Universal Applicator for Digitally-Controlled Pressing Force and Impact Velocity Insertion of Microneedles into Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Human Skin
2.3. Production of Dissolving Microneedle Arrays
2.4. Microneedle Arrays
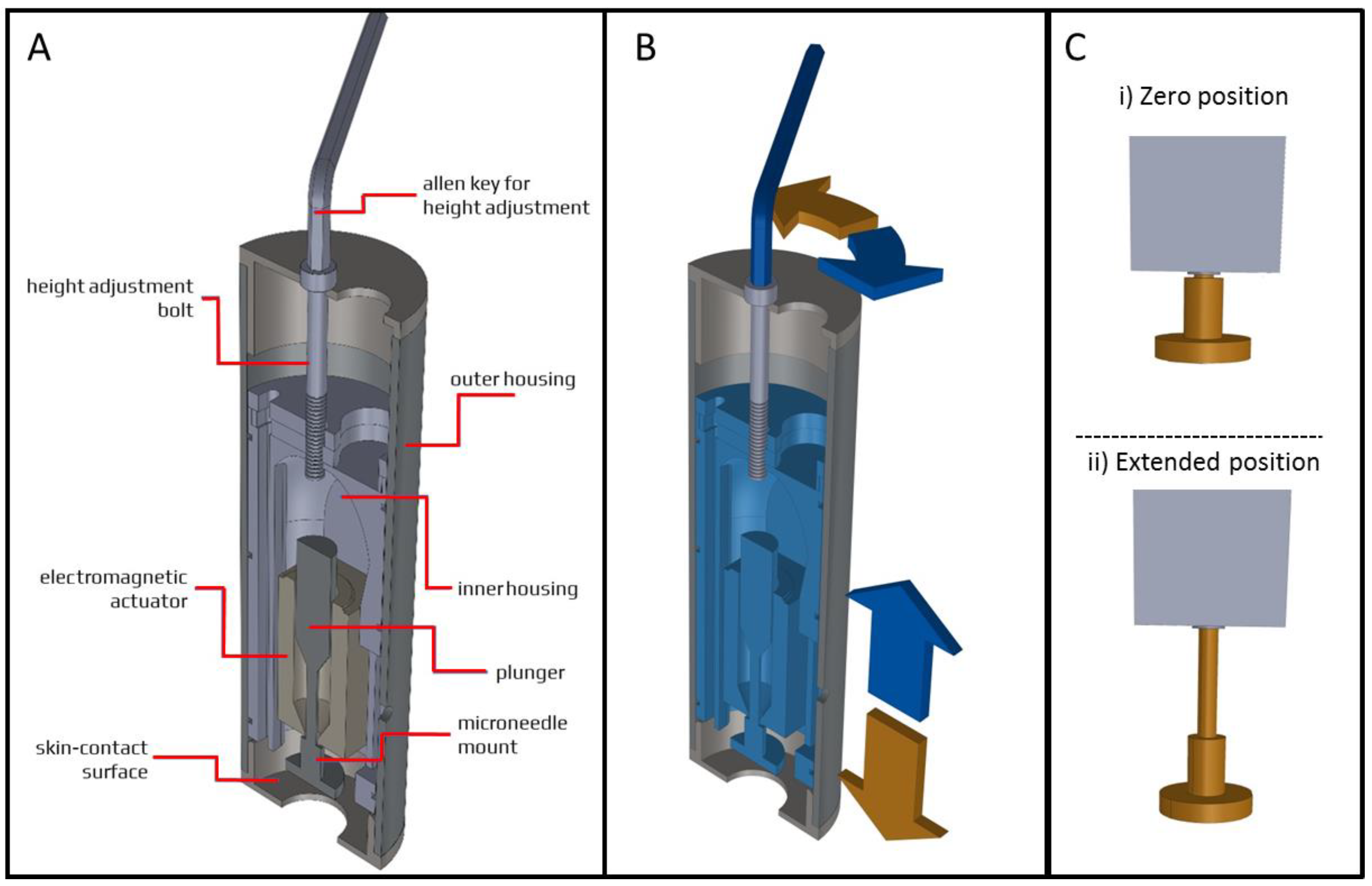
2.5. Applicator Design
2.6. Pressing Force and Impact Insertion Application
2.7. Microneedle Applicator Controller
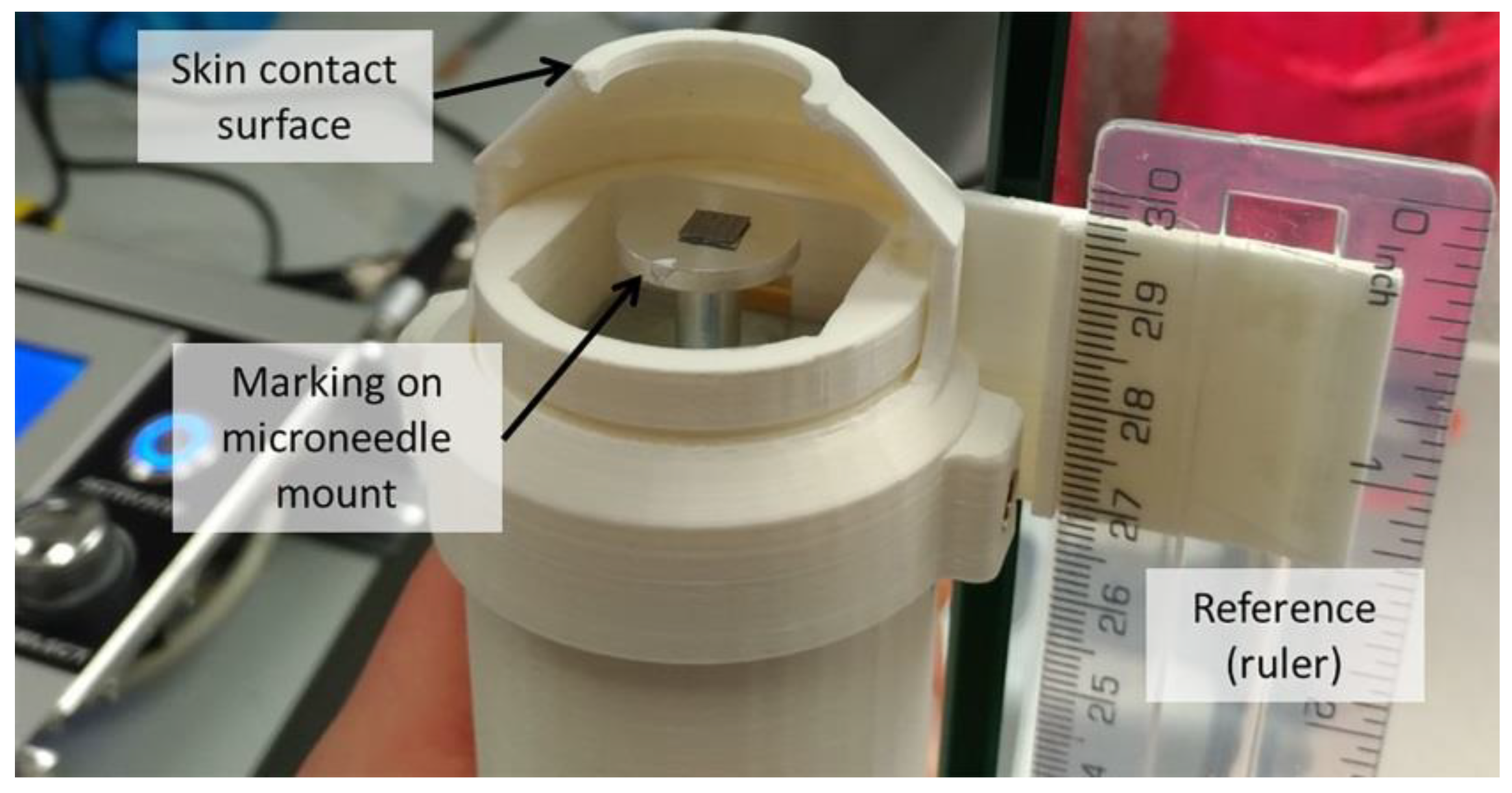
2.8. Force Calibration for Pressing Force Application
2.9. Calibration of Impact Velocity for Impact Insertion
2.10. Influence of the Applicator’s Angle as a Function of the Pulse Width
2.11. Application of MNAs onto Ex Vivo Human Skin
2.12. Determination of Penetration Efficiency by a Trypan Blue Assay
2.13. Calculation of Penetration Parameters
2.14. Normalization of Penetration Efficiency
2.15. Delivery of Fluorescently Labeled Ovalbumin into Pierced Skin
3. Results
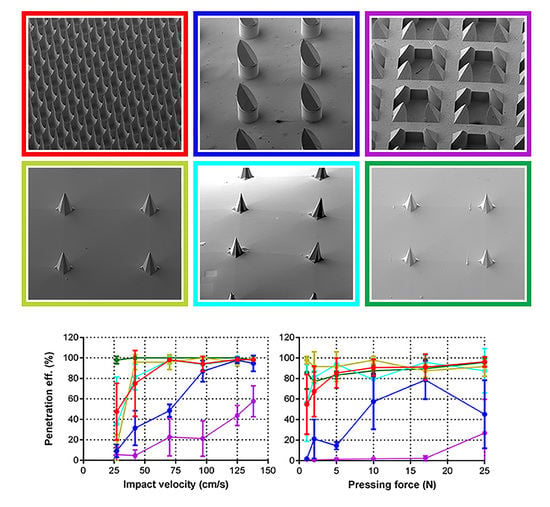
3.1. Microneedles Appearance
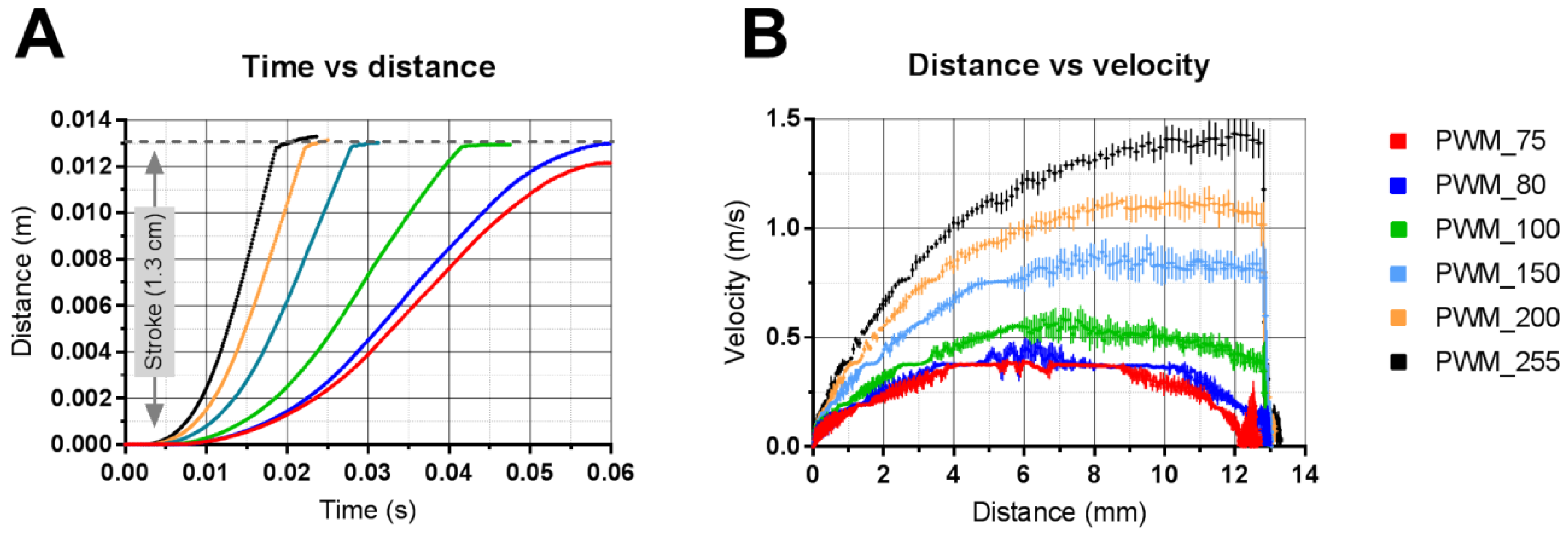
3.2. Applicator Setting: Velocity
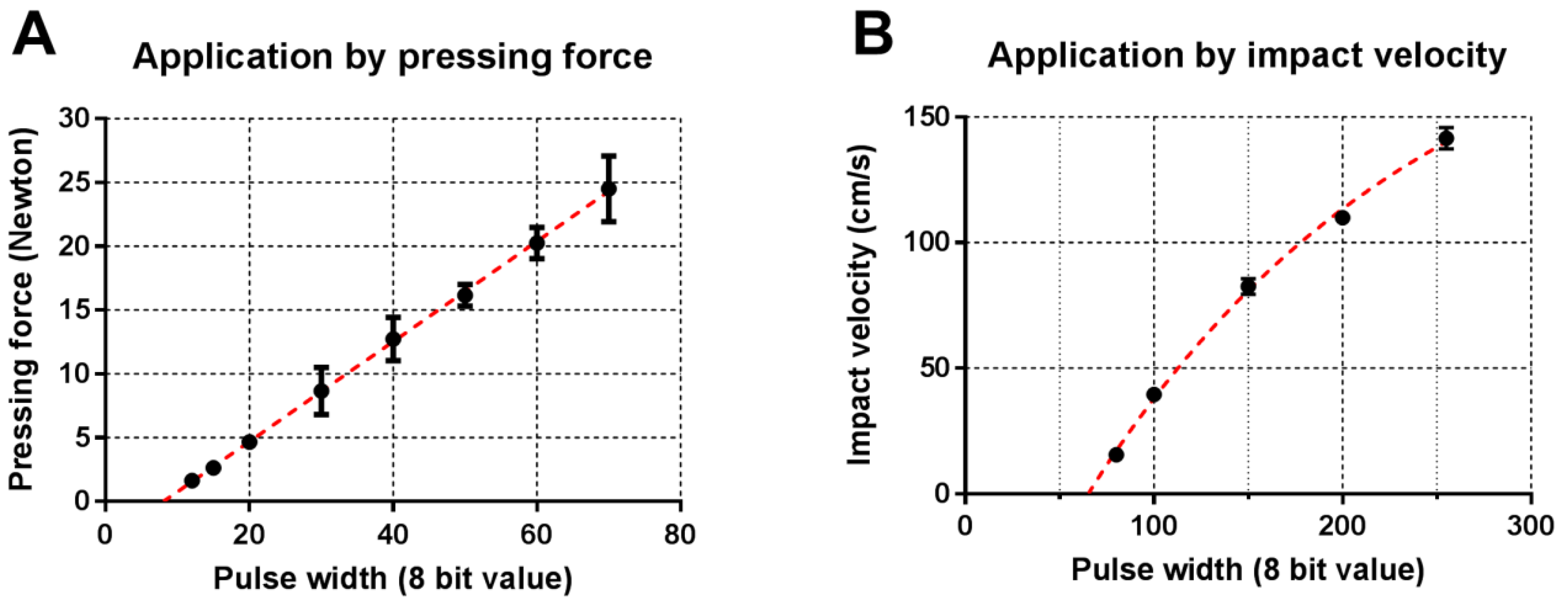
3.3. Calibration of Applicator
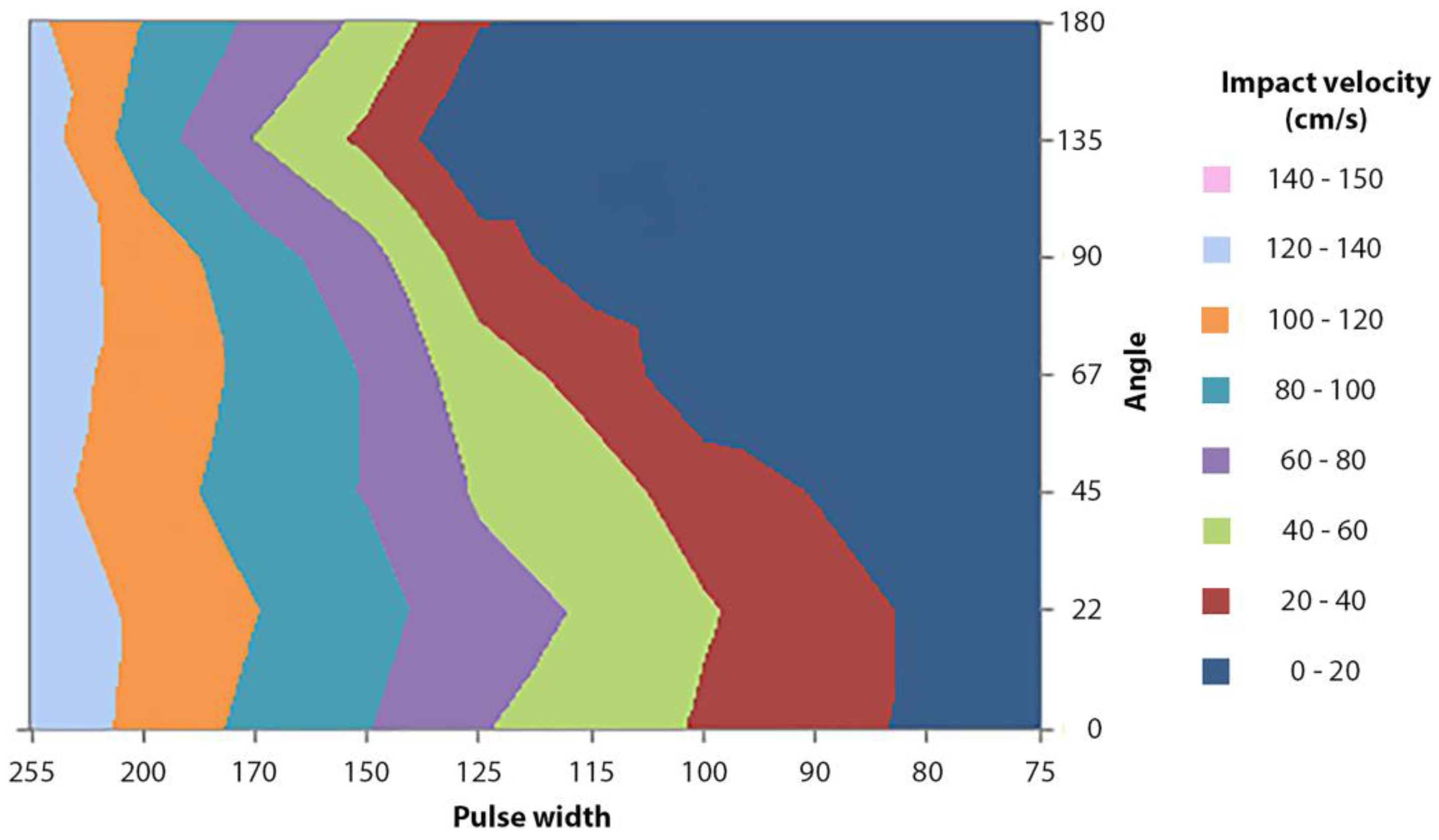
3.4. Influence of the Applicator’s Angle on the Impact Velocity
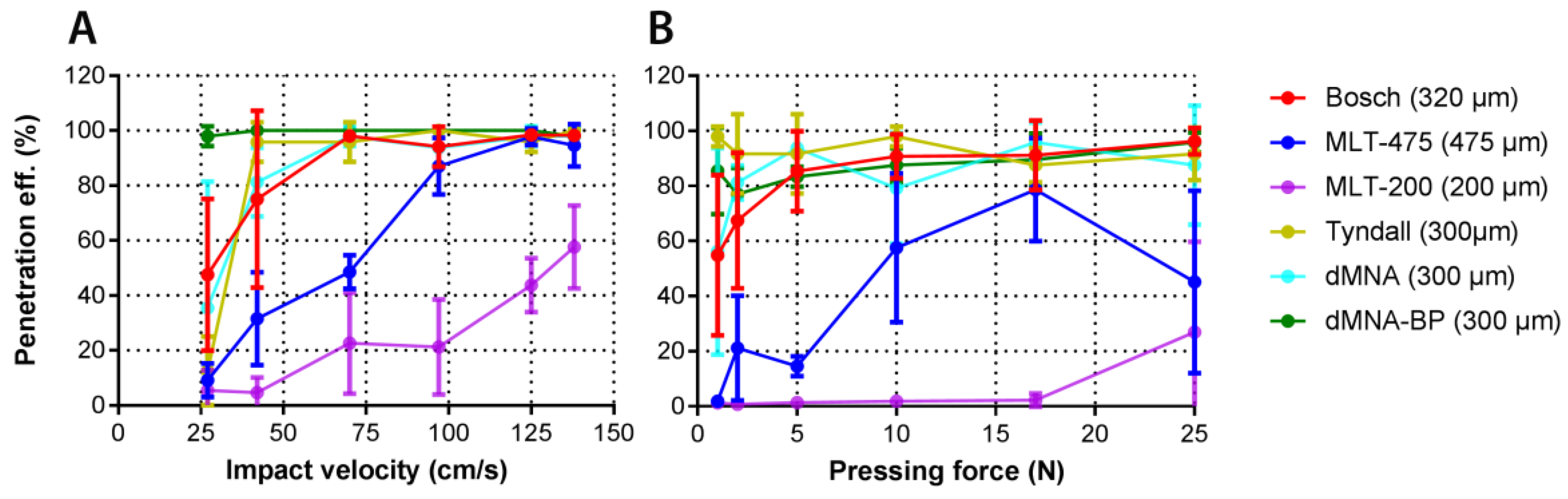
3.5. Penetration of Human Skin by Pressing Force and Impact Application
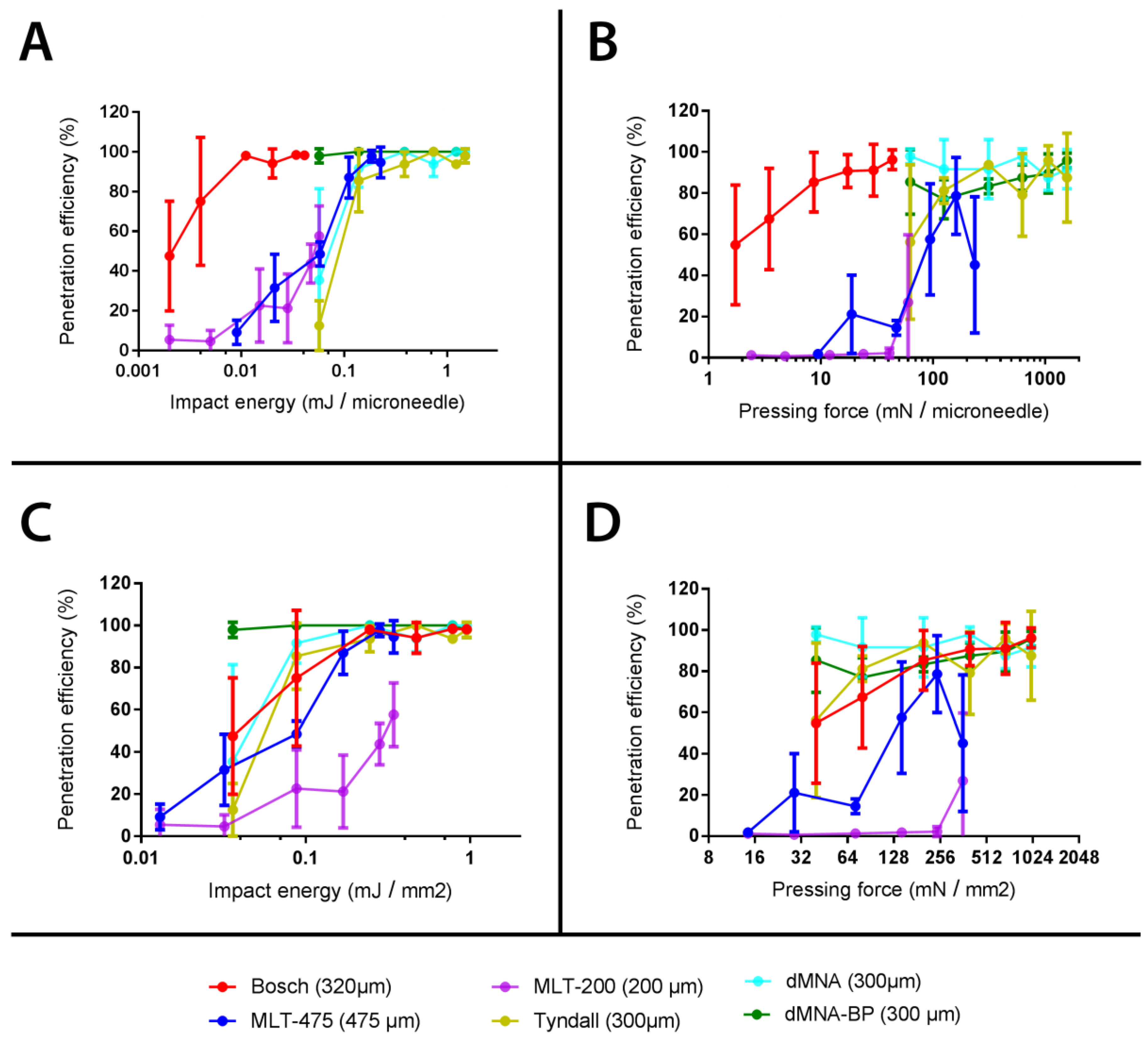
3.6. Calculation of Penetration Parameters
3.7. Relation between Penetration Efficiency and Antigen Dose Delivered into the Skin
4. Discussions
4.1. Microneedle Applicator
4.2. Skin Penetration by Microneedles
4.3. Delivery of a Model Antigen in Relation with the Penetration Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauri, A.M.; Armstrong, G.L.; Hutin, Y.J.F. The global burden of disease attributable to contaminated injections given in health care settings. Int. J. STD AIDS 2004, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, N.R.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. Recent advances in the administration of vaccines for infectious diseases: Microneedles as painless delivery devices for mass vaccination. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ita, K. Transdermal delivery of drugs with microneedles: Strategies and outcomes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, G.; Hirschberg, H. Needle-free vaccine delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Park, J.H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, M.; Monkare, J.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Kersten, G. Dissolving Microneedle Patches for Dermal Vaccination. Pharm. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, T.R.; Dunne, N.J.; Cunningham, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Review of patents on microneedle applicators. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2011, 5, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S.; Langer, R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S. Micro-scale devices for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelke, L.; Winter, G.; Hook, S.; Engert, J. Recent insights into cutaneous immunization: How to vaccinate via the skin. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4663–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, Y.N.; Naik, A.; Garrison, J.; Guy, R.H. Iontophoretic drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 619–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Bose, V.G.; Langer, R.; Weaver, J.C. Electroporation of mammalian skin: A mechanism to enhance transdermal drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10504–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, M.I.; Smith, E.; John, D.N.; Kalavala, M.; Edwards, C.; Anstey, A.; Morrissey, A.; Birchall, J.C. Clinical administration of microneedles: Skin puncture, pain and sensation. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxhed, N.; Samel, B.; Nordquist, L.; Griss, P.; Stemme, G. Painless drug delivery through microneedle-based transdermal patches featuring active infusion. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larraneta, E.; Lutton, R.E.M.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: Materials science, manufacture and commercial development. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2016, 104, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraneta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles: A New Frontier in Nanomedicine Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuan-Mahmood, T.M.; McCrudden, M.T.; Torrisi, B.M.; McAlister, E.; Garland, M.J.; Singh, T.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles for intradermal and transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Maaden, K.; Luttge, R.; Vos, P.J.; Bouwstra, J.; Kersten, G.; Ploemen, I. Microneedle-based drug and vaccine delivery via nanoporous microneedle arrays. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edens, C.; Dybdahl-Sissoko, N.C.; Weldon, W.C.; Oberste, M.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Inactivated polio vaccination using a microneedle patch is immunogenic in the rhesus macaque. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4683–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, B.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hou, J.; Bai, B.; Shen, H.; Mao, P. DNA-based vaccination against hepatitis B virus using dissolving microneedle arrays adjuvanted by cationic liposomes and CpG ODN. Drug Deliv. 2015, 23, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilieva, E.V.; Kalluri, H.; McAllister, D.; Taherbhai, M.T.; Esser, E.S.; Pewin, W.P.; Pulit-Penaloza, J.A.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I. Improved immunogenicity of individual influenza vaccine components delivered with a novel dissolving microneedle patch stable at room temperature. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrdoljak, A.; Allen, E.A.; Ferrara, F.; Temperton, N.J.; Crean, A.M.; Moore, A.C. Induction of broad immunity by thermostabilised vaccines incorporated in dissolvable microneedles using novel fabrication methods. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, J.J.; Arya, J.M.; McClain, M.A.; Frew, P.M.; Meltzer, M.I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedle patches: Usability and acceptability for self-vaccination against influenza. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonificio, A.; Ghartey-Tagoe, E.; Gallorini, S.; Baudner, B.; Chen, G.H.; Singh, P.; O′Hagan, D.T.; Kommareddy, S. Fabrication of cell culture-derived influenza vaccine dissolvable microstructures and evaluation of immunogenicity in guinea pigs. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2930–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, A.P.; Prow, T.W.; Crichton, M.L.; Chen, X.F.; Fernando, G.I.P.; Kendall, M.A.F. Targeted, Needle-Free Vaccinations in Skin using Multi layered, Densely-Packed Dissolving Microprojection Arrays. Small 2010, 6, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Maaden, K.; Sekerdag, E.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J. Impact-insertion applicator improves reliability of skin penetration by solid microneedle arrays. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, M.; Priester, M.I.; Romeijn, S.; Nejadnik, M.R.; Monkare, J.; O′Mahony, C.; Jiskoot, W.; Kersten, G.; Bouwstra, J. Hyaluronan-based dissolving microneedles with high antigen content for intradermal vaccination: Formulation, physicochemical characterization and immunogenicity assessment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maaden, K.; Heuts, J.; Camps, M.; Pontier, M.; Terwisscha van Scheltinga, A.; Jiskoot, W.; Ossendorp, F.; Bouwstra, J. Hollow microneedle-mediated micro-injections of a liposomal HPV E743-63 synthetic long peptide vaccine for efficient induction of cytotoxic and T-helper responses. J. Control. Release 2018, 269, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbaan, F.J.; Bal, S.M.; van den Berg, D.J.; Groenink, W.H.; Verpoorten, H.; Luttge, R.; Bouwstra, J.A. Assembled microneedle arrays enhance the transport of compounds varying over a large range of molecular weight across human dermatomed skin. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbaan, F.J.; Bal, S.M.; van den Berg, D.J.; Dijksman, J.A.; van Hecke, M.; Verpoorten, H.; van den Berg, A.; Luttge, R.; Bouwstra, J.A. Improved piercing of microneedle arrays in dermatomed human skin by an impact insertion method. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Maaden, K.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J. Microneedle technologies for (trans)dermal drug and vaccine delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
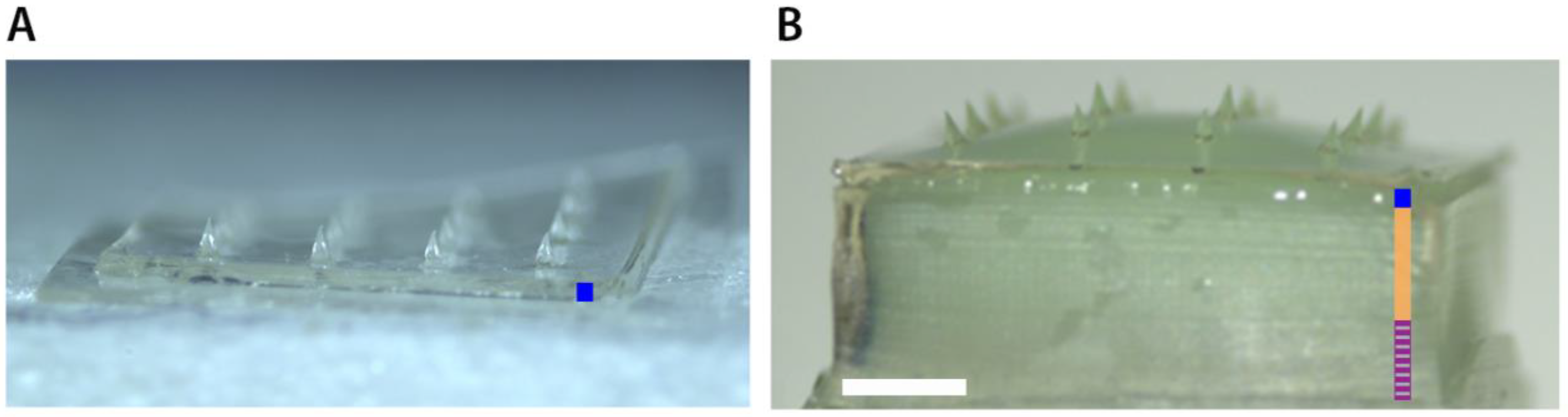

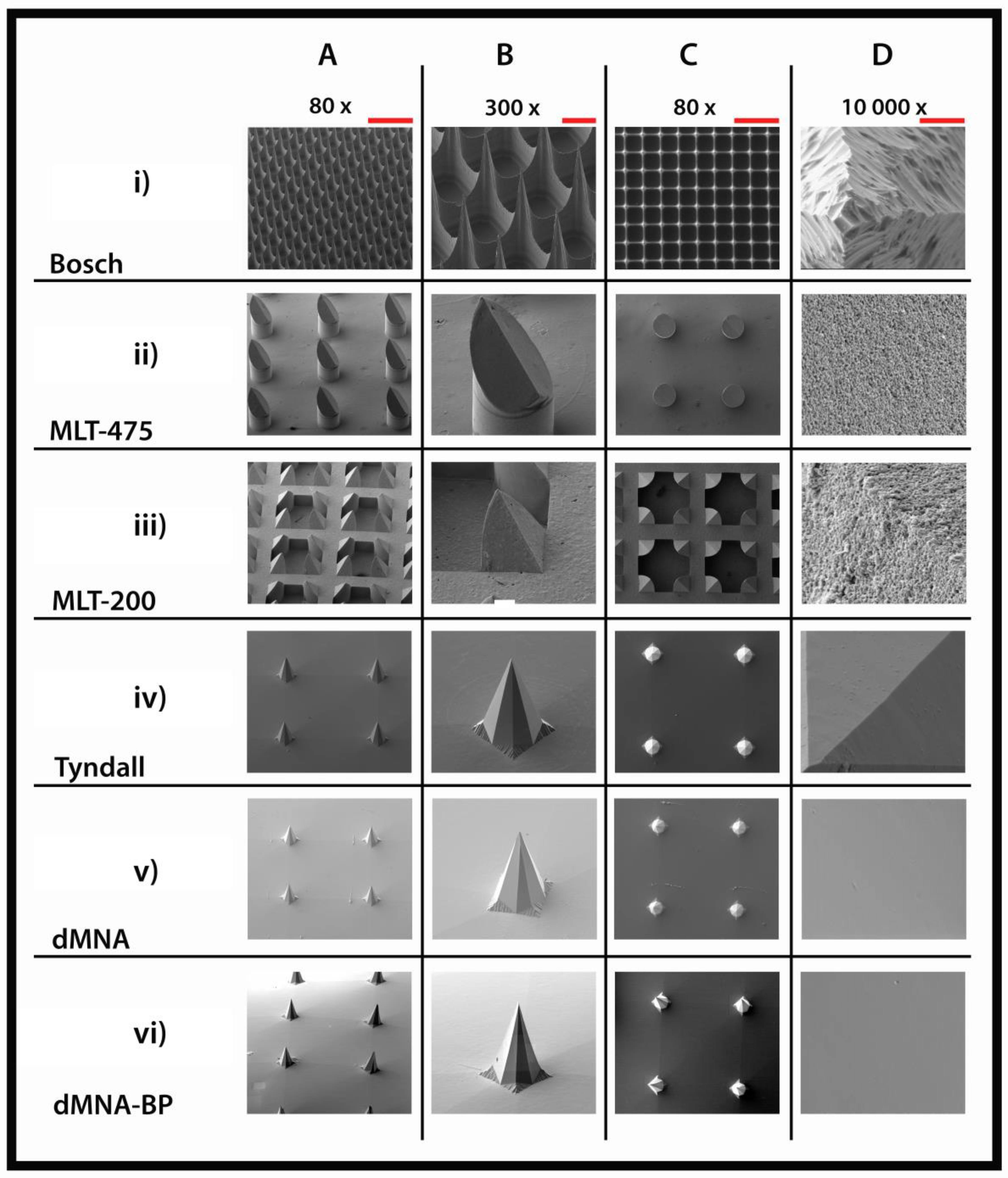

| Microneedle Array | Material | Array Geometry | Microneedle Length (µm) | Microneedle Density (cm−1) | Backplate Surface (mm2) | Number of MNs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bosch | Silicon | Square (5 × 5 mm) | 320 | 2304 | 25 | 576 |
| MLT-475 | Ceramic | Circular (d = 9 mm) | 475 | 150 | 69 | 105 |
| MLT-200 | Ceramic | Circular (d = 9 mm) | 200 | 600 | 69 | 414 |
| Tyndall | Silicon | Square (5 × 5 mm) | 300 | 64 | 25 | 16 |
| dMNA | Hyaluronan | Square (5 × 5 mm) | 300 | 64 | 25 | 16 |
| dMNA-BP | Hyaluronan | Square (5 × 5 mm) | 300 | 64 | 25 | 16 |
| Bosch | MLT-200 | MLT-475 | Tyndall | dMNA | dMNA-BP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tip diameter (µm) | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 7.6 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.3 |
| Pulse Width (8 Bit Value) | Impact Velocity (cm/s) | Impact Energy (mJ) |
|---|---|---|
| 90 | 27.40 | 0.94 |
| 104 | 42.50 | 2.16 |
| 136 | 70.60 | 6.06 |
| 174 | 97.40 | 11.85 |
| 221 | 125.70 | 19.43 |
| 250 | 138.10 | 23.84 |
| Reproducibility of Skin Piercing | Bosch (300 µm) | MLT-475 (475 µm) | MLT-200 (200 µm) | Tyndall (300 µm) | dMNA (300 µm) | dMNA-BP (300 µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSD (%) (125–138 cm/s) | 1 | 6 | 25 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| RSD (%) (17–25 N) | 9 | 42 | 121 | 9 | 16 | 7 |
| Microneedle Array | Impact Energy Per: | Pressing Force Per: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNA (mJ) | Individual MN (mJ) | mm2 (mJ) | MNA (N) | Individual MN (mN) | mm2 (mN) | |
| Bosch (300 µm) | 0.97 | 0.002 | 0.04 | 1.4 | 2.4 | 56.0 |
| MLT-475 (475 µm) | 5.47 | 0.052 | 0.08 | 6.3 | 59.8 | 91.4 |
| MLT-200 (200 µm) | 21.85 | 0.053 | 0.31 | >25.0 * | >60.1 * | >360.2 * |
| Tyndall (300 µm) | <1.00 * | <0.063 | <0.04 | <1.0 * | <62.5 * | <40.0 * |
| dMNA (300 µm) | 1.28 | 0.080 | 0.05 | <1.0 * | <62.5 * | <40.0 * |
| dMNA-BP (300 µm) | <1.00 * | <0.063 | <0.04 | <1.0 * | <62.5 * | <40.0 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leone, M.; Van Oorschot, B.H.; Nejadnik, M.R.; Bocchino, A.; Rosato, M.; Kersten, G.; O’Mahony, C.; Bouwstra, J.; Van der Maaden, K. Universal Applicator for Digitally-Controlled Pressing Force and Impact Velocity Insertion of Microneedles into Skin. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040211
Leone M, Van Oorschot BH, Nejadnik MR, Bocchino A, Rosato M, Kersten G, O’Mahony C, Bouwstra J, Van der Maaden K. Universal Applicator for Digitally-Controlled Pressing Force and Impact Velocity Insertion of Microneedles into Skin. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(4):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040211
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeone, Mara, Bart H. Van Oorschot, M. Reza Nejadnik, Andrea Bocchino, Matteo Rosato, Gideon Kersten, Conor O’Mahony, Joke Bouwstra, and Koen Van der Maaden. 2018. "Universal Applicator for Digitally-Controlled Pressing Force and Impact Velocity Insertion of Microneedles into Skin" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 4: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040211
APA StyleLeone, M., Van Oorschot, B. H., Nejadnik, M. R., Bocchino, A., Rosato, M., Kersten, G., O’Mahony, C., Bouwstra, J., & Van der Maaden, K. (2018). Universal Applicator for Digitally-Controlled Pressing Force and Impact Velocity Insertion of Microneedles into Skin. Pharmaceutics, 10(4), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040211