Monitoring of Anti-Hepatitis E Virus Antibody Seroconversion in Asymptomatically Infected Blood Donors: Systematic Comparison of Nine Commercial Anti-HEV IgM and IgG Assays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Specimen
2.2. Serological Testing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
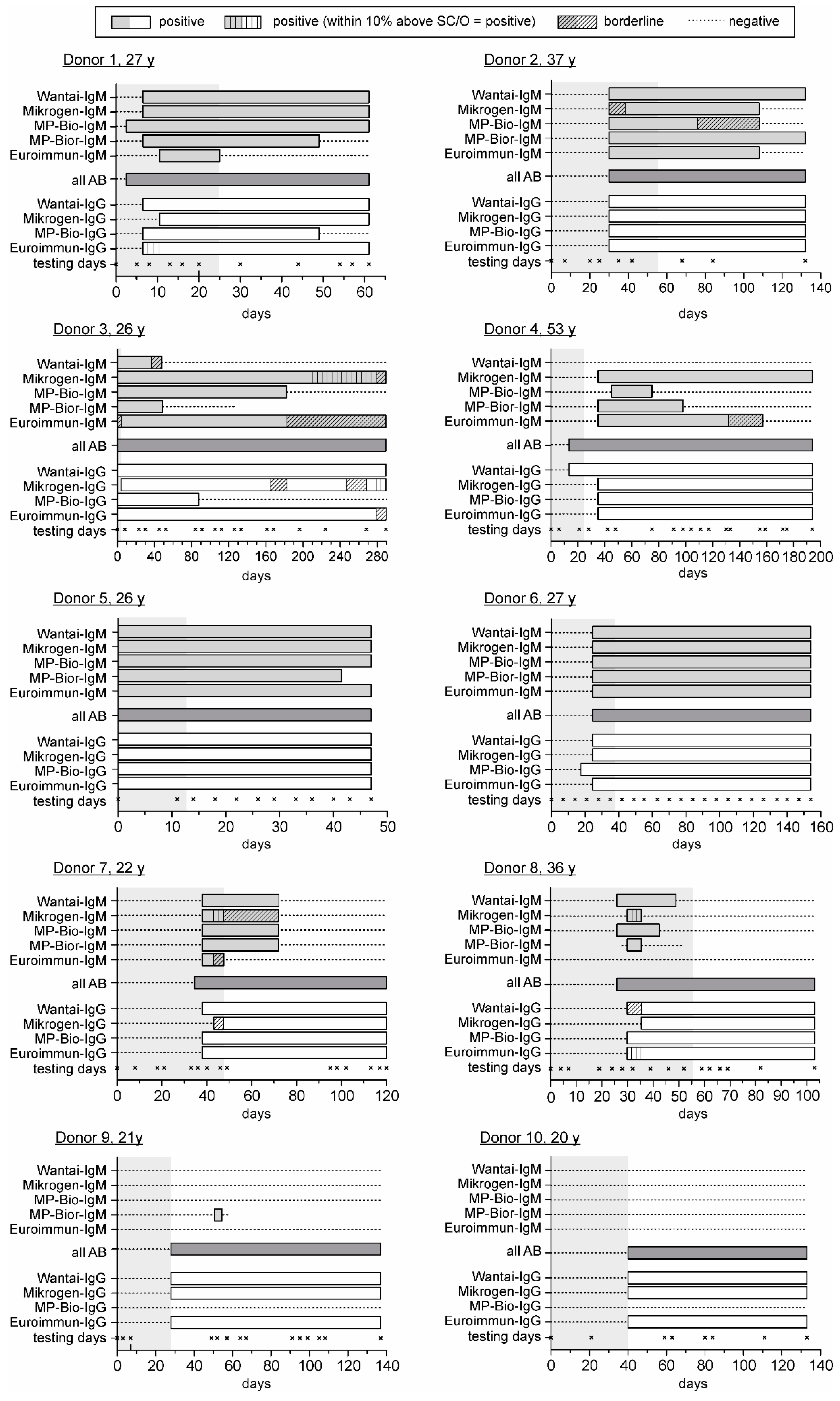
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of the Analytical Sensitivities by Analysis of Serial Dilution Samples
3.2. Comparison of the HEV Seroconversion Panels
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamar, N.; Bendall, R.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Xia, N.S.; Ijaz, S.; Izopet, J.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E. Lancet 2012, 379, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgen, K.; Herremans, T.; Duizer, E.; Vennema, H.; Rutjes, S.; Bosman, A.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Koopmans, M. Non-travel related Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 infections in the Netherlands; a case series 2004–2006. BMC Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, H.R.; Kamar, N.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E in developed countries: Current status and future perspectives. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischke, S.; Behrendt, P.; Bock, C.T.; Jilg, W.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H. Hepatitis E in Germany—An under-reported infectious disease. Dtsch. Arzteblatt Int. 2014, 111, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Peron, J.M.; Bureau, C.; Poirson, H.; Mansuy, J.M.; Alric, L.; Selves, J.; Dupuis, E.; Izopet, J.; Vinel, J.P. Fulminant liver failure from acute autochthonous hepatitis E in France: Description of seven patients with acute hepatitis E and encephalopathy. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, H.C.; van der Poel, W.H.; Brandstatter, G. Hepatitis E: An overview. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, D.; Guthmann, J.P.; Klovstad, H.; Hamid, N.; Tatay, M.; Ciglenecki, I.; Nizou, J.Y.; Nicand, E.; Guerin, P.J. High mortality associated with an outbreak of hepatitis E among displaced persons in Darfur, Sudan. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christensen, P.B.; Engle, R.E.; Hjort, C.; Homburg, K.M.; Vach, W.; Georgsen, J.; Purcell, R.H. Time trend of the prevalence of hepatitis E antibodies among farmers and blood donors: A potential zoonosis in Denmark. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Selves, J.; Mansuy, J.M.; Ouezzani, L.; Peron, J.M.; Guitard, J.; Cointault, O.; Esposito, L.; Abravanel, F.; Danjoux, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus and chronic hepatitis in organ-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Kamar, N.; Sandres-Saune, K.; Garrouste, C.; Dubois, M.; Mansuy, J.M.; Muscari, F.; Sallusto, F.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J. Characteristics of autochthonous hepatitis E virus infection in solid-organ transplant recipients in France. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, R.E.; Yu, C.; Emerson, S.U.; Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) capsid antigens derived from viruses of human and swine origin are equally efficient for detecting anti-HEV by enzyme immunoassay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4576–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuy, J.M.; Peron, J.M.; Bureau, C.; Alric, L.; Vinel, J.P.; Izopet, J. Immunologically silent autochthonous acute hepatitis E virus infection in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 912–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicand, E.; Grandadam, M.; Teyssou, R.; Rey, J.L.; Buisson, Y. Viraemia and faecal shedding of HEV in symptom-free carriers. Lancet 2001, 357, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.; Walker, D.; Mast, E.; Fields, H. Report of a collaborative study to assess the suitability of a reference reagent for antibodies to hepatitis E virus. Biol. J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Stand. 2002, 30, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Engle, R.E.; Bryan, J.P.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies to hepatitis E virus by class capture enzyme immunoassay. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abravanel, F.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Lhomme, S.; Miedouge, M.; Peron, J.M.; Alric, L.; Rostaing, L.; Kamar, N.; Izopet, J. Performance of anti-HEV assays for diagnosing acute hepatitis E in immunocompromised patients. J. Clin.Virol. 2013, 58, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendall, R.; Ellis, V.; Ijaz, S.; Ali, R.; Dalton, H. A comparison of two commercially available anti-HEV IgG kits and a re-evaluation of anti-HEV IgG seroprevalence data in developed countries. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobeniuc, J.; Meng, J.; Reuter, G.; Greene-Montfort, T.; Khudyakova, N.; Dimitrova, Z.; Kamili, S.; Teo, C.G. Serologic assays specific to immunoglobulin M antibodies against hepatitis E virus: Pangenotypic evaluation of performances. Clinical Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, e24–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Thevenet, I.; Mansuy, J.M.; Saune, K.; Vischi, F.; Peron, J.M.; Kamar, N.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J. Good performance of immunoglobulin M assays in diagnosing genotype 3 hepatitis E virus infections. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2009, 16, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuy, J.M.; Bendall, R.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Saune, K.; Miedouge, M.; Ellis, V.; Rech, H.; Destruel, F.; Kamar, N.; Dalton, H.R.; et al. Hepatitis E virus antibodies in blood donors, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2309–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, K.S.; Endy, T.P.; Gibbons, R.V.; Laras, K.; Mammen, M.P., Jr.; Sedyaningsih, E.R.; Seriwatana, J.; Glass, J.S.; Narupiti, S.; Corwin, A.L. Evaluation of diagnostic assays for hepatitis E virus in outbreak settings. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1581–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pas, S.D.; Streefkerk, R.H.; Pronk, M.; de Man, R.A.; Beersma, M.F.; Osterhaus, A.D.; van der Eijk, A.A. Diagnostic performance of selected commercial HEV IgM and IgG ELISAs for immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnegg, A.; Burgisser, P.; Andre, C.; Kenfak-Foguena, A.; Canellini, G.; Moradpour, D.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Cavassini, M.; Darling, K.E. An analysis of the benefit of using HEV genotype 3 antigens in detecting anti-HEV IgG in a European population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, J.J.; Preiss, J.; Schemmerer, M.; Huber, B.; Jilg, W. Test Performance Characteristics of Anti-HEV IgG Assays Strongly Influence Hepatitis E Seroprevalence Estimates. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blood Advisory Committee, Topic I: Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) and Blood Transfusion Safety. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/advisorycommittees/committeesmeetingmaterials/bloodvaccinesandotherbiologics/bloodproductsadvisorycommittee/ucm319542.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2016).
- Avellon, A.; Morago, L.; Garcia-Galera, M.; Munoz, M.; Echevarria, J.M. Comparative sensitivity of commercial tests for hepatitis E genotype 3 virus antibody detection. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, T.; Diekmann, J.; Eberhardt, M.; Knabbe, C.; Dreier, J. Hepatitis E in blood donors: Investigation of the natural course of asymptomatic infection. Eurosurveillance 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer, T.; Diekmann, J.; Johne, R.; Eberhardt, M.; Knabbe, C.; Dreier, J. Novel approach for the detection of Hepatitis E virus infection in German blood donors. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2708–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, J.; Juhl, D. Autochthonous Hepatitis E Virus Infections: A New Transfusion-Associated Risk? Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2014, 41, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.C.; Ge, S.X.; Li, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.J.; Nong, Y.; Guo, Q.S.; Zhang, J.; Ng, M.H.; Xia, N.S. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus infection, rural southern People’s Republic of China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seriwatana, J.; Shrestha, M.P.; Scott, R.M.; Tsarev, S.A.; Vaughn, D.W.; Myint, K.S.; Innis, B.L. Clinical and epidemiological relevance of quantitating hepatitis E virus-specific immunoglobulin M. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuy, J.M.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Calot, J.P.; Peron, J.M.; Alric, L.; Agudo, S.; Rech, H.; Destruel, F.; Izopet, J. High prevalence of anti-hepatitis E virus antibodies in blood donors from South West France. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, C.W.; Li, L.P.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, Y.W.; Chen, X.F. Comparison of the reliability of two ELISA kits for detecting IgM antibody against hepatitis E virus. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi/Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2008, 42, 667–671. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.C.; Su, C.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Lin, S.F.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, J.C. Application of serologic assays for diagnosing acute hepatitis E in national surveillance of a nonendemic area. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norder, H.; Karlsson, M.; Mellgren, A.; Konar, J.; Sandberg, E.; Lasson, A.; Castedal, M.; Magnius, L.; Lagging, M. Diagnostic Performance of Five Assays for Anti-Hepatitis E Virus IgG and IgM in a Large Cohort Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Peron, J.M.; Alric, L.; Rostaing, L.; Kamar, N.; Izopet, J. Performance of a new rapid test for detecting anti-hepatitis E virus immunoglobulin M in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 70, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Lu, Y.; Howard, T.; Anderson, D.; Fong, P.Y.; Hu, W.P.; Chia, C.P.; Guan, M. Comparison of a new immunochromatographic test to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rapid detection of immunoglobulin m antibodies to hepatitis e virus in human sera. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylis, S.A.; Blümel, J.; Mizusawa, S.; Matsubayashi, K.; Sakata, H.; Okada, Y. World Health Organization International Standard to harmonize assays for detection of hepatitis E virus RNA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi-Tamisier, M.; Moal, V.; Gerolami, R.; Colson, P. Discrepancy between anti-hepatitis E virus immunoglobulin G prevalence assessed by two assays in kidney and liver transplant recipients. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 56, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biomex, HEV Serokonversion Panel. Available online: http://www.biomex.de/produkteservice/produkte/validierung/seroconversion-panels/ (accessed on 17 August 2016).
- Bendall, R.; Ellis, V.; Ijaz, S.; Thurairajah, P.; Dalton, H.R. Serological response to hepatitis E virus genotype 3 infection: IgG quantitation, avidity, and IgM response. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, J.P.; Tsarev, S.A.; Iqbal, M.; Ticehurst, J.; Emerson, S.; Ahmed, A.; Duncan, J.; Rafiqui, A.R.; Malik, I.A.; Purcell, R.H.; et al. Epidemic hepatitis E in Pakistan: Patterns of serologic response and evidence that antibody to hepatitis E virus protects against disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Kamili, S.; Dar, M.Y.; Moecklii, R.; Jameel, S. Hepatitis E and long-term antibody status. Lancet 1993, 341, 1355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kmush, B.L.; Labrique, A.B.; Dalton, H.R.; Ahmed, Z.B.; Ticehurst, J.R.; Heaney, C.D.; Nelson, K.E.; Zaman, K. Two Generations of “Gold Standards”: The Impact of a Decade in Hepatitis E Virus Testing Innovation on Population Seroprevalence. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Anti-HEV ELISA | Assay Type | Antigen/Origin | Analysis and Serostatus Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| IgM assays | |||
| Wantai HEV IgM ELISA (Sanbio 1) | qualitative, µ-chain capture | recombinant antigen ORF-2 C-terminal, genotype 4 [30] |
|
| recomWell HEV IgM (Mikrogen GmbH 2), new version (08/2012) | quantitative, indirect | recombinant antigen ORF-3 C-terminal, genotype 1, 2 and 3 [22] |
|
| HEV IgM ELISA 3.0 (MP Biomedicals 3) | qualitative, indirect | 1 recombinant antigen, ORF-2 C-terminal (Chinese strain), genotype 1 |
|
| Assure HEV IgM Rapid Test (MP Biomedical 3) | qualitative, reverse-flow immunochr | 1 recombinant antigen, ORF-2 C-terminal (Chinese strain), genotype 1 |
|
| Anti-HEV ELISA (IgM, Euroimmun 4) | qualitative, indirect | 1 recombinant antigen ORF-2 (USA strain), genotype 3 |
|
| All antibody assays (IgA, IgM, IgG) | |||
| HEV ELISA 4.0 (MP Biomedicals) | qualitative, direct | 1 recombinant antigen, ORF-2 C-terminal (Chinese strain), genotype 1 |
|
| IgG assays | |||
| Wantai HEV IgG ELISA (Sanbio 1) | qualitative, indirect | recombinant antigen ORF-2 C-terminal, genotype 4 [30] |
|
| recomWell HEV IgG (Mikrogen GmbH 2) | quantitative, indirect | recombinant antigen ORF-2 C-terminal, genotype 1 and 3 |
|
| HEV ELISA (MP Biomedicals 3) | qualitative | 3 recombinant antigens, ORF 2 and ORF 3 (Burmese, Mexican strains), genotype 1 and US type 2 |
|
| Anti-HEV ELISA (IgG, Euroimmun 4) | quantitative (IU/mL), indirect | 1 recombinant antigen ORF-2 (USA strain), genotype 3 |
|
| Assay | WHO-Ref (GT 1) IU/mL (Dilution) | Donor Sample (GT 3) (Dilution) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Limit | Linearity (R2) * | Detection Limit | Linearity (R2) * | |
| Anti-HEV IgM | ||||
| Wantai | 1:4 | 0.9937 | 1:16 | 0.9994 |
| Mikrogen | 1:4 | 0.9474 | 1:32 | 0.9199 |
| MP-Bio | 1:8 | 0.9950 | 1:64 | 0.9824 |
| Euroimmun | 1:4 | 0.9499 | 1:16 | 0.9186 |
| All-AB | ||||
| MP-Bio | 1:64 | 0.9969 | 1:32 | 0.9819 |
| Anti-HEV IgG | ||||
| Wantai | 0.4 (1:256) | 0.9324 | 0.6 (1:32) | 0.9857 |
| Mikrogen | 3.1 (1:32) | 0.9197 | 1.1 (1:16) | 0.9799 |
| MP Biomedical | 1.5 (1:64) | 0.9508 | 1.1 (1:16) | 0.9490 |
| Euroimmun | 1.5 (1:64) | 0.9934 | 1.1 (1:16) | 0.9973 |
| IgM | IgG | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor | Wantai | Mikrogen | MP-Bio | MP-Bio Rapid | Euroimmun | Range Detection | Maximum Difference | Wantai | Mikrogen | MP-Bio | Euroimmun | Range Detection | Maximum Difference | |||||||||||
| Day | SC | Day | SC | Day | SC | Day | SC | Day | SC | Day | SC | Day | SC | Day | SC | Day | SC | |||||||
| 1 | 8 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 13 | 1 | 5–13 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 13 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 8–13 | 5 | ||
| 2 | 35 | 3 | 42 | 2 | 35 | 3 | 35 | 3 | 35 | 3 | 35–42 | 7 | 35 | 3 | 35 | 3 | 35 | 3 | 35 | 3 | 35 | - | ||
| 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 0–8 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0–8 | 8 | ||
| 4 | - | 0 | 42 | 3 | 48 | 2 | 42 | 3 | 42 | 3 | 42–48 | 6 | 21 | 3 | 42 | 2 | 42 | 2 | 42 | 2 | 21–42 | 21 | ||
| 5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | - | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | - | ||
| 6 | 28 | 3 | 28 | 3 | 28 | 3 | 28 | 3 | 28 | 3 | 28 | 0 | 28 | 2 | 28 | 2 | 21 | 3 | 28 | 2 | 21–28 | 7 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 3 | 40 | 3 | 40 | 3 | 40 | 3 | 40 | 3 | 40 | 0 | 40 | 3 | 49 | 2 | 40 | 3 | 40 | 3 | 40–49 | 9 | ||
| 8 | 28 | 3 | 32 | 2 | 28 | 3 | 32 | 2 | - | 0 | 28–32 | 4 | 39 | 2 | 39 | 2 | 32 | 3 | 32 | 3 | 32–39 | 7 | ||
| 9 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | 52 | 3 | - | 0 | 52 | - | 49 | 3 | 49 | 3 | - | 0 | 49 | 3 | 49 | 0 | ||
| 10 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | - | 59 | 3 | 59 | 3 | - | 0 | 59 | 3 | 59 | - | ||
| SC * | 20 | 21 | 23 | 25 | 18 | - | - | 28 | 24 | 23 | 28 | - | - | |||||||||||
| Study Cohort Sens./Spec. (No. Patients/Total) | Assay | Analytical Sensitivity | Sens. (%) | Spec. (%) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT 1 | GT 3 | |||||
| blood donors, GT3 (10/145) WHO Ref., GT1 | Wantai | dilution 1:4 | dilution 1:16 | (+) | n.d. | this study |
| Mikrogen | dilution 1:4 | dilution 1:32 | + | n.d. | ||
| MP-Bio | dilution 1:8 | dilution 1:64 | ++ | n.d. | ||
| Euroimmun | dilution 1:4 | dilution 1:16 | (-) | n.d. | ||
| MP-Bio rapid | n.d. | n.d. | +++ | n.d. | ||
| patients: confirmed HEV infection, GT1 + 3 (36/88) cohort a (98/98) | Wantai | titer >64.000 | titer >64.000 | 75 | >99 | [22] a |
| Mikrogen | titer 32.000 | titer 16.000 | 74 | 99 | ||
| MP-Bio | titer >64.000 | titer 4.000 | 74 | 84 | ||
| patients: acute hepatitis, GT3 (14/52) | Wantai | n.d. | n.d. | 65.4 | n.d. | [26] a |
| Mikrogen | 75.0 | n.d. | ||||
| MP-Bio | 59.6 | n.d. | ||||
| Euroimmun | 61.5 | n.d. | ||||
| patients: acute hepatitis, GT1 + 3 (50/50) patients: HEV-RNA/IgG negative (406/406) | MP Bio | n.d. | n.d. | 88 | 99.5 | [19] |
| MP Bio rapid | 82 | 100 | ||||
| patients: a: suspected (71/71) b: suspected RNA+ (35/35) c: confirmed HEV (55/55) patients: rheumatic factor+, anti-HAV + (104/104) | Wantai | n.d. | n.d. | a: 83.08 b: 97.14 c: 87.27 | 100 | [33] |
| MP-Bio | a: 78.46 b: 74.29 c: 67.27 | 89.11 | ||||
| patients: HEV infection RNA+, GT1-4 (50/50) cohort b (229) | Mikrogen | n.d. | n.d. | 92 | 95.6 | [18] |
| MP-Bio | 72 | 93 | ||||
| patients: suspected HEV infection, GT 1, 3, 4 (309/309) same cohort (309/309) | Mikrogen | n.d. | n.d. | 93.3 | 88.4 | [34] |
| MP-Bio | 80.0 | 86.1 | ||||
| patients: a: immunocompromised (40/40) b: immunocompetent (44/44) blood donors, HEV-RNA/IgG negative (223/223) | Wantai | n.d. | n.d. | a: 85 b: 97.7 | 99.6 | [16] a |
| patients: a: symptomatic (82/82) b: asymptomatic (174/174) cohort c (496/496) | MP-Bio | n.d. | n.d. | a: 42 b: 72 | 74 | [21] a |
| patients: suspected HEV infection, GT unknown (66/66), WHO Ref., GT1, dilution two patient samples * same cohort (66/66) | Mikrogen | 16 IU/mL | *1/53, *1/43 | 38 | 99 | [35] a |
| Euroimmun | 24 IU/mL | *1/35, *1/22 | 24 | 100 | ||
| patients: a: immunocompromised (30/30) b: immunocompetent (30/30) cohort d (60/60) | Wantai | n.d. | n.d. | a: 83.3 b: 96.7 | 96.7 | [36] |
| Study Cohort Sens./Spec. (No. Patients/Total) | Assay | Analytical Sensitivity | Sens. (%) | Spec. (%) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT 1 | GT 3 | |||||
| blood donors, GT3 (10/145) WHO Ref., GT1 | Wantai | 0.4 IU/mL | 0.6 IU/mL | +++ | n.d. | this study |
| Mikrogen | 3.1 IU/mL | 1.1 IU/mL | ++ | n.d. | ||
| MP-Bio | 1.5 IU/mL | 1.1 IU/mL | + | n.d. | ||
| Euroimmun | 1.5 IU/mL | 1.1 IU/mL | +++ | n.d. | ||
| patients: confirmed HEV infection, GT1 + 3 * WHO Ref., GT1 | Wantai | 0.69 IU/mL titer >12,800 * | titer 1.600 * | n.d. | n.d. | [22] a |
| Mikrogen | 3.16 IU/mL titer >12,800 * | titer 3.200 * | n.d. | |||
| MP-Bio | 2.63 IU/mL titer 3200 * | titer 100 * | n.d. | |||
| patients: seroconversion after acute hepatitis (GT3) (10/40) | Wantai | n.d. | n.d. | 72.5 | n.d. | [26] a |
| Mikrogen | 72.5 | n.d. | ||||
| MP-Bio | 70.0 | n.d. | ||||
| Euroimmun | 57.5 | n.d. | ||||
| patients: acute hepatitis (15/15) | Wantai | n.d. | n.d. | 93 | n.d. | [23] a |
| MP Bio | n.d. | n.d. | 53 | n.d. | ||
| patients: a: acute hepatitis b: follow-up acute hepatitis (18/50) | Wantai | 0.25 IU/mL | n.d. | a: 98 b: 100 | n.d. | [17] |
| MP-Bio | 2.5 IU/mL | a: 53 b: 50 | n.d. | |||
| patients: suspected HEV infection (309) same cohort (309/309) | Mikrogen | n.d. | n.d. | 86.7 | 77.9 | [34] |
| MP-Bio | 73.3 | 65.3 | ||||
| patients: a: immunocompromised (40/40) b: immunocompetent (44/44) blood donors, HEV-RNA/IgG negative (223/223) | Wantai | n.d. | n.d. | a: 45 b: 93.2 | 97.8 | [16] a |
| patients: a: symptomatic (82/82) b: asymptomatic (174/174) cohort c (496/496) | MP-Bio | n.d. | n.d. | a: 51 b: 89 | 86 | [21] a |
| blood donors patients: suspected hepatitis E, liver disease, liver transplantation, GT unknown (216/216) WHO Ref., GT1 | Mikrogen | 0.9 IU/mL | n.d. | 62 | 99 | [35] a |
| Euroimmun | 2.2 IU/mL | n.d. | 42 | 99 | ||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vollmer, T.; Diekmann, J.; Eberhardt, M.; Knabbe, C.; Dreier, J. Monitoring of Anti-Hepatitis E Virus Antibody Seroconversion in Asymptomatically Infected Blood Donors: Systematic Comparison of Nine Commercial Anti-HEV IgM and IgG Assays. Viruses 2016, 8, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080232
Vollmer T, Diekmann J, Eberhardt M, Knabbe C, Dreier J. Monitoring of Anti-Hepatitis E Virus Antibody Seroconversion in Asymptomatically Infected Blood Donors: Systematic Comparison of Nine Commercial Anti-HEV IgM and IgG Assays. Viruses. 2016; 8(8):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080232
Chicago/Turabian StyleVollmer, Tanja, Juergen Diekmann, Matthias Eberhardt, Cornelius Knabbe, and Jens Dreier. 2016. "Monitoring of Anti-Hepatitis E Virus Antibody Seroconversion in Asymptomatically Infected Blood Donors: Systematic Comparison of Nine Commercial Anti-HEV IgM and IgG Assays" Viruses 8, no. 8: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080232
APA StyleVollmer, T., Diekmann, J., Eberhardt, M., Knabbe, C., & Dreier, J. (2016). Monitoring of Anti-Hepatitis E Virus Antibody Seroconversion in Asymptomatically Infected Blood Donors: Systematic Comparison of Nine Commercial Anti-HEV IgM and IgG Assays. Viruses, 8(8), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080232





