Spinal Cord Ventral Horns and Lymphoid Organ Involvement in Powassan Virus Infection in a Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and POWV Infection
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Virus Titration
2.4. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.5. Immunohistochemistry for GFAP and CD11b
2.6. Immunofluorescence (IF) in Paraffin Sections
2.7. Dual Staining Protocols
2.8. TUNEL Assay (Terminal Deoxynucleotidyltransferase-Mediated dUTP Nick End-Labeling)
3. Results
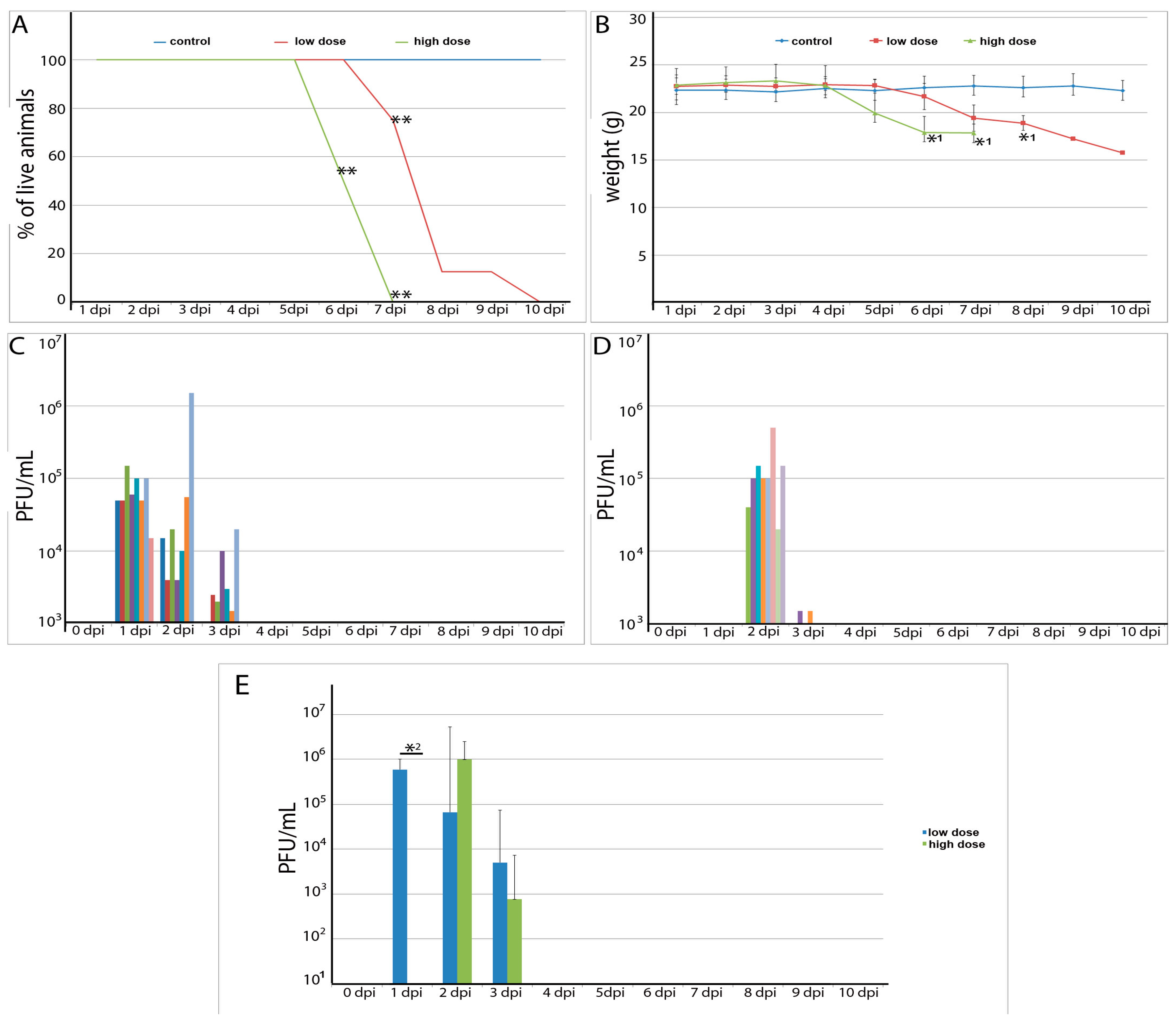
3.1. Clinical Observations
3.2. Viremia
3.3. Histopathological Observations
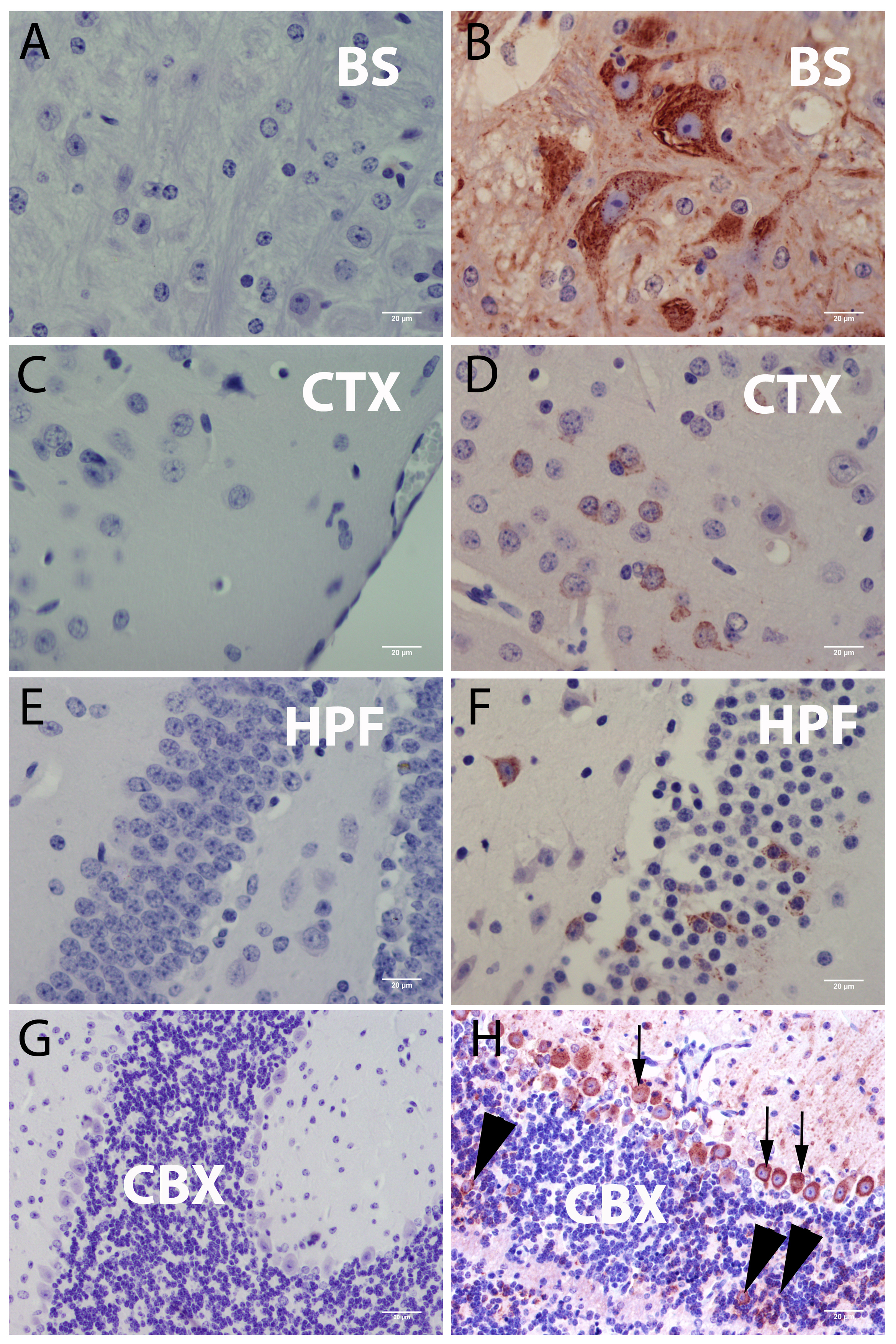
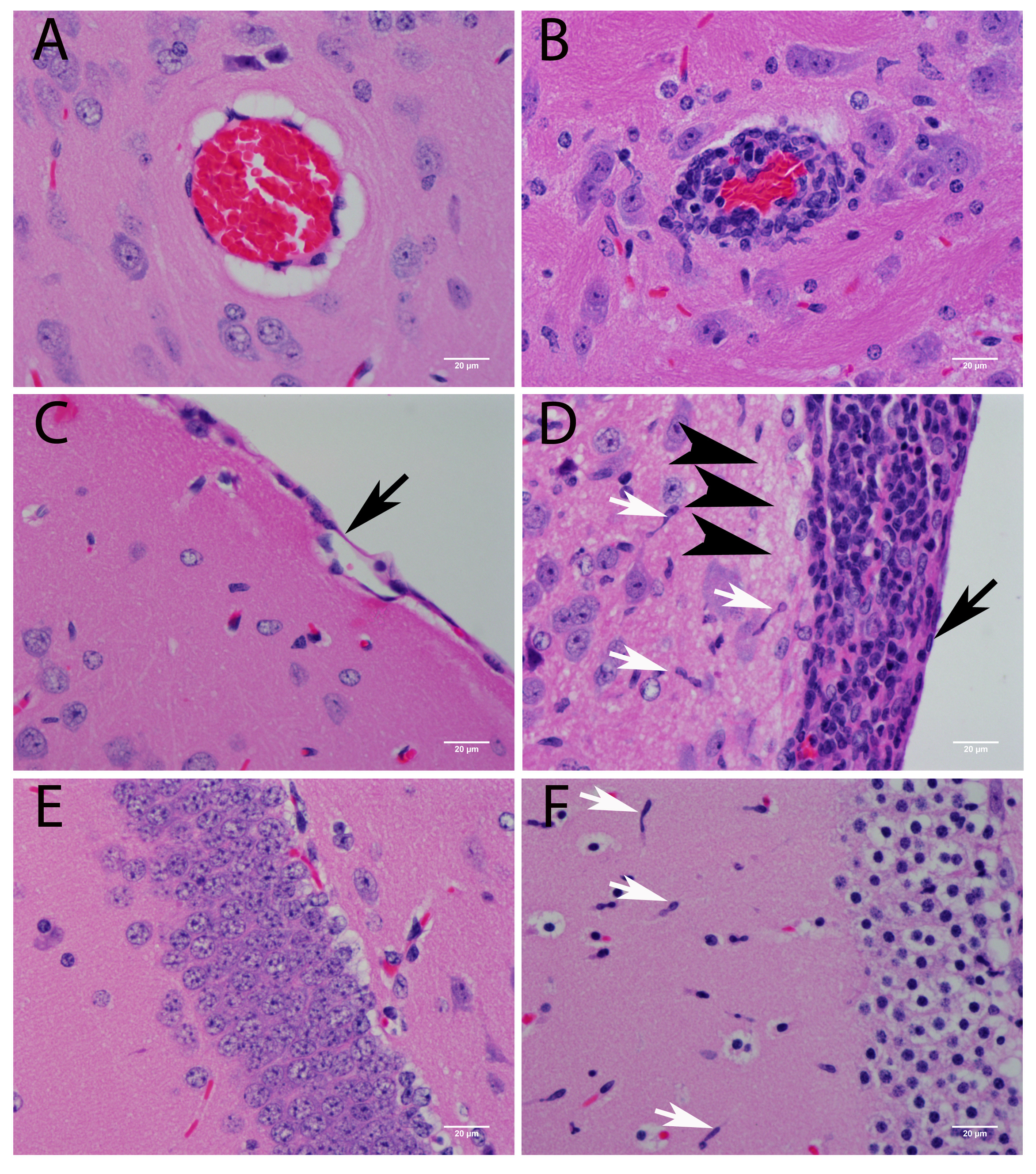
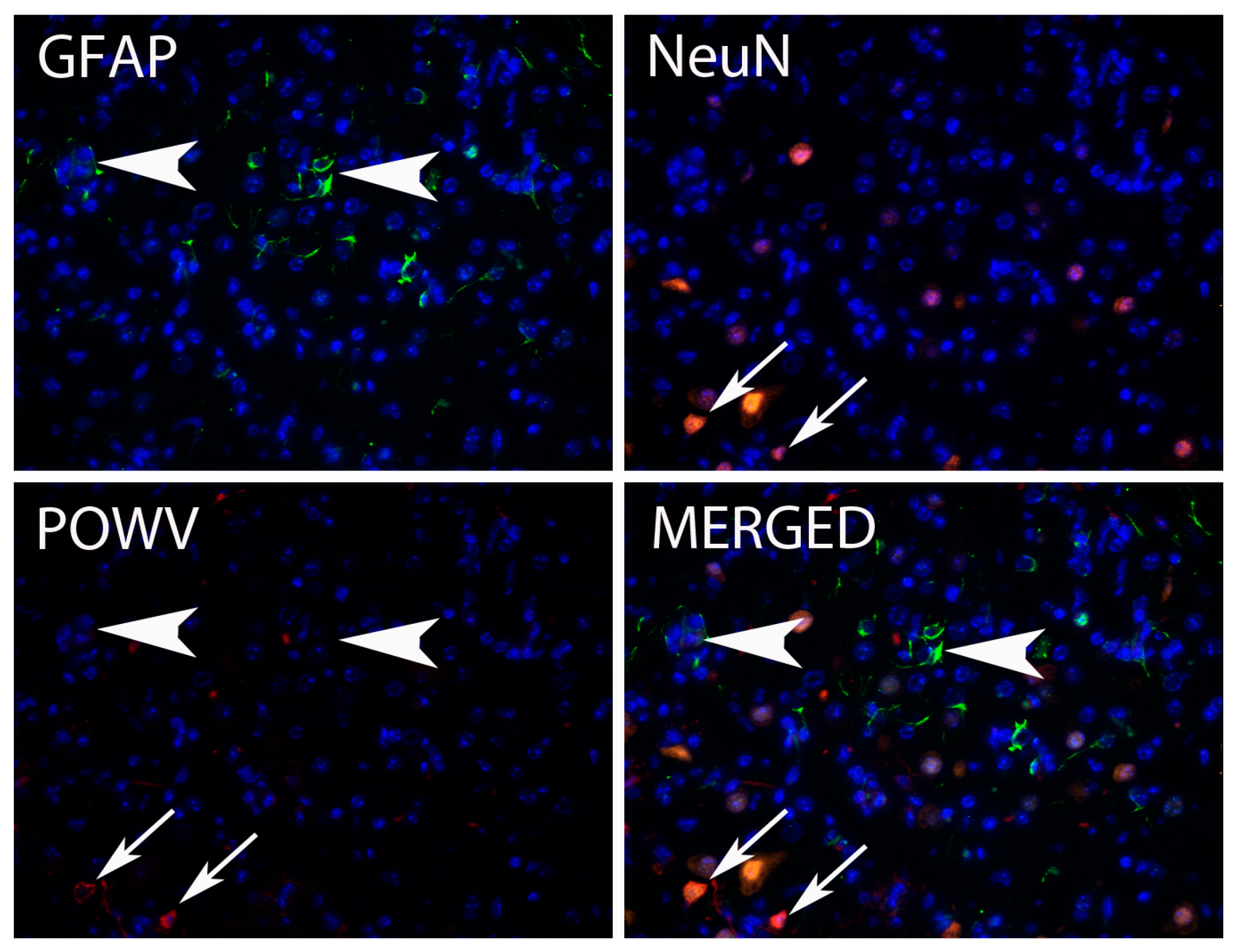
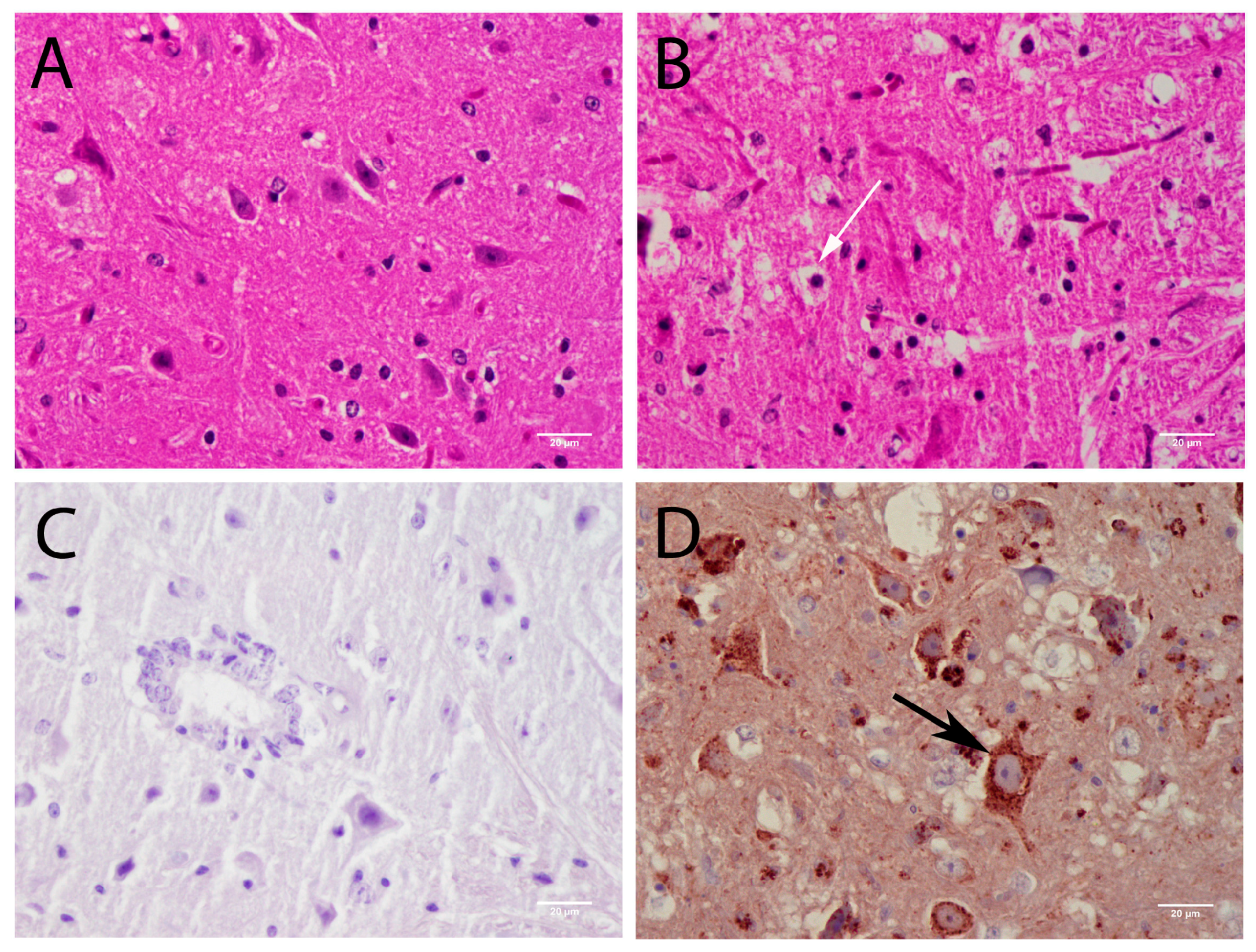
3.3.1. Central Nervous System
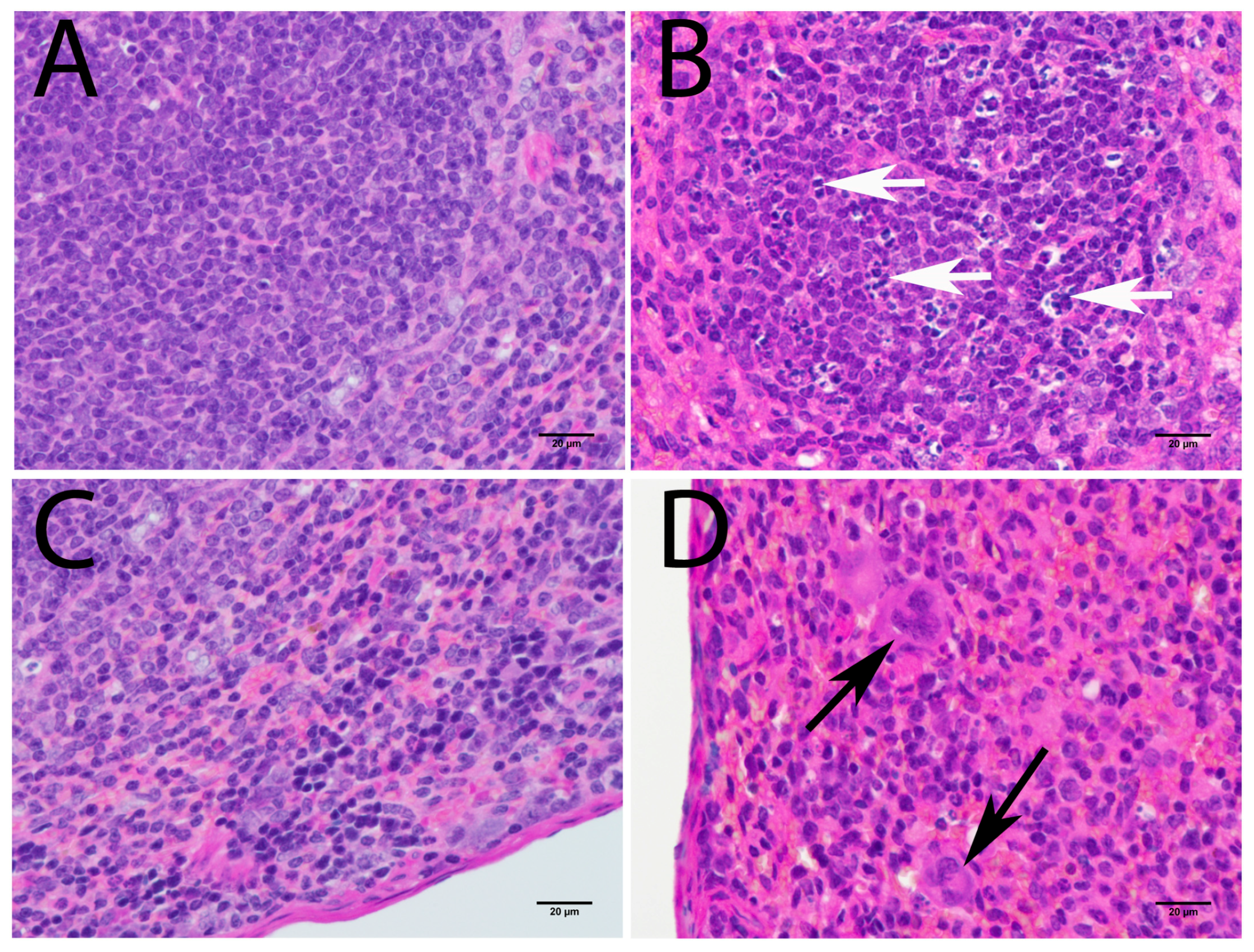
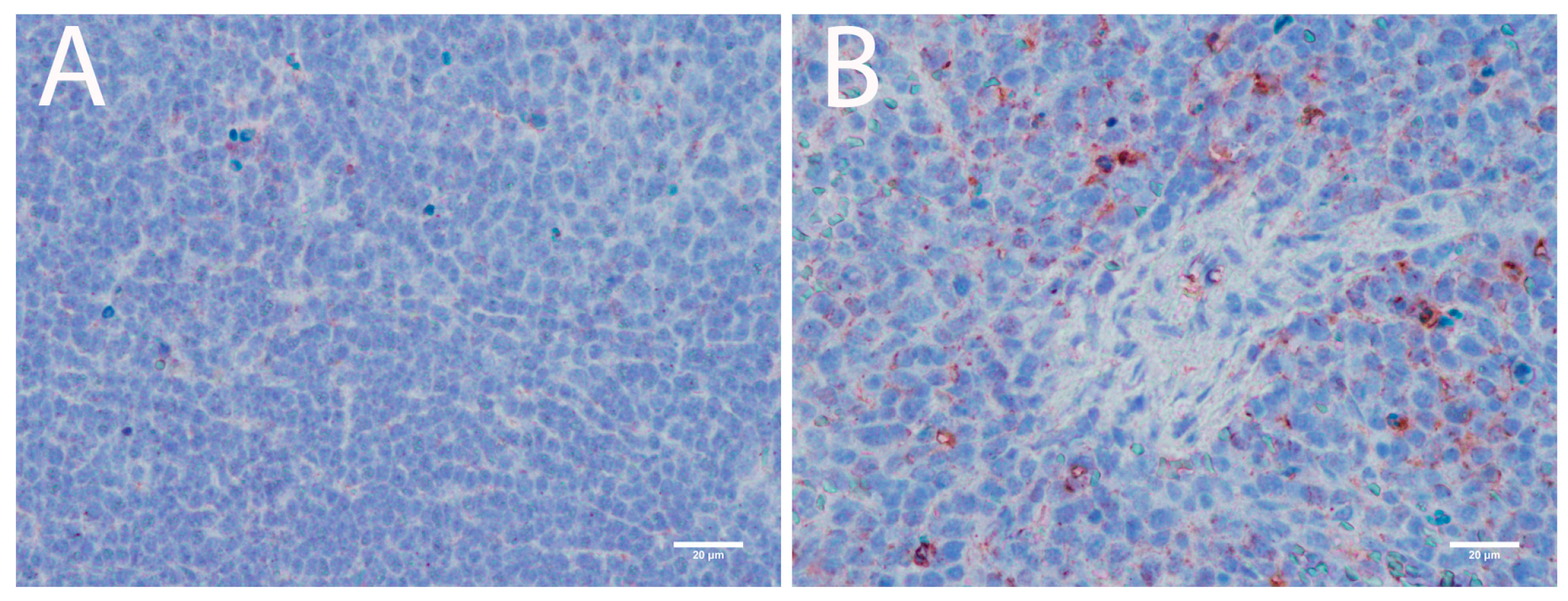
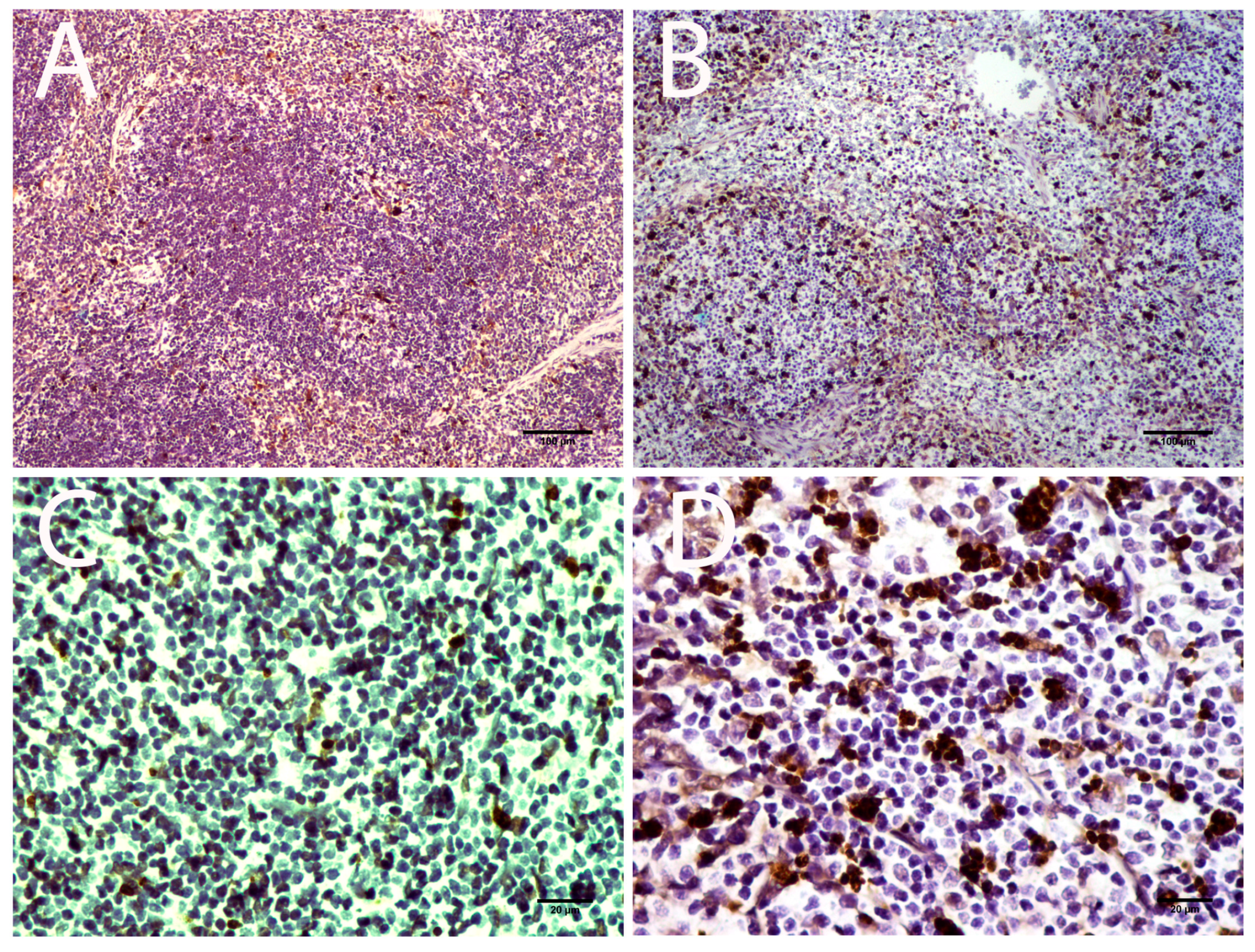
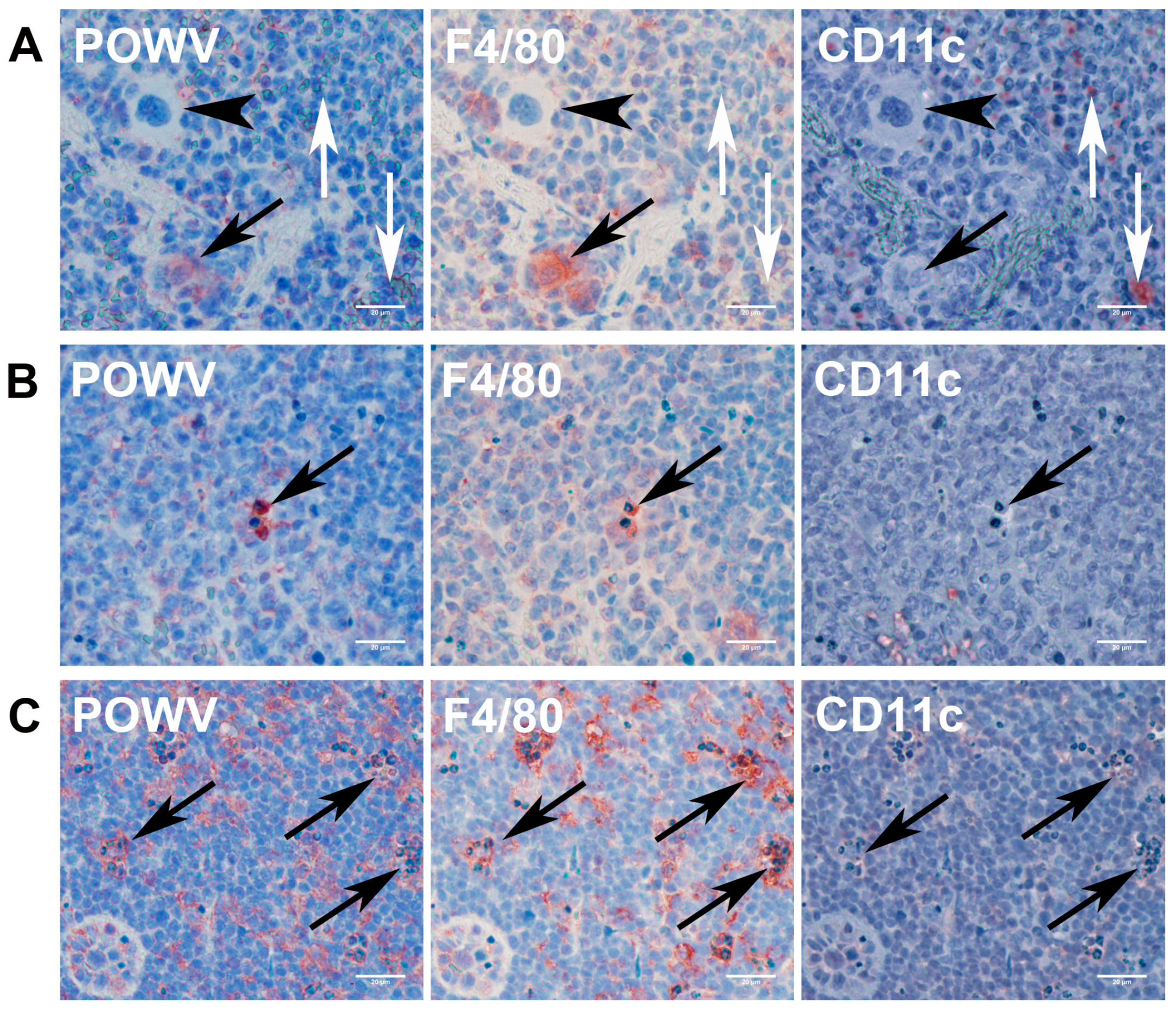
3.3.2. Lymphoid Organs
3.3.3. Nonlymphoid Organs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebel, G.D. Update on powassan virus: Emergence of a North American tick-borne flavivirus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierson, T.C.; Diamond, M.S. Flavivirus. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Grard, G.; Moureau, G.; Charrel, R.N.; Lemasson, J.J.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Gallian, P.; Gritsun, T.S.; Holmes, E.C.; Gould, E.A.; de Lamballerie, X. Genetic characterization of tick-borne flaviviruses: New insights into evolution, pathogenetic determinants and taxonomy. Virology 2007, 361, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Karabatsos, N.; Dalrymple, J.M.; Shope, R.E.; Porterfield, J.S.; Westaway, E.G.; Brandt, W.E. Antigenic relationships between flaviviruses as determined by cross-neutralization tests with polyclonal antisera. J. Gen. Virol. 1989, 70 Pt 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamanin, V.A.; Pletnev, A.G.; Rubin, S.G.; Zlobin, V.I. Differentiation of strains of tick-borne encephalitis virus by means of RNA-DNA hybridization. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71 Pt 7, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotto, P.M.; Gould, E.A.; Gao, G.F.; Harvey, P.H.; Holmes, E.C. Population dynamics of flaviviruses revealed by molecular phylogenies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khoury, M.Y.; Camargo, J.F.; White, J.L.; Backenson, B.P.; Dupuis, A.P., II; Escuyer, K.L.; Kramer, L.; St George, K.; Chatterjee, D.; Prusinski, M.; et al. Potential role of deer tick virus in powassan encephalitis cases in lyme disease-endemic areas of New York, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, N.P.; Wang, H.; Dupuis, M.; Hull, R.; Ebel, G.D.; Gilmore, E.J.; Faust, P.L. Fatal case of deer tick virus encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholam, B.I.; Puksa, S.; Provias, J.P. Powassan encephalitis: A case report with neuropathology and literature review. CMAJ 1999, 161, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raval, M.; Singhal, M.; Guerrero, D.; Alonto, A. Powassan virus infection: Case series and literature review from a single institution. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, D.M.; Donohue, W.L. Powassan virus: Isolation of virus from a fatal case of encephalitis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1959, 80, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinten, S.R.; Beckett, G.A.; Gensheimer, K.F.; Pritchard, E.; Courtney, T.M.; Sears, S.D.; Woytowicz, J.M.; Preston, D.G.; Smith, R.P., Jr.; Rand, P.W.; et al. Increased recognition of powassan encephalitis in the United States, 1999–2005. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008, 8, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease control and Prevention (CDC), Powassan virus. Available online: Http://www.Cdc.Gov/powassan/ (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Smith, R.; Woodall, J.P.; Whitney, E.; Deibel, R.; Gross, M.A.; Smith, V.; Bast, T.F. Powassan virus infection. A report of three human cases of encephalitis. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1974, 127, 691–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolova, M.P.; Isachkova, L.M.; Shestopalova, N.M.; Pogodina, V.V. Experimental encephalitis in monkeys caused by the Powassan virus. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 1985, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isachkova, L.M.; Shestopalova, N.M.; Frolova, M.P.; Reingold, V.N. Light and electron microscope study of the neurotropism of Powassan virus strain p-40. Acta Virol. 1979, 23, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, M.R.; Aronson, J.F.; Campbell, G.A.; Jones, S.; Feldmann, H.; Barrett, A.D. An animal model for the tickborne flavivirus—Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebel, G.D.; Kramer, L.D. Short report: Duration of tick attachment required for transmission of Powassan virus by deer ticks. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruzek, D.; Dobler, G.; Donoso Mantke, O. Tick-borne encephalitis: Pathogenesis and clinical implications. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2010, 8, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayasaka, D.; Nagata, N.; Fujii, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Sata, T.; Suzuki, R.; Gould, E.A.; Takashima, I.; Koike, S. Mortality following peripheral infection with tick-borne encephalitis virus results from a combination of central nervous system pathology, systemic inflammatory and stress responses. Virology 2009, 390, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, M.; Yoshii, K.; Sakai, M.; Hasebe, R.; Ichii, O.; Kariwa, H. Tick-borne flaviviruses alter membrane structure and replicate in dendrites of primary mouse neuronal cultures. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bily, T.; Palus, M.; Eyer, L.; Elsterova, J.; Vancova, M.; Ruzek, D. Electron tomography analysis of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in human neurons. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Baer, A.; Kehn-Hall, K. Viral concentration determination through plaque assays: Using traditional and novel overlay systems. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e52065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, M.; Teletin, M.; Antal, C.; Wendling, O.; Auwerx, J.; Heikkinen, S.; Khetchoumian, K.; Argmann, C.A.; Dgheem, M. Histopathology in mouse metabolic investigations. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, K.M.; Messing, A.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. A novel modification of the avidin-biotin complex method for immunohistochemical studies of transgenic mice with murine monoclonal antibodies. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1992, 40, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.R.; Shi, S.R.; Chen, C.; Young, L.; Yang, C.; Cote, R.J. Comparative study of antigen retrieval heating methods: Microwave, microwave and pressure cooker, autoclave, and steamer. Biotech. Histochem. 1996, 71, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierck, B.P.; Iperen, L.V.; Gittenberger-De Groot, A.C.; Poelmann, R.E. Modified indirect immunodetection allows study of murine tissue with mouse monoclonal antibodies. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1994, 42, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, R.; Friedl, P. Detection of immobilized proteins on nitrocellulose membranes using a biotinylation-dependent system. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 273, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.I.; Almeida, M.F.; Paula, F.E.; Rodrigues, A.H.; Saranzo, A.M.; Paula, A.E.; Silva, M.L.; Correa, V.M.; Acrani, G.O.; Neder, L.; et al. Experimental infection of suckling mice by subcutaneous inoculation with Oropouche virus. Virus Res. 2012, 170, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, M.S.; Martins, T.C.; Seco, F.; do Carmo, A. An improved and cost-effective methodology for the reduction of autofluorescence in direct immunofluorescence studies on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Eur. J. Histochem. 2007, 51, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mullen, R.J.; Buck, C.R.; Smith, A.M. NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 1992, 116, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valentino, K.L.; Jones, E.G.; Kane, S.A. Expression of GFAP immunoreactivity during development of long fiber tracts in the rat CNS. Brain Res. 1983, 285, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaissi, E.; Mostratos, A. Assessment of substrates for horseradish peroxidase in enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 58, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinryb, I. The behavior of horseradish peroxidase at high hydrogen peroxide concentrations. Biochemistry 1966, 5, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolman, D.; Newell, G.A.; Thurlow, M.D. A kinetic study of the reaction of horseradish peroxidase with hydrogen peroxide. Can. J. Biochem. 1975, 53, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrieli, Y.; Sherman, Y.; Ben-Sasson, S.A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 119, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.E.; Pennell, R.I.; Meijer, P.J.; Ishikawa, A.; Dixon, R.A.; Lamb, C. Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell 1998, 92, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, T.; Galfre, G.; Secher, D.S.; Milstein, C. Monoclonal xenogeneic antibodies to murine cell surface antigens: Identification of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens. Eur. J. Immunol. 1978, 8, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelpi, E.; Preusser, M.; Garzuly, F.; Holzmann, H.; Heinz, F.X.; Budka, H. Visualization of central european tick-borne encephalitis infection in fatal human cases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, G.L.; Marfin, A.A.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Gubler, D.J. West Nile virus. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratkin, J.D.; Leis, A.A.; Stokic, D.S.; Slavinski, S.A.; Geiss, R.W. Spinal cord neuropathology in human West Nile virus infection. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2004, 128, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bogovic, P.; Lotric-Furlan, S.; Strle, F. What tick-borne encephalitis may look like: Clinical signs and symptoms. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2010, 8, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aendekerk, R.P.; Schrivers, A.N.; Koehler, P.J. Tick-borne encephalitis complicated by a polio-like syndrome following a holiday in central Europe. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 1996, 98, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, S.; Brune, N.; Kesselring, J. Detection of anterior horn lesions by MRI in central European tick-borne encephalomyelitis. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellinger, P.D.; Schmutzhard, E.; Fiebach, J.B.; Pfausler, B.; Maier, H.; Schwab, S. Poliomyelitic-like illness in central European encephalitis. Neurology 2000, 55, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossier, E.; Harrison, R.J.; Lemieux, B. A case of Powassan virus encephalitis. CMAJ 1974, 110, 1173–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.S.; Wherrett, B.A.; Mahdy, M.S. Powassan virus meningoencephalitis: A case report. CMAJ 1979, 121, 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- Hicar, M.D.; Edwards, K.; Bloch, K. Powassan virus infection presenting as acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in Tennessee. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.C. Leg weakness associated with Powassan virus infection—Ontario. Can. Dis. Wkly. Rep. 1989, 15, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.B.; Costantini, F.; Gorgacz, E.J.; Lee, J.J.; Racaniello, V.R. Transgenic mice expressing a human poliovirus receptor: A new model for poliomyelitis. Cell 1990, 63, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, R.J.; Schittone, S.A.; Tyler, K.L. Experimental reovirus-induced acute flaccid paralysis and spinal motor neuron cell death. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, B.; Gottlieb, D.; Diamond, M.S. Infection and injury of neurons by West Nile encephalitis virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13203–13213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, J.; Payne, J.; Harper, J.; Frazer, L.; Eastwood, S.; Wilson, S.; Lowther, S.; Lunt, R.; Warner, S.; Carr, M.; et al. Evaluation of a mouse model for the West Nile virus group for the purpose of determining viral pathotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillpotts, R.J.; Stephenson, J.R.; Porterfield, J.S. Antibody-dependent enhancement of tick-borne encephalitis virus infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 1985, 66, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahantarig, A.; Ruzek, D.; Vancova, M.; Janowitz, A.; St'astna, H.; Tesarova, M.; Grubhoffer, L. Tick-borne encephalitis virus infection of cultured mouse macrophages. Intervirology 2009, 52, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecky, J.; Grubhoffer, L.; Tomkova, E. Interaction of tick/borne encephalitis virus with mouse peritoneal macrophages. The effect of antiviral antibody and lectin. Acta Virol. 1991, 35, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Labuda, M.; Austyn, J.M.; Zuffova, E.; Kozuch, O.; Fuchsberger, N.; Lysy, J.; Nuttall, P.A. Importance of localized skin infection in tick-borne encephalitis virus transmission. Virology 1996, 219, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkova, D. The significance of the skin and the regional lymph nodes in the penetration and multiplication of tickborne encephalitis virus after subcutaneous infection of mice. Acta Virol. 1968, 12, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McNally, A.K.; Anderson, J.M. Macrophage fusion and multinucleated giant cells of inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 713, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helming, L.; Gordon, S. The molecular basis of macrophage fusion. Immunobiology 2007, 212, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, L.C.; Jenkins, S.J.; Allen, J.E.; Taylor, P.R. Tissue-resident macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Haan, J.M.; Kraal, G. Innate immune functions of macrophage subpopulations in the spleen. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, R.I.; Hermance, M.E.; Gelman, B.B.; Thangamani, S. Spinal Cord Ventral Horns and Lymphoid Organ Involvement in Powassan Virus Infection in a Mouse Model. Viruses 2016, 8, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080220
Santos RI, Hermance ME, Gelman BB, Thangamani S. Spinal Cord Ventral Horns and Lymphoid Organ Involvement in Powassan Virus Infection in a Mouse Model. Viruses. 2016; 8(8):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080220
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Rodrigo I., Meghan E. Hermance, Benjamin B. Gelman, and Saravanan Thangamani. 2016. "Spinal Cord Ventral Horns and Lymphoid Organ Involvement in Powassan Virus Infection in a Mouse Model" Viruses 8, no. 8: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080220
APA StyleSantos, R. I., Hermance, M. E., Gelman, B. B., & Thangamani, S. (2016). Spinal Cord Ventral Horns and Lymphoid Organ Involvement in Powassan Virus Infection in a Mouse Model. Viruses, 8(8), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080220





