Optimization and Characterization of Candidate Strain for Coxsackievirus A16 Inactivated Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cells and CA16 Viruses
2.3. Determination of Viral Titer
2.4. Characterization of CA16 Viral Particles by Electron Microscopy
2.5. Neutralization Assay
2.6. Viral Genome Sequencing
2.7. Viral Growth Assay
2.8. Pilot Production of CA16 Vaccine
2.9. Mouse Immunization
2.10. Western Blot
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of CA16CC024 Vaccine Strain
3.2. Adaptation of CA16 Strains to Vero Cells
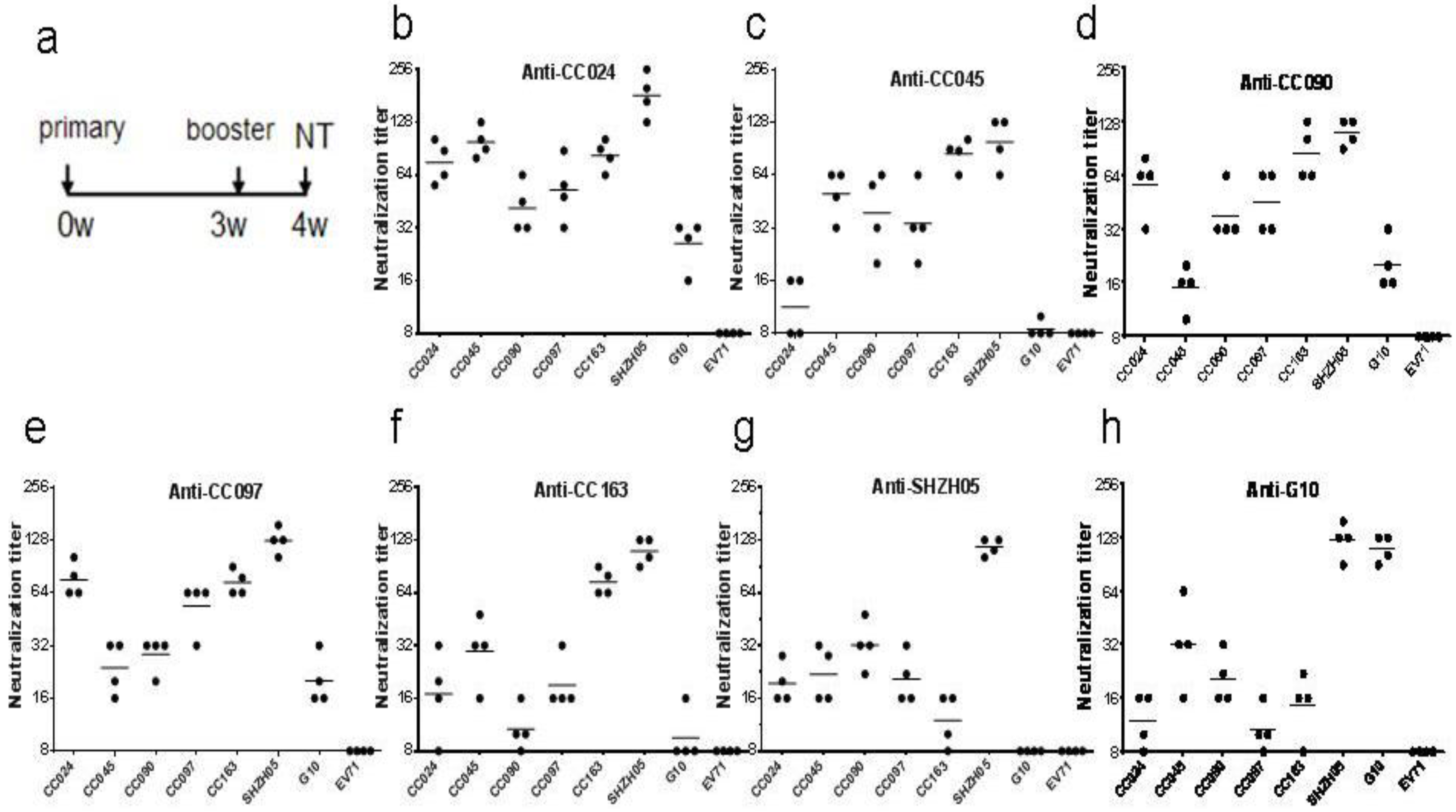

3.3. Biological Characterization of CA16CC024 Vaccine Strain

3.4. Cloning and Identification of CA16CC024 in Vero Cells
| Characteristic | CC024 | CC-16 Passage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11th | 13th | 15th | |||
| Genetic Homology | VP1 | - | - | - | - |
| VP2 | - | - | - | - | |
| VP3 | - | - | - | - | |
| VP4 | Arg(51) | Lys | Lys | Lys | |
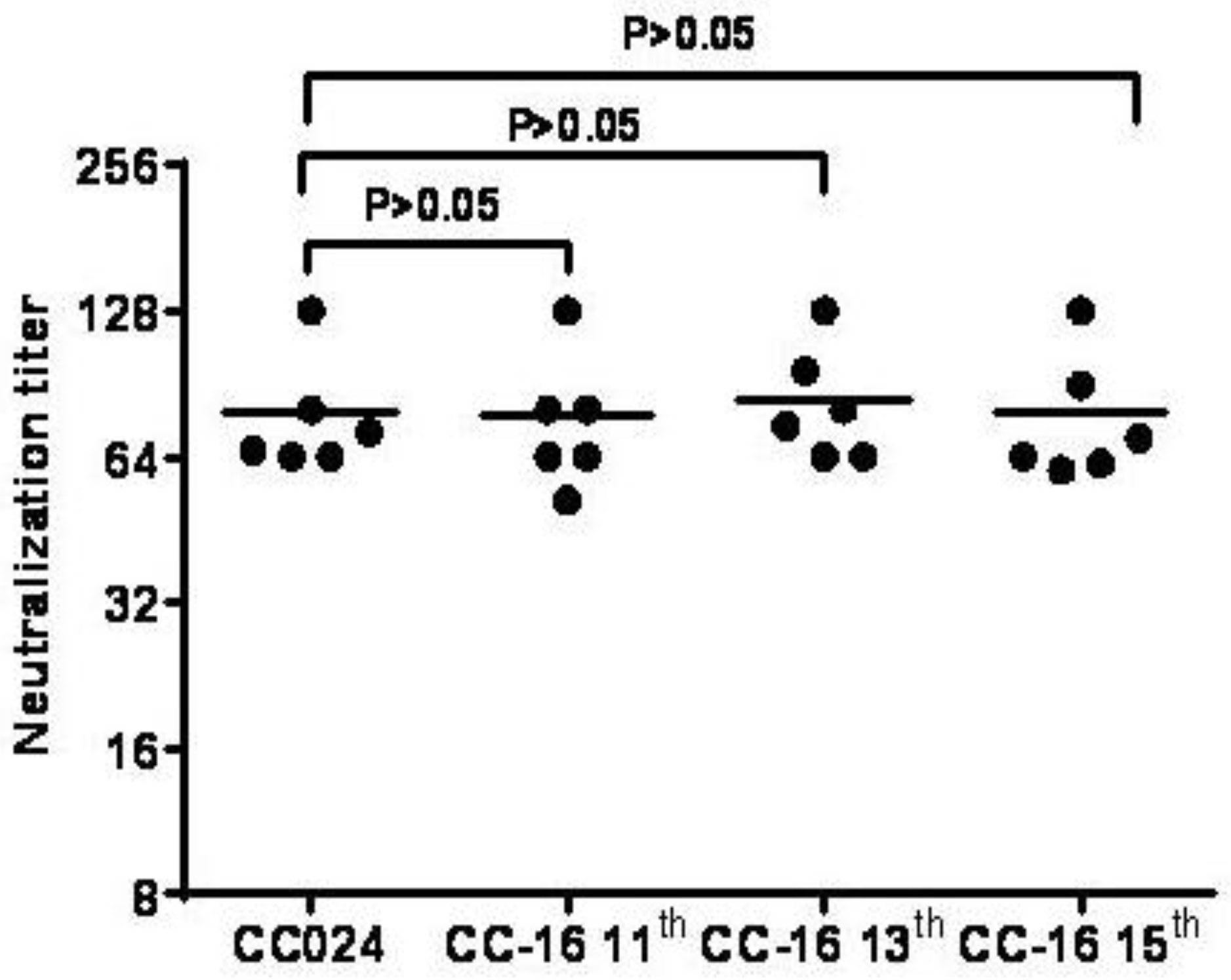
3.5. Preliminary Upstream Process Development
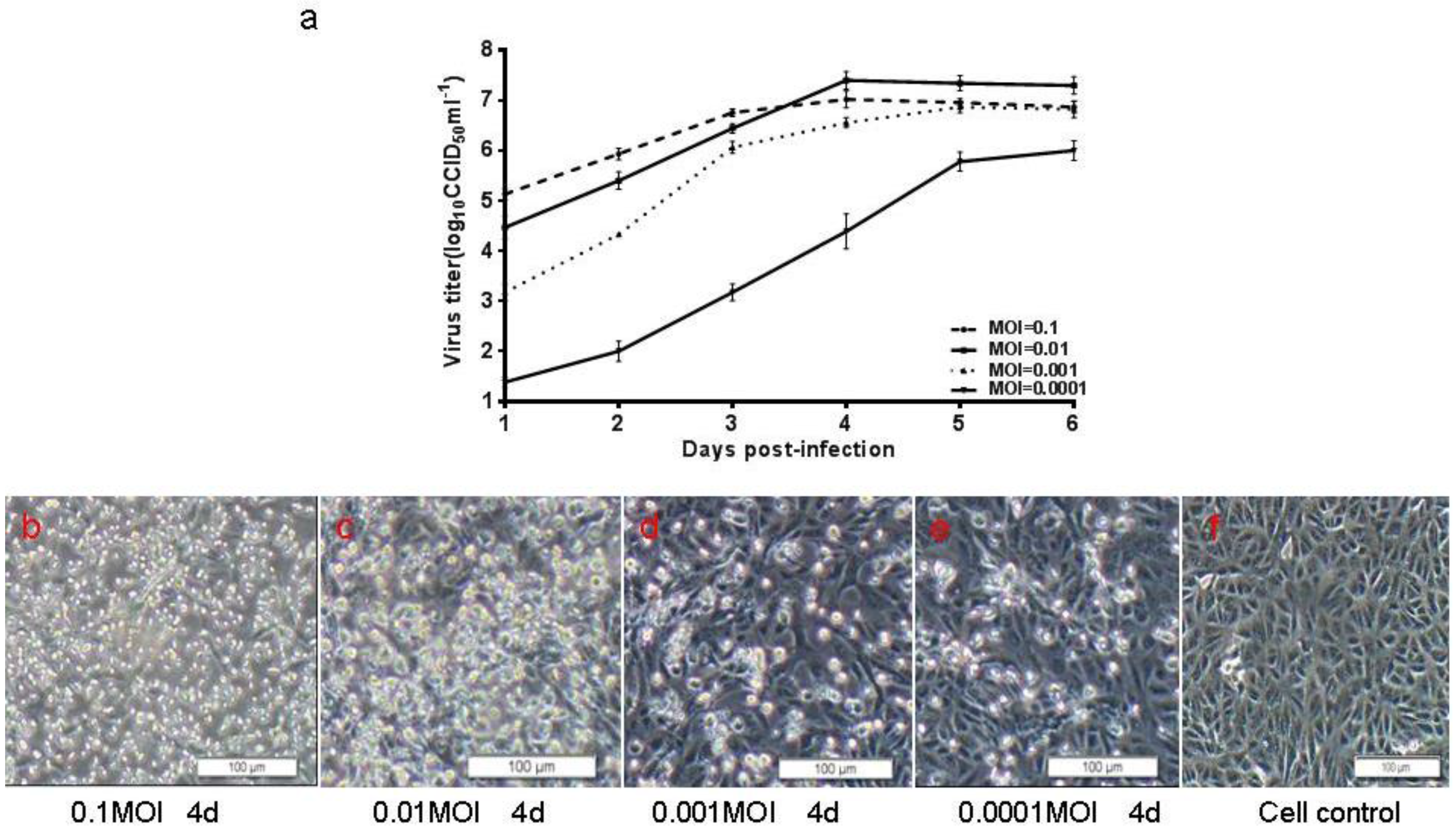
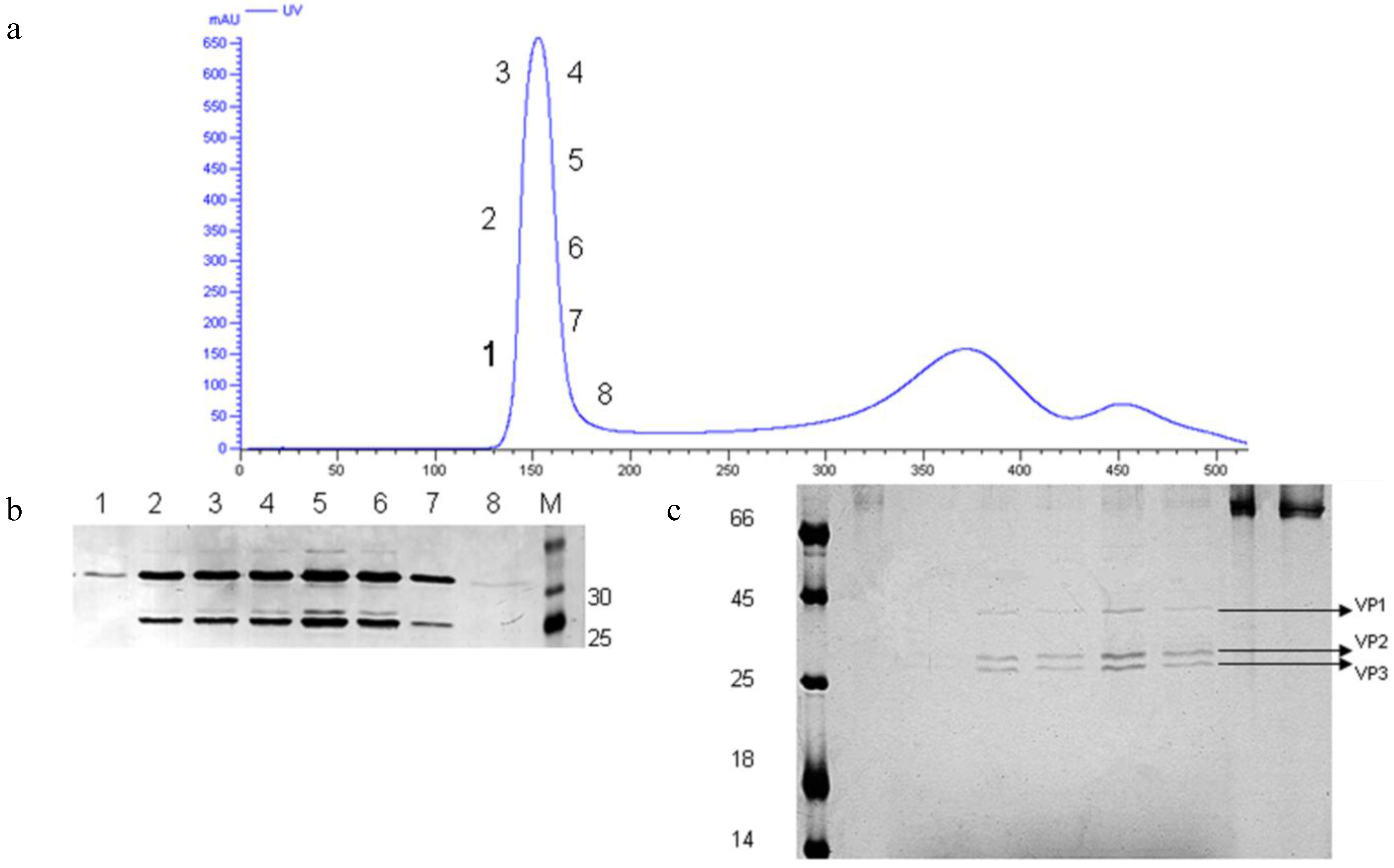
3.6. Preliminary Downstream Process and Identification
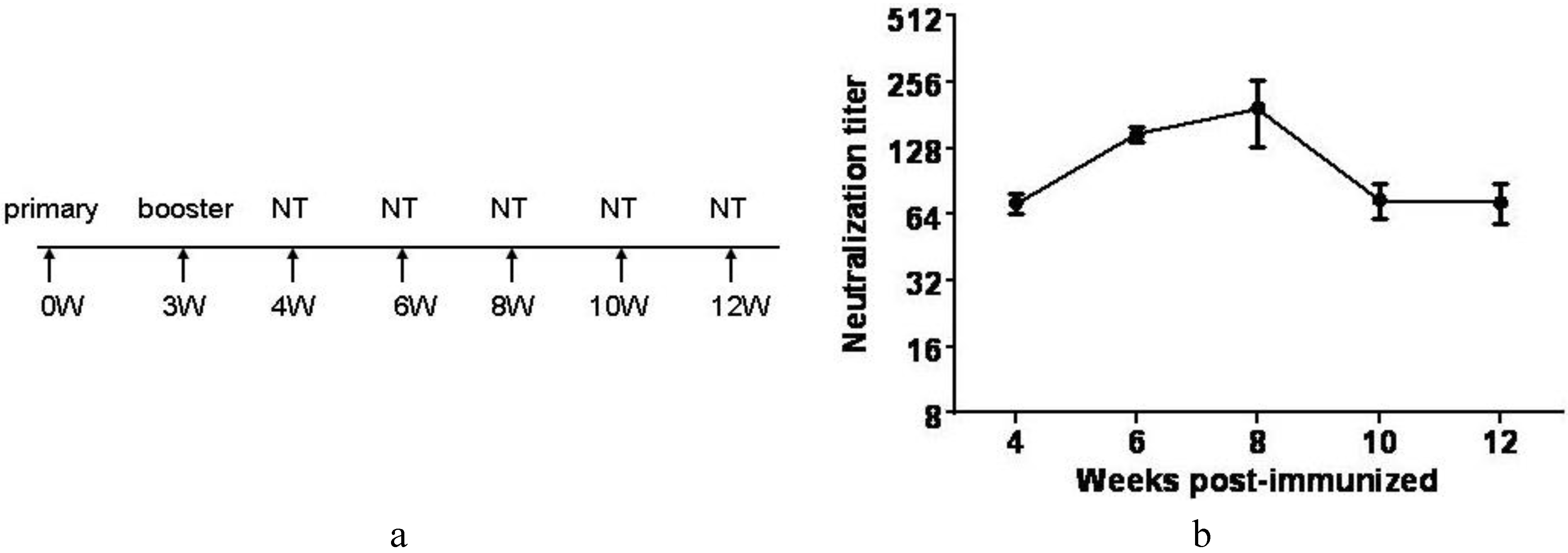
3.7. Inactivated CA16CC-16 Vaccine Elicits Humoral Immunity in Mice
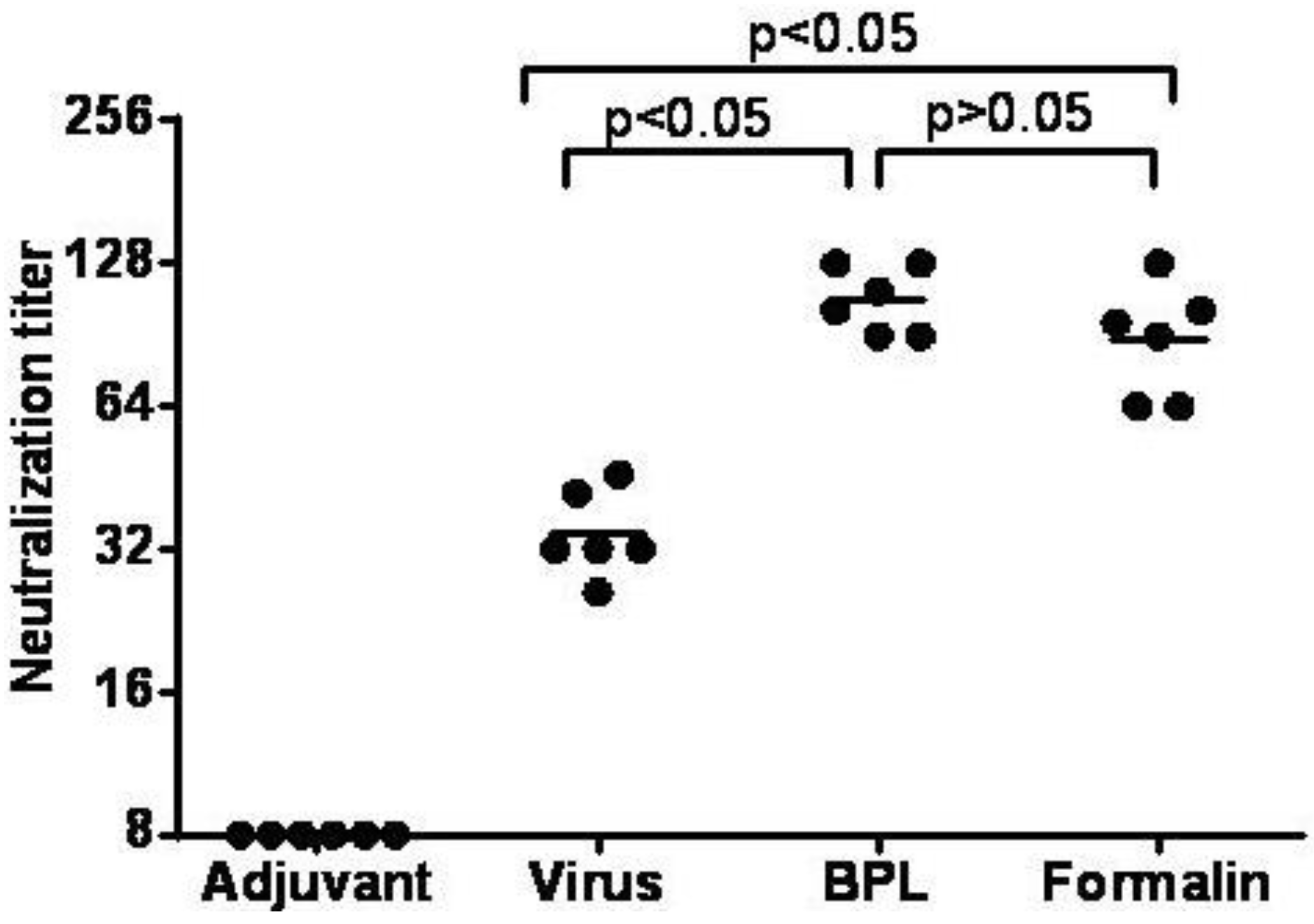
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
References
- McMinn, P.C. An overview of the evolution of enterovirus 71 and its clinical and public health significance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.C.; Liang, Z.L.; Meng, F.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Mao, Q.Y.; Chu, K.; Song, X.F.; Yao, X.; Li, J.X.; Ji, H.; et al. Retrospective study of the incidence of HFMD and seroepidemiology of antibodies against EV71 and CoxA16 in prenatal women and their infants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.C.; Liang, Z.L.; Li, X.L.; Ge, H.M.; Meng, F.Y.; Mao, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Hu, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, J.X.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an enterovirus 71 vaccine in healthy Chinese children and infants: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Yan, D.M.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, D.Y.; Ji, F.; Wang, X.J.; Gao, Y.J.; Chen, L.; et al. An outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with subgenotype C4 of human enterovirus 71 in Shandong, China. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 44, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Jin, Q.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Hou, Y. The complete genome of Enterovirus 71 China strain. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 2001, 44, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.C.; Chang, H.L.; Yan, T.R.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chen, K.T. An eight-year study of epidemiologic features of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Sanefuji, M.; Kusuhara, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Kira, R.; Torisu, H.; Hara, T. Rhombencephalitis and coxsackievirus A16. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, L.W.; Koh, B.K.; Chan, K.P.; Chua, L.T.; James, L.; Goh, K.T. Epidemiology and control of hand, foot and mouth disease in Singapore, 2001–2007. Ann. Acad. Med. Singapore 2009, 38, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.R.; Doane, F.W.; Rhodes, A.J. Report of an outbreak of febrile illness with pharyngeal lesions and exanthem: Toronto, summer 1957; isolation of group A Coxsackie virus. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1958, 79, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urquhart, G.E. A survey of coxsackie A16 virus antibodies in human sera. J. Hyg. 1984, 93, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Lu, F.L.; Wu, M.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Huang, L.M. Fatal coxsackievirus A16 infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004, 23, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.T., Jr.; Landing, B.H.; Lennette, E.H.; Mc, A.R. Fatal infection in an infant associated with Coxsackie virus group A, type 16. N. Engl. J. Med. 1963, 268, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, C.C.; Lau, S.K.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, M.X.; Tsoi, H.W.; Chan, K.H.; Chen, X.C.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Emergence of enterovirus 71 “double-recombinant” strains belonging to a novel genotype D originating from southern China: First evidence for combination of intratypic and intertypic recombination events in EV71. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, E.; Liu, L.; Che, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Tang, D.; Dong, C.; Yang, L.; et al. The effect of enterovirus 71 immunization on neuropathogenesis and protein expression profiles in the thalamus of infected rhesus neonates. Virology 2012, 432, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, W.; Ren, J.; Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Mao, N.; Xu, S.; Zhu, S.; Cui, A.; et al. An emerging recombinant human enterovirus 71 responsible for the 2008 outbreak of hand foot and mouth disease in Fuyang city of China. Virol. J. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Mao, Q.; Gao, F.; Wang, J. Progress on the research and development of human enterovirus 71 (EV71) vaccines. Front. Med. 2013, 7, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Song, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Baek, S.H. In vitro anti-enterovirus 71 activity of gallic acid from Woodfordia fruticosa flowers. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Wang, J. EV71 vaccine, an invaluable gift for children. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yan, K.; Feng, Y.; Huang, X.; Ku, Z.; Cai, Y.; Liu, F.; Shi, J.; Huang, Z. A virus-like particle vaccine for coxsackievirus A16 potently elicits neutralizing antibodies that protect mice against lethal challenge. Vaccine 2012, 30, 6642–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.; Li, N.; Yu, X.; Yao, X.; Li, F.; Lu, F.; Zhuang, H.; Liang, Z.; Wang, J. Antigenicity, animal protective effect and genetic characteristics of candidate vaccine strains of enterovirus 71. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Chou, A.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Wu, S.C.; Liu, S.J.; Chow, Y.H.; Su, I.J.; Klein, M. Production of EV71 vaccine candidates. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2012, 8, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chang, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Wei, W.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.F. Protection from lethal challenge in a neonatal mouse model by circulating recombinant form coxsackievirus A16 vaccine candidates. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifity percent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Guo, H.; Li, J.; Ren, S.; Wei, Z.; Bao, W.; Hu, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Circulating HFMD-associated coxsackievirus A16 is genetically and phenotypically distinct from the prototype CV-A16. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, S.; Fry, E.; Blakemore, W.; Abu-Ghazaleh, R.; Jackson, T.; King, A.; Lea, S.; Newman, J.; Stuart, D. Dissecting the roles of VP0 cleavage and RNA packaging in picornavirus capsid stabilization: The structure of empty capsids of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 9743–9752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.; Guo, M.S.; Lin, F.H.; Hsiao, K.N.; Weng, S.Y.; Chou, A.H.; Wang, J.R.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Su, I.J.; Liu, C.C. Immunological and biochemical characterization of coxsackie virus A16 viral particles. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, N.; Hansen, J.; Blaas, D.; Brunak, S. Cleavage site analysis in picornaviral polyproteins: Discovering cellular targets by neural networks. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 2203–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.N.; Lin, Y.C.; Fann, C.; Liao, N.S.; Shih, S.R.; Ho, M.S. Protection against lethal enterovirus 71 infection in newborn mice by passive immunization with subunit VP1 vaccines and inactivated virus. Vaccine 2001, 20, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Chou, A.H.; Lien, S.P.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Guo, M.S.; Chow, Y.H.; Yang, W.S.; Chang, K.H.; et al. Identification and characterization of a cross-neutralization epitope of Enterovirus 71. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4362–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.Y.; Chang, C.P.; Tsai, H.H.; Lee, C.D.; Lian, W.C.; Ih Jen, S.; Sai, I.H.; Liu, C.C.; Chou, A.H.; Lu, Y.J.; et al. Selection and characterization of vaccine strain for Enterovirus 71 vaccine development. Vaccine 2012, 30, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, A.; Tagaya, I.; Yoneyama, T. Epidemic of hand, foot and mouth disease associated with enterovirus 71 infection. Intervirology 1978, 9, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iakovenko, M.L.; Korotkova, E.A. Evolution of vaccine poliovirus strains. Vopr. Virusol. 2008, 53, 45–48, following back cover. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foo, D.G.; Alonso, S.; Chow, V.T.; Poh, C.L. Passive protection against lethal enterovirus 71 infection in newborn mice by neutralizing antibodies elicited by a synthetic peptide. Microbes. Infect. 2007, 9, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlecken, D.H.; Pelgrim, R.P.; Ruminski, S.; Bakker, W.A.; van der Pol, L.A. Comparison of initial feasibility of host cell lines for viral vaccine production. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbfuss, B.; Wolff, M.; Morenweiser, R.; Reichl, U. Purification of cell culture-derived human influenza A virus by size-exclusion and anion-exchange chromatography. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 96, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govorkova, E.A.; Murti, G.; Meignier, B.; de Taisne, C.; Webster, R.G. African green monkey kidney (Vero) cells provide an alternative host cell system for influenza A and B viruses. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5519–5524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Lee, Y.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Yu, C.K. Formaldehyde-inactivated human enterovirus 71 vaccine is compatible for co-immunization with a commercial pentavalent vaccine. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2772–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.-F. Optimization and Characterization of Candidate Strain for Coxsackievirus A16 Inactivated Vaccine. Viruses 2015, 7, 3891-3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072803
Li J, Liu G, Liu X, Yang J, Chang J, Zhang W, Yu X-F. Optimization and Characterization of Candidate Strain for Coxsackievirus A16 Inactivated Vaccine. Viruses. 2015; 7(7):3891-3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072803
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingliang, Guanchen Liu, Xin Liu, Jiaxin Yang, Junliang Chang, Wenyan Zhang, and Xiao-Fang Yu. 2015. "Optimization and Characterization of Candidate Strain for Coxsackievirus A16 Inactivated Vaccine" Viruses 7, no. 7: 3891-3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072803
APA StyleLi, J., Liu, G., Liu, X., Yang, J., Chang, J., Zhang, W., & Yu, X.-F. (2015). Optimization and Characterization of Candidate Strain for Coxsackievirus A16 Inactivated Vaccine. Viruses, 7(7), 3891-3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072803