Changes in Diversification Patterns and Signatures of Selection during the Evolution of Murinae-Associated Hantaviruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
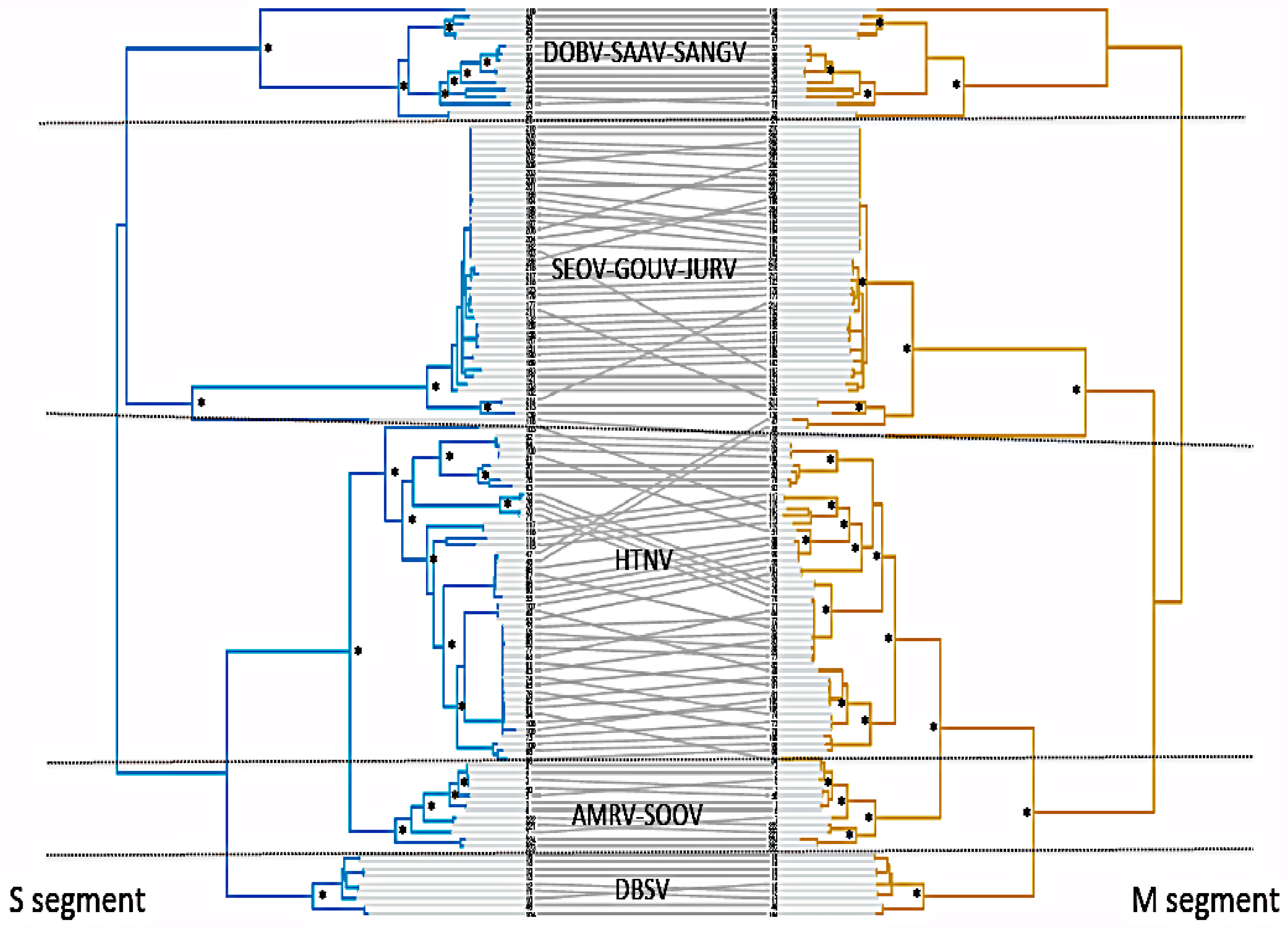
2.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.2. Molecular Signatures of Selection
| Methods | S segment (small dataset) | S segment (large dataset) | M segment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| positively selected aa sites | percentage of negatively selected aa sites | positively selected aa sites | percentage of negatively selected aa sites | positively selected aa sites | percentage of negatively selected aa sites | |
| SLAC | 43 * | 85% | 43 * | 90% | no site | 86% |
| FEL | 43 * | 89% | no site | 92% | no site | 90% |
| iFEL | 43 * | 88% | no site | 91% | no site | 90% |
| FUBAR | 43 * | 98% | 43 * | 98% | no site | 97% |
| MEME | 3, 4, 23, 39, 43 *, 69, 70, 71, 129, 183, 190, 209, 221, 233, 265, 313, 332, 334, 336, 357, 365, 369 | not tested | 2, 3, 4, 7, 23, 27, 39, 43 *, 69, 70, 75, 181, 209, 214, 221, 265, 310, 311, 312, 313, 326, 334, 336, 343, 365, 369, 396, 397, 398, 403, 405, 408 | not tested | 22, 29, 99, 189, 212, 208, 318, 340, 345, 377, 420, 461, 462, 540, 544, 635, 642, 643, 725, 766, 780, 810, 817, 821, 877, 942, 969, 995, 1003, 1048 | not tested |
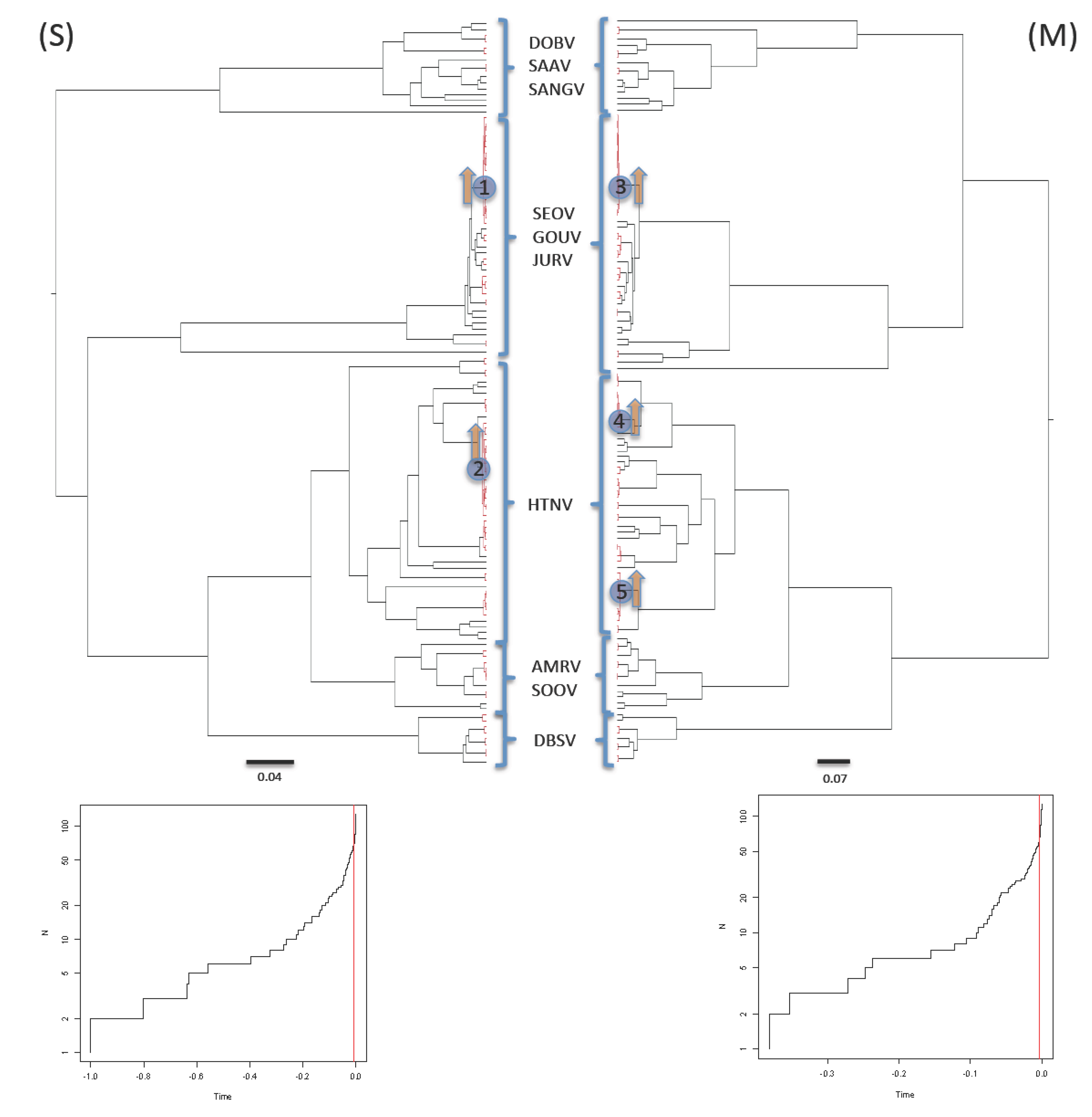
2.3. Shifts in Diversification Rates and Patterns
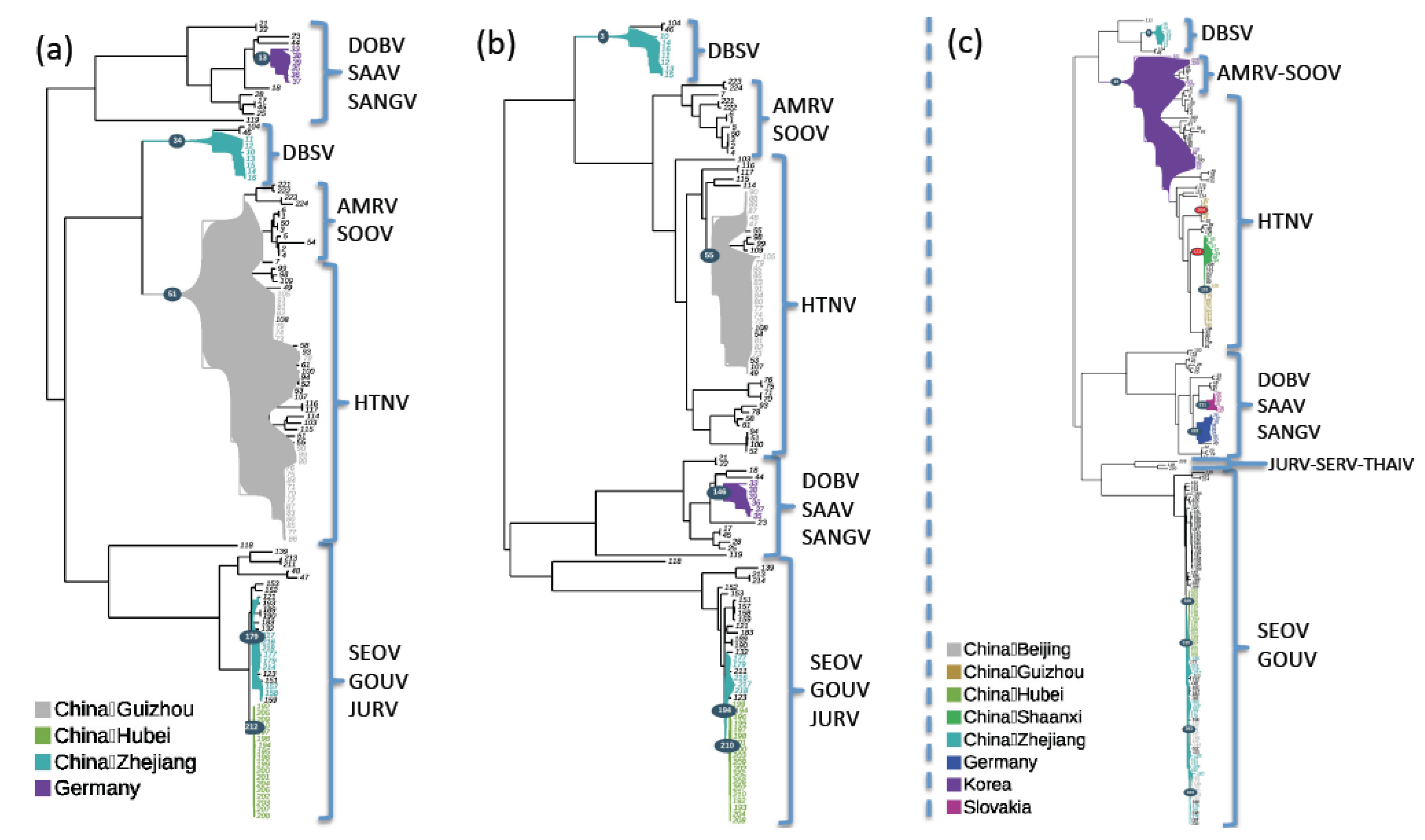
2.4. Geographic Structuration Analyses
3. Discussion
3.1. Molecular Signatures of Selection
3.2. Co-Divergence between S and M Segments
3.3. Shifts in Diversification Rates
3.4. Ecological Drivers of the Diversification Rate Variability
3.5. Sampling Effects
4. Experimental
4.1. Sequences Acquisition
4.2. Molecular Signature of Selection
4.3. Phylogeny and Congruence between M and S Segment Trees
4.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
| Model | Segment S | Segment M | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LH | AIC | LH | AIC | |
| Pure birth (Yule) | 537.98 | −1073.96 | 674.65 | −1347.31 |
| Birth death (BD) | 540.18 | −1076.36 | 755.33 | −1506.7 |
4.5. Shifts in Diversification Rates and Patterns
4.6. Geographic Structuration Analyses
5.Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Reusken, C.; Heyman, P. Factors driving hantavirus emergence in Europe. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, L.J.; Logue, C.H.; Atkinson, B.; Baker, N.; Galbraith, S.E.; Carroll, M.W.; Brooks, T.; Hewson, R. The continued emergence of hantaviruses: Isolation of a Seoul virus implicated in human disease, United Kingdom, October 2012. Euro Surveill. 2013, 18, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Meheretu, Y.; Cizkova, D.; Tesikova, J.; Welegerima, K.; Tomas, Z.; Kidane, D.; Girmay, K.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Bryja, J.; Gunther, S.; et al. High diversity of RNA viruses in rodents, Ethiopia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2047–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelle, B.; Torres-Perez, F. Hantaviruses in the americas and their role as emerging pathogens. Viruses 2010, 2, 2559–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henttonen, H.; Buchy, P.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Jittapalapong, S.; Herbreteau, V.; Laakkonen, J.; Chaval, Y.; Galan, M.; Dobigny, G.; Charbonnel, N.; et al. Recent discoveries of new hantaviruses widen their range and question their origins. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1149, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.C.; Sargianou, M.; Papa, A.; Chra, P.; Starakis, I.; Panos, G. Epidemiology of Hantavirus infections in humans: A comprehensive, global overview. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 40, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in visitors to a national park—Yosemite Valley, California, 2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2012, 61, 952. [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri, A.; Strandin, T.; Hepojoki, J.; Sironen, T.; Henttonen, H.; Makela, S.; Mustonen, J. Uncovering the mysteries of hantavirus infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyusnina, A.; Heyman, P.; Baert, K.; Stuyck, J.; Cochez, C.; Plyusnin, A. Genetic characterization of seoul hantavirus originated from norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) captured in Belgium. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, G.; Feyeux, C.; Mollard, N.; Chantegret, C.; Audia, S.; Rebibou, J.M.; Spagnolo, G.; Bour, J.B.; Denoyel, G.A.; Sagot, P.; et al. Severe Seoul hantavirus infection in a pregnant woman, France, October 2012. Euro Surveill. 2013, 18, e20464. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, S.; Nguyen, S.T.; Boldgiv, B.; Fukui, D.; Araki, K.; Dang, C.N.; Ohdachi, S.D.; Nguyen, N.X.; Pham, T.D.; Boldbaatar, B.; et al. Novel bat-borne hantavirus, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumibcay, L.; Kadjo, B.; Gu, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Lim, B.K.; Cook, J.A.; Song, J.W.; Yanagihara, R. Divergent lineage of a novel hantavirus in the banana pipistrelle (Neoromicia nanus) in Cote d'Ivoire. Virol. J. 2012, 9, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Witkowski, P.T.; Auste, B.; Nowak, K.; Weber, N.; Fahr, J.; Mombouli, J.V.; Wolfe, N.D.; Drexler, J.F.; Drosten, C.; et al. Hantavirus in bat, Sierra Leone. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.P.; Lin, X.D.; Wang, W.; Tian, J.H.; Cong, M.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, M.R.; Zhou, R.H.; Wang, J.B.; Li, M.H.; et al. Phylogeny and origins of hantaviruses harbored by bats, insectivores, and rodents. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.; Holmes, E.C.; Charleston, M.A. Hantavirus evolution in relation to its rodent and insectivore hosts: No evidence for codivergence. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.K.; Owen, R.D.; Jonsson, C.B. Phylogenetic exploration of hantaviruses in Paraguay reveals reassortment and host switching in South America. Virol. J. 2011, 8, e399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemirov, K.; Henttonen, H.; Vaheri, A.; Plyusnin, A. Phylogenetic evidence for host switching in the evolution of hantaviruses carried by Apodemus mice. Virus Res. 2002, 90, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, D.M.; Yu, C.; Zhou, J.Z.; Fu, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.Z. Genetic characterization of hantaviruses isolated from Guizhou, China: Evidence for spillover and reassortment in nature. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.L.; Roossinck, M.J. Genetic diversity in RNA virus quasispecies is controlled by host-virus interactions. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6566–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.; Shackelton, L.A.; Holmes, E.C. Rates of evolutionary change in viruses: Patterns and determinants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ojosnegros, S.; Agudo, R.; Sierra, M.; Briones, C.; Sierra, S.; Gonzalez-Lopez, C.; Domingo, E.; Cristina, J. Topology of evolving, mutagenized viral populations: Quasispecies expansion, compression, and operation of negative selection. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, e207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigen, M. Error catastrophe and antiviral strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13374–13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuer, R.; Boone, J.D.; Netski, D.; Morzunov, S.P.; St Jeor, S.C. Temporal and spatial analysis of Sin Nombre virus quasispecies in naturally infected rodents. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9544–9554. [Google Scholar]
- Sironen, T.; Kallio, E.R.; Vaheri, A.; Lundkvist, A.; Plyusnin, A. Quasispecies dynamics and fixation of a synonymous mutation in hantavirus transmission. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzauti, M.; Plyusnina, A.; Henttonen, H.; Plyusnin, A. Accumulation of point mutations and reassortment of genomic RNA segments are involved in the microevolution of Puumala hantavirus in a bank vole (Myodes glareolus) population. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzauti, M.; Plyusnina, A.; Henttonen, H.; Plyusnin, A. Microevolution of Puumala hantavirus during a complete population cycle of its host, the bank vole (Myodes glareolus). PLoS One 2013, 8, e64447. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, A.L.; Friedman, R. Evolutionary diversification of protein-coding genes of hantaviruses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.D.; Wang, W.; Guo, W.P.; Zhang, X.H.; Xing, J.G.; Chen, S.Z.; Li, M.H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Plyusnin, A.; et al. Cross-species transmission in the speciation of the currently known murinae-associated hantaviruses. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11171–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.H.; Vastermark, A.; Camp, J.V.; McAllister, R.; Remold, S.K.; Chu, Y.K.; Bruder, C.; Jonsson, C.B. The murine model for Hantaan virus-induced lethal disease shows two distinct paths in viral evolutionary trajectory with and without ribavirin treatment. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10997–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C.; Grenfell, B.T. Discovering the phylodynamics of RNA viruses. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C. What can we predict about viral evolution and emergence? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charleston, M.A.; Perkins, S.L. Traversing the tangle: Algorithms and applications for cophylogenetic studies. J. Biomed. Inform. 2006, 39, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, A.; Shackelton, L.A.; Holmes, E.C. Family level phylogenies reveal modes of macroevolution in RNA viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.N. The Coevolutionary Process; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1994; p. 387. [Google Scholar]
- Streicker, D.G.; Lemey, P.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Rupprecht, C.E. Rates of viral evolution are linked to host geography in bat rabies. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Perez, F.; Palma, R.E.; Hjelle, B.; Holmes, E.C.; Cook, J.A. Spatial but not temporal co-divergence of a virus and its mammalian host. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 4109–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Ebihara, H.; Ogino, M.; Araki, K.; Kariwa, H.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Li, D.; Hang, C.; et al. Genetic diversity of hantaviruses isolated in china and characterization of novel hantaviruses isolated from Niviventer confucianus and Rattus rattus. Virology 2000, 278, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.H.; Lin, F.; Zhang, Y.G.; Si, B.Y.; Kang, X.P.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, Y.C.; et al. The first complete genomic characterization of an Amur virus isolate from China. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2185–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, L.J.; Kariwa, H.; Lokugamage, K.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Arikawa, J.; Takashima, I.; Kang, J.I.; Moon, S.S.; Chung, S.Y.; Kim, E.J.; et al. Soochong virus: An antigenically and genetically distinct hantavirus isolated from Apodemus peninsulae in Korea. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugot, J.P.; Plyusnina, A.; Herbreteau, V.; Nemirov, K.; Laakkonen, J.; Lundkvist, A.; Supputamongkol, Y.; Henttonen, H.; Plyusnin, A. Genetic analysis of Thailand hantavirus in Bandicota indica trapped in Thailand. Virol. J. 2006, 3, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyusnina, A.; Ibrahim, I.N.; Plyusnin, A. A newly recognized hantavirus in the Asian house rat (Rattus tanezumi) in Indonesia. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, P.; Yap, G.; Low, H.T.; Siew, C.C.; Kek, R.; Ng, L.C.; Bucht, G. Molecular characterization of two hantavirus strains from different rattus species in Singapore. Virol. J. 2010, 7, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempa, B.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Auste, B.; Aniskin, V.; Meisel, H.; Denys, C.; Koivogui, L.; ter Meulen, J.; Kruger, D.H. Hantavirus in African wood mouse, Guinea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 838–840. [Google Scholar]
- Nemirov, K.; Vapalahti, O.; Lundkvist, A.; Vasilenko, V.; Golovljova, I.; Plyusnina, A.; Niemimaa, J.; Laakkonen, J.; Henttonen, H.; Vaheri, A.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Dobrava hantavirus carried by the striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius) in Estonia. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Klempa, B.; Avsic-Zupanc, T.; Clement, J.; Dzagurova, T.K.; Henttonen, H.; Heyman, P.; Jakab, F.; Kruger, D.H.; Maes, P.; Papa, A.; et al. Complex evolution and epidemiology of Dobrava-Belgrade hantavirus: Definition of genotypes and their characteristics. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyusnin, A. Genetics of hantaviruses: Implications to taxonomy. Arch. Virol. 2002, 147, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vienne, D.M.; Giraud, T.; Martin, O.C. A congruence index for testing topological similarity between trees. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 3119–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, H.; Hasegawa, M. Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlasiuk, G.; Nachman, M.W. Adaptation and constraint at Toll-like receptors in primates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2172–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos de Matos, A.; McFadden, G.; Esteves, P.J. Positive evolutionary selection on the RIG-I-Like receptor genes in mammals. PLoS One 2013, 8, e81864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiropoulou, C. Molecular biology of hantavirus infection. In The Bunyaviridae: Molecular and Cellular Biology; Plyusnin, A., Elliott, R.M., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lober, C.; Anheier, B.; Lindow, S.; Klenk, H.D.; Feldmann, H. The Hantaan virus glycoprotein precursor is cleaved at the conserved pentapeptide WAASA. Virology 2001, 289, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Elliott, R.M. Golgi localization of Hantaan virus glycoproteins requires coexpression of G1 and G2. Virology 2002, 300, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A.P. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevenet, F.; Jung, M.; Peeters, M.; de Oliveira, T.; Gascuel, O. Searching for virus phylotypes. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Lee, P.W.; Johnson, K.M. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J. Infect. Dis. 1978, 137, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C. The Evolution and Emergence of RNA Viruses; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, H.K.; Day, T. Risk factors for the evolutionary emergence of pathogens. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 1455–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleaveland, S.; Laurenson, M.K.; Taylor, L.H. Diseases of humans and their domestic mammals: Pathogen characteristics, host range and the risk of emergence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.; Guerri, J.; Moreno, P. Genetic variability and evolutionary dynamics of viruses of the family Closteroviridae. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, e151. [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim, J.O.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Purifying selection can obscure the ancient age of viral lineages. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 3355–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikawa, J.; Schmaljohn, A.L.; Dalrymple, J.M.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Characterization of Hantaan virus envelope glycoprotein antigenic determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies. J. Gen. Virol. 1989, 70, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.W.; Kamrud, K.I.; Elgh, F.; Custer, D.; Schmaljohn, C.S. DNA vaccination with hantavirus M segment elicits neutralizing antibodies and protects against seoul virus infection. Virology 1999, 255, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenison, S.; Yamada, T.; Morris, C.; Anderson, B.; Torrez-Martinez, N.; Keller, N.; Hjelle, B. Characterization of human antibody responses to four corners hantavirus infections among patients with hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3000–3006. [Google Scholar]
- Gott, P.; Zoller, L.; Darai, G.; Bautz, E.K. A major antigenic domain of hantaviruses is located on the aminoproximal site of the viral nucleocapsid protein. Virus Genes 1997, 14, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgh, F.; Lundkvist, A.; Alexeyev, O.A.; Wadell, G.; Juto, P. A major antigenic domain for the human humoral response to Puumala virus nucleocapsid protein is located at the amino-terminus. J. Virol. Methods 1996, 59, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukinen, P.; Vaheri, A.; Plyusnin, A. Hantavirus nucleocapsid protein: A multifunctional molecule with both housekeeping and ambassadorial duties. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 1693–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.Z.; Worobey, M. Homologous recombination in negative sense RNA viruses. Viruses 2011, 3, 1358–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C. Molecular clocks and the puzzle of RNA virus origins. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3893–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, M.; Ruzek, D.; Krivanec, K.; Zoller, G.; Essbauer, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Zanotto, P.M.; Hufert, F.T.; Dobler, G. Relation of genetic phylogeny and geographical distance of tick-borne encephalitis virus in central Europe. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznick, D.N.; Ricklefs, R.E. Darwin’s bridge between microevolution and macroevolution. Nature 2009, 457, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, N.R.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Lemey, P. Toward a quantitative understanding of viral phylogeography. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Orton, R.J.; Wright, C.F.; Morelli, M.J.; Juleff, N.; Thebaud, G.; Knowles, N.J.; Valdazo-Gonzalez, B.; Paton, D.J.; King, D.P.; Haydon, D.T. Observing micro-evolutionary processes of viral populations at multiple scales. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, e20120203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C. Evolutionary history and phylogeography of human viruses. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.J.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Persistent hantavirus infections: Characteristics and mechanisms. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyusnin, A.; Morzunov, S.P. Virus evolution and genetic diversity of hantaviruses and their rodent hosts. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 256, 47–75. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer, D.A.; Holland, J.J. Rapid evolution of RNA viruses. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1987, 41, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.Q.; Wang, X.J.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.L.; Song, S.X.; Zhang, W.Y.; Qian, Q.; Li, Y.P.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z.Q.; et al. Spatiotemporal trends and climatic factors of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome epidemic in Shandong Province, China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qian, Q.; Wang, Z.Q.; Glass, G.E.; Song, S.X.; Zhang, W.Y.; Li, X.J.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.J.; Fang, L.Q.; et al. Using geographic information system-based ecologic niche models to forecast the risk of hantavirus infection in Shandong Province, China. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg 2011, 84, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, D.M.; Li, M.H.; Ren, G.D.; Duan, Z.X.; Fu, Z.F.; Plyusnin, A.; Zhang, Y.Z. Molecular diversity and phylogeny of Hantaan virus in Guizhou, China: Evidence for Guizhou as a radiation center of the present Hantaan virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, D.Y.; Chen, W.; Li, J.L.; Luo, F.; Li, Q.; Ling, J.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xiong, H.R.; Ding, X.H.; et al. Genetic analysis of hantaviruses and their rodent hosts in central-south China. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.D.; Guo, W.P.; Wang, W.; Zou, Y.; Hao, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.J.; Dong, X.; Qu, Y.G.; Li, M.H.; Tian, H.F.; et al. Migration of Norway rats resulted in the worldwide distribution of Seoul hantavirus today. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Zhou, D.J.; Tian, J.H.; Yu, B.; Guo, W.P.; Wang, W.; Li, M.H.; Wu, T.P.; Peng, J.S.; Plyusnin, A.; et al. Dynamics of hantavirus infections in humans and animals in Wuhan city, Hubei, China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Beaulieu, J.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Donoghue, M.J. Understanding angiosperm diversification using small and large phylogenetic trees. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR)—Genome database with visualization and analysis tools. Available online: http://www.viprbrc.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2013).
- Pond, S.L.; Frost, S.D.; Muse, S.V. HyPhy: Hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.L.; Frost, S.D. Datamonkey: Rapid detection of selective pressure on individual sites of codon alignments. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2531–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, W.; Poon, A.F.; Frost, S.D.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Datamonkey 2010: A suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaptive Evolution Server @ Datamonkey.org. Available online: http://www.datamonkey.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2014).
- Murrell, B.; Moola, S.; Mabona, A.; Weighill, T.; Sheward, D.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Scheffler, K. FUBAR: A fast, unconstrained bayesian approximation for inferring selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vienne, D. Icong Congruence Index. Available online: http://max2.ese.u-psud.fr/icong/ (accessed on 1 October 2013).
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4. Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Charleston, M. Cophylogeny. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/cophylogeny/software (accessed on 1 October 2013).
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rawlence, N.; Rambaut, A. A rough guide to BEAST 1.4. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Main_Page/ (accessed on 1 February 2013).
- Nee, S.; May, R.M.; Harvey, P.H. The reconstructed evolutionary process. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 344, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabosky, D.L. Likelihood methods for detecting temporal shifts in diversification rates. Evolution 2006, 60, 1152–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v1.5. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer (accessed on 4 March 2014).
- Harmon, L.J.; Weir, J.T.; Brock, C.D.; Glor, R.E.; Challenger, W. GEIGER: Investigating evolutionary radiations. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Fitzpatrick, B.M.; Fordyce, J.A. A parametric method for assessing diversification-rate variation in phylogenetic trees. Evolution 2013, 67, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.T.; Wild, R.; Elliot, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Balke, M.; Inward, D.J.; Lees, D.C.; Ranaivosolo, R.; Eggleton, P.; Barraclough, T.G.; et al. Accelerated species inventory on Madagascar using coalescent-based models of species delineation. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Species delimitation server. Available online: http://species.h-its.org/ptp/ (accessed on 1 November 2013).
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of Taxa and Mixed Models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.E.; Santini, F.; Brock, C.; Alamillo, H.; Dornburg, A.; Rabosky, D.L.; Carnevale, G.; Harmon, L.J. Nine exceptional radiations plus high turnover explain species diversity in jawed vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13410–13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PhyloType. Available online: http://phylotype.org/ (accessed on 1 June 2013).
- Kühnert, D.; Stadler, T.; Vaughan, T.G.; Drummond, A.J. Simultaneous reconstruction of evolutionary history and epidemiological dynamics from viral sequences with the birth-death SIR model. arXiv 2013. arXiv:1308.5140. [Google Scholar]
- EDENext. Available online: http://www.edenext.eu/ (accessed on 25 February 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Castel, G.; Razzauti, M.; Jousselin, E.; Kergoat, G.J.; Cosson, J.-F. Changes in Diversification Patterns and Signatures of Selection during the Evolution of Murinae-Associated Hantaviruses. Viruses 2014, 6, 1112-1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6031112
Castel G, Razzauti M, Jousselin E, Kergoat GJ, Cosson J-F. Changes in Diversification Patterns and Signatures of Selection during the Evolution of Murinae-Associated Hantaviruses. Viruses. 2014; 6(3):1112-1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6031112
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastel, Guillaume, Maria Razzauti, Emmanuelle Jousselin, Gael J. Kergoat, and Jean-François Cosson. 2014. "Changes in Diversification Patterns and Signatures of Selection during the Evolution of Murinae-Associated Hantaviruses" Viruses 6, no. 3: 1112-1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6031112
APA StyleCastel, G., Razzauti, M., Jousselin, E., Kergoat, G. J., & Cosson, J.-F. (2014). Changes in Diversification Patterns and Signatures of Selection during the Evolution of Murinae-Associated Hantaviruses. Viruses, 6(3), 1112-1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6031112




