eEF1A Interacts with the NS5A Protein and Inhibits the Growth of Classical Swine Fever Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
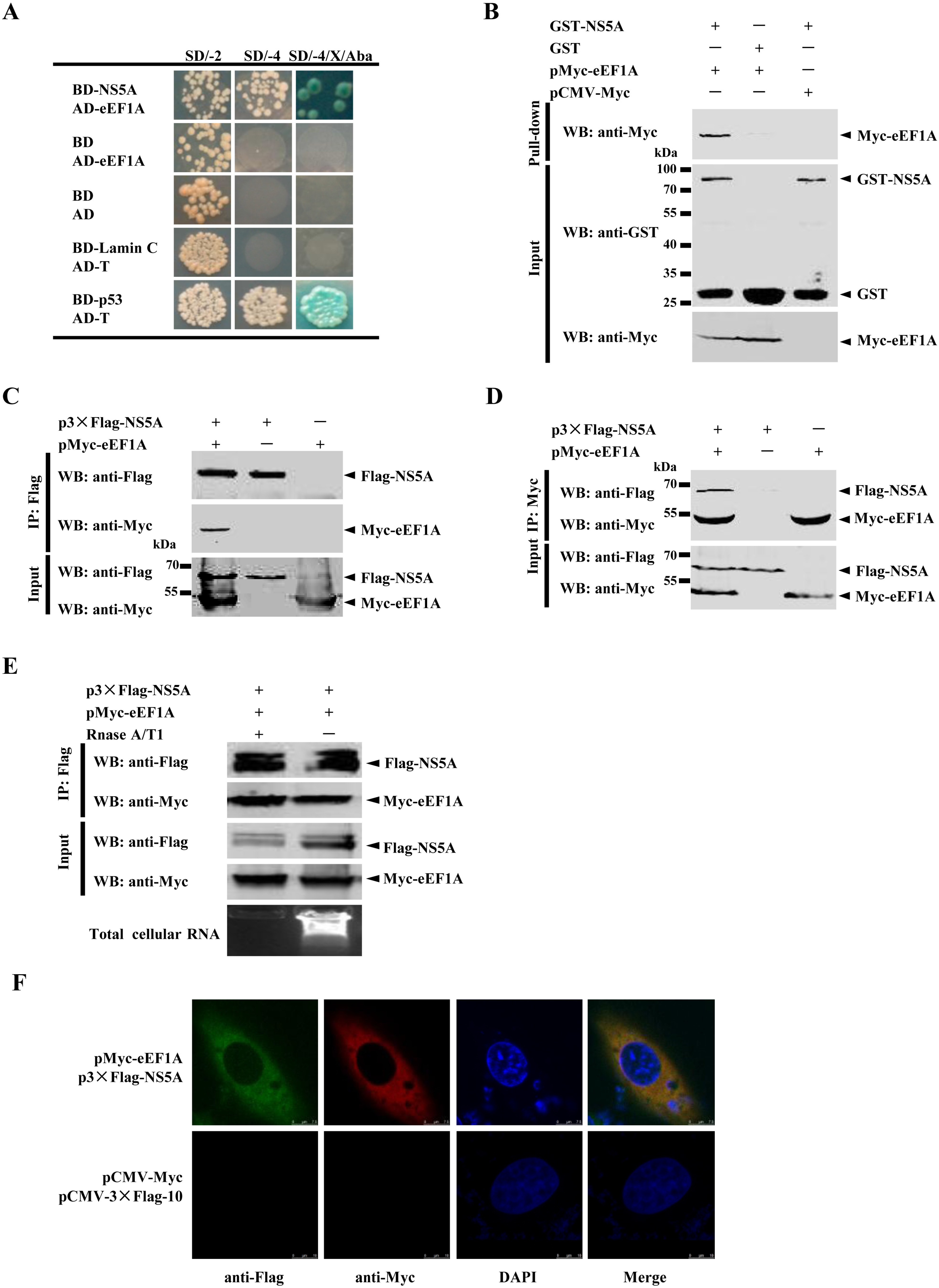
2.1. NS5A Interacts with eEF1A
2.2. The Domain I of eEF1A is Critical for the NS5A–eEF1A Interaction

2.3. Overexpression of eEF1A Inhibits CSFV Replication
2.4. Knockdown of eEF1A by Lentivirus-Mediated shRNAs Enhances CSFV Replication
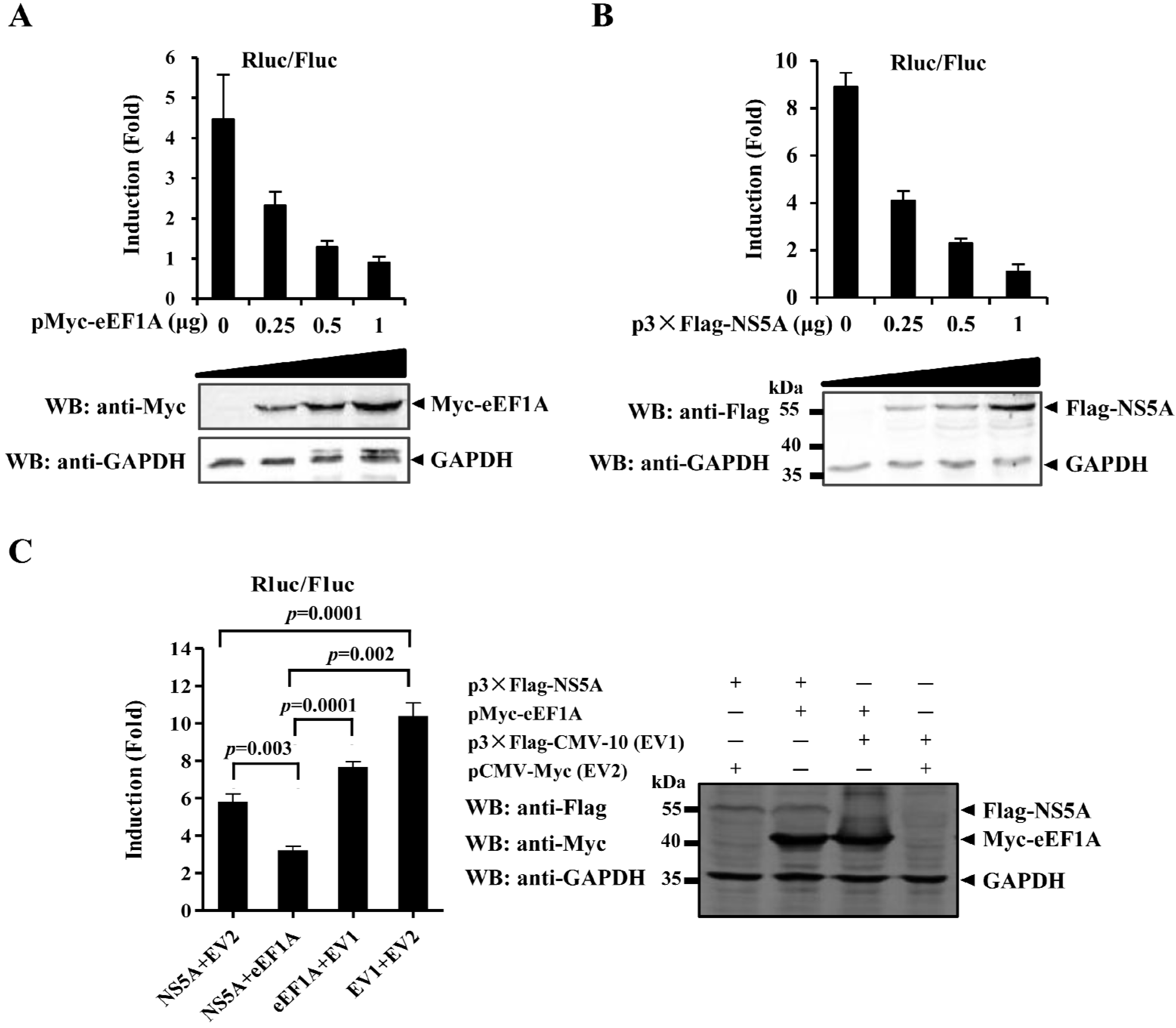
2.5. eEF1A Reduces the Translation Efficiency of CSFV IRES

2.6. eEF1A Interacts with the CSFV IRES
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells, Viruses and Virus Titration Assay
| Primers | Sequences (5ʹ→3ʹ) | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 3×FLAG-NS5A-FP | GCGAATTCATCAAGTAATTACATTCTAGAGC | Amplification of NS5A |
| 3×FLAG-NS5A-RP | ACGGATCCTTACAGTTTCATAGAATACAC | |
| Myc-NS5A-FP | GAATTCATTCAAGTAATTACATTC | Amplification of NS5A |
| Myc-NS5A-RP | ATCTCGAGTTACAGTTTCATAGAATACACTTTTGCA | |
| GST-NS5A-FP | CGGAATTCATGTCAAGTAATTACATTCTAGAGCTCC | Amplification of NS5A |
| GST-NS5A-RP | ATCTCGAGTTACAGTTTCATAGAATACACTTTTGCA | |
| Myc-eEF1A-FP | CGAGATCTATATGGGAAAGGAGAAGACTCACATC | Amplificationof eEF1A |
| Myc-eEF1A-RP | ATCTCGAGTTATCATTTAGCCTTCTGAGC | |
| Myc-eEF1A-FP(1-333) | CGAGATCTATATGGGAAAGGAGAAGACTCACATC | Amplification of eEF1A mutant(1-333) |
| Myc-eEF1A-RP(1-333) | ATCTCGAGTTATGGGTCATTTTTGCTGTCACC | |
| Myc-eEF1A-FP(1-237) | CGAGATCTATATGGGAAAGGAGAAGACTCACATC | Amplification of eEF1A mutant(1-237) |
| Myc-eEF1A-RP(1-237) | ATCTCGAGTTATGGTAGAATGCAATCCAGAGC | |
| Myc-eEF1A-FP(238-462) | CGAGATCTATATGCCAACTCGTCCAACTGACAAGC | Amplification of eEF1A mutant(238-462) |
| Myc-eEF1A-RP(238-462) | CGAGATCTATATGGGAAAGGAGAAGACTCACATC | |
| Myc-eEF1A-FP(201-333) | CGAGATCTATATGCTGGAGCCAAGTGCTAATATG | Amplification of eEF1A mutant(201-333) |
| Myc-eEF1A-RP(201-333) | ATCTCGAGTTATGGGTCATTTTTGCTGTCACC | |
| FUGW-eEF1A-FP | ACAGGCCATTACGGCCATGGGAAAGGAGAAGACTC | Amplification of eEF1A |
| FUGW-eEF1A-RP | TACGGCCGAGGCGGCCTTATCATTTAGCCTTCTGAGC |
4.2. Construction of Expression Vectors
4.3. Yeast Two-Hybrid Screen
4.4. Plasmid Transfection
4.5. GST Pulldown Assay
4.6. Coimmunoprecipitation Assay
4.7. Confocal Microscopy
4.8. Construction of a Stable Cell Line Overexpressing eEF1A
4.9. Gene Knockdown by shRNAs
4.10. Real-Time RT-PCR
4.11. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.12. Streptavidin Pulldown Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moennig, V. Introduction to classical swine fever: virus, disease and control policy. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 73, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Becher, P.; Thiel, H.J. Genus Pestivirus (Flaviviridae). In The Springer Index of Viruses; Tidona, C.A., Darai, G., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Thiel, H.J.; Rice, C.M. Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1101–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, S.P.; Jackson, R.J. Pestivirus internal ribosome entry site (IRES) structure and function: Elements in the 5ʹ-untranslated region important for IRES function. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5024–5033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Gao, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Specific interaction between the classical swine fever virus NS5B protein and the viral genome. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 3888–3896. [Google Scholar]
- Pankraz, A.; Thiel, H.J.; Becher, P. Essential and nonessential elements in the 3ʹ nontranslated region of bovine viral diarrhea virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9119–9127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheng, C.; Zhu, Z.L.; Yu, J.L.; Wan, L.Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, J.; Gu, F.K.; Xiao, M. Characterization of NS3, NS5A and NS5B of classical swine fever virus through mutation and complementation analysis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xiao, J.; Sheng, C.; Wang, J.; Jia, L.; Zhi, Y.M.; Li, G.Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, M. Classical swine fever virus NS5A regulates viral RNA replication through binding to NS5B and 3ʹ UTR. Virology 2012, 432, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Marcotrigiano, J.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Rice, C.M. The NS5A protein of hepatitis C virus is a zinc metalloprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48576–48587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalliampakou, K.I.; Kalamvoki, M.; Mavromara, P. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A protein downregulates HCV IRES-dependent translation. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.C.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, H.Y.; Liao, P.J.; Chang, M.F. Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein down-regulates the expression of spindle gene Aspm through PKR-p38 signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 29396–29404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masaki, T.; Suzuki, R.; Murakami, K.; Aizaki, H.; Ishii, K.; Murayama, A.; Date, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Miyamura, T.; Wakita, T.; Suzuki, T. Interaction of hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A with core protein is critical for the production of infectious virus particles. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7964–7976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.; Griffin, S.; Harris, M. Domain III of NS5A contributes to both RNA replication and assembly of hepatitis C virus particles. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Welsch, C.; Yi, M.; Lemon, S.M. Regulation of the production of infectious genotype 1a hepatitis C virus by NS5A domain III. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6645–6656. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhu, Z.L.; Yu, J.L.; Wan, L.Z.; Chen, J. Influence of NS5A protein of classical swine fever virus (CSFV) on CSFV internal ribosome entry site-dependent translation. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2923–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, K.S.; Humphreys, J.; Hobbs, W.; Smith, G.B.; Ravel, J.M. Determination of the amounts of the protein synthesis initiation and elongation factors in wheat germ. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 17967–17973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Condeelis, J. Elongation factor 1 alpha, translation and the cytoskeleton. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateyak, M.K.; Kinzy, T.G. eEF1A: Thinking Outside the Ribosome. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 21209–21213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, A.; Crosby, S.R.; Burton, D.R.; Lilley, F.; Murphy, M.F. Actin bundling and polymerisation properties of eukaryotic elongation factor 1 alpha (eEF1A), histone H2A-H2B and lysozyme in vitro. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 176, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasikumar, A.N.; Perez, W.B.; Kinzy, T.G. The many roles of the eukaryotic elongation factor 1 complex. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Pogany, J.; Tupman, S.; Esposito, A.M.; Kinzy, T.G.; Nagy, P.D. Translation elongation factor 1A facilitates the assembly of the tombusvirus replicase and stimulates minus-strand synthesis. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, W.; Khan, K.A.; Tripathy, M.K.; Dichamp, I.; Keita, M.; Rohr, O.; Herbein, G. Inhibition of ER stress-mediated apoptosis in macrophages by nuclear-cytoplasmic relocalization of eEF1A by the HIV-1 Nef protein. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, K.; Wei, T.; Li, D.; Qin, F.; Warrilow, D.; Lin, M.H.; Sivakumaran, H.; Apolloni, A.; Abbott, C.M.; Jones, A.; et al. Eukaryotic elongation factor 1 complex subunits are critical HIV-1 reverse transcription cofactors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9587–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.M.; Perez, D.R.; French, R.; Merrick, W.C.; Donis, R.O. The NS5A protein of bovine viral diarrhoea virus interacts with the alpha subunit of translation elongation factor-1. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2935–2943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.J.; Cheng, D.; Li, N.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, Q.H.; Tu, C.; Tong, G.Z.; Qiu, H.J. Evaluation of a multiplex real-time RT-PCR for quantitative and differential detection of wild-type viruses and C-strain vaccine of classical swine fever. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 126, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; He, L.; Kang, K.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y. Screening of cellular proteins that interact with the classical swine fever virus non-structural protein 5A by yeast two-hybrid analysis. J. Biosci. 2014, 86, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kang, K.; Ning, P.; Peng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Cui, H.; Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Heat shock protein 70 is associated with CSFV NS5A protein and enhances viral RNA replication. Virology 2015, 482, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Ma, Q.; Cao, C. The nucleocapsid protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus inhibits cell cytokinesis and proliferation by interacting with translation elongation factor 1alpha. J. Virol. 2013, 82, 6962–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Shi, D.; Li, C.; Feng, L. EF1A interacting with nucleocapsid protein of transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus and plays a role in virus replication. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, W.G.; Basu, M.; Elrod, E.J.; Germann, M.W.; Brinton, M.A. Identification of cis-acting nucleotides and a structural feature in West Nile virus 3ʹ-terminal RNA that facilitate viral minus strand RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7622–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thivierge, K.; Cotton, S.; Dufresne, P.J.; Mathieu, I.; Beauchemin, C.; Ide, C.; Fortin, M.G.; Laliberte, J.F. Eukaryotic elongation factor 1A interacts with Turnip mosaic virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and VPg-Pro in virus-induced vesicles. Virology 2008, 377, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Hamada, K.; Sakurai, K.; Yoshii, A.; Suzuki, M.; Namba, S.; Hibi, T. In vivo interaction between Tobacco mosaic virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and host translation elongation factor 1A. Virology 2006, 347, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Pogany, J.; Panavas, T.; Xu, K.; Esposito, A.M.; Kinzy, T.G.; Nagy, P.D. Translation elongation factor 1A is a component of the tombusvirus replicase complex and affects the stability of the p33 replication cofactor. Virology 2009, 385, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, Y.H.; Chou, S.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Chang, Y.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Jung, M.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, M.R.; Chang, M.F.; Chang, S.C. Hepatitis C virus NS4A inhibits cap-dependent and the viral IRES-mediated translation through interacting with eukaryotic elongation factor 1A. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 13, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamovsky, I.; Ivannikov, M.; Kandel, E.S.; Gershon, D.; Nudler, E. RNA-mediated response to heat shock in mammalian cells. Nature 2006, 440, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, J.L.; Brinton, M.A. Translation elongation factor-1 alpha interacts with the 3ʹ stem-loop region of West Nile virus genomic RNA. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6433–6444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, W.G.; Blackwell, J.L.; Shi, P.Y.; Brinton, M.A. Interaction between the cellular protein eEF1A and the 3ʹ-terminal stem-loop of West Nile virus genomic RNA facilitates viral minus-strand RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10172–10187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; He, W.R.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Qin, H.Y.; Li, L.F.; Dong, H.; et al. Thioredoxin 2 is a novel E2-interacting protein that inhibits the replication of classical swine fever virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8510–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friis, M.B.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Belsham, G.J. Modulation of translation initiation efficiency in classical swine fever virus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8681–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.H.; Li, Y.F.; He, F.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Han, W.; Qiu, H.J. Rapid recovery of classical swine fever virus directly from cloned cDNA. J. Integr. Agrc. 2013, 5, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Feng, S.; Wang, J.-H.; He, W.-R.; Qin, H.-Y.; Dong, H.; Li, L.-F.; Yu, S.-X.; Li, Y.; Qiu, H.-J. eEF1A Interacts with the NS5A Protein and Inhibits the Growth of Classical Swine Fever Virus. Viruses 2015, 7, 4563-4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082833
Li S, Feng S, Wang J-H, He W-R, Qin H-Y, Dong H, Li L-F, Yu S-X, Li Y, Qiu H-J. eEF1A Interacts with the NS5A Protein and Inhibits the Growth of Classical Swine Fever Virus. Viruses. 2015; 7(8):4563-4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082833
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Su, Shuo Feng, Jing-Han Wang, Wen-Rui He, Hua-Yang Qin, Hong Dong, Lian-Feng Li, Shao-Xiong Yu, Yongfeng Li, and Hua-Ji Qiu. 2015. "eEF1A Interacts with the NS5A Protein and Inhibits the Growth of Classical Swine Fever Virus" Viruses 7, no. 8: 4563-4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082833
APA StyleLi, S., Feng, S., Wang, J.-H., He, W.-R., Qin, H.-Y., Dong, H., Li, L.-F., Yu, S.-X., Li, Y., & Qiu, H.-J. (2015). eEF1A Interacts with the NS5A Protein and Inhibits the Growth of Classical Swine Fever Virus. Viruses, 7(8), 4563-4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082833





