Porcine Circovirus 2 Deploys PERK Pathway and GRP78 for Its Enhanced Replication in PK-15 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus and Cell Lines
2.2. Plasmid Construction and siRNA
2.3. Virus Infection, Treatments with Chemicals and Transfection
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Xbp1 Splicing
2.6. TUNEL Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Quantification of Virus Titer
2.9. Cell Viability Measurement
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
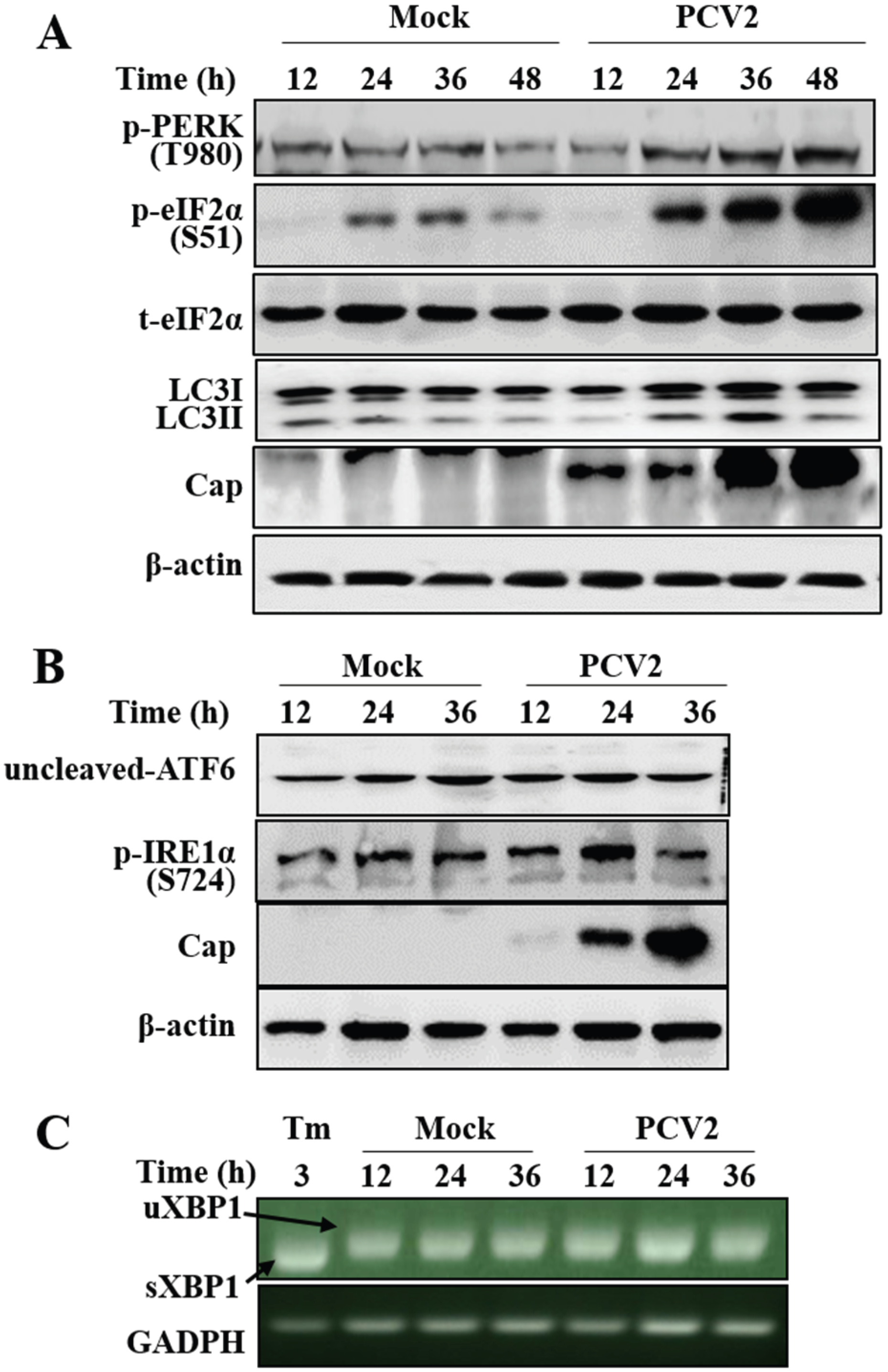
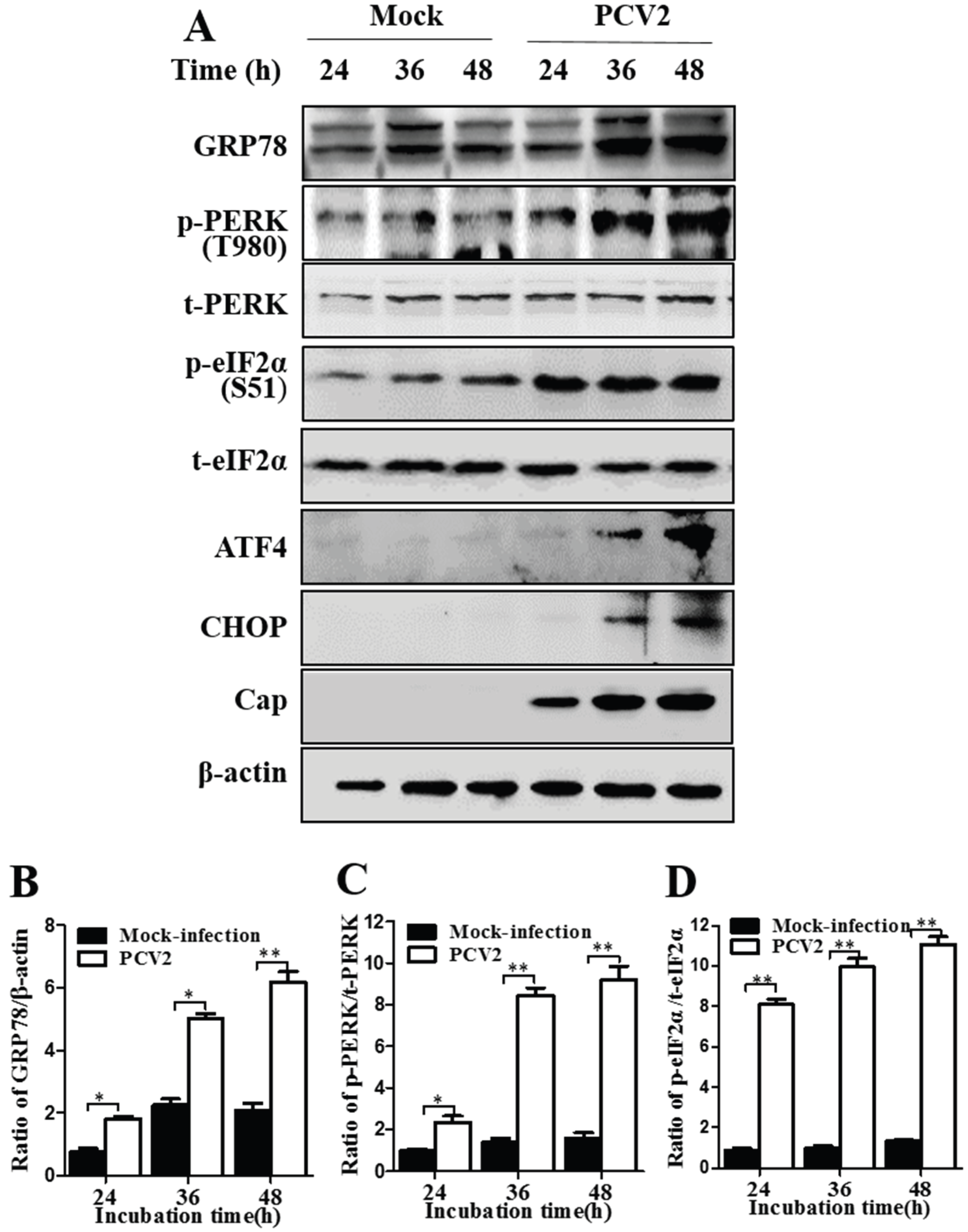
3.1. PCV2 Infection Induced Unfolded Protein Response via PERK Pathway
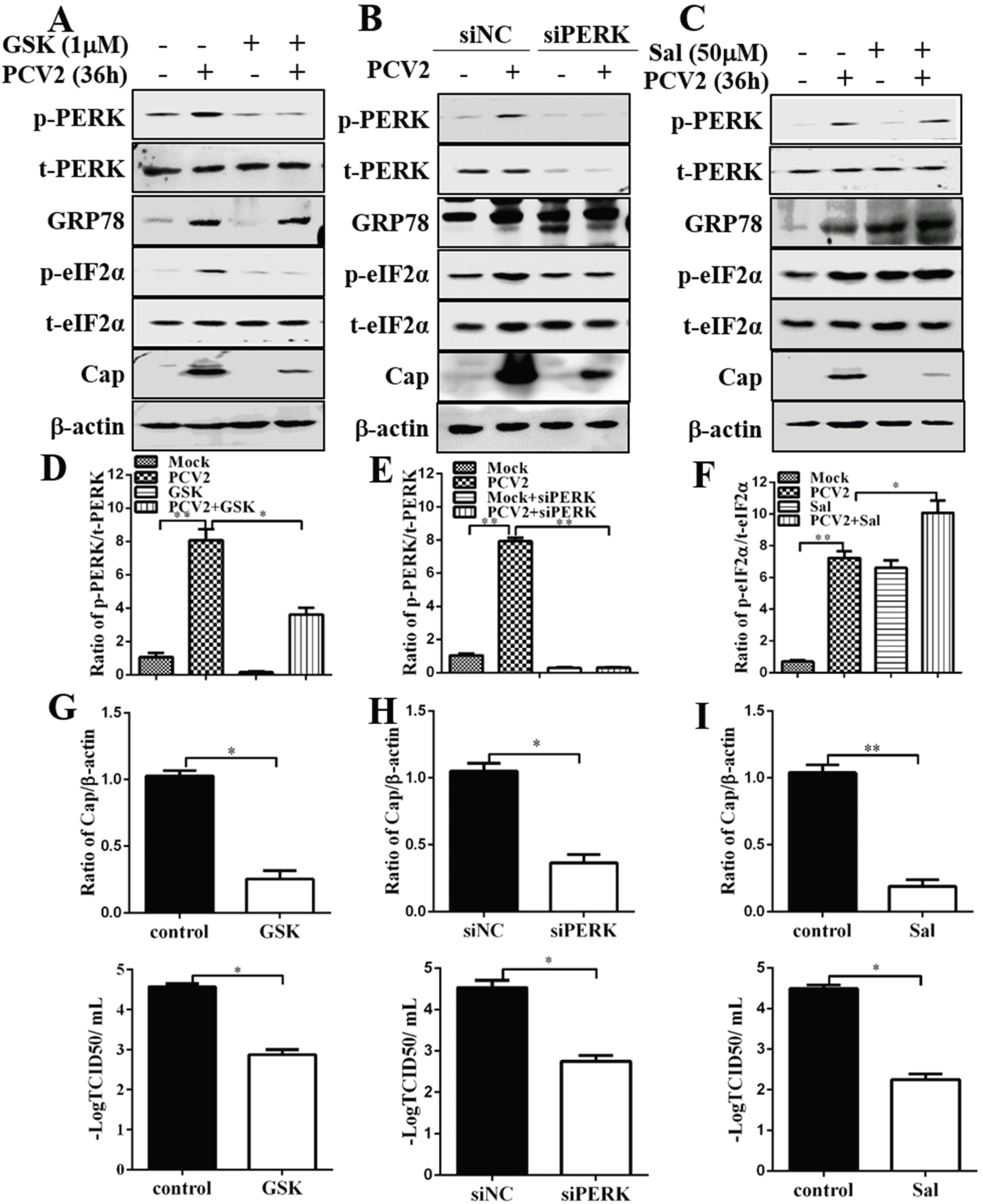
3.2. Inhibition of PERK and eIF2α Dephosphorylation Reduced PCV2 Replication
3.3. GRP78 Positively Regulated PCV2 Replication
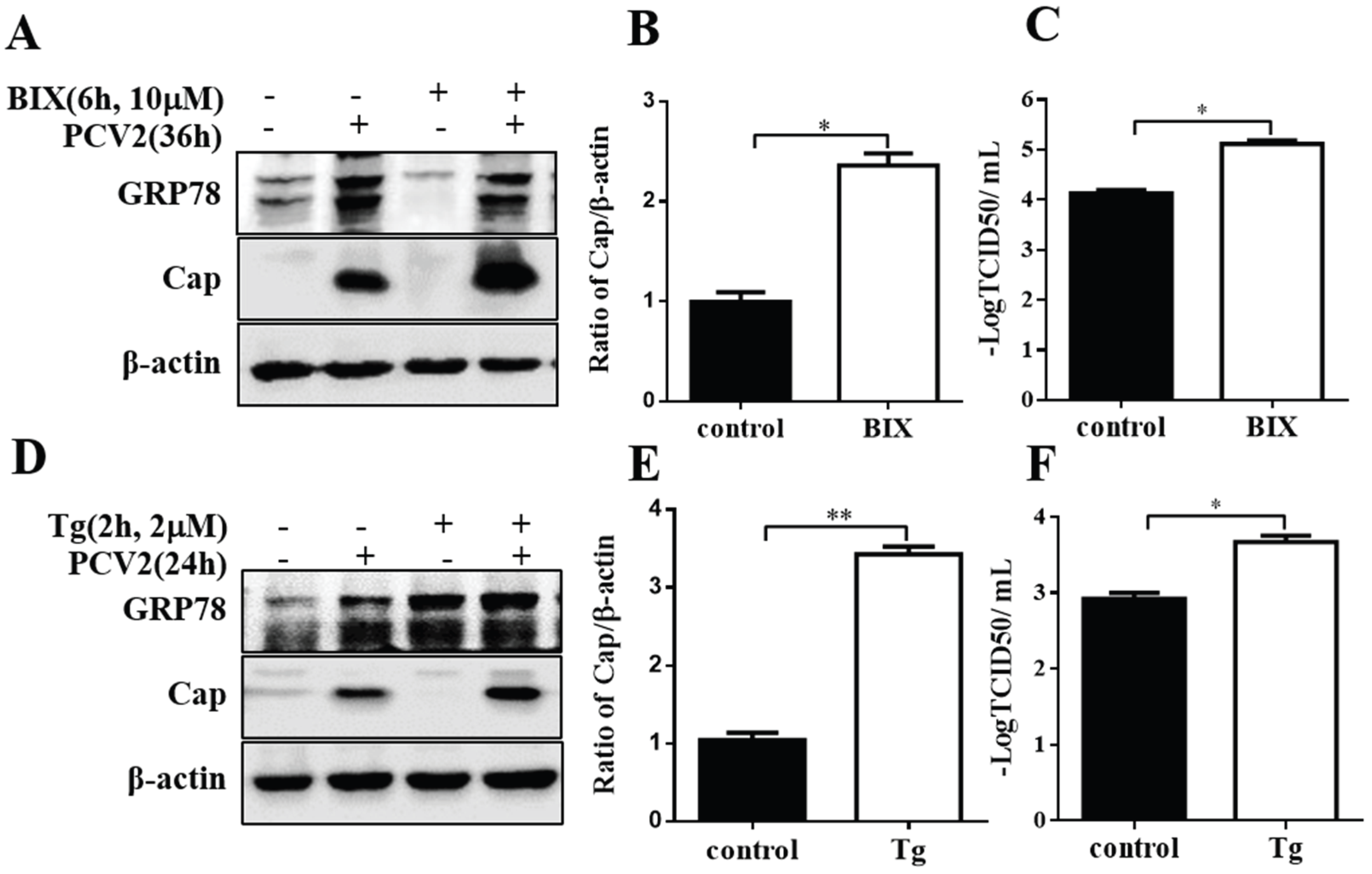
3.4. Chemical ER Chaperones Modulated PCV2 Replication and Apoptosis
3.5. Pharmacological Treatments, Plasmid Transfection and RNA Interference Did Not affect Cell Viability
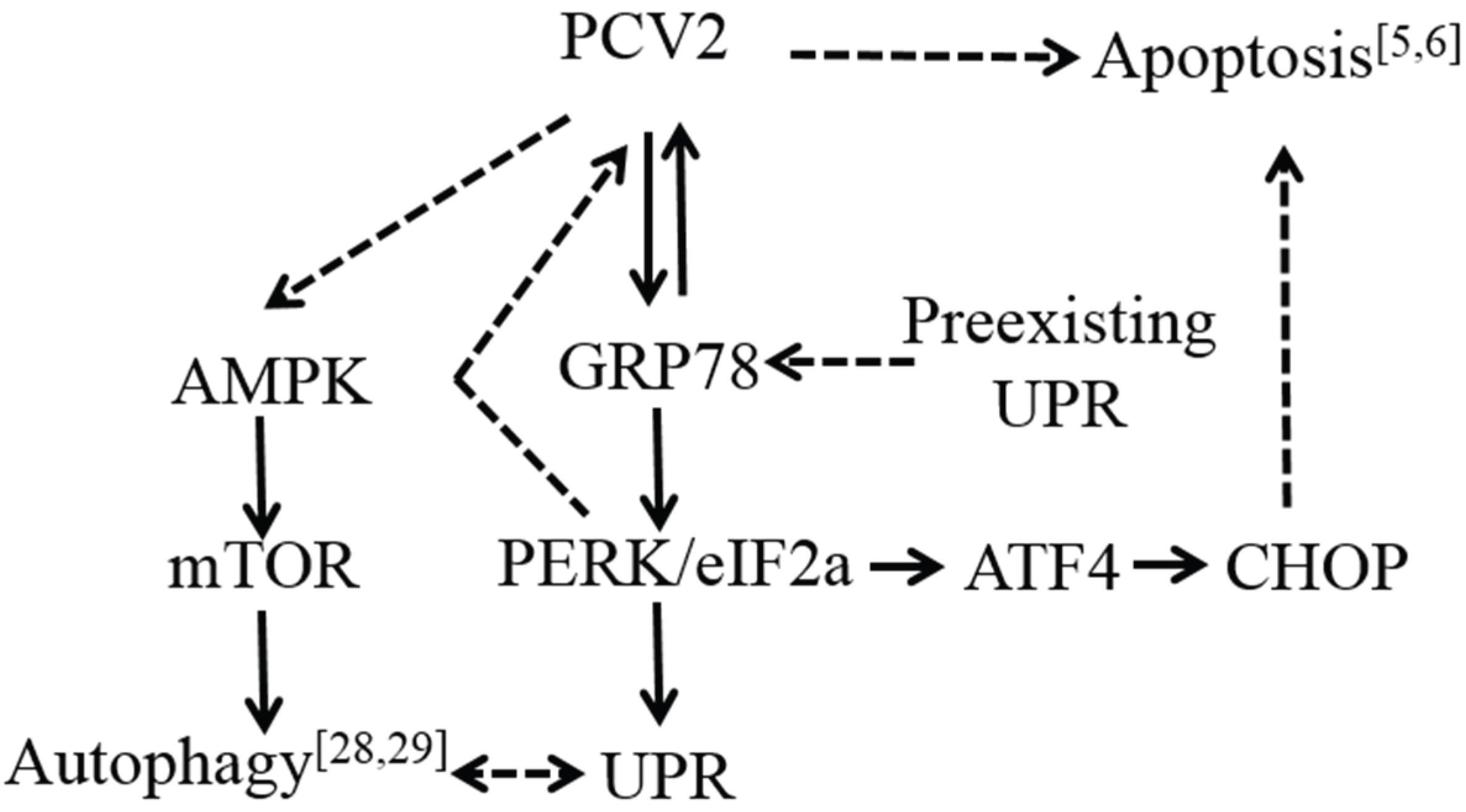
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Opriessnig, T.; Meng, X.J.; Halbur, P.G. Porcine circovirus type 2 associated disease: Update on current terminology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and intervention strategies. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2007, 19, 591–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankertz, A.; Mankertz, J.; Wolf, K.; Buhk, H.J. Identification of a protein essential for replication of porcine circovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankertz, J.; Buhk, H.J.; Blaess, G.; Mankertz, A. Transcription analysis of porcine circovirus (PCV). Virus Genes 1998, 16, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawagitgul, P.; Morozov, I.; Bolin, S.R.; Harms, P.A.; Sorden, S.D.; Paul, P.S. Open reading frame 2 of porcine circovirus type 2 encodes a major capsid protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, I.; Du, Q.; Chua, H.; Kwang, J. The ORF3 protein of porcine circovirus type 2 is involved in viral pathogenesis in vivo. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5065–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, I.; Kwang, J. Characterization of a previously unidentified viral protein in porcine circovirus type 2-infected cells and its role in virus-induced apoptosis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8262–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, C.; Segales, J.; Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Folch, J.M.; Rodriguez-Arrioja, G.M.; Duran, C.O.; Balasch, M.; Plana-Duran, J.; Domingo, M. Identification of porcine circovirus in tissues of pigs with porcine dermatitis and nephropathy syndrome. Vet. Rec. 2000, 146, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankertz, A.; Caliskan, R.; Hattermann, K.; Hillenbrand, B.; Kurzendoerfer, P.; Mueller, B.; Schmitt, C.; Steinfeldt, T.; Finsterbusch, T. Molecular biology of Porcine circovirus: Analyses of gene expression and viral replication. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 98, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.K. Porcine circovirus: Transcription and DNA replication. Virus Res. 2012, 164, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, N.; Opriessnig, T.; Grasland, B.; Jestin, A. Epidemiology and transmission of porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2). Virus Res. 2012, 164, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segales, J. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) infections: Clinical signs, pathology and laboratory diagnosis. Virus Res. 2012, 164, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.J. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2): Pathogenesis and interaction with the immune system. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2013, 1, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, N.M.; Meng, X.J. Efficacy and future prospects of commercially available and experimental vaccines against porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2). Virus Res. 2012, 164, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resendes, A.R.; Majo, N.; Segales, J.; Mateu, E.; Calsamiglia, M.; Domingo, M. Apoptosis in lymphoid organs of pigs naturally infected by porcine circovirus type 2. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2837–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, R.; Dardari, R.; Chaiyakul, M.; Czub, M. Porcine circovirus-2 capsid protein induces cell death in PK15 cells. Virology 2014, 468–470, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senft, D.; Ronai, Z.A. UPR, autophagy, and mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Snapp, E.L.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Prywes, R. Stable binding of ATF6 to BiP in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Brandizzi, F. IRE1: ER stress sensor and cell fate executor. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Frank, C.L.; Korth, M.J.; Sopher, B.L.; Novoa, I.; Ron, D.; Katze, M.G. Control of PERK eIF2α kinase activity by the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced molecular chaperone P58IPK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15920–15925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S. The ER chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Methods 2005, 35, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, B.M.; Walter, P. Unfolded proteins are IRE1-activating ligands that directly induce the unfolded protein response. Science 2011, 333, 1891–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, J.E.; Grose, C. Varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein expression differentially induces the unfolded protein response in infected cells. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, C.; Uta, M.; Branza-Nichita, N. Modulation of the unfolded protein response by the human hepatitis B virus. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benali-Furet, N.L.; Chami, M.; Houel, L.; de Giorgi, F.; Vernejoul, F.; Lagorce, D.; Buscail, L.; Bartenschlager, R.; Ichas, F.; Rizzuto, R.; et al. Hepatitis C virus core triggers apoptosis in liver cells by inducing ER stress and ER calcium depletion. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4921–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jheng, J.R.; Ho, J.Y.; Horng, J.T. ER stress, autophagy, and RNA viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiramel, A.I.; Brady, N.R.; Bartenschlager, R. Divergent roles of autophagy in virus infection. Cells 2013, 2, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, F.; Shuai, J.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Porcine circovirus type 2 induces autophagy via the AMPK/ERK/TSC2/mTOR signaling pathway in PK-15 cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12003–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Xu, F.; Li, J.; Shuai, J.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Porcine circovirus type 2 explores the autophagic machinery for replication in PK-15 cells. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Pae, H.O.; Zheng, M.; Park, R.; Kim, Y.M.; Chung, H.T. Carbon monoxide induces heme oxygenase-1 via activation of protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase and inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis triggered by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.H.; Li, H.; Yasumura, D.; Cohen, H.R.; Zhang, C.; Panning, B.; Shokat, K.M.; Lavail, M.M.; Walter, P. IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science 2007, 318, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyadomari, S.; Mori, M. Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilpin, D.F.; McCullough, K.; Meehan, B.M.; McNeilly, F.; McNair, I.; Stevenson, L.S.; Foster, J.C.; Ellis, J.A.; Krakowka, S.; Adair, B.M.; et al. In vitro studies on the infection and replication of porcine circovirus type 2 in cells of the porcine immune system. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2003, 94, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axten, J.M.; Medina, J.R.; Feng, Y.; Shu, A.; Romeril, S.P.; Grant, S.W.; Li, W.H.; Heerding, D.A.; Minthorn, E.; Mencken, T.; et al. Discovery of 7-methyl-5-(1-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-yl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (GSK2606414), a potent and selective first-in-class inhibitor of protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7193–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyce, M.; Bryant, K.F.; Jousse, C.; Long, K.; Harding, H.P.; Scheuner, D.; Kaufman, R.J.; Ma, D.; Coen, D.M.; Ron, D.; et al. A selective inhibitor of eIF2α dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 2005, 307, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, R.K.; Mao, C.; Baumeister, P.; Austin, R.C.; Kaufman, R.J.; Lee, A.S. Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone protein GRP78 protects cells from apoptosis induced by topoisomerase inhibitors: Role of ATP binding site in suppression of caspase-7 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20915–20924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammoun, H.L.; Chabanon, H.; Hainault, I.; Luquet, S.; Magnan, C.; Koike, T.; Ferre, P.; Foufelle, F. GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 119, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ni, M.; Lee, B.; Barron, E.; Hinton, D.R.; Lee, A.S. The unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP is required for endoplasmic reticulum integrity and stress-induced autophagy in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, T.; Kanemoto, S.; Hara, H.; Morimoto, N.; Morihara, T.; Kimura, R.; Tabira, T.; Imaizumi, K.; Takeda, M. A molecular chaperone inducer protects neurons from ER stress. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, U.; Yilmaz, E.; Ozcan, L.; Furuhashi, M.; Vaillancourt, E.; Smith, R.O.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science 2006, 313, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Kong, L.; Yu, X. The expanding roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in virus replication and pathogenesis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, H.F.; Audas, T.E.; Liang, G.; Lu, R.R. Herpes simplex virus-1 disarms the unfolded protein response in the early stages of infection. Cell Stress Chaperones 2012, 17, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hendershot, L.M.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Zhou, H.; Wey, S.; Baumeister, P.; Lee, A.S. Regulation of PERK signaling and leukemic cell survival by a novel cytosolic isoform of the UPR regulator GRP78/BiP. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Bertolotti, A.; Zeng, H.; Ron, D. Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell survival during the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattem, K.M.; Wek, R.C. Reinitiation involving upstream ORFs regulates ATF4 mRNA translation in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11269–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabas, I.; Ron, D. Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S. Glucose-regulated proteins in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, S.P.; Shurtleff, A.C.; Costantino, J.A.; Tritsch, S.R.; Retterer, C.; Spurgers, K.B.; Bavari, S. HSPA5 is an essential host factor for Ebola virus infection. Antivir. Res. 2014, 109, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.C.; Wu, J.L.; Hong, J.R. Betanodavirus up-regulates chaperone GRP78 via ER stress: Roles of GRP78 in viral replication and host mitochondria-mediated cell death. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, E.; Haller, D. Structure-function analysis of the tertiary bile acid TUDCA for the resolution of endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, P.S.; Ayaub, E.A.; Zhou, W.; Yum, V.; Dickhout, J.G.; Ask, K. The therapeutic effects of 4-phenylbutyric acid in maintaining proteostasis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 61, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Z.; Deng, H.X.; Lou, W.Z.; Sun, X.Y.; Song, M.W.; Tao, J.; Xiao, B.X.; Guo, J.M. Growth inhibitory effect of 4-phenyl butyric acid on human gastric cancer cells is associated with cell cycle arrest. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C. Correlation of the cyclin A expression level with porcine circovirus type 2 propagation efficiency. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hottel, W.; Powers, L.; Monick, M.; Varga, S.; Hassan, I. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) inhibits respiratory syncytial virus replication. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, A4050. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, I.H.; Zhang, M.S.; Powers, L.S.; Shao, J.Q.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Rutkowski, D.T.; Legge, K.; Monick, M.M. Influenza A viral replication is blocked by inhibition of the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) stress pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4679–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Achazi, K.; Niedrig, M. Tick-borne encephalitis virus triggers inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) and transcription factor 6 (ATF6) pathways of unfolded protein response. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Tikoo, S.K.; Babiuk, L.A. Nuclear localization of the ORF2 protein encoded by porcine circovirus type 2. Virology 2001, 285, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Qi, B.; Gu, Y.; Xu, F.; Du, H.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Porcine Circovirus 2 Deploys PERK Pathway and GRP78 for Its Enhanced Replication in PK-15 Cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020056
Zhou Y, Qi B, Gu Y, Xu F, Du H, Li X, Fang W. Porcine Circovirus 2 Deploys PERK Pathway and GRP78 for Its Enhanced Replication in PK-15 Cells. Viruses. 2016; 8(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yingshan, Baozhu Qi, Yuanxing Gu, Fei Xu, Huahua Du, Xiaoliang Li, and Weihuan Fang. 2016. "Porcine Circovirus 2 Deploys PERK Pathway and GRP78 for Its Enhanced Replication in PK-15 Cells" Viruses 8, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020056
APA StyleZhou, Y., Qi, B., Gu, Y., Xu, F., Du, H., Li, X., & Fang, W. (2016). Porcine Circovirus 2 Deploys PERK Pathway and GRP78 for Its Enhanced Replication in PK-15 Cells. Viruses, 8(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020056






