HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma—A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ
Abstract
:1. HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia
2. HTLV-1 Viral Gene Expression and Regulation
3. HTLV-1 Infection and Its Outcomes
3.1. HTLV-1 Transmission Requires Cell-to-Cell Contacts
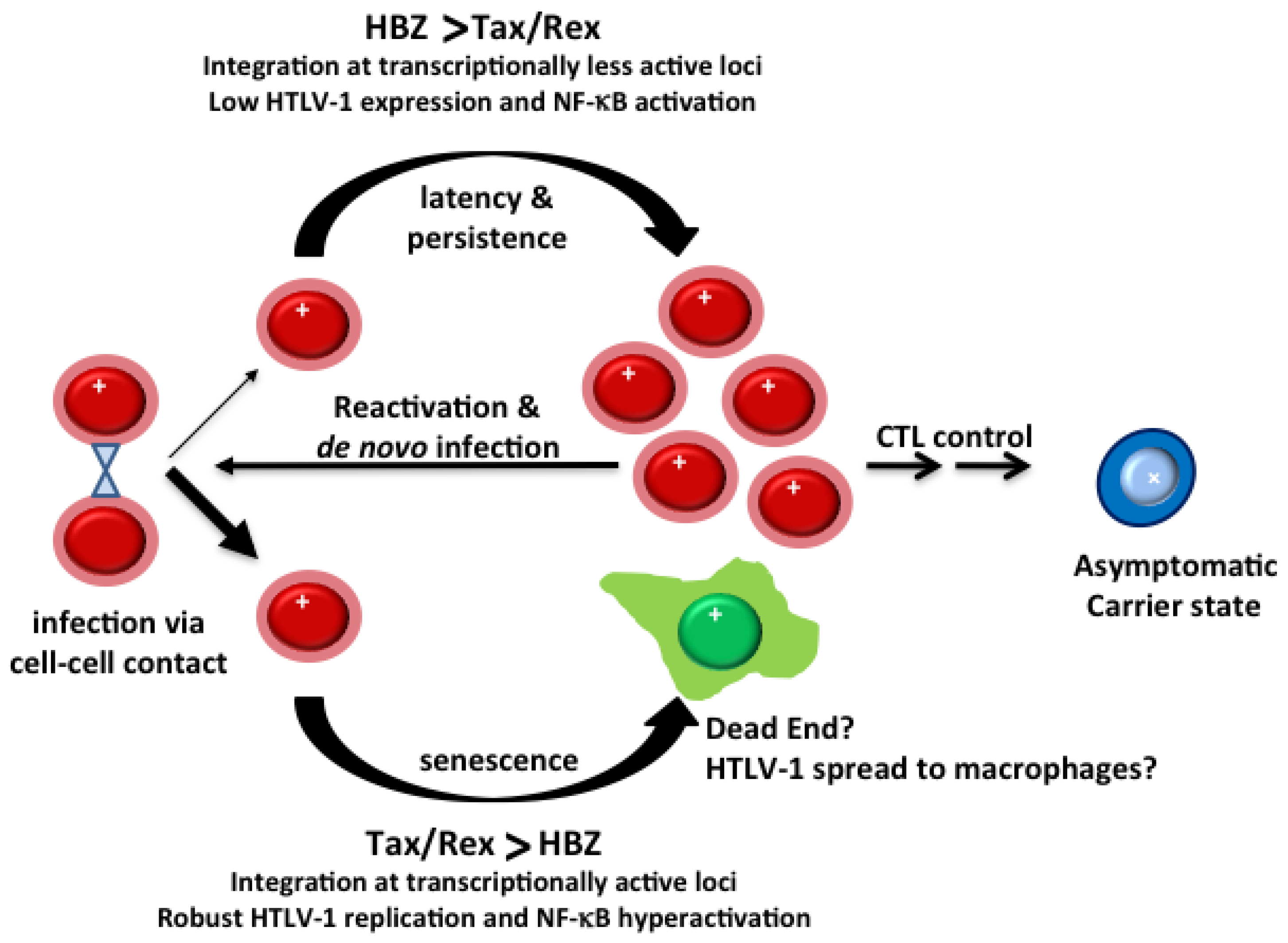
3.2. Evolution of HTLV-1-Infected T-Cells In Vivo
3.3. Clonal Expansion of HTLV-1-Infected T-Cells In Vivo
3.4. HTLV-1 Infection in Cell Culture
3.5. HTLV-1 Infection in Rabbits
3.6. Tax, NF-κB Hyperactivation, and Senescence
3.7. Does Cellular Senescence Facilitate the Spread of HTLV-1 to Innate Immune Cells?
4. Oligoclonal Expansion of HTLV-1-Infected Cells
4.1. HBZ Mitigates the Senescence Response Induced by Tax and Promotes “Latent” HTLV-1 Infection
4.2. Attenuation of NF-κB Activation and Loss of Senescence Response Facilitate Clonal Expansion of HTLV-1-Infected Cells in Vitro
5. HTLV-1 Tax, Genomic Instability, and ATL Development
5.1. ATLs Are Associated with Extensive Genomic Instability
5.2. Tax and DNA Double-Strand Breaks
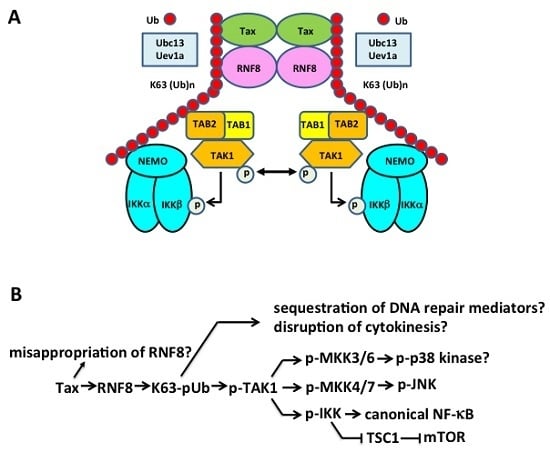
5.3. Tax Hijacks Key Mediators of DNA Damage Repair to Activate TAK1, IKK/NF-κB, and Other Kinases
5.4. The Pleiotropic Effect of Tax on Cell Signaling Explained?
5.5. HTLV-1, Tax, and Chromosome Instability
6. HBZ and ATL Development
6.1. HBZ Gene Expression
6.2. HBZ RNA, HBZ, and usHBZ
6.3. HBZ Antagonizes Many of the Activities of Tax
6.4. HBZ Promotes T-Cell Proliferation
7. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
7.1. The Balance between Tax and HBZ Regulates Viral Latency and Persistence
7.2. The Indispensable Role of Tax and HBZ in ATL Development
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological aspects and world distribution of HTLV-1 infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.P.; Matsuoka, M. Natural history of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and approaches to therapy. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6047–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Jeang, K.T. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukasaki, K.; Hermine, O.; Bazarbachi, A.; Ratner, L.; Ramos, J.C.; Harrington, W., Jr.; O’Mahony, D.; Janik, J.E.; Bittencourt, A.L.; Taylor, G.P.; et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A proposal from an international consensus meeting. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Green, P.L. The HBZ gene, a key player in HTLV-1 pathogenesis. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, K.; Nagata, Y.; Kitanaka, A.; Shiraishi, Y.; Shimamura, T.; Yasunaga, J.; Totoki, Y.; Chiba, K.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Nagae, G.; et al. Integrated molecular analysis of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 BZIP factor (HBZ) gene has a growth-promoting effect on adult T-cell leukemia cells. Rinsho Ketsueki 2008, 49, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Zhao, T.; Yoshida, M.; Miyazato, P.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, K.; Ohshima, K.; Green, P.L.; Ohkura, N.; et al. HTLV-1 BZIP factor induces T-cell lymphoma and systemic inflammation in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.; Zimmerman, B.; Li, M.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 antisense-encoded gene, HBZ, promotes T-lymphocyte proliferation. Blood 2008, 112, 3788–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-I basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, M.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Keats, J.J.; Cibulskis, K.; Sougnez, C.; Schinzel, A.C.; Harview, C.L.; Brunet, J.P.; Ahmann, G.J.; Adli, M.; et al. Initial genome sequencing and analysis of multiple myeloma. Nature 2011, 471, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marriott, S.J.; Semmes, O.J. Impact of HTLV-I Tax on cell cycle progression and the cellular DNA damage repair response. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5986–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majone, F.; Semmes, O.J.; Jeang, K.T. Induction of micronuclei by HTLV-I Tax: A cellular assay for function. Virology 1993, 193, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majone, F.; Jeang, K.T. Clastogenic effect of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax oncoprotein correlates with unstabilized DNA breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32906–32910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmes, O.J.; Majone, F.; Cantemir, C.; Turchetto, L.; Hjelle, B.; Jeang, K.T. HTLV-I and HTLV-II Tax: Differences in induction of micronuclei in cells and transcriptional activation of viral LTRS. Virology 1996, 217, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.; Fenizia, C.; Gold, H.; de Castro-Amarante, M.F.; Buchmann, C.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Franchini, G. ORF-I and ORF-II-encoded proteins in HTLV-1 infection and persistence. Viruses 2011, 3, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Feuer, G.; Barker, E. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) p12I down-modulates ICAM-1 and -2 and reduces adherence of natural killer cells, thereby protecting HTLV-1-infected primary CD4+ T cells from autologous natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity despite the reduction of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on infected cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9707–9717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pise-Masison, C.A.; de Castro-Amarante, M.F.; Enose-Akahata, Y.; Buchmann, R.C.; Fenizia, C.; Washington Parks, R.; Edwards, D.; Fiocchi, M.; Alcantara, L.C., Jr.; Bialuk, I.; et al. Co-dependence of HTLV-1 p12 and p8 functions in virus persistence. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraragi, H.; Michael, B.; Nair, A.; Silic-Benussi, M.; Ciminale, V.; Lairmore, M. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 mitochondrion-localizing protein P13II sensitizes jurkat T cells to ras-mediated apoptosis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9449–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, V.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Sinha-Datta, U.; Bellon, M.; Valeri, V.; Washington Parks, R.; Cecchinato, V.; Fukumoto, R.; Nicot, C.; Franchini, G. Suppression of HTLV-1 replication by Tax-mediated rerouting of the p13 viral protein to nuclear speckles. Blood 2011, 118, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, L.; Vanderplasschen, A.; Ciminale, V.; Heremans, H.; Dangoisse, O.; Jauniaux, J.C.; Toussaint, J.F.; Zelnik, V.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; et al. Oncoviral bovine leukemia virus G4 and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 p13(II) accessory proteins interact with farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silic-Benussi, M.; Cavallari, I.; Zorzan, T.; Rossi, E.; Hiraragi, H.; Rosato, A.; Horie, K.; Saggioro, D.; Lairmore, M.D.; Willems, L.; et al. Suppression of tumor growth and cell proliferation by p13II, a mitochondrial protein of human T cell leukemia virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6629–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicot, C.; Dundr, M.; Johnson, J.M.; Fullen, J.R.; Alonzo, N.; Fukumoto, R.; Princler, G.L.; Derse, D.; Misteli, T.; Franchini, G. HTLV-1-encoded p30II is a post-transcriptional negative regulator of viral replication. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Fujisawa, J.; Matsuoka, M. Transcriptional control of spliced and unspliced human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 BZIP factor (HBZ) gene. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9359–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manel, N.; Kim, F.J.; Kinet, S.; Taylor, N.; Sitbon, M.; Battini, J.L. The ubiquitous glucose transporter glut-1 is a receptor for HTLV. Cell 2003, 115, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Bouttier, M.; Vassy, R.; Seigneuret, M.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Janvier, S.; Heveker, N.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Perret, G.; Jones, K.S.; et al. HTLV-1 uses HSPG and neuropilin-1 for entry by molecular mimicry of VEGF165. Blood 2009, 113, 5176–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.S.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Bertolette, D.C.; Huang, Y.; Ruscetti, F.W. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate attachment and entry of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 virions into CD4+ T cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12692–12702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igakura, T.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Goon, P.K.; Taylor, G.P.; Weber, J.N.; Griffiths, G.M.; Tanaka, Y.; Osame, M.; Bangham, C.R. Spread of HTLV-I between lymphocytes by virus-induced polarization of the cytoskeleton. Science 2003, 299, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, A.L.; Igakura, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Engagement of specific T-cell surface molecules regulates cytoskeletal polarization in HTLV-1-infected lymphocytes. Blood 2005, 106, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derse, D.; Hill, S.A.; Lloyd, P.A.; Chung, H.; Morse, B.A. Examining human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 infection and replication by cell-free infection with recombinant virus vectors. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8461–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurov, D.; Ilinskaya, A.; Heidecker, G.; Lloyd, P.; Derse, D. Quantitative comparison of HTLV-1 and hiv-1 cell-to-cell infection with new replication dependent vectors. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejmeddine, M.; Barnard, A.L.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Human T-lymphotropic virus, type 1, tax protein triggers microtubule reorientation in the virological synapse. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29653–29660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejmeddine, M.; Negi, V.S.; Mukherjee, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Orth, K.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1-Tax and ICAM-1 act on T-cell signal pathways to polarize the microtubule-organizing center at the virological synapse. Blood 2009, 114, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.S.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Huang, Y.K.; Bertolette, D.C.; Ruscetti, F.W. Cell-free HTLV-1 infects dendritic cells leading to transmission and transformation of CD4(+) T cells. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Manuel, S.L.; Khan, Z.K.; Ahuja, J.; Quann, K.; Wigdahl, B. DC-SIGN mediates cell-free infection and transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 by dendritic cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10908–10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro-Amarante, M.F.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; McKinnon, K.; Washington Parks, R.; Galli, V.; Omsland, M.; Andresen, V.; Massoud, R.; Brunetto, G.; Caruso, B.; et al. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 infection of the three monocyte subsets contributes to viral burden in humans. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, C.; Thoma-Kress, A.K. Molecular mechanisms of HTLV-1 cell-to-cell transmission. Viruses 2016, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais-Correia, A.M.; Sachse, M.; Guadagnini, S.; Robbiati, V.; Lasserre, R.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Alcover, A.; Thoulouze, M.I. Biofilm-like extracellular viral assemblies mediate HTLV-1 cell-to-cell transmission at virological synapses. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworski, E.; Narayanan, A.; Van Duyne, R.; Shabbeer-Meyering, S.; Iordanskiy, S.; Saifuddin, M.; Das, R.; Afonso, P.V.; Sampey, G.C.; Chung, M.; et al. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells secrete exosomes that contain Tax protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22284–22305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dooren, S.; Pybus, O.G.; Salemi, M.; Liu, H.F.; Goubau, P.; Remondegui, C.; Talarmin, A.; Gotuzzo, E.; Alcantara, L.C.; Galvao-Castro, B.; et al. The low evolutionary rate of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 confirmed by analysis of vertical transmission chains. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, B.; Hanon, E.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Is human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I really silent? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R.; Osame, M. Cellular immune response to HTLV-1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6035–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanon, E.; Hall, S.; Taylor, G.P.; Saito, M.; Davis, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Usuku, K.; Osame, M.; Weber, J.N.; Bangham CR, L.H. Abundant tax protein expression in CD4+ T cells infected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) is prevented by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood 2000, 15, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, G.; Okayama, A.; Watanabe, T.; Aizawa, S.; Stuver, S.; Mueller, N.; Hsieh, C.C.; Tsubouchi, H. The clonal expansion of human T lymphotropic virus type 1-infected T cells: A comparison between seroconverters and long-term carriers. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okayama, A.; Stuver, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Ishizaki, J.; Tanaka, G.; Kubuki, Y.; Mueller, N.; Hsieh, C.C.; Tachibana, N.; Tsubouchi, H. Role of HTLV-1 proviral DNA load and clonality in the development of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in asymptomatic carriers. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 110, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeki, K.; Hisada, M.; Maloney, E.M.; Hanchard, B.; Okayama, A. Proviral loads and clonal expansion of HTLV-1-infected cells following vertical transmission: A 10-year follow-up of children in Jamaica. Intervirology 2009, 52, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, H.A.; Bangham, C.R. Integration site and clonal expansion in human chronic retroviral infection and gene therapy. Viruses 2014, 6, 4140–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.B.; Rowan, A.G.; Melamed, A.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1-infected T cells contain a single integrated provirus in natural infection. Blood 2012, 120, 3488–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.B.; Melamed, A.; Niederer, H.; Valganon, M.; Laydon, D.; Foroni, L.; Taylor, G.P.; Matsuoka, M.; Bangham, C.R. The role of HTLV-1 clonality, proviral structure, and genomic integration site in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 3925–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derse, D.; Crise, B.; Li, Y.; Princler, G.; Lum, N.; Stewart, C.; McGrath, C.F.; Hughes, S.H.; Munroe, D.J.; Wu, X. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 integration target sites in the human genome: Comparison with those of other retroviruses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6731–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meekings, K.N.; Leipzig, J.; Bushman, F.D.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1 integration into transcriptionally active genomic regions is associated with proviral expression and with HAM/TSP. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Maeda, M.; Morikawa, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Nosaka, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of tax gene in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Nosaka, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Maeda, M.; Mueller, N.; Okayama, A.; Matsuoka, M. Silencing of human T-cell leukemia virus type I gene transcription by epigenetic mechanisms. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Merling, R.; Xia, Z.; Giam, C.Z. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection leads to arrest in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8442–8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, S.; Zahoor, M.A.; Zhi, H.; Ho, Y.K.; Giam, C.Z. Regulation of human T-lymphotropic virus type I latency and reactivation by HBZ and Rex. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.L.; Giam, C.Z. Activation of the anaphase promoting complex by HTLV-1 tax leads to senescence. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, H.; Yang, L.; Kuo, Y.L.; Ho, Y.K.; Shih, H.M.; Giam, C.Z. NF-κB hyper-activation by HTLV-1 tax induces cellular senescence, but can be alleviated by the viral anti-sense protein HBZ. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.D.; Ye, J.; Xie, L.; Green, P.L. Transformation studies with a human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 molecular clone. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 116, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derse, D.; Heidecker, G.; Mitchell, M.; Hill, S.; Lloyd, P.; Princler, G. Infectious transmission and replication of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 2495–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sawa, H.; Lewis, M.J.; Orba, Y.; Sheehy, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ichinohe, T.; Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y.; Katano, H.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Thymus-derived leukemia-lymphoma in mice transgenic for the Tax gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerenberg, M.; Hinrichs, S.H.; Reynolds, R.K.; Khoury, G.; Jay, G. The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science 1987, 237, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, W.J.; Kimata, J.T.; Wong, F.H.; Zutter, M.; Ley, T.J.; Ratner, L. Development of leukemia in mice transgenic for the tax gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995, 92, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, S.; Tobe, T.; Hatanaka, M. Tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype. Oncogene 1992, 7, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panfil, A.R.; Al-Saleem, J.J.; Green, P.L. Animal models utilized in HTLV-1 research. Virology 2013, 4, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodon, M.D.; Villaudy, J.; Gazzolo, L.; Haines, R.; Lairmore, M. What we are learning on HTLV-1 pathogenesis from animal models. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Kesic, M.; Yin, H.; Yu, L.; Green, P.L. Kinetic analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 gene expression in cell culture and infected animals. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3788–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzatti, R.; Vogel, J.; Jay, G. The human T-lymphotropic virus type I tax gene can cooperate with the ras oncogene to induce neoplastic transformation of cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 1990, 10, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmes, O.J.; Barret, J.F.; Dang, C.V.; Jeang, K.T. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax masks c-Myc function through a cAMP-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9730–9738. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zahoor, M.A.; Philip, S.; Zhi, H.; Giam, C.Z. NF-κB inhibition facilitates the establishment of cell lines that chronically produce human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 viral particles. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3496–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, A.; Banerjee, P.; Sieburg, M.; Planelles, V.; Li, F.; Feuer, G. Induction of cell cycle arrest by human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax in hematopoietic progenitor (CD34+) cells: Modulation of p21cip1/waf1 and p27kip1 expression. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14069–14078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Fuente, C.; Santiago, F.; Chong, S.Y.; Deng, L.; Mayhood, T.; Fu, P.; Stein, D.; Denny, T.; Coffman, F.; Azimi, N.; et al. Overexpression of p21(waf1) in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells and its association with cyclin A/cdk2. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 7270–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhi, H.; Liu, M.; Kuo, Y.L.; Giam, C.Z. Induction of p21(CIP1/WAF1) expression by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax requires transcriptional activation and mrna stabilization. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereseto, A.; Washington, P.R.; Rivadeneira, E.; Franchini, G. Limiting amounts of p27kip1 correlates with constitutive activation of cyclin E-CDK2 complex in HTLV-I-transformed T-cells. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlichlia, K.; Moldenhauer, G.; Daniel, P.T.; Busslinger, M.; Gazzolo, L.; Schirrmacher, V.; Khazaie, K. Immediate effects of reversible HTLV-1 tax function: T-cell activation and apoptosis. Oncogene 1995, 10, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.P.; Irvine, J.; Blyth, K.; Cameron, E.R.; Onions, D.E.; Campbell, M.E. Tumours derived from HTLV-I tax transgenic mice are characterized by enhanced levels of apoptosis and oncogene expression. J. Pathol. 1998, 186, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoudi, A.; Semmes, O.J. The HTLV-1 tax oncoprotein attenuates DNA damage induced G1 arrest and enhances apoptosis in p53 null cells. Virology 2003, 305, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Walsh, I.; Waterfield, M.; Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappab signaling pathway governs trail gene expression and human T-cell leukemia virus-I tax-induced T-cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40385–40388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Yamaoka, S.; Goto, T.; Nakai, M.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Hatanaka, M. The human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein induces apoptosis which is blocked by the Bcl-2 protein. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3374–3379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsukahara, T.; Kannagi, M.; Ohashi, T.; Kato, H.; Arai, M.; Nunez, G.; Iwanaga, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Ohtani, K.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Induction of Bcl-x(L) expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax through NF-kappaB in apoptosis-resistant T-cell transfectants with Tax. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7981–7987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Higuchi, M.; Makokha, G.N.; Matsuki, H.; Yoshita, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Fujii, M. HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein stimulates ROS production and apoptosis in T cells by interacting with USP10. Blood 2013, 122, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenicke, L.; Zender, L. Immune surveillance of senescent cells—Biological significance in cancer- and non-cancer pathologies. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.M. Making sense out of antisense transcription in human T-cell lymphotropic viruses (HTLVs). Viruses 2011, 3, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerc, I.; Polakowski, N.; André-Arpin, C.; Cook, P.; Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.M.; Lemasson, I. An interaction between the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper factor (HBZ) and the KIX domain of p300/CBP contributes to the downregulation of tax-dependent viral transcription by HBZ. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23903–23913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, I.; Lewis, M.R.; Polakowski, N.; Hivin, P.; Cavanagh, M.H.; Thebault, S.; Barbeau, B.; Nyborg, J.K.; Mesnard, J.M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) bZIP protein interacts with the cellular transcription factor CREB to inhibit HTLV-1 transcription. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudray, G.; Gachon, F.; Basbous, J.; Biard-Piechaczyk, M.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J.M. The complementary strand of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 RNA genome encodes a bZIP transcription factor that down-regulates viral transcription. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12813–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Yasunaga, J.; Satou, Y.; Nakao, M.; Takahashi, M.; Fujii, M.; Matsuoka, M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 bZIP factor selectively suppresses the classical pathway of NF-kappaB. Blood 2009, 113, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, H.; Zahoor, M.A.; Shudofsky, A.M.; Giam, C.Z. KSHV vCyclin counters the senescence/G1 arrest response triggered by NF-κB hyperactivation. Oncogene 2014, 34, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenot, J.D.; Gavin, M.A.; Rudensky, A.Y. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, C.; Oh, U.; Fugo, K.; Takenouchi, N.; Griffith, C.; Yao, K.; Newhook, T.E.; Ratner, L.; Jacobson, S. Foxp3 represses retroviral transcription by targeting both NF-κB and CREB pathways. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelli, E.; Dastrange, M.; Oukka, M. Foxp3 interacts with nuclear factor of activated T cells and NF-κB to repress cytokine gene expression and effector functions of T helper cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5138–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ishii, N.; Ine, S.; Ikeda, S.; Fujimura, T.; Ndhlovu, L.C.; Soroosh, P.; Tada, K.; Harigae, H.; Kameoka, J.; et al. Regulatory T cell-like activity of Foxp3+ adult T cell leukemia cells. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, S.; Ariumi, Y.; Shimotohno, K. p21(Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1) prevents apoptosis as well as stimulates growth in cells transformed or immortalized by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-encoded tax. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7291–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Nakahata, S.; Hamasaki, M.; Saito, Y.; Kawano, Y.; Hidaka, T.; Yamashita, K.; Umeki, K.; Taki, T.; Taniwaki, M.; et al. Downregulation of CDKN1A in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma despite overexpression of CDKN1A in human T-lymphotropic virus 1-infected cell lines. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6966–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeang, K.T.; Giam, C.Z.; Majone, F.; Aboud, M. Life, death, and tax: Role of HTLV-I oncoprotein in genetic instability and cellular transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31991–31994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, F.J.; Marriott, S.J. Genomic instability driven by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) oncoprotein, tax. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7230–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeang, K.T.; Widen, S.G.; Semmes, O.J.; Wilson, S.H. HTLV-I trans-activator protein, tax, is a trans-repressor of the human beta-polymerase gene. Science 1990, 247, 1082–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydoun, H.H.; Cherian, M.A.; Green, P.; Ratner, L. Inducible nitric oxide synthase mediates DNA double strand breaks in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-induced leukemia/lymphoma. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgnaoui, S.M.; Fryrear, K.A.; Nyalwidhe, J.O.; Guo, X.; Semmes, O.J. The viral oncoprotein tax sequesters DNA damage response factors by tethering MDC1 to chromatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32897–32905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haoudi, A.; Daniels, R.C.; Wong, E.; Kupfer, G.; Semmes, O.J. Human T-cell leukemia virus-I tax oncoprotein functionally targets a subnuclear complex involved in cellular DNA damage-response. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 37736–37744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Guo, X.; Durkin, S.S.; Fryrear, K.F.; Ward, M.D.; Semmes, O.J. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein prevents DNA damage-induced chromatin egress of hyperphosphorylated CHK2. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29431–29440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkin, S.S.; Guo, X.; Fryrear, K.A.; Mihaylova, V.T.; Gupta, S.K.; Belgnaoui, S.M.; Haoudi, A.; Kupfer, G.M.; Semmes, O.J. HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein subverts the cellular DNA damage response via binding to DNA-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 36311–36320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.K.; Zhi, H.; Bowlin, T.; Dorjbal, B.; Philip, S.; Zahoor, M.A.; Shih, H.M.; Semmes, O.J.; Schaefer, B.; Glover, J.N.; et al. HTLV-1 tax stimulates ubiquitin E3 ligase, ring finger protein 8, to assemble lysine 63-linked polyubiquitin chains for TAK1 and IKK activation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Wang, C.; Spencer, E.; Yang, L.; Braun, A.; You, J.; Slaughter, C.; Pickart, C.; Chen, Z.J. Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell 2000, 103, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ea, C.K.; Deng, L.; Xia, Z.P.; Pineda, G.; Chen, Z.J. Activation of IKK by TNFalpha requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Z.J. Expanding role of ubiquitination in NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, A.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitin-mediated activation of TAK1 and IKK. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3214–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shembade, N.; Harhaj, N.S.; Yamamoto, M.; Akira, S.; Harhaj, E.W. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein requires the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 for NF-kappaB activation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13735–13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Gohda, J.; Inoue, J. Activation of the ikappab kinase complex by HTLV-1 tax requires cytosolic factors involved in tax-induced polyubiquitination. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Long, W.; Peng, C.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, A.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Wong, C.C.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. HTLV-1 tax functions as a ubiquitin E3 ligase for direct IKK activation via synthesis of mixed-linkage polyubiquitin chains. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Sun, S.C. Retroviral oncoprotein Tax deregulates NF-kappaB by activating Tak1 and mediating the physical association of Tak1-IKK. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.K.; Zhi, H.; Debiaso, D.; Philip, S.; Shih, H.M.; Giam, C.Z. HTLV-1 tax-induced rapid senescence is driven by the transcriptional activity of NF-κB and depends on chronically activated IKKα and p65/RelA. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9474–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, M. Role of K63-linked polyubiquitination in NF-kappaB signalling: Which ligase catalyzes and what molecule is targeted? J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinder, J.B.; Attwood, K.M.; Dellaire, G. Reading, writing, and repair: The role of ubiquitin and the ubiquitin-like proteins in DNA damage signaling and repair. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartocci, C.; Denchi, E.L. Put a ring on it: Regulation and inhibition of RNF8 and RNF168 ring finger E3 ligases at DNA damage sites. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolas, N.K.; Chapman, J.R.; Nakada, S.; Ylanko, J.; Chahwan, R.; Sweeney, F.D.; Panier, S.; Mendez, M.; Wildenhain, J.; Thomson, T.M.; et al. Orchestration of the DNA-damage response by the RNF8 ubiquitin ligase. Science 2007, 318, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailand, N.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Faustrup, H.; Melander, F.; Bartek, J.; Lukas, C.; Lukas, J. RNF8 ubiquitylates histones at DNA double-strand breaks and promotes assembly of repair proteins. Cell 2007, 131, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.S.; Truong, L.N.; Aslanian, A.; Shi, L.Z.; Li, Y.; Hwang, P.Y.; Koh, K.H.; Hunter, T.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Berns, M.W.; et al. The RING finger protein RNF8 ubiquitinates Nbs1 to promote DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43984–43994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yuan, J.; Lou, Z. Sumoylation of MDC1 is important for proper DNA damage response. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3008–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, Y.T.; Chin, K.T.; Siu, K.L.; Yee Wai, C.E.; Jeang, K.T.; Jin, D.Y. TORC1 and TORC2 coactivators are required for tax activation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeats. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7052–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyborg, J.K.; Egan, D.; Sharma, N. The HTLV-1 Tax protein: Revealing mechanisms of transcriptional activation through histone acetylation and nucleosome disassembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1799, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Heidenreich, O.; Kitajima, I.; McGuire, K.; Li, Q.; Su, B.; Nerenberg, M. Constitutively activated JNK is associated with HTLV-1 mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 1996, 13, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chariot, A. The NF-kappaB-independent functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol 2009, 19, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.F.; Kuo, H.P.; Chen, C.T.; Hsu, J.M.; Chou, C.K.; Wei, Y.; Sun, H.L.; Li, L.Y.; Ping, B.; Huang, W.C.; et al. IKK beta suppression of TSC1 links inflammation and tumor angiogenesis via the mTOR pathway. Cell 2007, 130, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmerich, C.H.; Ordureau, A.; Strickson, S.; Arthur, J.S.; Pedrioli, P.G.; Komander, D.; Cohen, P. Activation of the canonical IKK complex by K63/M1-linked hybrid ubiquitin chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15247–15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peloponese, J.M., Jr.; Haller, K.; Miyazato, A.; Jeang, K.T. Abnormal centrosome amplification in cells through the targeting of Ran-binding protein-1 by the human T cell leukemia virus type-1 Tax oncoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18974–18979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, Y.P.; Chan, S.F.; Jeang, K.T.; Jin, D.Y. The retroviral oncoprotein tax targets the coiled-coil centrosomal protein TAX1BP2 to induce centrosome overduplication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.Y.; Spencer, F.; Jeang, K.T. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 oncoprotein Tax targets the human mitotic checkpoint protein MAD1. Cell 1998, 93, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hong, S.; Tang, Z.; Yu, H.; Giam, C.Z. HTLV-I Tax directly binds the Cdc20-associated anaphase-promoting complex and activates it ahead of schedule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellon, M.; Baydoun, H.H.; Yao, Y.; Nicot, C. HTLV-I Tax-dependent and -independent events associated with immortalization of human primary T lymphocytes. Blood 2010, 115, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luijsterburg, M.S.; Acs, K.; Ackermann, L.; Wiegant, W.W.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Larsen, D.H.; Khanna, K.K.; van Attikum, H.; Mailand, N.; Dantuma, N.P. A new non-catalytic role for ubiquitin ligase RNF8 in unfolding higher-order chromatin structure. EMBO J 2012, 31, 2511–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahwan, R.; Gravel, S.; Matsusaka, T.; Jackson, S.P. Dma/RNF8 proteins are evolutionarily conserved E3 ubiquitin ligases that target septins. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plans, V.; Guerra-Rebollo, M.; Thomson, T.M. Regulation of mitotic exit by the RNF8 ubiquitin ligase. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirlando, R.; Felsenfeld, G. Ctcf: Making the right connections. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, Y.; Miyazato, P.; Ishihara, K.; Yaguchi, H.; Melamed, A.; Miura, M.; Fukuda, A.; Nosaka, K.; Watanabe, T.; Rowan, A.G.; et al. The retrovirus HTLV-1 inserts an ectopic CTCF-binding site into the human genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3054–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, S.; Halin, M.; Vargas, A.; Lemasson, I.; Mesnard, J.M.; Barbeau, B. Upregulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 antisense transcription by the viral tax protein. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2048–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbeau, B.; Peloponese, J.M.; Mesnard, J.M. Functional comparison of antisense proteins of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 in viral pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnard, J.M.; Barbeau, B.; Devaux, C. HBZ, a new important player in the mystery of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2006, 108, 3979–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawatsuki, A.; Yasunaga, J.I.; Mitobe, Y.; Green, P.L.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor protein targets the Rb/E2F-1 pathway to promote proliferation and apoptosis of primary CD4 T cells. Oncogene 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto-Taguchi, N.; Satou, Y.; Miyazato, P.; Ohshima, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Katagiri, K.; Kinashi, T.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor induces inflammation through labile Foxp3 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernin, C.; Thenoz, M.; Pinatel, C.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; Nazaret, N.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; Wattel, E.; Mortreux, F. HTLV-1 bZIP factor HBZ promotes cell proliferation and genetic instability by activating oncomirs. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6082–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlmann, A.S.; Villaudy, J.; Gazzolo, L.; Castellazzi, M.; Mesnard, J.M.; Duc, D.M. HTLV-1 HBZ cooperates with jund to enhance transcription of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene (hTERT). Retrovirology 2007, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuma, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Takemoto, K.; Sugata, K.; Mitobe, Y.; Takenouchi, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor impairs anti-viral immunity by inducing co-inhibitory molecule, T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT). PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charvet, C.; Canonigo, A.J.; Becart, S.; Maurer, U.; Miletic, A.V.; Swat, W.; Deckert, M.; Altman, A. Vav1 promotes T cell cycle progression by linking TCR/CD28 costimulation to FOXO1 and p27kip1 expression. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5024–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Tax Activities | Functional Consequences | HBZ Activities | Functional Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| CREB, CBP/p300, P/CAF, TORC interaction | Activate viral transcription | CREB, CBP/p300 interaction | Suppress viral gene expression |
| Association with MTOC | Promote formation of virological synapse and cell–cell transmission | Rex inhibition | Suppress viral gene expression and particle production |
| RNF8, UBC13 interaction and activation | Stimulate K63-linked polyubiquitin chain assembly | NF-κB DNA-binding disruption and p65/RelA degradation | Suppress Tax-mediated canonical NF-κB activation |
| TAK1, IKK, MKK, JNK, mTOR, etc. activation | Activate c-Jun/AP and SRF | Prevent senescence induction | |
| Canonical NF-κB activation | Induce expression of cytokines, cytokine receptors, adhesion molecules, anti-apoptotic factors, etc. | Promote viral latency and persistence of virus-infected cells | |
| p21WAF1 and p27KIP1 up-regulation | Induce senescence | ||
| NIK, p100 interaction Non-canonical NF-κB activation | Induce expression of cytokines, cytokine receptors, adhesion molecules, anti-apoptotic factors, etc. | E2F1 activation | Promote cell proliferation and apoptosis |
| Survivin up-regulation (HBZ RNA) | Prevent apoptosis | ||
| CDK 2/4 activation E2F1 activation | Promote cell cycle progression | Onco-miRs activation | Promote cell proliferation |
| Cyclin D1 activation P53, Rb, DLG1 inactivation | hTERT activation BDNF/TrkB activation | ||
| PCNA activation | Wnt5a, JunD activation | ||
| CENP-B repression | |||
| hTERT activation | Promote cell immortalization | Foxp3 induction and functional inactivation | Modify T-cells |
| P53 inactivation Sequestration of DDR mediator MDC1 Inactivation of DDR mediators CHK1 and CHK2 Suppression of DNA Polβ expression | Induce genomic instability | Bim repression via Foxo3a IFNγ repression Activation of mTOR/suppression of autophagy | Promote cell survival during stress response |
| Activation of APC/C | Promote aneurploidy, cytokinesis defect, and senescence | TIGIT induction | Impair antiviral immunity and promote immune evasion |
| RANBP1, TaxBP2 (Rootletin isoform 2) interaction | Promote centrosome amplification or fragmentation |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giam, C.-Z.; Semmes, O.J. HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma—A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ. Viruses 2016, 8, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060161
Giam C-Z, Semmes OJ. HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma—A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ. Viruses. 2016; 8(6):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060161
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiam, Chou-Zen, and Oliver John Semmes. 2016. "HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma—A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ" Viruses 8, no. 6: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060161
APA StyleGiam, C.-Z., & Semmes, O. J. (2016). HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma—A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ. Viruses, 8(6), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8060161