Cross-Species Antiviral Activity of Goose Interferons against Duck Plague Virus Is Related to Its Positive Self-Feedback Regulation and Subsequent Interferon Stimulated Genes Induction
Abstract
:1 Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.3. Viral TCID50 Detection
2.4. RNA Isolation and Real-Time qPCR
2.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.6. Detection of Viral Copies
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
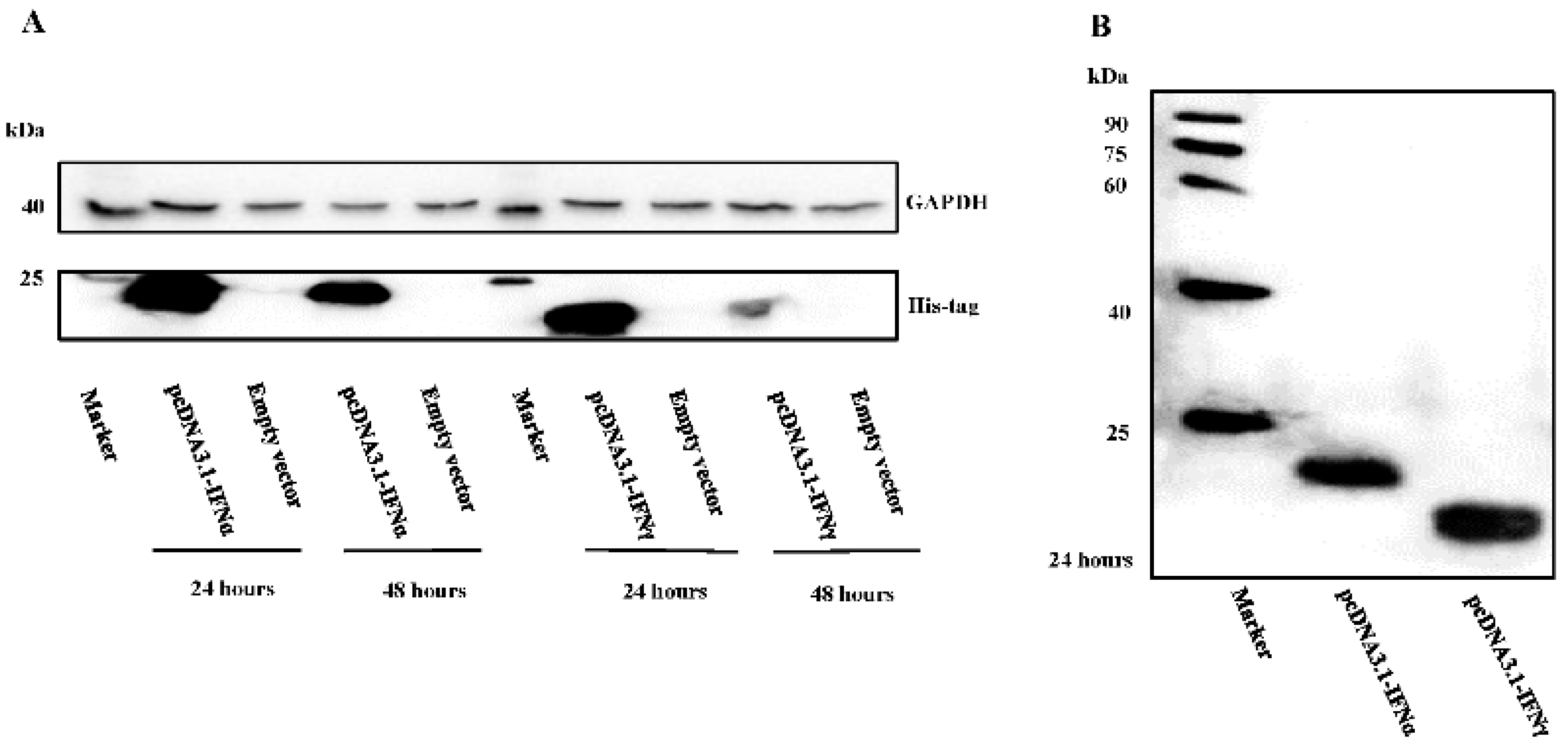
3.1. Characterization of Goose IFNα and IFNγ Expression
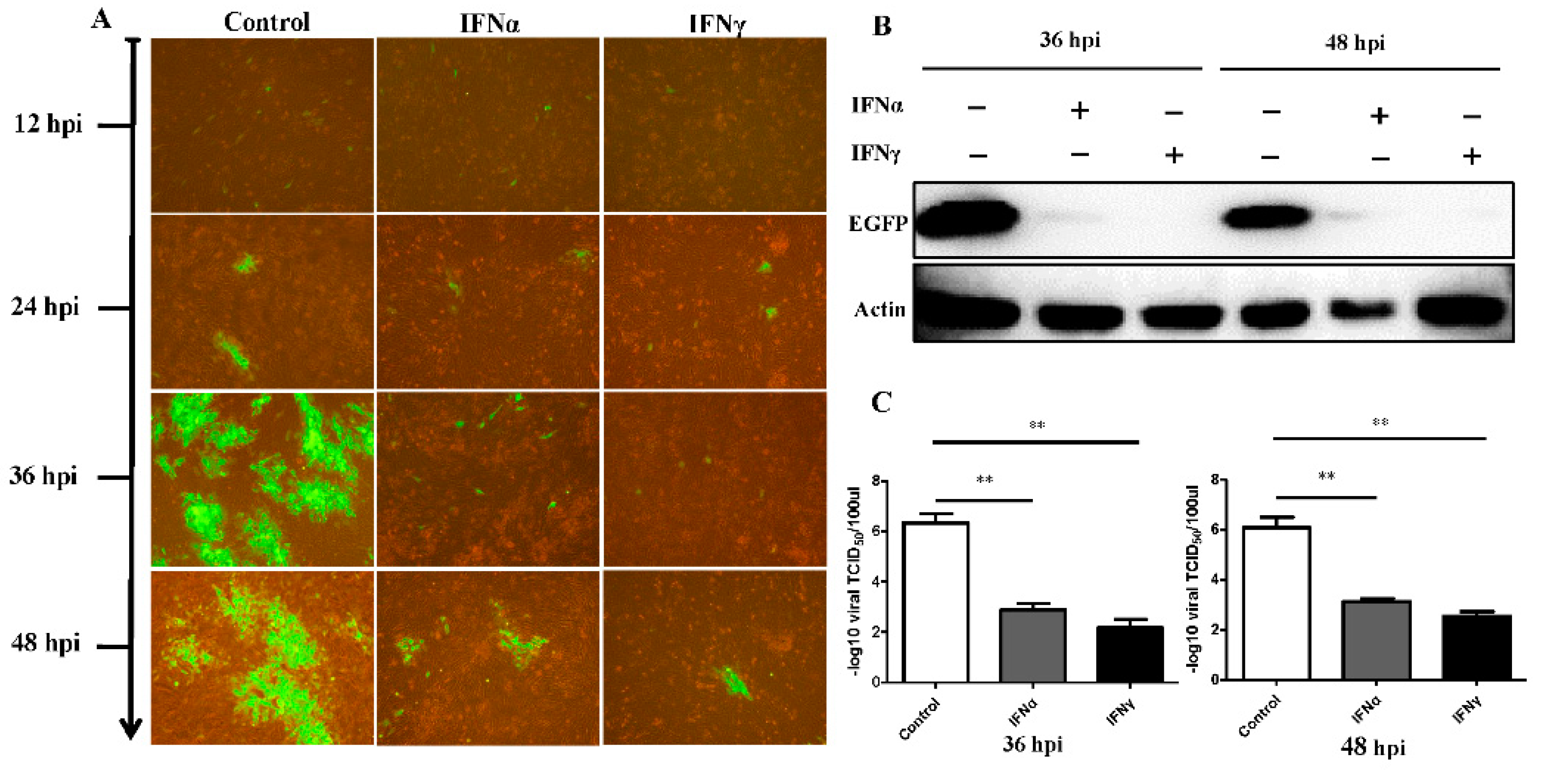
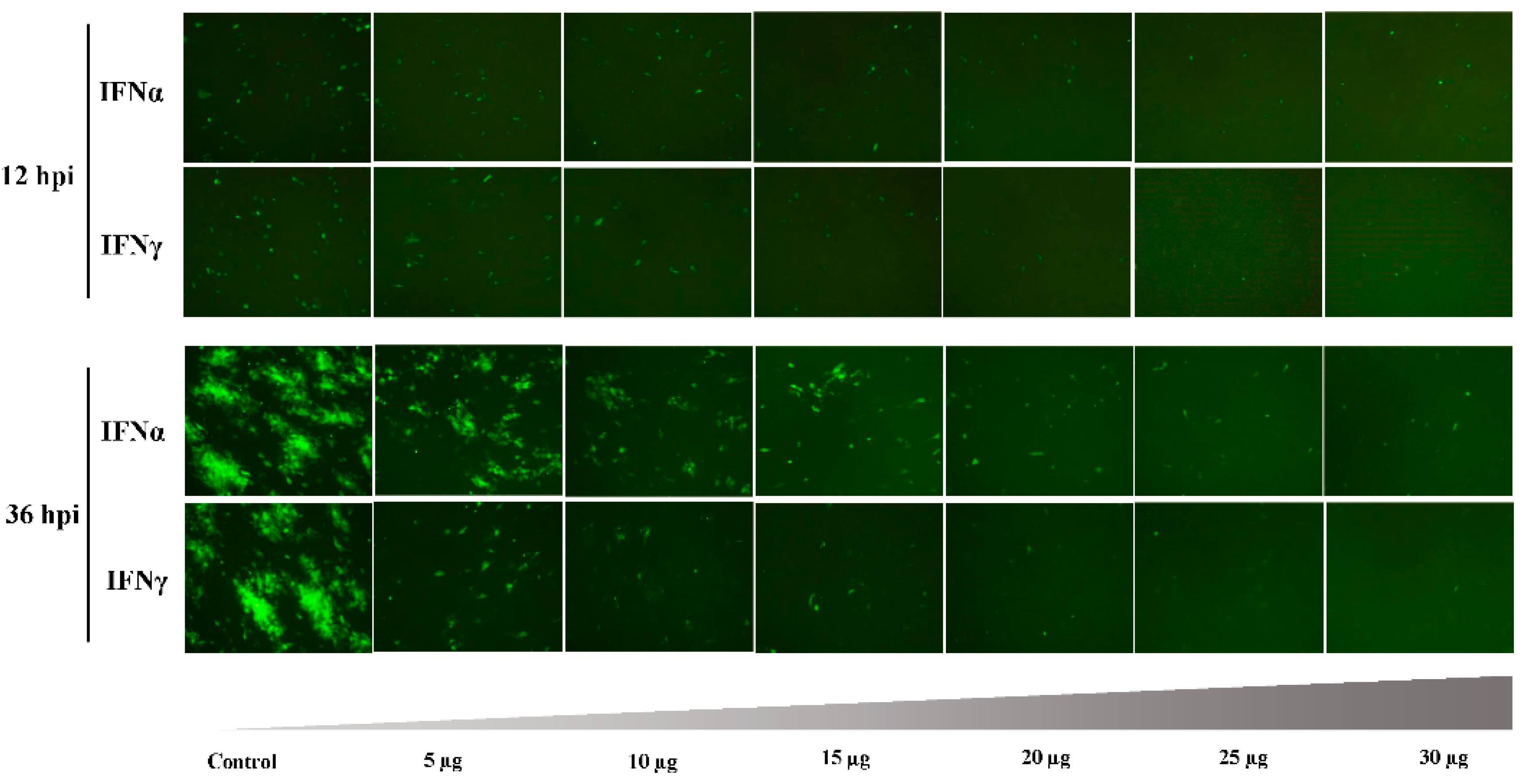
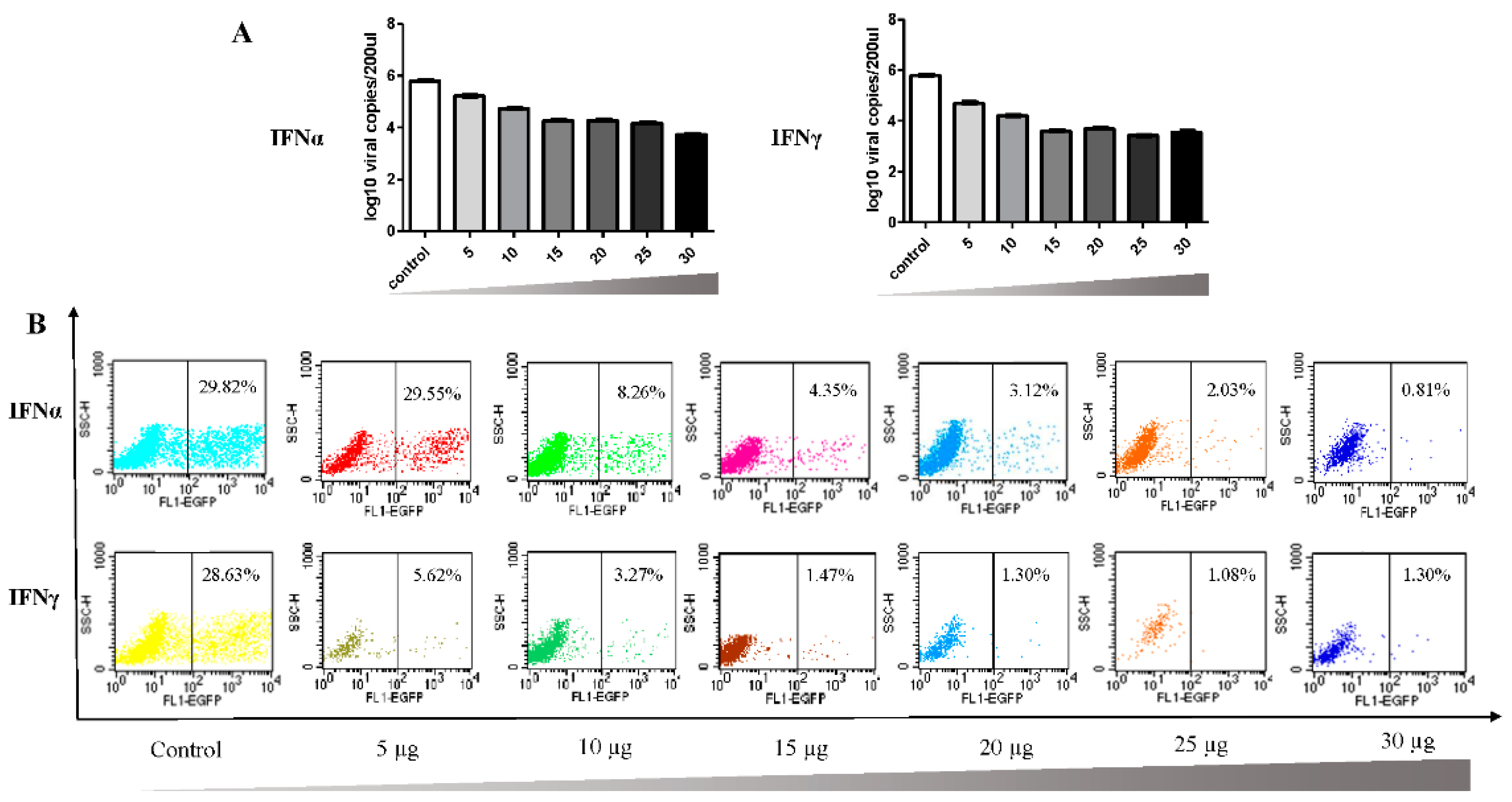
3.2. Antiviral Effect of Goose IFNα and IFNγ
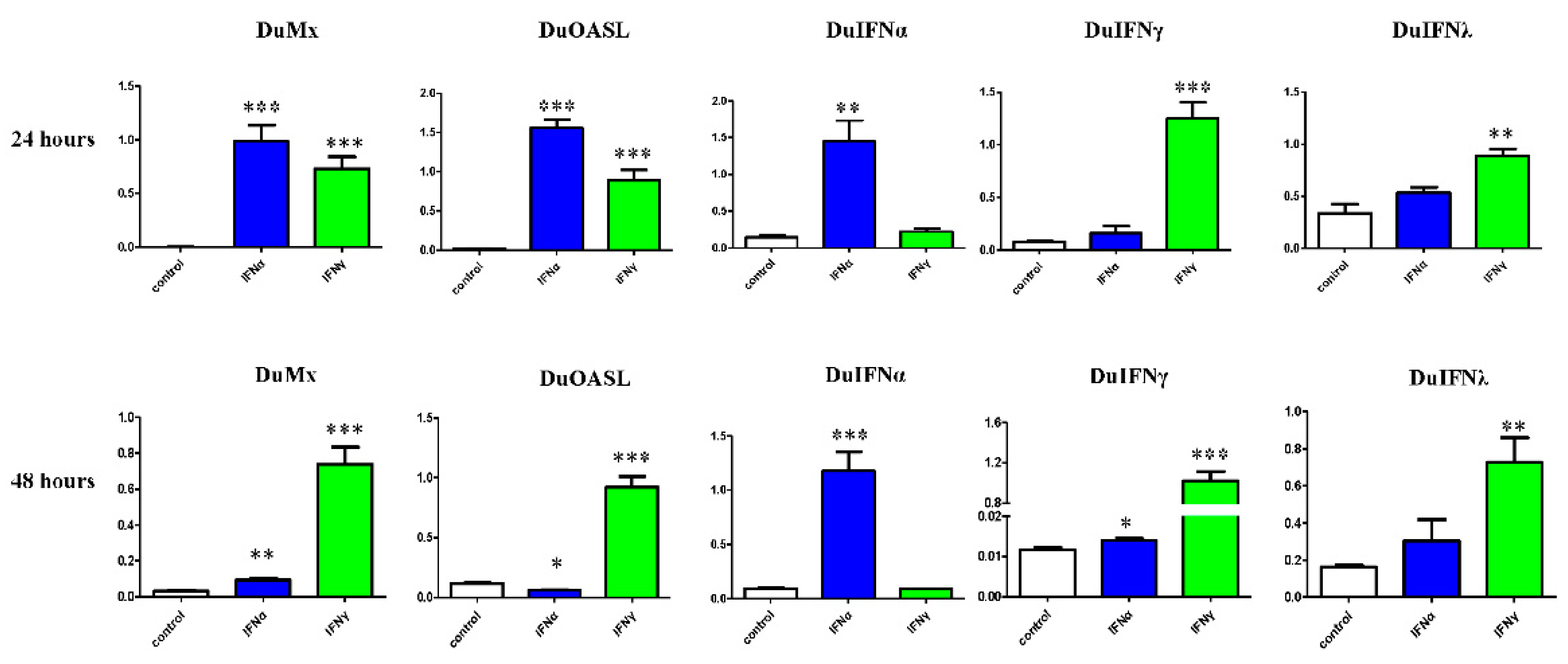
3.3. GEFs and DEFs Display Similar Positive Feedback Regulation by Goose IFN and Subsequent ISG Induction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRRs | pattern recognition receptors |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| IFN | interferon |
| Mx | myxovirus resistance |
| OASL | oligoadenylate synthetases-like |
| ISGs | IFN-stimulated genes |
| DPV | duck plague virus |
| IBV | infectious bronchitis virus |
| IBDV | infectious bursal disease virus |
| MDV | Marek’s disease virus |
References
- Samuel, C.E. Antiviral actions of interferons. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 778–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, A.J.; Williams, B.R. Interferon-inducible antiviral effectors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; Sekellick, M.J.; Marcus, P.I.; Choi, I.S.; Collisson, E.W. Chicken interferon type I inhibits infectious bronchitis virus replication and associated respiratory illness. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2001, 21, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, C.W.; Cao, Y.C.; Lim, B.L. The in vivo and in vitro effects of chicken interferon α on infectious bursal disease virus and newcastle disease virus infection. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.M.; Heller, E.D.; Leitner, G.; Davidson, I. Effect of native chicken interferon on MDV replication. Acta Virol. 1999, 43, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zeng, Y.; Yin, J.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Ren, X. Cloning, prokaryotic expression, and biological analysis of recombinant chicken IFN-gamma. Hybridoma 2010, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, U.; Kock, J.; Schlicht, H.J.; Staeheli, P. Recombinant duck interferon: A new reagent for studying the mode of interferon action against hepatitis B virus. Virology 1995, 212, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, U.; Chisari, F.V. Recombinant duck interferon gamma inhibits duck hepatitis B virus replication in primary hepatocytes. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3162–3168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.T.; Ma, B.; Mi, J.W.; Jin, H.Y.; Xu, L.N.; Wang, J.W. Cloning, in vitro expression and bioactivity of goose interferon α. Cytokine 2006, 34, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.T.; Ma, B.; Mi, J.W.; Jin, H.Y.; Xu, L.N.; Wang, J.W. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of goose interferon γ. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 117, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, M.; Karaca, K.; Foster, D.; Sharma, J.M. Molecular and functional characterization of turkey interferon. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 8159–8163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, P.; Sonnemans, D.; Smith, L.M. Avian IFN-γ genes: Sequence analysis suggests probable cross-species reactivity among galliforms. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998, 18, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, O.; Staeheli, P.; Schwemmle, M.; Kochs, G. Mx GTPases: Dynamin-like antiviral machines of innate immunity. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Ghosh, A.; Sarkar, S.N. OASL—A new player in controlling antiviral innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 12, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, S.; Roberts, P.C.; Brown, L.E.; Truong, H.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Archer, D.R.; Barber, G.N. Essential role for the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase PKR in innate immunity to viral infection. Immunity 2000, 13, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Takaoka, A.; Taniguchi, T. Type I interferon gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 2006, 25, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaoka, A.; Yanai, H. Interferon signalling network in innate defence. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spieker, J.O.; Yuill, T.M.; Burgess, E.C. Virulence of six strains of duck plague virus in eight waterfowl species. J. Wildl. Dis. 1996, 32, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keel, M.K.; Stallknecht, D.; Cobb, D.; Cunningham, M.; Goekjian, V.; Gordon-Akhvlediani, S.; Fischer, J.R. The epizootiology of anatid herpesvirus 1 infection in free-flying waterfowl: A comparison of latent and active infections among native waterfowl, captive-reared released ducks, and peridomestic or feral ducks. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Qu, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, D.; Liu, L.; Li, N.; Yue, R.; Li, C.; Liu, S. The comprehensive diagnosis and prevention of duck plague in northwest Shandong Province of China. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2892–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniakowski, G.; Samorek-Salamonowicz, E. First survey of the occurrence of duck enteritis virus (DEV) in free-ranging Polish water birds. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savan, R.; Ravichandran, S.; Collins, J.R.; Sakai, M.; Young, H.A. Structural conservation of interferon gamma among vertebrates. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmyter, J.; Rawls, W.E.; Melnick, J.L. A human interferon that crosses the species line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 59, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresser, I.; Bandu, M.T.; Brouty-boye, D.; Tovey, M. Pronounced antiviral activity of human interferon on bovine and porcine cells. Nature 1974, 251, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckler, C.E.; Baron, S. Antiviral action of mouse interferon in heterologous cells. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 91, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fringuelli, E.; Urbanelli, L.; Tharuni, O.; Proietti, P.C.; Bietta, A.; Davidson, I.; Franciosini, M.P. Cloning and expression of pigeon IFN-γ gene. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhelst, J.; Hulpiau, P.; Saelens, X. Mx proteins: Antiviral gatekeepers that restrain the uninvited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Silverman, R.H. 2-5A-dependent RNase molecules dimerize during activation by 2-5A. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 4133–4137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Justesen, J.; Hartmann, R.; Kjeldgaard, N.O. Gene structure and function of the 2’-5’-oligoadenylate synthetase family. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 1593–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, R.H. Viral encounters with 2’,5’-oligoadenylate synthetase and RNase L during the interferon antiviral response. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12720–12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.C.; Moore, P.A.; LaFleur, D.W.; Tombal, B.; Pitha, P.M. Characterization of the interferon regulatory factor-7 and its potential role in the transcription activation of interferon a genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29210–29217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, I.; Durbin, J.E.; Levy, D.E. Differential viral induction of distinct interferon-α genes by positive feedback through interferon regulatory factor-7. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6660–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magor, K.E.; Miranzo Navarro, D.; Barber, M.R.; Petkau, K.; Fleming-Canepa, X.; Blyth, G.A.; Blaine, A.H. Defense genes missing from the flight division. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Primer Name | Nucleotide Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Goose | IFNα (F) | CAGCACCACATCCACCAC |
| IFNα (R) | TACTTGTTGATGCCGAGGT | |
| IFNγ (F) | TGAGCCAGATTGTTTCCC | |
| IFNγ (R) | CAGGTCCACGAGGTCTTT | |
| IFNλ (F) | GAGCTCTCGGTGCCCGACC | |
| IFNλ (R) | CTCAGCGGCCACGCAGCCT | |
| Mx (F) | TTCACAGCAATGGAAAGGGA | |
| Mx (R) | ATTAGTGTCGGGTCTGGGA | |
| OASL (F) | CAGCGTGTGGTGGTTCTC | |
| OASL (R) | AACCAGACGATGACATACAC | |
| actin (F) | CCGTGACATCAAGGAGAA | |
| actin (R) | GAAGGATGGCTGGAAGAG | |
| Duck | IFNα (F) | TCCTCCAACACCTCTTCGAC |
| IFNα (R) | GGGCTGTAGGTGTGGTTCTG | |
| IFNγ (F) | CATACTGAGCCAGATTGTTACCC | |
| IFNγ (R) | TCACAGCCTTGCGTTGGA | |
| IFNλ (F) | GTGCCTGACCGACTCCTCCT | |
| IFNλ (R) | CCCAGAGGGCTGATGCGAAG | |
| Mx (F) | TGCTGTCCTTCATGACTTCG | |
| Mx (R) | GCTTTGCTGAGCCGATTAAC | |
| OASL (F) | TCTTCCTCAGCTGCTTCTCC | |
| OASL (R) | ACTTCGATGGACTCGCTGTT | |
| β-actin (F) | GATCACAGCCCTGGCACC | |
| β-actin (R) | CGGATTCATCATACTCCTGCTT | |
| DPV | UL30 (F) | TTTCCTCCTCCTCGCTGAGTG |
| UL30 (R) | CCAGAAACATACTGTGAGAGTG | |
| Plasmid construction | pcDNA-IFNα (F) | CTA GCTAGC GACATGGAC TGCAGCCCCCTGCGCCTCCACGACAG |
| pcDNA-IFNα (R) | CGG GAATTC TTA GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTG GCGCATGGCGCGGGTGAGGCG | |
| pcDNA-IFNγ (F) | CTA GCTAGC GACATGGAC TGTTCTGGAAGTGCTCTATTTCTTAG | |
| pcDNA-IFNγ (R) | CGG GAATTC TTA GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTG ACATCTGCATCTCTTTGGAGAC | |
| Plasmid construction | pEGFP-IFNα (F) | ATCTCGAGCTCAAGCTTC GAATTC ATGCCTGGGCCATCAGCCCCAC |
| (one-step cloning) | pEGFP-IFNα (R) | GGTGGATCCCGGGCCCGC GGTACC AC GCGCATGGCGCGGGTGAGGCG |
| pEGFP-IFNγ (F) | ATCTCGAGCTCAAGCTTC GAATTC GCCACC ATGACTTGCCAGACCTACTGCTTG | |
| pEGFP-IFNγ (R) | GGTGGATCCCGGGCCCGC GGTACC AC ACATCTGCATCTCTTTGGAGAC |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, Y.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.; Yang, Q.; et al. Cross-Species Antiviral Activity of Goose Interferons against Duck Plague Virus Is Related to Its Positive Self-Feedback Regulation and Subsequent Interferon Stimulated Genes Induction. Viruses 2016, 8, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070195
Zhou H, Chen S, Zhou Q, Wei Y, Wang M, Jia R, Zhu D, Liu M, Liu F, Yang Q, et al. Cross-Species Antiviral Activity of Goose Interferons against Duck Plague Virus Is Related to Its Positive Self-Feedback Regulation and Subsequent Interferon Stimulated Genes Induction. Viruses. 2016; 8(7):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070195
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Hao, Shun Chen, Qin Zhou, Yunan Wei, Mingshu Wang, Renyong Jia, Dekang Zhu, Mafeng Liu, Fei Liu, Qiao Yang, and et al. 2016. "Cross-Species Antiviral Activity of Goose Interferons against Duck Plague Virus Is Related to Its Positive Self-Feedback Regulation and Subsequent Interferon Stimulated Genes Induction" Viruses 8, no. 7: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070195
APA StyleZhou, H., Chen, S., Zhou, Q., Wei, Y., Wang, M., Jia, R., Zhu, D., Liu, M., Liu, F., Yang, Q., Wu, Y., Sun, K., Chen, X., & Cheng, A. (2016). Cross-Species Antiviral Activity of Goose Interferons against Duck Plague Virus Is Related to Its Positive Self-Feedback Regulation and Subsequent Interferon Stimulated Genes Induction. Viruses, 8(7), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070195






