Conformational Masking and Receptor-Dependent Unmasking of Highly Conserved Env Epitopes Recognized by Non-Neutralizing Antibodies That Mediate Potent ADCC against HIV-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Mechanisms Used by HIV to Evade Antibody-Mediated Protection
Conformational Changes in Env during Viral Entry and Budding
3. Identification of Epitope Cluster A of gp120 as a Target for Potent Fc-Mediated Effector Function
4. Structure of the A32 Subregion of Epitope Cluster A
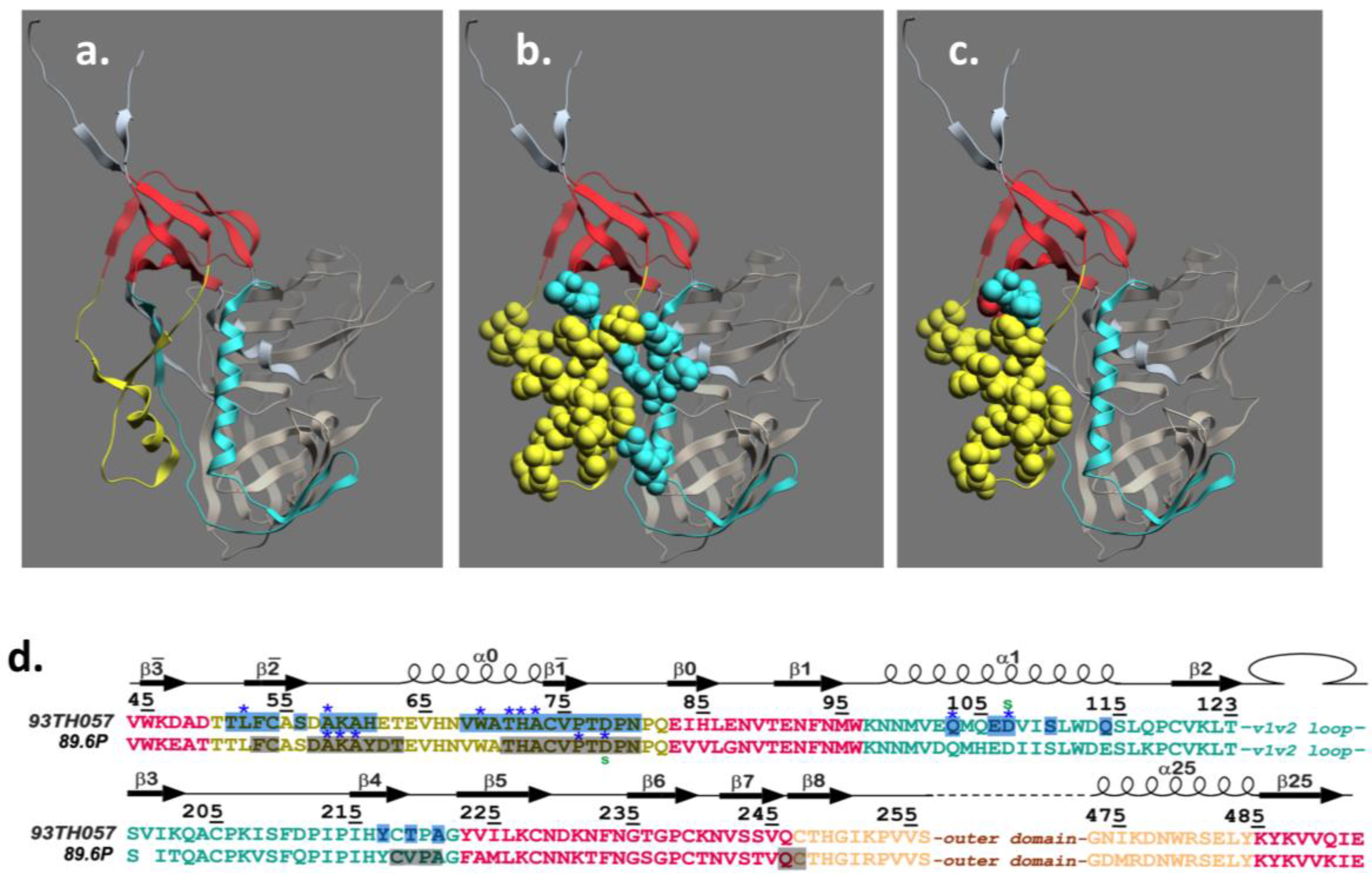
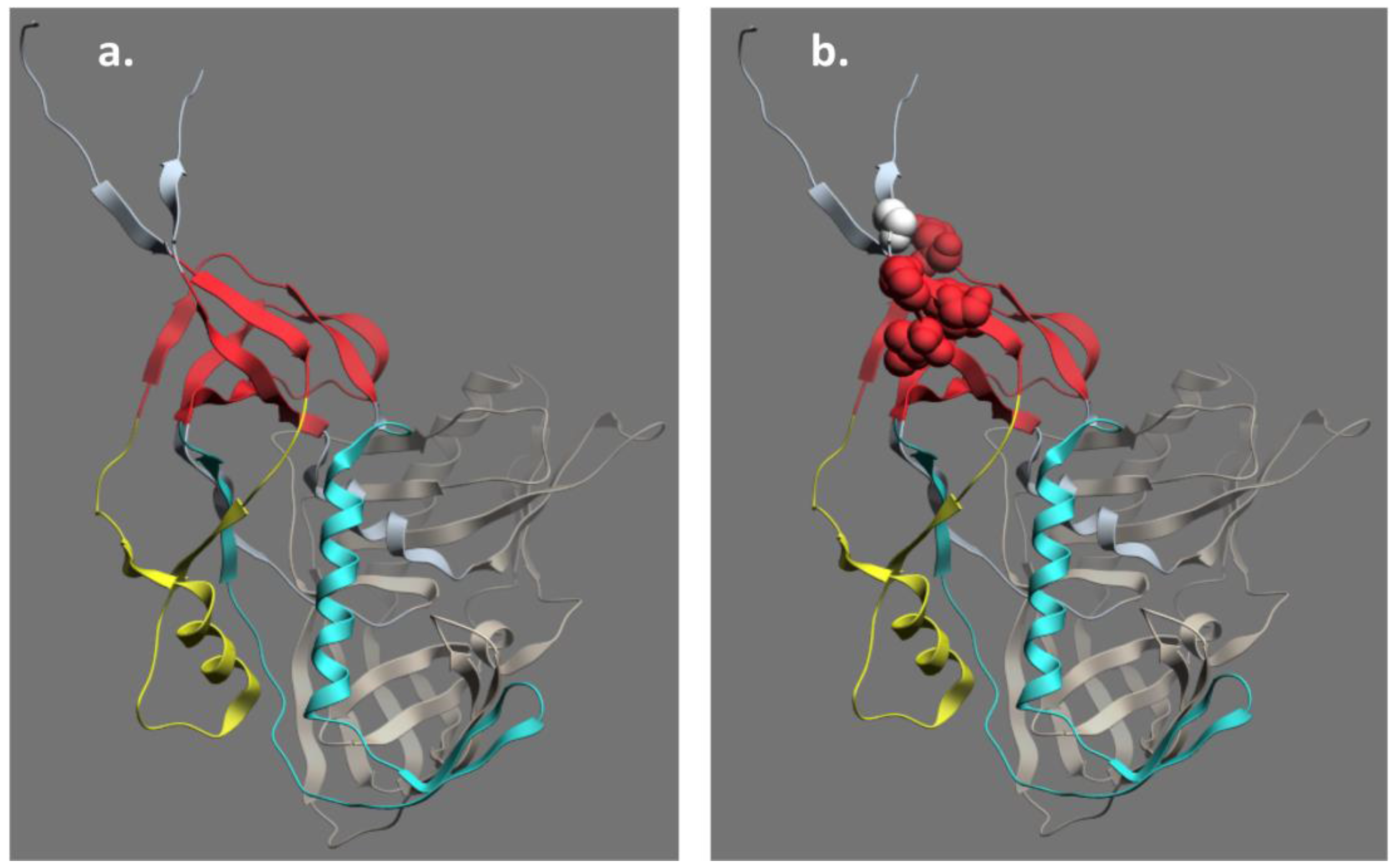
5. Structure of the C11 Subregion of Epitope Cluster A
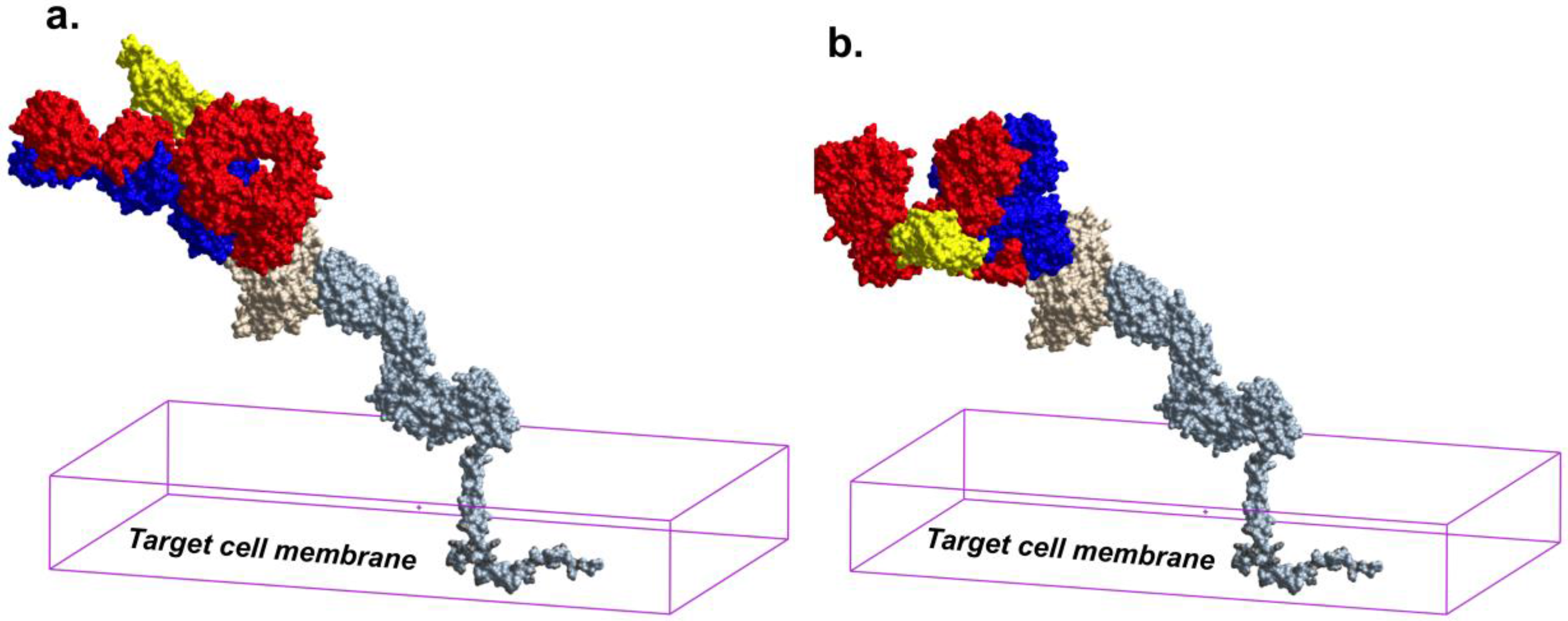
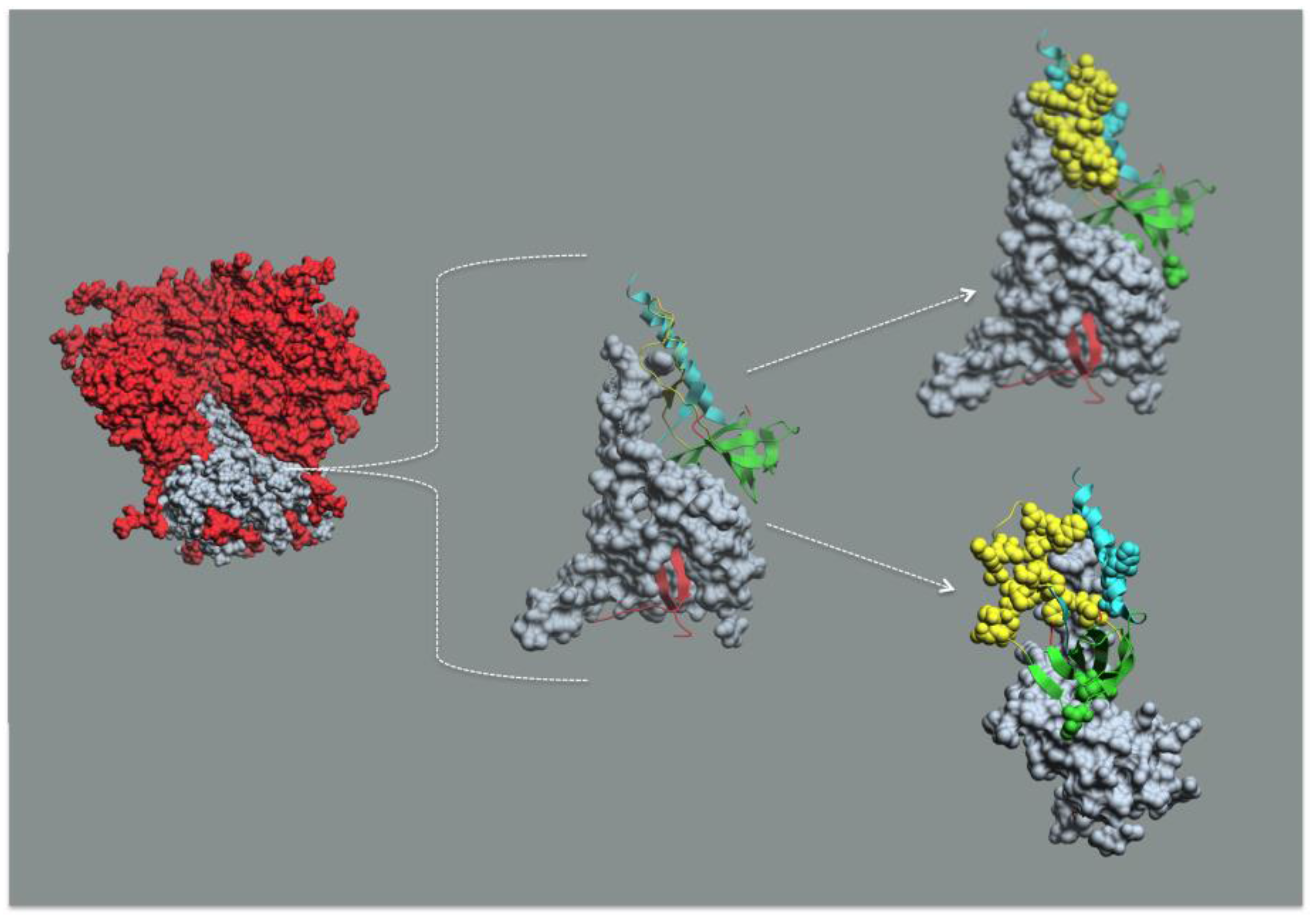
6. Epitope Cluster A Is Conformationally Masked on Virions and Partially Formed in Unliganded Soluble Env Trimer Analogs
7. Receptor Dependent Conformational Unmasking of Epitope Cluster A
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emini, E.A.; Nara, P.L.; Schleif, W.A.; Lewis, J.A.; Davide, J.P.; Lee, D.R.; Kessler, J.; Conley, S.; Matsushita, S.; Putney, S.D.; et al. Antibody-mediated in vitro neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 abolishes infectivity for chimpanzees. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3674–3678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emini, E.A.; Schleif, W.A.; Nunberg, J.H.; Conley, A.J.; Eda, Y.; Tokiyoshi, S.; Putney, S.D.; Matsushita, S.; Cobb, K.E.; Jett, C.M.; et al. Prevention of HIV-1 infection in chimpanzees by gp120 v3 domain-specific monoclonal antibody. Nature 1992, 355, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putkonen, P.; Thorstensson, R.; Ghavamzadeh, L.; Albert, J.; Hild, K.; Biberfeld, G.; Norrby, E. Prevention of HIV-2 and sivsm infection by passive immunization in cynomolgus monkeys. Nature 1991, 352, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresman, L.; Jia, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Stephens, E.B.; Sahni, M.; Narayan, O.; Joag, S.V. Neutralizing antibodies administered before, but not after, virulent shiv prevent infection in macaques. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1998, 14, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.W.; Liska, V.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Vlasak, J.; Xu, W.; Ayehunie, S.; Cavacini, L.A.; Posner, M.R.; Katinger, H.; Stiegler, G.; et al. Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mascola, J.R.; Stiegler, G.; VanCott, T.C.; Katinger, H.; Carpenter, C.B.; Hanson, C.E.; Beary, H.; Hayes, D.; Frankel, S.S.; Birx, D.L.; et al. Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/siv chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parren, P.W.; Marx, P.A.; Hessell, A.J.; Luckay, A.; Harouse, J.; Cheng-Mayer, C.; Moore, J.P.; Burton, D.R. Antibody protects macaques against vaginal challenge with a pathogenic R5 simian/human immunodeficiency virus at serum levels giving complete neutralization in vitro. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8340–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessell, A.J.; Hangartner, L.; Hunter, M.; Havenith, C.E.; Beurskens, F.J.; Bakker, J.M.; Lanigan, C.M.; Landucci, G.; Forthal, D.N.; Parren, P.W.; et al. Fc receptor but not complement binding is important in antibody protection against HIV. Nature 2007, 449, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldt, B.; Rakasz, E.G.; Schultz, N.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Swiderek, K.; Weisgrau, K.L.; Piaskowski, S.M.; Bergman, Z.; Watkins, D.I.; Poignard, P.; et al. Highly potent HIV-specific antibody neutralization in vitro translates into effective protection against mucosal shiv challenge in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18921–18925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shingai, M.; Donau, O.K.; Plishka, R.J.; Buckler-White, A.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J.; Nason, M.C.; Montefiori, D.; Moldt, B.; Poignard, P.; et al. Passive transfer of modest titers of potent and broadly neutralizing anti-HIV monoclonal antibodies block shiv infection in macaques. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2061–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessell, A.J.; Poignard, P.; Hunter, M.; Hangartner, L.; Tehrani, D.M.; Bleeker, W.K.; Parren, P.W.; Marx, P.A.; Burton, D.R. Effective, low-titer antibody protection against low-dose repeated mucosal shiv challenge in macaques. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessell, A.J.; Rakasz, E.G.; Poignard, P.; Hangartner, L.; Landucci, G.; Forthal, D.N.; Koff, W.C.; Watkins, D.I.; Burton, D.R. Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2g12 is effective in protection against mucosal shiv challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessell, A.J.; Rakasz, E.G.; Tehrani, D.M.; Huber, M.; Weisgrau, K.L.; Landucci, G.; Forthal, D.N.; Koff, W.C.; Poignard, P.; Watkins, D.I.; et al. Broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies 2f5 and 4e10 directed against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 membrane-proximal external region protect against mucosal challenge by simian-human immunodeficiency virus shivba-l. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.R.; Hessell, A.J.; Keele, B.F.; Klasse, P.J.; Ketas, T.A.; Moldt, B.; Dunlop, D.C.; Poignard, P.; Doyle, L.A.; Cavacini, L.; et al. Limited or no protection by weakly or nonneutralizing antibodies against vaginal shiv challenge of macaques compared with a strongly neutralizing antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11181–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, R.; Igarashi, T.; Haigwood, N.; Buckler-White, A.; Ogert, R.; Ross, W.; Willey, R.; Cho, M.W.; Martin, M.A. Neutralizing antibody directed against the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein can completely block HIV-1/siv chimeric virus infections of macaque monkeys. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.M.; Phogat, S.K.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Wagner, D.; Phung, P.; Goss, J.L.; Wrin, T.; Simek, M.D.; Fling, S.; Mitcham, J.L.; et al. Broad and potent neutralizing antibodies from an african donor reveal a new HIV-1 vaccine target. Science 2009, 326, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.M.; Simek, M.D.; Priddy, F.; Gach, J.S.; Wagner, D.; Zwick, M.B.; Phogat, S.K.; Poignard, P.; Burton, D.R. A limited number of antibody specificities mediate broad and potent serum neutralization in selected HIV-1 infected individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.R.; Mascola, J.R. Antibody responses to envelope glycoproteins in HIV-1 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.K. Honing a harder-hitting hammerhead improves broadly neutralizing antibody breadth and potency. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, F.; Diskin, R.; Scheid, J.F.; Gaebler, C.; Mouquet, H.; Georgiev, I.S.; Pancera, M.; Zhou, T.; Incesu, R.B.; Fu, B.Z.; et al. Somatic mutations of the immunoglobulin framework are generally required for broad and potent HIV-1 neutralization. Cell 2013, 153, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.K.; DeVico, A.L.; Gallo, R.C. Antibody persistence and t-cell balance: Two key factors confronting HIV vaccine development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15614–15621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moog, C.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Teillaud, J.L.; Biedma, M.E.; Holl, V.; van Ham, G.; Heyndrickx, L.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Katinger, D.; Vcelar, B.; et al. Protective effect of vaginal application of neutralizing and nonneutralizing inhibitory antibodies against vaginal shiv challenge in macaques. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugast, A.S.; Chan, Y.; Hoffner, M.; Licht, A.; Nkolola, J.; Li, H.; Streeck, H.; Suscovich, T.J.; Ghebremichael, M.; Ackerman, M.E.; et al. Lack of protection following passive transfer of polyclonal highly functional low-dose non-neutralizing antibodies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rompay, K.K.; Berardi, C.J.; Dillard_Telm, S.; Tarara, R.P.; Canfield, D.R.; Valverde, C.R.; Montefiori, D.C.; Cole, K.S.; Montelaro, R.C.; Miller, C.J. Passive immunization of newborn rhesus macaques prevents oral simian immunodeficiency virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forthal, D.N.; Landucci, G.; Cole, K.S.; Marthas, M.; Becerra, J.C.; van Rompay, K. Rhesus macaque polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies inhibit simian immunodeficiency virus in the presence of human or autologous rhesus effector cells. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9217–9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florese, R.H.; Van Rompay, K.K.; Aldrich, K.; Forthal, D.N.; Landucci, G.; Mahalanabis, M.; Haigwood, N.; Venzon, D.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Marthas, M.L.; et al. Evaluation of passively transferred, nonneutralizing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating IgG in protection of neonatal rhesus macaques against oral sivmac251 challenge. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4028–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.K. Qualitative and quantitative variables that affect the potency of Fc-mediated effector function in vitro and in vivo: Considerations for passive immunization using non-neutralizing antibodies. Curr. HIV Res. 2013, 11, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.K. Role of Fc-mediated antibody function in protective immunity against HIV-1. Immunology 2014, 142, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.K.; Guan, Y.; Kamin-Lewis, R.; Sajadi, M.; Pazgier, M.; Devico, A.L. Epitope target structures of Fc-mediated effector function during HIV-1 acquisition. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forthal, D.; Hope, T.J.; Alter, G. New paradigms for functional HIV-specific nonneutralizing antibodies. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, M.E.; Dugast, A.S.; Alter, G. Emerging concepts on the role of innate immunity in the prevention and control of HIV infection. Ann. Rev. Med. 2012, 63, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancera, M.; Zhou, T.; Druz, A.; Georgiev, I.S.; Soto, C.; Gorman, J.; Huang, J.; Acharya, P.; Chuang, G.Y.; Ofek, G.; et al. Structure and immune recognition of trimeric pre-fusion HIV-1 env. Nature 2014, 514, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, J.P.; Cupo, A.; Sok, D.; Stanfield, R.L.; Lyumkis, D.; Deller, M.C.; Klasse, P.J.; Burton, D.R.; Sanders, R.W.; Moore, J.P.; et al. Crystal structure of a soluble cleaved HIV-1 envelope trimer. Science 2013, 342, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyumkis, D.; Julien, J.P.; de Val, N.; Cupo, A.; Potter, C.S.; Klasse, P.J.; Burton, D.R.; Sanders, R.W.; Moore, J.P.; Carragher, B.; et al. Cryo-em structure of a fully glycosylated soluble cleaved HIV-1 envelope trimer. Science 2013, 342, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, J.B.; Gorman, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Z.; Arthos, J.; Burton, D.R.; Koff, W.C.; Courter, J.R.; Smith, A.B., III; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Conformational dynamics of single HIV-1 envelope trimers on the surface of native virions. Science 2014, 346, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyner, A.S.; Willis, J.R.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Aiken, C. Maturation-induced cloaking of neutralization epitopes on HIV-1 particles. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, A.S.; Jacobs, A.; Finnegan, C.M.; Stiegler, G.; Katinger, H.; Blumenthal, R. Exposure of the membrane-proximal external region of HIV-1 gp41 in the course of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated fusion. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnegan, C.M.; Berg, W.; Lewis, G.K.; DeVico, A.L. Antigenic properties of the human immunodeficiency virus transmembrane glycoprotein during cell-cell fusion. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12123–12134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Lee, J.H.; Doores, K.J.; Murin, C.D.; Julien, J.P.; McBride, R.; Liu, Y.; Marozsan, A.; Cupo, A.; Klasse, P.J.; et al. Supersite of immune vulnerability on the glycosylated face of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, D.; Lanzavecchia, A. Broadly neutralizing antiviral antibodies. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 705–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, S.A.; Scharf, L.; West, A.P., Jr.; Bjorkman, P.J. Antibody engineering for increased potency, breadth and half-life. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2015, 10, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimidi, R.P.; Klein, J.S.; Politzer, M.S.; Bai, S.; Seaman, M.S.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; West, A.P., Jr.; Bjorkman, P.J. Intra-spike crosslinking overcomes antibody evasion by HIV-1. Cell 2015, 160, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Pazgier, M.; Sajadi, M.M.; Kamin-Lewis, R.; Al-Darmarki, S.; Flinko, R.; Lovo, E.; Wu, X.; Robinson, J.E.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Diverse specificity and effector function among human antibodies to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein epitopes exposed by CD4 binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E69–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillette, M.; Desormeaux, A.; Medjahed, H.; Gharsallah, N.E.; Coutu, M.; Baalwa, J.; Guan, Y.; Lewis, G.; Ferrari, G.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. Interaction with cellular CD4 exposes HIV-1 envelope epitopes targeted by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, G.; Pollara, J.; Kozink, D.; Harms, T.; Drinker, M.; Freel, S.; Moody, M.A.; Alam, S.M.; Tomaras, G.D.; Ochsenbauer, C.; et al. An HIV-1 gp120 envelope human monoclonal antibody that recognizes a C1 conformational epitope mediates potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (adcc) activity and defines a common adcc epitope in human HIV-1 serum. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7029–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilen, C.B.; Tilton, J.C.; Doms, R.W. Molecular mechanisms of HIV entry. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 726, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilen, C.B.; Tilton, J.C.; Doms, R.W. HIV: Cell binding and entry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenthal, R.; Durell, S.; Viard, M. HIV entry and envelope glycoprotein-mediated fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40841–40849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Cupo, A.; Julien, J.P.; Sanders, R.W.; Wilson, I.A.; Moore, J.P.; Lee, K.K. Antibody potency relates to the ability to recognize the closed, pre-fusion form of HIV Env. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVico, A.L. CD4-induced epitopes in the HIV envelope glycoprotein, gp120. Curr. HIV Res. 2007, 5, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Garcia, N.K.; Cupo, A.; Matsui, T.; Julien, J.P.; Sanders, R.W.; Wilson, I.A.; Moore, J.P.; Lee, K.K. CD4-induced activation in a soluble HIV-1 Env trimer. Structure 2014, 22, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Krausslich, H.G. HIV-1 assembly, budding, and maturation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Aiken, C. Maturation-dependent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particle fusion requires a carboxyl-terminal region of the gp41 cytoplasmic tail. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9999–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Aiken, C. Maturation of the viral core enhances the fusion of HIV-1 particles with primary human t cells and monocyte-derived macrophages. Virology 2006, 346, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyma, D.J.; Kotov, A.; Aiken, C. Evidence for a stable interaction of gp41 with pr55(gag) in immature human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particles. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9381–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Ablan, S.; Freed, E.O.; Tanaka, Y. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env-mediated membrane fusion by viral protease activity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, R.S.; Paradis, T.; Hartshorn, K.L.; Vogt, M.; Ho, D.D.; Hirsch, M.S.; Leban, J.; Sato, V.L.; Schooley, R.T. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against cells infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 156, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyerly, H.K.; Matthews, T.J.; Langlois, A.J.; Bolognesi, D.P.; Weinhold, K.J. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus IIIB glycoprotein (gp120) bound to CD4 determinants on normal lymphocytes and expressed by infected cells serves as target for immune attack. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 4601–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyerly, H.K.; Reed, D.L.; Matthews, T.J.; Langlois, A.J.; Ahearne, P.A.; Petteway, S.R., Jr.; Weinhold, K.J. Anti-gp 120 antibodies from HIV seropositive individuals mediate broadly reactive anti-HIV ADCC. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1987, 3, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rook, A.H.; Lane, H.C.; Folks, T.; McCoy, S.; Alter, H.; Fauci, A.S. Sera from HTLV-III/LAV antibody-positive individuals mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against HTLV-III/LAV-infected T cells. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tyler, D.S.; Stanley, S.D.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Gorny, M.K.; Shadduck, P.P.; Langlois, A.J.; Matthews, T.J.; Bolognesi, D.P.; Palker, T.J.; Weinhold, K.J. Identification of sites within gp41 that serve as targets for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by using human monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3276–3282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finnegan, C.M.; Berg, W.; Lewis, G.K.; DeVico, A.L. Antigenic properties of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope during cell-cell fusion. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11096–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengistu, M.; Ray, K.; Lewis, G.K.; DeVico, A.L. Antigenic properties of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein gp120 on virions bound to target cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, B.F.; Gilbert, P.B.; McElrath, M.J.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Tomaras, G.D.; Alam, S.M.; Evans, D.T.; Montefiori, D.C.; Karnasuta, C.; Sutthent, R.; et al. Immune-correlates analysis of an HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsignori, M.; Pollara, J.; Moody, M.A.; Alpert, M.D.; Chen, X.; Hwang, K.K.; Gilbert, P.B.; Huang, Y.; Gurley, T.C.; Kozink, D.M.; et al. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating antibodies from an HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial target multiple epitopes and preferentially use the VH1 gene family. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11521–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVico, A.; Fouts, T.; Lewis, G.K.; Gallo, R.C.; Godfrey, K.; Charurat, M.; Harris, I.; Galmin, L.; Pal, R. Antibodies to CD4-induced sites in HIV gp120 correlate with the control of shiv challenge in macaques vaccinated with subunit immunogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17477–17482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouts, T.R.; Bagley, K.; Prado, I.J.; Bobb, K.L.; Schwartz, J.A.; Xu, R.; Zagursky, R.J.; Egan, M.A.; Eldridge, J.H.; LaBranche, C.C.; et al. Balance of cellular and humoral immunity determines the level of protection by HIV vaccines in rhesus macaque models of HIV infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E992–E999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.A.; Tuero, I.; Demberg, T.; Vargas-Inchaustegui, D.A.; Musich, T.; Xiao, P.; Venzon, D.; LaBranche, C.; Montefiori, D.C.; DiPasquale, J.; et al. HIV-1 CD4-induced (CD4i) gp120 epitope vaccines promote b and t-cell responses that contribute to reduced viral loads in rhesus macaques. Virology 2014, 471–473, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barouch, D.H.; Alter, G.; Broge, T.; Linde, C.; Ackerman, M.E.; Brown, E.P.; Borducchi, E.N.; Smith, K.M.; Nkolola, J.P.; Liu, J.; et al. HIV-1 vaccines. Protective efficacy of adenovirus/protein vaccines against siv challenges in rhesus monkeys. Science 2015, 349, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, L.H.; Chung, A.W.; Isitman, G.; Kelleher, A.D.; Parsons, M.S.; Amin, J.; Cooper, D.A.; Stratov, I.; Navis, M.; Kent, S.J. Specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses associated with slow progression of HIV infection. Immunology 2013, 138, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambotte, O.; Pollara, J.; Boufassa, F.; Moog, C.; Venet, A.; Haynes, B.F.; Delfraissy, J.F.; Saez-Cirion, A.; Ferrari, G. High antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses are correlated with strong cd8 t cell viral suppressive activity but not with b57 status in HIV-1 elite controllers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, S.E.; Rollman, E.; Chung, A.W.; Center, R.J.; Hejdeman, B.; Stratov, I.; Hinkula, J.; Wahren, B.; Karre, K.; Kent, S.J.; et al. Nk cell function and antibodies mediating adcc in HIV-1-infected viremic and controller patients. Viral Immunol. 2011, 24, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.W.; Navis, M.; Isitman, G.; Wren, L.; Silvers, J.; Amin, J.; Kent, S.J.; Stratov, I. Activation of NK cells by adcc antibodies and HIV disease progression. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2011, 58, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.W.; Navis, M.; Isitman, G.; Centre, R.; Finlayson, R.; Bloch, M.; Gelgor, L.; Kelleher, A.; Kent, S.J.; Stratov, I. Activation of nk cells by adcc responses during early HIV infection. Viral Immunol. 2011, 24, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.W.; Isitman, G.; Navis, M.; Kramski, M.; Center, R.J.; Kent, S.J.; Stratov, I. Immune escape from HIV-specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) pressure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7505–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, G.; Teigen, N.; Davis, B.T.; Addo, M.M.; Suscovich, T.J.; Waring, M.T.; Streeck, H.; Johnston, M.N.; Staller, K.D.; Zaman, M.T.; et al. Sequential deregulation of nk cell subset distribution and function starting in acute HIV-1 infection. Blood 2005, 106, 3366–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, P.; Kim, J.; Sapiega, V.; Landay, A.L.; Bremer, J.W.; Mestecky, J.; Reichelderfer, P.; Kovacs, A.; Cohn, J.; Weiser, B.; et al. Women with cervicovaginal antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity have lower genital HIV-1 RNA loads. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forthal, D.N.; Landucci, G.; Keenan, B. Relationship between antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, plasma HIV type 1 RNA, and CD4+ lymphocyte count. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2001, 17, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Sindhu, S.T.; Toma, E.; Morisset, R.; Vincelette, J.; Menezes, J.; Ahmad, A. Evidence for a correlation between antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating anti-HIV-1 antibodies and prognostic predictors of HIV infection. J. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 21, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranchat, C.; Van de Perre, P.; Simonon-Sorel, A.; Karita, E.; Benchaib, M.; Lepage, P.; Desgranges, C.; Boyer, V.; Trepo, C. Maternal humoral factors associated with perinatal human immunodeficiency virus type-1 transmission in a cohort from kigali, rwanda, 1988–1994. J. Infect. 1999, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, L.L.; Cassutt, K.J.; Knigge, K.; Khattri, R.; Margolick, J.; Rinaldo, C.; Kleeberger, C.A.; Nishanian, P.; Henrard, D.R.; Phair, J. HIV-1 gp120-specific antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity correlates with rate of disease progression. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, M.; Landers, D.; Williams-Herman, D.; Wara, D.; Viscarello, R.R.; Hammill, H.A.; Kline, M.W.; Shearer, W.T.; Charlebois, E.D.; Kohl, S. Association between anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity antibody titers at birth and vertical transmission of HIV-1. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Morisset, R.; Thomas, R.; Menezes, J. Evidence for a defect of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic (adcc) effector function and anti-HIV gp120/41-specific ADCC-mediating antibody titres in HIV-infected individuals. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1994, 7, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broliden, K.; Sievers, E.; Tovo, P.A.; Moschese, V.; Scarlatti, G.; Broliden, P.A.; Fundaro, C.; Rossi, P. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and neutralizing activity in sera of HIV-1-infected mothers and their children. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1993, 93, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, L.A.; Katzenstein, D.A.; Hendry, R.M.; Boone, E.J.; Vujcic, L.K.; Williams, C.C.; Zeger, S.L.; Saah, A.J.; Rinaldo, C.R., Jr.; Phair, J.P.; et al. Possible beneficial effects of neutralizing antibodies and antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity in human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1990, 6, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljunggren, K.; Moschese, V.; Broliden, P.A.; Giaquinto, C.; Quinti, I.; Fenyo, E.M.; Wahren, B.; Rossi, P.; Jondal, M. Antibodies mediating cellular cytotoxicity and neutralization correlate with a better clinical stage in children born to human immunodeficiency virus-infected mothers. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo-Amaize, E.; Nishanian, P.G.; Heitjan, D.F.; Rezai, A.; Esmail, I.; Korns, E.; Detels, R.; Fahey, J.; Giorgi, J.V. Serum and effector-cell antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity remains high during human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease progression. J. Clin. Immunol. 1989, 9, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudsmit, J.; Ljunggren, K.; Smit, L.; Jondal, M.; Fenyo, E.M. Biological significance of the antibody response to HIV antigens expressed on the cell surface. Arch. Virol. 1988, 103, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljunggren, K.; Bottiger, B.; Biberfeld, G.; Karlson, A.; Fenyo, E.M.; Jondal, M. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-inducing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus. Presence at different clinical stages. J. Immunol. 1987, 139, 2263–2267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fouts, T.R.; Tuskan, R.; Godfrey, K.; Reitz, M.; Hone, D.; Lewis, G.K.; DeVico, A.L. Expression and characterization of a single-chain polypeptide analogue of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120-CD4 receptor complex. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11427–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Roman, V.R.; Florese, R.H.; Patterson, L.J.; Peng, B.; Venzon, D.; Aldrich, K.; Robert-Guroff, M. A simplified method for the rapid fluorometric assessment of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 308, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnathan, D.G.; Wetzel, K.S.; Yu, J.; Lee, S.T.; Johnson, B.A.; Paiardini, M.; Yan, J.; Morrow, M.P.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Weiner, D.B.; et al. Activated CD4+CCR5+ T cells in the rectum predict increased siv acquisition in sivgag/tat-vaccinated rhesus macaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, P.; Tolbert, W.D.; Gohain, N.; Wu, X.; Yu, L.; Liu, T.; Huang, W.; Huang, C.C.; Kwon, Y.D.; Louder, R.K.; et al. Structural definition of an antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity response implicated in reduced risk for HIV-1 infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12895–12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.P.; McCutchan, F.E.; Poon, S.W.; Mascola, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y.; Ho, D.D. Exploration of antigenic variation in gp120 from clades a through f of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by using monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 8350–8364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pancera, M.; Majeed, S.; Ban, Y.E.; Chen, L.; Huang, C.C.; Kong, L.; Kwon, Y.D.; Stuckey, J.; Zhou, T.; Robinson, J.E.; et al. Structure of HIV-1 gp120 with gp41-interactive region reveals layered envelope architecture and basis of conformational mobility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finzi, A.; Xiang, S.H.; Pacheco, B.; Wang, L.; Haight, J.; Kassa, A.; Danek, B.; Pancera, M.; Kwong, P.D.; Sodroski, J. Topological layers in the HIV-1 gp120 inner domain regulate gp41 interaction and CD4-triggered conformational transitions. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollara, J.; Bonsignori, M.; Moody, M.A.; Liu, P.; Alam, S.M.; Hwang, K.K.; Gurley, T.C.; Kozink, D.M.; Armand, L.C.; Marshall, D.J.; et al. HIV-1 vaccine-induced c1 and v2 env-specific antibodies synergize for increased antiviral activities. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7715–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaras, G.D.; Ferrari, G.; Shen, X.; Alam, S.M.; Liao, H.X.; Pollara, J.; Bonsignori, M.; Moody, M.A.; Fong, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Vaccine-induced plasma iga specific for the c1 region of the HIV-1 envelope blocks binding and effector function of IgG. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9019–9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.P.; Willey, R.L.; Lewis, G.K.; Robinson, J.; Sodroski, J. Immunological evidence for interactions between the first, second, and fifth conserved domains of the gp120 surface glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6836–6847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koup, R.A.; Robinson, J.E.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Pikora, C.A.; Blais, B.; Roskey, A.; Panicali, D.; Sullivan, J.L. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity directed by a human monoclonal antibody reactive with gp120 of HIV-1. AIDS 1991, 5, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsmadi, O.; Herz, R.; Murphy, E.; Pinter, A.; Tilley, S.A. A novel antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity epitope in gp120 is identified by two monoclonal antibodies isolated from a long-term survivor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pollara, J.; Bonsignori, M.; Moody, M.A.; Pazgier, M.; Haynes, B.F.; Ferrari, G. Epitope specificity of human immunodeficiency virus-1 antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity [adcc] responses. Curr. HIV Res. 2013, 11, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santra, S.; Tomaras, G.D.; Warrier, R.; Nicely, N.; Liao, H.X.; Pollara, J.; Liu, P.; Alam, S.M.; Zhang, R.; Cocklin, S.; et al. Human non-neutralizing HIV-1 envelope monoclonal antibodies limit the number of founder viruses during shiv mucosal infection in rhesus macaques. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor, D.; Bomsel, M. The broadly neutralizing HIV-1 IgG 2f5 elicits gp41-specific antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in a fcgammari-dependent manner. AIDS 2011, 25, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezareh, M.; Hessell, A.J.; Jensen, R.C.; van de Winkel, J.G.; Parren, P.W. Effector function activities of a panel of mutants of a broadly neutralizing antibody against human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 12161–12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldt, B.; Schultz, N.; Dunlop, D.C.; Alpert, M.D.; Harvey, J.D.; Evans, D.T.; Poignard, P.; Hessell, A.J.; Burton, D.R. A panel of IgG 1 B12 variants with selectively diminished or enhanced affinity for fcgamma receptors to define the role of effector functions in protection against HIV. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10572–10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldt, B.; Shibata-Koyama, M.; Rakasz, E.G.; Schultz, N.; Kanda, Y.; Dunlop, D.C.; Finstad, S.L.; Jin, C.; Landucci, G.; Alpert, M.D.; et al. A nonfucosylated variant of the anti-HIV-1 monoclonal antibody B12 has enhanced fcgammariiia-mediated antiviral activity in vitro but does not improve protection against mucosal shiv challenge in macaques. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6189–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.; Mengistu, M.; Yu, L.; Lewis, G.K.; Lakowicz, J.R.; DeVico, A.L. Antigenic properties of the HIV envelope on virions in solution. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helseth, E.; Olshevsky, U.; Furman, C.; Sodroski, J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 envelope glycoprotein regions important for association with the gp41 transmembrane glycoprotein. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 2119–2123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thali, M.; Furman, C.; Helseth, E.; Repke, H.; Sodroski, J. Lack of correlation between soluble CD4-induced shedding of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 exterior envelope glycoprotein and subsequent membrane fusion events. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 5516–5524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Mahony, E.; Holm, G.H.; Kassa, A.; Sodroski, J. Role of the gp120 inner domain beta-sandwich in the interaction between the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein subunits. Virology 2003, 313, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavitt, M.; Park, E.J.; Sidorov, I.A.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Quinnan, G.V., Jr. Concordant modulation of neutralization resistance and high infectivity of the primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mn strain and definition of a potential gp41 binding site in gp120. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, J.; Jacobs, A.; Caffrey, M. Role of the HIV gp120 conserved domain 5 in processing and viral entry. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 7788–7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sen, J.; Rong, L.; Caffrey, M. Role of the HIV gp120 conserved domain 1 in processing and viral entry. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 32644–32649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merk, A.; Subramaniam, S. HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structure. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsahafi, N.; Debbeche, O.; Sodroski, J.; Finzi, A. Effects of the i559p gp41 change on the conformation and function of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) membrane envelope glycoprotein trimer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Igarashi, T.; Haigwood, N.L.; Sadjadpour, R.; Donau, O.K.; Buckler, C.; Plishka, R.J.; Buckler-White, A.; Martin, M.A. Transfer of neutralizing IgG to macaques 6 h but not 24 h after shiv infection confers sterilizing protection: Implications for HIV-1 vaccine development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15131–15136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.P.; Picot, V.; Longuet, C.; Nabel, G.J. Report of the cent gardes HIV vaccine conference: The b-cell response to HIV. Part 2: Non-neutralizing antibodies: Fondation merieux conference center, veyrier du lac, france 5–7 november 2012. Vaccine 2013, 31, 2984–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, L.J.; Yam, P.T.; Jiang, X.M.; Vandegraaff, N.; Li, P.; Poumbourios, P.; Donoghue, N.; Hogg, P.J. Disulfide exchange in domain 2 of CD4 is required for entry of HIV-1. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, L.J.; Yam, P.T.; Jiang, X.M.; Hogg, P.J. Disulfide exchange in CD4. BioFactors 2003, 17, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, A.; Schmidt, B.; Fazekas de St Groth, B.; Sanejouand, Y.H.; Hogg, P.J. Evidence for a domain-swapped CD4 dimer as the coreceptor for binding to class II mhc. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6873–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, L.J.; Azimi, I.; Tabrett, C.A.; Hogg, P.J. Reduced monomeric CD4 is the preferred receptor for HIV. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40793–40799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, N.; Killick, M.; Jugnarain, V.; Papathanasopoulos, M.; Capovilla, A. Disulfide reduction in CD4 domain 1 or 2 is essential for interaction with HIV glycoprotein 120 (gp120), which impairs thioredoxin-driven CD4 dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10455–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, O.; Dautry-Varsat, A.; Goud, B.; Marechal, V.; Subtil, A.; Heard, J.M.; Danos, O. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nef induces accumulation of CD4 in early endosomes. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willey, R.L.; Maldarelli, F.; Martin, M.A.; Strebel, K. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpu protein induces rapid degradation of CD4. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neil, S.J.; Zang, T.; Bieniasz, P.D. Tetherin inhibits retrovirus release and is antagonized by HIV-1 vpu. Nature 2008, 451, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, N.; Goff, D.; Katsura, C.; Jorgenson, R.L.; Mitchell, R.; Johnson, M.C.; Stephens, E.B.; Guatelli, J. The interferon-induced protein BST-2 restricts HIV-1 release and is downregulated from the cell surface by the viral vpu protein. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillette, M.; Coutu, M.; Richard, J.; Batraville, L.A.; Dagher, O.; Bernard, N.; Tremblay, C.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Roger, M.; Finzi, A. The HIV-1 gp120 CD4-bound conformation is preferentially targeted by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating antibodies in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, R.A.; Hamlin, R.E.; Monroe, A.; Moldt, B.; Hotta, M.T.; Rodriguez Caprio, G.; Fierer, D.S.; Simon, V.; Chen, B.K. HIV-1 vpu antagonism of tetherin inhibits antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic responses by natural killer cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6031–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, J.F.; Heyer, L.N.; von Bredow, B.; Weisgrau, K.L.; Moldt, B.; Burton, D.R.; Rakasz, E.G.; Evans, D.T. Tetherin antagonism by vpu protects HIV-infected cells from antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6425–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batraville, L.A.; Richard, J.; Veillette, M.; Labbe, A.C.; Alary, M.; Guedou, F.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Poudrier, J.; Finzi, A.; Roger, M. Short communication: Anti-HIV-1 envelope immunoglobulin GS in blood and cervicovaginal samples of beninese commercial sex workers. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2014, 30, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.; Veillette, M.; Batraville, L.A.; Coutu, M.; Chapleau, J.P.; Bonsignori, M.; Bernard, N.; Tremblay, C.; Roger, M.; Kaufmann, D.E.; et al. Flow cytometry-based assay to study HIV-1 gp120 specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 208, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillette, M.; Coutu, M.; Richard, J.; Batraville, L.A.; Desormeaux, A.; Roger, M.; Finzi, A. Conformational evaluation of HIV-1 trimeric envelope glycoproteins using a cell-based elisa assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, L.; Jiang, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; He, Y.; Strick, N.; Neamati, N.; Debnath, A.K. Identification of n-phenyl-n′-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidin-4-yl)-oxalamides as a new class of HIV-1 entry inhibitors that prevent gp120 binding to CD4. Virology 2005, 339, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaLonde, J.M.; Kwon, Y.D.; Jones, D.M.; Sun, A.W.; Courter, J.R.; Soeta, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Princiotto, A.M.; Wu, X.; Schon, A.; et al. Structure-based design, synthesis, and characterization of dual hotspot small-molecule HIV-1 entry inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4382–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalonde, J.M.; Le-Khac, M.; Jones, D.M.; Courter, J.R.; Park, J.; Schon, A.; Princiotto, A.M.; Wu, X.; Mascola, J.R.; Freire, E.; et al. Structure-based design and synthesis of an HIV-1 entry inhibitor exploiting X-ray and thermodynamic characterization. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, N.; Schon, A.; Princiotto, A.M.; Lalonde, J.M.; Courter, J.R.; Soeta, T.; Ng, D.; Wang, L.; Brower, E.T.; Xiang, S.H.; et al. Small-molecule CD4 mimics interact with a highly conserved pocket on HIV-1 gp120. Structure 2008, 16, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, P.D.; Wyatt, R.; Robinson, J.; Sweet, R.W.; Sodroski, J.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structure of an HIV gp120 envelope glycoprotein in complex with the CD4 receptor and a neutralizing human antibody. Nature 1998, 393, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schon, A.; Madani, N.; Klein, J.C.; Hubicki, A.; Ng, D.; Yang, X.; Smith, A.B., III; Sodroski, J.; Freire, E. Thermodynamics of binding of a low-molecular-weight CD4 mimetic to HIV-1 gp120. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10973–10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, N.; Princiotto, A.M.; Schon, A.; LaLonde, J.; Feng, Y.; Freire, E.; Park, J.; Courter, J.R.; Jones, D.M.; Robinson, J.; et al. CD4-mimetic small molecules sensitize human immunodeficiency virus to vaccine-elicited antibodies. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6542–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, J.M.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, S.; Levy, D.N.; Wang, W.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M.; Derdeyn, C.A.; Allen, S.; et al. Antigenic conservation and immunogenicity of the HIV coreceptor binding site. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.; Stricher, F.; Misse, D.; Sironi, F.; Pugniere, M.; Barthe, P.; Prado-Gotor, R.; Freulon, I.; Magne, X.; Roumestand, C.; et al. Rational design of a CD4 mimic that inhibits HIV-1 entry and exposes cryptic neutralization epitopes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Herrewege, Y.; Morellato, L.; Descours, A.; Aerts, L.; Michiels, J.; Heyndrickx, L.; Martin, L.; Vanham, G. CD4 mimetic miniproteins: Potent anti-HIV compounds with promising activity as microbicides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, P.; Luongo, T.S.; Louder, M.K.; McKee, K.; Yang, Y.; Kwon, Y.D.; Mascola, J.R.; Kessler, P.; Martin, L.; Kwong, P.D. Structural basis for highly effective HIV-1 neutralization by CD4-mimetic miniproteins revealed by 1.5 a cocrystal structure of gp120 and m48u1. Structure 2013, 21, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.; Veillette, M.; Brassard, N.; Iyer, S.S.; Roger, M.; Martin, L.; Pazgier, M.; Schon, A.; Freire, E.; Routy, J.P.; et al. CD4 mimetics sensitize HIV-1-infected cells to adcc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2687–E2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parren, P.W.; Mondor, I.; Naniche, D.; Ditzel, H.J.; Klasse, P.J.; Burton, D.R.; Sattentau, Q.J. Neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by antibody to gp120 is determined primarily by occupancy of sites on the virion irrespective of epitope specificity. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klasse, P.J.; Sattentau, Q.J. Occupancy and mechanism in antibody-mediated neutralization of animal viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2091–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, J.B.; Mothes, W. Structure and dynamics of the native HIV-1 Env trimer. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5752–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewis, G.K.; Finzi, A.; DeVico, A.L.; Pazgier, M. Conformational Masking and Receptor-Dependent Unmasking of Highly Conserved Env Epitopes Recognized by Non-Neutralizing Antibodies That Mediate Potent ADCC against HIV-1. Viruses 2015, 7, 5115-5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092856
Lewis GK, Finzi A, DeVico AL, Pazgier M. Conformational Masking and Receptor-Dependent Unmasking of Highly Conserved Env Epitopes Recognized by Non-Neutralizing Antibodies That Mediate Potent ADCC against HIV-1. Viruses. 2015; 7(9):5115-5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092856
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewis, George K., Andrés Finzi, Anthony L. DeVico, and Marzena Pazgier. 2015. "Conformational Masking and Receptor-Dependent Unmasking of Highly Conserved Env Epitopes Recognized by Non-Neutralizing Antibodies That Mediate Potent ADCC against HIV-1" Viruses 7, no. 9: 5115-5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092856
APA StyleLewis, G. K., Finzi, A., DeVico, A. L., & Pazgier, M. (2015). Conformational Masking and Receptor-Dependent Unmasking of Highly Conserved Env Epitopes Recognized by Non-Neutralizing Antibodies That Mediate Potent ADCC against HIV-1. Viruses, 7(9), 5115-5132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092856




