Ultrastructural Characterization of Membrane Rearrangements Induced by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Virus Propagation, and Time-Course Analysis of PEDV Infection
2.2. Extracellular Virus Titration
2.3. Isolation of the Total RNA and Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR)
2.4. Immunofluorescence Analyses
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.6. Immuno-Electron Microscopy
3. Results
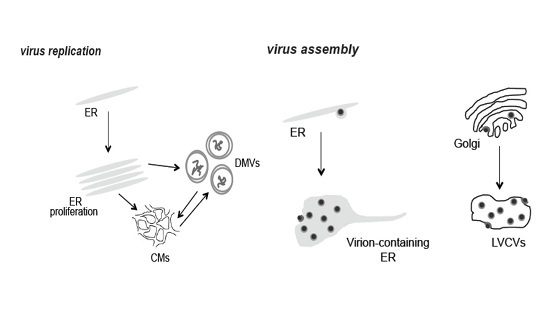
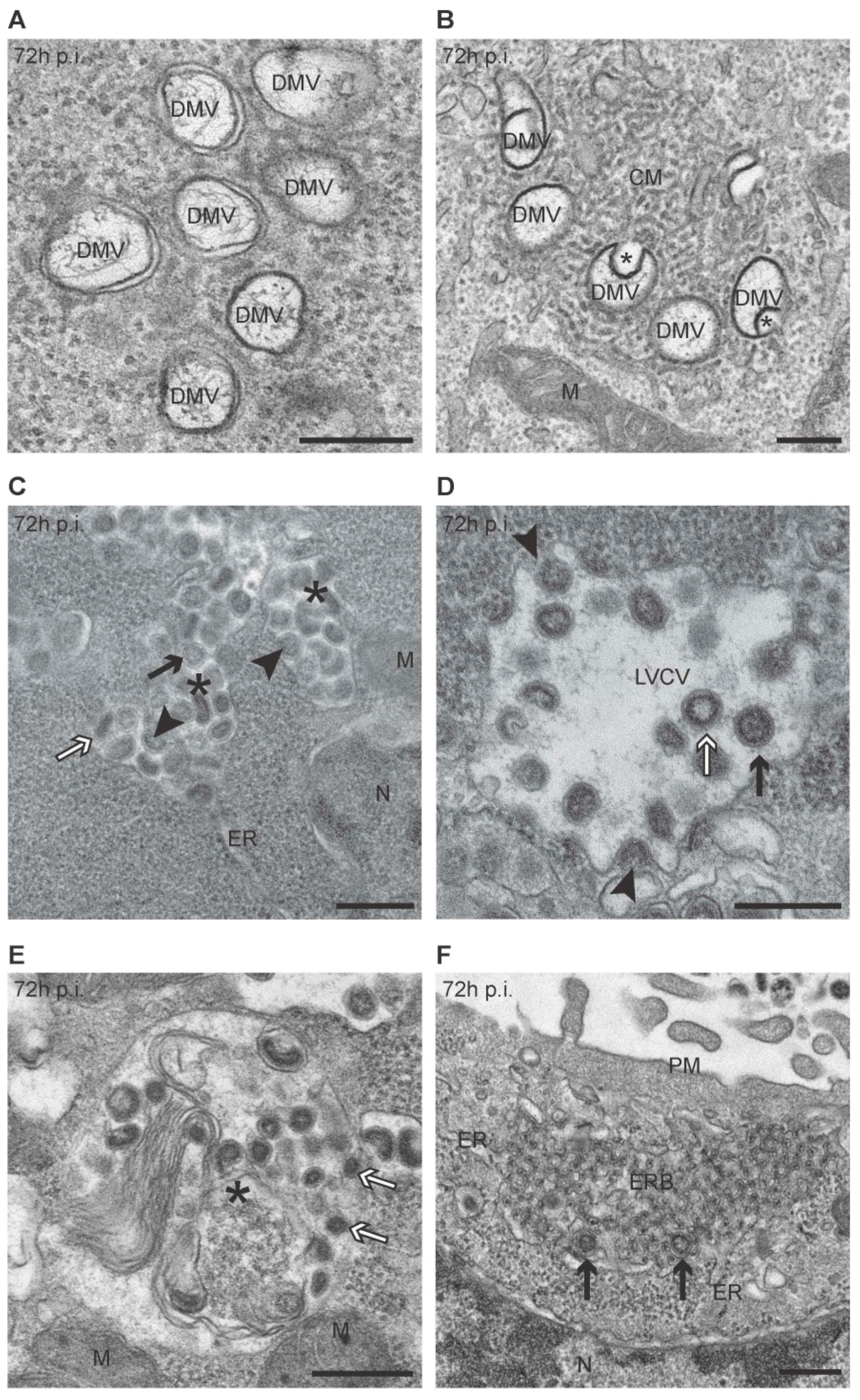
3.1. PEDV Induces the Formation of Multiple Membranous Structures
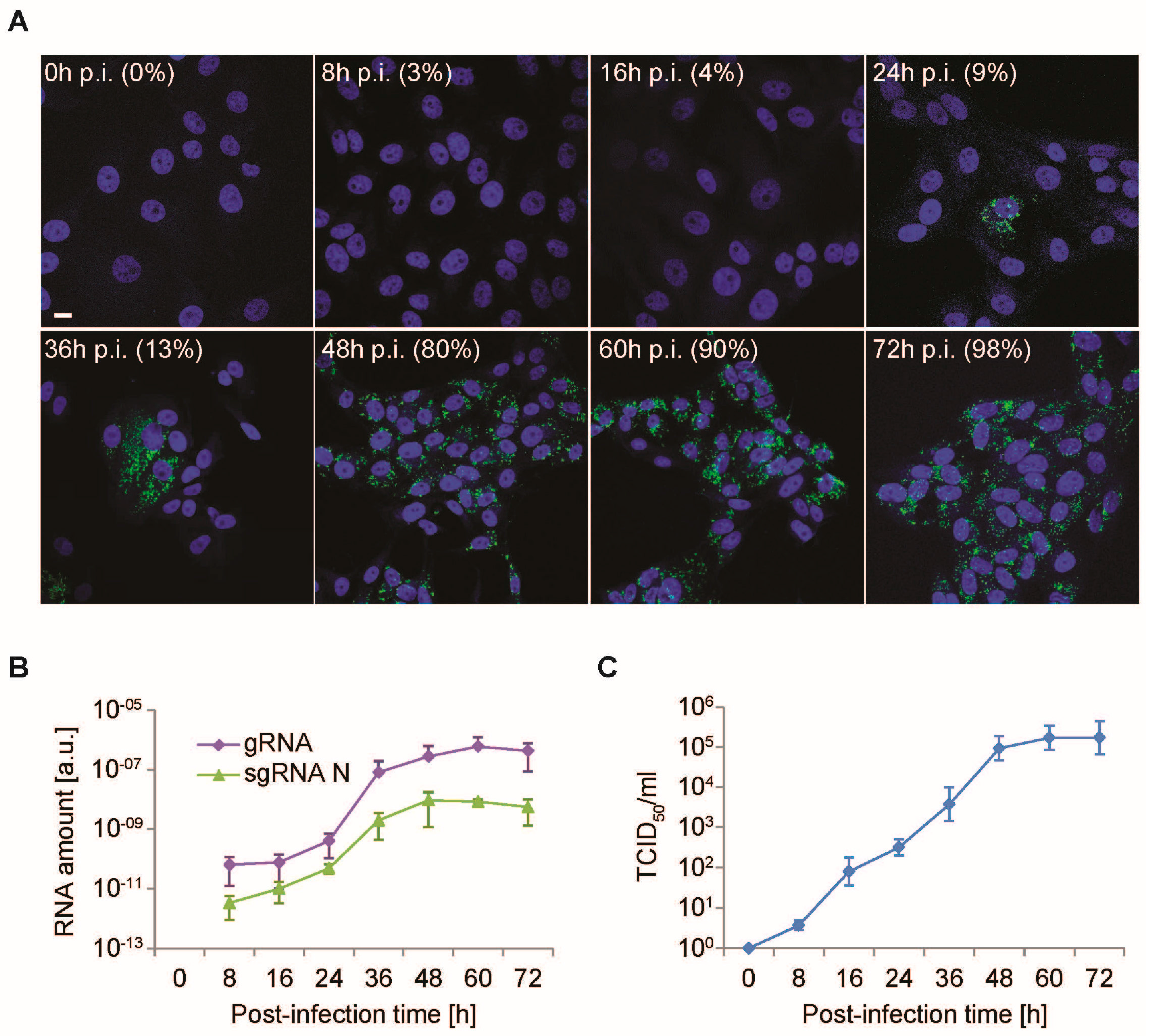
3.2. Time-Course PEDV Infection and Measurement of Cellular Lifecycle Parameters
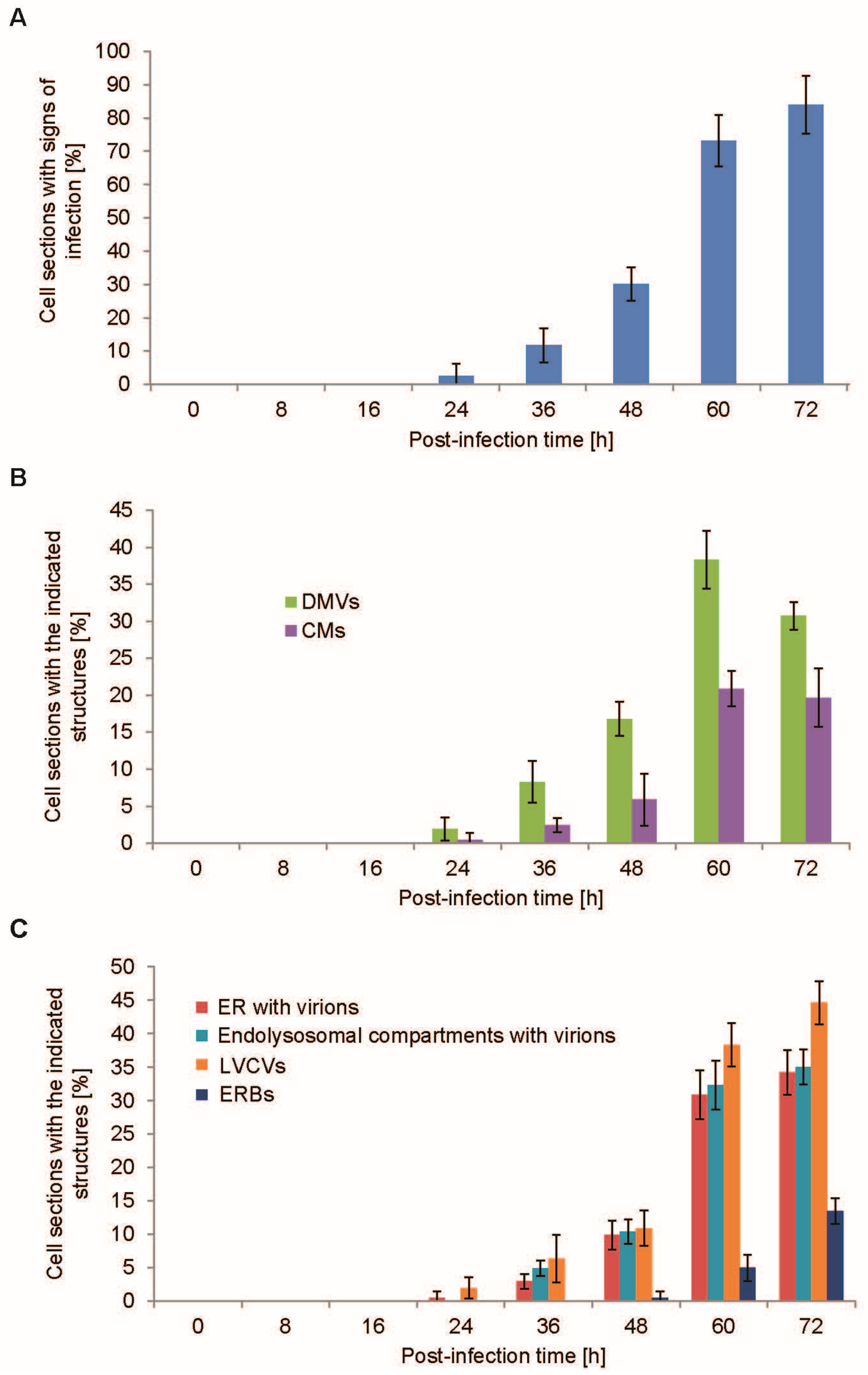
3.3. Quantification of the PEDV-Induced Structures over the Course of an Infection
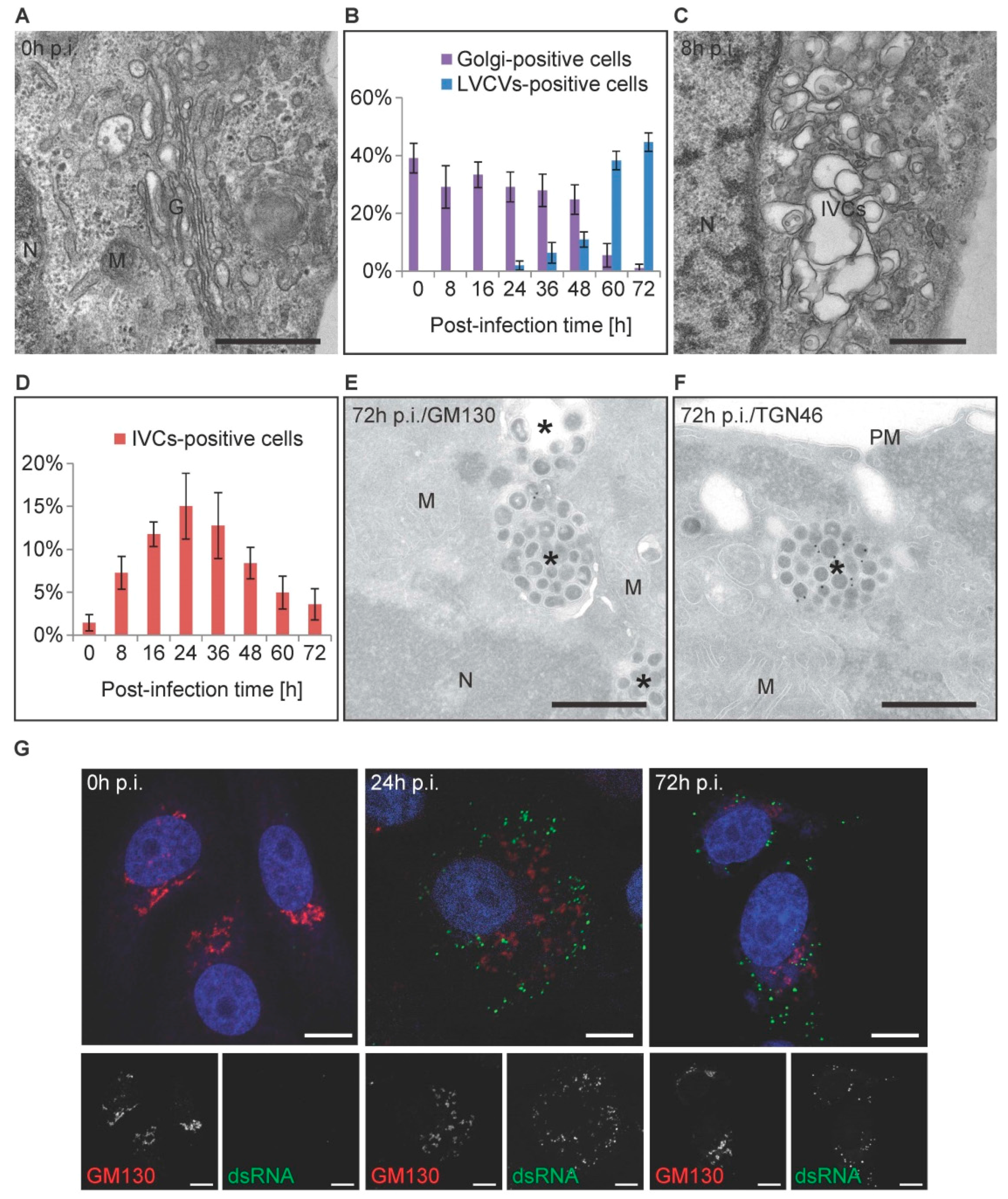
3.4. The Golgi Complex Undergoes Reorganization over the Course of a PEDV Infection
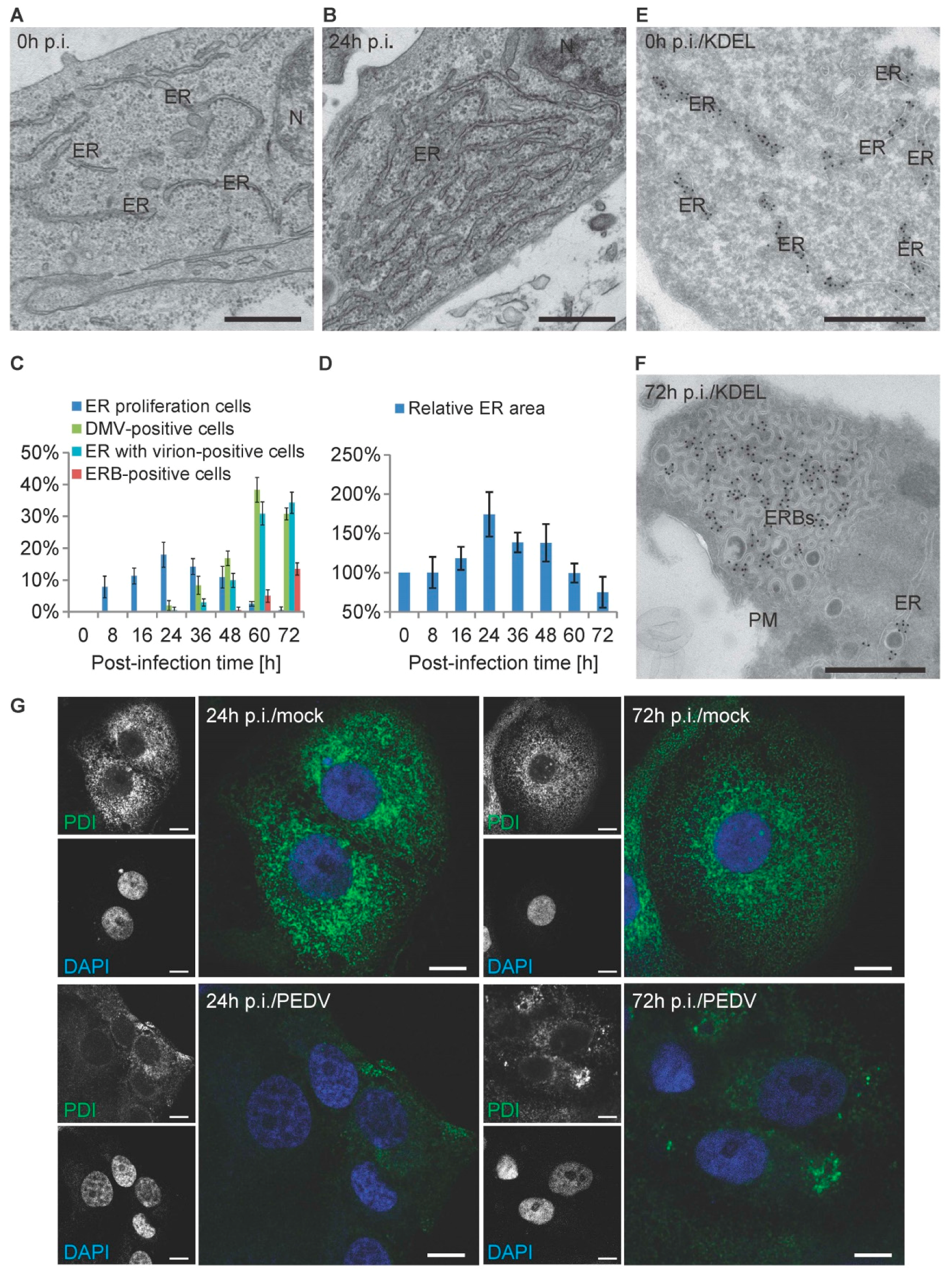
3.5. PEDV Infections Involve ER Membrane Rearrangements in Vero Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Lau, C.C.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, J.H.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Song, D.S.; Park, B.K. Molecular epidemiology and phylogenetic analysis of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) field isolates in Korea. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egberink, H.F.; Ederveen, J.; Callebaut, P.; Horzinek, M.C. Characterization of the structural proteins of porcine epizootic diarrhea virus, strain CV777. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, G.W.; Hoang, H.; Schwartz, K.J.; Burrough, E.R.; Sun, D.; Madson, D.; Cooper, V.L.; Pillatzki, A.; Gauger, P.; Schmitt, B.J.; et al. Emergence of Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States: Clinical signs, lesions, and viral genomic sequences. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensaert, M.B.; de Bouck, P. A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch. Virol. 1978, 58, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Deng, F.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; He, Q. New variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, China, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mole, B. Deadly pig virus slips through US borders. Nature 2013, 499, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.; Chen, J.; Lee, W.M.; Janda, M.; Ahlquist, P. Alternate, virus-induced membrane rearrangements support positive-strand RNA virus genome replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11263–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, R.R.; Calderita, G.; Arranz, R.; Fontana, J.; Granzow, H.; Risco, C. Virus factories: Associations of cell organelles for viral replication and morphogenesis. Biol. Cell 2005, 97, 147–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.; Krijnse-Locker, J. Modification of intracellular membrane structures for virus replication. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulasli, M.; Verheije, M.H.; de Haan, C.A.; Reggiori, F. Qualitative and quantitative ultrastructural analysis of the membrane rearrangements induced by coronavirus. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, C.A.; Rottier, P.J. Molecular interactions in the assembly of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2005, 64, 165–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: Update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoops, K.; Kikkert, M.; Worm, S.H.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C.; van der Meer, Y.; Koster, A.J.; Mommaas, A.M.; Snijder, E.J. SARS-coronavirus replication is supported by a reticulovesicular network of modified endoplasmic reticulum. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruebner, B.H.; Hirano, T.; Slusser, R.J. Electron microscopy of the hepatocellular and Kupffer-cell lesions of mouse hepatitis, with particular reference to the effect of cortisone. Am. J. Pathol. 1967, 51, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- David-Ferreira, J.F.; Manaker, R.A. An electron microscopy studyof the development of a mouse hepatitis virus in tissue culture cells. J. Cell Biol. 1965, 24, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoboda, D.; Nielson, A.; Werber, A.; Higginson, J. An electron microscopic study of viral hepatitis in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 1962, 41, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.K.; Hou, M.H.; Chang, C.F.; Hsiao, C.D.; Huang, T.H. The SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein-forms and functions. Antivir. Res. 2014, 103, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Dobie, F.; Ballantine, M.; Leeson, A.; Li, Y.; Bastien, N.; Cutts, T.; Andonov, A.; Cao, J.; Booth, T.F.; et al. Analysis of multimerization of the SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tooze, J.; Tooze, S.A.; Fuller, S.D. Sorting of progeny coronavirus from condensed secretory proteins at the exit from the trans-Golgi network of AtT20 cells. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, W.B.; McIntosh, K.; Dees, J.H.; Chanock, R.M. Morphogenesis of avian infectious bronchitis virus and a related human virus (strain 229E). J. Virol. 1967, 1, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orenstein, J.M.; Banach, B.; Baker, S.C. Morphogenesis of coronavirus HCoV-NL63 in cell culture: A transmission electron microscopic study. Open Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 2, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wilde, A.H.; Raj, V.S.; Oudshoorn, D.; Bestebroer, T.M.; van Nieuwkoop, S.; Limpens, R.W.; Posthuma, C.C.; van der Meer, Y.; Barcena, M.; Haagmans, B.L.; et al. MERS-coronavirus replication induces severe in vitro cytopathology and is strongly inhibited by cyclosporin A or interferon-α treatment. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, H.J.; Neuman, B.W.; Bickerton, E.; Keep, S.M.; Alrashedi, H.; Hall, R.; Britton, P. Extensive coronavirus-induced membrane rearrangements are not a determinant of pathogenicity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Caplen, F.V.; Matsuoka, Y.; Wilcox, G.E.; Compans, R.W. Replication and morphogenesis of avian coronavirus in Vero cells and their inhibition by monensin. Virus Res. 1984, 1, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, C.S.; Tatti, K.M.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Rollin, P.E.; Comer, J.A.; Lee, W.W.; Rota, P.A.; Bankamp, B.; Bellini, W.J.; Zaki, S.R. Ultrastructural characterization of SARS coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijder, E.J.; van der Meer, Y.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.; Onderwater, J.J.; van der Meulen, J.; Koerten, H.K.; Mommaas, A.M. Ultrastructure and origin of membrane vesicles associated with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication complex. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5927–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanueva, I.J.; Carrascosa, J.L.; Risco, C. Structural maturation of the transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7952–7964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.L.; Tan, S.H.; See, E.E.; Ooi, E.E.; Ling, A.E. Proliferative growth of SARS coronavirus in Vero E6 cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almsherqi, Z.A.; McLachlan, C.S.; Mossop, P.; Knoops, K.; Deng, Y. Direct template matching reveals a host subcellular membrane gyroid cubic structure that is associated with SARS virus. Redox Rep. 2005, 10, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almsherqi, Z.A.; Landh, T.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Deng, Y. Chapter 6: Cubic membranes the missing dimension of cell membrane organization. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 274, 275–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banach, S.B.; Orenstein, J.M.; Fox, L.M.; Randell, S.H.; Rowley, A.H.; Baker, S.C. Human airway epithelial cell culture to identify new respiratory viruses: Coronavirus NL63 as a model. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 156, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.A.; Castrillon, J.C.; Diosa-Toro, M.; Betancur, J.G.; St Laurent, G., 3rd; Smit, J.M.; Urcuqui-Inchima, S. Complex interaction between dengue virus replication and expression of miRNA-133a. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz Silva, M.; van der Ende-Metselaar, H.; Mulder, H.L.; Smit, J.M.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A. Mechanism and role of MCP-1 upregulation upon chikungunya virus infection in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, M.; Wyler, R. Propagation of the virus of porcine epidemic diarrhea in cell culture. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Ortega, M.E.; Beltran-Figueroa, R.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.E.; Juarez-Ramirez, M.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A.; Hernandez-Villegas, E.N.; Becerra-Hernandez, J.F.; Sarmiento-Silva, R.E. Isolation and characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus associated with the 2014 disease outbreak in Mexico: Case report. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibbard, S.; Mitchell, D.; Porcerelli, J. Internal consistency of the object relations and social cognition scales for the Thematic Apperception Test. J. Personal. Assess. 2001, 77, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, P.N.; Meyer, H.; Wachtel, I.; Eibl, J.; Dorner, F. Determination of the inactivation kinetics of hepatitis A virus in human plasma products using a simple TCID50 assay. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Lv, X.; Herrler, G.; Enjuanes, L.; Zhou, X.; Qu, B.; Meng, F.; Cong, C.; et al. Porcine aminopeptidase N mediated polarized infection by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in target cells. Virology 2015, 478, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degtyarev, M.; de Maziere, A.; Orr, C.; Lin, J.; Lee, B.B.; Tien, J.Y.; Prior, W.W.; van Dijk, S.; Wu, H.; Gray, D.C.; et al. Akt inhibition promotes autophagy and sensitizes PTEN-null tumors to lysosomotropic agents. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabouille, C. Quantitative aspects of immunogold labeling in embedded and nonembedded sections. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 117, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slot, J.W.; Geuze, H.J. Cryosectioning and immunolabeling. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2480–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, M.; Bujny, M.V.; Zeuschner, D.; Geerts, W.J.; Griffith, J.; Petersen, C.M.; Cullen, P.J.; Klumperman, J.; Geuze, H.J. SNX1 defines an early endosomal recycling exit for sortilin and mannose 6-phosphate receptors. Traffic 2008, 9, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiro, L.S.; Schieble, J.H.; Lennette, E.H. Electron microscopic studies of coronavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1971, 12, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemeijer, M.C.; Vonk, A.M.; Monastyrska, I.; Rottier, P.J.; de Haan, C.A. Visualizing coronavirus RNA synthesis in time by using click chemistry. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5808–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storrie, B.; White, J.; Rottger, S.; Stelzer, E.H.; Suganuma, T.; Nilsson, T. Recycling of golgi-resident glycosyltransferases through the ER reveals a novel pathway and provides an explanation for nocodazole-induced Golgi scattering. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1505–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, J.; Ishikawa, K.; Arita, M.; Taniguchi, K. ACBD3-mediated recruitment of PI4KB to picornavirus RNA replication sites. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noiva, R.; Lennarz, W.J. Protein disulfide isomerase. A multifunctional protein resident in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 3553–3556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lasecka, L.; Baron, M.D. The nairovirus nairobi sheep disease virus/ganjam virus induces the translocation of protein disulphide isomerase-like oxidoreductases from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface and the extracellular space. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Gao, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Q. Transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus infection induces dramatic changes in the tight junctions and microfilaments of polarized IPEC-J2 cells. Virus Res. 2014, 192, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Guo, H.; Zeng, W.; Yan, G.; Memon, A.M.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus induces autophagy to benefit its replication. Viruses 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Abe, A.; Abedin, M.J.; Abeliovich, H.; Acevedo Arozena, A.; Adachi, H.; Adams, C.M.; Adams, P.D.; Adeli, K.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy 2016, 12, 1–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orrenius, S.; Ericsson, J.L.; Ernster, L. Phenobarbital-induced synthesis of the microsomal drug-metabolizing enzyme system and its relationship to the proliferation of endoplasmic membranes. A morphological and biochemical study. J. Cell Biol. 1965, 25, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuolo, J.; Bulotta, S.; Verderio, C.; Benfante, R.; Borgese, N. Selective activation of the transcription factor ATF6 mediates endoplasmic reticulum proliferation triggered by a membrane protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7832–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qinfen, Z.; Jinming, C.; Xiaojun, H.; Huanying, Z.; Jicheng, H.; Ling, F.; Kunpeng, L.; Jingqiang, Z. The life cycle of SARS coronavirus in Vero E6 cells. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 73, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Cong, Y.; Veenendaal, T.; Klumperman, J.; Shi, D.; Mari, M.; Reggiori, F. Ultrastructural Characterization of Membrane Rearrangements Induced by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Viruses 2017, 9, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090251
Zhou X, Cong Y, Veenendaal T, Klumperman J, Shi D, Mari M, Reggiori F. Ultrastructural Characterization of Membrane Rearrangements Induced by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Viruses. 2017; 9(9):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090251
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xingdong, Yingying Cong, Tineke Veenendaal, Judith Klumperman, Dongfang Shi, Muriel Mari, and Fulvio Reggiori. 2017. "Ultrastructural Characterization of Membrane Rearrangements Induced by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection" Viruses 9, no. 9: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090251
APA StyleZhou, X., Cong, Y., Veenendaal, T., Klumperman, J., Shi, D., Mari, M., & Reggiori, F. (2017). Ultrastructural Characterization of Membrane Rearrangements Induced by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Viruses, 9(9), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9090251