Z.; Bligh, S.W.A. Oral fast-dissolving drug delivery membranes prepared from electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone ultrafine fibers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055104. [Google Scholar]
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured fibers via electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.L.; Huang, Z.M.; Han, X.J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.S.; Chen, L.S. Coaxial electrospun poly(L-lactic acid) ultrafine fibers for sustained drug delivery. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2006, 45, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Kny, E. Electrospun Materials for Tissue Engineering and Biomedical Applications: Research, Design and Commercialization; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston/Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780081010228. [Google Scholar]
- Grafahrend, D.; Heffels, K.-H.; Beer, M.V.; Gasteier, P.; Möller, M.; Boehm, G.; Dalton, P.D.; Groll, J. Degradable polyester scaffolds with controlled surface chemistry combining minimal protein adsorption with specific bioactivation. Nat. Mater. 2010, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi Ji, S.; Messersmith Phillip, B.; Yoo Hyuk, S. Decoration of electrospun nanofibers with monomeric catechols to facilitate cell adhesion. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 14, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, L.R. 9-electrospun fibers for drug and molecular delivery a2-guarino, vincenzo. In Electrofluidodynamic Technologies (Efdts) for Biomaterials and Medical Devices; Ambrosio, L., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston/Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.-G.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, X.; Chian, W.; Liao, Y.-Z.; Li, Y. Zero-order drug release cellulose acetate nanofibers prepared using coaxial electrospinning. Cellulose 2013, 20, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizaw, M.; Thompson, J.; Faglie, A.; Lee, S.-Y.; Neuenschwander, P.; Chou, S.-F. Electrospun fibers as a dressing material for drug and biological agent delivery in wound healing applications. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Duan, X.-P.; Li, Y.-M.; Yang, D.-P.; Long, Y.-Z. Electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, E.; Grootveld, M.; Soares, G.; Henriques, M. Cyclodextrin-based hydrogels toward improved wound dressings. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Yan, S.; Li, X. Antitumor activities of emulsion electrospun fibers with core loading of hydroxycamptothecin via intratumoral implantation. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 425, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deluzio, T.G.B.; Penev, K.I.; Mequanint, K. Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes as potential oxygen delivery vehicles in tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2014, 4, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, R.; Abbasipour, M. Electrospinning as a versatile method for fabricating coreshell, hollow and porous nanofibers. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enizi, A.; Zagho, M.; Elzatahry, A. Polymer-based electrospun nanofibers for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, T.K.; Konkimalla, V.B. Poly-e-caprolactone based formulations for drug delivery and tissue engineering: A review. J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, G. A three-dimensional polycaprolactone scaffold combined with a drug delivery system consisting of electrospun nanofibers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Huang, X.B.; Cai, X.M.; Lu, J.; Yuan, J.; Shen, J. The influence of fiber diameter of electrospun poly(lactic acid) on drug delivery. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repanas, A.; Glasmacher, B. Dipyridamole embedded in polycaprolactone fibers prepared by coaxial electrospinning as a novel drug delivery system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, N.J.; Le Beux, C.; Miao, J.; Linhardt, R.J.; Alauzun, J.G.; Laurencin, D.; Gilbert, R.J. The effect of surface modification of aligned poly-L-lactic acid electrospun fibers on fiber degradation and neurite extension. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.-F.; Carson, D.; Woodrow, K.A. Current strategies for sustaining drug release from electrospun nanofibers. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulery, B.D.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biomedical applications of biodegradable polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 832–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Espinar, F.J.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Blanco-Méndez, J. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Vogensen, S.B.; Brewster, M.E.; Konradsdottir, F. Effects of cyclodextrins on drug delivery through biological membranes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2532–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, K.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning jets and nanofibrous structures. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 013403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrell, H.R.; Iksoo, C. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216. [Google Scholar]
- Ziabicki, A. Fundamentals of Fibre Formation; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Bang, H.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Lee, S.G. The change of bead morphology formed on electrospun polystyrene fibers. Polymer 2003, 44, 4029–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospinning of uniform polystyrene fibers: The effect of solvent conductivity. Polymer 2008, 49, 5336–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C. Effects of working parameters on electrospinning. In One-Dimensional Nanostructures: Electrospinning Technique and Unique Nanofibers; Li, Z., Wang, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.H.; Yang, E.L.; Li, N.; Wang, S.Y. Effect of different salts on electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) polymer solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 103, 3865–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Duchene, D. Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Review: A history of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10940–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, E.; Sánchez-Trujillo, M.A.; Moyano, J.R.; Villaverde, J.; Gómez-Pantoja, M.E.; Pérez-Martínez, J.I. Enhanced solubilisation of six pahs by three synthetic cyclodextrins for remediation applications: Molecular modelling of the inclusion complexes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.X.; Bai, L.; Xu, X.M.; He, J.; Pan, S.Z. Inclusion complexation, encapsulation interaction and inclusion number in cyclodextrin chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiers, A. Sur la fermentation de la fecule par l’action du ferment butyrique. Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. 1891, 112, 536–538. [Google Scholar]
- Lakkakula, J.R.; Krause, R.W.M. A vision for cyclodextrin nanoparticles in drug delivery systems and pharmaceutical applications. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 877–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Rai, A.K. Cyclodextrins in delivery systems: Applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, W.J.; Hedges, A.R. Properties and applications of cyclodextrins. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 1996, 33, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sharma, R.; Banerjee, U.C. Biotechnological applications of cyclodextrins. Biotechnol. Adv. 2002, 20, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejtli, J. Introduction and general overview of cyclodextrin chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S.; Mathias, N. Topographie der cyclodextrin-einschlußverbindungen, VII. Röntgenstrukturanalyse des α-cyclodextrin. Krypton-pentahydrats. Zum einschlußmechanismus des modell-enzyms. Chem. Ber. 1976, 109, 503–517. [Google Scholar]
- Harata, K. Structural aspects of stereodifferentiation in the solid state. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1803–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, Y.; Hirayama, F.; Arima, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Saenger, W.; Uekama, K. Cyclodextrin-based isolation of ostwald’s metastable polymorphs occurring during crystallization. Chem. Commun. 2006, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapiot, F.; Tilloy, S.; Monflier, E. Cyclodextrins as supramolecular hosts for organometallic complexes. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Jarho, P.; Másson, M.; Järvinen, T. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uekama, K.; Hirayama, F.; Irie, T. Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2045–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.W.; Gray, J.E.; Weaver, R.N. Cyclodextrin nephrosis in the rat. Am. J. Pathol. 1976, 83, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, K.; Mera, Y.; Segawa, Y. Acute toxicity study of γ-cyclodextrin (γ-CD) in mice and rats. Pharmacometrics 1983, 26, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Irie, T.; Uekama, K. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. Iii. Toxicological issues and safety evaluation. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, Y.; Irie, T.; Uekama, K.; Fukunaga, K.; Pitha, J. Differential effects of α-, β- and γ-cyclodextrins on human erythrocytes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 186, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, S.; Grebe, A.; Bakke, S.S.; Bode, N.; Halvorsen, B.; Ulas, T.; Skjelland, M.; De Nardo, D.; Labzin, L.I.; Kerksiek, A.; et al. Cyclodextrin promotes atherosclerosis regression via macrophage reprogramming. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 333ra350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajewski, R.A.; Traiger, G.; Bresnahan, J.; Jaberaboansar, P.; Stella, V.J.; Thompson, D.O. Preliminary safety evaluation of parenterally administered sulfoalkyl ether β-cyclodextrin derivatives. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantner, I.; Erben, R.G. Long-term parenteral administration of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin causes bone loss. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szente, L.; Szejtli, J. Cyclodextrins as food ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, V.J.; He, Q. Cyclodextrins. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frömming, K.-H.; Szejtli, J. Pharmacokinetics and toxicology of cyclodextrins. In Cyclodextrins in Pharmacy; Frömming, K.-H., Szejtli, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, J.C.D.; Martins, T.E.A.; Veiga, F.; Ferraz, H.G. Cyclodextrins and ternary complexes: Technology to improve solubility of poorly soluble drugs. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 47, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S. Introduction. In Cyclodextrins: Properties and Industrial Applications; Amiri, S., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, J.; Bhasikuttan, A.C.; Nau, W.M.; Pal, H. Host−guest complexation of neutral red with macrocyclic host molecules: Contrasting pka shifts and binding affinities for cucurbit[7]uril and β-cyclodextrin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5132–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jeong, K.; Park, H.; Jung, S. Preference prediction for the stable inclusion complexes between cyclodextrins and monocyclic insoluble chemicals based on monte carlo docking simulations. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 54, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Purdy, W.C. Cyclodextrins and their applications in analytical chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omari, M.M.; Zughul, M.B.; Davies, J.E.D.; Badwan, A.A. Effect of buffer species on the complexation of basic drug terfenadine with β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 58, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekharsky, M.V.; Inoue, Y. Complexation thermodynamics of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1875–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, K.; Pabreja, K.; Ramana, M.V.; Lather, V. Dissolution behavior of β-cyclodextrin molecular inclusion complexes of aceclofenac. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.-M.; Dong, T.; He, Y.; Taguchi, Y.; Oishi, A.; Nishida, H.; Inoue, Y. Inclusion complex formation between α-cyclodextrin and biodegradable aliphatic polyesters. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, M.; Schlatter, G.; Gallet, S.; Baati, R.; Pollet, E.; Gaillard, C.; Averous, L.; Fajolles, C.; Hebraud, A. The study of the pseudo-polyrotaxane architecture as a route for mild surface functionalization by click chemistry of poly(ε-caprolactone)-based electrospun fibers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusa, C.C.; Wei, M.; Bullions, T.A.; Rusa, M.; Gomez, M.A.; Porbeni, F.E.; Wang, X.; Shin, I.D.; Balik, C.M.; White, J.L.; et al. Controlling the polymorphic behaviors of semicrystalline polymers with cyclodextrins. Cryst. Growth Design 2004, 4, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Cyclodextrin-functionalized mesostructured silica nanoparticles for removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 497, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Poly-cyclodextrin cryogels with aligned porous structure for removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS) from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 335, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotronia, M.; Kavetsou, E.; Loupassaki, S.; Kikionis, S.; Vouyiouka, S.; Detsi, A. Encapsulation of oregano (Origanum onites L.) essential oil in β-cyclodextrin (β-CD): Synthesis and characterization of the inclusion complexes. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwa, G.; Kumar, S.; Chhabra, L.; Mahant, S.; Rao, R. Essential coil–cyclodextrin complexes: An updated review. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2017, 89, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelikin, A.N.; Ehrhardt, C.; Healy, A.M. Materials and methods for delivery of biological drugs. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of nanofibers from non-polymeric systems: Electrospun nanofibers from native cyclodextrins. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 404, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyar, T.; El-Shafei, A.; Wang, X.; Hacaloglu, J.; Tonelli, A.E. The solid channel structure inclusion complex formed between guest styrene and host γ-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 55, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaci, F.; Ertas, Y.; Uyar, T. Enhanced thermal stability of eugenol by cyclodextrin inclusion complex encapsulated in electrospun polymeric nanofibers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8156–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaci, F.; Sen, H.S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Functional electrospun polymeric nanofibers incorporating geraniol–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: High thermal stability and enhanced durability of geraniol. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Q.-X. The driving forces in the inclusion complexation of cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbolat, M.F.; Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Drug delivery system based on cyclodextrin-naproxen inclusion complex incorporated in electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 115, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadlej-Sosnowska, N.; Kozerski, L.; Bednarek, E.; Sitkowski, J. Fluorometric and NMR studies of the naproxen–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in aqueous solutions. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2000, 37, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, A.; Gogoi, P.; Saikia, M.D. Interaction of naproxen with β-cyclodextrin and its derivatives/polymer: Experimental and molecular modeling studies. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 72, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akduman, C.; Ozguney, I.; Kumbasar, E.P. Electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane mats containing naproxen-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Autex Res. J. 2014, 14, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
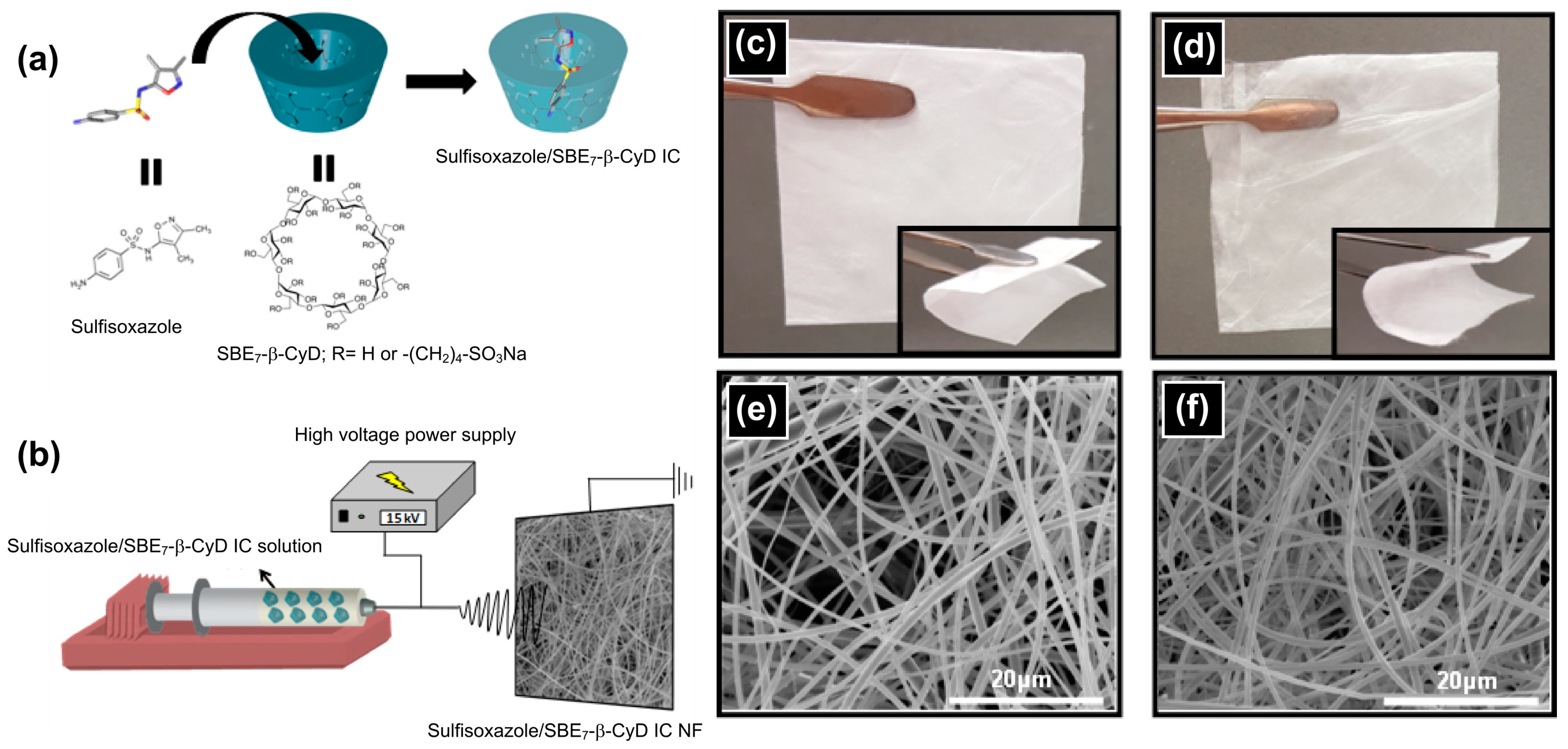
- Aytac, Z.; Sen, H.S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Sulfisoxazole/cyclodextrin inclusion complex incorporated in electrospun hydroxypropyl cellulose nanofibers as drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, E.E. Sulfonamide antibiotics. Prim. Care Update Ob Gyns 1998, 5, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonglairoum, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Panomsuk, S.; Kaomongkolgit, R.; Opanasopit, P. Fabrication of mucoadhesive chitosan coated polyvinylpyrrolidone/cyclodextrin/clotrimazole sandwich patches for oral candidiasis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Yu, L.; Lv, Y. Voriconazole composited polyvinyl alcohol/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin nanofibers for ophthalmic delivery. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafaka, P.I.; Okur, N.U.; Mone, M.; Giannakopoulou, S.; Er, S.; Pavlidou, E.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Two different approaches for oral administration of voriconazole loaded formulations: Electrospun fibers versus β-cyclodextrin complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprasit, W.; Akkaramongkolporn, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Kaomongkolgit, R.; Opanasopit, P. Fast releasing oral electrospun PVP/CD nanofiber mats of taste-masked meloxicam. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 487, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.; Balfour, J.A. Meloxicam. Drugs 1996, 51, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samprasit, W.; Akkaramongkolporn, P.; Kaomongkolgit, R.; Opanasopit, P. Cyclodextrin-based oral dissolving films formulation of taste-masked meloxicam. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.P.F.; Rocha, C.M.S.L.; Oliveira, M.F.; Gontijo, S.M.L.; Agudelo, R.R.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Cortés, M.E. Nanofibers containing tetracycline/β-cyclodextrin: Physico-chemical characterization and antimicrobial evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakasam, A.; Elavarasu, S.S.; Natarajan, R.K. Antibiotics in the management of aggressive periodontitis. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, S252–S255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusein, N.; Blagbrough, I.S.; Beeton, M.L.; Bolhuis, A.; De Bank, P.A. Electrospun zein/pcl fibrous matrices release tetracycline in a controlled manner, killing staphylococcus aureus both in biofilms and ex vivo on pig skin, and are compatible with human skin cells. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusein, N.; Blagbrough, I.S.; De Bank, P.A. Zein/polycaprolactone electrospun matrices for localised controlled delivery of tetracycline. Drug Deliv.Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusein, N.; De Bank, P.A.; Blagbrough, I.S.; Bolhuis, A. Killing bacteria within biofilms by sustained release of tetracycline from triple-layered electrospun micro/nanofibre matrices of polycaprolactone and poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate). Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusein, N.; Blagbrough, I.S.; De Bank, P.A. Electrospun matrices for localised controlled drug delivery: Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from layers of polycaprolactone and poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate). Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2012, 2, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusein, N.; De Bank, P.; Blagbrough, I.S. Polycaprolactone electrospun nanofibers for controlled drug delivery. In The Encyclopedia of Biomedical Polymers and Polymeric Biomaterials; Mishra, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Volume 7, pp. 5239–5249. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Tamoxifen-loaded silk fibroin electrospun fibers. Mater. Lett. 2016, 178, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stygar, D.; Muravitskaya, N.; Eriksson, B.; Eriksson, H.; Sahlin, L. Effects of serm (selective estrogen receptor modulator) treatment on growth and proliferation in the rat uterus. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2003, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.K.; Zhao, H.; Fuqua, S.A.W. Selective estrogen receptor modulators: Structure, function, and clinical use. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3172–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, S.O.L.; Cotrim, M.A.P.; Oréfice, R.L.; Carvalho, S.G.; Dutra, J.A.P.; de Paula Careta, F.; Resende, J.A.; Villanova, J.C.O. Electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) matrices containing silver sulfadiazine complexed with β-cyclodextrin as a new pharmaceutical dosage form to wound healing: Preliminary physicochemical and biological evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangman, P.; Pundee, C.; Opasanon, S.; Muangman, S. A prospective, randomized trial of silver containing hydrofiber dressing versus 1% silver sulfadiazine for the treatment of partial thickness burns. Int. Wound J. 2010, 7, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytac, Z.; Uyar, T. Core-shell nanofibers of curcumin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex and polylactic acid: Enhanced water solubility and slow release of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.Z.; Williams, G.R.; Hou, X.X.; Zhu, L.M. Electrospun curcumin-loaded fibers with potential biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudakaran, S.V.; Venugopal, J.R.; Vijayakumar, G.P.; Abisegapriyan, S.; Grace, A.N.; Ramakrishna, S. Sequel of MgO nanoparticles in PLACL nanofibers for anti-cancer therapy in synergy with curcumin/β-cyclodextrin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Li, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.; Cui, W.; Zou, J.; Zhou, S. Release modulation and cytotoxicity of hydroxycamptothecin-loaded electrospun fibers with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inoculations. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.; Amiri, S.; Bahrami, S.H. Pcl-based nanofibers loaded with ciprofloxacin/cyclodextrin containers. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.; Alves, G.; Oliveira, P.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A. Intranasal delivery of ciprofloxacin to rats: A topical approach using a thermoreversible in situ gel. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, P.; Wei, Q. Preparation and characterization of electrospun polyvinyl alcoholstyrylpyridinium/β-cyclodextrin composite nanofibers: Release behavior and potential use for wound dressing. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbás, E.; Balogh, A.; Bocz, K.; Müller, J.; Kiserdei, É.; Vigh, T.; Sinkó, B.; Marosi, A.; Halász, A.; Dohányos, Z.; et al. In vitro dissolution–permeation evaluation of an electrospun cyclodextrin-based formulation of aripiprazole using μflux™. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panichpakdee, J.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Electrospinning of asiaticoside/2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex-loaded cellulose acetate fiber mats: Release characteristics and potential for use as wound dressing. Polymer 2014, 38, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Dogan, S.Y.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Release and antibacterial activity of allyl isothiocyanate/β-cyclodextrin complex encapsulated in electrospun nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 120, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Lugo, A.C.; Lim, L.T. Controlled release of allyl isothiocyanate using soy protein and poly(lactic acid) electrospun fibers. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Antimetastasis and antitumor efficacy promoted by sequential release of vascular disrupting and chemotherapeutic agents from electrospun fibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigh, T.; Démuth, B.; Balogh, A.; Galata, D.L.; Van Assche, I.; Mackie, C.; Vialpando, M.; Van Hove, B.; Psathas, P.; Borbás, E.; et al. Oral bioavailability enhancement of flubendazole by developing nanofibrous solid dosage forms. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, V.P.; Sy, J.C. Modulation of Drug Release Rate from Electrospun Fibers. U.S. Patent US20080220054A1, 11 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kazsoki, A.; Szabó, P.; Domján, A.; Balázs, A.; Bozó, T.; Kellermayer, M.; Farkas, A.; Balogh-Weiser, D.; Pinke, B.; Darcsi, A.; et al. Microstructural distinction of electrospun nanofibrous drug delivery systems formulated with different excipients. Mol. Pharm. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filée, P.; Freichels, A.; Jéröme, C.; Aquil, A.; Colige, A.; Tateu, V.T. Chitosan-Based Biomimetic Scaffolds and Methods for Preparing the Same. U.S. Patent WO2011151225A1, 13 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Puškárová, A.; Bučková, M.; Kraková, L.; Pangallo, D.; Kozics, K. The antibacterial and antifungal activity of six essential oils and their cyto/genotoxicity to human hel 12469 cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnemore, H. The essential oils. Nature 1927, 119, 920. [Google Scholar]
- Toscano-Garibay, J.D.; Arriaga-Alba, M.; Sánchez-Navarrete, J.; Mendoza-García, M.; Flores-Estrada, J.J.; Moreno-Eutimio, M.A.; Espinosa-Aguirre, J.J.; González-Ávila, M.; Ruiz-Pérez, N.J. Antimutagenic and antioxidant activity of the essential oils of citrus sinensis and citrus latifolia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonglairoum, P.; Chuchote, T.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Opanasopit, P. Encapsulation of plai oil/2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) electrospun nanofibers for topical application. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonglairoum, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Kaomongkolgit, R.; Opanasopit, P. Fabrication and evaluation of nanostructured herbal oil/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin/polyvinylpyrrolidone mats for denture stomatitis prevention and treatment. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2016, 17, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Dai, Y.; Cui, H. Antibacterial poly(ethylene oxide) electrospun nanofibers containing cinnamon essential oil/beta-cyclodextrin proteoliposomes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.H.; Wu, H.; Zong, M.H.; Jing, Y.R.; Han, S.Y. Encapsulation of cinnamon essential oil in electrospun nanofibrous film for active food packaging. Food Control 2016, 59, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.H.; Feng, K.; Liu, F.J.; Lou, W.Y.; Li, N.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H. Fabrication of electrospun polylactic acid nanofilm incorporating cinnamon essential oil/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for antimicrobial packaging. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Wen, P.; Yang, H.; Li, N.; Lou, W.Y.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H. Enhancement of the antimicrobial activity of cinnamon essential oil-loaded electrospun nanofilm by the incorporation of lysozyme. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munhuweyi, K.; Caleb, O.J.; van Reenen, A.J.; Opara, U.L. Physical and antifungal properties of β-cyclodextrin microcapsules and nanofibre films containing cinnamon and oregano essential oils. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, R.; Lan, W.; Qin, W. Fabrication of electrospun polylactic acid/cinnamaldehyde/β-cyclodextrin fibers as an antimicrobial wound dressing. Polymers 2017, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhifi, W.; Bellili, S.; Jazi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Mnif, W. Essential oils’ chemical characterization and investigation of some biological activities: A critical review. Medicines 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Antunes, M.; da Silva Dannenberg, G.; Fiorentini, Â.M.; Pinto, V.Z.; Lim, L.T.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Antimicrobial electrospun ultrafine fibers from zein containing eucalyptus essential oil/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytac, Z.; Kusku, S.I.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Encapsulation of gallic acid/cyclodextrin inclusion complex in electrospun polylactic acid nanofibers: Release behavior and antioxidant activity of gallic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 63, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascheroni, E.; Fuenmayor, C.A.; Cosio, M.S.; Di Silvestro, G.; Piergiovanni, L.; Mannino, S.; Schiraldi, A. Encapsulation of volatiles in nanofibrous polysaccharide membranes for humidity-triggered release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Hacaloglu, J.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospun polystyrene fibers containing high temperature stable volatile fragrance/flavor facilitated by cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Nur, Y.; Hacaloglu, J.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospinning of functional poly(methyl methacrylate) nanofibers containing cyclodextrin-menthol inclusion complexes. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 125703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyar, T.; Hacaloglu, J.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospun polyethylene oxide (PEO) nanofibers containing cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3949–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayaci, F.; Uyar, T. Encapsulation of vanillin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex in electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanowebs: Prolonged shelf-life and high temperature stability of vanillin. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loong-Tak Lim, S.D.F.M.; Gopinadhan, P.; Jayasankar Subramanian, J. Alan Sullivan Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Volatile Organic Compounds. U.S. Patent US20160330952A1, 17 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aytac, Z.; Keskin, N.O.S.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant α-tocopherol/γ-cyclodextrin–inclusion complex encapsulated poly(lactic acid) electrospun nanofibrous web for food packaging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Kusku, S.I.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Quercetin/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex embedded nanofibres: Slow release and high solubility. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, S.M.; Scampicchio, M.; Mahon, P.J.; Sbarski, I.; Wang, J.; Kingshott, P. Controlled release of retinyl acetate from β-cyclodextrin functionalized poly(vinyl alcohol) electrospun nanofibers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.F.; Suarez, D.; Rocha, J.C.B.; de Carvalho Teixeira, A.V.N.; Cortés, M.E.; De Sousa, F.B.; Sinisterra, R.D. Electrospun nanofibers of polycd/PMAA polymers and their potential application as drug delivery system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 54, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costoya, A.; Ballarin, F.M.; Llovo, J.; Concheiro, A.; Abraham, G.A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Hmdso-plasma coated electrospun fibers of poly(cyclodextrin)s for antifungal dressings. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouerghemmi, S.; Degoutin, S.; Tabary, N.; Cazaux, F.; Maton, M.; Gaucher, V.; Janus, L.; Neut, C.; Chai, F.; Blanchemain, N.; et al. Triclosan loaded electrospun nanofibers based on a cyclodextrin polymer and chitosan polyelectrolyte complex. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, A.; Mehrabi, F.; Shamspur, T.; Sheibani, H.; Mostafavi, A. Encapsulation and controlled release of vitamin b2 using peracetyl-β-cyclodextrin polymer-based electrospun nanofiber scaffold. Pharm. Chem. J. 2018, 52, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, A.A.; Montaser, A.S.; Abdel Azeem, R.A.; Mounier, M.M. Eco-friendly gelatin-based electrospun fibers to control the release of chloramphenicol. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.J.; Branchflower, R.V.; Burke, T.R.; Lees, D.E.; Pohl, L.R. Bone marrow toxicity in vitro of chloramphenicol and its metabolites. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1982, 64, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinté, P.; Mariotte, A.; Anand, P.; Keller, L.; Idoux-Gillet, Y.; Huck, O.; Fioretti, F.; Tenenbaum, H.; Georgel, P.; Wenzel, W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of active nanofibrous polymeric membrane bearing nanocontainers of atorvastatin complexes. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 2651–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhban, M.; Nouri, M.; Mokhtari, J. Electrospinning of cyclodextrin functionalized chitosan/pva nanofibers as a drug delivery system. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, A.; von Recum, T.T.; Julius, N.K.; Travis, S.; Iryna, M. Therapeutic Agent Delivery System and Method. U.S. Patent US20150010608A1, 8 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cecone, C.; Caldera, F.; Trotta, F.; Bracco, P.; Zanetti, M. Controlled release of deet loaded on fibrous mats from electrospun pmda/cyclodextrin polymer. Molecules 2018, 23, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Cyclodextrin nanofibers by electrospinning. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6903–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of nanofibers from non-polymeric systems: Polymer-free nanofibers from cyclodextrin derivatives. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospun gamma-cyclodextrin ([gamma]-CD) nanofibers for the entrapment of volatile organic compounds. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22891–22895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of polymer-free nanofibers from cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6218–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Umu, O.C.O.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial electrospun nanofibers from triclosan/cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Aytac, Z.; Kilic, M.E.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Encapsulation of camphor in cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibers via polymer-free electrospinning: Enhanced water solubility, high temperature stability, and slow release of camphor. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 5436–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. Fabrication of electrospun eugenol/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibrous webs for enhanced antioxidant property, water solubility, and high temperature stability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. Electrospun nanofibers from cyclodextrin inclusion complexes with cineole and p-cymene: Enhanced water solubility and thermal stability. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Kayaci-Senirmak, F.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of cyclodextrin/linalool-inclusion complex nanofibers: Fast-dissolving nanofibrous web with prolonged release and antibacterial activity. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Kayaci-Senirmak, F.; San Keskin, N.O.; Kusku, S.I.; Durgun, E.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Fast-dissolving, prolonged release, and antibacterial cyclodextrin/limonene-inclusion complex nanofibrous webs via polymer-free electrospinning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7325–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Kayaci-Senirmak, F.; San Keskin, N.O.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of polymer-free cyclodextrin/geraniol-inclusion complex nanofibers: Enhanced shelf-life of geraniol with antibacterial and antioxidant properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46089–46099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. Thymol/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibrous webs: Enhanced water solubility, high thermal stability and antioxidant property of thymol. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, Z.I.; Celebioglu, A.; Kilic, M.E.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Menthol/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibers: Enhanced water-solubility and high-temperature stability of menthol. J. Food Eng. 2018, 224, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Kayaci-Senirmak, F.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Polymer-free nanofibers from vanillin/cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: High thermal stability, enhanced solubility and antioxidant property. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant vitamin e/cyclodextrin inclusion complex electrospun nanofibers: Enhanced water solubility, prolonged shelf life, and photostability of vitamin E. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5404–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, Z.I.; Celebioglu, A.; Kilic, M.E.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Fast-dissolving carvacrol/cyclodextrin inclusion complex electrospun fibers with enhanced thermal stability, water solubility, and antioxidant activity. J. Mater. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultee, A.; Bennik, M.H.J.; Moezelaar, R. The phenolic hydroxyl group of carvacrol is essential for action against the food-borne pathogen bacillus cereus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beena; Kumar, D.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of thymol and carvacrol based schiff bases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
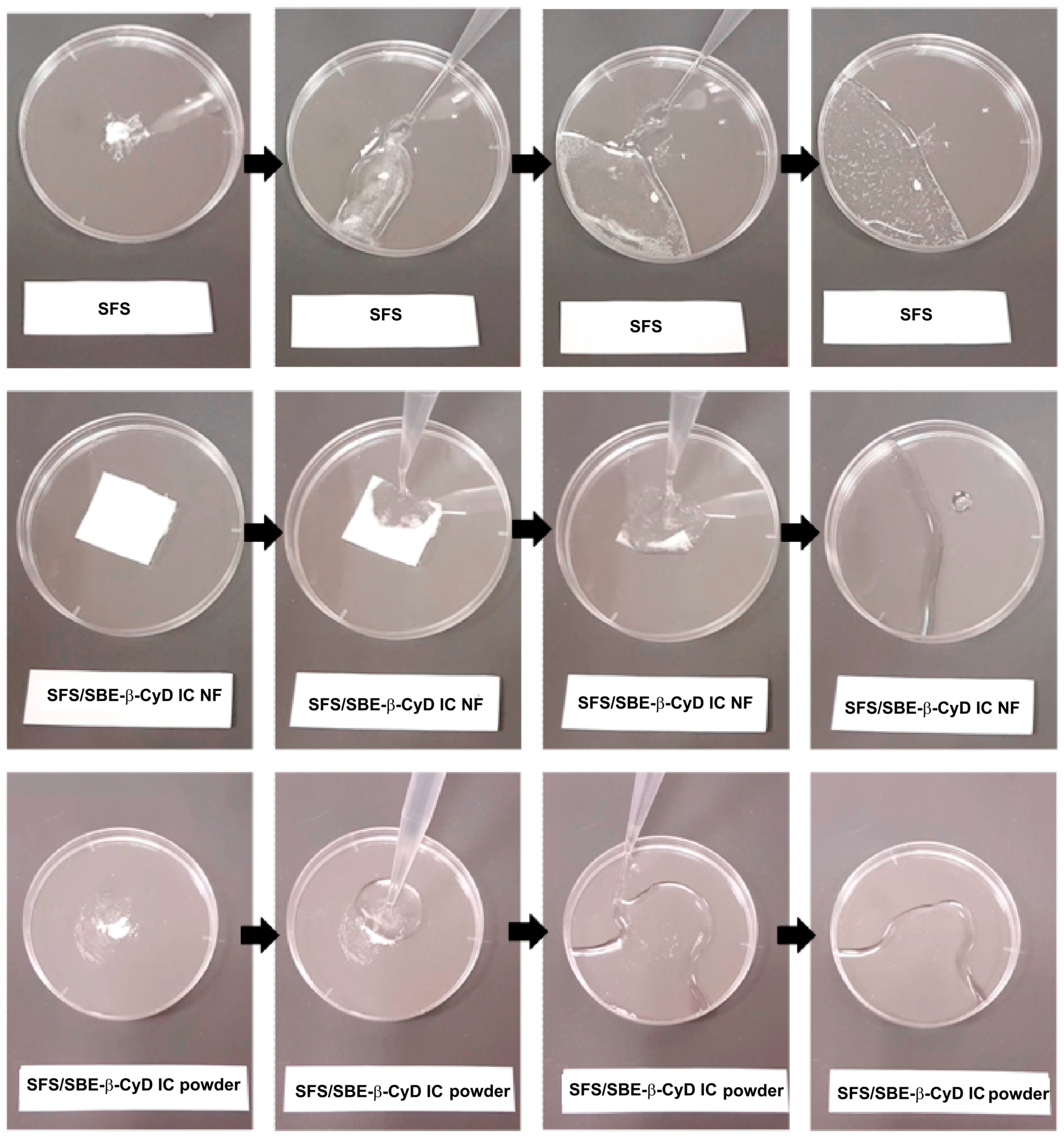
- Yildiz, Z.I.; Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Polymer-free electrospun nanofibers from sulfobutyl ether7-beta-cyclodextrin (SBE7-β-CD) inclusion complex with sulfisoxazole: Fast-dissolving and enhanced water-solubility of sulfisoxazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, A.; Horváthová, T.; Fülöp, Z.; Loftsson, T.; Harasztos, A.H.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Electroblowing and electrospinning of fibrous diclofenac sodium-cyclodextrin complex-based reconstitution injection. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigh, T.; Horváthová, T.; Balogh, A.; Sóti, P.L.; Drávavölgyi, G.; Nagy, Z.K.; Marosi, G. Polymer-free and polyvinylpirrolidone-based electrospun solid dosage forms for drug dissolution enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
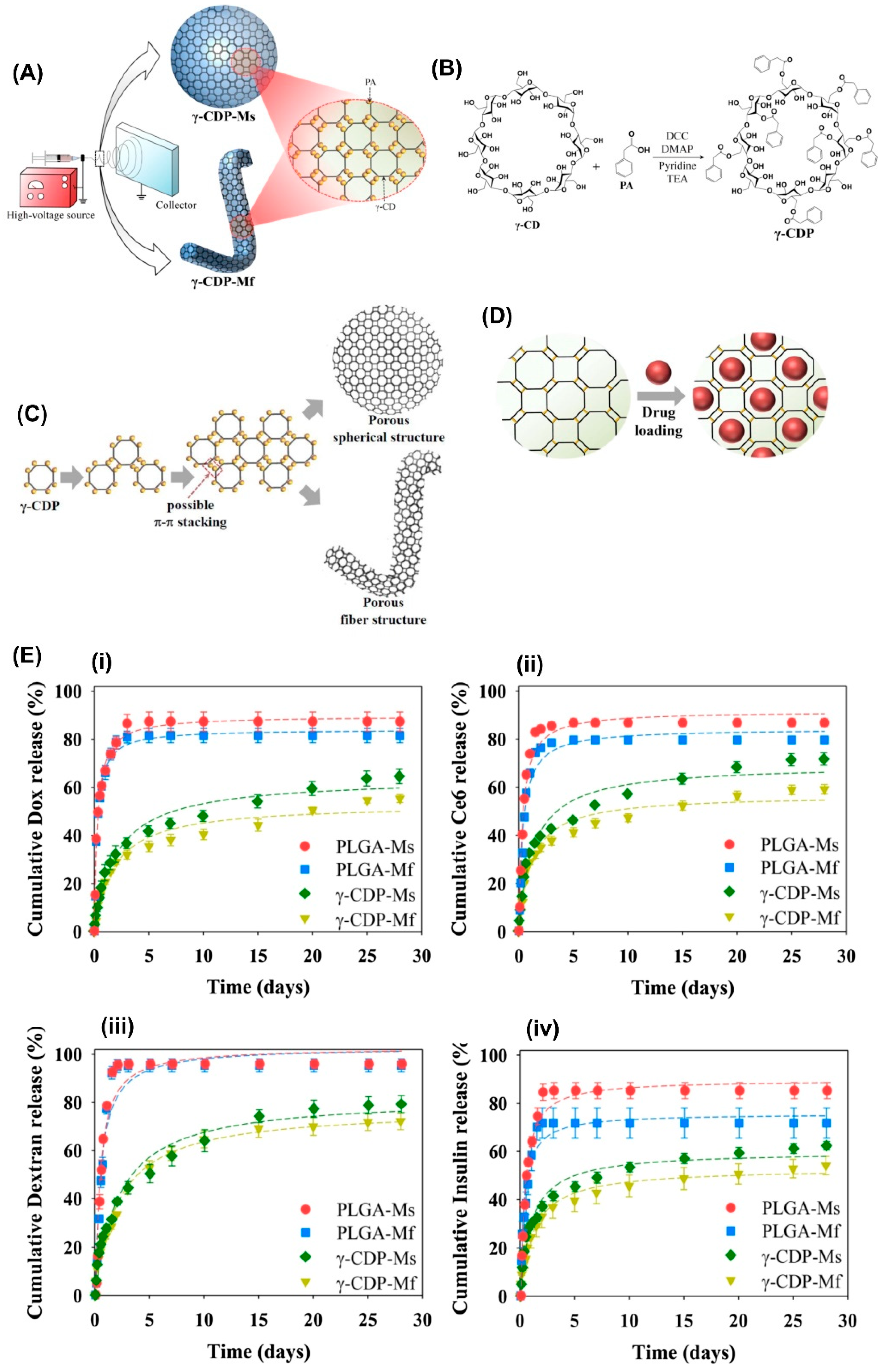
- Yu, H.S.; Lee, J.M.; Youn, Y.S.; Oh, K.T.; Na, K.; Lee, E.S. γ-cyclodextrin-phenylacetic acid mesh as a drug trap. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. Electrospun crosslinked poly-cyclodextrin nanofibers: Highly efficient molecular filtration thru host-guest inclusion complexation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Li, D. New organic nanoporous polymers and their inclusion complexes. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CyD Type | Polymer Additive | Active Molecule | Release Data | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-CyD | PCL | Naproxen (NAP) | Higher NAP release with CyD | [88] |
| β-CyD, HP-β-CyD | Pellethane (TPU) | Naproxen (NAP) | 10 h (NAP-TPU), 32 h (NAP/β-CyD/TPU), 120 h (NAP, HP-β-CyD/TPU) | [91] |
| HP-β-CyD | Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) | Sulfisoxazole (SFS) | 720 min (PCL-PCL-HPC/SFS/HP-β-CyD-IC-NF), >720 min (HPC/SFS/HP-β-CyD-IC-NF) | [92] |
| HP-β-CyD | PVP, PVA, Thiolated chitosan (CS-SH) | Clotrimazole (CZ) | For all nanofibers 80% in 480 min | [94] |
| HP-β-CyD | PVA | Voriconazole (VRC) | 8 h for 100% release | [95] |
| β-CyD, HP-β-CyD | PVP | Meloxicam (MX) | For all nanofibers, 20 min for 100% release | [97] |
| HP-β-CyD | PVP | Meloxicam (MX) | Rapid release (<10 min) | [99] |
| β-CyD | PCL | Tetracycline (TCN) | Drug release occurred up to 2 weeks | [100] |
| HP-β-CyD | Silk fibroin (SF) | Tamoxifen (TAM) | 10% in 22 days in PBS, 50–60% in PBS-EtOH (30%) in 22 days) | [107] |
| β-CyD | PCL | Silver sulfadiazine (SAg) | 80% release from PCL/SAg, 66% release from PCL/SAg/β-CyD | [110] |
| HP-β-CyD | PLLA | Curcumin (CUR) | Higher release at pH of 1. CyD increased drug release. | [112] |
| β-CyD | PVA | Curcumin (CUR) | Higher drug content increased the release rate. | [113] |
| β-CyD | Poly (l-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone) (PLACL) | Curcumin (CUR) | 1% CUR interacting with MgO nanoparticles showed higher inhibition of breast cancer cells. | [114] |
| HP-β-CyD | Poly(dl-lactic acid)–poly(ethylene glycol) (PELA) | Hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT) | Higher CyD content increased release rate. The release was slow and took many weeks. | [115] |
| α-CyD and β-CyD | PCL | Ciprofloxacin | Higher release with initial higher drug loading | [116] |
| SBE-β-CyD | PEO | Aripiprazole (ARP) | Rapid release in 2 min | [119] |
| HP-β-CyD | Cellulose acetate | Asiaticoside (AC) | Higher release with CyD and initial burst release within 300 min | [120] |
| β-CyD | PVA | Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) | Higher release at 75 °C and followed by 50 and 30 °C. | [121] |
| β-CyD | PEO | Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) | Higher release with increasing relative humidity | [122] |
| HP-β-CyD | Poly(ethylene glycol)-polylactide (PELA) | Combretastatin A-4 (CA4) and hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT) | Sustained release of CA4 over 30 days, fibers showed significant antitumor efficacy and tumor vasculature destruction | [123] |
| HP-β-CyD | PVP | Flubendazole | The release of a dose of 40 mg in 15 min | [124] |
| M-β-CyD | PLLA | Doxorubicin (DOX) | 17% Decrease in the burst release was observed and followed by a quantifiable sustained release up to 2 days. | [125] |
| HP-β-CyD | PVA | Metoclopramide hydrochloride (MH) | Burst release: 90% release in 2 min | [126] |
| β-CyD derivative | Chitosan | β-Lactamase BlaP protein | CyD increased the stability of the embedded protein | [127] |
| HP-β-CyD | PVP | Plai oil | The release rate ranged was in the order of 10% > 20%~30% plai oil within 24 h. | [131] |
| HP-β-CyD | PVP | Herbal oil | Very rapid release: 50% release in 1 min | [132] |
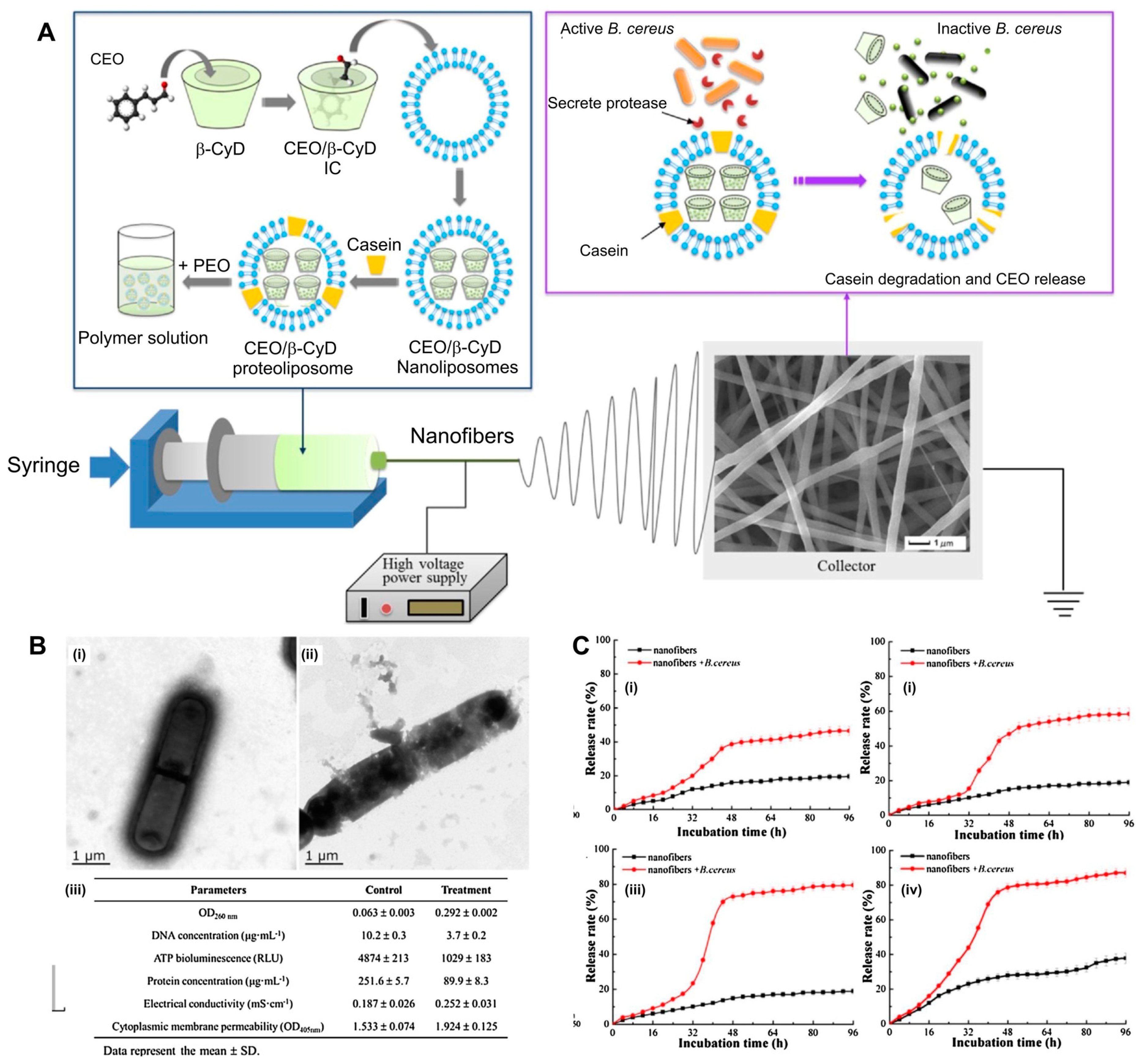
| β-CyD | PEO | Cinnamon (CEO) | Controlled release in nanofibers via bacterial protease. | [133] |
| β-CyD | PVA | Cinnamon (CEO) | Nanofibers showed excellent antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. | [134] |
| β-CyD | PLA | Cinnamon (CEO) | High antimicrobial activity due to released CEO | [135] |
| β-CyD | PVA | Cinnamon (CEO) | Stronger antimicrobial activity with incorporated lysozyme | [136] |
| β-CyD | Chitosan and PVA | Oregano and cinnamon EOs | Lower release of Oregano EO than CEO | [137] |
| β-CyD | PLA | Cinnamaldehyde (CA) | Higher release with increasing CA content | [138] |
| β-CyD | Zein | Eucalyptus EO | Higher antimicrobial activity with increasing EEO content | [140] |
| HP-β-CyD | PLA | Gallic acid | Increasing release rate with CyD incorporation | [141] |
| β-CyD | Pullulan | Perillaldehyde | Higher release with increasing humidity | [142] |
| α-CyD | Xanthan | Hexanal | CyD increased the release rate | [147] |
| γ-CyD | PLA | α-Tocopherol (α-TC) | CyD increased higher release of α-TC. | [148] |
| β-CyD | PAA | Quercetin | Nanofibers showed enhanced release rate than the films | [149] |
| β-CyD | PVA | Retinyl acetate (RA) | Slower release with CyD incorporation | [150] |
| CyD Type | Polymer Additive | Active Molecule | Release Data | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyCyD | PMAA | Propranolol hydrochloride (PROP) | 40% Release (uniaxial PMAA:polyCyD (60:40, 80:20), 20% release from coaxial fibers | [151] |
| PolyCyD | PCL, PVP | Fluconazole | Burst release ((FLU-poly-α-CyD)-IC/PCL and (FLU-poly-β-CyD)-IC/PCL mats showed a burst of 85% in the first 15 min) | [152] |
| HP-β-CyD | Chitosan, citric acid (as cross-linker) | Triclosan | Higher release at lower pH (5.5), 80% release in 10 h | [153] |
| PolyCyD (peracetyl-β-CyD polymer) | - | Vitamin B2 | 60% (pH = 1.2) and 40% (pH = 7.4) release after 170 h | [154] |
| Poly aldehyde β-CyD (PA-β-CyD). | Gelatin | Chloramphenicol | Burst release for gelatin/drug (90% in 30 min), 90% release in 48 h for 7.5 and 10 wt.% PA-β-CyD | [155] |
| Poly-amino-β-CyD | PCL | Atorvastatin calcium trihydrate | TNF-α inhibition reached about 60% at 48 h (no dose effect), and up to 80% for IL-6, depending on the dose | [157] |
| Chitosan grafted carboxymethyl-β-CyD (CM β-CyD) | Chitosan | Salicylic acid | 90% after 24 h at 37 °C, 84% after 24 h at 20 °C | [158] |
| Thiolated CyD | pEVOH/sH-CyD/PMDI | Vancomycin | Slow release | [159] |
| β-CyD | β-CyD/PMDA polymer | N,N-diethyl-3-toluamide (DEET) | Sustained release of all loaded DEET in 2 weeks. | [160] |
| CyD type | Active molecule | Release data | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD | Triclosan | Rapid release on contact with water and significant inhibition against E. coli and S. aureus | [165] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD | Camphor | In gas phase, faster release at higher temp., faster for the HP-β-CyD system | [166] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD, and M-β-CyD | Eugenol | Rapid release on contact with water, enhanced antioxidant activity than eugenol itself | [167] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD | Cineole and p-cymene | Rapid release along with the fiber dissolution | [168] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD, and M-β-CyD | Linalool | Rapid release, significant inhibition against the growth of E. coli and S. aureus | [169] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD and M-β-CyD | Limonene | 25% Release M-β-CyD/limonene-IC-NF, 51% release HP-β-CyD/limonene-IC-NF, 88% release HP-γ-CyD/limonene-IC-NF in 100 days | [170] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD and M-β-CyD | Geraniol | Long-term stability of geraniol in gas phase | [171] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD and M-β-CyD | Thymol | Immediately on contact with water | [172] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD | Menthol | Rapid release along with the fiber dissolution | [173] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-γ-CyD and M-β-CyD | Vanillin | Immediately on contact with water, enhanced antioxidant activity with nanofibers | [174] |
| HP-β-CyD | Vitamin E | Rapid and enhanced release, higher antioxidant activity with CyD | [175] |
| HP-β-CyD, HP-β-CyD | Carvacrol | Rapid release on contact with water | [176] |
| SBE7-β-CyD | Sulfisoxazole | Rapid and enhanced release of sulfisoxazole on contact with water | [179] |
| HP-β-CyD | Diclofenac sodium | Release in few minutes | [180] |
| HP-β-CyD | Spironolactone | Total release in 1 h | [181] |
| Phenylacetic-β-CyD | Doxorubicin, fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran (FITC-dextran), recombinant human insulin (FITC-labeled insulin) and chlorin e6 | 50% Release of drugs in vitro in 30 days, ~100% release of chlorin in vivo on day 28 | [182] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of Cyclodextrin Functional Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010006
Topuz F, Uyar T. Electrospinning of Cyclodextrin Functional Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleTopuz, Fuat, and Tamer Uyar. 2019. "Electrospinning of Cyclodextrin Functional Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010006
APA StyleTopuz, F., & Uyar, T. (2019). Electrospinning of Cyclodextrin Functional Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics, 11(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010006






