Rational Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of γ-CD-Containing Cross-Linked Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel as a Prednisone Delivery Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Section
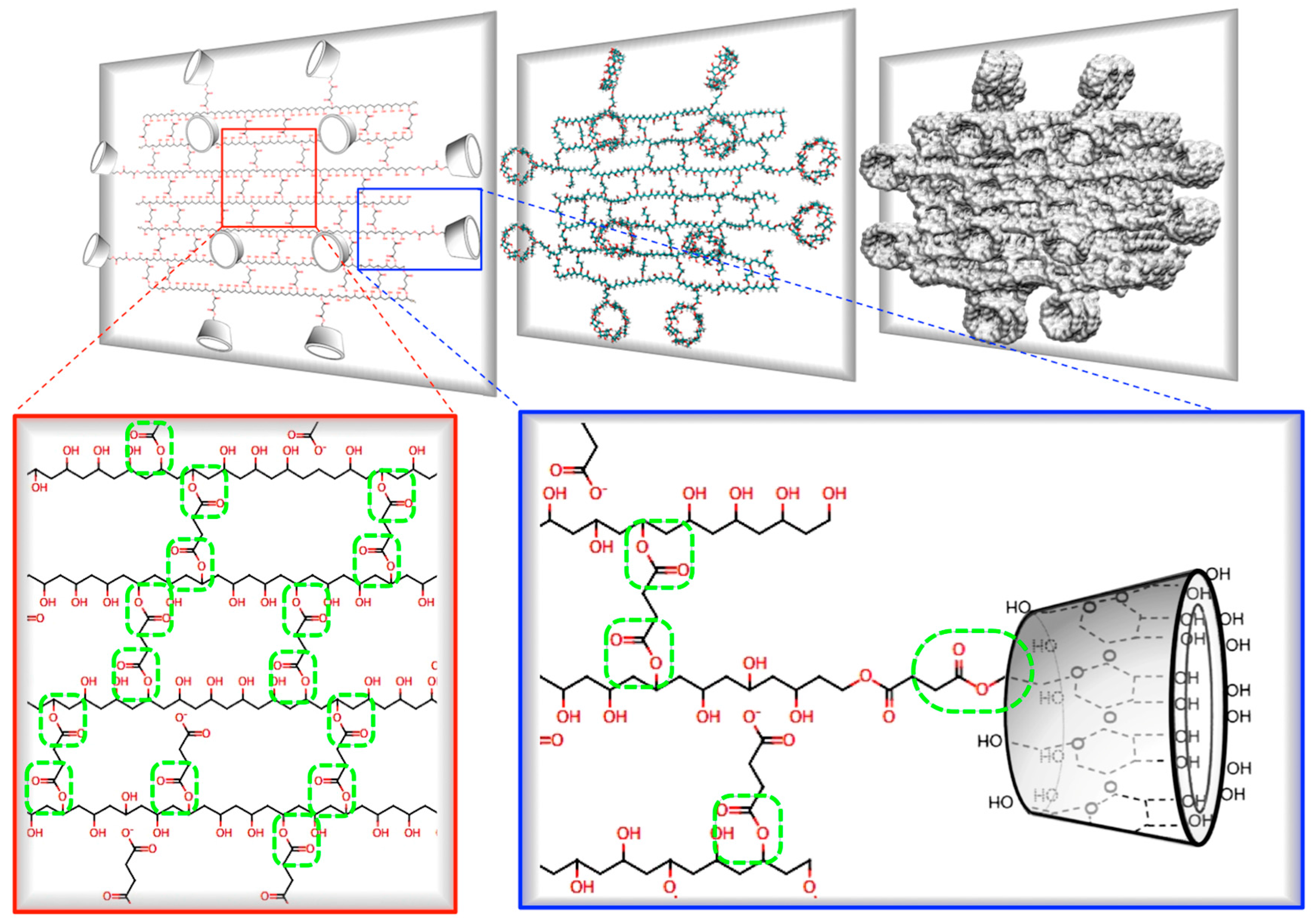
2.1.1. Building Molecular Structures
2.1.2. In-Silico Calculation of Interaction Energies
2.1.3. Molecular Dynamic Simulation (MDS)
2.2. Experimental Section
2.2.1. Materials
2.2.2. Synthesis of γ-CDHSAs
2.2.3. Swelling Studies
2.2.4. Infrared Spectroscopy
2.2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.2.7. Loading of Prednisone γ-CDHSA1, γ-CDHSA2 and γ-CDHSA3 in Model Solutions
2.2.8. Drug Release Studies of γ-CDHSAs
2.2.9. Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability
2.2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
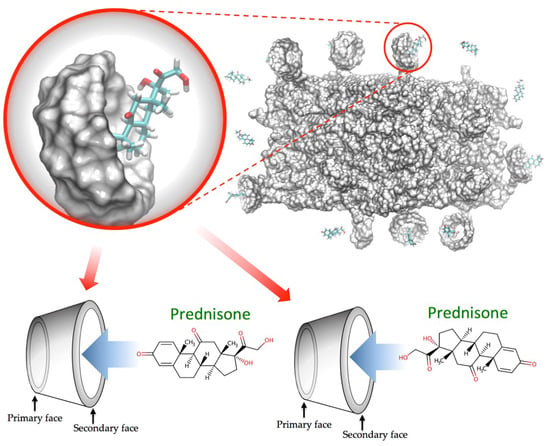
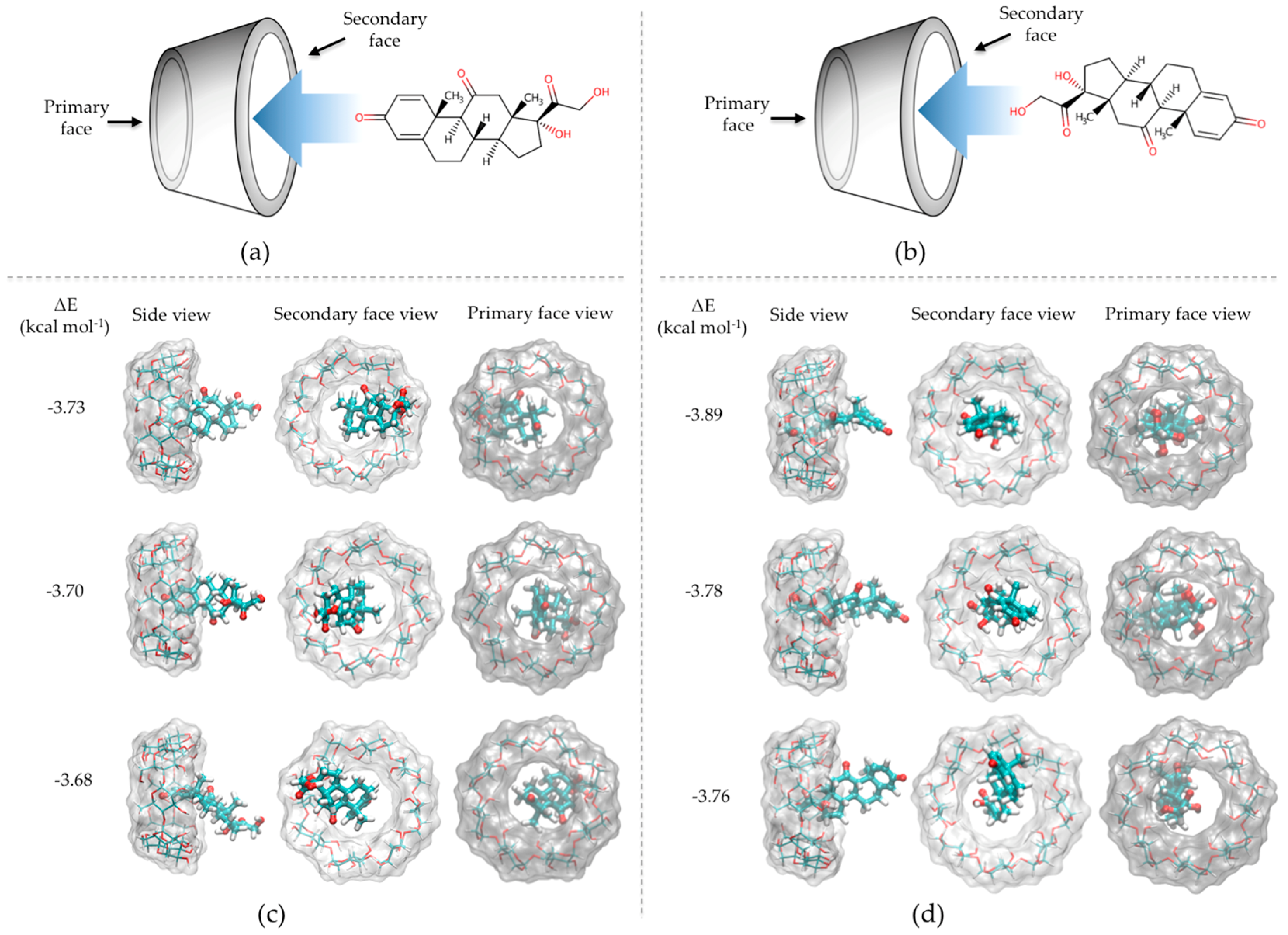
3.1. In-Silico Interaction Energy Study
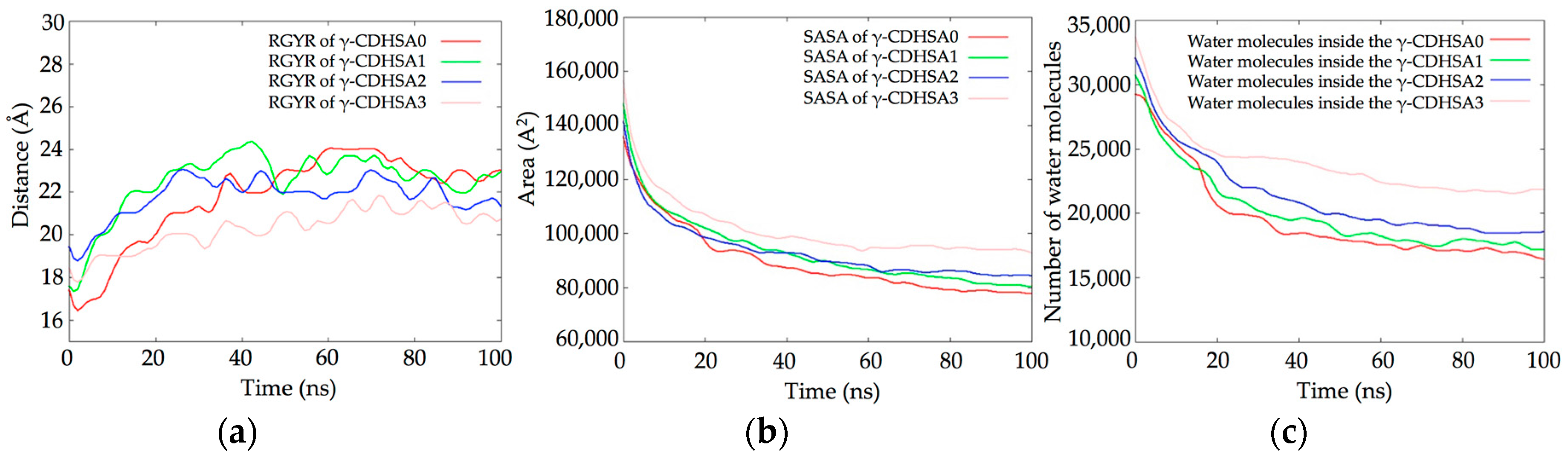
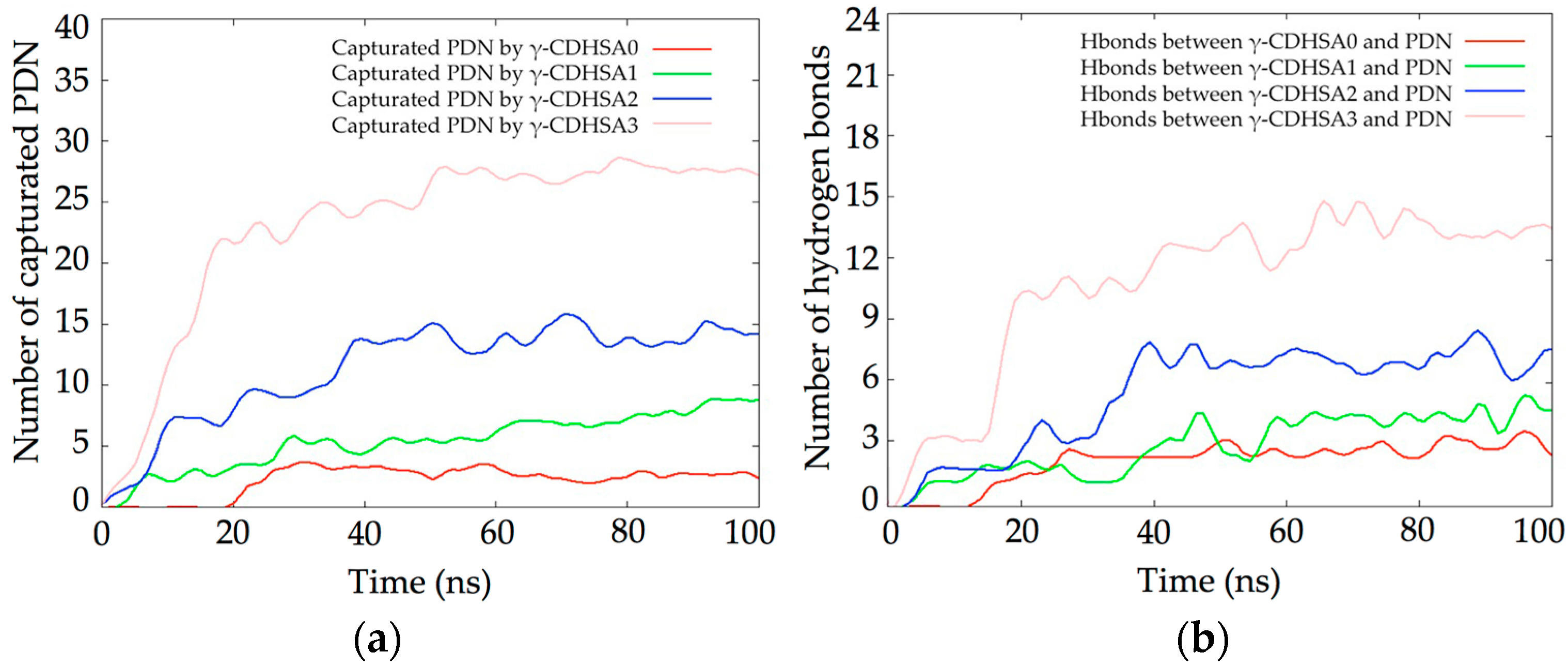
3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations (MDS) Studies
3.3. Preparation of γ-CDHSAs
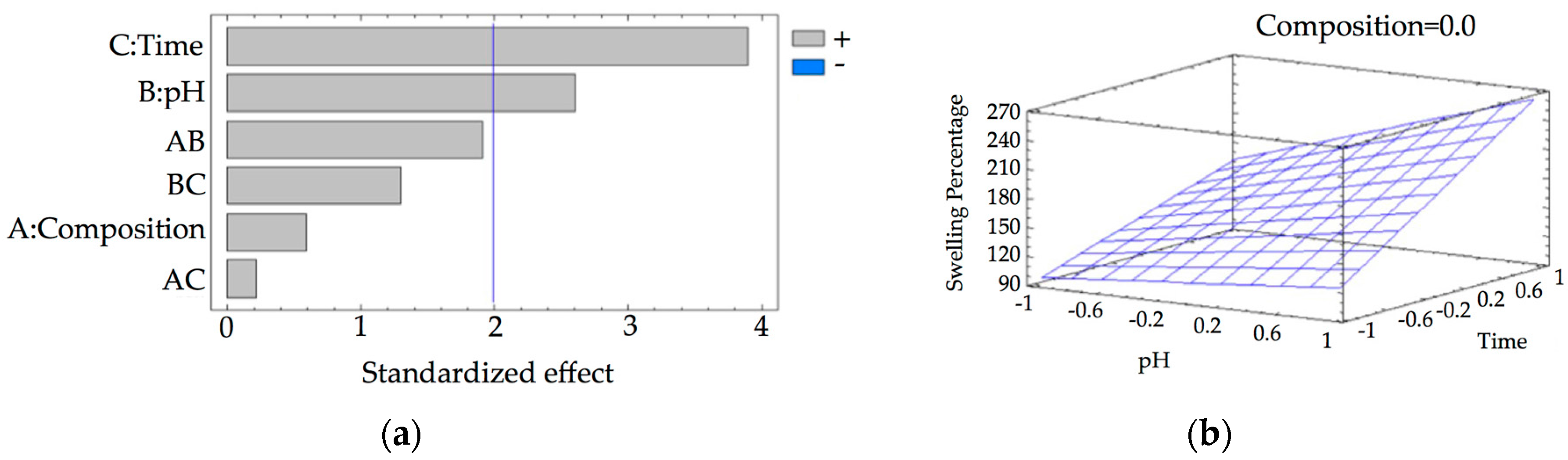
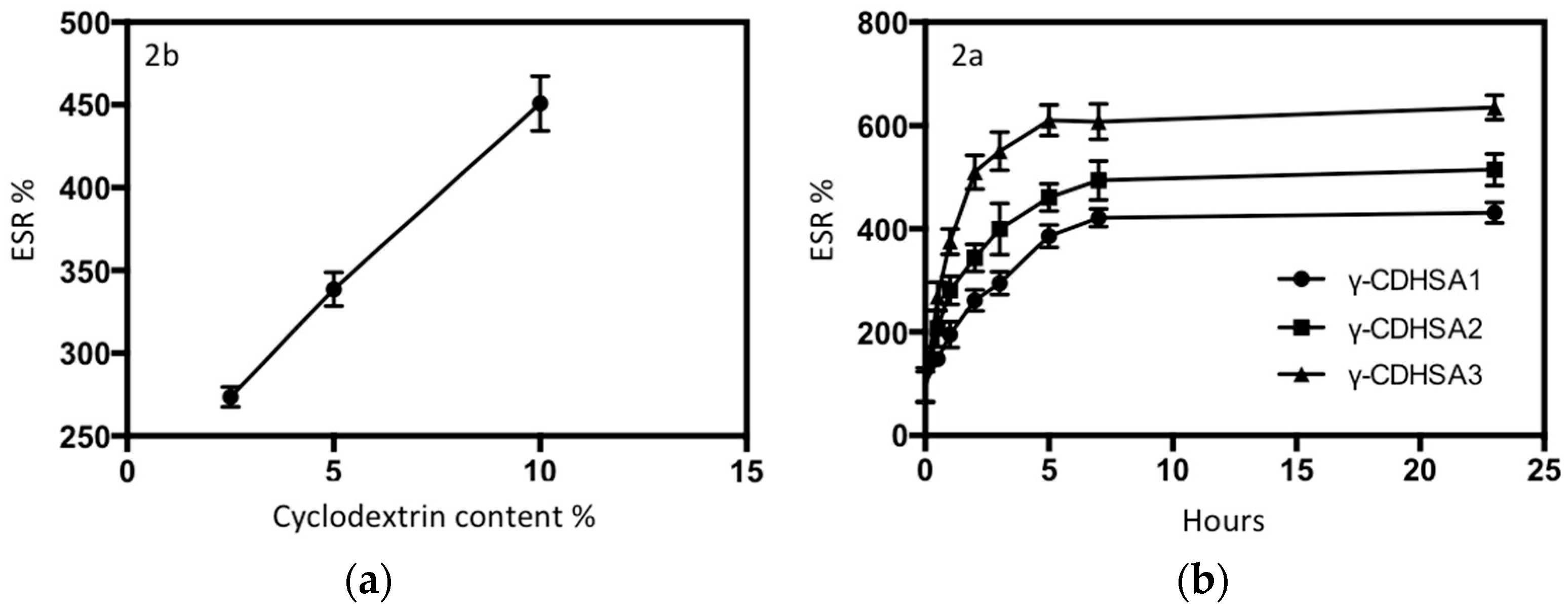
3.4. ESR
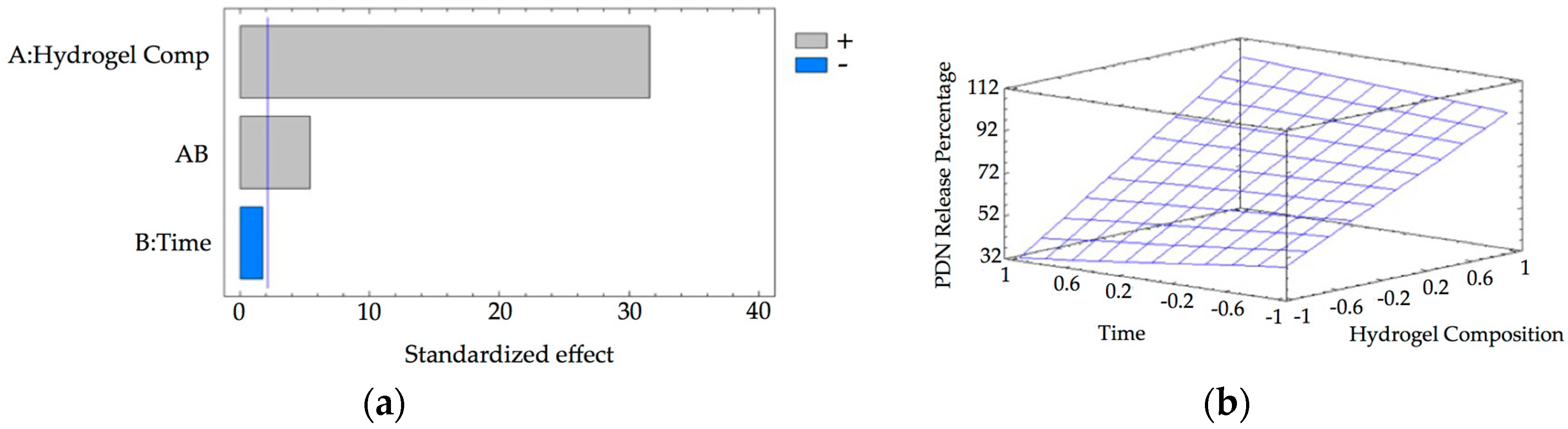
3.5. Drug Loading and In Vitro Release Behavior of γ-CDHSAs
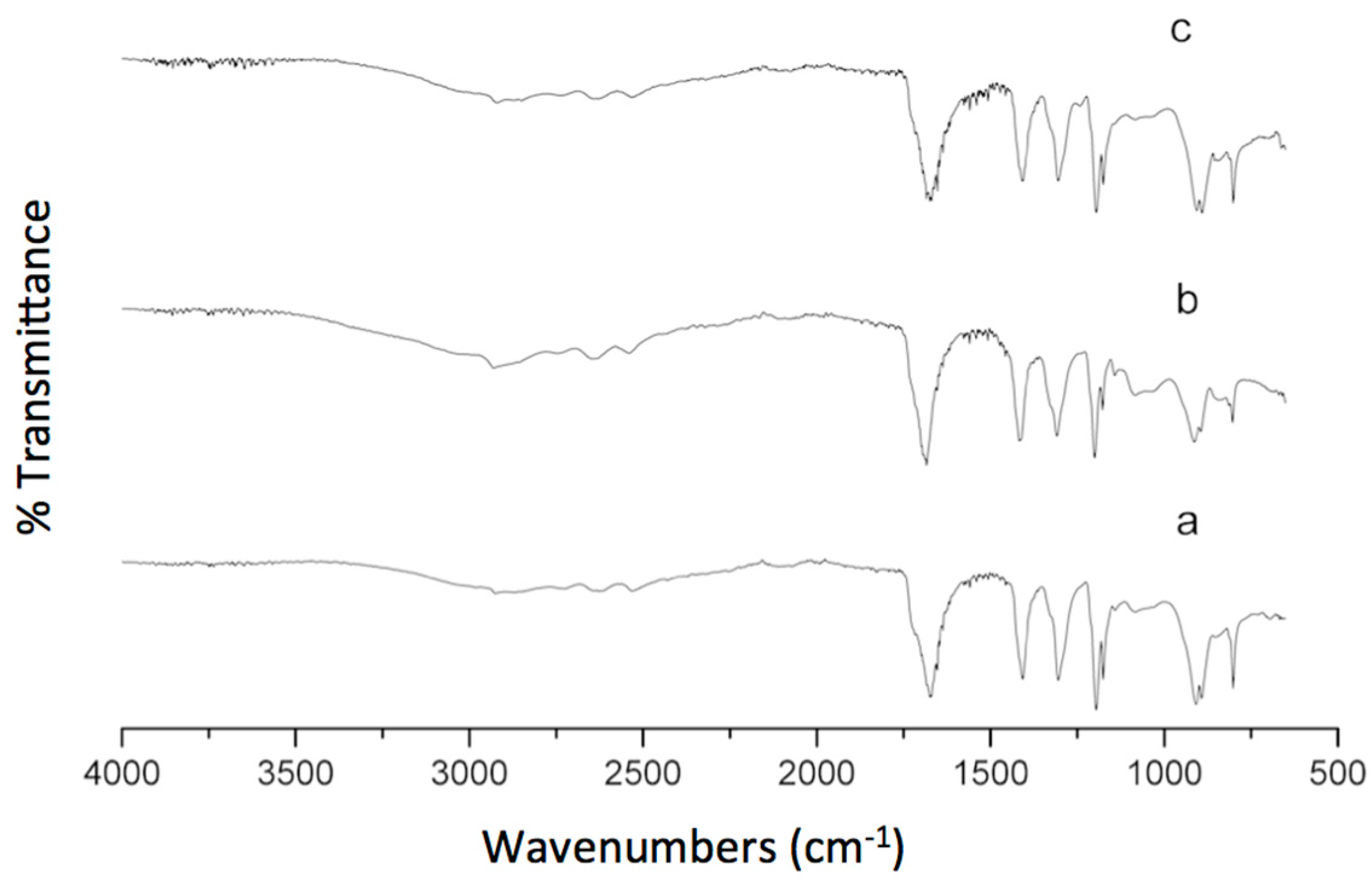
3.6. FTIR Analysis
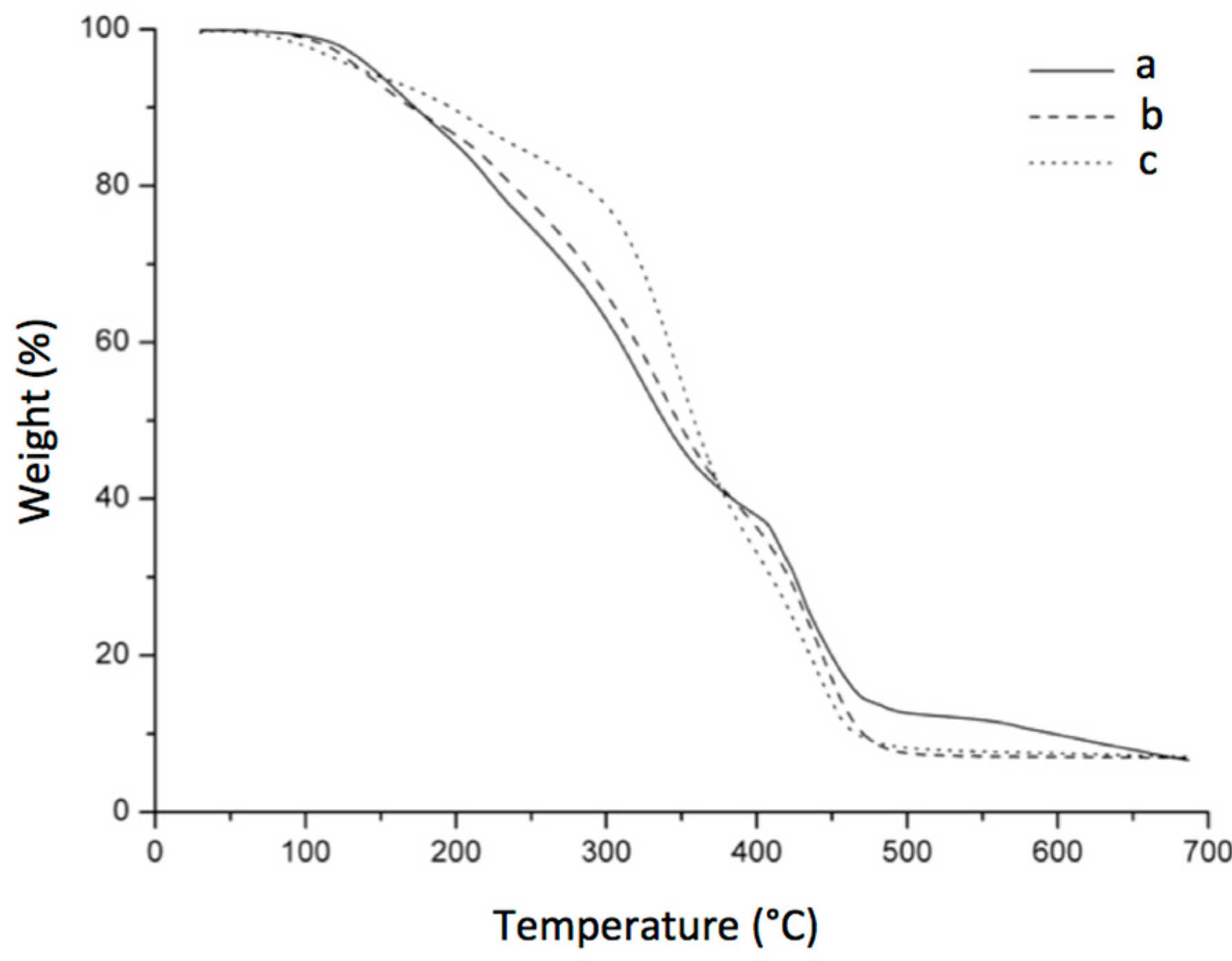
3.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.8. SEM Analysis: Sample Preparation and Viewing
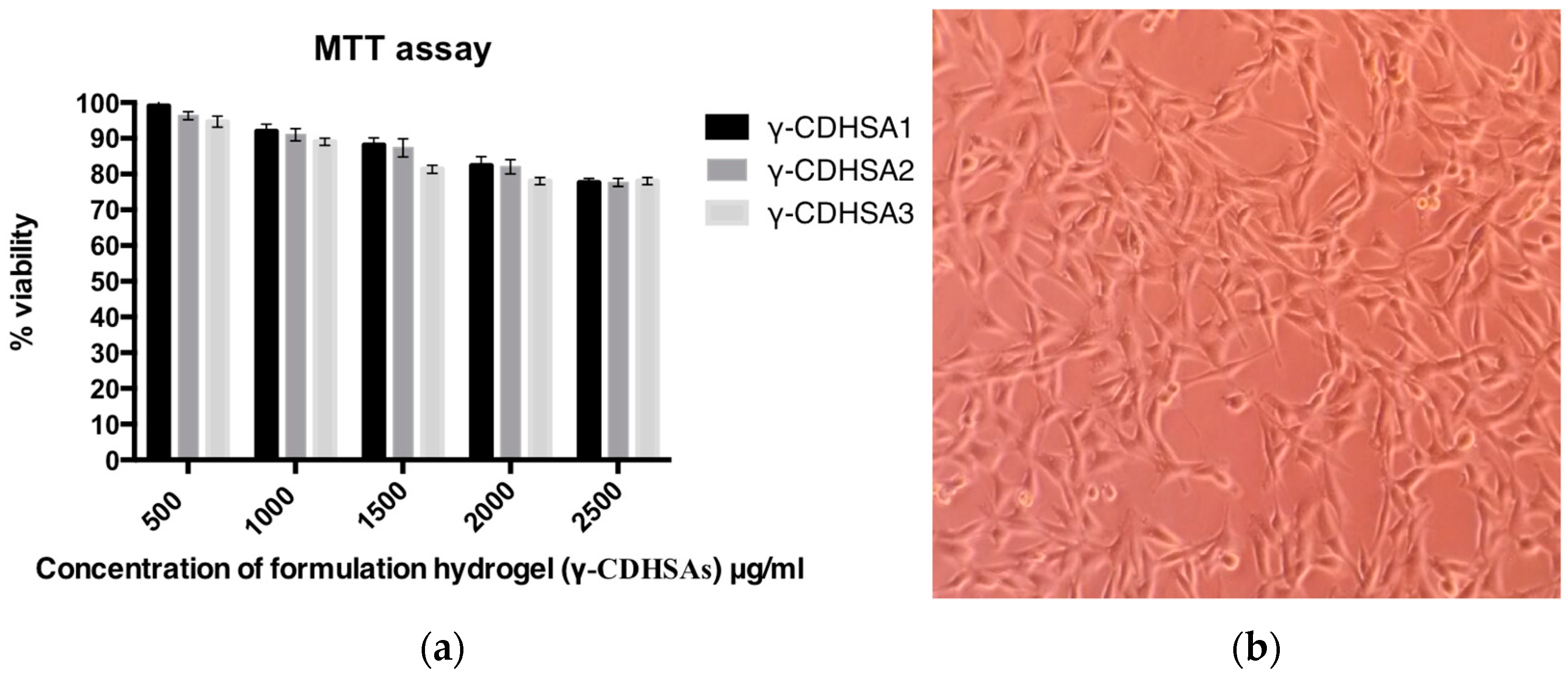
3.9. Evaluation of γ-CDHSAs Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Senyigit, T.; Ozer, O. Corticosteroids for Skin Delivery: Challenges and New Formulation Opportunities. In Glucocorticoids-New Recognition of Our Familiar Friend, 1st ed.; Qian, X., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 24; ISBN 978-953-51-0872-6. [Google Scholar]
- Balzus, B.; Sahle, F.; Honzke, S.; Gerecke, C.; Schumacher, F.; Hedtrich, S.; Kleuser, B.; Bodmeier, R. Formulation and Ex Vivo Evaluation of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Controlled Delivery of Corticosteroids to the Skin and the Corneal Epithelium. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 115, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerii, M.; Benaglia, M.; Caggiano, C.; Papi, A.; Strillacci, A.; Lazzarini, G.; Campieri, M.; Gionchetti, P.; Rizzello, F.; Spisni, E. Drug Delivery by Polymeric Micelles: An in vitro and in vivo study to deliver lipophilic substances to colonocytes and selectively target inflamed colon. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnubhakthula, S.; Elupula, R.; Durán-Lara, E.F. Recent Advances in Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery for Melanoma Cancer Therapy: A Mini Review. J. Drug Deliv. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical Applications of hydrogels: A Review of Patents and Commercial Products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanuel, F.S.; Santos, K.S.R.; Monte-Alto-Costa, A.; de Oliveira, M.G. Combined Nitric Oxide-releasing Poly(vinyl alcohol) Film/F127 Hydrogel for Accelerating Wound Healing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 130, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YamaguchiJ, M.; Ishida, J.; Yoshitake, T.; Nakamura, M. Determination of Prednisolone and Prednisone in Plasma by Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 242, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1984, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database; CID = 5865. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5865 (accessed on 24 January 2018).
- Bordi, F.; Paradossi, G.; Rinaldi, C.; Ruzicka, B. Chemical and Physical Hydrogels: Two Casesystems Studied by Quasi Elastic Light Scattering. Phys. A 2002, 304, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, O.; Avila-salas, F.; Marican, A.; Fuentealba, N.; Villaseñor, J.; Arenas-Salinas, M.; Argandoña, Y.; Durán-Lara, E.F. Methamidophos Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using a Super Adsorbent Based on Crosslinked Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Fei, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Synthesis, Characterization, Mechanical Properties and Biocompatibility of Interpenetrating Polymer Network–super-porous Hydrogel Containing Sodium Alginate. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambi, T.; Li, Y.; Lee, D.S. Injectable Hydrogels for Sustained Release of Therapeutic Agents. J. Control. Release. 2017, 267, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, R.J.; Lee, A.L.Z.; Voo, Z.X.; Venkataraman, S.; Koh, B.W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Hedrick, J.L. Biodegradable Strain-Promoted Click Hydrogels for Encapsulation of Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles and Sustained Release of Therapeutics. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.N.; McGuinness, G.B.; Ramos, M.E.; Kajiyama, C.E.; Thiré, R.M. Properties of PVA Hydrogel Wound-Care Dressings Containing UK Propolis. Macromol. Symp. 2016, 368, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Sierra, D.M.; Perea-Mesa, Y.P. Manufacturing and Evaluation of Chitosan, PVA and Aloe Vera hydrogels for Skin Applications. DYNA 2017, 84, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.; Hong, B.; Nam, S.Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Rhim, J.W.; Lee, S.B.; Moon, G.Y. Swelling Behavior and Drug Release of Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogel Cross-Linked with Poly(acrylic acid). Macromol. Res. 2008, 16, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.; Kuo, T.Y.; Liu, F.H.; Hwang, Y.H.; Ho, M.H.; Wang, D.M.; Lai, J.Y.; Hsieh, H.J. Use of Dicarboxylic Acids to Improve and Diversify the Material Properties of Porous Chitosan Membranes. J Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9015–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, D.; Engelke, A.; Wenz, G. Solubilizing Steroidal Drugs by β-cyclodextrin Derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, H.; Teshirogi, T. Cyclodextrin-grafted Chitosan Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MarvinSketch Program Version 17.29 (For OSX), ChemAxon Ltd., Budapest, Hungary, 2018. Available online: https://chemaxon.com/products/marvin (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery, J.A., Jr.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.; Burant, J. Gaussian 03, Revision C.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Steed, J.W. Triggered Formation of Thixotropic Hydrogels by Balancing Competitive Supramolecular Synthons. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 11699–11705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, W.G.; Jain, R.K. Method of Making Ester-Crosslinked Chitosan Support Materials and Products Thereof. U.S. Patent 5874551, 23 February 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Saraydin, D.; Karadağ, E.; Sahiner, N.; GüVen, O. Incorporation of Malonic Acid Into Acrylamide Hydrogel by Radiation Technique and Its Effect on Swelling Behavior. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 3217–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.T.; Chang, C.H.; Li, Y.D.; Wu, M.F.; Lin, C.P.; Han, J.L.; Chen, S.H.; Hsieh, K.H. Development of Chitosan/dicarboxylic Acid Hydrogels as Wound Dressing Materials. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2011, 26, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderruten, N.E.; Valverde, J.D.; Zuluaga, F.; Ruiz-Durántez, E. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan Hydrogels Cross-linked with Dicarboxylic Acids. React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 84, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Taguchi, T.; Aoki, H.; Murabayashi, S.; Mitamura, Y.; Tanaka, J.; Tateishi, T. pH-responsive Swelling Behavior of Collagen Gels Prepared by Novel Crosslinkers Based on Naturally Derived di- or Tricarboxylic Acids. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Im, J.S.; Baek, S.T.; Lee, J.O.; Azuma, Y.; Yoshinaga, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Crosslinked Hyperbranched Polyglycidol Hydrogel Films. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2006, 43, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S.; Storz, J.; Storz, H.; Lohmann, D.; Lechner, D.; Kulicke, W.M. Hydrogels Based on Barboxymethyl Cassava Starch Cross-linked with di- or Polyfunctional Carboxylic Acids: Synthesis, Water Absorbent Behavior and Rheological Characterizations. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchacka, E.; Potaczek, P.; Paduszyński, P.; Karłowicz-Bodalska, K.; Han, T.; Han, S. New Effective Azelaic Acid Liposomal Gel Formulation of Enhanced Pharmaceutical Bioavailability. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, M. Supramolecular Polymer Hydrogels from Bolaamphiphilic L-Histidine and Benzene Dicarboxylic Acids: Thixotropy and Significant Enhancement of Eu III Fluorescence. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 14650–14659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, B.D.; Nair, D.P.; Boeckl, M.S.; Leber, E.R. Hydrogels Formed by Non-Covalent Linkages. US Patent 6949590, 27 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Avila-Salas, F.; Sandoval, C.; Caballero, J.; Guiñez-Molinos, S.; Santos, L.S.; Cachau, R.E.; González-Nilo, F.D. Study of Interaction Energies Between the PAMAM Dendrimer and Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug Using a Distributed Computational Strategy and Experimental Analysis by ESI-MS/MS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.; Avila-Salas, F.; Santos, L.S.; Iturmendi, N.; Moine, V.; Cheynier, V.; Saucier, C. Rosé Wine Fining Using Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone: Colorimetry, Targeted Polyphenomics, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Salas, F.; Marican, A.; Villaseñor, J.; Arenas-Salinas, M.; Argandoña, Y.; Caballero, J.; Durán-Lara, E.F. In-Silico Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of a Nanostructured Hydrogel as a Dimethoate Removal Agent. Manomaterials 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.J.P. Optimization of Parameters for Semiempirical Methods VI: More Modifications to the NDDO Approximations and Re-optimization of Parameters. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.J.P. MOPAC2016 Computational Chemistry, Version 16.111L (LINUX); Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2016. Available online: http://openmopac.net/downloads.html (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Case, D.A.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Giese, T.J.; Gohlke, H.; Goetz, A.W.; Greene, D.; Homeyer, N.; et al. AMBER 2017; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. Available online: http://ambermd.org/#AmberTools (accessed on 28 December 2017).
- Martínez, L.; Andrade, R.; Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. Software News and Update Packmol: A Package for Building Initial Configurations for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Automatic AtomT and Bond TypeP in Molecular Mechanical Calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DE Shaw Research. Schrödinger Release: Desmond/Maestro, Molecular Dynamics System, Release 2017-4, Maestro Version 11.4.011; DE Shaw Research: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vergara-Jaque, A.; Comer, J.; Monsalve, L.; González-Nilo, F.D.; Sandoval, C. Computationally Efficient Methodology for Atomic-level Characterization of Dendrimer-Drug Complexes: A Comparison of Amine- and Acetyl-terminated PAMAM. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 6801–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Chen, P.; Yang, X. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of PAMAM Dendrimer in Aqueous Solution. Polymer 2015, 46, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; Kelley, C. Gnuplot 5.0: An Interactive Plotting Program, Official Gnuplot Documentation, 2015. Available online: http://sourceforge.net/projects/gnuplot (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- BIOVIA-Discovery Studio Visualizer (DS Visualizer) Software, Version 4.5 (for Linux), Accelrys Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018. Available online: http://www.accelrys.com (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- Xu, J.; Li, X.; Sun, F. Cyclodextrin-containing Hydrogels for Contact Lenses as a Platform for Drug Incorporation and Release. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhu, S. Cyclodextrin-containing Hydrogels as an Intraocular Lens for Sustained Drug Release. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.V.; Shivakumar, H. Investigation of Swelling Behavior and Mechanical Properties of a pH-sensitive Superporous Hydrogel Composite. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kipcak, A.S.; Ismail, O.; Doymaz, I.; Piskin, S. Modeling and Investigation of the Swelling Kinetics of Acrylamide-Sodium Acrylate Hydrogel. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 281063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Brazel, C.S. On the Importance and Mechanisms of Burst Release in Matrix-controlled Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Studies on Adsorption of Dyes on Beta-cyclodextrin Polymer. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 90, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spectral Database for Organic Compounds SDBS. Available online: http://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp/sdbs/cgi-bin/direct_frame_disp.cgi?sdbsno=2707 (accessed on 5 January 2018).
- Ramesan, M.T.; Jayakrishnan, P.; Anilkumar, T.; Mathew, G. Influence of Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles on the Structural, Mechanical and Dielectric Properties of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) Blend Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 1992–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurarslan, A.; Shen, J.; Caydamli, Y.; Tonelli, A.E. Pyriproxyfen Cyclodextrin Inclusion Compounds. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2015, 82, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, R.; Rusa, M.; Rusa, C.C.; López, D.; Mijangos, C.; Tonelli, A.E. Controlling PVA Hydrogels with γ-Cyclodextrin. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9620–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caires, C.F.J.; Lima, L.S.; Carvalho, C.T.; Ionashiro, M. Thermal Behaviour of Succinic Acid, Sodium Succinate and its Compounds with Some Bivalent Transitions Metal Ions in Dynamic N2 and CO2 Atmospheres. Eclet. Quim. 2010, 35, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Chemical Structure | 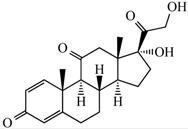 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C21H26O5 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Solubility in water (20 °C–25 °C) | Very slightly soluble |
| Mol. Wt. | 358.434 g mol−1 |
| Melting point | 230–235 °C |
| Wavelength (λ, nm) | 254 nm |
| Hydrogel Formulation | γ-CD Proportion (%) | Copolymer Concentration % PVA/SA w/w | Hydrogel at 25 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-CDHSA1 | 2.44 | 20% | Yes |
| γ-CDHSA2 | 4.76 | 20% | Yes |
| γ-CDHSA3 | 9.1 | 20% | Yes |
| Id. | Hydrogel | Average ΔE kcal mol−1 | Id. | Hydrogel | Average ΔE kcal mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PVAc-Oxalic ac/γ-CD | −1.71 ± 0.05 | 11 | PVAc-Adipic acid/γ-CD | −2.14 ± 0.03 |
| 2 | PVAc-Malonic acid/γ-CD | −1.73 ± 0.07 | 12 | PVAc-Pimelic acid/γ-CD | −2.20 ± 0.07 |
| 3 | PVAc-Succinic acid/γ-CD | −2.67 ± 0.03 | 13 | PVAc-Suberic acid/γ-CD | −2.23 ± 0.04 |
| 4 | PVAc-Malic acid/γ-CD | −2.34 ± 0.08 | 14 | PVAc-Azelaic acid/γ-CD | −2.40 ± 0.02 |
| 5 | PVAc-Fumaric acid/γ-CD | −2.08 ± 0.04 | 15 | PVAc-Phthalic acid/γ-CD | −2.54 ± 0.09 |
| 6 | PVAc-Maleic acid/γ-CD | −1.98 ± 0.07 | 16 | PVAc-Isophthalic acid/γ-CD | −2.60 ± 0.06 |
| 7 | PVAc-Citraconic acid/γ-CD | −1.97 ± 0.04 | 17 | PVAc-Terephthalic acid/γ-CD | −2.70 ± 0.05 |
| 8 | PVAc-Itaconic acid/γ-CD | −1.88 ± 0.09 | 18 | PVAc-2,5-pyridine acid/γ-CD | −2.40 ± 0.09 |
| 9 | PVAc-Tartaric acid/γ-CD | −2.10 ± 0.03 | 19 | PVAc-Aspartic acid/γ-CD | −2.83 ± 0.08 |
| 10 | PVAc-Glutaric acid/γ-CD | −2.21 ± 0.05 | 20 | PVAc-Glutamic acid/γ-CD | −2.63 ± 0.07 |
| Composite | Amount of Loaded PDN (mg g Dried Hydrogel−1) Concentration of Aqueous Soaking Solution 0.22 mg mL−1 |
|---|---|
| γ-CDHSA1 | 8.36 ± 0.92 |
| γ-CDHSA2 | 9.02 ± 1.23 |
| γ-CDHSA3 | 10.1 ± 1.41 |
| γ-CD Proportion (%) | Time of Release (h) | PDN Release Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 (−1) | 1 (−1) | 14.01 |
| 0 (−1) | 1 (−1) | 13.90 |
| 0 (−1) | 48 (1) | 18.06 |
| 0 (−1) | 48 (1) | 28.02 |
| 2.44 (−0.4637) | 8 (−0.70213) | 65.77 |
| 2.44 (−0.4637) | 8 (−0.70213) | 63.42 |
| 2.44 (−0.4637) | 8 (−0.70213) | 68.69 |
| 2.44 (−0.4637) | 8 (−0.70213) | 69.43 |
| 2.44 (−0.4637) | 8 (−0.70213) | 62.62 |
| 2.44 (−0.4637) | 8 (−0.70213) | 63.33 |
| 4.76 (0.0462) | 24.5 (0) | 73.79 |
| 4.76 (0.0462) | 24.5 (0) | 75.53 |
| 4.76 (0.0462) | 24.5 (0) | 78.42 |
| 4.76 (0.0462) | 24.5 (0) | 80.09 |
| 4.76 (0.0462) | 24.5 (0) | 75.63 |
| 4.76 (0.0462) | 24.5 (0) | 78.20 |
| 9.10 (1) | 1 (−1) | 89.27 |
| 9.10 (1) | 1 (−1) | 85.60 |
| 9.10 (1) | 48 (1) | 98.89 |
| 9.10 (1) | 48 (1) | 99.41 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marican, A.; Avila-Salas, F.; Valdés, O.; Wehinger, S.; Villaseñor, J.; Fuentealba, N.; Arenas-Salinas, M.; Argandoña, Y.; Carrasco-Sánchez, V.; Durán-Lara, E.F. Rational Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of γ-CD-Containing Cross-Linked Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel as a Prednisone Delivery Platform. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010030
Marican A, Avila-Salas F, Valdés O, Wehinger S, Villaseñor J, Fuentealba N, Arenas-Salinas M, Argandoña Y, Carrasco-Sánchez V, Durán-Lara EF. Rational Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of γ-CD-Containing Cross-Linked Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel as a Prednisone Delivery Platform. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarican, Adolfo, Fabián Avila-Salas, Oscar Valdés, Sergio Wehinger, Jorge Villaseñor, Natalia Fuentealba, Mauricio Arenas-Salinas, Yerko Argandoña, Verónica Carrasco-Sánchez, and Esteban F. Durán-Lara. 2018. "Rational Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of γ-CD-Containing Cross-Linked Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel as a Prednisone Delivery Platform" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010030
APA StyleMarican, A., Avila-Salas, F., Valdés, O., Wehinger, S., Villaseñor, J., Fuentealba, N., Arenas-Salinas, M., Argandoña, Y., Carrasco-Sánchez, V., & Durán-Lara, E. F. (2018). Rational Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of γ-CD-Containing Cross-Linked Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel as a Prednisone Delivery Platform. Pharmaceutics, 10(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010030