Complete Genome Analysis of a Rabbit Rotavirus Causing Gastroenteritis in a Human Infant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rotavirus Strains
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. RT-PCR
2.4. Nucleotide Sequencing
2.5. Determination of the 5’ and 3’ Ends
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Analysis
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Complete Genome Sequencing of BE5028
| Strain Name | VP7 | VP4 | VP6 | VP1 | VP2 | VP3 | NSP1 | NSP2 | NSP3 | NSP4 | NSP5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVA/Human-tc/USA/Wa/1974/G1P[8] | G1 | P[8] | I1 | R1 | C1 | M1 | A1 | N1 | T1 | E1 | H1 |
| RVA/Human-tc/USA/DS-1/1976/G2P[4] | G2 | P[4] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A2 | N2 | T2 | E2 | H2 |
| RVA/Human-tc/JPN/AU-1/1982/G3P[9] | G3 | P[9] | I3 | R3 | C3 | M3 | A3 | N3 | T3 | E3 | H3 |
| RVA/Human-wt/BEL/BE5028/2012/G3P[14] | G3 | P[14] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M3 | A9 | N2 | T6 | E5 | H3 |
| RVA/Human-wt/BEL/B4106/2000/G3P[14] | G3 | P[14] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M3 | A9 | N2 | T6 | E5 | H3 |
| RVA/Rabbit-tc/ITA/30-96/1996/G3P[14] | G3 | P[14] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M3 | A9 | N2 | T6 | E5 | H3 |
| RVA/Rabbit-tc/CHN/N5/1992/G3P[14] | G3 | P[14] | I17 | R3 | C3 | M3 | A9 | N1 | T1 | E3 | H2 |
| RVA/Human-wt/AUS/RCH272/2012/G3P[14] | G3 | P[14] | I2 | R3 | C3 | M3 | A9 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
| RVA/Rabbit-tc/NLD/K1130027/2011/G6P[11] | G6 | P[11] | I2 | R2 | C2 | M2 | A13 | N2 | T6 | E2 | H3 |
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
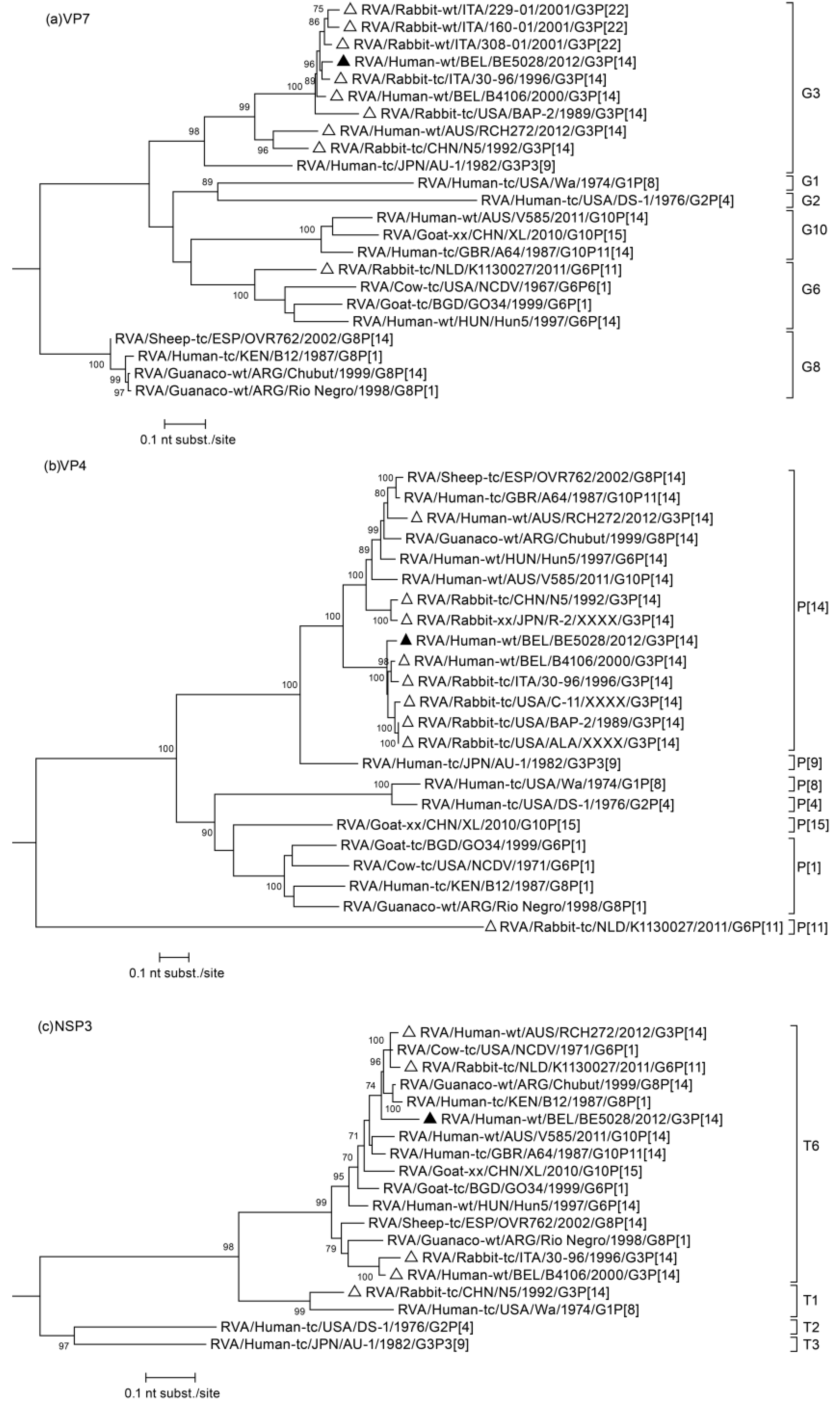
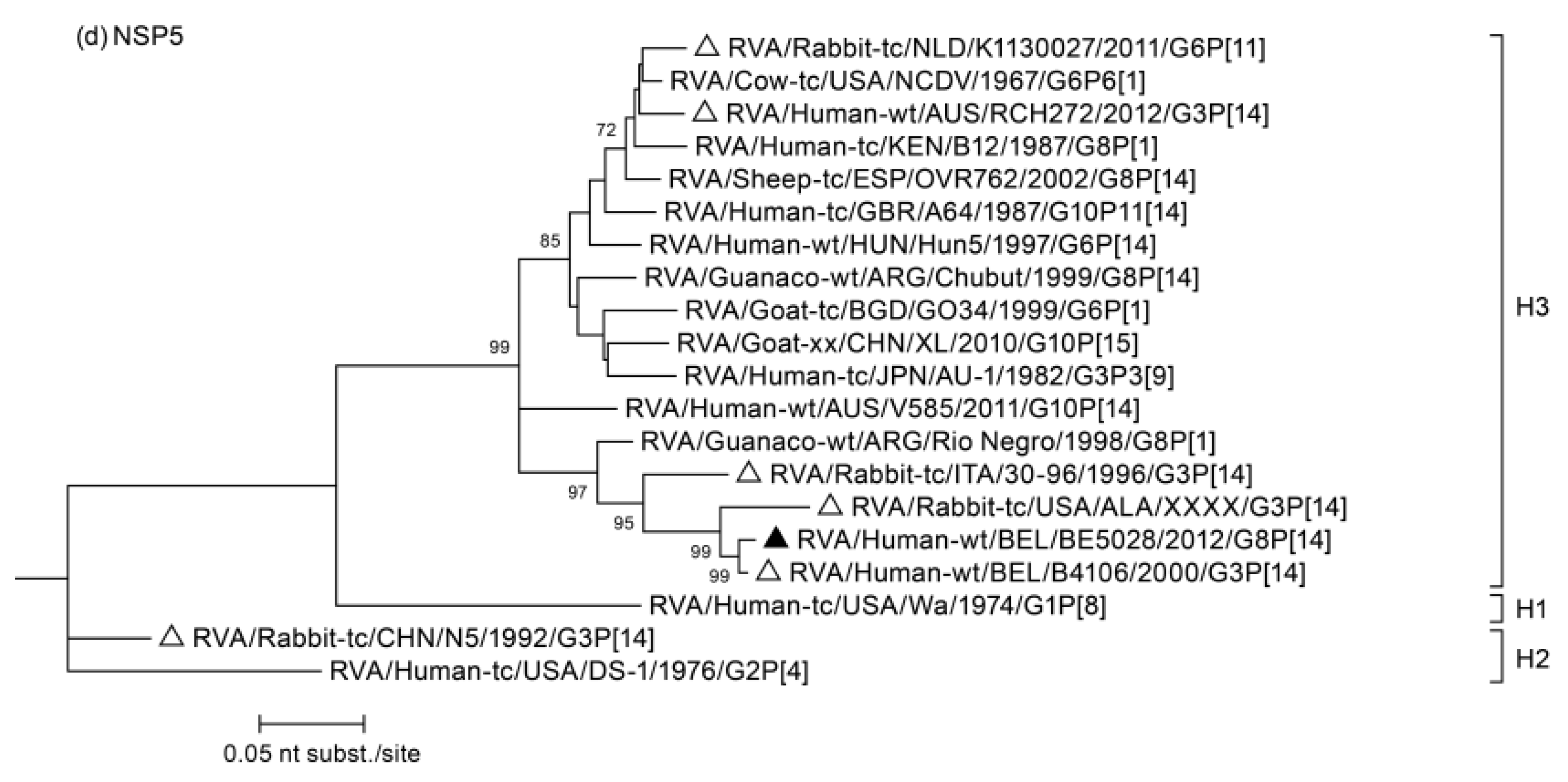
3.3. Duplication in NSP5 Segment

4. Discussion
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bishop, R. Discovery of rotavirus: Implications for child health. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, S81–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, M.K.; Kapikian, A.Z. Rotaviruses and their replication. In Fields of Virology; Fields, B.N., Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1917–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Estes, M.K.; Cohen, J. Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 410–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pesavento, J.B.; Crawford, S.E.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V.V. Rotavirus proteins: Structure and assembly. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 309, 189–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bányai, K.; László, B.; Duque, J.; Steele, A.D.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Gentsch, J.R.; Parashar, U.D. Systematic review of regional and temporal trends in global rotavirus strain diversity in the pre rotavirus vaccine era: Insights for understanding the impact of rotavirus vaccination programs. Vaccine 2012, 30 (Suppl. 1), A122–A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojnar, E.; Sachsenröder, J.; Twardziok, S.; Reetz, J.; Otto, P.H.; Johne, R. Identification of an avian group A rotavirus containing a novel VP4 gene with a close relationship to those of mammalian rotaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; Heiman, E.; Arijs, I.; Delbeke, T.; McDonald, S.M.; Palombo, E.A.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Palombo, P.; Patton, J.T.; et al. Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-Like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3204–3219. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; Saiada, F.; Hassan, Z.; Heylen, E.; Azim, T.; Van Ranst, M. Complete genomic analysis of a Bangladeshi G1P[8] rotavirus strain detected in 2003 reveals a close evolutionary relationship with contemporary human Wa-like strains. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, N.; Hoshino, Y. Global distribution of rotavirus serotypes/genotypes and its implication for the development and implementation of an effective rotavirus vaccine. Rev. Med. Virol. 2005, 15, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Van Ranst, M. Genotype constellation and evolution of group A rotaviruses infecting humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parreño, V.; Bok, K.; Fernandez, F.; Gomez, J. Molecular characterization of the first isolation of rotavirus in guanacos (Lama guanicoe). Arch. Virol. 2004, 149, 2465–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Potgieter, C.A.; Ciarlet, M.; Parreño, V.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K.; Garaicoechea, L.; Palombo, E.A.; Novo, L.; Zeller, M.; et al. Are human P[14] rotavirus strains the result of interspecies transmissions from sheep or other ungulates that belong to the mammalian order Artiodactyla? J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2917–2929. [Google Scholar]
- De Leener, K.; Rahman, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; Van Hoovels, L.; Goegebuer, T.; van der Donck, I.; Van Ranst, M. Human infection with a P[14], G3 lapine rotavirus. Virology 2004, 325, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Rahman, M.; Martella, V.; Xuelei, Y.; De Vos, S.; De Leener, K.; Ciarlet, M.; Buonavoglia, C.; Van Ranst, M. Full genomic analysis of human rotavirus strain B4106 and lapine rotavirus strain 30/96 provides evidence for interspecies transmission. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, D.; Jiang, Q.; Lin, H.; Li, C.; Si, C.; Qu, L. Full genomic analysis of rabbit rotavirus G3P[14] strain N5 in China: Identification of a novel VP6 genotype. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bányai, K.; Forgách, P.; Erdélyi, K.; Martella, V.; Bogdán, A.; Hocsák, E.; Havasi, V.; Melegh, B.; Szucs, G. Identification of the novel lapine rotavirus genotype P[22] from an outbreak of enteritis in a Hungarian rabbitry. Virus Res. 2005, 113, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martella, V.; Ciarlet, M.; Lavazza, A.; Camarda, A.; Lorusso, E.; Terio, V.; Ricci, D.; Cariola, F.; Gentile, M.; Cavalli, A.; et al. Lapine rotaviruses of the genotype P[22] are widespread in Italian rabbitries. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 111, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Laso, J.; Roman, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Cervera, I.; Head, J.; Rodriguez-Avial, I.; Picazo, J.J. Diversity of the G3 genes of human rotaviruses in isolates from Spain from 2004 to 2006: Cross-species transmission and inter-genotype recombination generates alleles. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Yang, F.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xie, J.; Feng, Y.; Bao, X.; Guo, H.; et al. Characterization of a novel G3P[3] rotavirus isolated from a lesser horseshoe bat: A distant relative of feline/canine rotaviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12357–12366. [Google Scholar]
- Schoondermark-van de Ven, E.; Van Ranst, M.; de Bruin, W.; van den Hurk, P.; Zeller, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; Heylen, E. Rabbit colony infected with a bovine-like G6P[11] rotavirus strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isherwood, B.; Desselberger, U.; Iturriza-go, M.; Gray, J.I.M. Reassortment in vivo: Driving force for diversity of human rotavirus strains isolated in the United Kingdom between 1995 and 1999. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3696–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Nakagomi, T.; Koshimura, Y.; Nakagomi, O. Direct evidence for genome segment reassortment between concurrently-circulating human rotavirus strains. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martella, V.; Bányai, K.; Matthijnssens, J.; Buonavoglia, C.; Ciarlet, M. Zoonotic aspects of rotaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, C.M.; Manuelpillai, N.M.; Cowley, D.; Roczo-Farkas, S.; Buttery, J.P.; Crawford, N.W.; Kirkwood, C.D. Genetic characterization of a novel G3P[14] rotavirus strain causing gastroenteritis in 12 year old Australian child. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 25, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambden, P.R.; Cooke, S.J.; Caul, E.O.; Clarke, I.N. Cloning of noncultivatable human rotavirus by single primer amplification. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Rahman, M.; Yang, X.; Delbeke, T.; Arijs, I.; Kabue, J.; Muyembe, J.T.; Van Ranst, M. G8 rotavirus strains isolated in the Democratic Republic of Congo belong to the DS-1-like genogroup. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, P.; Matthijnssens, J.; Rahman, M.; Van Ranst, M. RotaC: A web-based tool for the complete genome classification of group A rotaviruses. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, K.B.; Nicholas, H.B.J.; Deerfield, D.W. GeneDoc: Analysis and visualization of Genetic variation. EMBnet News 1997, 4, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, R.; Roper, R.L.; Upton, C. JDotter: A Java interface to multiple dotplots generated by dotter. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bányai, K.; Matthijnssens, J.; Szücs, G.; Forgách, P.; Erdélyi, K.; van Ranst, M.; Lorusso, E.; Decaro, N.; Elia, G.; Martella, V. Frequent rearrangement may explain the structural heterogeneity in the 11th genome segment of lapine rotaviruses. Acta Vet. Hung. 2009, 57, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinzoni, R.C.; Mattion, N.M.; Burrone, O.; Gonzalez, A.; La Torre, J.L.; Scodeller, E. A Isolation of group A swine rotaviruses displaying atypical electropherotypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gorziglia, M.; Nishikawa, K.; Fukuhara, N. Evidence of duplication and deletion in super short segment 11 of rabbit rotavirus Alabama strain. Virology 1989, 170, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattion, N.M.; Bellinzoni, R.C.; Blackhall, J.O.; Estes, M.K.; Gonzalez, S.; La Torre, J.L.; Scodeller, E.A. Genome rearrangements in porcine rotaviruses: Biochemical and biological comparisons between a supershort strain and its standard counterpart. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gault, E.; Schnepf, N.; Poncet, D.; Servant, A.; Teran, V.; Garbarg-Chenon, A. A human rotavirus with rearranged genes 7 and 11 encodes a modified NSP3 protein and suggests an additional mechanism for gene rearrangement. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7305–7314. [Google Scholar]
- Zeller, M.; Heylen, E.; De Coster, S.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J. Full genome characterization of a porcine-like human G9P[6] rotavirus strain isolated from an infant in Belgium. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, T.; Hoshino, Y. Whole genome sequence and phylogenetic analyses reveal human rotavirus G3P[3] strains Ro1845 and HCR3A are examples of direct virion transmission of canine/feline rotaviruses to humans. Virology 2008, 380, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bányai, K.; Esona, M.D.; Mijatovic, S.; Kerin, T.K.; Pedreira, C.; Mercado, J.; Balmaseda, A.; Perez, M.C.; Patel, M.M.; Gentsch, J.R. Zoonotic bovine rotavirus strain in a diarrheic child, Nicaragua. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bányai, K.; Papp, H.; Dandár, E.; Molnár, P.; Mihály, I.; Van Ranst, M.; Martella, V.; Matthijnssens, J. Whole genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of a zoonotic human G8P[14] rotavirus strain. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heylen, E.; Batoko Likele, B.; Zeller, M.; Stevens, S.; De Coster, S.; Conceição-Neto, N.; Van Geet, C.; Jacobs, J.; Ngbonda, D.; Van Ranst, M.; et al. Rotavirus surveillance in Kisangani, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, reveals a high number of unusual genotypes and gene segments of animal origin in non-vaccinated symptomatic children. PLoS One 2014, 9, e100953. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Hadj, M.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Fodha, I.; Benhamida-rebai, M.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; Trabelsi, A. Feline origin of rotavirus strain, Tunisia, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonica, M.B.; Zeller, M.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; Heylen, E. Complete Genome Analysis of a Rabbit Rotavirus Causing Gastroenteritis in a Human Infant. Viruses 2015, 7, 844-856. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7020844
Bonica MB, Zeller M, Van Ranst M, Matthijnssens J, Heylen E. Complete Genome Analysis of a Rabbit Rotavirus Causing Gastroenteritis in a Human Infant. Viruses. 2015; 7(2):844-856. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7020844
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonica, Melisa Berenice, Mark Zeller, Marc Van Ranst, Jelle Matthijnssens, and Elisabeth Heylen. 2015. "Complete Genome Analysis of a Rabbit Rotavirus Causing Gastroenteritis in a Human Infant" Viruses 7, no. 2: 844-856. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7020844
APA StyleBonica, M. B., Zeller, M., Van Ranst, M., Matthijnssens, J., & Heylen, E. (2015). Complete Genome Analysis of a Rabbit Rotavirus Causing Gastroenteritis in a Human Infant. Viruses, 7(2), 844-856. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7020844





