Current Peptide and Protein Candidates Challenging HIV Therapy beyond the Vaccine Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HIV-1 Vaccine Development
3. Alternative HIV Gene Therapies
3.1. Adoptive T Cell Transfer and Immunotherapy
3.2. Peptides and Proteins for HIV Therapy
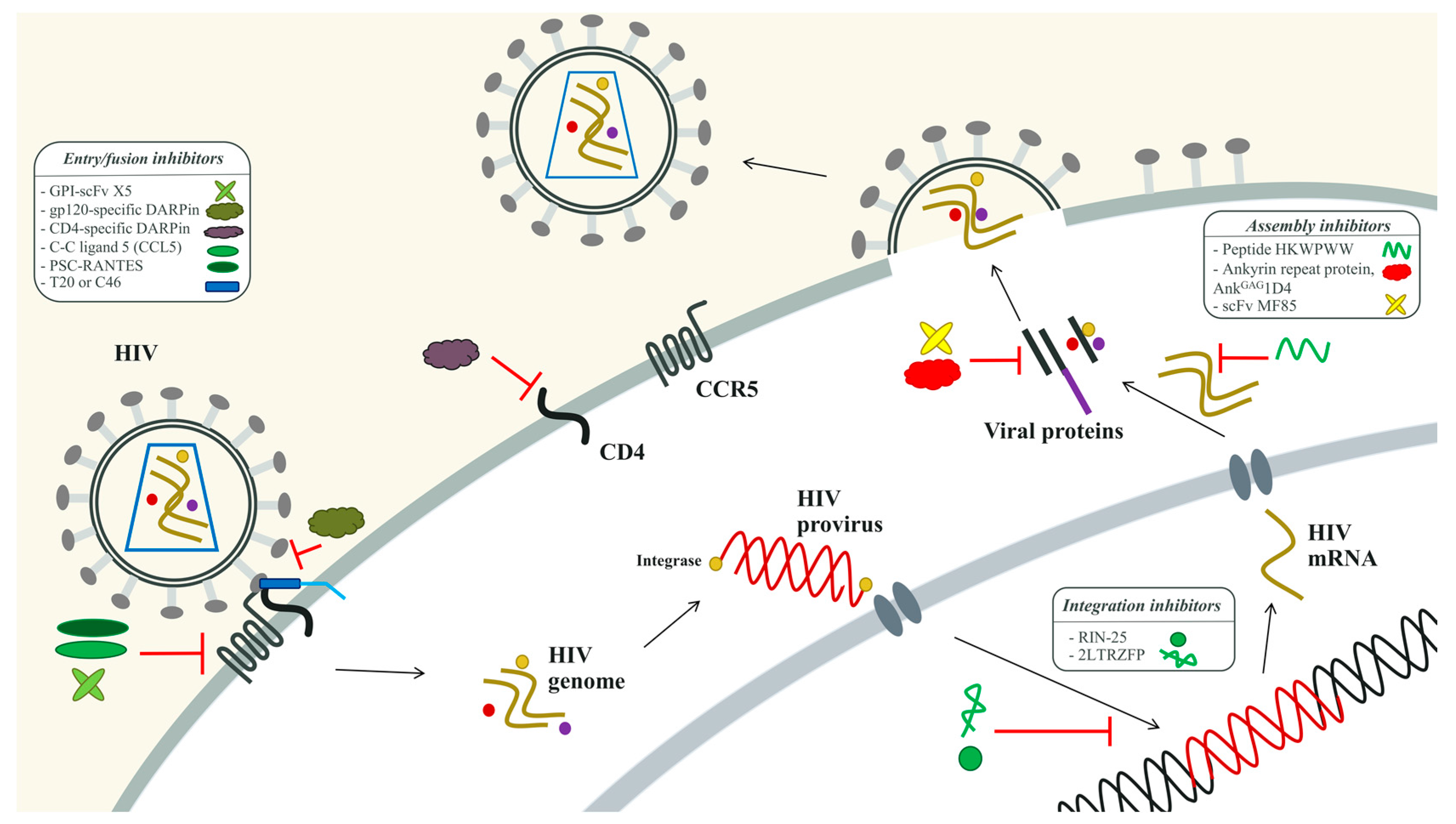
3.2.1. The HIV-1 Entry Inhibitors
3.2.2. The HIV-1 Integration Inhibitors
3.2.3. The HIV-1 Assembly Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lloyd, A. HIV infection and AIDS. Papua New Guinea Med. J. 1996, 39, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. Origins of HIV and the AIDS pandemic. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatzmann, D.; Champagne, E.; Chamaret, S.; Gruest, J.; Guetard, D.; Hercend, T.; Gluckman, J.C.; Montagnier, L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature 1984, 312, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Kwon, D.S.; Torensma., R.; van Vliet, S.J.; van Duijnhoven, G.C.; Middel, J.; Cornelissen, I.L.; Nottet, H.S.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Littman, D.R.; et al. DC-SIGN, a dendritic cell-specific HIV-1-binding protein that enhances trans-infection of T cells. Cell 2000, 100, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulak, J.; Singhal, P.C. HIV-1 and kidney cells: Better understanding of viral interaction. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 2010, 115, e15–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, M.; Balakumaran, B.; Chen, P.; Negri, D.R.; Cara, A.; Chen, B.K.; Klotman, M.E. Renal epithelial cells produce and spread HIV-1 via T-cell contact. AIDS 2014, 28, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, M.; Iser, D.; Lewin, S.R. Human immunodeficiency virus infection and the liver. World J. Hepatol. 2012, 4, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, K.A.; Ferreira, F.; Mandke, P.; Chau, E.; Aggarwal, N.R.; D’Alessio, F.R.; Lambert, A.A.; Kirk, G.; Blankson, J.; Drummond, M.B.; et al. HIV Impairs Lung Epithelial Integrity and Enters the Epithelium to Promote Chronic Lung Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorosko, S.M.; Connor, R.I. Primary human mammary epithelial cells endocytose HIV-1 and facilitate viral infection of CD4+ T lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10533–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, C.A.; Watkins, B.A.; Kufta, C.; Dubois-Dalcq, M. Infection of brain microglial cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is CD4 dependent. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiley, C.A.; Schrier, R.D.; Nelson, J.A.; Lampert, P.W.; Oldstone, M.B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 7089–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.C.; McNamara, L.A.; Onafuwa-Nuga, A.; Shackleton, M.; Riddell, J., IV; Bixby, D.; Savona, M.R.; Morrison, S.J.; Collins, K.L. HIV-1 utilizes the CXCR4 chemokine receptor to infect multipotent hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, L.A.; Collins, K.L. Hematopoietic stem/precursor cells as HIV reservoirs. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2011, 6, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naswa, S.; Marfatia, Y.S. Pre-exposure prophylaxis of HIV. Indian J. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2011, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rey, D. Post-exposure prophylaxis for HIV infection. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, S.; Dunn, D.T.; Desai, M.; Dolling, D.I.; Gafos, M.; Gilson, R.; Sullivan, A.K.; Clarke, A.; Reeves, I.; Schembri, G.; et al. Pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent the acquisition of HIV-1 infection (PROUD): Effectiveness results from the pilot phase of a pragmatic open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrman, G.; Hogue, I.B.; Palmer, S.; Jennings, C.; Spina, C.A.; Wiegand, A.; Landay, A.L.; Coombs, R.W.; Richman, D.D.; Mellors, J.W.; et al. Depletion of latent HIV-1 infection in vivo: A proof-of-concept study. Lancet 2005, 366, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siliciano, J.D.; Kajdas, J.; Finzi, D.; Quinn, T.C.; Chadwick, K.; Margolick, J.B.; Kovacs, C.; Gange, S.J.; Siliciano, R.F. Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, C.V.; Staskus, K.; Wietgrefe, S.W.; Rothenberger, M.; Reilly, C.; Chipman, J.G.; Beilman, G.J.; Khoruts, A.; Thorkelson, A.; Schmidt, T.E.; et al. Persistent HIV-1 replication is associated with lower antiretroviral drug concentrations in lymphatic tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costiniuk, C.T.; Jenabian, M.A. Cell-to-cell transfer of HIV infection: Implications for HIV viral persistence. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2346–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Decker, J.M.; Wang, S.; Hui, H.; Kappes, J.C.; Wu, X.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Salazar, M.G.; Kilby, J.M.; Saag, M.S.; et al. Antibody neutralization and escape by HIV-1. Nature 2003, 422, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsignori, M.; Liao, H.X.; Gao, F.; Williams, W.B.; Alam, S.M.; Montefiori, D.C.; Haynes, B.F. Antibody-virus co-evolution in HIV infection: Paths for HIV vaccine development. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, B.F.; Mascola, J.R. The quest for an antibody-based HIV vaccine. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.A.; Schramm, C.A.; Gorman, J.; Moore, P.L.; Bhiman, J.N.; DeKosky, B.J.; Ernandes, M.J.; Georgiev, I.S.; Kim, H.J.; Pancera, M.; et al. Developmental pathway for potent V1V2-directed HIV-neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2014, 509, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Lee, J.H.; Doores, K.J.; Murin, C.D.; Julien, J.P.; McBride, R.; Liu, Y.; Marozsan, A.; Cupo, A.; Klasse, P.J.; et al. Supersite of immune vulnerability on the glycosylated face of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheid, J.F.; Mouquet, H.; Ueberheide, B.; Diskin, R.; Klein, F.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Pietzsch, J.; Fenyo, D.; Abadir, A.; Velinzon, K.; et al. Sequence and structural convergence of broad and potent HIV antibodies that mimic CD4 binding. Science 2011, 333, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancera, M.; Zhou, T.; Druz, A.; Georgiev, I.S.; Soto, C.; Gorman, J.; Huang, J.; Acharya, P.; Chuang, G.Y.; Ofek, G.; et al. Structure and immune recognition of trimeric pre-fusion HIV-1 Env. Nature 2014, 514, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ofek, G.; Laub, L.; Louder, M.K.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Longo, N.S.; Imamichi, H.; Bailer, R.T.; Chakrabarti, B.; Sharma, S.K.; et al. Broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by a gp41-specific human antibody. Nature 2012, 491, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascola, J.R.; Lewis, M.G.; Stiegler, G.; Harris, D.; VanCott, T.C.; Hayes, D.; Louder, M.K.; Brown, C.R.; Sapan, C.V.; Frankel, S.S.; et al. Protection of Macaques against pathogenic simian/human immunodeficiency virus 89.6PD by passive transfer of neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4009–4018. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steichen, J.M.; Kulp, D.W.; Tokatlian, T.; Escolano, A.; Dosenovic, P.; Stanfield, R.L.; McCoy, L.E.; Ozorowski, G.; Hu, X.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; et al. HIV vaccine design to target germline precursors of glycan-dependent broadly neutralizing antibodies. Immunity 2016, 45, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Kerkhof, T.L.; de Taeye, S.W.; Boeser-Nunnink, B.D.; Burton, D.R.; Kootstra, N.A.; Schuitemaker, H.; Sanders, R.W.; van Gils, M.J. HIV-1 escapes from N332-directed antibody neutralization in an elite neutralizer by envelope glycoprotein elongation and introduction of unusual disulfide bonds. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, I.S.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Zhou, T.; Kwon, Y.D.; Staupe, R.P.; Moquin, S.; Chuang, G.Y.; Louder, M.K.; Schmidt, S.D.; Altae-Tran, H.R.; et al. Delineating antibody recognition in polyclonal sera from patterns of HIV-1 isolate neutralization. Science 2013, 340, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoofs, T.; Klein, F.; Braunschweig, M.; Kreider, E.F.; Feldmann, A.; Nogueira, L.; Oliveira, T.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Parrish, E.H.; Learn, G.H.; et al. HIV-1 therapy with monoclonal antibody 3BNC117 elicits host immune responses against HIV-1. Science 2016, 352, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caskey, M.; Klein, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Seaman, M.S.; West, A.P., Jr.; Buckley, N.; Kremer, G.; Nogueira, L.; Braunschweig, M.; Scheid, J.F.; et al. Viraemia suppressed in HIV-1-infected humans by broadly neutralizing antibody 3BNC117. Nature 2015, 522, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sips, M.; Krykbaeva, M.; Diefenbach, T.J.; Ghebremichael, M.; Bowman, B.A.; Dugast, A.S.; Boesch, A.W.; Streeck, H.; Kwon, D.S.; Ackerman, M.E.; et al. Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in tissues as a potent mechanism for preventive and therapeutic HIV vaccine strategies. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitisuttithum, P.; Gilbert, P.; Gurwith, M.; Heyward, W.; Martin, M.; van Griensven, F.; Hu, D.; Tappero, J.W.; Choopanya, K.; Bangkok Vaccine Evaluation Group. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled efficacy trial of a bivalent recombinant glycoprotein 120 HIV-1 vaccine among injection drug users in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, N.M.; Forthal, D.N.; Harro, C.D.; Judson, F.N.; Mayer, K.H.; Para, M.F. rgp120 HIV Vaccine Study Group. Placebo-controlled phase 3 trial of a recombinant glycoprotein 120 vaccine to prevent HIV-1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pitisuttithum, P.; Nitayaphan, S.; Thongcharoen, P.; Khamboonruang, C.; Kim, J.; de Souza, M.; Chuenchitra, T.; Garner, R.P.; Thapinta, D.; Polonis, V.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of combinations of recombinant subtype E and B human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein 120 vaccines in healthy Thai adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruyn, G.; Rossini, A.J.; Chiu, Y.L.; Holman, D.; Elizaga, M.L.; Frey, S.E.; Burke, D.; Evans, T.G.; Corey, L.; Keefer, M.C. Safety profile of recombinant canarypox HIV vaccines. Vaccine 2004, 22, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitisuttithum, P.; Rerks-Ngarm, S.; Bussaratid, V.; Dhitavat, J.; Maekanantawat, W.; Pungpak, S.; Suntharasamai, P.; Vanijanonta, S.; Nitayapan, S.; Kaewkungwal, J.; et al. Safety and reactogenicity of canarypox ALVAC-HIV (vCP1521) and HIV-1 gp120 AIDSVAX B/E vaccination in an efficacy trial in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, B.F.; Gilbert, P.B.; McElrath, M.J.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Tomaras, G.D.; Alam, S.M.; Evans, D.T.; Montefiori, D.C.; Karnasuta, C.; Sutthent, R.; et al. Immune-correlates analysis of an HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phogat, S.; Wyatt, R.T.; Karlsson Hedestam, G.B. Inhibition of HIV-1 entry by antibodies: Potential viral and cellular targets. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 262, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, S.P.; Mehrotra, D.V.; Duerr, A.; Fitzgerald, D.W.; Mogg, R.; Li, D.; Gilbert, P.B.; Lama, J.R.; Marmor, M.; del Rio, C.; et al. Efficacy assessment of a cell-mediated immunity HIV-1 vaccine (the Step Study): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, test-of-concept trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.E.; Allen, M.; Moodie, Z.; Churchyard, G.; Bekker, L.G.; Nchabeleng, M.; Mlisana, K.; Metch, B.; de Bruyn, G.; Latka, M.H.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the HVTN 503/Phambili study of a clade-B-based HIV-1 vaccine in South Africa: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled test-of-concept phase 2b study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, B.F.; Burton, D.R. Developing an HIV vaccine. Science 2017, 355, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejchal, R.; Doores, K.J.; Walker, L.M.; Khayat, R.; Huang, P.S.; Wang, S.K.; Stanfield, R.L.; Julien, J.P.; Ramos, A.; Crispin, M.; et al. A potent and broad neutralizing antibody recognizes and penetrates the HIV glycan shield. Science 2011, 334, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.R.; Qin, L.; Zhang, D.; Smith, D.H.; Tran, A.C.; Dull, T.J.; Groopman, J.E.; Capon, D.J.; Byrn, R.A.; Finer, M.H. Targeting of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells by CD8+ T lymphocytes armed with universal T-cell receptors. Blood 1994, 84, 2878–2889. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitsuyasu, R.T.; Anton, P.A.; Deeks, S.G.; Scadden, D.T.; Connick, E.; Downs, M.T.; Bakker, A.; Roberts, M.R.; June, C.H.; Jalali, S.; et al. Prolonged survival and tissue trafficking following adoptive transfer of CD4zeta gene-modified autologous CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells in human immunodeficiency virus-infected subjects. Blood 2000, 96, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.H.; Lobritz, M.A.; Nguyen, S.; Lassen, K.; Delair, S.; Posta, F.; Bryson, Y.J.; Arts, E.J.; Chou, T.; Lee, B. A quantitative affinity-profiling system that reveals distinct CD4/CCR5 usage patterns among human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian immunodeficiency virus strains. J. Vriol. 2009, 83, 11016–11026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Kitchen, S.G.; Chen, I.S.; Ng, H.L.; Zack, J.A.; Yang, O.O. HIV-1-specific chimeric antigen receptors based on broadly neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6999–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, M.; Mesojednik, T.; Romano Ibarra, G.S.; Sahni, J.; Bernard, A.; Sommer, K.; Scharenberg, A.M.; Rawlings, D.J.; Wagner, T.A. Engineering HIV-resistant, anti-HIV chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maus, M.V.; Haas, A.R.; Beatty, G.L.; Albelda, S.M.; Levine, B.L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Kalos, M.; June, C.H. T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors can cause anaphylaxis in humans. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Xu, X.; Ogg, G.S.; Hansasuta, P.; Dong, T.; Rostron, T.; Luzzi, G.; Conlon, C.P.; Screaton, G.R.; McMichael, A.J.; et al. Rapid death of adoptively transferred T cells in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Blood 1999, 93, 1506–1510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Wang, W.; Cheng, L.; Li, G.; Wen, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Zhou, P.; Su, L. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored anti-HIV scFv efficiently protects CD4 T cells from HIV-1 infection and deletion in hu-PBL mice. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binz, H.K.; Stumpp, M.T.; Forrer, P.; Amstutz, P.; Pluckthun, A. Designing repeat proteins: Well-expressed, soluble and stable proteins from combinatorial libraries of consensus ankyrin repeat proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, Y.L.; Pluckthun, A. DARPins and other repeat protein scaffolds: Advances in engineering and applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, A.; Friedrich, N.; Krarup, A.; Weber, J.; Stiegeler, E.; Dreier, B.; Pugach, P.; Robbiani, M.; Riedel, T.; Moehle, K.; et al. Conformation-dependent recognition of HIV gp120 by designed ankyrin repeat proteins provides access to novel HIV entry inhibitors. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5868–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, A.; Rusert, P.; Berlinger, L.; Ruprecht, C.R.; Mann, A.; Corthesy, S.; Turville, S.G.; Aravantinou, M.; Fischer, M.; Robbiani, M.; et al. CD4-specific designed ankyrin repeat proteins are novel potent HIV entry inhibitors with unique characteristics. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugach, P.; Krarup, A.; Gettie, A.; Kuroda, M.; Blanchard, J.; Piatak, M., Jr.; Lifson, J.D.; Trkola, A.; Robbiani, M. In vivo binding and retention of CD4-specific DARPin 57.2 in macaques. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Weber, I.T.; Harrison, R.W.; Leis, J. Identification of amino acids in HIV-1 and avian sarcoma virus integrase subsites required for specific recognition of the long terminal repeat Ends. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 4173–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, M.M.; Veazey, R.S.; Offord, R.; Mosier, D.E.; Dufour, J.; Mefford, M.; Piatak, M., Jr.; Lifson, J.D.; Salkowitz, J.R.; Rodriguez, B.; et al. Prevention of vaginal SHIV transmission in rhesus macaques through inhibition of CCR5. Science 2004, 306, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secchi, M.; Longhi, R.; Vassena, L.; Sironi, F.; Grzesiek, S.; Lusso, P.; Vangelista, L. Enhancement of anti-HIV-1 activity by hot spot evolution of RANTES-derived peptides. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secchi, M.; Vassena, L.; Morin, S.; Schols, D.; Vangelista, L. Combination of the CCL5-derived peptide R4.0 with different HIV-1 blockers reveals wide target compatibility and synergic cobinding to CCR5. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6215–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Blondel, G.; Brassat, D.; Bauer, J.; Lassmann, H.; Liblau, R.S. CCR5 blockade for neuroinflammatory diseases--beyond control of HIV. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, C.T.; Shugars, D.C.; Greenwell, T.K.; McDanal, C.B.; Matthews, T.J. Peptides corresponding to a predictive alpha-helical domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 are potent inhibitors of virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9770–9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolstein, O.; Boyd, M.; Millington, M.; Impey, H.; Boyer, J.; Howe, A.; Delebecque, F.; Cornetta, K.; Rothe, M.; Baum, C.; et al. Preclinical safety and efficacy of an anti-HIV-1 lentiviral vector containing a short hairpin RNA to CCR5 and the C46 fusion inhibitor. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, B.P.; Levin, B.R.; Zhang, J.; Sahakyan, A.; Boyer, J.; Carroll, M.V.; Colon, J.C.; Keech, N.; Rezek, V.; Bristol, G.; et al. Engineering cellular resistance to HIV-1 infection in vivo using a dual therapeutic lentiviral vector. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, F.G.; Egerer, L.; Brauer, F.; Gerum, C.; Schwalbe, H.; Dietrich, U.; von Laer, D. Mutations in gp120 contribute to the resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to membrane-anchored C-peptide maC46. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4844–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craigie, R. HIV integrase, a brief overview from chemistry to therapeutics. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 23213–23216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesplede, T.; Wainberg, M.A. Resistance against integrase strand transfer inhibitors and relevance to HIV persistence. Viruses 2015, 7, 3703–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, W.E., Jr.; McDougall, B.; Tran, D.; Selsted, M.E. Anti-HIV-1 activity of indolicidin, an antimicrobial peptide from neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 63, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchand, C.; Krajewski, K.; Lee, H.F.; Antony, S.; Johnson, A.A.; Amin, R.; Roller, P.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Pommier, Y. Covalent binding of the natural antimicrobial peptide indolicidin to DNA abasic sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5157–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkhachornphop, S.; Jiranusornkul, S.; Kodchakorn, K.; Nangola, S.; Sirisanthana, T.; Tayapiwatana, C. Designed zinc finger protein interacting with the HIV-1 integrase recognition sequence at 2-LTR-circle junctions. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamaikawin, W.; Saoin, S.; Nangola, S.; Chupradit, K.; Sakkhachornphop, S.; Hadpech, S.; Onlamoon, N.; Ansari, A.A.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Boulanger, P.; et al. Combined antiviral therapy using designed molecular scaffolds targeting two distinct viral functions, HIV-1 genome integration and capsid assembly. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougel, M.; Cimarelli, A.; Darlix, J.L. Implications of the nucleocapsid and the microenvironment in retroviral reverse transcription. Viruses 2010, 2, 939–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouvenet, N.; Laine, S.; Pessel-Vivares, L.; Mougel, M. Cell biology of retroviral RNA packaging. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didierlaurent, L.; Houzet, L.; Morichaud, Z.; Darlix, J.L.; Mougel, M. The conserved N-terminal basic residues and zinc-finger motifs of HIV-1 nucleocapsid restrict the viral cDNA synthesis during virus formation and maturation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 4745–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussupt, V.; Sette, P.; Bello, N.F.; Javid, M.P.; Nagashima, K.; Bouamr, F. Basic residues in the nucleocapsid domain of Gag are critical for late events of HIV-1 budding. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rocquigny, H.; Shvadchak, V.; Avilov, S.; Dong, C.Z.; Dietrich, U.; Darlix, J.L. Targeting the viral nucleocapsid protein in anti-HIV-1 therapy. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, M.Y.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S.; You, J.; Myung, H. Selection and characterization of peptides specifically binding to HIV-1 psi (psi) RNA. Virus Res. 2004, 106, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pustowka, A.; Dietz, J.; Ferner, J.; Baumann, M.; Landersz, M.; Konigs, C.; Schwalbe, H.; Dietrich, U. Identification of peptide ligands for target RNA structures derived from the HIV-1 packaging signal psi by screening phage-displayed peptide libraries. ChemBioChem 2003, 4, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, J.; Koch, J.; Kaur, A.; Raja, C.; Stein, S.; Grez, M.; Pustowka, A.; Mensch, S.; Ferner, J.; Moller, L.; et al. Inhibition of HIV-1 by a peptide ligand of the genomic RNA packaging signal Psi. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druillennec, S.; Dong, C.Z.; Escaich, S.; Gresh, N.; Bousseau, A.; Roques, B.P.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C. A mimic of HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein impairs reverse transcription and displays antiviral activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4886–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingappa, J.R.; Reed, J.C.; Tanaka, M.; Chutiraka, K.; Robinson, B.A. How HIV-1 Gag assembles in cells: Putting together pieces of the puzzle. Virus Res. 2014, 193, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadzadeh, S.; Rajabibazl, M.; Fourozandeh, M.; Rasaee, M.J.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Mohammadi, M. Production of recombinant scFv against p24 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by phage display technology. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2014, 33, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nangola, S.; Urvoas, A.; Valerio-Lepiniec, M.; Khamaikawin, W.; Sakkhachornphop, S.; Hong, S.S.; Boulanger, P.; Minard, P.; Tayapiwatana, C. Antiviral activity of recombinant ankyrin targeted to the capsid domain of HIV-1 Gag polyprotein. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMichael, A.J.; Picker, L.J. Unusual antigen presentation offers new insight into HIV vaccine design. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 46, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, M.N.; Okeoma, C.M. Exosomes: Implications in HIV-1 Pathogenesis. Viruses 2015, 7, 4093–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, K.A.; Wang, H.; Slaughter, A.; Feng, L.; Kessl, J.J.; Koh, Y.; Wang, W.; Ballandras-Colas, A.; Patel, P.A.; Fuchs, J.R.; et al. Allosteric integrase inhibitor potency is determined through the inhibition of HIV-1 particle maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8690–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, R.; Chen, Y.; Fischer, T.; Tedaldi, E.; Napoli, A.; Zhang, Y.; Karn, J.; Hu, W.; Khalili, K. Elimination of HIV-1 genomes from human T-lymphoid cells by CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, R.J.; Wang, T.; Koundakjian, D.; Hultquist, J.F.; Lamothe-Molina, P.; Monel, B.; Schumann, K.; Yu, H.; Krupzcak, K.M.; Garcia-Beltran, W.; et al. A genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies a restricted set of HIV host dependency factors. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Vaccines | Types | Results | Immunogens | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAX003 | Passive vaccine | No vaccine efficacy | gp120 of HIV-1 subtypes B and E (strains MN and A244) | [36] |
| VAX004 | Passive vaccine | No vaccine efficacy | gp120 of HIV-1 subtypes B (strains MN and GNE8) | [37] |
| STEP (HVTN502) | Active vaccine: T-cell activation | No vaccine efficacy, increased HIV infection rates | Subtype B, MRKAd5-gag/pol/nef | [43] |
| Phambili (HVTN503) | Active vaccine: T-cell activation | No vaccine efficacy | Subtype B, MRKAd5-gag/pol/nef | [44] |
| RV114 | Passive and active vaccine | Estimated efficacy 31% at 42 months | Prime: subtype B and A/E ALVAC-HIV-gag-pr-gp41-gp120 Boost: subtypes B and E AIDSVAX B/E (gp120 subunit proteins) | [40,41] |
| Peptides or Proteins | Types | Targets | Efficacy | Clinical Trials | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunoglobulin-Based Molecules | |||||
| GPI-scFv X5 | Entry inhibitor | CCR5, CXCR4 co-receptor | Protects CD4+ T cells from R5, X4, and dual-tropic HIV-1; can be immunogenic and generate HIV-1 mutants in long-term infections | Preclinical trial | [54] |
| scFv MF85 | Assembly inhibitor | HIV-1 p24 | High binding activity towards p24 antigen; not suitable for protein folding in cytoplasm | Ongoing research | [85] |
| Non-Immunoglobulin-Based Molecules | |||||
| gp120-specific DARPin | Entry inhibitor | HIV-1 gp120 | Target gp120 with high affinity and specificity; would drive HIV-1 mutation in HIV-1 Envelope | Ongoing research | [57] |
| CD4-specific DARPin | Entry inhibitor | CD4 molecule | Targets CD4 with high affinity to inhibit HIV entry; rapidly cleared from the circulation | Ongoing research | [58,59] |
| C-C ligand 5 (CCL5) | Entry inhibitor | CCR5 co-receptor | Binds to CCR5 molecule to inhibit HIV entry | Ongoing research | [60] |
| PSC-RANTES | Entry inhibitor | CCR5 co-receptor | Inhibits HIV-1 vaginal transmission in monkey model | Preclinical trial | [61] |
| T20 | Fusion inhibitor | HIV-1 gp41, NHR | Antiviral peptide approved by FDA for inhibiting HIV-1 entry; has to inject twice daily and can develop HIV-1-resistant strains | Phase II | [65] |
| C46 | Fusion inhibitor | HIV-1 gp41, NHR | More effective than T20; can develop HIV-1-resistant strains | Phase I/II | [66,67,68] |
| RIN-25 | Integration inhibitor | HIV-1 IN | Exhibits IN-inhibitory activity | Ongoing research | [72] |
| 2LTRZFP | Integration inhibitor | HIV-1 LTR | Targets HIV-1 2LTR to block HIV-1 integration | Ongoing research | [73,74] |
| Peptide competitor, HKWPWW | Assembly inhibitor | HIV-1 ψ-RNA | Inhibits HIV-1 assembly by binding to packaging signal of genomic RNA | Ongoing research | [80,81,82] |
| Ankyrin repeat protein, AnkGAG1D4 | Assembly inhibitor | HIV-1 p24 | Binds to N-terminal of HIV-1 capsid, limited effects in HIV-1 heavy infection | Ongoing research | [74,86] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chupradit, K.; Moonmuang, S.; Nangola, S.; Kitidee, K.; Yasamut, U.; Mougel, M.; Tayapiwatana, C. Current Peptide and Protein Candidates Challenging HIV Therapy beyond the Vaccine Era. Viruses 2017, 9, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100281
Chupradit K, Moonmuang S, Nangola S, Kitidee K, Yasamut U, Mougel M, Tayapiwatana C. Current Peptide and Protein Candidates Challenging HIV Therapy beyond the Vaccine Era. Viruses. 2017; 9(10):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100281
Chicago/Turabian StyleChupradit, Koollawat, Sutpirat Moonmuang, Sawitree Nangola, Kuntida Kitidee, Umpa Yasamut, Marylène Mougel, and Chatchai Tayapiwatana. 2017. "Current Peptide and Protein Candidates Challenging HIV Therapy beyond the Vaccine Era" Viruses 9, no. 10: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100281
APA StyleChupradit, K., Moonmuang, S., Nangola, S., Kitidee, K., Yasamut, U., Mougel, M., & Tayapiwatana, C. (2017). Current Peptide and Protein Candidates Challenging HIV Therapy beyond the Vaccine Era. Viruses, 9(10), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9100281