Oral Bioavailability and Lymphatic Transport of Pueraria Flavone-Loaded Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems Containing Sodium Taurocholate in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Animals
2.2. Preparation of Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems (SMEDDS)
2.3. Preparation of PF Suspensions (Pueraria Flavones (PFs)-Suspension)
2.4. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.5. Determination of PFs
2.6. Loading Content (LC) of PFs in SMEDDS
2.7. Release Study In Vitro
2.8. Oral Bioavailability and Lymphatic Transport
2.8.1. Protocol Design
2.8.2. Processing of Blood Samples
2.8.3. Calculation of Pharmacokinetic Parameters and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Self-Microemulsifying Behavior
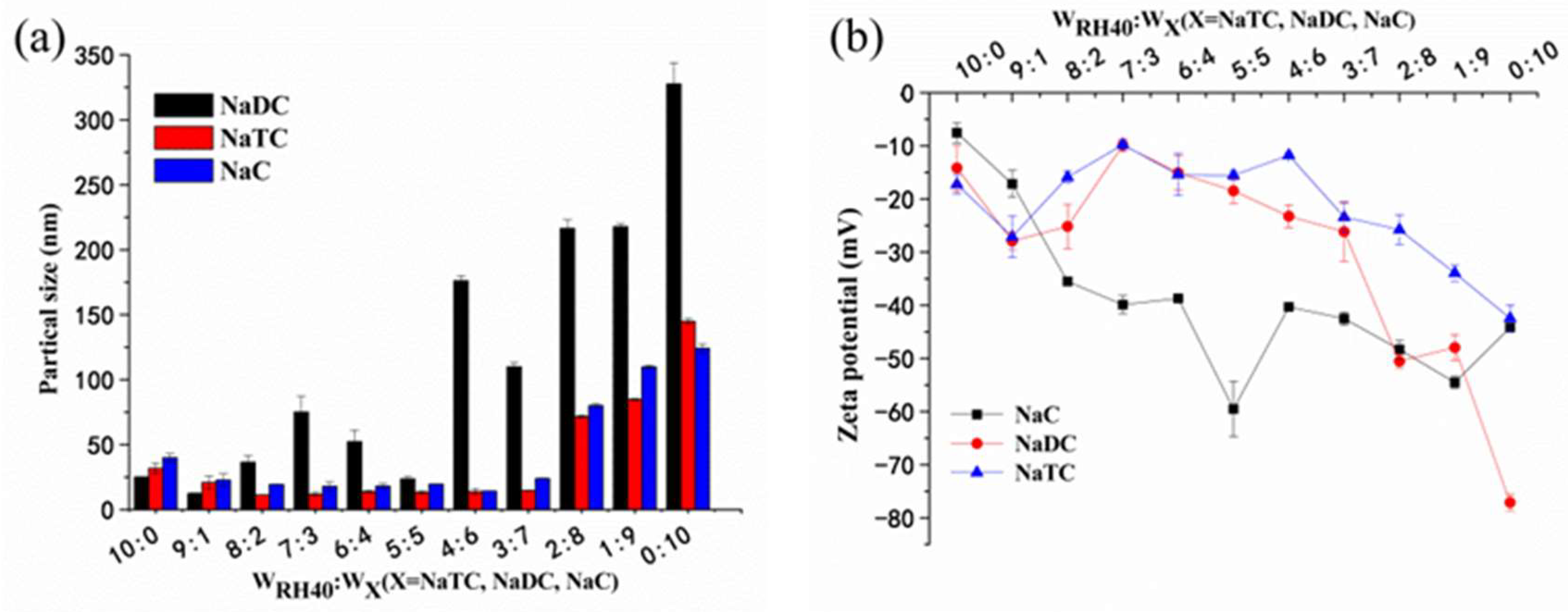
3.2. Droplet Size and Zeta Potential of Blank SMEDDS
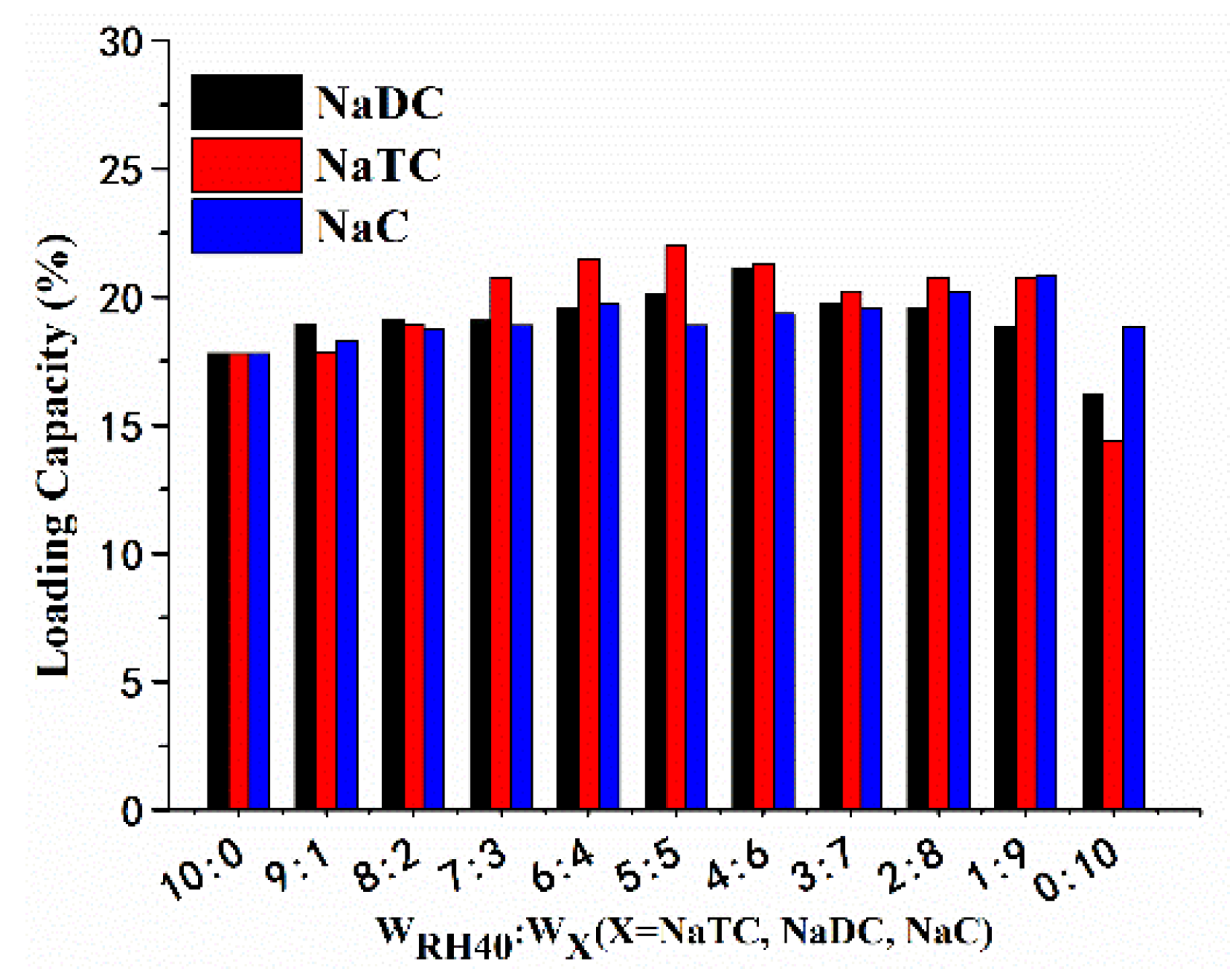
3.3. LC in SMEDDS
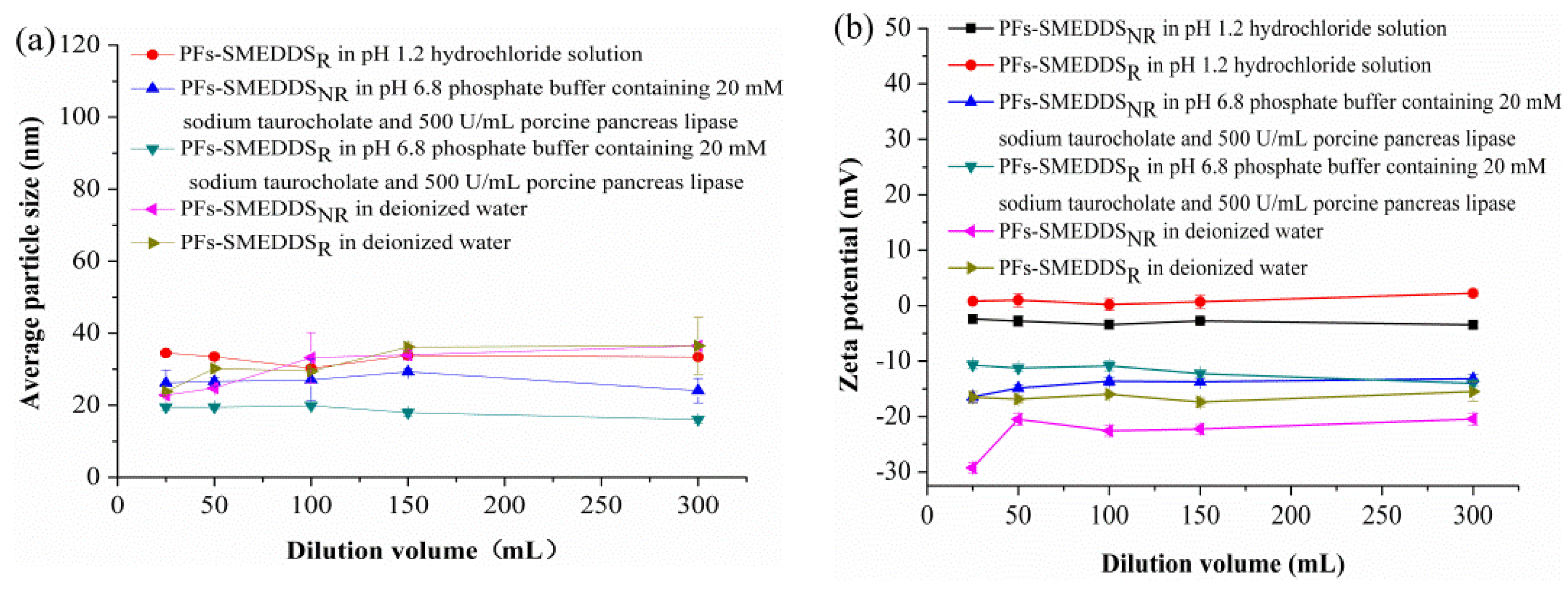
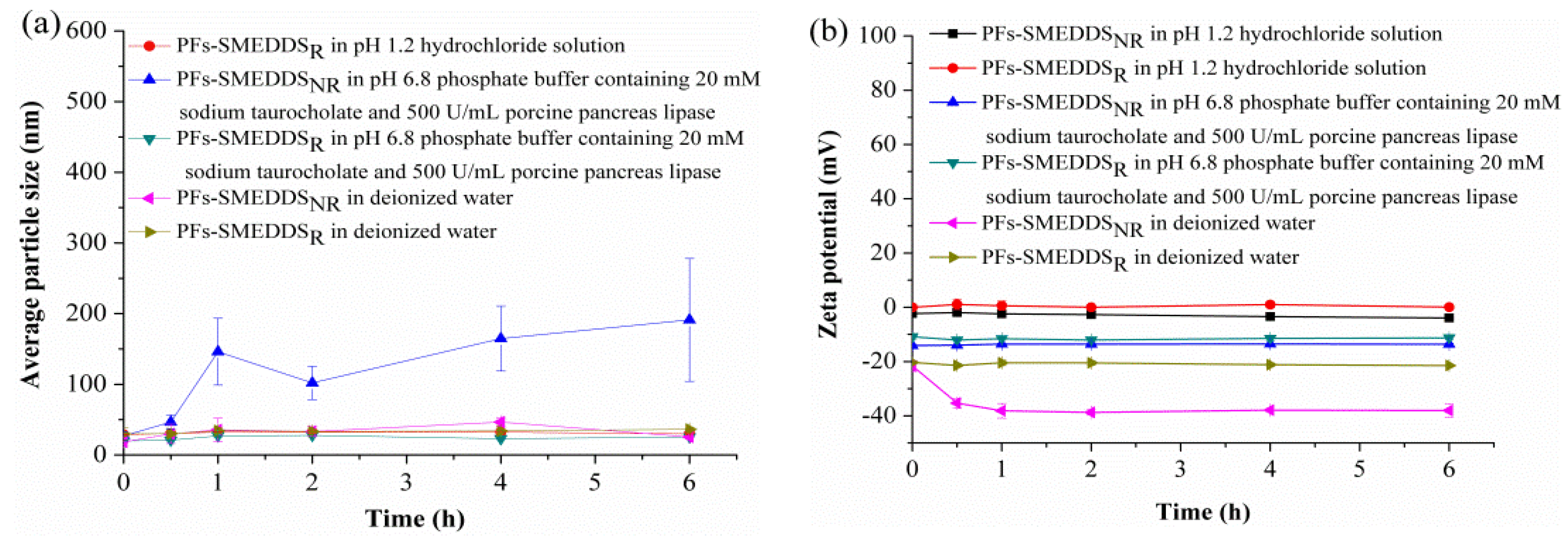
3.4. Mean Particle Size and Zeta Potential of PFs-SMEDDS
3.5. In Vitro Release Rate
3.6. Oral Bioavailability and Lymphatic Transport
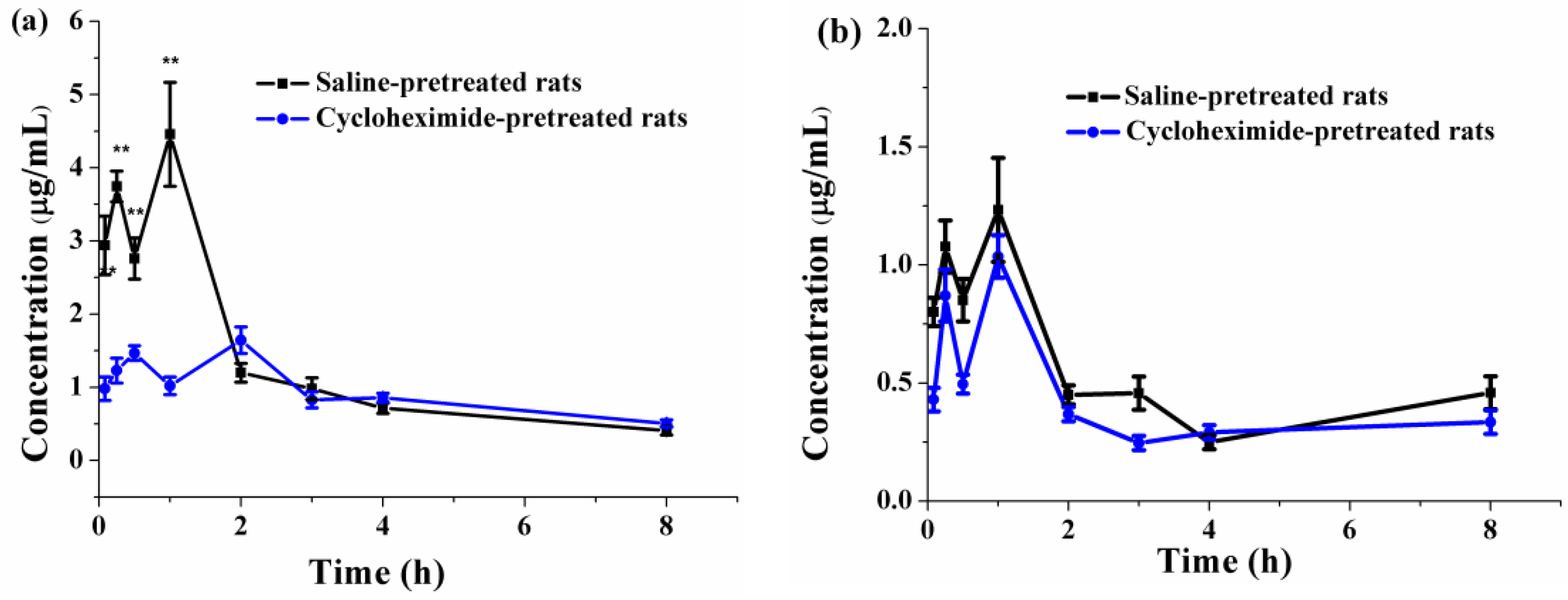
3.6.1. Determination of PFs in Plasma
3.6.2. Pharmacokinetics
3.6.3. Effects of Lymphatic Transport on the Oral Absorption of PFs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holm, R.; Mullertz, A.; Mu, H. Bile salts and their importance for drug absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.G.; Kumar, A.; Gide, P.S. Self emulsifying drug delivery system for enhanced solubility and dissolution of glipizide. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morakul, B.; Suksiriworapong, J.; Chomnawang, M.T.; Langguth, P.; Junyaprasert, V.B. Dissolution enhancement and in vitro performance of clarithromycin nanocrystals produced by precipitation-lyophilization-homogenization method. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConville, C.; Friend, D. Development and characterisation of a self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDSs) for the vaginal administration of the antiretroviral UC-781. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qi, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W. Nanoemulsions coated with alginate/chitosan as oral insulin delivery systems: Preparation, characterization, and hypoglycemic effect in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Miyako, Y.; Khalef, N.; Matsuzaki, K.; Pinal, R. Solubility enhancement of hydrophobic compounds by cosolvents: Role of solute hydrophobicity on the solubilization effect. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 393, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, D.W.; Son, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, S.G.; Song, S.H.; Chae, B.R.; Choi, Y.W. Development of a solidified self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SMEDDS) for atorvastatin calcium with improved dissolution and bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.N.; Jiang, S.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Liao, J.; Yin, Z.G. Preparation and evaluation of nattokinase-loaded self-double-emulsifying drug delivery system. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Tan, Y.; Tian, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Food protein-stabilized nanoemulsions as potential delivery systems for poorly water-soluble drugs: Preparation, in vitro characterization, and pharmacokinetics in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 521–533. [Google Scholar]
- Sakloetsakun, D.; Dunnhaupt, S.; Barthelmes, J.; Perera, G.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Combining two technologies: Multifunctional polymers and self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for oral insulin administration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, J.C. Development of a Solid Supersaturatable Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System of Docetaxel with Improved Dissolution and Bioavailability. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Long, X.Y.; Yuan, F. Preparation and evaluation of berbenine hydrochloride self-microemulsion containing natural emulsifier in vitro and in vivo. Chin. J. New Drugs 2012, 21, 2794–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, T.; Plakogiannis, F.M. Development and oral bioavailability assessment of a supersaturated self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) of albendazole. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.G.; Lu, Z.Y.; Wang, L. Restrictive Effect of Puerarin on Myocardial Infarct Area in Dogs and Its Possible Mechanism. J. Tongji Med. Univ. 2000, 19, 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.M.; Zhao, C.S.; Tang, X.; Chen, D.; He, Z. Study on the bioavailability of puerarin from Pueraria lobata isoflavone self-microemulsifying drug-delivery systems and tablets in rabbits by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2005, 19, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.X.; Zhang, G.Y.; Sun, S.L.; Fan, H.B.; Sun, C.; Zhang, S.Y. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Pueraria Flavones by a Novel Solid Self-microemulsifying Drug Delivery System (SMEDDS) Dropping Pills. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Meng, S.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.X. A brief review on herbal pharmacokinetics study for puerarin and flavone of radix puerariae lobatae. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2009, 15, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.P.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, K.D. Studies on isoflavones from radix puerariae drug carrier systems. Chin. Pharm. J. 1998, 33, 598–601. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Wang, M.; Sun, D.D.; Sun, S.L.; Sun, C.; Liu, J.G.; Guan, Q.X. Evaluation of the cytotoxicity and intestinal absorption of a self-emulsifying drug delivery system containing sodium taurocholate. Eur. J Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. On the role of bile salts in the digestion of emulsified lipids. Food Hydrocolloids 2016, 60, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Wilde, P.; Macierzanka, A.; Mackie, A. The role of bile salts in digestion. Adv. Colloid Interfacs Sci. 2011, 165, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.L.; Tan, T.W.; Janson, J.C. Purification of the isoflavonoid puerarin by adsorption chromatography on cross-linked 12% agarose. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1057, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Que, L. Enhanced bioavailability of silymarin by self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, H.; Kamiya, N.; Watanabe, J.; Yokoyama, H.; Hirata, A.; Fujii, T.; Shimizu, I.; Ito, S.; Goto, M. Oral delivery of diclofenac sodium using a novel solid-in-oil suspension. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 313, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Hu, R.; Wang, B.; Gui, Y.; Cheng, G.; Gao, S.; Ye, L.; Tang, J. Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for improving the bioavailability of huperzine A by lymphatic uptake. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Song, J.; You, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, K.; Song, J.; Guo, Q.; Li, P.; Wu, C.; Hu, H. Microemulsions containing long-chain oil ethyl oleate improve the oral bioavailability of piroxicam by increasing drug solubility and lymphatic transportation simultaneously. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershanik, T.; Benita, S. Self-dispersing lipid formulations for improving oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Luo, G.A. Development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems. Prog Pharm. Sci. 2006, 30, 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Thi, T.D.; Van Speybroeck, M.; Barillaro, V.; Martens, J.; Annaert, P.; Augustijns, P.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Vermant, J.; Van den Mooter, G. Formulate-ability of ten compounds with different physicochemical profiles in SMEDDS. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.D. Pharmaceutics, 7th ed.; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Dong, J.F.; Chen, J.; Eastoe, J.; Li, X. Design and optimization of a new self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 330, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Fan, W.; Jiang, S.; Ma, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Ahmad, E.; Dong, X.; Zhao, W.; Wu, W. Size-dependent translocation of nanoemulsions via oral delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21660–21672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhai, X.; Xue, K.; Hu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, G.; Si, L. Intestinal absorption and intestinal lymphatic transport of sirolimus from self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems assessed using the single-pass intestinal perfusion (SPIP) technique and a chylomicron flow blocking approach: Linear correlation with oral bioavailabilities in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Porter, C.J.H.; Charman, W.N. Intestinal lymphatic drug transport: An update. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 50, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.; Gameiro, P.; Guimarães, C. Study of partition of nitrazepam in bile salt micelles and the role of lecithin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 24, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhawat, P.B.; Pokharkar, V.B. Understanding peroral absorption: Regulatory aspects and contemporary approaches to tackling solubility and permeability hurdles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, H.F.; Lu, C.H.; Fan, Y.N. The pathway of absorption and conveying of puerarin microemulsion-in-oil. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2009, 44, 798–802. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.S.; Long, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.F.; Lou, Q.; Liao, H.M. Study of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system in promoting lymphatic and hematological transport of puerarin in rats after oral administration. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharm. 2015, 26, 809–813. [Google Scholar]
- Dahan, A.; Hoffman, A. Evaluation of a chylomicron flow blocking approach to investigate the intestinal lymphatic transport of lipophilic drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | PFs-Suspension | PFs-SMEDDSNR |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 1.23 ± 0.22 | 4.46 ± 0.71 ** |
| Tmax (h) | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 |
| AUC0→8 (μg·min/mL) | 240.73 ± 16.54 | 618.67 ± 47.99 ** |
| MRT0→8 (min) | 198.00 ± 9.65 | 134.55 ± 8.51 ** |
| Parameters | PFs-Suspension | PFs-SMEDDSNR |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 1.03 ± 0.09 | 1.67 ± 0.15 ∆∆ |
| Tmax (h) | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.50 ± 0.77 ∆ |
| AUC0→8 (μg·min/mL) | 192.29 ± 10.06 | 438.50 ± 16.90 ∆∆ |
| MRT0→8 (min) | 199.02 ± 9.48 | 193.08 ± 3.27 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, J.; Ji, D.; Sun, S.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Sun, B.; Guan, Q. Oral Bioavailability and Lymphatic Transport of Pueraria Flavone-Loaded Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems Containing Sodium Taurocholate in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030147
Qiao J, Ji D, Sun S, Zhang G, Liu X, Sun B, Guan Q. Oral Bioavailability and Lymphatic Transport of Pueraria Flavone-Loaded Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems Containing Sodium Taurocholate in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030147
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Jin, Danyang Ji, Shilin Sun, Guangyuan Zhang, Xin Liu, Bingxue Sun, and Qingxiang Guan. 2018. "Oral Bioavailability and Lymphatic Transport of Pueraria Flavone-Loaded Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems Containing Sodium Taurocholate in Rats" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030147
APA StyleQiao, J., Ji, D., Sun, S., Zhang, G., Liu, X., Sun, B., & Guan, Q. (2018). Oral Bioavailability and Lymphatic Transport of Pueraria Flavone-Loaded Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems Containing Sodium Taurocholate in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030147